Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1651. |
Two girls of weights 40 kg and 60 kg stand at A and B and are 10 m apart. They pull on a massless string stretched between them. Then they will meet at : |
|
Answer» 4 m from A `x=(m_(1)xx0+m_(2)xx10)/(m_(1)+m_(2))=(60xx10)/(100)=6m`  Thus two girls will meet at a distance 6 m from pt. A. |
|
| 1652. |
Supposein theaboveproblem, youdecidetoleaksomeairfromthe tiressincethemanufacturersuggestskeepingthepressureat 210kPa..( themanufacturer's specificationare forthetireswhichare " cold " ) .If youletoutsufficient airsothat thepressurereturs to 210k P.a. whatpercentageof theairmoleculesdid youlet outof thetires? supposethatyouleavethe carandgofora lunchandwhencomebackthe tireshavecooleddownto 37^@CNowwhatis thegaugepressure ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`8.82 % , 28.65 KPA` | |
| 1653. |
The magnetic dipole moment of acurrent carrying coil does not depend upon |
|
Answer» NUMBER of TURNS of the coil |
|
| 1654. |
The length of the wire shown in figure between the pulleys is 1.5m and its mass is 12.0g. Find the frequency of vibration with which the wire vibrates in owo loops leaving the middle point of the wire between the pulleys at rest. |
|
Answer» Solution :`T=9xx9.8N` `F=(2)/(2L) SQRT((T)/(m..l))=70HZ` |
|
| 1655. |
A compound microscope uses an orjective lens of focal length 4 cm and eyepiece lens of focal Length 10cm. AN object is placed at 6 cm from the objective lens. Calculate the magnifying power of the compound microscope. Also calculate the length of the mircroscope. |
|
Answer» Solution :`(1)/(v_(0))- (1)/(u_(0)) = ( 1)/(f_(0))` `f_(0) = 4 cm, u_(0) = - 6 cm` `(1)/(v_(0)) = (1)/(4) - (1)/(6) = (1)/(12) rArr v_(0) = 12 cm` magnification by objective, `m_(0) = (v_(0))/(|u_(0)|)` `= (12)/(6) = 2 ` Magnification by EYEPIECE `m_(E) = ( 1+ ( D)/( f_(e))) ` or `( D)/( f_(e))` `= ( 1+ ( 25)/( 10)) ` or `(25)/(10)` magnification power of the microscope `m= m _(0) xx m_(e )` `= 2 xx 3.5 ` or `2 xx 2.5 ` =7 or 5 Length of the microscope , `L = | v_(0) | +| u_(0)|` `L= |v_(0)|+f_(e)` `u_(e ) = ?, v_(e) = D = - 25 cm, f_(e ) = 10CM` `(1)/(u_(e )) = ( 1)/( v_(e)) - (1)/(f_(e))= - (1)/(25) - ( 1)/(10) = - (7)/( 50)` `u_(e ) = - ( 50)/( 7) cm` `:. L = 12 + ( 50)/( 7)` = 19.1 cm |
|
| 1656. |
Prove that if a space vehicle travels along a parabolic path with the Earth (or some other planet) at its focus, the total mechanical energy of the vehicle is zero. |
|
Answer» But the distance from the FOCUS to the apex is` r_0=f=p//2` (SEE Problem 10.4), and the radius of curvature at this point is Ro=p (see Problem 3.13). Substituting these values we see that the total energy is zero. In compliance with the law of CONSERVATION of energy it will be zero at any other point of the path as well. |
|
| 1657. |
The principal of parallel axes theorem states MI of a body about an axis is equal to_____ of MI about axis passing through the CM and _____ of mass and square of distance between two axes. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :[PARALLEL, PRODUCT] | |
| 1658. |
If the focal length of a double convex lens is 12 cm and radii of curvatures of faces are 10 cm and 15 cm respectively, what is the refractive index of the lens? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`f=12cm, R_1 = 10 CM, R_2=-15 cm, N=?` `1/5 = (n-1) (1/R_1-1/R_2), 1/12= (n-1)(1/10 + 1/15), n=1.5` |
|
| 1659. |
The magnification of an object placed in front of a convex lens is +2. The focal length of the lens is 2.0 meters. Find the distance by which object has to be moved to obtain a magification of -2 ( in meters) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1660. |
Define the terms (i) 'cut-off voltage' and (ii) 'threshold frequency' in relation to phenomenon of photoelecric effect. Using Einstein's photoelectric equation show how the cutt-off voltage and threshold frequency for a given photosensitive material can be determined with the help of a suitable plot/graph. |
|
Answer» Solution :2nd part: Einstein's equation: `eV_(0) = H (f-f_(0))` where, `V_(0)`= cut-off voltage due to frequency f of incident LIGHT, `f_(0)` = threshold frequency Now, `V_(0) = (hf)/(E) - (hf_(0))/(e)` This is of the form `y = mx + c`. So the graph of `V_(0)` vs f will be a STRAIGHT line AB of slope `(h)/(e)`. The point of intersection of AB with the f-axis given the value of `f_(0)`. For any incident frequency, corresponding to any point C on AB, the ordinate OD gives the value of the cut-off voltage `V_(0)`. 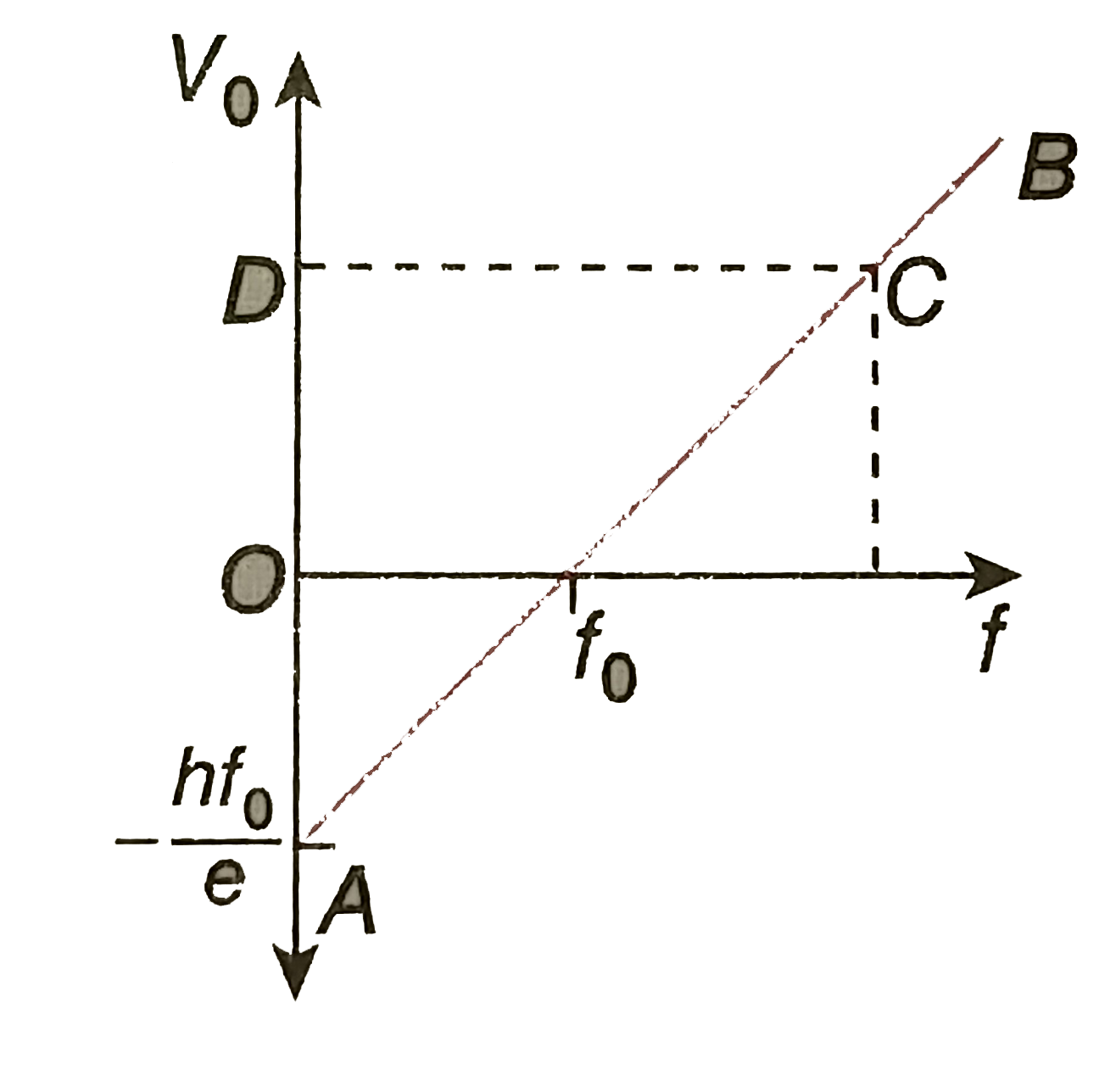
|
|
| 1661. |
Two objects of equal volume V=1 m^(3) and different densities d_(1) =500kg//m^(3) and d_(2) =1000kg // m^(3) are gluod to each other so that their contact surface is flat and has an area A=0.1 m^(2) When the objects are submerged in a certain liquid they float in stable equilibrium the contact surface being parallel to the surface of the liquid (see the diagram) How deep (H in meters) can the contact surface be in the liquid so that the objects are not torn apart? The maximum force that the glue can with stand is F=250 N (Neglect atmospheric pressure) |
|
Answer» `d_(1) Vg+F-(dVg-dgAH)=0` `d_(2)Vg-F-(dVg+dgAH)=0` (For each object, the ter, in parentheses indicates the "effective" buoyancy force) Combining the last TWO equations yields the answer `H=[(d_(2)-d_(1)) Vg-2F]//[(d_(1)+d_(2)) gA]` |
|
| 1662. |
Mention the inference of Davission Garmer experiment |
|
Answer» Solution :The inference of this experiment is that an electron BEAM BEHAVES as a MATTER wave. Hence the experiment proves de BROGLIE's hypothesis. |
|
| 1663. |
If C is the restoring couple per unit radian twist and I is the moment of inertia, then the dimensional representation of 2pisqrt(I/(c)) will be : |
|
Answer» `[M^(0)L^(0)T^(0)]` `I=ML^(2)` and `C=ML^(2)T^(-2)` `:.sqrt((I)/(C))=(T^(2))^(1//2)=T^(1)` HENCE `(b)` is CORRECT. |
|
| 1665. |
How does drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor vary with increase in temperature ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :It DECREASES with INCREASE in TEMPERATURE. | |
| 1666. |
A core with the shape and dimensions in millimeters shown in Fig. 30.14 has been manufactured of a ferromagnetic material whose magnetization curve is shown in Fig. 29.9a (p. 76). One layer of wire of 0.6 mm diameter (including insulation) was closely wound on the core. Find the inductance of the coil for a current of 200 mA flowing in it. Find the energy of the magnetic field and the energy density. |
|
Answer» `w piD//d=80pi//0.6=420` The magnetic FIELD strength is `H=(iw)/(l)-(iw)/(PI D_(m))=(I D)/(dD_(m))` where `D_(m)=120nm` is twice the distance from cho axis of revolution of the torus to the centro of tbo gonorating circle. Knowing the magnetic field strength and making use of the graph of Fig. 20.9a, we find the induction of the field. Applying the FORMULA `w_(m)= BH//2 ` we find the energy density, and multiplying this by the VOLUME of the core we find the total onergy of the magnetic field. The INDUCTANCE is found using the formula `W_(m)-Li^2//2` |
|
| 1667. |
The substances which acequire charges on rubbing are said to be ................ . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1668. |
The box of a pin hole camera of length L has a hole of radius a. It is assumed that when the hole is illuminated by a parallel beam of light of wavelength lambda the speed of the spot (obtained on the opposite wall of the camera) is the sum of its geometrical spread and the spread due to diffraction. The spot would then have its minimum size (say b_("min")) when ..... |
|
Answer» `alpha=(lambda^(2))/(L) and b_(MIN)=((2lambda^(2))/(L))`  Condition for FIRST mimimum, In `d sin theta= N lambda` `d=a sin theta=(y)/(D)=(a)/(L)` `n=1` `:.axx(a)/(L)= lambda` `:.a^(2)=lambdaL` `:.a=sqrt(lambdaL)` Size of spot means diameter `=a+a` `=2a` `=2sqrt(lambdaL)` `=sqrt(4lambdaL)` |
|
| 1669. |
The magnitude of electric intensity at a distance 'x' from a charge 'q' is E. An identical charge is placed at a distance '2x' from it. Then the magnitude of the force it experience is |
|
Answer» `EQ` |
|
| 1670. |
Two metal sphers of masses m_(1) and m_(2) are suspended from a common point by a light insulting strings of same length. The length of each string is same. The spheres are given positive charges q_(1) and q_(2). Figure A shows angles made by the strings with vertical are different where as for figure B same. Then, which of the following is possible |
|
Answer» For figure `A m_(1) GT m_(2) and q_(1) = q_(2)` |
|
| 1671. |
Two bodiesare projected from the same pointwith equalspeeds in suchdirections thatthey both strikethe same point on a planewhose inclination is beta.If alphathe angleof projectionof the first body with the horizontal , showthat the ratio of theirtime of flights is (sin (alpha - beta))/(cos alpha) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Let `alpha` be the angle of PROJECTION of the second by . `R =(u^(2))/(G cos^(2) beta) [sin (2alpha - beta)-sin beta]` Range of boththe bodies is sametherefore , `sin(2alpha - beta) = sin (2alpha - beta) or sin 2alpha = pi- (2alpha - beta)` `alpha = (pi)/(2) -(alpha- beta)` Now `T = (2 u sin (alpha - beta))/(g cos beta) and T =(2 usin (alpha - beta))/(g COSE beta)` `therefore (T)/(T) = (2 sin (alpha - beta))/(2 sin (alpha - beta)) = (sin(alpha - beta))/(sin{(pi)/(2) (alpha- beta)-beta})` `sin =((alpha - beta))/(sin((pi)/(2)-alpha)) = (sin(alpha - beta))/(cos alpha)` 
|
|
| 1672. |
Draw a ray diagram of an astronomical telescope for the final image formed at least distance of distinct vision? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1673. |
Using the concept of drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor, deduce the relationship between current density and resistivity of the conductor. |
|
Answer» Solution : DRIFT velocity of charge carriers is the CONSTANT velocity ACQUIRED by them in a conductor on applyingan external electric field E on it. The CURRENT density J through a conductor depends on the drift velocity as per relation : J= ne `v_d` , where n = number density of charge carriers (electrons). But `v_d = (eE)/(m) tau `, where `tau` is the relaxation time. ` therefore J= "ne" [(eE)/(m) tau] = ("ne"^2)/(m) tau E` However , `(m)/("ne"^2 tau) = rho`the resistivity of the material of conductor. Thus, we conclude that `J = E/rho " or" rho = E/J` It means that resistivity of a conductor is given by the RATIO of electric field applied .E. and the current density .J.. |
|
| 1675. |
Draw a sketch of a plane electromagnetic wave propagating along the z-direction. Depict clearly the directions of electric and magnetic fields varying sinusoidally with z. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 1676. |
What is efficiency of a treansformer , can it achieve 100%. |
|
Answer» `pi/6` |
|
| 1677. |
Wave which cannot travel in vacuum is |
|
Answer» X-rays |
|
| 1678. |
Temperature dependence of resistivity rho(T) of semiconductors,insulators and metals is significally based on which of the following factors? |
|
Answer» number of CHARGE CARRIERS can change with temperature T |
|
| 1679. |
Thelength of the tube of a microscope is 14 cm and its magnifying power for normal eye is 25. The focal length of the eyepiece is 5 cm . The distanceof the object from the objective is |
|
Answer» 2.4 CM |
|
| 1680. |
A long solenoid of length 'l' having carries a current I. Deduce the expression for the magnetic field in the interior of the solenoid. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider a long solenoid having n turns PER unit length as shown in Fig. The upper view of dots in the FIGURE is like a uniform current sheet COMING out of the PLANE of the paper . From the right hand rule, the field due to this is to the left at point Q (above) and to the right at point P (below). The lower row of crosses in the figure is like a uniform current sheet going into the plane of the paper. The field at any point above it (P as well as Q) is to the right. The two field reinforce each other at P and exactly cancel at Q. Thus, a uniform magnetic field `vecB` is present along the axis of solenoid at any point inside the solenoid and the zero at any point outside the solenoid. Consider a rectangular Amperian loop abcd. Along cd the magnetic field is zero as explained is at right ANGLE to bc or da. `:. oint vecB . vecdl = int_(a)^(b) vecB . vecdl + int_b^cvecB . vecdl + int_c^d vecB . vecdl + int_d^a vecB . vecdl` `= int_a^b vecB . vecdl = int_a^b B dl = B int_a^b dl = B. Delta l "[where " ab = Delta l `(say)] According to Ampere.s circuital law `oint vecB cdot vecdl = mu_0` (current enclosed in length `Delta l` ) `= mu_0 (n Delta l I) "" [ :. ` Number of turns = `n Delta l` ] Hence, we have `B Delta l = mu_0 n Delta l I` `implies B = mu_0 n l` The direction of the field is given by the right hand rule. If the solenoid has a total length l and total number of turnsN, then `B = (mu_0 N I)/(l)`. 
|
|
| 1681. |
(b) Write the Lens Maker's formula and use it to obtain the range of mu (The refractive index of the material of the lens) for which the focal length of and equiconvex lens, kept in air, would have a greater magnitude than that of the radius of curvature of its two surfaces. |
|
Answer» Solution :Lens Maker's FORMULA is `(1)/(f)=(mu-1)((1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(1)))` Here `R_(1)=R,R_(2)=-R` `(1)/(f)=(nu-1)((1)/(R_(1))+(1)/(R_(1)))IMPLIES(1)/(f)=(mu-1)((2)/(R))` `mu-1=(R)/(2f)` When `fgtR` `mu-1lt(1)/(2)impliesmult1+(1)/(2)` `mult(3)/(2)`. |
|
| 1682. |
An object moving horizontally with kinetic energy of 800 J experiences a constant opposing force of 100 N while moving from a to b (where ab=2m). The energy of particle at b is |
|
Answer» 700 J |
|
| 1683. |
What does the lamp do? |
|
Answer» It TRANSMUTES LIGHT into DARKNESS |
|
| 1684. |
In a simple pendulum experiment, length is measured as 31.4 cm with an accuracy of Imm. The time for 100 oscillations of pendulum is 112.0s with an accuracy of 0.01s. The percentage accuracy in g is |
|
Answer» 1 |
|
| 1685. |
Is photoelectric emission possible at all frequencies ? |
| Answer» Solution :No, photoelectric emission is possible only if the ENERGY of the INCIDENT photon is greater than the work function `(W_0 = hv_0)` of the METAL. Hence , the frequency v of the incident radiation MUST be greater then the THRESHOLD frequency `v_0` | |
| 1686. |
At what angle an object be projected so that the horizonal range is equal to the maximum height ? |
|
Answer» `TAN^( -1)1` |
|
| 1687. |
A satellite A of mass m is at a distance of r from the surface of the earth. Another satellite B of mass 2m is at a distance of 2r from the the earth's centre. Their time periods are in the ratio of |
|
Answer» `1:2` |
|
| 1688. |
Variation in potential is maximum if one goes. |
|
Answer» along the lineof force. Along the line of force, `theta` is `0^(@)`, hence `d V` is maximum. So the VARIATION of potential is maximum along the line of force. |
|
| 1689. |
Find the equation of the plane passing through the line of intersection of the planes 2x-y=0,3z-y=0 and perpendicular to the plane 4x+5y-3z=8 |
|
Answer» `30^circ` |
|
| 1690. |
A current carrying conductor is bent in the form of a circular ring and is placed in the plane of the paper. ( ## EXP_SPS_PHY_XII_C04_E05_027_Q01 .png" width="80%">: What is the direction of the magnetic field at the centre of the ring? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Out of the PLANE of the RING. | |
| 1691. |
A long narrow slit is illuminated by blue light and the diffraction pattern is obtained on a white screen:-How the width of bands change as the distance from the centre increases? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :WIDTH of BANDS DECREASES from the CENTRE of the bands. | |
| 1692. |
A train moving towards a hill at a spped 72 km/her sounds a whistle of frequency 500 Hz. A wind is blowing from the hill at a speed of 36 km/hr. If the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s, the frequency heard by a man on the hill is |
|
Answer» 532.5 Hz Here observer is at rest ` therefore"" f. = ((340 - 10)/(340 -10 - 20)) 500 = 532.3 ` Hz so correct choice is (a). |
|
| 1693. |
A long narrow slit is illuminated by blue fight and the diffraction pattern is obtained on a white screen:-What happens to the width of patten, if yellow fight is used instead of blue light? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The PATTERN EXPANDS or BANDWIDTH INCREASES | |
| 1694. |
In a series L-C-R circuit R = 100Omega, L = 1H and C= 1 mu E The half power bandwidth is …….. |
|
Answer» 100 `=100/1` =100 |
|
| 1695. |
Assertion: In Rutherford's experiment, a-particles from a sodium source were allowed to fall on a 104 mm thick gold foil. Most of the particles passed straight through the foil. Reason : The entire positive charge and nearly whole of the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus. |
|
Answer» both ASSERTION and Reason are both are both wrong |
|
| 1696. |
When10^(14)electrons are removed froma neutrol metal sphere, the charge on the sphere becomes |
|
Answer» `16 muC ` |
|
| 1697. |
A particle moves on a path as shown. The particle takes 10 seconds in going from starting point to the final point. What is the average velocity vector of the particle ? |
|
Answer» `0.5hati+hatj` Average VELOCITY `= ("Total DISPLACEMENT ")/("Total TIME ")` `= (5hati+5hatj)/(10)=0.5hati+0.5hatj` 
|
|
| 1698. |
Consider a metal ring kept on top of a fixed solenoid (say on a cardboard) as per figure. The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current is suddenly switched on, the metal ring jumps up. Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :There was no magnetic FLUX LINKED with the metal ring in the beginning. When the current is suddenly SWITCHED on and the direction of current is as SHOWN in the FIGURE the magnetic flux linked with the metal ring (downward) increases and anticlockwise current is induced in the metal ring (seen from top) this current is in opposite direction to that in the solenoid and they repel each other and the ring will move upward. | |
| 1699. |
Faintest stars are called |
|
Answer» ZERO magnitude stars |
|
| 1700. |
The earth's field departs from its dipole shape substantially at large distances (greater than about 30.000 km). What agencies may be responsible for this distortion? |
| Answer» Solution :(e} At GREAT HEIGHTS from the surface of Earth (more than 30,000 km) magnetic field of Earth get modified due to the presence of ions in the ionosphere which are greatly affected by SOLAR WIND. This is the reason for distortion in the magnetic field of Earth at this HEIGHT. | |