Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1501. |
A fibre optic cable has a transparent core of refractive index 1.6 and the cladding has a refractive index of 1.5. An optical signal travels along path A and another signal travels along path B such that it strikes the core – cladding interface at an angle of incidence theta that is just greater than the critical angle. Length of the cable is 1500 m. (a) Find the time difference between the two signals reaching the other end of the cable. (b) A digital signal shown in the Figure. is transmitted through the cable. Find maximum frequency so that the crest from path A never arrives with a trough from path B at the receiving end of the cable. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1502. |
निम्न मे से कौन सी संख्या एक अपरिमेय संख्या है - |
|
Answer» `SQRT (4/25)` |
|
| 1503. |
A circle is drawn with centre as charge +q. a. What is the work done in moving a charge +q from B to C along the circumference of the circle? If the charge +q is first taken from B to A and then from A to C, on which path work done will be more? |
|
Answer» Solution :a. No WORK is done. (Equi POTENTIAL SURFACE PROPERTY) B. Work done will be same. (p.d. is same irrespective of path) |
|
| 1504. |
(A): The current density remains constant in a conductor of non uniform cross-section, carrying steady current. (R): The drift speed of electrons is cosntant in a conductor of non-uniform cross-sec tion which is carrying current. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A' |
|
| 1505. |
(A): A dimensionless quantity may have unit. (R) : Two physical quantities having same dimensions, may havc different units. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are TRUE and (R) is the correct EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 1506. |
The refractive indiced of water and glass are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. A ray of light travelling in water is incident on the water glass interface at 30^@. What is the angle of refraction in glass ? |
|
Answer» `sin^-1(3/4)` |
|
| 1507. |
In the setup shown, fird acceleration of the block C. |
|
Answer» `3m//s^(2)UARR` |
|
| 1508. |
(a) Define the term conductivity of a metallic wire. Write its SI unit.(b) Using the concept of free electrons in a conductor, derive the expression for the conductivity ofa wire in terms of number density and relaxation time. Hence obtain the relation between current density and the applied electric field E. |
Answer» Solution : On APPLYING a potential difference V across the ends of a CONDUCTOR of length l, the electric field `E = V/l` Force experienced by an electron F = e E` = (eE)/(l)`in a DIRECTION opposite to that of E. ` therefore ` Acceleration of electron in a direction opposite to that of E will be ` a= F/m = e/m. V/l` If the AVERAGE time between two successive collisions suffered by an electron be `tau` , the drift velocity of electron will be `v_d = a tau= e/m. V/l.tau ` But in terms of drift velocity magnitude of electric current is given by `I = nAev_d = nAe.e/m.V/l.tau = (nAe^2)/(m) tau.V/l` ` therefore ` Conductance `G = I/V = (nAe^2)/(ML) tau` and conductivity`sigma = (Gl)/(A) = ("ne"^2)/(m) tau` ` therefore ` current density `J = I/A = ("ne"^2 tau V)/(ml) = ("ne"^2 tau)/(m) . E = sigma E` In term of vectors , we have`vecJ = sigma vecE` |
|
| 1509. |
20 gof helium ( M= 4)in a cylinderundera piston aretransferredinfinitelyslowly forma stateofvolume V_(1) = 0.032 m ^(2) and pressurep_(1) = 4.1 atmto a stateof volumeV_(2) = 0.009 m^(3)andp_(2) = 15.5atm. Whatmaximumtemperaturewill thegasreachifthe prssuredecreaselinearly with volume ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :[489.5 K] | |
| 1510. |
How does a capacitor store energy ? And obtain the formula for the energy stored in the capacitor ? |
Answer» Solution :Take uncharged conductors 1 and 2 as shown in figure. 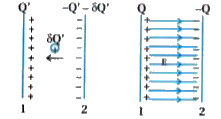 Imagine a process of transferring charge from conductor 2 to conductor 1 bit by bit so that at the ends, conductor 1 gets charge. In transferring POSITIVE charge from conductor 2 to conductor 1 work will be done externally, because at any stage conductor 1 ts at a higher potential than conductor 2. To calculate the total work by in a small step involving ttansfer of an infinitesimally amount of charge. Consider the situation when the conductors 1 and 2 have charges Q. and -Q. RESPECTIVELY. The potential difference V. between conductors 1 to 2 is `V=(Q)/(C)` where C is the capacitance of the system. A small charge `deltaQ`. is TRANSFERRED from conductor 2 to 1, then work done, `deltaW=V.deltaQ` `:. deltaW=(QdeltaQ)/(C)` Total work done to bringing charge Q fron conductor 2 to 1 is obtain by integration, `W= intdW` `W= intdW` `:.W=int_(0)^(Q)(Q)/(C)deltaQ :.W=(1)/(C)int_(0)^(Q).deltaQ=(1)/(C) [((Q.)^(2))/(2)]_(0)^(Q)` `=(1)/(C)[(Q^(2))/(2)]:.W=(Q^(2))/(2C)` Since, electrostatic force is conservative thb work is stored in the form of the potentia energy of the system of two conductors likE capacitors. Hence, potential energy of capacitor can be seen as the energy stored in ELECTRIC field between plates. `:.` The potential energy , `U =(Q^(2))/(2C)` other equivalent forms of this equation If Q=CV then `U=(1)/(2)CV^(2)` and if `C=(Q)/(V)` `U=(1)/(2)CV` |
|
| 1511. |
The correct graph representing the relation between energy (E) of the photoelectrons and frequency v of the incident light is : |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 1512. |
Three concentric metallic spherical shell A,B and C or radii a,b and c(a lt b lt c) have surface charge densities -sigma, + sigma and -sigma. Respectively. The potential of shel A is : |
|
Answer» `(sigma//epsilon_(0))(a+b-C)` |
|
| 1513. |
A prism having angle A^(@) (which is very small) is placed in front of a point source S at a small distance d. A screen is placed at a large distance D as shown in the figure-6.113. Find the fringe width of interference pattern given that source is emitting light of wavelength lambda and refractive index of prism is mu. |
| Answer» | |
| 1514. |
The faintest sound the human ear can detect at a frequency of I kHz (fair which the ear is most sensitive) corresponds to an intensity of about 10^(-12)W//m^2 (the d threshold of hearing). Determine the pressure amplitude and maximum displacement associated with this sound assuming the density of air = 1.3kg//m^3 and velocity of soimtl in air= 332 m/s |
|
Answer» `2.94 XX 10^(-5) N//m^(2), 1.1 xx 10^(-11) m` |
|
| 1515. |
Why did everyone get scared when the new ball flew in? |
|
Answer» Because they did not WANT a NEW ball |
|
| 1516. |
Three capacitors with capacitances of 1muF, 2muF and 3muFare connected in series. Each capacitor gets punctured, if a potential difference just exceeding 100 volt is applied. If the group is connected across 220 volt circuit then the capacitor most likely to puncture first is |
|
Answer» CAPACITANCE `1muF` |
|
| 1517. |
Which of the statements given in Exercise 14.1 is true for p-type semiconductors? |
|
Answer» Solution :Statement (d) is TRUE for p-type semiconductors, according to which: (d) Holes are majority CARRIERS and TRIVALENT atoms are the dopants. |
|
| 1518. |
When a voltage of 120V is impressed across the primary ofa transformer , the current in the primary is 1.85mA . Find the voltage across the secondary , when it delivers 150mA . The transformer has an efficiencyof 95% |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Data SUPPLIED , `V_P = 120 V,I_P= 1.85 A , I_S = 150 mA = 150 xx 10^(-3)A ` `ETA = (V_S I_S)/(V_P I_P)` `V_S = (eta V_PI_P)/(I_S) = (0.95 xx 120 xx 1.85)/(150 xx 10^(-3) ) = 1406 V` |
|
| 1519. |
The graph between sine of angle of refraction (sin r ) in medium 2 and sine of angleof incidence (sin i ) in medium 1 indicates that (atn 36^(@) ~~ 3/4) |
|
Answer» TOTAL internal reflection can TAKE place |
|
| 1520. |
The refractive angle of a prism is 1.5. A ray of light is incident at an angle of 40^(@) on a face of the prism. What will be the limiting angle of the prism for emergence of the ray from the other face. [sin 41^(@)19' = 0.6602' sin25^(@)22' = 0.4284] |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1521. |
A lamp is hanging at a height 40 cm from the centre of a table. If its height is increased by 10 cm the illuminance on the table will decrease by |
| Answer» ANSWER :d | |
| 1522. |
A certain atom is in the state in which S=2, the total angular momentum sqrt(2 ħ), and the magnetic moment is equal to zero. Write the spectral symbol of the corresponding term. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :From `M= ħsqrt(J+1)=SQRT(2 ħ)` we find `J=1`. From the zero value of the MAGNETIC moment we find `g=0` or `1+(1xx2L(L+1)+2xx3)/(2xx1xx2)=0` `1+(-L(L+1)+8)/(4)=0` or `12=L(L+1)` Hence `L=3`. The STATE is `.^(5)F_(1)`. |
|
| 1523. |
The wave relevant to telecommunications are |
|
Answer» VISIBLE LIGHT |
|
| 1524. |
Passage : In the circuit shown in figure : Current through R_(1)is independent of : |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 1525. |
Absolute refraction index eta,is given by |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`(C_e)`/`(C_v)` | |
| 1526. |
An aeroplane is flying with the velocity of V_(1) =800 kmph relative to the air towards south. A wind with velocity of V_(2) =15 ms^(-1)is blowing from West to East. What is the velocity of the aeroplane with respect to the earth. |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 1527. |
A particle having 2 C charge passes through magnetic field of 4hatkT and some uniform electric field with velocity 25hatj. If the Lorentz force acting on it is 400hatiN, find the electric field in this region. |
|
Answer» `200hati` Here, q = 2C, `vecv=25hatjms^(-1),vecB=4hatkT,vecF=400hati` `therefore400hati=2[vecE+(25)(4)(hatjxxhatk)]` `therefore400hati=2vecE+200hati` `therefore2vecE=200hati` `thereforevecE=100hatiVm^(-1)` `thereforevecE=100hatiVm^(-1)` |
|
| 1528. |
Assertion:- Clouds are white. Reason:- Scattering of all colours are same. |
|
Answer» If both Assertion & REASON are True & Reason is a CORRECT EXPLANATION of the Assertion. |
|
| 1529. |
Four atoms of hydrogen combine to form an ""_2^4He atom with a release of energy of |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 1530. |
A long cylindrical shell carries positive surface charge a in the upper half and negative surface charge -a in the lower half. The electric field lines around the cylinder will look like figure given in : (Figures are schematic and not drawn to scale) |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 1531. |
(a) Define the term 'conductivity' of a metallic wire. Write its SI unit. (b) Using the concept of free electrons in a conductor, derive the expression for the conductivity of a wire in te'rms of number density and relaxation time. Hence obtain the relation between current density and the applied electric field E. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) The resistivity and conductivity are PROPORTIONALLY constant and, therefore, depend only on the material the wire is made of not the geometry of wire. The reciprocal of resistivity of the material of a conductor is called conductivity. S.I unit = mho - `m^(-1)`/ siemen `m^(-1)`. (b) Let us consider a wire of length l and cross-sectional area A. When potential V is applied at the terminals of wire then electric field F. generate inside the conductor and all the `e^(-1)` flow towards the+ ve terminal of bett'ery with drift velocity Vd. Let the conductor no. of `e^(-1)`per units. Volue is N then no. of `e^(-)`in it . = Volume of wire `xx e^(-1)` density = area `xx` lenght XN = Aln. If charge of each electron ,is e, then total frequency charge q = NALE If the time taken by the ELECTRONS to cover the distance l is = `Detla = l//Vd` Floing current`i = (q) /(Deltat)` `i = (n Ale)/(l//Vd) = nAeVd` We know that currentdensity `J = (i)/(A)= (cancel(nAe)V_(d))/(cancel(A))` `J = "ne"Vd` Drift volocity `V_(d) = ((eEtau)/(m))` Where, `tau =` Relaxtion time Then,`J = ne ((eEtau)/(m))` `J = (ne^(2) tauF)/(m)` `J = sigma E` where `sigma = ("ne"^(2)tau)/(m)`. 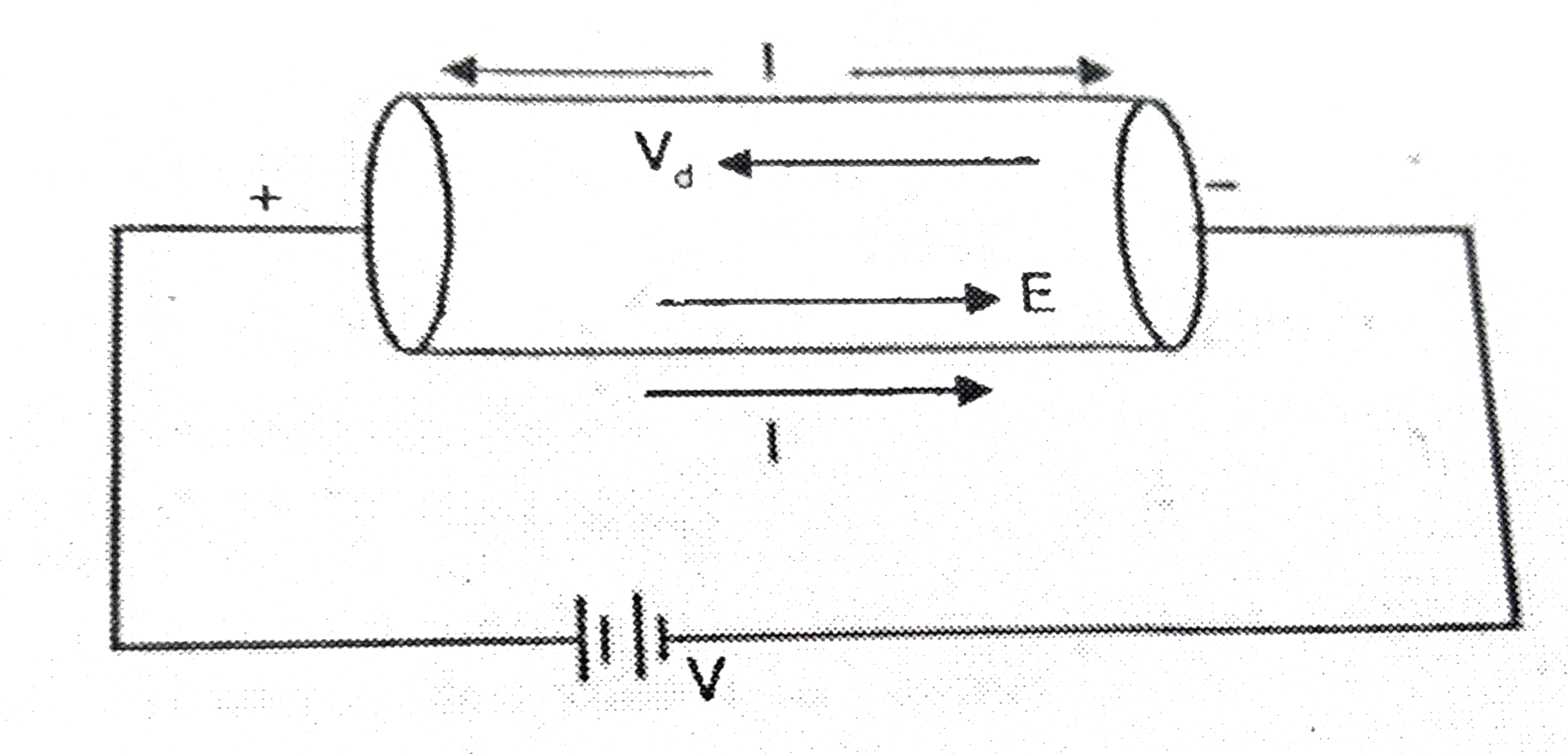
|
|
| 1532. |
Draw a graph of angle of deviation versus the angle of incidence in a refracting prism. |
Answer» Solution :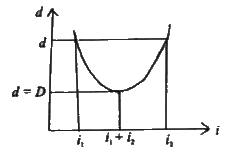 For d = D CALLED the angle of minimum deviation, the REFRACTION in the PRISM becomes symmetric. For a THIN prism, deviation PRODUCEDBY it, does not depend on the angle of incidence. Deviation is a constant quantity for a given prism. |
|
| 1533. |
A convex lens of focal length 24 cm (mu = 1.5) is totally immersed in water (mu = 1.33). Find its focal length in water. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`(1)/(F)=(mu-1) ((1)/(R_1)-(1)/(R_2))` WHENTHE LENSIS in AIR , ` (1)/(24 cm) = (1.5-1) ((1)/(R_1)-(1)/(R_2))` …(i) whenthe lensis inwater `(1)/(f) = ((1.5 )/(1.33)-1) ((1)/(R_1)-(1)/(R_2))`….(ii) Dividingthe expression(i) by (ii), weget `(f)/(24 cm) = (0.5 )/( 0.125 )` `f=96 cm` |
|
| 1534. |
A lift of mass m is supported by a cable that can with stand a force of 3mg. Find the shortest distance in which the lift can be stopped when it is descending with a speed of 3/4. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1535. |
Every EM wave has certain frequency. Name two parameters of an em wave that oscillate with this frequency. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ELECTRIC FIELD VECTOR and MAGNETIC field vector. | |
| 1536. |
The maximum process of increasing the strength of a signal using an electronic circuit is called |
|
Answer» AMPLIFICATION |
|
| 1537. |
Nuclides of " "_(92)^(235)U can undergoes nuclear fission when bombarded by ............... . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :THERMAL (or SLOW MOVING) NEUTRONS | |
| 1538. |
Which of the following circular rods, (given radius r and length l) each made of the same material and whose ends are maintaind at the same temperature diff. will conduct most heat ? |
|
Answer» `R=2r_(o)L=2l_(o)` `:.(dQ)/(dt)prop(r^(2))/(l)` Now `(r^(2))/(l)` will be maximum, when `r=2r_(0)` and `l=l_(0)` `:.` Correct choice is (c ). |
|
| 1539. |
An electrical meter of internal resistance 20Omega gives a full scale deflection when one milliampere current flows through it. The maximum current, that can be measured by using three resistors of resistance 12Omega each, in milliamperes is : |
|
Answer» 10 |
|
| 1540. |
A child is looking at a reflection of the Sun in a pool of water. When the puts on a pair of Polaroid sunglasses with a vertical transmission axis, she can no longer see the reflection. At what angle is she looking at the pool of water ? |
|
Answer» `45.0^(@)` |
|
| 1541. |
A metalic square loop ABCD is moving in its own plane with velocity v is in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to its plane as shown in the figure . An electric field is induced |
|
Answer» In AD , but not in BC |
|
| 1542. |
What flows through a garden hose at a volume flow rate dV/dt of 450cm^(3)//s. What |
|
Answer» Solution :The current I of negative charge is due to the electrons in the water molecules moving through the hose. The current is the RATE at which that negative charge passes through any plane that cuts COMPLETELY across the hose. Calculations: Calculations: We can write the current in terms of the number of molecules that pass through such a plane per second as i=(charge per electron) (electrons per molecule) (molecules per second) or `i=(e) (10) (d N)/(dt)` We SUBSTITUTE 10 electrons per molecule because a water `(H_2O)` molecule contains 8 electrons in the SINGLE oxygen atom and 1 electron in each of the two hydrogen atoms. We can express the rate dN/dt in terms of the given volume flow rate dV/dt by first writing (molecule per second)=(molecules per mole) (moles per unit mass) `xx ("mass per unit volume") ("volume per second")` "Molecules per mole" is Avogadro.s number `N_A.` "Moles per unit mass" is the inverse of the mass per mole, which is the molar mass M of water. "Mass per unit volume" is the (mass) density `p_("mass")` of water. The volume per second is the volume flow rate dV/dt. Thus, we have `(d N)/(dt)=N_(A) (1/M)p_("mass") ((d V)/(dt))=(N_(A) p_("mass"))/(M) (d V)/(dt)` SUBSTITUTING this into the equation for i, we find `i=10eN_(A) M^(-1) p_("mass") (d V)/(dt)` We know that Avogadro.s number `N_A.` is `6.02 xx 10^(23)` molecules/mol, or `6.02 xx 10^(23)" mol"^(-1),` and from Table 15-1 we know that the density of water `p_("mass")` pris under normal conditions is 1000 kg/m`""^(3)`. We can get the molar mass of water from the molar masses listed in Appendix F (in grams per mole): We add the molar mass of oxygen (16 g/mol) to twice the molar mass of hydrogen (1 g/mol), obtaining 18 g/mol = 0.018 kg/mol. So, the current of negative charge due to the electrons in the water is `i=(10) (1.6 xx 10^(-19C)) (6.02 xx 10^(23) "mol"^(-1)) xx (0.018 kg//mol)^(-1) (1000 kg//m^(3)) (450 xx 10^(-6) m^(3)//s)` `=2.41 xx 10^(7) C//s=2.41 xx 10^(7)A` =24.1MA. This current of negative charge is exactly compensated by a current of positive charge associated with the nuclei of the three atoms that make up the water molecule. Thus, there is no net flow of charge through the hose. |
|
| 1543. |
In the circuit shown epsilon_(1) and epsilon_(2) are two ideal sources of unknown emf. Some currents are shown in some branches of the circuit. Potential difference appearing across resistance 6Omega is V_(A)-V_(B)=10V. Then |
|
Answer» The current in the CD branch is 5 AMP `epsilon_(1)=40V` `epsilon_(2)=68V` `R=9Omega` and current through `4Omega=5` amp 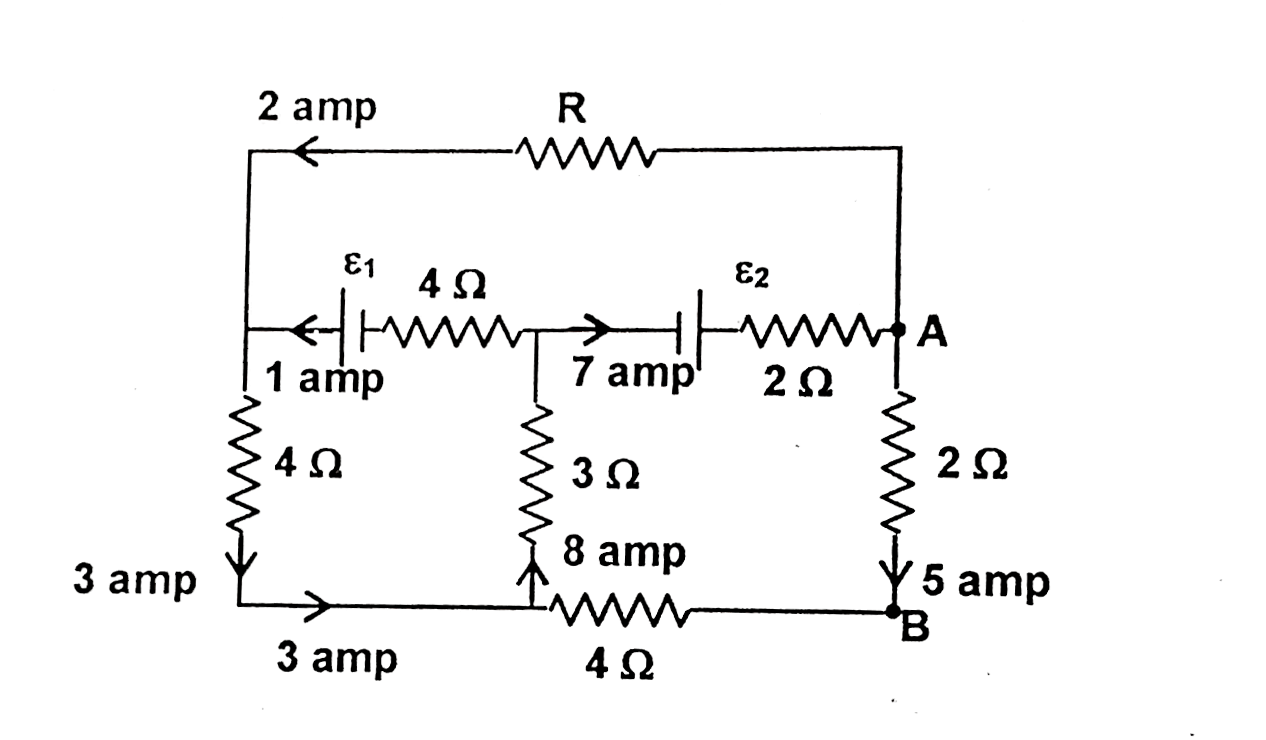
|
|
| 1544. |
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is (a) suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. (b) used to treat muscular strain. (c) used as a diagnostic tool in medicine. Write in brief, how these waves can be produced. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) Microwave REGION of the electromagnetic spectrum is used for radar SYSTEM used in aircraft NAVIGATION. Microwaves are produced by special vacuum tubes e.g., klystrons, magnetrons and Gunn diodes. (b) Infrared rays are used to treat MUSCULAR strain. These waves are produced by hot bodies and molecules. (c) X-rays are used as a diagnostic tool in medicine. X-rays are produced by bombarding high energy electrons on a metal target. |
|
| 1545. |
Four indentical rods of same material are joined end to end to from a square. If the temperature difference between the ends of a diagonal is 100^(@)C, then the temperature difference between the ends of othe diagonal will be : |
|
Answer» `0^(@)C` |
|
| 1546. |
Two batteries of difference emf's and internal resistance are connected in parallel to one another. |
|
Answer» EQUIVALENT emf will be grater than either of the emf's Equivalent internal resistance of this combination will be the same as equivalent resistance when the two resistances are connected in parallel. We know that in parallel combination of two resistances, EFFECTIVE resistance is less than the MINIMUM of two. Hence, only option (d) is correct. |
|
| 1547. |
A bulb is placed at a depth of 2sqrt(7) m in water and a floating opaque disc is placed over the bulb so that the bulb is not visible from the surface. What is the minimum diameter of the disc? |
Answer» Solution : As shown in figure, LIGHT from bulb will not emerge out of water if at the edge of disc, `i gt theta_cor sintheta_c` Now if R is the radius of disc and h is the depth of bulb from it, `sin i = (R )/(sqrt( R^2 +h^2)) ` and` sin theta_c = (1)/(mu )` So equation (1) becomes `(R )/( sqrt(R^2+h^2))gt(1)/(mu)orR gt(h )/( sqrt(mu^2-1)) ` here `h=2 sqrt(7)mand mu= ( 4//3)` So `R_(min) = ( 2 sqrt(7))/( sqrt((16 //9)-1))= 6M ` So DIAMETER of disc = 2R = 2 `xx` 6 = 12 m |
|
| 1548. |
An electron beam passes through a magnetic field of2xx10^(-3) T and electric field of 3xx10^(-4) V/m at right angles to it. Its specific charge is 1.75xx10^(11)C//kg^(-1). What is the radius of the path in which it is deflected, if there is no deflection, when both fields are acting ? |
|
Answer» 0.43 m Also `BeV=(mv^(2))/(r) or v=(Ber)/(m)` or `r=(mv)/(Be)=(1.5xx10^(7))/(2xx10^(-3)xx1*75xx10^(11))` `=(1500)/(200)xx(1)/(175)=(15)/(350)XX100 cm=(30)/(7) cm=4*3 cm` |
|
| 1549. |
A tightly-wound, long solenoid having 50 turns/cm, Carries a current of 4.00 A. Find the magnetic intensity Hand the magnetic field B at the centre of the solenoid. What will be the values of these quantities if an iron core is inserted in the solenoid and the magnetization l in the core is 4.00 xx 10^(6) A/m? |
|
Answer» Solution :The magnetic intensity H at the CENTRE of a long solenoid is H = ni `=50xx10^(2)m^(-1)xx4A=2xx10^(4)A//m` The magnetic FIELD `B = μ_(0)H` `=4pixx10^(-7)T-m//Axx2xx10^(4)A//m` `=8pixx10^(-3)T=25mT` The value ofH does not change as the iron core is inserted and remains `2xx10^(4)A//m`. The magnetic field B becomes `B=mu_(0)(H+I)=(4pixx10^(-7)t-m//A)(2xx10^(4)+4XX10^(6))A//m=5.05T` It should be noted that the magnetic intensity H is very small as COMPARED to the MAGNETIZATION I in presence of the iron core. |
|
| 1550. |
Obtain Gauss law from Coulomb 's law . |
|
Answer» Solution :Gauss lawstates that if a charge Q is enclosed by an arbitrary closed surface then the TOTAL electric flux `Phi_(E)` through the closed surface is `Phi_(E)oint vecE.dvecA= (Q_("end"))/(epsilon_(0))` A positive point charge Q is surrounded by an imaginary sphere of radius r as shown in FIGURE. We can calculate the total electric flux through the closed surface of the sphere using the equation . 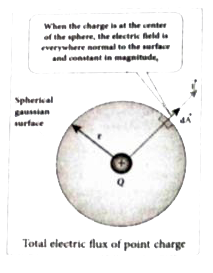 `Phi_(E)=ointvecE .dvecA= oint EdAcos theta ` The electric field of the point charge is DIRECTED radially outward at all point on the surface of the sphere . Therefore the direction of the area element `dvecA` is along the electric field `vecE` and `theta= 0^(@)` . `Phi_(E)=oint EdA ` since cos `0^(@)=1 ` E is uniform on the surface of the sphere `Phi_(E) = Eoint dA` Substituting for `oint dA = 4pir^(2)` and E `= (1)/(4piepsilon_(0))Q ` in equation 3 we GET `Phi_(E)= (1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(q)/(r^(2))xx4pir^(2)= 4pi(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))= (Q)/(epsilon_(0))` The equation (4) is called as Gauss.s law . The remarkable point about this result is that the equation ( 4) is equally true for any arbitrary shaped which encloses the charge Q. |
|