Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2201. |
Solids are classified as ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2202. |
A positive charge of 20 mu C is placed 2 m away from a negative charge of 20 mu C. Determine the electric field at a point 2 m away from each charges. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2203. |
An ideal gas is confined to a container whose volume is fixed. If the container holds n moles of gas, by what factor will the pressure increase if the absolute temperature is increased by a factor of 2? |
|
Answer» <P>`(2)/((nR))` |
|
| 2204. |
The three light bulbs in the circuit below are identical, and the battery has zero internal resistance, When switch S is closed to cause buil 1 to light, which of the ther two bulbs increase (s) in brightness ? |
|
Answer» <P>Neither bulb 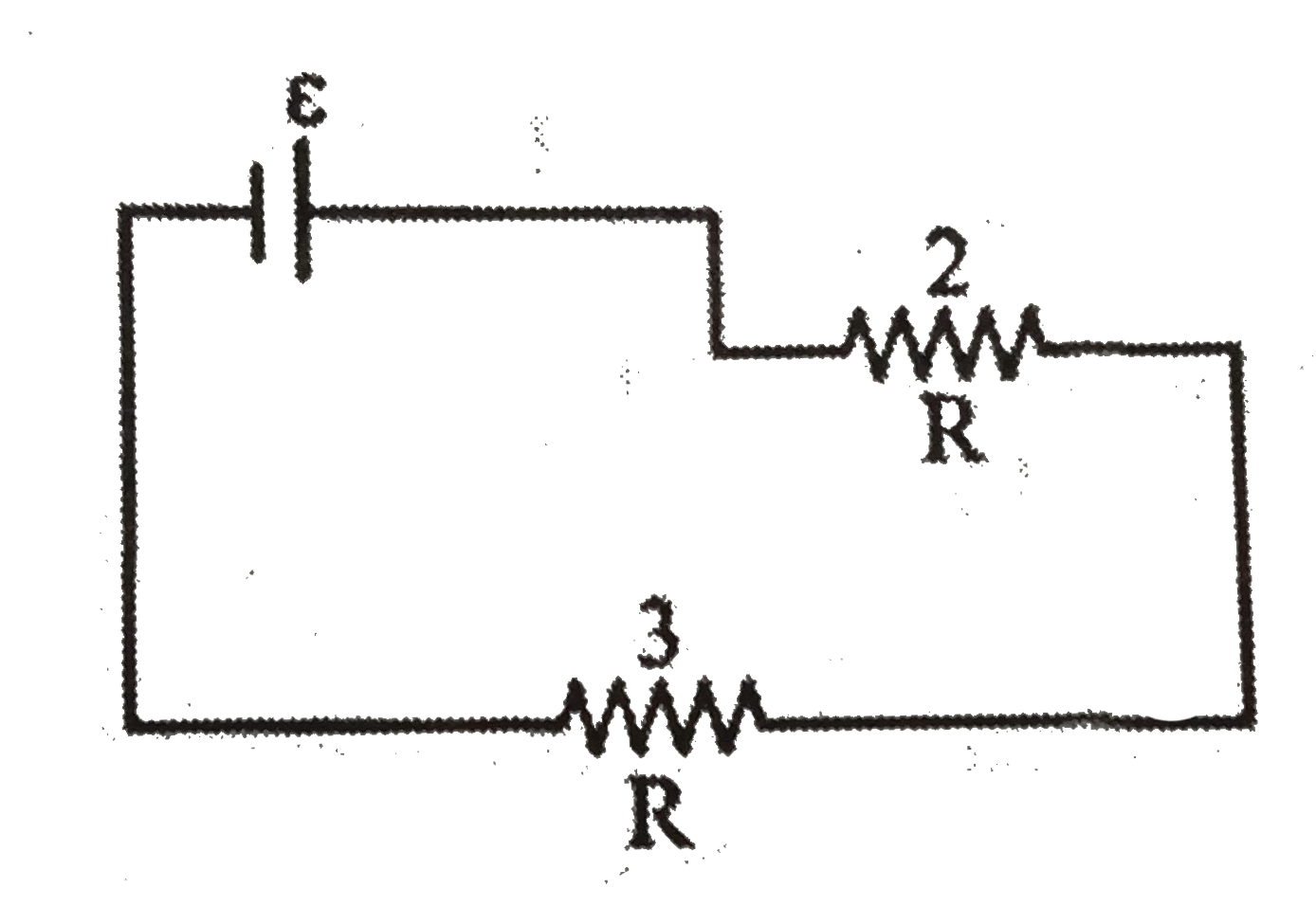 Oldsituation `P_(2)=((epsi)/(2))^(2)1/R=(epsi^(2))/(4R)` `P_(3)=((epsi)/(2))^(2)1/R=(epsi^(2))/(4R)` 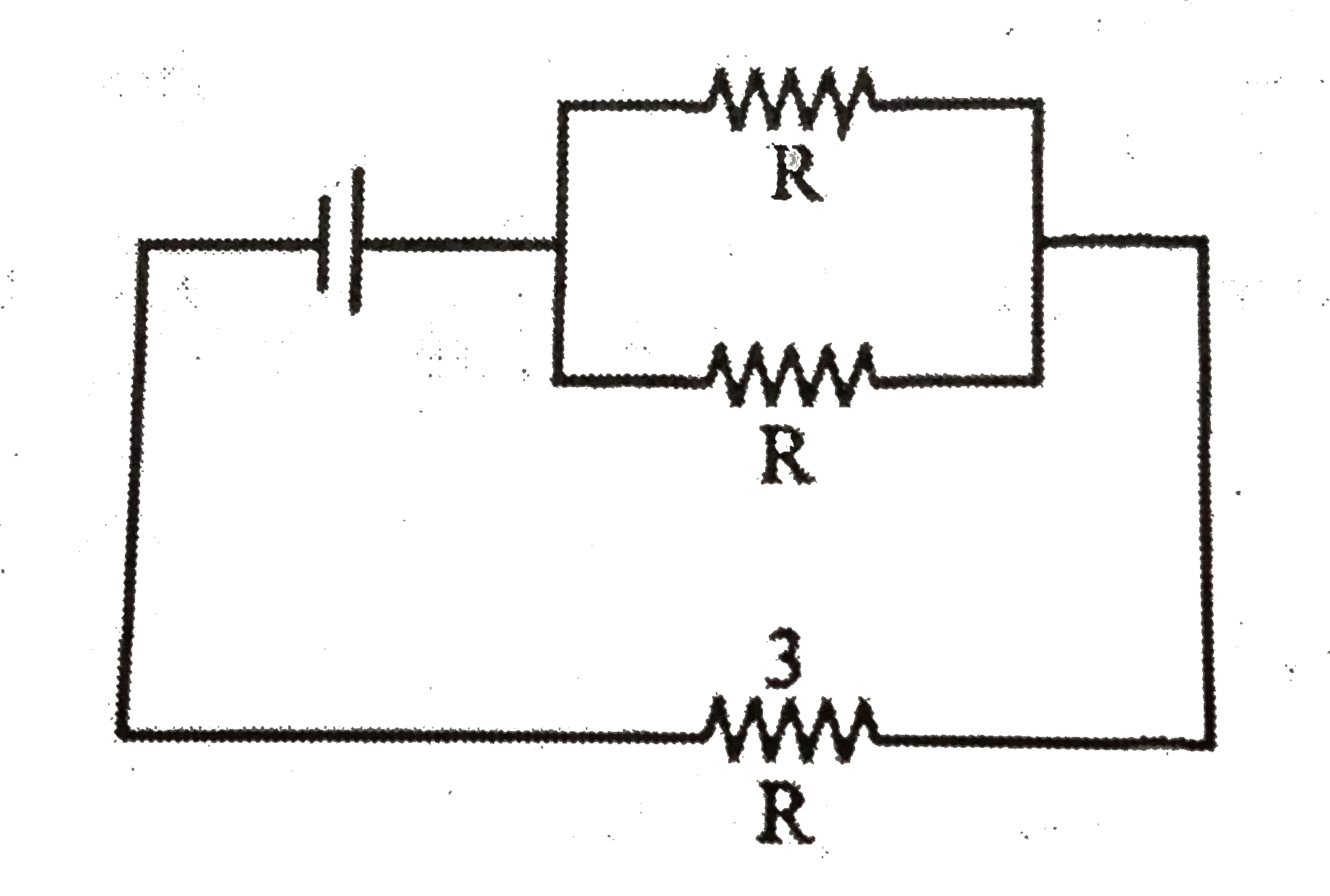 NEWSITUATION `P_(2)` wil be lasser than `(epsi^(2))/(4R)` `P_(3)` will be more than `(epsi^(2))/(4R)` |
|
| 2205. |
A vertical metallic pole falls down through the plane of the magnetic meridian. Will any elf be produced between it's ends. Give reasons for yours answer. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No e.m.f will be induced because the METALLIC pole neither intercepts the horizontal component `B^H` nor the vertical component `B^V` of EARTH .s MAGNETIC field. | |
| 2206. |
Six identical capacitors of each capacitance C_0are arranged as shown in fig .In column-I, equivalent capacitance between two selected points is defined . Match them for their value given in Column-II {:("COLUMN - I","COLUMN - II"),("A) " C_(AB),"p) "2C_0),("B) " C_(AC),"q) "3/2C_0),("C) " C_(OA),"r) " 5/3C_0),("D) " C_(OB),"s) "4/3C_0):} |
|
Answer» <P> |
|
| 2207. |
What is diffraction ? Who discovered it? What kind of diffraction phenomenon occurs in waves ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The phenomenon of waves around the opaque (obstacle) is called diffraction. Accurate definition of diffraction : Diffraction is the physical effect produced by the limited part of the wavefront Diffraction was FIRST discovered by a scientist named Grimaldy. Diffraction phenomenon occur in sound waves, light waves, water waves or matter waves. Diffraction depends on the wavelength of wave `lamda` and width of slit d. That is on the ratio `(lamda)/(d)`. Due to the diffraction phenomenon that occurs SIMULTANEOUSLY in the dark and bright area NEAR the geometric shadow of opaque object Our eyes or optical devices such as telescopes and microscope seem to have a limit on resolving power due to diffraction. The colours appearing on the CD are actually due to the diffraction effects. The true understanding of diffraction can only be explained by wave theory. There are TWO types of diffraction that are obtained from the waves that incident on the slit. (i) If the spherical WAVEFRONTS incident on the slit, then the diffraction called Fresne diffraction. (ii) If the plane wavefronts incident on the slit then the diffraction called Fraunhoffe: diffraction. |
|
| 2208. |
A ray of light is incident at 50^@ on the middle of one of the two mirrors arranged at an angle of 60^@ between them. The ray then touches the second mirror, get reflected back to the first mirror, making an angle of incidence of |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 2209. |
Some common mediums in which speed of sound waves is measured are mentioned below? 1. Air 2. Steel 3. Copper 4. Water What is the correct increasing order.of the speed of sound ? |
|
Answer» 1 lt4lt2lt3 |
|
| 2210. |
Two point charges Q and -3Q are placed at some distance apart. If the electric field at the location of Q is E, the field at the location of -3Q is |
|
Answer» `vec(E)` |
|
| 2211. |
Two balls of mass 'm' and ' ( m)/( 10)' hang at the two ends of a string that passes through a fixed tube and one of the balls lies in the tube, while the other is outside of the tube. The mass ' (m)/( 10)' is rotating about PQ, as shown in figure. Coefficient of friction between the tube and the ball is '1'. Ball which is insid the tube remains in rest and the time period of revolution of the smaller ball is maximum . Find the angle 'theta' which is made by the string with vertical PQ. |
|
Answer» `53^(@)` |
|
| 2212. |
What kind of magnetic field is produced due to straight solenoid ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The magnetic FIELD produced by a solenoid is SIMILAR to that produced by a BAR magnet. | |
| 2213. |
At what time PE will be equal to half of the total energy (TE) :- |
| Answer» Solution :`(1)/(2)KA^2 sin^2 omegat=(1)/(2)((KA^(2))/(2))impliest=(T)/(8)` | |
| 2214. |
The electric and magnetic fields, associated with an em wave, propagating along z axis can be represted by: |
|
Answer» `[VECE = E_0hati, VECB = B_0hatj]` |
|
| 2215. |
The charge and mass of electron was accurately known in the year _____ and the first model of atom was suggested by _____. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :1910, THOMSON | |
| 2216. |
Obtain an expression for the magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron in a hydrogen atom, and hence find the value of Bohr magneton. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let e represent the charge on the particle electron. Let R be the radius of a circular path. Let the electron revolve in an anticlockwise direction. CONVENTIONAL current is taken as clockwise. So magnetic MOMENT can be visualised to be pointing inwards towards the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the orbit. By definition, electric current `""I="charge"/"time"` i.e., `""I=e/T` where, T is the time period of revoulution of electron The period of REVOLUTION of revolution of electron, `""T="circumference"/"speed"` `""T=(2pir)/v` `therefore ""I=(ev)/(2pir)` Magnetic moment associated with the orbiting electron, `""m=1A=mu_(l),` where, `""mu_(l)=` magnetic moment due to orbital motion. Hence, `""mu_(l)=((ev)/(2pir))(pir^(2))` i.e.,`""mu_(l)=(e/(2m_(e)))(m_(e)vr)""` where, angular momentum `l=m_(e)vr` `therefore ""mu_(l)=(e/(2m_(e)))l` The direction of `vec(mu_(l))` is opposite to the direction of angular momentum. The expression `mu_(l)=(evr)/2` for I orbit electron is called Bohr magneton. `mu_(l)=1.6 times 10^(-19) times 2.18 times 10^(6) times 0.53 times 10^(-10) div 2=9.24 times 10^(-24)Am^(2)`. 
|
|
| 2217. |
A thick rope of rubber of density 1.5 (kg)/m^3 Young's modulus 5 xx 10^6 N/M^2 and length 8m is hung from the ceiling of a room . The increase in length due to its own weight is |
|
Answer» a)`9.6 XX 10^(-5) m ` |
|
| 2218. |
A zener diode is used as |
|
Answer» half-wave RECTIFIER. |
|
| 2219. |
Two polarising sheet have their polarising directions parallel so that the intensity of the trasmitted light in maximum. Through what angle must the either sheet be turned if the intensity is to drop by one- half? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, `I = (I_(o))/(2)` Using MALUS law, `I = I_(o) cos^(2) theta` `(l_(o))/(2) = I_(o) cos^(2) theta` `cos THETS = pm (1)/(sqrt(2))` `theta pm 45^(@), pm 135^(@)` |
|
| 2220. |
The coefficient of the thermal conductivity of copper is 9 times that of steel . In the composite sylindrical bar shown in the figure , what will be the temperature at the junction of copper and steel ? |
|
Answer» `75^(@)` `:.` In EQUILIBRIUM `Q_(1)=Q_(2)`. `:.(k_(1)A(100-T)t)/(18)=(k_(2)A(T-0)t)/(6)` `rArr(9k_(2)(100-T))/(18)(k_(2)T)/(6)rArrT=75^(@)C` Correct choice is (a). |
|
| 2221. |
An object producing a pitch of 100 h=Hz approaches a stationary person in a straight line with a velocityof 200 m/s. Velocity of sound is 300 m/s. The person will note a change in frequency, as the object flies past him equal to |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 2222. |
What happens to the impedance and current amplitude at resonant frequency ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Impedance becomes minimum and CURRENT AMPLITUDE becomes MAXIMUM . | |
| 2223. |
The frequency of ultraviolet light is of the order of: |
|
Answer» `10^7` HZ |
|
| 2224. |
A substance of mass 4.953 g occupies 1.5 cm^(-3)of volume . The density of the substance (in g cm^(-3) ) With correct number of significant figures is |
|
Answer» 3.3 |
|
| 2225. |
(A): Voltage is not proportional to current in the case of non-ohmic devices. (R): Voltage is equal to product of resistance and current. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A' |
|
| 2226. |
The earth's core is known to contain iron. Yet geologists do not regard this as a source of the earth's magnetism. Why ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The TEMPERATURE of the core is GREATER than the curle temperature of the iron. So it is not ferromagnetic. | |
| 2227. |
The 6563ÅHalpha line emitted by hydrogen in a star is found to be red shifted by 15Å. Estimate the speed with which the star is receding from the Earth. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`lamda=6563xx10^(-10)m, Delta lamda=15xx10^(-10)m, lamda.=lamda+Delta lamda=6578xx10^(-10)m` `lamda. -lamda=(-v)/C lamda` `:.v=(-(lamda. -lamda)c)/(lamda)=(-Delta lamda . c)/(lamda)=(-15xx10^(-10)xx3xx10^(8))/(6563xx10^(-10))=-6.86xx10^(5)m//s` |
|
| 2228. |
Explain the terms 'mass defect' and 'packing fraction'. What is the relation between mass defect and binding energy. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION : Mass defect : Difference between the SUM of the masses of the nucleons of a nucleus and NUCLEAR mass. `Deltam = [Zm_(p) + (A - Z)m_(n)]-M` Packing fraction : It is the RATIO of difference between nuclear mass and mass number of the mass number or it is the mass CORRECTION for the nucleon. `P.E.=(M-A)/(A)` Binding energy `=Delta mc^(2)=Delta m931 MeV` |
|
| 2229. |
(A): Electric appliances with metallic body have three connections, whereas an electric bulb has a two pin connection. (R): Three pin connections reduce heating of connecting wires. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the CORRECT explanation of 'A' |
|
| 2230. |
Radius of central zone of circular zone plate is . 2.3mm Wavelength of incident light is . 5893 Å Source is at a distance of .6 m Then the distance of first image will be |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 2231. |
Identify the French artist who prepared a series of four prints visualising his dream of a world from the following: |
|
Answer» Kitagewa Utamaro |
|
| 2232. |
The atom of hydrogen absorbs 12.75 eV of energy in ground state. Then what will be the change in orbital angular momentum of the electron in it. |
|
Answer» `(h)/(2pi)` `12.75=-(13.6)/(n^(2))+(13.6)/(1^(2))` `:. (13.6)/(n^(2))=0.85` `:.n^(2)=(13.6)/(0.85) :. n^(2)=16 :.n=4` `:.`Angular momentum in `4^(th)` orbit `l_(4)=(4H)/(2pi)` `:.` Change in angular momentum `=l_(4)-l_(1)` `=(4h)/(2pi-(h)/(2pi)` `=(3h)/(2pi)` |
|
| 2233. |
One watt hour equals to |
|
Answer» 3.6X10^3 Calorie |
|
| 2234. |
In the previous problem, calculate the units of energy consumed per day if the electric motor is used for 3 hours a day. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :1.8 UNITS | |
| 2235. |
A pebble of mass 0.05 kg is thrown vertically upwards. Give the direction and magnitude of the net force on the pebble. [Ignore air resistance] a) during its upward motion b) during its downward motion c) at the highest point where it is momentarily at rest. Do your answers change if the pebble was thrown at an angle of 45° with the horizontal direction? |
|
Answer» Solution :When a body is thrown vertically upwards (or) it moves vertically downwards, gravitational PULL of earth gives it a uniform acceleration `a = +g = +9.8 ms^(-2)`in the DOWNWARD DIRECTION. Therefore, the net force on the pebble in all the three cases is vertically downwards. As m = 0.05 kg and `a = + 9.8 m//s^(2)` `therefore` In all the three case, `F = ma = 0.05^(@) 9.8 = 0.49N`. Vertically downwards. If the pebble were thrown at an angle of 45° with the HORIZONTAL direction, it will have horizontal and vertical components of velocity. These components do not affect the force on the pebble. Hence our answers do not alter in any case. HOWEVER in each case (C), the pebble will not be at rest. It will have horizontal component of velocity at highest point. |
|
| 2236. |
Let y gt 0 be the region of space with a uniform and constant magnetic field B hat(k). A particle with charge and mass m travels along the y-axis and enters in magnetic field at origin with speed v_(0) in region in particle is subjected to an additional friction force vec(F)= - k vec(v). Assumethat particle remains in region y gt 0. |
|
Answer» `x=(kmv_(0))/(k^(2)+(qB)^(2))` `ma_(x) = -kv_(x) + qv_(y) B` `ma_(y) = -kv_(y) - qv_(x)B` At `t = 0, v_(x) = 0" " v_(y) = v_(0) "" x = 0 "" y = 0` finally `v_(x) = 0 "" v_(x) = 0 "" x = x_(1) "" y = y_(1)` `m_(x)o = -kx_(1) - qx_(1) B` `rArrx_(1) = (qBmv_(0))/(k^(2) + (qB)^(2)) rArr y_(1) = (kmv_(0))/(k^(2) + (qB)^(2))` |
|
| 2237. |
The arithmetic mean of several measurements is called. |
|
Answer» practical value |
|
| 2238. |
Two point charges +1muC and +4muC are placed at points (0,0) (30, 0). Then as we move along x-axis |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2239. |
What is meant by the sensitivity of a potentiometer of any given length ? |
|
Answer» Solution :A potentiometer is said to be sensitive if : (i) It can measure very SMALL potential differences. (II) For a small CHANGE in potential difference being measured it shows large change in balancing LENGTH. |
|
| 2241. |
Using Huygen's principle construct a refracted wavefront when a plane wavefront is incident on plane surface from an optically denser meidum side. Using this figure, obtain the condition of critical angle and total internal reflection. |
|
Answer» Solution :When a plane wavefront AB TRAVELLING in an optically DENSER MEDIUM of refractive index `n_(1)` with a speed `c_(1)` is incident on the SURFACE of a rarer medium at an angle of incidence `i`, then the wavelets spread in the rarer medium of refractive index `n_(2)`. (where `n_(2)ltn_(1)`) with a speed `c_(2)` (where `c_(2)gtc_(1)`). Thus, a refracted wavefront CD is formed as shown in figure. As `c_(2) gt c_(1)`, hence obviously the angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence (i.e., `rgti`). However, Snell.s law holds good, according to which `(sini)/(sinr)=(n_(2))/(n_(1))=(c_(1))/(c_(2))` Condition for critical angle: As angle `i` increases, value of angle r also increases. if for a certain value of `i=i_(c)`, the angle of refraction just becomes `90^(@)`, then `(sini_(c))/(sin90^(@))=(n_(2))/(n_(1))=(c_(2))/(c_(1)) or sini_(c)=(n_(2))/(n_(1))=(c_(1))/(c_(2))=(1)/(n_(12))` This angle `i_(c)` is called the critical angle. Condition for total internal reflection: If angle of incidence `igti_(c)`, then it is not possible to find refracted wavefront. in such a case no refraction takes place and whole wavefront is totally reflected back into the denser medium. it is known as the phenomenon of total internal reflection. |
|
| 2242. |
An alternating voltage of 141.4 V (rms) is applied to a vacuum diode as shown in the figure. The maximum potential difference across the condenser will be |
|
Answer» `100 V` |
|
| 2243. |
Assertion : Television signals are received through sky-wave propagation Reason : The ionosphere reflects eletro magnetic waves of frequencies greater than a certain critical frequency. |
|
Answer» ASSERTION and REASON are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion |
|
| 2244. |
A galvanometer may be converted into an ammeter by connecting a sutable ……………in its ……………… . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :LOW RESISTANCE, PARALLEL | |
| 2245. |
A ring of charge with radius 0.5 m has 0.002 pi m gap. If the ring carries a charge of +1 C, the electric field at the centre is |
|
Answer» `7.5 xx 10^(7).NC^(-1)` |
|
| 2246. |
Define intensity of radiation in photon picture of light. Write its SI unit. |
| Answer» Solution :In PHOTON picture of light, INTENSITY of radiation is defined as the energy TRANSFERRED to a surface per unit area per unit time by the photons striking on the surface. Its SI unit is watt/`m^(2)` (W`m^(2)`). | |
| 2247. |
When a glass prism of refractive angle 60^(@) immersed in a liquid, its angle of minimum deviation (delta_(m)) = 30^(@). The critical angle of glass w.r.t liquid medium is : |
|
Answer» `45^(@)` `=(sin(60^(@)+30^(@))/(2))/(sin60^(@)/(@))=(sin45^(@))/(SIN30^(@))=sqrt(2)` `sin C = (1)/(sqrt(2)) rArr C = sqrt(2)` |
|
| 2248. |
An electron is revolving around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom in an orbit of radius nine times the radius of the first orbit Angular momentum of the electron in this orbit is. |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 2249. |
Across a long conductor 2A current is flowing. At 10 cm from it another 5cm long condutor carries 3A. The value of B at short conductor and force on it, in the multiple of 10^(-6) are |
|
Answer» 4T, 6N |
|
| 2250. |
The amplitude of the modulating wave is 2//5 th of the amplitude of the carrier wave. The percentage modulation |
|
Answer» 20 |
|