Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in Current Affairs.
This section includes 7 InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your Current Affairs knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1. |
Hygroscopic substance among the following is |
|
Answer» CALCIUM OXIDE |
|
| 2. |
Hydrochloric acid is used to clean the metal surface before the metal surface is subjected to galvanisation. Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :Galvanization is the process of coating zinc on the surfacr of iron by using electrolysis. Iron is associated with impurities like oxides and carbonates on its surface. All these impurities being basic in nature are REMOVED by TREATING it with HYDROCHLORIC ACID. This enables unifrom and firm coating of TINE on the surface of iron. | |
| 3. |
Hydrochloric acid is a ________ acid. (monobasic/ dibasic) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4. |
Hydrated sodium sulphate and hydrated copper sulphate are taken in two air tight containers X and Y respectively. When blue coloured CoCl_(2) is introduced into the two containers, there is colour change in one container. Identify the container and give reaseons in support of your answer. |
|
Answer» Solution :Hydrated SODIUM sulphate `RARR Na_(2)SO_(4)*10H_(2)O` Hydrated copper sulphater `rarr CuSO_(4)*5H_(2)O` As hydrated sodium sulphate is efflorescent in nature it loses water of crystallization. BLUE coloured `CoC1_(2)` present in container "X" absorbs moisture and turns to pink coloured `CoC1_(2)*2H_(2)O` `UNDERSET("blue")(CoC1_(2)) overset("moisture")(rarr) underset("pink")(CoC1_(2)*2H_(2)O)` |
|
| 5. |
Hydrated sodium aluminium silicate is called ______. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6. |
How is sodium chloride extracted from sea water? |
| Answer» Solution :The major SOURCE of sodium CHLORIDE is sea water. The salt obtained due to the EVAPORATION of sea water is CALLED CRUDE salt,because of thepresence of sandandclay particles.Crude salt is dissolved in water and thus thesoluble component ie sodium chloride is extracted and then recrystallized . | |
| 7. |
How is plaster of Paris manufactured ? Mention its applications. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :When GYPSUM is HEATED over a long period of time it partially loses its water ofcrystallization and plaster of Paris `(CaSO_(4).1//2 H_(2)O)` is OBTAINED. It is applied on thebody parts to set FRACTURED bones properly. It is also used for casting statues, toys and decorativematerials. Modern black board chalks and ceiling panels are also made from plaster of Paris. |
|
| 8. |
How is milk powder prepared from milk ? |
| Answer» Solution :Milk is sent through an atomizer as a RESULT it is converted to small droplets and hance surface AREA INCREASES. Due to increased surface, RATE of evaporation of water becomes more at room temperature. In this way the entire water undergose evaporation leaving behind fat particles which are converted to powder by ADDING other ingredients. | |
| 9. |
How is glassmanufactured? Mention different types of glass, their ingredints, properties and application. |
|
Answer» Solution :Manufacture of glass : Glass is made up of silica or sand, limestone, feldspar as MAJOR rew material. Broken pieces of glass called culled culletare added to the RAW material. Some other ingredients like red LEAD, aluminium oxide, manganese oxide, chromium oxide etc are used to impart specific characteristics to glass. The rewmaterials are mixed in the required proportion and melted in a glass tank furnace or pot furnace. Cullet initiates the melting process at a lower temperature. Three major techniques are applied on the molten glass obtained in the process of melting for the manufacture of different products of glass. (i) Blowing of glass : This technique is used for the manufacture of laboratory glassware, bottles etc. (ii) Optical glass : Molten glass is pressed into circular shape from which different optical glasses are manufactured. (iii) Sheet glass/float glass : Molten glass obtained from theglass tank furnace is PLACED on molten bath of tin. Themolten glass spreads on the bath of molten tin with uniform thickness from which sheet glass/float glassis drawn. The different shapes of molten glass obtained from the above three techniques are then subjected to cooling process called annealing at controlled temperature in a longtunnel type annealing chamber. General properties of glass : Glass is a supercooled liquid. Molten glass obtained from glass manufacturing furnaces is allowed to cool down slowly. During cooling , viscosity of glass increasesmanifolds below therange of its freezing temperature and loses itsability to flow. Hence it appears like solid. Glass is transparent, highly chemical resistant, a bad conductor of heat and electricity and it can be easily MOULDED into desired shapes. 
|
|
| 10. |
How is concrete made ? |
| Answer» Solution :It is prepared by mixing cement gravel, andsand in the ratio of `1 : 2 : 3 ` by WEIGHT and REQUIRED quantity of water. | |
| 11. |
How is cementmanufactured ? Mention theareas of application ofcement. |
|
Answer» Solution :Manufacture of cement : The raw MATERIALS used for manufacture of Portland cement are limestone and clay. Cement can be produced in two different processes. (i) Dry process (ii) Wet process In thedryprocess, limestone and clay are used in definiteproportion to achieve the desired property of the cement. The mixture is pulverized (making fine powder) using pulverizer and then heated to ` 1500^(@) C " to "1600^(@)C` to form clinkers (nodules of mixed powder which becomes very HARD after heating). These clinkers are again pulverized to form fine powder and small quantity of gypsum is added andthus cement is produced. In wet process, water is added to the pulverized mixture and a slurry is obtained . Then the slurry is strongly heated to form clinkers. USES of cement Grouting : Grouting is a technique used in construction activities. Pure cement or cementmixed with SAND and water in definite proportion is applied in the gaps of construction material like bricks, tiles etc., for making the surface smooth and STRENGTHENING the structure. Cement mortar:It is a construction material prepared by mixing cement and sand in the ratio of ` 1: 4` by weight. This mixture is converted into thick slurry by adding required quantity of water. It is used for joining bricks and plastering. Concrete : It is also a construction material prepared bymixing cement, gravel and sand in the ratio of ` 1:2:3` by weight and required quantity of water . It is used for casting roofs, pillars, beams etc. Reinforced cement concrete (RCC): When cement concrete is reinforced usingstructural steel, it is called reinforced cement concrete. RCC provides huge strength and durability to the structure. It is used for theconstruction of bridges, railway sleepers, prefabricated structures, columns, beams roofs etc. |
|
| 12. |
How do you distinguish physical change and chemical change? |
|
Answer» Solution :The FOLLOWING table gives the comparative STUDY of physical and chemical change. `{:("Physical change","Chemical change"),(("i")" Molecularcomposition of the matter does not change","MOLECULAR composition of matter changes."),(("ii")" No new SUBSTANCE is formed . Only the physical appearance or BEHAVIOR changes. ","New substance is formed."),(("iii")" This change is called temporary or reversible because the previous form of matter can easily be revied.","This change is called permanent or irreversible because the previous form of matter cannot be revived by physical processes."):}` |
|
| 13. |
How do you distinguish metals and non - metals with respect to electronic arrangement? |
| Answer» Solution :Metals GENERALLY possess 1 to 3 electrons in their outermost shellsandtheytendto lose electrons to FORM POSITIVE ions CALLED cations . Nonmetals possess 4 to7 electrons in their valence shells and they tend to gain electrons to form NEGATIVE ions called anions. | |
| 14. |
How do not the energy of orbits in an atom vary? |
| Answer» Solution :The energy of the orbit INCREASES with increase in DISTANCE from THENUCLEUS. | |
| 15. |
How can you harvest water in household? |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) At the individual LEVEL, minimizing the wastage in DAILY activities. (2) UTILIZING the RAIN water to recharge the GROUND water which is called rain water harvesting. |
|
| 16. |
How can the constituents of compounds and mixtures be separated respectively ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The constituents of COMPOUNDS and mixture can be SEPARATED by chemical and PHYSICAL METHODS respectively. | |
| 17. |
How are the delicate colours of auroras caused ? |
| Answer» Solution :When high energetic ELECTRONS from the SUN collide with the molecles like `N_(2)" and "O_(2)` present in the ATMOSPHERE cause DELICATE colours of AURORAS. | |
| 18. |
How are springs formed? |
| Answer» Solution :GROUND water while travelling through a NETWORK of CRACKS and fissures emerges from below the surface of the earth. At this point the aquifer surface meets the ground surface and water flows on to the surface of earth with high PRESSURE. This is called spring water. | |
| 19. |
How are paints and plastic emulsions prepared ? |
| Answer» Solution :Paints are nothing but the coloring MATERIALS dissolved in the suspension of basic LEAD carbonate in linseed OIL. Plastic emulsion is a kind of paint which is prepared by dissolving coloured plastics in AMYL acetate. Thedurability of plastic emulsion is MUCH more than that of basic lead carbonate paints. | |
| 20. |
How are bricks manufactured ? |
| Answer» Solution :Bricks are made by using clay. The right proportion of water is added to clay and kneaded PROPERLY. The kneaded clay is PRESSED in the shape of BRICK andheated at high temperature (about `1000^(@) C`) andthis process hardens thebrick. Bricks are the STRUCTURAL material used for construction of walls ofbuildings. | |
| 21. |
How are bicarbonates added to water? How can they be removed by boiling? Give equations. |
|
Answer» Solution :The presence of bicarbonates in water results due to the dissolution of `CO_(2)` gas in RAIN water. This water flows across a wide area with different types of rocks. Calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate present in the rocks react with the water containing `CO_(2)` there by forming the corresponding bicarbonates. Bicarbonates being highly soluble in water imparts hardness to water. The hardness caused by these BICARBONATE salts is called temporary hardness. When the water containing temporary hardness is subjected to boiling these bicarbonates get converted to insoluble carbonates and can be REMOVES by filtration. `Ca(HCO_(3))_(2) rarr CaCO_(3) + H_(2)O + CO_(2)` `Mg(HCO_(3))_(2) rarr MgCO_(3) +H_(2)O + CO_(2)` |
|
| 22. |
Hot water bags are generally used for reducing body pain. Can they also be used to keep us warm in winter? Explain. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The specific heat capacity of WATER is very high. Hence it can lose a hot of heat without much decrease in its temperature. The heat lost by water can INCREASE the temperature of the other SUBSTANCES which is in contact with it. Therefore hot water bags can used to keep out body WARM in winter. | |
| 23. |
Heating solid ammonium chloride involves change in the ___________. |
|
Answer» physical state only Itinvolves both sublimation (physical CHANGE) and chemical decomposition (chemical change) |
|
| 24. |
Heating of a mixture consisting of potassiumm nitrate , carbon and sulphur involves which of the following chemical changes ? |
|
Answer» DECOMPOSITION and combination. `2KNO_(3)OVERSET(Delta)to2KNO_(2)+O_(2)` `C+O_(2)toSO_(2)` `C+O_(2)toCO_(2)` Hence , thetype of chemical change involved is decomposition and combination. |
|
| 25. |
Hard water is fit for dyeing clothes. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :HARD water is unfit for DYEING clothes as it make colour fade. | |
| 26. |
H_(2)SO_(4) is used in the manufacture of fertilizers. The property exploited in H_(2)SO_(4) is |
|
Answer» FORMATION of soluble SALTS |
|
| 27. |
Graphite is used in the manufacture of crucibles where a small quantity of metals can be melted. It is also used as electrodes. Which of the following properties of graphite is not exploited in these two given applications? |
|
Answer» Highly RESISTANCE to chemicals. |
|
| 28. |
Graphite is usedas a pencil lead because |
|
Answer» it has a HIGH MELTING point. |
|
| 29. |
Graphite is a good conductor of heat. |
|
Answer» Solution :FALSE REASON : Graphite is a good conductor of electricity but BAD conductorof heat. |
|
| 30. |
Graphite is a _________ conductor of heat. |
|
Answer» Graphite is a bad CONDUCTOR of HEAT. |
|
| 31. |
Glass in a/an |
|
Answer» amorphoussolid |
|
| 32. |
Given the balanced chemical equation for the laboratory preparation of oxygen gas. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`2H_(2)O_(2)OVERSET(MnO_(2))(to)2H_(2)O+O_(2)` | |
| 33. |
Give any two chemical properties of CO_(2)? |
|
Answer» Solution :TWO chemical properties of `CO_(2)` are (i) `CO_(2)` REACTS with alkali to form salt to form salt and water. This REACTION called neutralization `CO_(2)+2NaOHtoNa_(2)CO_(3)+H_(2)O` (ii) `CO_(2)` reacts with water to form carbonic acid. Hence `CO_(3)` is acidic in nature. `CO_(2)+H_(2)OtoH_(2)CO_(2)` |
|
| 34. |
Give two examples of metals which can exist can exist in liquid state below 35.^(@)C. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Mercury and GALLIUM are two EXAMPLES of metels which can exist in liquid state below `35^(@)C`. | |
| 35. |
Give two examples for sublimable substances. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The TWO EXAMPLES of sublimable substances are CAMPHOR and iodine. | |
| 36. |
Give the necessary chemical equationsand balance them.(a) Reaction of red hot iorn with steam to giveFe_(3)O_(4) .(b)burning magnesiun ribbon in an atmosphere of nitrogen.(c ) Displacement of copper from the solution of its sulphate by zinc. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a)`3Fe+underset("steam")(4H_(2)O)tounderset(("Ferroso FERRIC OXIDE"))(Fe_(3)O_(4)+4H_(2))` (b) `3Mg+N_(2) ""toMg_(3)N_(2)` ( c)`CuSO_(4)+Zn""to ZnSO_(4)+Cu` |
|
| 37. |
Give the electronic configuration and geometrical representation of the following elements. |
Answer» SOLUTION :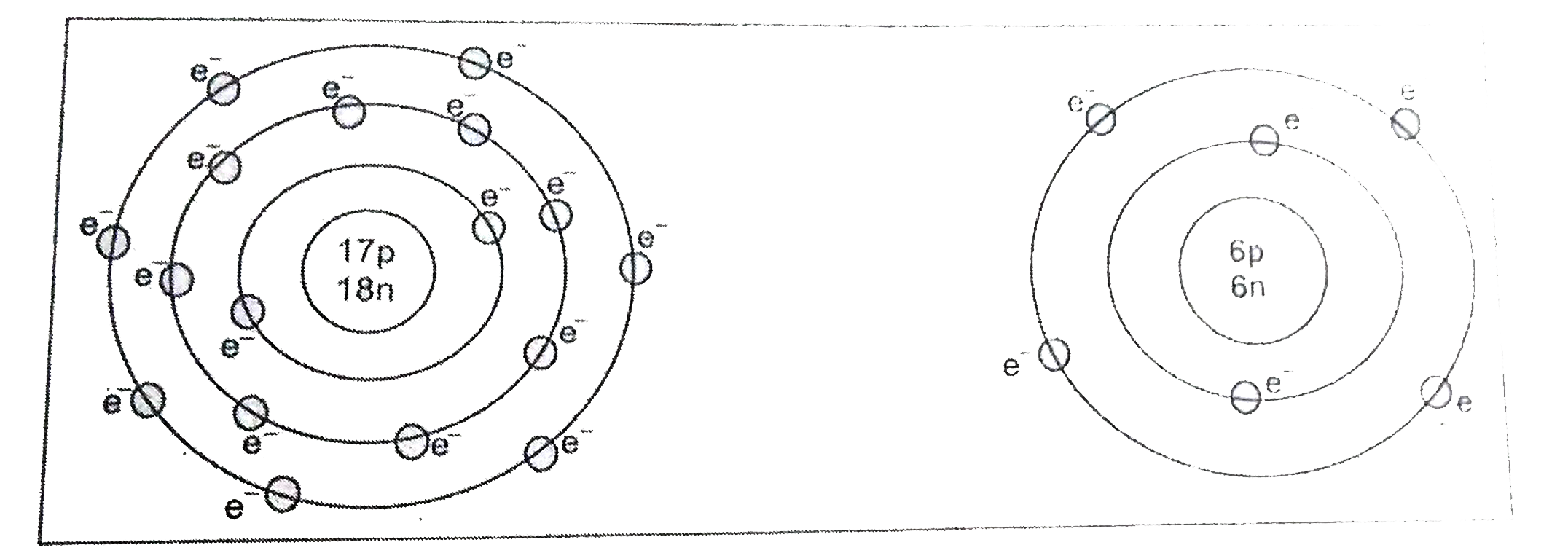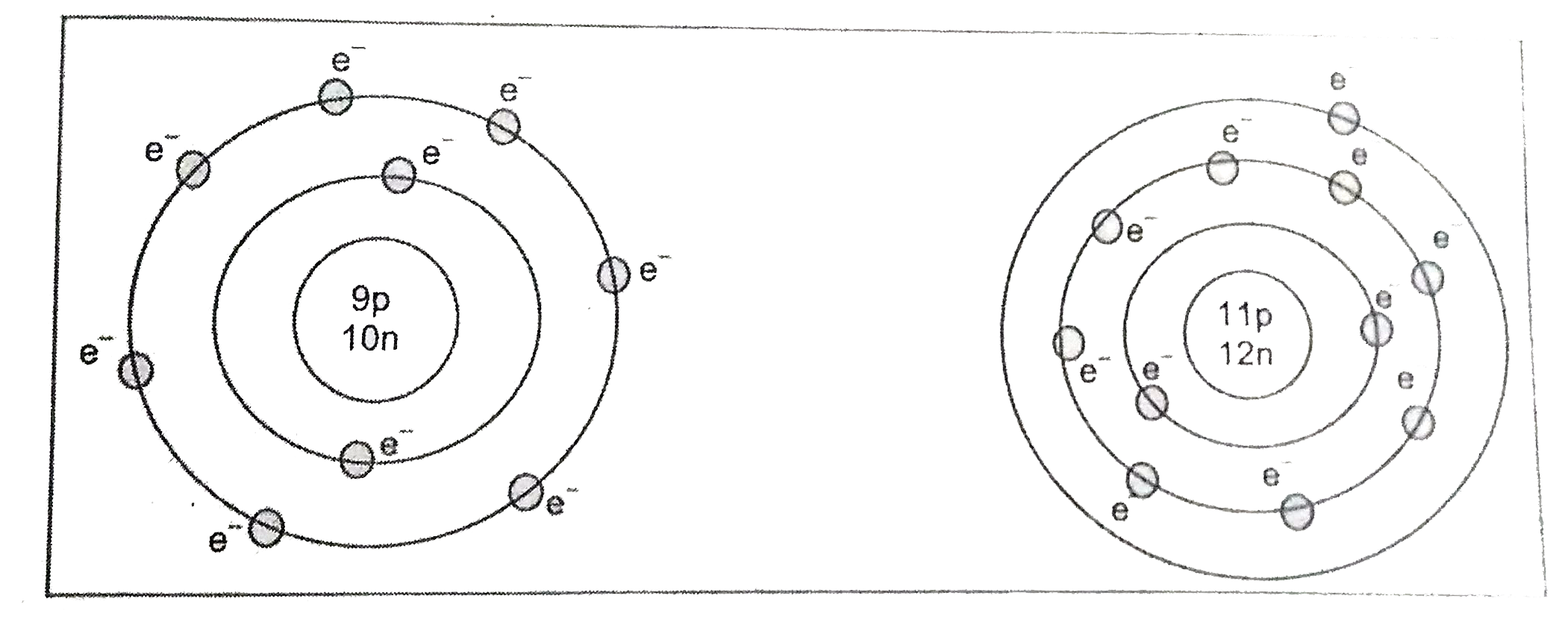 
|
|
| 38. |
Give the chemical properties of acids and bases by giving balanced chemical equations. |
|
Answer» Solution :Some important chemical properties of acids `{:("Reaction","Example"),("Reaction with metals: some metals displace",Zn"+"H_(2)SO_(4) rarr ZnSO_(4) "+"H_(2)),("hydrogen from the strong acids"(HC1, H_(2)SO_(4)).,Mg "+"2HC1 rarr MgC1_(2) "+"H_(2)),("These are called active metals.",),("Reaction with metal oxides: All dilute MINERAL",ZnO"+"H_(2)SO_(4) rarr ZnSO_(4)"+"H_(2)O),("acids react with METALLIC oxides to form their",CAO"+"2HNO_(3) rarr Ca(NO_(3))_(2)"+"H_(2)O),("respective metallic salts and WATER.",),("Reaction with metal carbonates: This",),("reaction also comes under neutralisation but",CaCO_(3)"+"2HC1 rarr CaC1_(2)"+"H_(2)O"+"CO_(2)),("accompanied by the release of"CO_(2)"gas along",MgCO_(3)"+"H_(2)SO_(4) rarr MgSO_(4)"+"CO_(2)"+"H_(2)O),("with the formation of salt and water.",):}` |
|
| 39. |
Give the characteristics of potable water. |
|
Answer» Solution :Characteristics of potable water are GIVEN below: (i) It should be FREE from suspended impurities and microorganisms. (ii) It should CONTAIN dissolved GASES such as `O_(2)` and `CO_(2)` (iii) It also should contain some dissolved SALTS especially common salt. |
|
| 40. |
Give the charactercs (symbol , change , mass) of all fundamental particles. |
| Answer» SOLUTION : `{:(,"symbol","Charge","MASS"),("Proton"," P",1.6xx10^(-19)C,1.67xx10^(-27)KG),("ELECTRON"," e",-1.6xx10^(-19)C,9.1xx10^(-31)Kg),("Neutron","N","Nil",1.72xx10^(-27)Kg):}` | |
| 41. |
Give some causes of depletion of water table. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Following are some causes of depletion of WATER table: (i) Scanty rain fall (ii) Deforestation (III) Increasing industrialization (iv) INCREASED AGRICULTURAL activities. |
|
| 42. |
Give schematic representation of classification of matter based on its composition. |
Answer» Solution :CLASSIFICATION of MATTER based on its COMPOSITION is SCHEMATICALLY represented below : 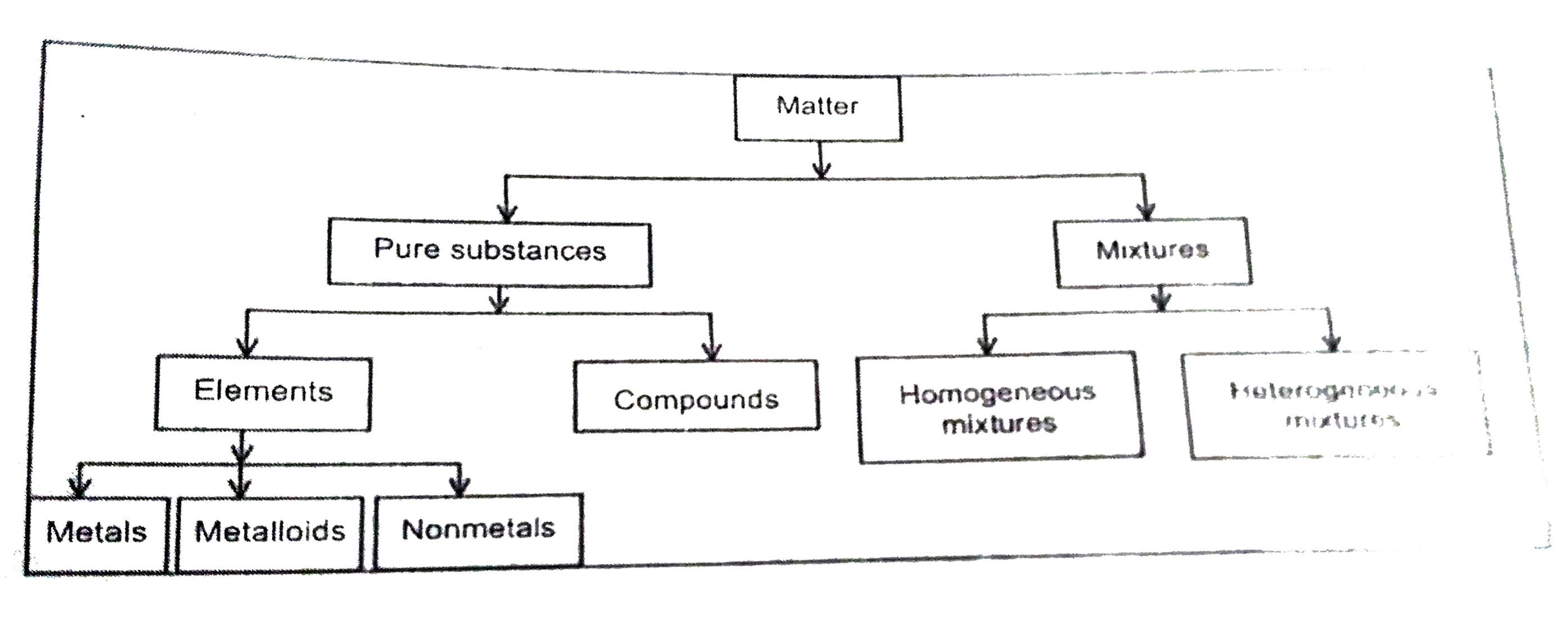
|
|
| 43. |
Give reasons for the following: (a) Sea water is unfit for usage and consumption (b) River water is considered as fresh water. (c ) Underground water does not contain suspended impurities. (d) Distilled water is used for laboratory processes. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) The presence of high proportion of dissolved SALTS makes sea water unfit for usage and consumption. (b) RIVER water takes a long course and flows over land from higher altitudes. As the proportion of dissolved salts is less than in saline water it is considered as fresh water. (c ) The underground water during seepage GETS filtered through various layers of soil and hence does not contain suspended impurities. (d)Since most of the chemical reactions take place in water, LABORATORY work requires pure water for carrying out various tests and reactions. Hence distilled water is used for laboratory processes. |
|
| 44. |
Give reasons for the following. (a) Leaves of plants appear to wilt in summer afternoons. (b) When perfume is sprayed on hand, we feel cool. (c ) Leaves of submerged aquatic plants contain wax coating. (d) Perspiration is greater in coastal areas than in non coastal areas |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Rate of evaporation (transpiration is maximum in the summer afternoos as temperature is maximum in the afternoon. (b) Evaporation of perfume taken heat from the BODY and we get cooling sensation. ( c) due to WEAK ADHESIVE forces between waxy material and water, the leaves of submerged aquatic plants are protected from decay. (d) Rate of evaporation is more in non-coastal since HUMIDITY is less. Rate of evaporation is less in coastal areas since humidity is more. Thus sweat does not evaporate readily in coastal areas. |
|
| 45. |
Give reason for the stability of inert gases. |
| Answer» Solution :Insert gases have 8 ELECTRONS in their VALENCE SHELL and they are stable . Helium , an inert gas has 2 electrons in the 1st shell which is its valence shell . It is stable because 1st shell cannot ACCOMMODATE more than two electrons. | |
| 46. |
Give equations for the dissociation of the following compounds in their solutions and write the formulae of the salts formed from them. (a) H_(2)SO_(4) (b) Mg(OH)_(2) |
|
Answer» Solution :`H_(2)SO_(4) rarr 2H^(+) + SO_(4)^(-)` LTBRGT `MG(OH)_(2) rarr Mg^(+2) + 2OH^(-)` `Mg(OH)_(2) + H_(2)SO_(4) rarr MgSO_(4) + 2H_(2)O` `Mg(OH)_(2) + H_(2)SO_(4) rarr Mg(HSO_(4))_(2) + H_(2)O` `MgHSO_(4) + Mg(OH)_(2) rarr Mg" "SO_(4) + H_(2)O` `Mg(OH)_(2) + H_(2)SO_(4) rarr Mg(OH)" "HSO_(4) + H_(2)O` `Mg(OH)(HSO_(4)) + H_(2)SO_(4) rarr Mg(HSO_(4)) + H_(2)O` |
|
| 47. |
Give an example of dibasic acid. How is it obtained from the corresponding nonmetal? Give balanced equations. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :SULPHURIC acid is a DIBASIC acid. `S + O_(2) rarr SO_(2)` `2SO_(2) + O_(2) rarr 2SO_(3)` `SO_(3) + H_(2)O rarr H_(2)SO_(4)` |
|
| 48. |
Give an example of a solution which gives us instant energy. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :GLUCOSE solution GIVEN INSTANT ENERGY. | |
| 49. |
Germanium is a _________ |
|
Answer» gas |
|
| 50. |
Generallyl, pickles are not stored in tin vessels because |
|
Answer» tin is COSTLY metal. |
|