Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 7901. |
A battery has an emf of 12 V and connected to a resistor of 3Omega. The current in the circuit is 3.93 A. Calculate (a) terminal voltage and the internal resistance of the battery (b) power delivered by the battery and power delivered to the resistor. |
|
Answer» Solution :The given VALUES `I=3.93A, xi = 12 V, R=3Omega` (a) The terminal voltage of the battery is equal to voltage drop ACROSS the resistor `V=IR=3.93xx3=11.79V` The internal resistance of the battery, `r=[(xi-V)/(V)]R=[(12-11.79)/(11.79)]xx3=0.05Omega` (b) The power delivered by the battery `P=I xi=3.93xx12=47.1W` The power delivered to the resistor `=I^(2)R=46.3W` The REMAINING power `=(47.1-46.3)P=0.772W` is delivered to the internal resistance and cannot be used to do useful work. (it is equal to `I^(2)r`). |
|
| 7902. |
A 50 kg skier skis directly down a frictionless slope angled at 10^(@) to the horizontal. Assume the skier moves in the negative direction of an x axis along the slope. A wind force with component F_(x) acts on the skier. What is F_(x) if the magnitude of the skier's velocity is (a) constant, (b) increasing at a rate of 1.0" m"//"s"^(2), and (c) increasing at a rate of 2.0" m"//"s"^(2) ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 85 N, (B) 35 N, ( c ) 12 N | |
| 7903. |
A 10 metre long potentiometer wire carries a steady current. A 1.018 volt standard cell is balanced at a length of 850 cm. find (i) the potential gradient along the wire and (ii) the maximum emf that can be measured. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7904. |
In metals and vaccum tubes charge carriers are |
|
Answer» ELECTRONS |
|
| 7905. |
What is plane polarised light ? |
| Answer» Solution :The LIGHT, in which vibrations of electric vectors are confined only in one PARTICULAR plane PERPENDICULAR to the DIRECTION of propagation of light, is CALLED plane polarised light. | |
| 7906. |
Read the following passage and then answer questions (a) — (e) on the basis of your understanding of the passage and the related studied concepts. Henry Becquerel, in 1896, discovered the radioactivity purely by accident when he observed that pieces of uraniumpotassiumsulphate emit something which are able to penetrate black paper as well as a silver foil. Subsequent experiments showed that radioactivity was a nuclear phenomenon in which a unstable nucleus undergoes a decay. Three types of radioactive decay occur in nature, namely (i) alpha-decay in which a helium nucleus, (" "_(2)^(4)He) is emitted, (ii) beta-decay in which electrons (or positrons) are emitted, and (iii) gamma-decay in which high energy photons are emitted. The decay rate of a radioactive sample is a measurable quantity and is known as 'activity'. A common way to characteristic decay rate of a substance is 'half-life period' (T_(1/2)) which is the time during which half of the radioactive material decays and one half remains intact. Another related measure is the average or mean life tau. It is related to T_(1/2) as per relation T_(1/2)=0.693tau. (a) What is radioactivity? (b) Give two examples of radioactive elements? (c) Out of three types of radioactive radiations which are deflected by an electric and a magnetic field and why? (d) A radioactive sample has a half-life period of 5 hours. What fraction of original sample remains undecayed after 20 hours. (e) Complete the following nuclear reaction : " "_(72)^(180)A overset(alpha)(to)A_(1)overset(beta^(-))(to)A_(2)overset(alpha)(to)A_(3)overset(gamma)(to)A_(4) |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) The phenomena of spontaneous emission of some particles, WITHOUT any outside stimulation, by an unstable nuclide is called radioactivity. (b) URANIUM and radium. (C) Alpha and beta particles because these are charged particles. (d) As `T_(1/2)=5h and t=20h=4T_(1/2)` `therefore` Fraction of radioactive sample left intact (undecayed)=`[1/2]^(4)=1/16 or 6.25%` (e) Completed reaction is : `" "_(72)^(180)A overset(alpha)(to)" "_(70)^(176)A_(1)overset(beta^(-))(to)" "_(71)^(176)A_(2)overset(alpha)(to)" "_(69)^(172)A_(3)overset(gamma)(to)" "_(69)^(172)A_(4)` |
|
| 7907. |
The relation between the circumference of an electron orbit in a hydrogen atom and the de Broglie wavelength of the electron in the same orbit is given by |
|
Answer» `2 pi R=n lambda` `lambda=(2pi r)/n` `:. n lambda =2 pi lambda` `lambda=2 pi r""(n=1)` |
|
| 7908. |
The drawing shows a top view of a square room. One wall is missing and the other three are each mirrors. From point p in the centre of the open side, a laser is fired, with the intent of hitting a small target located at the centre of one wall. Identify vector in whose direction the laser can be fired and score a hit, assuming that the light does not strike any mirror more than once. |
|
Answer» `hat(i)/3+hat(j)` `2xy=x^(2)-yx` `3xy=x^(2)` `y=x/3` `-XHAT(i)+x/3hat(j)` 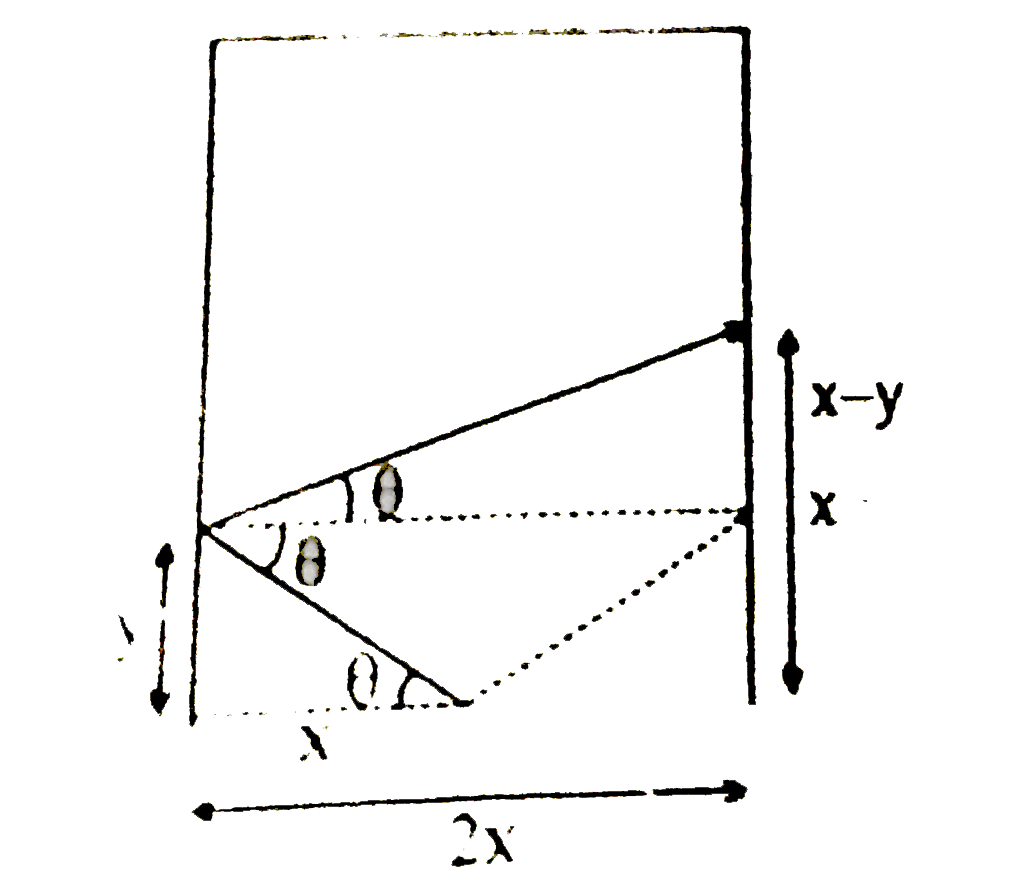
|
|
| 7909. |
The transverse displacement y(x,t) of a wave on a string is given by y (x,t) = e^(-(ax^(2) + bt^(2) + 2 sqrt("abxt"))) . This represents a : |
|
Answer» wave moving in -x direction with speed `sqrt((b)/(a))` `RARR ` speed of wave = `sqrt((b)/(a))` Correct choice , a. |
|
| 7910. |
(A) : An A.C. generator is based on the phenomenon of self induction. (R) : In single coil, we do not consider induction. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the correct EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 7911. |
Conductors turn into superconductors at ……………………. . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :LOW TEMPERATURES | |
| 7912. |
Which out of following cannot produce two coherent sources ? |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 7913. |
Three charges -q_(1), + q_(2) and -q_(3) are placed as shown in the figure. The x - component of the force on q_(1) is proportional to |
|
Answer» `(q_(2))/(B^(2))-(q_(3))/(a^(2))COSTHETA` |
|
| 7914. |
There is a uniformly charged nonconducting solid sphere made of amterial of dielectric constant one. If electric potenial at infinity be zero. Then the potential at its surface is V. if we take electric potential at its surface to be zero. Then the potential at the centre will be |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 7915. |
When radio waves are first amplified and in what process signal is extracted from them? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :DEMODULATION | |
| 7916. |
Which of the following qunatities related to an elcetron has a finite upper limit? |
|
Answer» mass |
|
| 7917. |
A uniform steel wire of density 7800 kg//m^(3) is 2.5 m long and weighs15.6xx10^(-3)kg.2.5 m long and weighs 15.6xx10^(-3) kg . If extends by 1.25 mm whenloaded by 8 kg, then the value of Young's modulus for steel will be |
|
Answer» `1.96xx10^(11)N//m^(2)` Area of cross section `=("Volume")/("Length")` `=("Mass")/("Density" xx "Length") =(15.6 xx 10^(-3))/(7800xx2.5)` `therefore A=8XX10^(-7)m^(2)` `therefore Y=(FL)/(Al)=(8xx9.8xx2.5)/((8xx10^(-7))xx1.25xx10^(-3))` `=1.96 xx 10^(11) N//m^(2)` |
|
| 7918. |
A light of wavelength 5500 Å falls normally on a slit of width 22 xx 10^(-5) cm. Calculate the angular position of the first two minima on either side of the central maxima : |
|
Answer» `14^(@) 29', 30^(@)` `d sin theta = n lambda` `sin theta = (n lambda)/(d) , n = 1` `sin theta_(1) = (lambda)/(d) = (5500 xx 10^(-8))/(22 xx 10^(-5)) = 1/4` Then `theta_(1) = 14^(@).29.` For second order n - 2 `sin theta_(2) = (2 lambda)/(d) = 1/2` Then `theta_(2) = 30^(@)` |
|
| 7919. |
Read the following passage and then answer questions (a) - (e) on the basis of your understanding of the passage and the related studied concepts. Rutherford was the pioneer who established the existence of the atomic nucleus. Result of Geiger and Marsden experiment on the scattering of a-particles from thin gold foils, performed at Rutherford’s suggestion, revealed that the distance of closest approach to a gold nucleus of an a-particle of kinetic energy 5.5 MeV is about 4.0 xx 10^(-14)m. The said scattering effect was explained by Rutherford by assuming that the Coulombian repulsive force was solely responsible for scattering. Since the positive charge is confined to the nucleus, the actual size of the nucleus has to be less than 4.0 xx 10^(-14)m. If we use a-particles of higher energies, the distance of closest approach to the gold nucleus will be still smaller. At some point the scattering will begin to be affected by the short range nuclear forces and differ from Rutherford’s calculations. From the distance at which deviations set it, nuclear size can be inferred. (a) Define MeV and express its value in terms of SI unit of energy. (b) What is distance of closest approach ? (c) Write an expression for distance of closest approach of a-particle to a gold nucleus. (d) What was Rutherford’s hypothesis regarding the existence of the atomic nucleus ? (e) How can you show that volume of the nucleus of an element is proportional to its mass number ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) One MeV is the energy gained by an electron (or a proton) when accelerated by a potential difference of 1 million volts. 1 MeV = `1.60xx 10^(-13) `J (b) Distance of closest approach ‘`r_(0)`’ of `ALPHA`-PARTICLE to a gold nucleus is that distance where `alpha`-particle comes to rest and its initial kinetic energy is completely converted into electrostatic potential energy. (c) Since `K=1/(4pi epsilon_(0)).((Ze)(2e))/r_(0) implies r_(0)=1/(4piepsilon_(0)).(2Ze^(2))/K` Where K=initial kinetic energy of `alpha`-particle and Z=atomic number of gold. (d) As per Rutherford.s hypothesis entire positive charge and most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in a small volume CALLED the nucleus with electrons revolving around the nucleus just as planets revolve sound the sun. (e) Since nuclear radius of a nucleus of mass number A is given as: `R=R_(0)xxA^(1/3)`, where `R_(0)=1.2xx10^(-15)m` Volume of nucleus `V=4/3piR^(3)=4/3piR_(0)^(3)A implies VpropA`. |
|
| 7920. |
Curved surface of a vessel has shape of truncated cone having semi-vertex angle 37^(@). Vessel is full of water (density rho=1000kg//m^(3)) upto a height of 12 cm and is placed on a smooth horizontal plane. Upper surface is opened to atmosphere. A hole of 1.5cm is made on curved wall of a height of 8cm from bottom as shown in figure. Area of water surface in the vessel is large as compared to the area of the hole. The initial horizontal range of water from point B is |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`V=sqrt(2gh)=1m//s` `- 8/100-3/5t-1/2xx10Xt^(2)` `t=1/5sec` `:. X=4/5xx1/5xx100=16cm` horizontal range from POINT `B=16-6=10cm` Force required to keep the vessel in equilibrium `=rhoAV^(2)cos37^(@)` `=0.12N` 
|
|
| 7921. |
If R is the radius of curvature of a spherical mirror and f is its length, then: |
|
Answer» R=f |
|
| 7922. |
Curved surface of a vessel has shape of truncated cone having semi-vertex angle 37^(@). Vessel is full of water (density rho=1000kg//m^(3)) upto a height of 12 cm and is placed on a smooth horizontal plane. Upper surface is opened to atmosphere. A hole of 1.5cm is made on curved wall of a height of 8cm from bottom as shown in figure. Area of water surface in the vessel is large as compared to the area of the hole. The initial horizontal force required to keep the vessel in static equilibrium |
|
Answer» `0.12N` `- 8/100-3/5t-1/2xx10Xt^(2)` `t=1/5sec` `:. X=4/5xx1/5xx100=16cm` horizontal range from point `B=16-6=10cm` Force REQUIRED to KEEP the vessel in EQUILIBRIUM `=rhoAV^(2)cos37^(@)` `=0.12N` 
|
|
| 7923. |
Read the following passage and then answer questions (a) — (e) on the basis of your understanding of the passage and the related studied concepts. Before the advent of Einstein’s special theory of relativity it was presumed that mass and energy were conserved separately in a reaction. But Einstein showed, from this theory of special relativity, equivalence of mass and energy and gave the famous mass-energy equivalence relation E = mc^(2), where c is the speed of light in vacuum. So now we speak about a unified law of conservation of energy considering mass-energy also as a form of energy. The most convincing evidence that of mass energy equivalence principle operates in nature comes from the results of nuclear physics. It is central to our understanding of nuclear energy and harnessing it as a source of electrical power. Using this principle, we can easily explain the concept of binding energy of nuclei as well as the Q-value of a nuclear process (either nuclear decay or nuclear reaction). (a) What is an atomic mass unit ? (b) Calculate the energy equivalent of one atomic unit and express your answer in MeV. (c) Define mass defect of a nucleus. (d) How is mass defect of a nucleus related to its binding energy ? (e) Name any two phenomenon where large amount of energy is produced in accordance with mass-energy equivalence. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) An unified atomic mass unit (u) is defined as `1/12`th of mass of (`" "_(6)^(12)C` atom. `1 u=1.66 xx 10^(-27) kg`. (b) Energy EQUIVALENT of1u,`E =1uxxc^(2)= 1.66xx10^(-27) xx (3 xx 10^(8))^(2)J=((1.66xx10^(-27))xx(3XX10^(8))^(2))/(1.60xx10^(-13)) MeV =931.5 MeV` (c) Mass defect of a nucleus is the difference between the sum of the masses of constituent nucleons of that nucleus and the mass of the nucleus. (d) Since mass of a nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of its constituent nucleons, energy is to be supplied to be nucleus if one wants to break the nucleus into constituent nucleons and this energy is termed binding energy of nucleus. Thus, binding energy is the energy equivalent of the mass defect of the nucleus. (e) Phenomena of NUCLEAR fission and nuclear fusion are TWO COMMON examples in which large amount of energy is released in accordance with mass-energy equivalence principle. |
|
| 7924. |
( ## EXP_SPS_PHY_XII_C04_E05_020_Q01 .png" width="80%">A gas chamber is filled with hydrogen and a magnetic field is applied to it, then exposed to gamma-ray.The gamma-ray hits the hydrogen atom and produces high energy electron, low energy electron and positron (electron having + ve charge). The above photo graph represents the trajectory of the particles.[Here magnetic field is applied Out of the plane of photo graph]Which force drives the particle in a circular path and write the mathematical from. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MAGNETIC LORENTZ FORCE | |
| 7925. |
Which line of the Balmer series has the maximum wavelength ? |
|
Answer» `H_(ALPHA)` LINE |
|
| 7926. |
In Fig., particles 1 and 2 are fixed in place on an axis, at a separation of L = 6.00 cm. Their charges are q_(1) = +e and q_(2) = -27e. Particle 3 with charge q_(3) = +4e is to be placed on the line between particles 1 and 2 , so that they produce a net electrostatic force vec(F)_("3,net") on it. (a) At what coordinate should particle 3 be placed to minimize the magnitude of that force ? (b) What is that minimum magnitude ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 1.50 CM, (B) `1.64 xx 10^(-23)N` | |
| 7927. |
In an ordinary dry cell the electrolyte is |
|
Answer» Zinc |
|
| 7928. |
Assertion : In transistor, common emitter configuration is used to make a NOT gate. Reason : In common emitter configuration, output voltage and input voltage have 180^(@) phase difference. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7929. |
Five identical capacitor plates, each of surface area 'A', are arranged such that adjacent plates are at distance 'd' apart. The alternate plates are joined together as shown in Fig.The capacitance of the arrangement is __________ . |
| Answer» Solution :`(4 eps_0A)/2`. The ARRANGEMENT BEHAVES as a parallel combination of four CAPACITORS, each having a capacitance of `(epsi_0A)/2`. | |
| 7930. |
In Ques, 136, the frequency v of the source is : |
|
Answer» `5xx10^(16)HZ` |
|
| 7931. |
Assertion: The television signals are propagated through sky waves.Reason: Television signals have freqeuncy in the range of 1000MHz to 2000MHz range. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7932. |
A battery consist of a variable number 'n' of identical cells (having internal resistance 'r' each) which are connected in series. The tem1inals of the battery are short-circuited and the current I is measured. Which of the graphs shows the correct relationship between I and n ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 7933. |
If modulation index is 1//2 and power of carrier wave is 2W. Then will be the total power in modulated wave ? |
|
Answer» `0.5` W |
|
| 7934. |
What is compound microscope ? Explain by figure of its construction. |
|
Answer» Solution :A simple microscope has a limited maximum magnification (`le 9`) for realistic focal lengths. For much larger magnification, one uses two lenses one compounding the effect of the other. This is known as a compound microscope. A schematic diagram of a compound microscope is shown in figure.  The lens nearest the object called the objective forms a real inverted, MAGNIFIED image of the object. This serves as the object for the second lens, the eyepiece, which functions essentially LIKE a simple microscope or magnifier, produces the final image which is enlarged and virtual. The first inverted image is thus near (at or within the focal plane of the eyepiece at a distance appropriate for final image formation at INFINITY, or a little CLOSER for image formation at the near point. Clearly the final image is inverted with respect to the original object. |
|
| 7935. |
1000 small water drops each of capacitance C join togethter to form one large spherical drop. The capacitance of bigge sphere is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 7936. |
A positively charged particle is released from rest in an uniform electric field. The electric potential energy of the charge |
|
Answer» remains a CONSTANT because the electric field is uniform. |
|
| 7937. |
(A): Isotopes of an element can be separated by using a mass spectrometer. (R) : Separation of isotopes is possible because of the difference in electron numbers of isotopes. |
|
Answer» Both .A. and .R. are true and .R. is the CORRECT explanation of .A. |
|
| 7938. |
find the dispersive power of flint glass. The refractive indices of flint glass for red, yellow and violet light are 1.613, 1.620 and 1.632 respectively. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The DISPERSIVE POWER is `OMEGA=(mu_v-mu_r)/(mu-1)` `=(1.632-1.613)/(1.620-1)=0.0306` |
|
| 7939. |
The main objective of an optical source is |
|
Answer» to CONVERT ELECTRICAL energy into an optical energy |
|
| 7940. |
In a Geiger-Marsden experiment, calculate the distance of the closest approach to the nucleus of Z = 80, when an a-particle of 8 MeV energy impinges on it before it comes momentarily to rest and reverses its direction. How will the distance of the closest opproach be affected when the kinetic energy of the o-particle is doubled? |
|
Answer» Solution :`((Ze)(2e))/(3pi epsi_(0)(r_(0)))=E` `r_(0)=(2Ze^(2))/(4pi epis_(0)(E))=(2Ze^(2))/(4pi epsi_(0)xxE)` `r_(0)=(9xx10^(9)xx2xx80xx(1.6xx10^(-19))^(2))/(8xx10^(6)xx(1.6xx10^(-19)))m` `=(18xx1.6xx10^(-10)xx80)/(8xx10^(6))` `=2.88xx10^(-14)m` `r_(0) prop (1)/(KE)` If K.E.becomes twice then `r_(0)=(r_(0))/(2)` i.e., distance of closet apporach becomes HALF. |
|
| 7941. |
The tuning circuit of a radio receiver has a resistance of 50Omega, an inductor of 10 mH and a variable capacitor. A 1 MHz radio wave produces a potential difference of 0.1 mV. The value of the capacitor to produce resonance is (take pi^(2)= 10) |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 7942. |
Find the torque of a force vec F =-3hati +hatj +5hatk acting a point vec r =7hati + 3hatj+hatk. (x= vec r xx vec F) |
|
Answer» `14 hat i` |
|
| 7943. |
Three resonant frequencies of a string are 90, 150 and 210 Hz. If the length of the string is 80 cm, what would be the speed of a transverse wave on this string? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`48m//s` | |
| 7944. |
A conducting frame I the shape of an equilateral Delta (mass m, side a) carrying a current l is placed vertically an a horizontal rough surface (coefficient of friction is mu). The frame is free to rotate about y-axis only. A magnetic field exists such that vecB=-B_(0)yhati. Then |
|
Answer» The maximum VELUE of `B_(0)` so that the frame does not rotate `(2mumg)/(Ia^(2))` `=Ixx((2dy)/(SQRT(3)))B_(0)Yxx(sqrt(3))/(2)` `impliestau=int_(0)^(sqrt(3)a)/(2))((2B_(0)I_(y)dy)/(sqrt(3)))XX((sqrt(3))/(2)a-y)` `=(2)/(sqrt(3))IB_(0)int^((sqrt(3))/(2)a)((sqrt(3))/(2)a-y)ydy=(IB_(0)a^(3))/(8)` `tau_("friction")=2{(mumg)/(a)int_(0)^((a)/(2))xdx}=(muga)/(4)` For the frame to rotate `(IB_(0)a^(3))/(8)lt(mumga)/(4)` `impliesB_(0)LE(2mumga)/(4)` `impliesle(2mumg)/(Ia^(2))` 
|
|
| 7945. |
जीवाणु -विज्ञान का जनक (Father of Bacteriology) कहते है : |
|
Answer» लुई पाश्चर को |
|
| 7946. |
In previous questions, the initial velocity of projection of stone is- |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 7947. |
A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of8 m^(-1) when palcedin an external magnetic field of is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.2 at a temperature of 16 k the magnetisation will be |
|
Answer» `(32/3)Am^(-1)` |
|
| 7948. |
Define critical angle. Prove that mu = 1sinC, where C is critical angle. |
| Answer» Solution :Critical angle is the angle of incidence. When a RAY of LIGHT travels from denser to rarer MEDIUM such that that angle of REFRACTION is `90@` USING `mu_dsinc` = `mu_rsin 90@` | |
| 7949. |
A source of sound emitting a sound of frequency f_0 and detector are moving with same speed v_0 as shown in the figure at t = 0. Take velocity of sound wave to be v v (gt gt v_(0)) For this situation mark out the correct statement(s): |
|
Answer» The frequency RECEIVED by the detector is always greater than `f_(0)` |
|
| 7950. |
The electron gets its drift speed under the influence of external force (due to applied electric field), Why the force does not give rise to acceleration of the electron? |
| Answer» Solution :Due to collisions with POSITIVE ions INSIDE the conductor the electron acquires only a DRIFT SPEED. | |



