Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in Current Affairs.
This section includes 7 InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your Current Affairs knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1. |
Generally when a person jumps into water in any water body, he is expected to sink. But he tends to float in the Dead Sea. How do you account for this? |
| Answer» Solution :DEAD sea consists of large quantity of dissolved SALTS to the EXTENT of saturation. Density of human body is LESS than the water present in dead sea. Therefore human body FLOATS. | |
| 2. |
Generally , the components of compound are separated by _________ . |
|
Answer» The COMPONENTS of the COMPOUND are separated by chemical methods. |
|
| 3. |
Generally, pickles are stored in |
|
Answer» tin vessels or GLASS vessels. |
|
| 4. |
Generally metals |
|
Answer» are SOLIDS |
|
| 5. |
Generally, hydrolysis of metal oxides gives |
|
Answer» acids |
|
| 6. |
Generally ___________ changes are reversible because there is no change in the __________ of the substance. |
|
Answer» Most of the physical change can be REVERSED SINCE there doesnot involve change in molecular composition of the SUBSTANCE. |
|
| 7. |
Generally, a netal gets corroded due to oxidation. Name a metal which becomes chemically resistant due to oxiadation. |
|
Answer» Zinc |
|
| 8. |
Generally a metal gas corroded due to oxidation. Name a meral which becomes chemically resistant due to oxidantion. |
|
Answer» Zinc |
|
| 9. |
Gases like nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide present in atmophere contribute to acid rain. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 10. |
Gases form homogeneous mixture due to their |
|
Answer» diffusiblity |
|
| 11. |
Gaseous products formed when gun powder is subjected to heating are dissolved in water. Identify the products formed on dissolution. |
|
Answer» `H_(2)CO_(3), HNO_(3)` |
|
| 12. |
Freezing point of water is 0^(@)C at ______ |
|
Answer» 76 CM of Hg |
|
| 13. |
Four types of reactions are given below in a particular order.(1)Displacement reaction (2)Combination reaction (3)Double displacement displacement(4) Decomposition reactionFollowing this sequence to arrange the reactiongiven below.(a)A+BtoAB.(b)ABtoA+B( c)AB+CtoCB+A(d) AC+BDtoAD+BC |
|
Answer» cadb (II)`A+BtoAB` (III)`AC+BDtoAD+BC` (IV)`ABtoA+B` |
|
| 14. |
Fountain ink pen leaks at hight altitudes. It is due to |
|
Answer» low atmospherisc presseure |
|
| 15. |
Formulae of sodium sulphite and sodium sulphate are respectively _________ and _________. |
|
Answer» `Na_(2)SO_(3),Na_(2)SO_(4)`are the fomulae of sodium SULPHITE and sodium SULPHATE RESPECTIVELY. |
|
| 16. |
Formula of washing soda is _________. |
|
Answer» (SODIUM carbonate DECAHYDRATE) |
|
| 17. |
Formation of clouds , mistand fog are the examples of ____________. |
|
Answer» chemical combination of`O_(2)and H_(2)O`. |
|
| 18. |
For the separation of the components of a mixture of iodine, iron filings and sawdust arrange processes in sequential order. (a) The mixture is covered with an inverted funnel. The outside surface of the funnel is wrapped with a moist filter paper and the mixture is gently heated. Iodine is separated. (b) A strong bar magnet is moved through the mixture. The iron filing are separated. (c ) I Sawdust is left after iodine separates. The mixture is exposed to wind to remove sawdust. |
|
Answer» B,a,c (i) A strong bar magnet is moved through the mixture. The iron filings are separated (ii) The mixture is COVERED with an inverted funnel. Theoutside SURFACE the funnel is wrapped with a moist filter paper and the mixture is gently. Heated. Is separated. (iii) SAWDUST is left after iodine separates. |
|
| 19. |
For the separation of components of a mixture of camphor, filings and sand, arrange the following processes in sequence. (a) Magnetic separation, (b) Distillation (c ) Sublimation, (d) Sedimentation and decantation |
|
Answer» Solution :a,c (i) Magnetic separation (II) Sublimation |
|
| 20. |
For each of the following reactions identify theproducts formed and balance the reaction.NaCl+AgNO_(3)to(b)Zn+HCl to |
|
Answer» Solution :(a)`NaCl+AgNO_(3)toNaNO_(3)+AgCl` (B)`Zn+2HCl toZnCl_(2)+H_(2)uarr` |
|
| 21. |
Explain water cycle and its role in rising the ground water table. |
Answer» Solution :Water which is so essential in so many ways derives its major source from rains. Water is added to the ATMOSPHERE in the form of water vapour by various processes. The water vapour so added to the atmosphere, being lighter than air, reaches the upper atmosphere. There, due to lower TEMPERATURE it gets condensed to form tiny water droplets which remain suspended in air. These small water droplets associated with the DUST particles form larger aggregates called micelles. They appear as clouds and when the quantity of water in the clouds increase, it causes RAIN. This rain water can form various types of water bodies in the form of surface water and can help recharge ground water level. This natural process of adding water to atmospheric air and its subsequent condensation to rain water is calledwater cycle. Thus, water cycle builds a natural balance in the ECOSYSTEM. 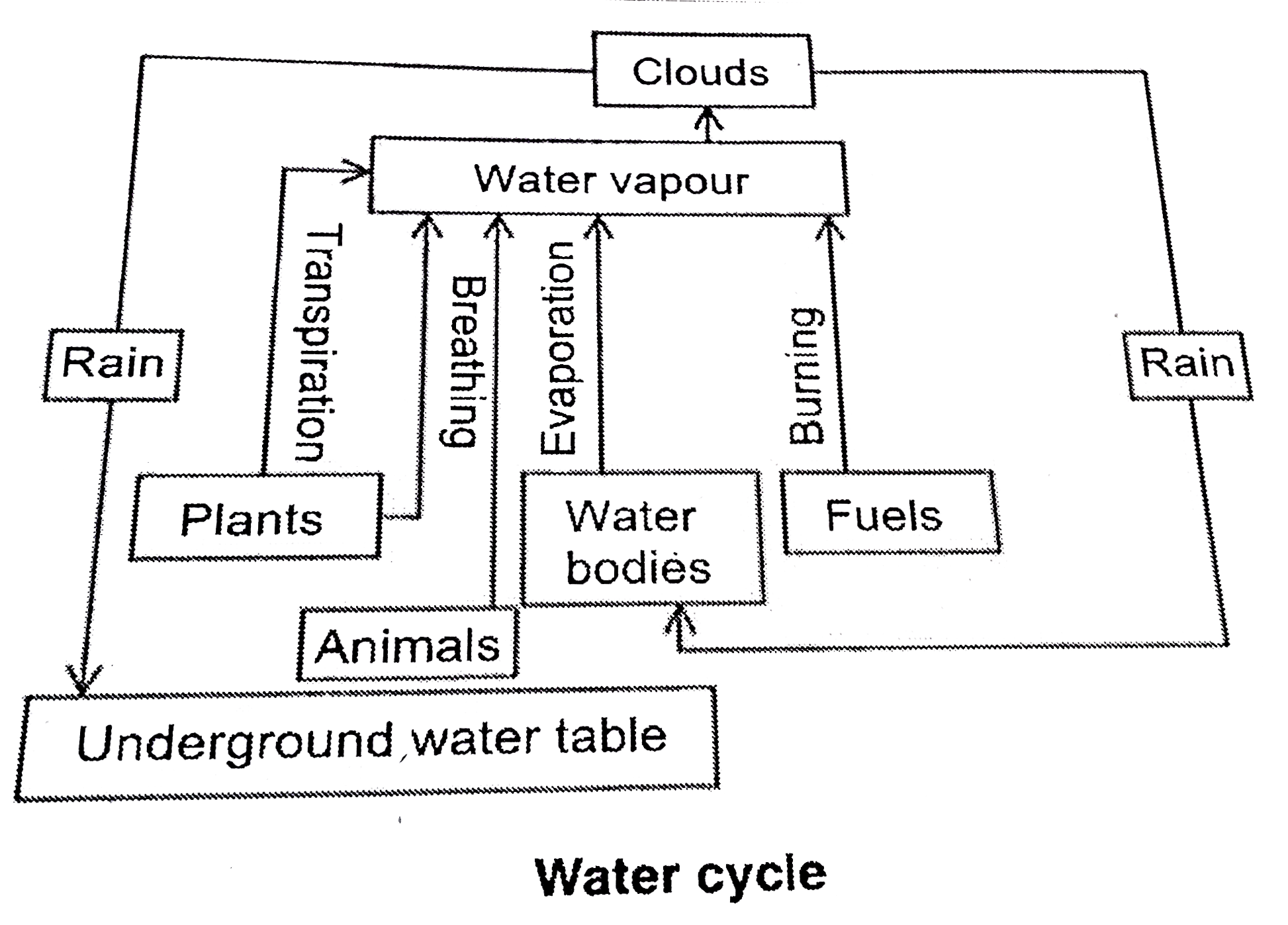
|
|
| 22. |
Explain the suitable method of separation of ammonium chloride from common salt. |
|
Answer» Solution :Mixture of sodium chloride and ammonuium chloride are taken in a flat basin and a funnel is inverted over it. The outer surface of the funnel is wrapped with a water soaked filter PAPER and the open end of the stem of the funnel is plugged with a piese of paper cotton to STOP the passge of any vapour. The basin is kept in a SAND bath. The sand bath is placed over a wire mesh kept on a tripod STAND and then is heated gently with the help of Bunsed burner. A white coloured fume is observed which condenses as white powdery substance when it comes in contact with colder wall of the funnel. The process of heating is continued till the evolution of white vapour is observed. Since ammonium chloride is a sublimable substance, it sublimes and then condenses as white powder. The substance LEFT over on the basin is sodium chloride which does not sublime. Ammonium chloride is scrapped off from the walls of the funnel and thus the mixture separated. |
|
| 23. |
Explain the significance of nitrogen, oxygen and water vapour present in the stratosphere |
| Answer» Solution :The nitrogen and OXYGEN which are major components of the atmosphere have very important associations with life. Nitrogen being an inactive component of atmosphere, dilutes the activity of oxygen. Oxygen, an ACTIVE component is considered to be a suppoter of life on earth, as it is respoonsible for carrying out the important processes like respiration and BURNING. WATER vapour along with dust rarticales is halpful in the formation of for, MIST, clouds etc. | |
| 24. |
Explain the role oxygen in the following (a) Repiration (b) Cutting and welding ( c) Explosion |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Respiration : Oxygen is required for repiration of living beings. In respiration burning of GLUCOSE takes place. Oxygen inhaled during respiration is utilized in oxidizing the glucose to carbon dioxide and water, which is accompanied with evolution of energy. `C_(6)H_(12)O_(6)to6CO_(2)+6H_(2)O+"energy"` (ii) Cutting and welding: A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen on burning gives oxy hydrogen flame of `2800^(@)C` temperature. While mixture of hydrogen and acetylene PRODUCES oxy acetylene flame which has `3300^(@)C` temperature. These flames easily melt the metals and hence used for cutting or welding them. (iii) Explosion: A mixture of coal, petroleum jelly liquid oxygen CALLED cartridge is used for blasting ROCKS. |
|
| 25. |
Explain the role of alum in the purification of water. |
| Answer» Solution :Alum is ADDED during sedimentation process to hasten the process of precipitation of suspended impurities. During the precipitation process, some BACTERIA also get trapped and are removed. | |
| 26. |
Explain the removal of temporary hardness of water by Clark's method. Give equations. |
|
Answer» Solution :Clark's method: This method involves the addition of slaked LIME to water either in solid or in liquid form. This RESULTS in conversion of soluble bicarbonates to insoluble carbonates. On FILTRATION SOFT water is obtained. `Ca(HCO_(3))_(2) + Ca(OH)_(2)rarr 2CaCO_(3) darr + 2H_(2)O` `MG(HCO_(3))_(2) + Ca(OH)_(2) rarr CaCO_(3) darr + MgCO_(3) darr + 2H_(2)O` |
|
| 27. |
Explain the process of sedimentation and decantation. |
|
Answer» Solution :Sedimentation and decantation In the mixture of sand and water, the HEAVIER solid particles settles at the bottom and can be separated by this process. Process : A mixture of sand water is taken in a beaker and kept still for some time. The heavier sand particles settle down at the bottom. The CLEAR water above it , is gently POURED off into another beaker with the help of a glass rod. The glass rod helps to pour off the liquid, without DISTURBING the solid settled at the bottom. The water collected in the second beaker is clear and the sand particles are left behind in the FIRST beaker. 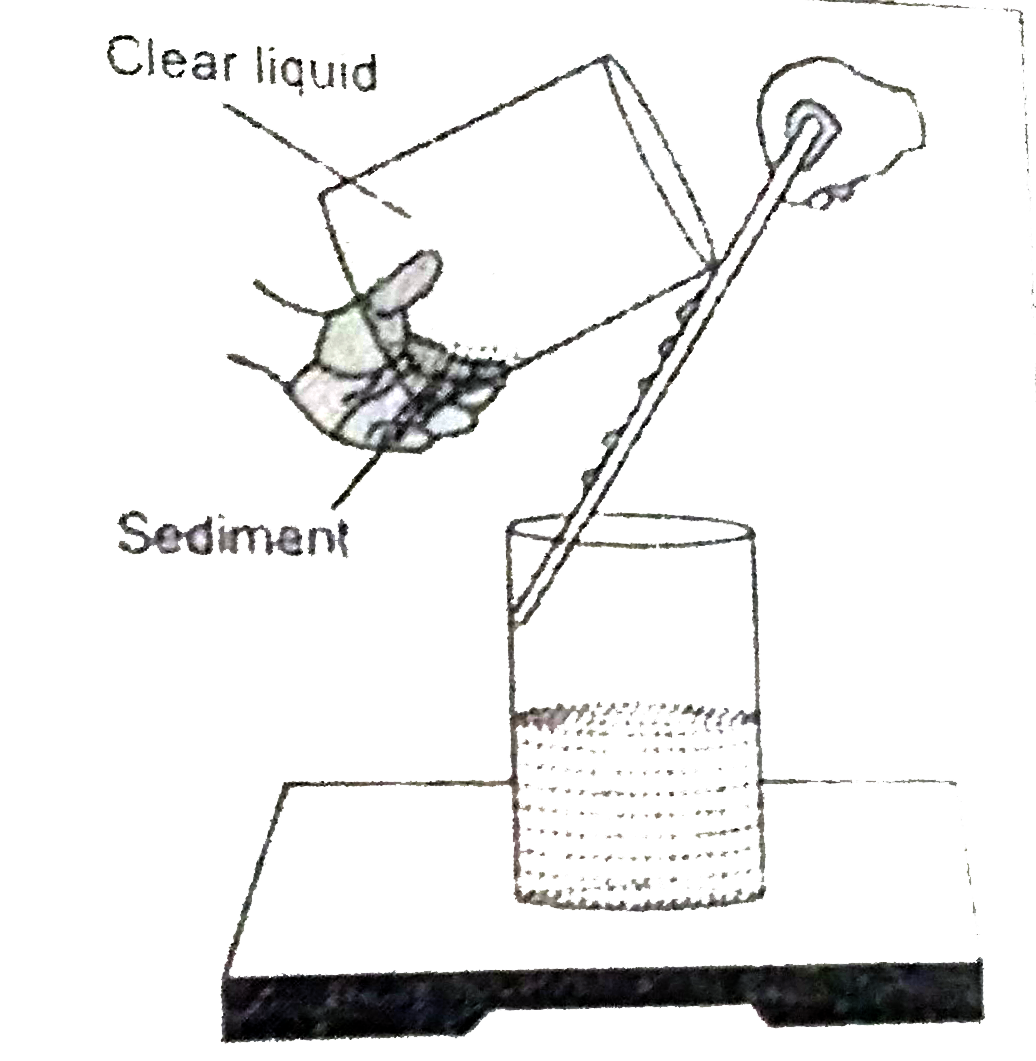
|
|
| 28. |
Explain the process of ntrogen fixation. |
|
Answer» Solution :Nitrogen is required for plants and animals to synthesizeproteins. Free nitrogen cannot be assimilated by plants. Hence the nitrogen presient in the atmosphere is converted into nitrogen compounds which can be easily assimilated by plants. The PROCESS of coonversion of atmopheic into nitrates is called nitrogen fixation. Duringlightening `N_(2)` combines with `O_(2)` to FORM NO which further rects with `O_(2)` to form `NO_(2)`. This gas dissolves in the water droplets of clouds and form `HNO_(3)` . During PRECIPITATION it reaches soil and reacts dissolves in the water droplets of clouds and form correponding nitrotes, these nitrates can be assimilated by plants. `N_(2)+O_(2)to2NO` `2NO+O_(2)to2NO_(2)` `4NO_(2)+2H_(2)O+O_(2)to4HNO_(3)` `4HNO_(3)+MCO_(3)toM(NO_(3))_(2)+CO_(2)+H_(2)O` Leguminous plants contain symbiotic bacteria in their root nodules which absorb atmospheric nitrogen and convert in into verious compounds of nitrogen. These compounds are easily assimilated by plants and also the soil BECOMES enriched with nitrogen compounds. |
|
| 29. |
Explain the process by which both removal of temporary hardness and permanent hardness is possible. |
|
Answer» Solution :By the addition of washing soda, we can remove both TEMPORARY as well as permanent hardness from water. Bicarbonate salts as well as sulphate and CHLORIDE salts undergo double decomposition REACTION with sodium carbonate. In these reactions, the insoluble carbonates formed get precipitated and are removed by FILTRATION. `Ca(HCO_(3))_(2)+NaCO_(3)rarrCaCO_(3)darr+2NaHCO_(3)` `MgSO_(4)+Na_(2)CO_(3)rarrCaCO_(3)darr+2NaCl` `CaCl_(2) + Na_(2)CO_(3) rarr CaCO_(3) darr + 2NaCl` `CaCl_(2) + Na_(2)CO_(3) rarr CaCO_(3) darr + 2NaCl` |
|
| 30. |
Explain theprinciple involved in the usage of chlorine in sterilisation of drinking water. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :CHLORINE is highly soluble in water. On dissolution of chlorine in water, hypochlorous ACID is formed which dissociates to given nascent oxygen. Nascent oxygen KILLS GERMS andbacteria. | |
| 31. |
Explain the principle behind the usage of electric prectric precipitators in industries and catalytic convrters in automobiles for controlling air pollution. |
| Answer» Solution :Electric PRECIPITATOR removes the supended particulate matter which are charged particles coming from thermal power plants, cement plants, steel plants so that smoke and ash entering the tmosphere in MINIMIZED. Catalytic converter contain CATALYSTS such as platinum on ceramic comb which convert harmfulgases to less HARMFUL gases, such as CO to `CO_(2)` and oxides of nitrogen to nitrogen. | |
| 32. |
Explain the ozone depletion. |
|
Answer» Solution :Ozone depletion: Ozone presnent in troposphere contributes to GREEN house effect. Ozone PRESENT in stratosphere PLAYS a vital role in protecting the life on earth's surface from harmful UV radiations. Ozone layer acts as a shiled as ABSORBS harmful UV radiations. Pollutants such as `CFC_(s)` when reach stratosphere react with zozone and thus depletes the ozone layer in a period of time. Hence, UV radiations reach tropospheric layer due to the holes created in zozone and affect plant and animal life. PREVENTION: Discovery of alternative substance for `CFC_(s)` used in refrigeration and aerosols. |
|
| 33. |
Explain the observable change taking place during reaction of iron with the aqueous solutions ofH_(2)SO_(4) and CuSO_(4) respectively. |
|
Answer» Solution :Fe on treatment with `H_(2)SO_(4)`liberates hydrogen gas. `Fe+H_(2)O_(4)toFeSO_(4)toH_(2)uarr` The solution turnsgree due to the FORMATION of `FeSO_(4)`. As Feis more reactive than Cu , it displace Cu from `CuSO_(4)` solution .Hence blue colour of`CuSO_(4)`solution disappears. `Fe+CuSO_(4)(AQ)toFeSO_(4)+Cu` |
|
| 34. |
Explain the naming of salts with examples. |
|
Answer» Solution :DERIVATION of names of salts: The name of a salt is basically derived from the ACID from which it is formed. The salts derived from the hyderacids are given names ending with 'ide' SUFFIX. If the salt contains a hydrogen, then hydrogen is added to the suffix. `{:("Formula of acid","Formula of base","Salt formed","Name of the salt"),(HC1,NaOH,NaC1,"Sodium chloride"),(H_(2)S,NaOH,Na_(2)S,"Sodium sulphide"),(H_(2)S,NaOH,NaHS,"Sodium hydrogen sulphide"):}` The salts derived from oxy acids are given names depending on the type of oxy acid. The salts of 'ous' acids are given 'ite' suffix and the salts of 'ic' acids are given 'ate' suffix. If hydrogen is present in the salt, hydrogen or bi is added to the name of the raddical. Examples `{:("Formula of acid","Formula of base","Formula of salt","Name of the salt"),(HH_(2)SO_(3),KOH,K_(2)SO_(3),"Potassium sulphite"),(,,KHSO_(3),"Potassium hydrogen sulphite"),(H_(2)SO_(4),NaOH,Na_(2)SO_(4),"Sodium sulphate"),(,,NaHSO_(4),"Sodium hydrogen sulphate"),(H_(3)PO_(4),NaOH,Na_(3)PO_(4),"Sodium phosphate"),(,,Na_(2)HPO_(4),"Disodium hydrogen phosphate"),(,,NaH_(2)PO_(4),"Sodium dihydrogen phosphate"):}` In the same way, the salts of nitrous acid and nitric acidare called nitrites and nitrates respectively. The salts of carbonic acid are called carbonates and bicarbonates of hydrogen carbonates. The positive ion part is called basic radical and the negative ion part is called acidic radical. |
|
| 35. |
Explain the formation ofthe compound formed by two elements withZ=20andZ=17 . |
|
Answer» Solution :`{:("Element","ATOMIC number","Electronic configuration"),(""Ca,""20,""2_(,)8_(,)8_(,)2),(""Cl,""17,""2_(,)8_(,)7):}` Ca loses TWO electrons to attain octet while Cl gains an electron to attain octet. Hence , the FORMULA of the compound is `Ca^(+2)Cl^(-1)` `CaCl_(2)` |
|
| 36. |
Explain the following of sodium chloride. |
| Answer» Solution :Sodium (Z=11)has electronic configuration of2 , 8 , 1 . By losing one ELECTRON , it forms`Na^(+)`ion which attains the configuration of neon that is 2 , 8. CHLORINE(Z =17 ) has electronic configuration of 2 , 8 , 7 . By gaining one electron it forms `Cl^(-)`ion which attains the configuration of argon that is 2 , 8 , 8 . since `Na^(+) andCl^(-)`ion carry opposite charges a strong force of attraction binds the TWO IONS together . thus , the compound sodium CHLORIDE is formed. | |
| 37. |
Explain the following methods of separation with suitable exampls (a) Distillation , (b) Filtration |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Distillation process Process : The solution of copper sulphate is taken in a round bottom FLASK called distillation flask. A thermometer and a condenser, known as Liebig's condenser,are attached with the round bottom flask with the help of adapters. Liebig's condenser is a long glass tube enclosed in a jacket of glass Cold water is circulated through the glass jacket continuously. The condenser leads to another flask called receiver to collect the liquid that gets separated from the solid during the process of distillation. The distillation flask is planced on a tripod STAND and heated with the help of a Bunsen burner. Observation : The solution starts boiling and water vapour obtained is passed through Liebig's condenser where it is converted to water due to condensation and collected in the receiver. Solid residue is observed in the distillation flask. Conclusion : Water present in the solution is vapourised leaving behind the non-volatile solid that is copper sulphate in the distillation flask and thus constituents of the copper sulphate solution are separated. (B) Filtration All sorts of insoluble solids can be separated from the liquid in this process. Process : A mixture of saw dust and water is taken in a beaker. A FILTER paper is folded in the form of a cone and fitted into a funnel by moistening it with a few drops of water. The mixture is poured GENTLY into the filter cone and collected into another beaker. Observation : The liquid collected is clear and transparent. Sawdust is found over the filter paper. Conclusion : The mixture of sawdust and water is separated through filtration process. The clear liquid that is collected in the another beaker on the filter paper are known as residue. 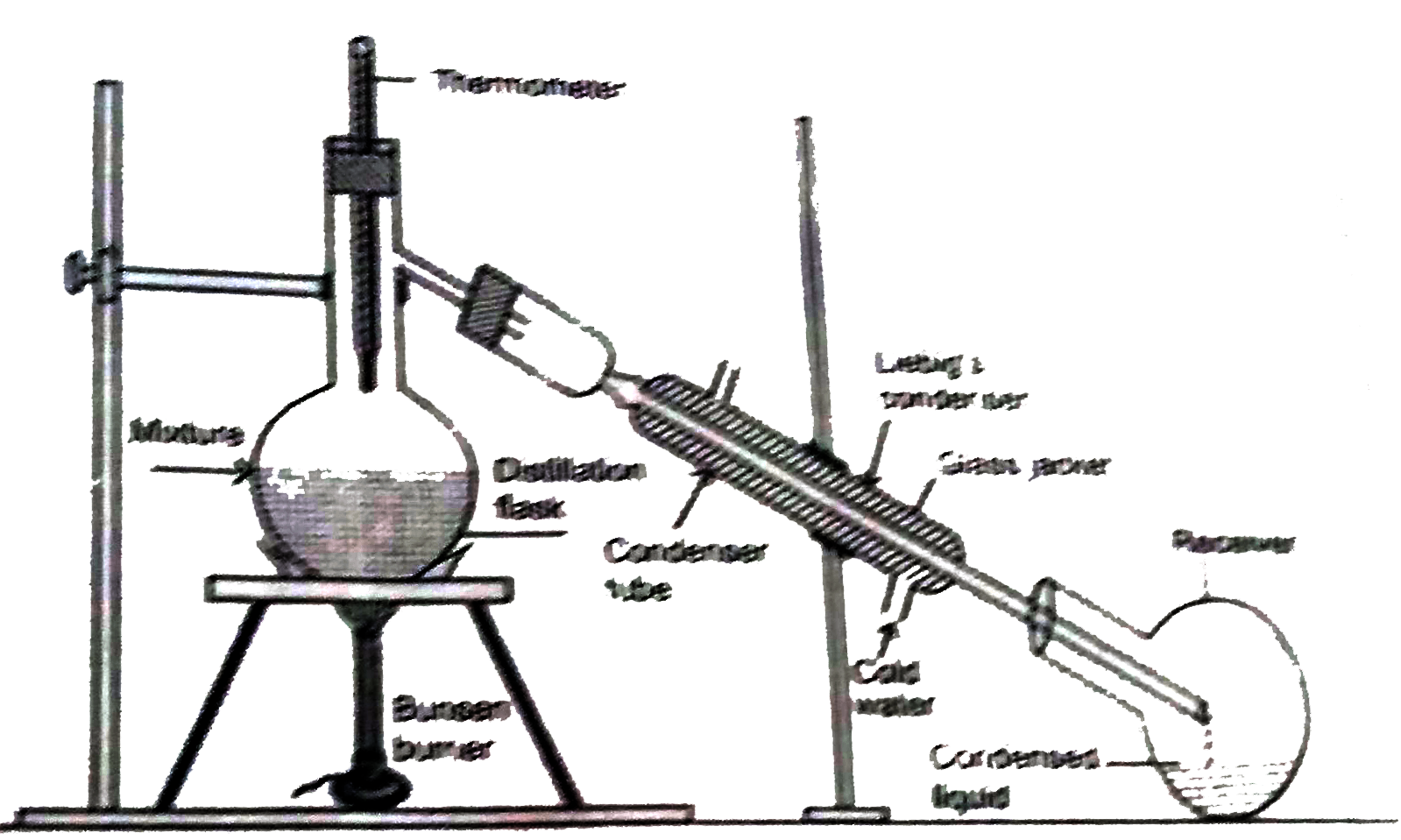 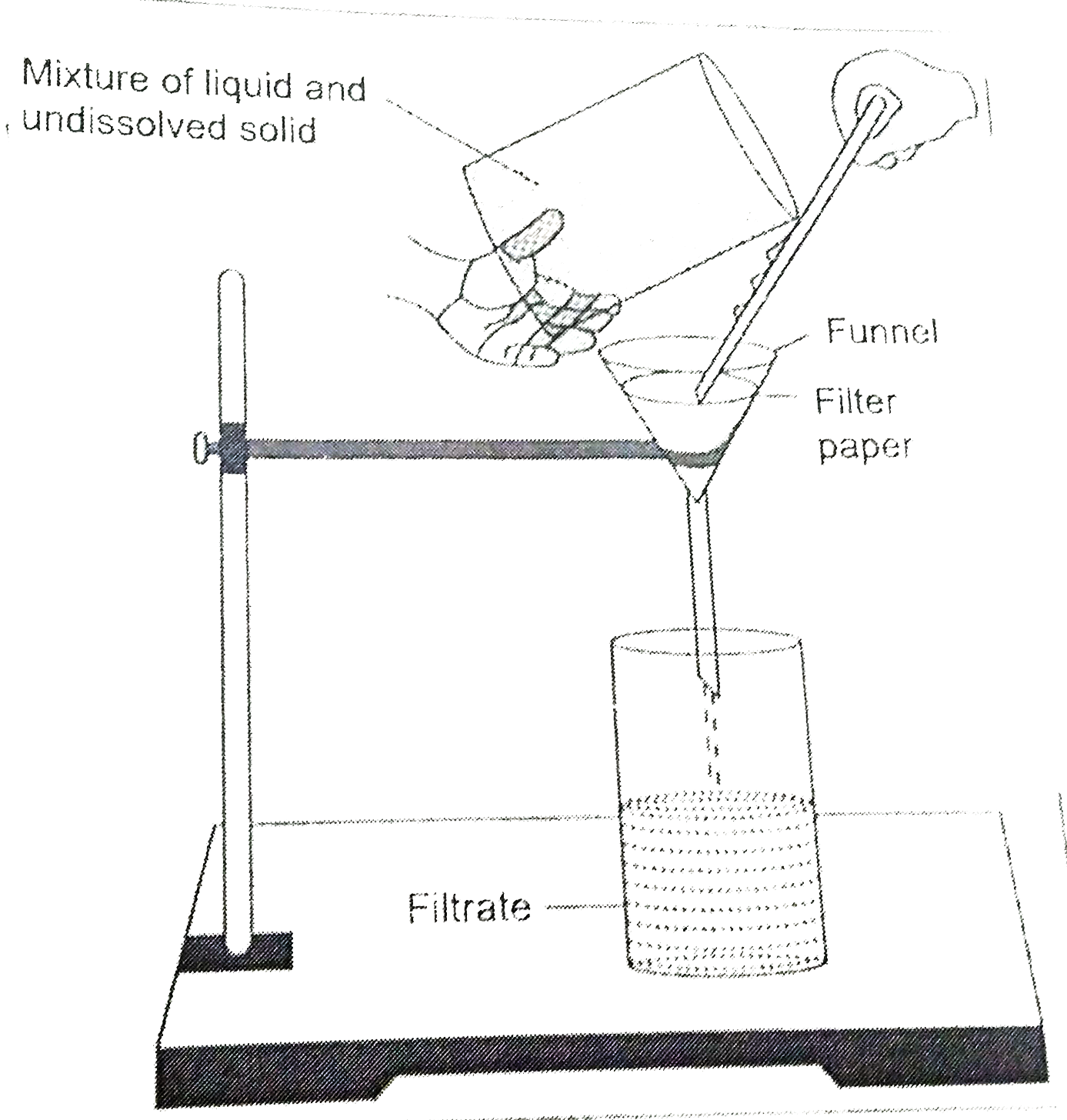
|
|
| 38. |
Explain the factors affecting rate of evaporation. |
|
Answer» Solution :Factors affecting the rate of evaporation Surface area : The rate evaporation of a liquid is directly proportional to the surface area of it. TEMPERATURE : With the increase of temperature, the rate of evaporation of a liquid increases. HUMIDITY : The rate of evaporation of a liquid is INVERSELY proportional to the AMOUNT of moisture present in the atmosphere (humidity). |
|
| 39. |
Explain the electrolysis of water to determine the volumetric composition of water with diagram |
|
Answer» Solution :Volumetric composition of water: The decomposition of water: The decomposition is a chemical change and it can be brought about by using VARIOUS froms of energy like light, electricity etc. The decomposition of a substance by passing electricity is called electrolysis. Principle: Since water is a poor conductor of electricity, little AMOUNT of sulphuric acid is added to water. This acidulated water on passage of electricity decomposes to give hydrogen and oxygen in 2 : 1 volume ratio. `2H_(2)Orarr2H_(2)+O_(2)` Process: The acidulated water is filled in two TEST tubes without any air bubbles. The two test tubes are inverted over two iron nails connected to positive and nagative terminals of a battery. These iron nails act as electrodes. The iron NAIL connected to positive terminal of battery is called anode and the one connected to negative terminal is called cathode. On passing electricity for some time, two gases are collected in the two test tubes. Correspondingdecrease in the volumes of solution in the test tubes indicates the volumes of gases formed. The gases in the respective test tubes can be identified by introducing a burning splinter. In test tube 'A' the splinter burns brilliantly. In test tube 'B', the splinter is putoff with a POP sound and the gas burns with pale blue flame. The former is identified as oxygen whereas the latter as hydrogen. The volumes of oxygen and hydrogen are found to be in 1 : 2 ratio. When water is formed from its constituent elements also,the combination reaction reveals that the volumetric composition of water corresponds to hydrogen and oxygen in 2 : 1 ratio. `2H_(2) + O_(2) rarr 2H_(2)O` 
|
|
| 40. |
Explain the corrosive action of acids and alkalies. Give examples. |
|
Answer» Solution :All acids and some alkalies SHOW corrosive action on skin as they form painful blisters when they come in CONTACT with skin. Example: `H_(2)SO_(4)` absorbs water from skin tissues and `HNO_(3)` reacts with skin proteins to form a pulp LIKE mass. NaOH and KOH are called caustic soda and caustic potash due to their causticising action on skin. |
|
| 41. |
Explain sublimation with suitable example. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Mixtureof sand Iodine (sublimable substance). Can be separated by a SIMPLE physical process called sublimation process. sublimation : Mixture of sand Iodine are TAKEN in a flat basin and a funnel is inverted over it. The outer surface is wrapped with a water soaked filter paper and the open end of the stem of the funnel is plugged with a piece of paper cotton to stop the passage of vapour. The basin is kept in a sand bath. The sand bath is placed over a wire MESH kept on a tripod stand and then is heated gantlt with help of Busen burner. Observation : A violet coloured fume is observed which condenese as violet powdery substance when it comes in contact with colder wall of the funnel of the funnel. The process of heating is continued till the evalution of violet vapour is observed. Conclusion : Since iodine is a sublimable substance, it sublimes and then condenses as violet powder. The substance left on the basin is sand which does not sublime. Iodine is scrapped off from the wall of the funnel and thus the mixture is separated. 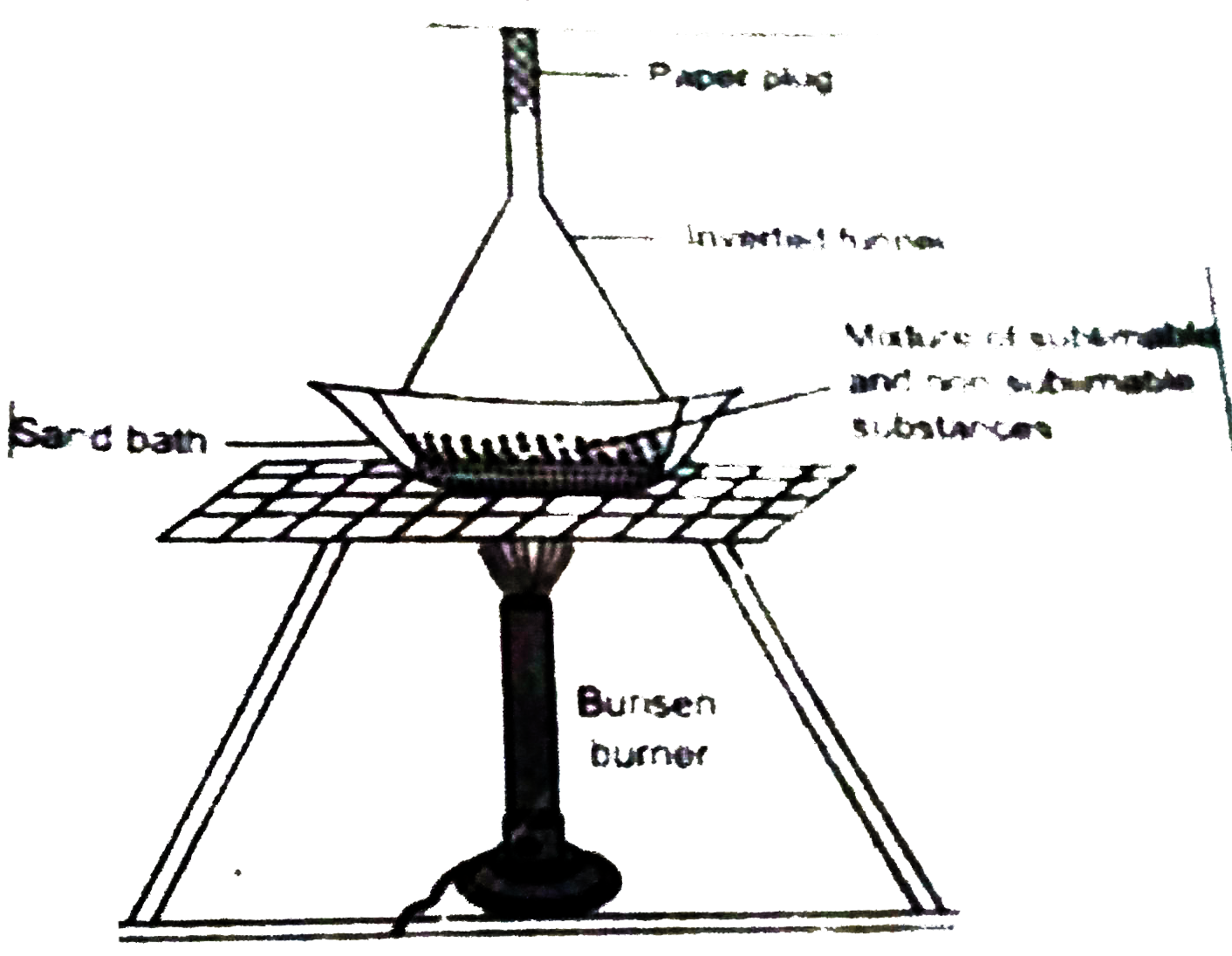
|
|
| 42. |
Explain in detail the modern structure of atom. |
|
Answer» Solution :The modern CONCEPT of atom envisages the following arrangement of fundamental paricles in an atom. (i)The protons and neutrons areconcentrated in a small region at the centre of an atom . Thiscentral part iis known as nucleus . The protons and neutrons present inside the nucleus are CALLED nucleons. (ii)The SIZE of the nucleus is very small when compared to the size of the size of atom . that means , there is vast empty space in the atom. (iii)Electrons revolve round the nucleus in a definnite fixed path which are called orbits or shells. (iv)In an atom , the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons inside the nucleus . since the protons and electrons carry equal and opposite charges , an atom is electrically neutral. (v)The varous orbits or shell are named asK, L,M,N . . . . or 1, 2, 3, 4 . . . . . and so on . the of themaximum number of electrons in the varous orbits are 2, 8, 18 , 32 . . . respectively . the energy of the orbit INCREASES with increse in distance from the nucleus. (vi)The OUTERMOST shell is called valance shell and it can never have more than 8 electrons in any atom. |
|
| 43. |
Explain hydrogenation of oils. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Catalytic additon of hydrogen to some unsatrated CARBON componds is called hydrgenation. This PRINCIPLE is used in the process of hyderogenation of oil or heardening of oils. Hydrogention of oils: Vegetable oils, containing greater percentage of carbon and oxygen but containing less percentage of hydrogen cannot be solidified easily. Example: Ground nut oil, Sunflower oil, Animal oils such as ghee which contain hydrogen in greater percentage get solididied easily under normal conditions. Vegetable oils get solidified when hydrogen gas is passed through them at high pressure and high TEMPERATURE in the presence of nickl catalyst. Example: PALM oil, vanaspathi, soap |
|
| 44. |
Explain different process of inter-conversions of states of matter. |
|
Answer» Solution :Interconversion of states of matter : The existence of matter in a particular state depends on two factors that is TEMPERATURE and pressure. Matter can be transformed from ONE state to another by altering the temperature and pressure and this phenomenon is CALLED interconversion of states of matter. Different types of interconversion of states of matter. Different types of interconversion of states of matter are given below. (i) Melting : The process which involves the change in state of matter from solid to liquid by heating is called melting or fusion. The temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid on heating at normal atmospheric pressue is called the melting point of the solid. Example : Ice changes to water at `0^(@)C` under normal atmopheric pressure. Hence `0^(@)C` is called melting point of ice. (ii) Boiling : The process which involves the change in state of matter from liquid changes into gas from the bulk of the liquid by heating at normal atmospheric pressure is called the boiling point of that liquid. Example : Water changes to water vapour at `100^(@)C` under normal atmospheric pressure. Hence `100^(@)C` is called boiling point of water. (iii) Condensation : The process which involves the change of matter from gas to liquid on cooling is called condensation. 0 Example : Conversion of water vapour or steam to water. (iv) solidification : The process involving the change of matter from liquid to solid on cooling is called solidification or freezing. The temperature at which freezing occurs at normal atmospheric pressure is called freezing point of that liquid. Example : Water changes to ice at `0^(@)C` under normal atmospheric pressure. Hence `0^(@)C` is called the freezing point of water. NOTE : Generally solids expand on melting and liquids contract on freezing. (v) Sublimation : The process by which some solid substances directly change into the vapour state without passing through the intermediate liquid state is called sublimation. The solid obtained on cooling the vapour is called sublimate and the vapour formed is called sublime. Example : Camphor, iodine etc., get converted to their RESPECTIVE vapour states directly under normal atmospheric pressure. |
|
| 45. |
Explain classification of matter based on it molecular composition with suitable examples. |
|
Answer» Solution :Matter can also be classified based on its composition in the following way irrespective of the state in which it exists. If the matter is made up of identical molecules, it is called pure substance. The matter which is made up of different types of molecules is called mixture. Molecules of matter are made up of still tinier particles called atoms. Atoms are the tiniest particles of matter which cannot exist independently. There are very few atoms which exist independently. These are the atoms of helium, neon, argon, krypton and xenon. They remain in the gaseous state in the atmophere and known as noble gases. Pure substances can further be classified into elements and compounds based on the nature of constiuent atoms present in their molecule. If the molecules of a pure substance contain identical atom(s), it is called an element. The pure substance in which the molecules are made up two or more different types of atoms is called compound. Classification of matter based on its composition is schematically represented below 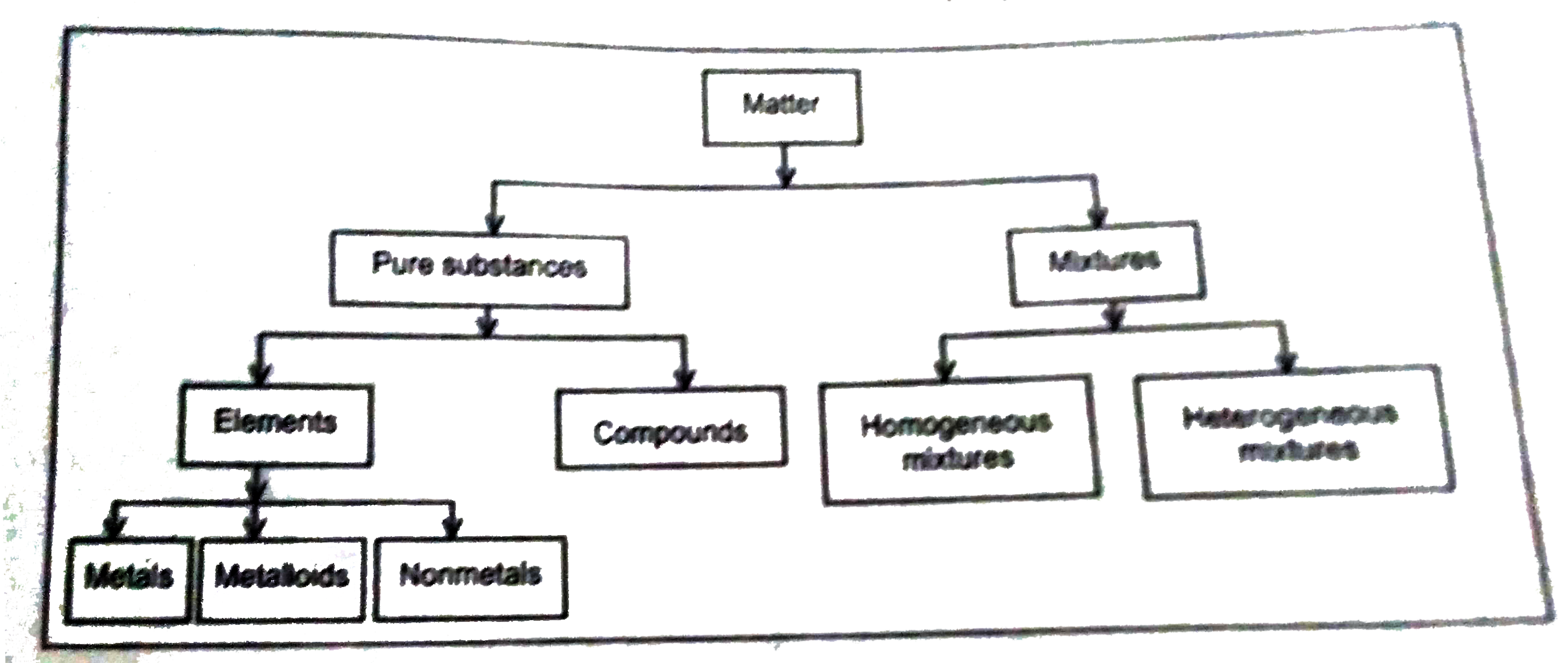 Element : an element is a substance which is constituted of only one kind of atoms and cannot be further divided by any physical or chemical means. Example : Hydrogen, oxygen, chlorine, sodium potassium etc. are the examples of elements . Molecules of these substances consist of only one TYPE of atoms. Molecules of different elements may contain different number of atoms. Atomicity of element. A molecule of hydrogen is made up of two atoms and hance its atomicity is two. Based on the atomicity, elements can be classified as follows: (i) Monoatomic elements : The elements in which each molecule contains only one atom. Example : `CU,AG,He` etc. (ii) Diatomic elements : the elements in which each molecule contains two atoms. Example : `H_(2),O_(2)N_(2)` etc. (iii) Polyatomic elements : the element in which each molecule contains more than two atoms. Example : `O_(3),P_(4),S_(8)` Compounds : A compound is a substance which is formed due to the chemical comination of two or more elements in definite propotion by mass. The constituents of a combination do not retain their properties and they can be separated only by chemical means. Example : Water, carbon dioxide, hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride, calcium carbonate etc, are a few examples of compounds. A molecule of carbon dioxide is constituted of a carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. Two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen combine chemically to form a molecule of water. Mixture : A mixture is a substance which is formed by mixing two or more substance (elements, compounds or both) physically in any propotion. No chemical reaction TAKES place during the formation of a mixture and all the constituents of mixture retain their properties. constituents of mixture can easily be separated by physical means. Example : solution of sugar and water is a mixture in which sugar and water both retain their properties and can be separated by a simple physical process that is evaporation. Muddy water is another example of mixture of mud and water which can easily be separated by filtration. Elements and compounds are the substance in which the composition is uniforn throughout the matter and hance they are said to by homogenous. But the composition of a mixture i.e., then proportion of its constituents may not be uniform throughout. Hence mixture may be homogeneous or HETEROGENEOUS. Examples of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture : A mixture of alcohol and water is an example of homogeneous mixture because of the constituents of this mixture is uniformly distributed. A mixture of sulphur and water is an example of heterogeneous mixture because sulphur remains nonuniformly distributed in water. |
|
| 46. |
Excess intake of O_(2) by a person results in several ill-effects. Which of the following activities leads toexcess in take O_(2) ? |
|
Answer» DEEP sea DIVING |
|
| 47. |
Evaporation is the process of conversion of |
|
Answer» a liquid to its GASEOUS state below the BOILING point of the substance |
|
| 48. |
Evaporation is a surface phenomenon. |
|
Answer» EVAPORATION takes PLACE from the SURFACE of a LIQUID and hence it is a surface phenomenon. |
|
| 49. |
Establish logically that water is a compound. |
| Answer» Solution :A pure substance is one which is made up of molecules CONTAINING same kind of atoms. In water all the molecules are made up of two HYDROGEN atoms and one oxygen atom. These constituents are PRESENT in a fixed PROPORTION by weight and HENCE it is a compound. | |
| 50. |
Earthen pitchers are more effective in Hyderabad than in Chennai. Justify. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The RATE of evaporation of water depends upon humidity (moisture present in stmosphere). The more is the humidity the less is the rate of evaporation. In coastal areas like Chennai moisture is more and hance the rate of evaporation of water is less. In case of non-coastal area like Hyderabad, moisture is less and hence the rate of evaporation is more. Therefore a higher rate of evaporation allows faster cooling of water in the EARTH pither in Hyderabad when COMPARED to the earthen PITCHER in Chennai. | |