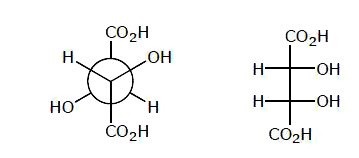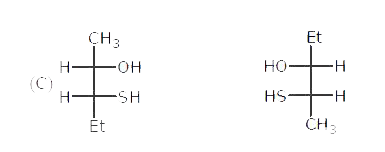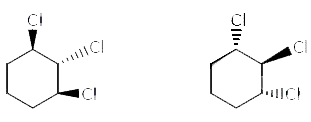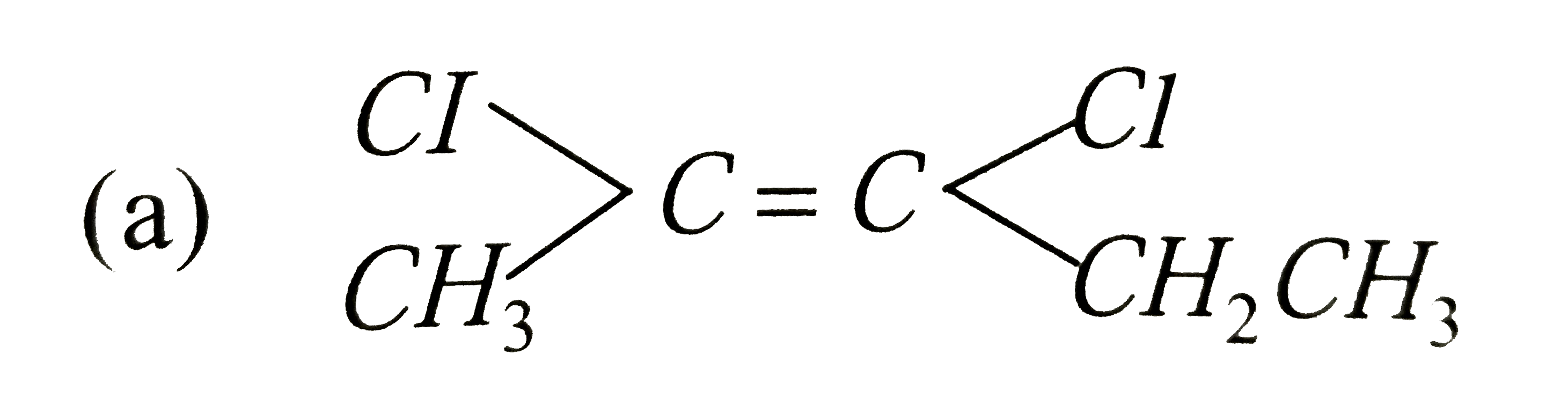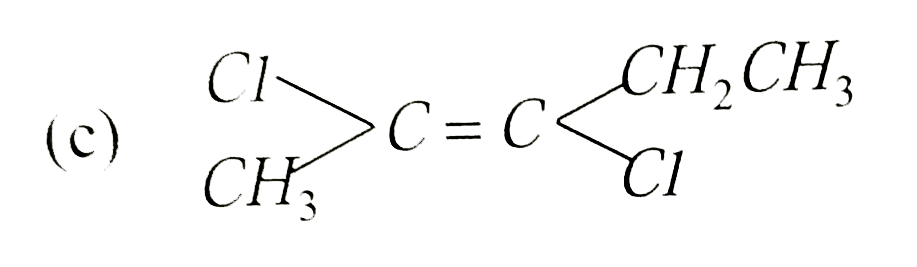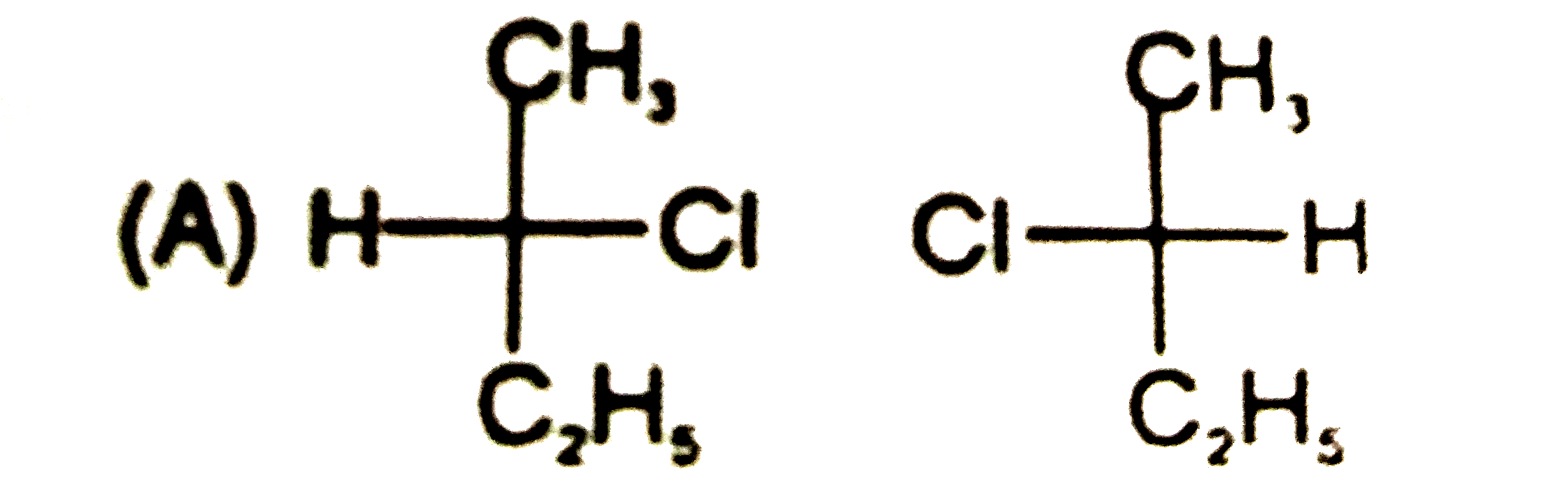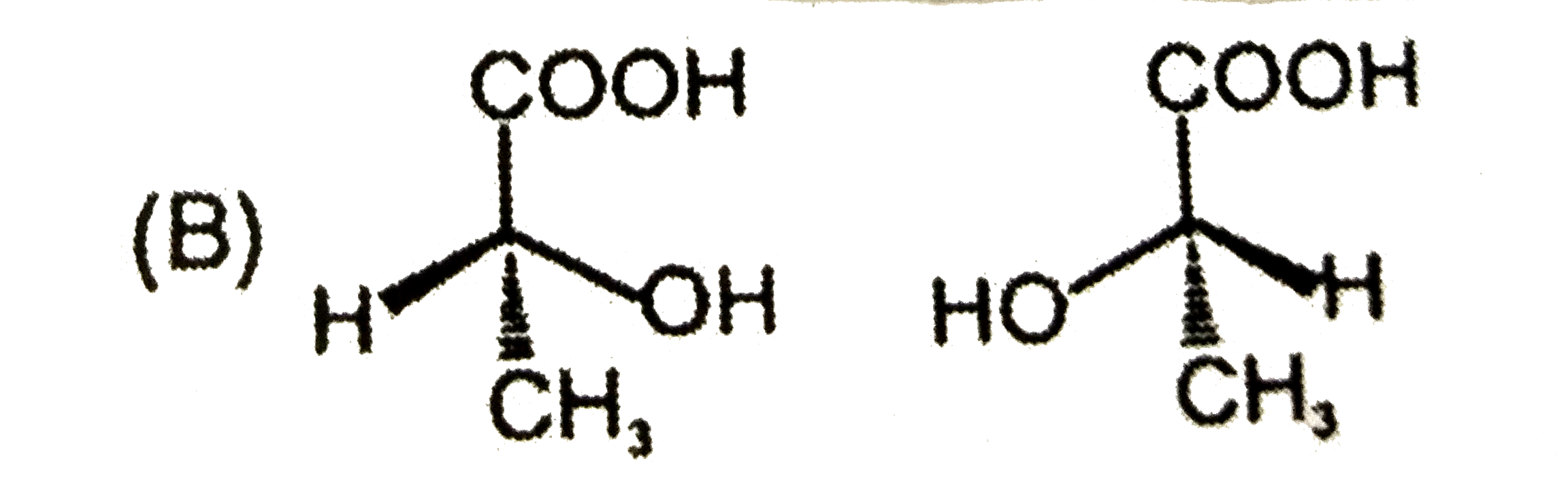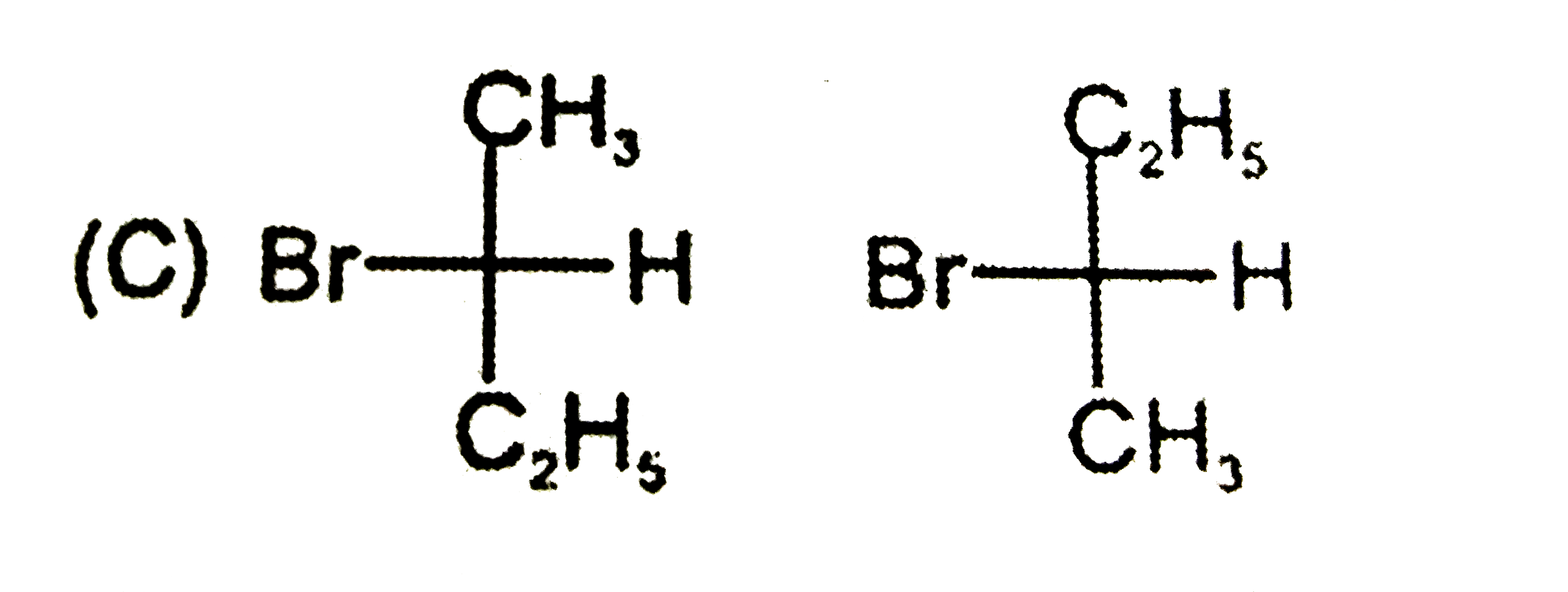Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in Current Affairs.
This section includes 7 InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your Current Affairs knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1. |
Which of the following compounds is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K ? |
|
Answer» `C_6H_5OCH_3` |
|
| 2. |
To a 25 mL H_(2)O_(2) solution excess of an acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 " mL of " 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate solution Calculate the volume strength of H_(2)O_(2) solution. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3. |
The suggested mechanism of a reaction is : (a) A+BhArrD("fast) "(b)A+Drarr2C("slow")Write the balanced equation of the reaction if its experimentally deduced rate equation is , rate k=[A]^(2)[B] Find the intermediate formed during the course of the reaction . Does the predicted rate law from the mechanism match the experimental rate law ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The overall reaction is the sum of the reaction (a) and (b) i.e.,`2A+Brarr2C` Here the intermediate is D. Now , `A+BhArrD,` `k=([D])/([A][B]) ("K = RATE constant")""...[1]` Rate EQUATION of the slowest step `k=[A][D]=k[A]xxK[A][B]` `=kK[A]^(2)[B]=k'[A]^(2)[B]`(where , kK=k') Yes , the predicted rate LAW from the mechanism MATCHES the EXPERIMENTAL rate law. |
|
| 4. |
Which of these changes with time for a first-order reaction A Rate of reaction B . Rate constant C . Half-life |
|
Answer» A only |
|
| 5. |
What is the hybridisation of central atom in the product obtained along with hydrofluoric acid when complete hydrolysis of Xenon Hexa Fluoride takes place ? |
|
Answer» `SP^(3)d^(2)` |
|
| 6. |
Which of the following amino acid forms sulphide bond in polypeptide |
|
Answer» Arg |
|
| 8. |
What is the major product of the following reaction CH_3C-=C-CH_2-CH_3overset("1 mole of " Cl_2)to |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 9. |
Which polymer is used in petrol tank linings ? |
|
Answer» Buna-S |
|
| 10. |
Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose ? |
|
Answer» Amylose Amylose and Glycogen are branched POLYMER of D-glucose |
|
| 11. |
The stability of ferric ionis due to |
|
Answer» half-filled d-orbitals `:. Fe^(3+) = 3d^(5)` . Thus`,Fe^(3+)` ION isquite stabledue to half-filledd-orbitals. |
|
| 12. |
Two important physical evidences supporting the synergic bonding in non-classical complexes are bond lengths and vibrational spectra. Vibrational spectra is based on the fact that the compression and extension of a bond may be analogous to the behaviour of a spring and obeys Hook's law. overline(v)=(1)/(2pic)sqrt((k)/(mu))cm^(-1) where, k=force force constant of the bond which is directly proportional to bonnd strength of CO mu=reduced mass of ligand overline(v)=stretching frequency of the CO bond c=velocity of light Q. In which of the following ligand, sigma-bond order does not change during synergic bonding in their respective complexes: |
|
Answer» CO |
|
| 13. |
Which type pf 'defect has the presence of cations in the interstitial sites ? |
|
Answer» FRENKEL defect |
|
| 14. |
Which of the following reagents can be used to convert primary amides into primary amines containing the same number of carbon atoms? |
|
Answer» `Br_(2) + NaOH` For example, `RCONH_(2)overset(LiAlH_(4))rarr RCH_(2)NH_(2)` `RCONH_(2)overset(Br_(2)+NaOH)rarr RNH_(2)` |
|
| 15. |
Two important physical evidences supporting the synergic bonding in non-classical complexes are bond lengths and vibrational spectra. Vibrational spectra is based on the fact that the compression and extension of a bond may be analogous to the behaviour of a spring and obeys Hook's law. overline(v)=(1)/(2pic)sqrt((k)/(mu))cm^(-1) where, k=force force constant of the bond which is directly proportional to bonnd strength of CO mu=reduced mass of ligand overline(v)=stretching frequency of the CO bond c=velocity of light Q. In which of the following complex stretching frequecy for CO ligand is least as well as bond energy of M-C bond is higher. |
|
Answer» (dien) `Mo(CO)_(3)` Extent of back bonding `alphaMo-CO` bond order `prop(1)/("STRETCHING frequency of CO")` |
|
| 16. |
Which carbohydrate is used in silvering of mirrors: |
|
Answer» Sucrose |
|
| 17. |
Two important physical evidences supporting the synergic bonding in non-classical complexes are bond lengths and vibrational spectra. Vibrational spectra is based on the fact that the compression and extension of a bond may be analogous to the behaviour of a spring and obeys Hook's law. overline(v)=(1)/(2pic)sqrt((k)/(mu))cm^(-1) where, k=force force constant of the bond which is directly proportional to bonnd strength of CO mu=reduced mass of ligand overline(v)=stretching frequency of the CO bond c=velocity of light Q. In Mn_(2)(CO)_(10) carbonyl complex, the d-orbital of Mn-atom which can not be involved in synergic bonding betwee Mn and CO ligands: |
|
Answer» `d_(xz)` |
|
| 18. |
Which is the incorrect order of bond angle :- |
|
Answer» `BF_(3) GT NH_(3) gt H_(2)O` |
|
| 19. |
The standard heats of formation in Kcal mol^(-1) of NO_(2)(g) and N_(2)O_(4)(g) are 8.0 and 2.0 respectively. The heat of dimerization of NO_(2) in Kcal is. Given : 2NO_(2)(g)hArr N_(2)O_(4)(g) |
|
Answer» 10 `=2-2(8)=-14 kcal`. |
|
| 20. |
Which one is the correct statement? |
|
Answer» (+) TARTARIC ACID and mesotartaric acid are TAUTOMERS |
|
| 21. |
whichof the following is notamongshortcomings ofbohr'smodal? |
|
Answer» bohrtheorycouldaccountfor thefinelinesin theatomicspectrum |
|
| 22. |
Which of the following is (are) not acceptable freezing point (s) of a one molal aqueous solution ifthe solute undergoes trimerisation to any extent ? (K_(F) of water =1.86K kg "mol"^(-1)) |
|
Answer» `-0.82^(@)C` |
|
| 23. |
What is the correct order of melting points of elements of first transition series? |
|
Answer» `Mn gt CR gt V gt Ti` |
|
| 24. |
What is Henderson equation ? |
|
Answer» Solution :HENDERSON equation is an equation which is used to determine the PH of an acid buffer with the help of the dissociation constant `K_a` oftheweak acid and concentration of the acid and the SALT used. `pH=pK_a+log.(["Salt")]/(["acid"])` For a basic buffer `pOH=pK_(b)+log.(["salt"])/(["BASE"])` |
|
| 25. |
Which reaction yields the greatest quantity of chlorine from a given quantity of hydrochloric acid |
|
Answer» WARMING CONC. HCl with `MnO_2` |
|
| 26. |
ZnO is colourless at room temperature , while yellow when hot. Why ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ZnO is colourless at ROOM temperature . When it is heated , it becomes YELLOW in colour . On HEATING , it loses oxygen and thereby forming free `Zn^(2+)` ions . The excess `Zn^(2+)` ions move to interstitial sites and the electrons ALSO occupy the interstitial positions . | |
| 27. |
Which of the following reagent is used for the separation of acetaldehyde from acetophenone. |
|
Answer» `NH_(2)OH` |
|
| 28. |
Which of the following products is formed by the reaction of manganese (II) ions salt with peroxodisulphate (S_2O_6^(2-))? |
|
Answer» `Mn_2O_7` |
|
| 29. |
Write main differences between the properties |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 30. |
Whichon reactionwith nitrousacidgivesyellowoilyliquid ? |
|
Answer» ETHYL AMINE |
|
| 31. |
Which base is not present in nucleic acids? |
|
Answer» CYTOSINE |
|
| 32. |
Which of the following alkaline earth metal ion has lowest ionic mobility in aqueous solutions ? |
|
Answer» `MG^(2+)` |
|
| 33. |
What is a ligand ? |
| Answer» Solution :A ligand is an ION or a molecule that can donate ONE of more UNSHARED pairs of ELECTRONS towards a metal ion in a COMPLEX. | |
| 34. |
Which of the following does not give flame test? |
|
Answer» Na |
|
| 35. |
Volume of 0.1 M NaOH needed for the neutralisation of 20 ml of 0.05 M oxalic acid is : |
|
Answer» 10 ml |
|
| 36. |
Which of the following can give monohydricalcohols ? |
|
Answer» ALKYL HALIDES |
|
| 37. |
Which statements is nottrueamongthe following |
|
Answer» AMINES are bases. |
|
| 38. |
Which of the following compound does not exist ? |
|
Answer» `IF_(7)` |
|
| 39. |
Which of the following compound results into benzene nitrile on its dehydration |
|
Answer» BENZOIC acid |
|
| 40. |
Which of the following solvent will have highest solubility of KCl ? |
|
Answer» `C_6 H_6(D=0)` |
|
| 41. |
When a solid changes into liquid, the entropy : |
|
Answer» increases |
|
| 42. |
Which of the following ions has smallest radii ? |
|
Answer» `MN^(2+)` |
|
| 43. |
Which of the following compounds will not gave Lassaigne's test for nitrogen ? |
|
Answer» `NH_(2)NH_(2)` |
|
| 44. |
Whatvolume of10 % (w/v) solutionof Na_(2)CO_(3) will be requiredto neturalise100 mL of HCl solutioncontaining 3.65 g of HCl ? |
|
Answer» `"Normality of HCL solution "=(3.65//36.5)/(100)xx1000=1N` `{:(" "N_(1)V_(1)=N_(2)V_(2)),((Na_(2)CO_(3))(HCl)),(1.89xxV_(1)=1xx100"or"V_(1)=100//1.89=52.9mL):}` |
|
| 45. |
Which scientist shows di-helix structure of DNA ? |
| Answer» Solution :Watson and Crick | |
| 46. |
Which of the following factor affect th rate of the reaction |
|
Answer» VOLUME |
|
| 47. |
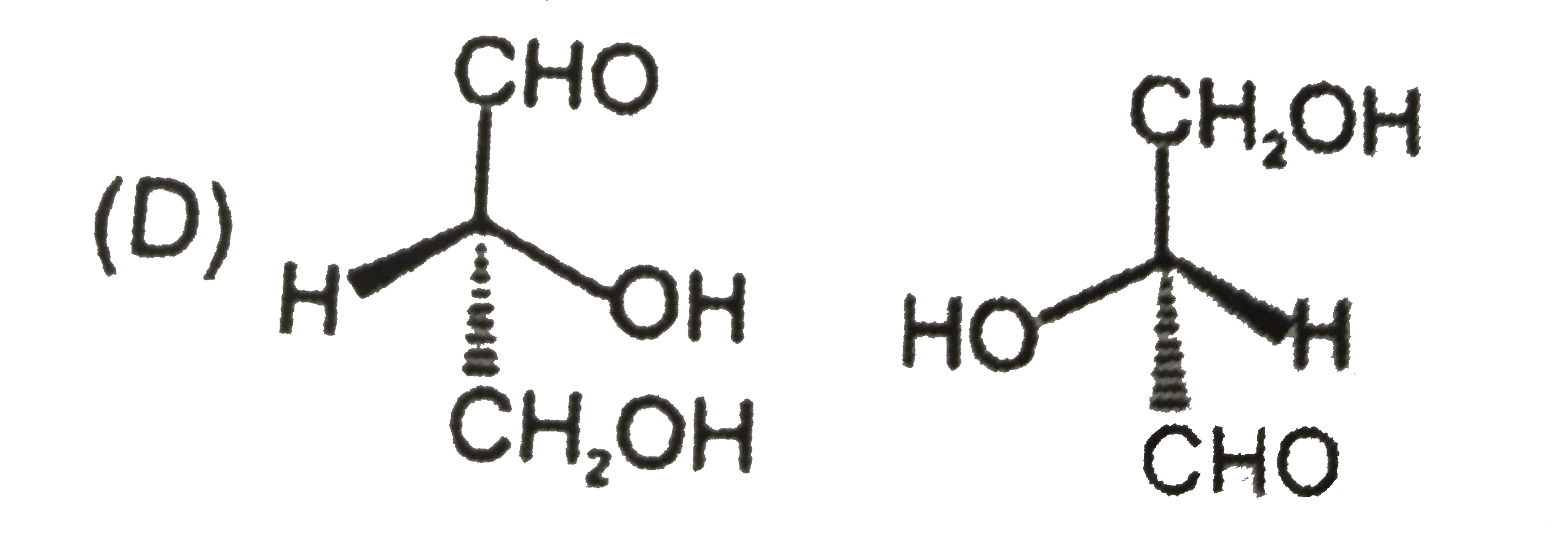
Which is not the pair of enantiomers ? |
|
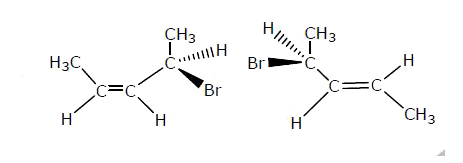
Answer»
|
|
| 48. |
Which of the following is not one of the products formed in the reaction? 2CH_3 - CH_2 -- CI+ 2Na -rarr^(dry ethanol) |
|
Answer» `CH_3- CH_3` |
|
| 49. |
What is the packing fraction of ._(26)^(56)Fe (Isotopic mass = 55.92066) |
|
Answer» `- 14.167` |
|
| 50. |
What is a peptide bond ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The covalent bond `-NH-CO-`FORMED `-NH_2` group of one amino acid and `-COOH` of the other with elimination of a molecule of `H_(2)O` is called a peptide bond. | |