Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1701. |
Three immiscible liquids of densities d_1 gt d_2 gt d_3 and refractive indies mu_1 gt mu_2 gt mu_3 are put in a beaker. The light of each liquid column is (h)/(3). A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot. |
|
Answer» Solution :`rArr` ACCORDING to formula, `"Virtual depth " = ("REAL depth")/("Refractive INDEX of denser medium w.r.t rarer medium")` .....(1) `rArr` From equation (i) (i) For first medium : `x_(1) = (h_1)/(((mu_1)/(mu_2)))=mu_2/(mu_1)(h/3) (because h_1 = h/3)`.........(2) (ii) For second medium : `x_2 = (h_2)/(((mu_2)/(mu_3)))` `rArr` From figure `h_2 = (h)/(3) + x_1` `thereforex_2= (h/3 + x_1)/(mu_1/m_3)= (mu_3)/(mu_2){h/3 + (mu_2/mu_1 xx h/3)}.......(3)` [ From equation (2)] (iii) For the third medium `x_3 = (h_3)/((mu_3/1))` `rArr` Thus, from figure `h_3 = h/3 xx x_2` `x_3 = ((h/3 +x_2))/(mu_3)` `= (1)/(mu_3)[h/2+ mu_3/mu_2{h/3 + (mu_2/mu_1 xx h/3)}]` [From equation (3)] `= 1/(mu_3)(h/3) +(1)/(mu_2){h/3 + (mu_2/mu_1 xx h/3)}` `= 1/mu_3(h/3) + 1/mu_2(h/3) + 1/(mu_1)(h/3)` `THEREFORE x_3 = h/3(1/mu_1 + 1/mu_2+1/m_3)` |
|
| 1702. |
Why are constantan and manganin used for making standard resistances ? |
| Answer» Solution :This is because CONSTANTAN and manganin show very weak DEPENDENCE of RESISTIVITY on TEMPERATURE. | |
| 1703. |
ThewavelengthH_a lineis6563Å. Calculatethe wavelengthofFirstmemberof Lymanseries |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`(1 )/( lamda _a) = R_n [(1)/(2^2) -(1)/(3^2)]=R_B[1/4 -1/9 ] = (5R_H)/(36 )` ` thereforelamda_a = ( 36 )/( 5R_H) `…….(1) (a)For LYMAN series`therefore(1)/( lamda_(IL ) ) = R_H[1/(I^2)-(1)/(2^2) ]= (3R_H )/(4 )` ` lamda _(IL ) =(4) /(3R_H)xx (5R_H)/(36 ) = (5)/(27 )` ` lamda _(IL ) =(5 )/(27 )xx lamda_a= (5)/( 27 ) xx 6563= 1215 Å` (b )forpachenseries`, (1) /(lamda_(IP)) =R_H [(1)/(3^2)-(1)/(4^2)]= (7R_H)/(16xx 9)` ` lamda_(I P) = ( 16xx 9)/(7 R_H)...... (3)` ` therefore(lamda _(IP) )/(lamda_a) = ( 9xx 16 )/(7 R_H) xx (5R_H)/( 36 ) = (20)/(7)` ` lamda _(IP)= (20 )/(7)xx lamda_a( 20xx6563)/(7 ) = 18751Å` |
|
| 1704. |
Match the frequency Bandwith the type of use |
|
Answer» a - E, b - F, C - h, d - g |
|
| 1705. |
What described "tiger in a jungle"? |
|
Answer» LOCKED in CONCRETE cell |
|
| 1706. |
Given figure is the part of some circuit. Charge on the capacitor in the circuit is given by q=3(3-e^(-1)), (coulomb) where t is time in seconds. Let V_(A), V_(B) and V_(C) be the potentials of points A, B and C, respectively. At t=0 if V_(A)=5 V and a constant current i_(0)=1 Amp flows through R=1Omega, then find the V_(P) (in volt) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`i=i_(0)+(DQ)/(DT)` `=1+3e^(-t)` 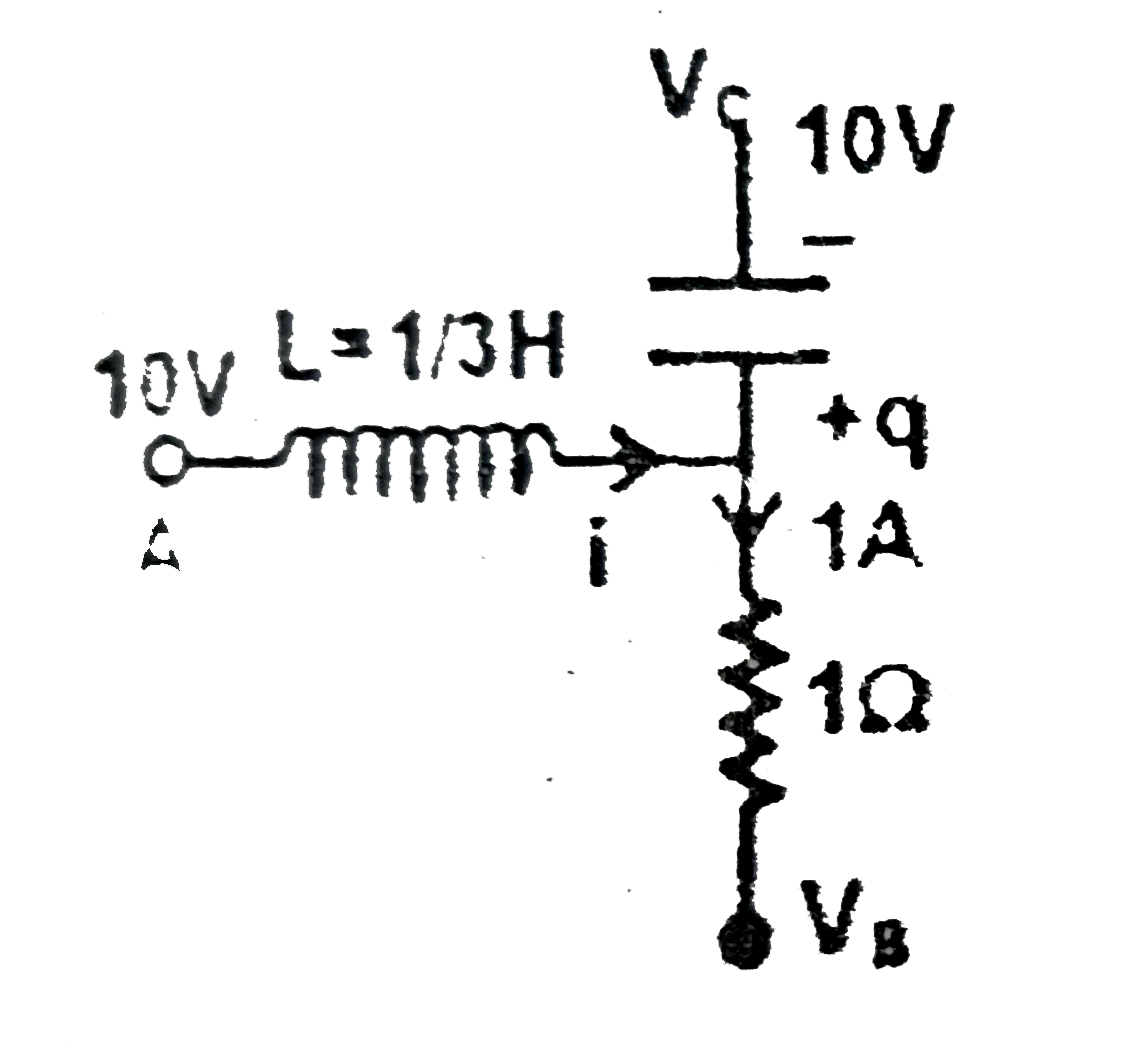
|
|
| 1707. |
Twelve equal capacitors are joined to form a cube. Find the equivalen capacitance between two opposite edges on the same plane? |
|
Answer» `(3C)/4` |
|
| 1708. |
Find the electric field at (A) (a) due to q, (b) due to charges induced on the inner surface of the shell and (c ) due to charges induced on the outer surface of the shell (Fig. 22-41). |
|
Answer» Solution :KEY IDEA First we NOTE that the CHARGE q is not symmetrically located in the shell. Nevertheless, the electric field due to a point charge is easy to calculate. `E_(q)=(q)/(4pi epsilon_(0)(5R//2)^(2))=(q)/(25pi epsilon_(0)R^(2))`. For finding the electric field due to the inner shell, we note that since the charge q is not symmetrically placed, the charge distribution on inner surface will not be symmetric. At the points close to q, charge density will be higher and lower at points farther away from the shell. If the charge was distributed uniformly, we could possibly use the FORMULA for the electric fiedl due to a uniformly charged shell at an external point. But this is not the case here. Not only that, we are not even aware of the pattern in which the induced charges will be distributed. Calculations: This dilemma can be easily resolved by concept of electrostatic shielding. We know that the effect of the charge q will be cancelled by the charges induced on the inner surface of the cavity: `vecE_(q)+vecE_("induced")=vec0`. `E_("in")=(q)/(25pi epsilon_(0)R^(2))`. To find the electric field due to the charge on the outer surface, we again do not know the pattern of induced charges on that surface. Without that, we cannot find the electric field at A. Let us use a neat trick. SUPPOSE the charge q was at the center of the shell. What would the charge distribution on the outer surface look like? Yes, it would be UNIFORM. From this position, when we move q, the charge on outer surface will not come to know about it because it has shielded from cavity. So the charge on the outer surface will still be uniform. Therefore, we can use the formula of the electric field due to a uniform shell: `vecE_("outer")=(kq)/(R^(2))`. So, the net electric field will be `vecE_("net")=(kq)/(R^(2))`. |
|
| 1709. |
An engine pumps a liquid of density ‘d’ continuously through a pipe of area A. If the speed with which the liquid passes through the pipe is V, then the rate at which K.E. is imparted to the liquid is : |
|
Answer» `1/2Ad V^3` |
|
| 1710. |
(A): A measurement which is less accurate is more precise. (R): Precision tells only about the resolution of measurement but not about accuracy. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the CORRECT explanation of (A) |
|
| 1711. |
A block of mass 3 kg which is on a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 30^(@) to the horizontal is connected by a cord passing over a light frictionless pulley to a second block of mass 2 kg hanging vertically. What is the acceleration of each block and what is the tension of the cord? |
|
Answer» `0.98 m//s^(2)` , 17.6 N |
|
| 1712. |
Name two types of waves belonging to the category of casty waves ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Long waves,MICROWAVES,STAND BROAD casty waves. | |
| 1713. |
A light stick of length l rests with its one end against the smooth wall and other end against the smooth horizontal floor as shown in the figure. The bug starts at rest from point B and moves such that the stick always remains at rest. a_(P) is the magnitude of acceleration of but of mass m, which depends upon its distance of x from the top end of the stick. Choose the correct option (s) |
|
Answer» `a_(P)=G/(sintheta)(1- d/l)` about pooint `O` `impliestau=(dL)/(dt)=(mlsintheta cos theta)(DV)/(dt)` `impliesmg(l-x)costheta=(mlsintheta costheta)(dv)/(dt)` `IMPLIES(dv)/(dt)=g/(sintheta)(1-x/l)` `implies(dv)/(dt)+g/(lsintheta)x =g/(sintheta)implies` Equation of SHM with mean position at point `A` `impliesT=2pisqrt((lsintheta)/g)` Time required `=T/4=(pi)/2 sqrt((lsintheta)/2)` 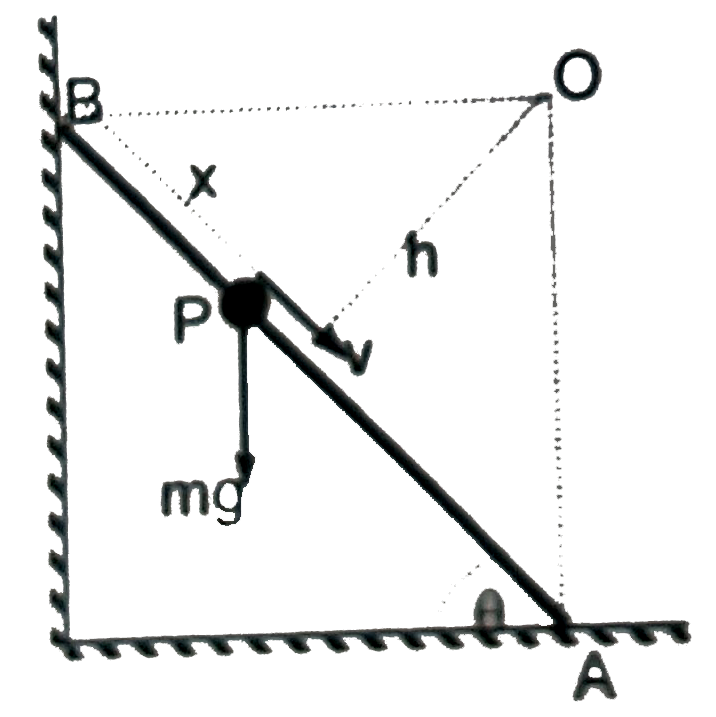
|
|
| 1714. |
The angular resolution of a 10 cm diameter telescope at a wavelength of 5000 a^(0) is of the order of |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 1715. |
Two long straight parallel current conductors are kept at a distance d from each other in air. The direction of current in both the conductors is the same. Find the magnitude and direction of the force between them. Hence, define one ampere. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider two straight parallel long current carrying conductors AB and CD carrying currents, `I_1 and I_2` RESPECTIVELY in same direction and let these be separated by a distance d. Now magnitude field `B_1` developed at a point Q on 2nd conductor due to current `I_1` flowing in 1st conductur is `B_1 = (mu_0 I_1)/(2 pi d)` As per right hand rule `B_2` is acting normal to the plane of the paper pointing inward. Thus, conductor CD carrying current `I_2` is in a MAGNETIC field which is perpendicular to its length. Therefore, force experienced by 2nd conductor CD due to `B_1` `F_(21) = B_1 I_2, l,` Where l = length of the 2nd condcutor or `F_(21) = (mu_0 I_1)/(2 pi d) I_2 l = (mu_0 I_1 I_2 l)/(2 pi d)` and force per unit length `(F_(21))/(l) = (mu_0 I_1 I_2)/(2 pi d) = (mu_0)/(4pi) CDOT (2 I_1 I_2)/(d)` The force `F_(21)` in accordance with Fleming.s LEFT hand rule is directed towards the conductor AB. In the same way, it is FOUND that force experienced per unit length of wire AB is `(F_(21))/(l) = (mu_0)/(4pi) cdot (2 I_1 I_2)/(d)` and is directed towards CD. 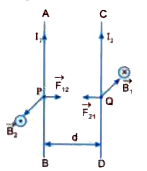
|
|
| 1716. |
Assertion: A charged by cannot attract another uncharged body. Reason: Oppositely charged boils attract each other. |
|
Answer» if both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct EXPLANATION of the Assertion. |
|
| 1717. |
Can power of a lens be negative? |
| Answer» Solution :Yes, it can be. The refracting POWERS of a PLANO CONCAVE and BICONCAVE lenses are NEGATIVE. | |
| 1718. |
A ray of light passes from air into a liquid. The glancing is 30^@. The deviation produced in tha ray of light is 15^@. The refractive index of liquid is : |
|
Answer» 1.224 |
|
| 1719. |
A laser emits a light pulse of duration tau = 0.13 ms and energy E = 10J. Find the mean pressure extered by such a light pulse when it is focussed into a spot of diameter d = 10mu m on a surface perpendicualr to the beam and possessing a reflection coefficient rho = 0.50. |
|
Answer» Solution :The mean pressure `lt p gt` is related to the force fexerted by the beam by `lt p gt xx (PID^(2))/(4) = F` The force `F` EQUALS momentum transferred per second. This is (assuming that photons, not reflected, are absorbed) `2rho(E)/(ctau) +(1-rho)(E)/(ctau) = (1+rho) (E)/(c tau)`. The first term is the momentum transfered on reflection (see problem (261)), the second on ABSORPTION. `lt p gt = (4(1_rho)E)/(pid^(2)c tau)` Substituting the values we get `lt p gt = 48.3` atomsphere. |
|
| 1720. |
When de-Broglie wavelength of electron in increased by 1% its momentum… |
|
Answer» INCREASE by 1% `dlambda prop -p^(2)DP therefore d lambda prop -(1)/(p^(2))dp` `therefore (dlambda)/(lambda)xx100=-(dp)/(p^(2))xxpxx100` `therefore (dp)/(p)xx100=-1%` `therefore` Momentum will decrease by 1% |
|
| 1721. |
The height of communication statellite from thesurface of the earth is approximately |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 1722. |
What is thomson effect ? |
| Answer» Solution :Thomson showed that if two points in a conductor are at DIFFERENT TEMPERATURES, the density of electrons at these points will differ and as a result the POTENTIAL difference is created between these points. Thomson EFFECT is also reversible. | |
| 1723. |
किसी घिरे हुए बंद पृष्ठ पर विधुतीय फ्लक्स भीतर स्थित आवेश का होता |
|
Answer» `1/epsilon_0`गुना |
|
| 1724. |
A hollow insulated conducting sphere is given a charges +10 mu C .What will be the electric field at the centre of thesphere it its radius is 2m ? |
|
Answer» Zero |
|
| 1725. |
What are different methods to release electrons ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :i. THERMIONIC EMISSION, PHOTOELECTRIC emission, Field emission, SECONDARY emission. | |
| 1726. |
Match the following Column I with Column II Code |
|
Answer» I-D , II- C , III- A , IV- B |
|
| 1727. |
Three identical plane mirrors AB, BC, AC are arranged as shown in the figure. Find the total number of images of a point object 'S' formed by the three mirrors. (S is at the centre of the system) |
|
Answer» 18 |
|
| 1728. |
Assertion (A) A wire bent into an irregular shape with the point P and Q fixed . If a current I passed through the Wire, then the area enclosed by the irregular portion of the Wire increases.Reason (R ) Opposite currents carrying Wires repel each other. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and REASON are TRUE and Reason is CORRECT EXPLANATION of Assertion. |
|
| 1729. |
Can a cyclotron be used to accelerate electron ? Why ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No, because, being very light, EVEN a small increase in energy makes electrons MOVING with a very HIGH SPEED . As a result, the electrons go quickly out of step with oscillating electric field. | |
| 1730. |
According to Newton, the viscous force acting between liquid layers of area A and velocity gradient (Deltav)/(Delta z)is given by F = - eta A (dv)/(dz) , where eta is constant called coefficient of viscosity. The dimensional formula of is |
|
Answer» `[ ML^(-2) T^(-2)]` |
|
| 1731. |
Plot a graph showing the variation of coulomb force (F)versus ((1)/(r^(2)))where r is the distancebetween the two charges of each pair of charges:(1 mu C ,2 muC ) and ( 2 mu C ,-3muC ) .Interpret the graphs obtained. |
|
Answer» Solution :Force between two charges `q_1mu C 1 XX 10^(-6) C and q_2 =2 muC = 2xx10 ^(-6) C ` separated by a distance r, ` F= (1)/( 4pi in _0).(q_1q_2)/(r^(2)) = ( 9xx 10 ^(9) xx1xx 10 ^(-6) xx 2xx 10^(-6))/( r^(2)) =(18xx10^(-3))/(r^(2)) N` and force between two charges `q_1.=2 muC =2 xx 10 ^(-6) C and q_2. =-3muC =-3xx 10 ^(-6) `C separated by a distance r, the force `F. =(1)/(4piin _0) .(q_1.q_2.)/(r^(2)) =(9xx 10 ^(9) xx (2xx10^(-6))xx (-3xx10^(-6)))/(r^(2))` `"" =(54 xx 10^(-3))/(r^(2)) N` Graph SHOWING variation of force F and F. VERSUS `(1)/(r^(2)) ` is shown in adjoining From the graph we note following points: (i) Both the graphs are straight line graphs. As force F is repulsive, its graph is in 1st quadrant. But force F. is attractive and the graph is in 4th quadrant. (II) ` As |oversetto F| =3 |oversetto F| , ` hence slope of F `-(1)/(r^(2)) ` graph for second pair of charges is 3 times as compared to that for first pair of charges. 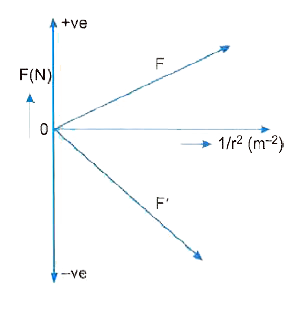
|
|
| 1732. |
Which one of the following represents corrent magnetic field lines ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 1733. |
An object of mass 26 kg floats in the air and it is in the equilibrium state.Air density is 1.3 kg m^(-3). The volume of the object is |
|
Answer» `10 m^3` |
|
| 1734. |
If the source of light used in a Young.s Double Slit Experiment is changedfromred to blue , then |
|
Answer» the frings will become brighter |
|
| 1735. |
On which one of the factors do the nature of the tehrmal radiation depends inside an encolsure? |
|
Answer» NATURE of walls |
|
| 1736. |
The junction diode in the following circuit requires a minimum current of 1 mA to be above the knee point (0.7V) of its 1-V characteristic curve . The voltage across the diode is independent of current above the knee point . If V_B = 5V , then the maximum value of R so that the voltage is above the knee point will be |
|
Answer» `4.3kOmega` Hence voltage across RESISTANCE R is 5 - 0.7 `=4.3V` usig `V = iR implies 4.3 = 1XX10^(-3)xxR implies R = 4.3kOmega` |
|
| 1737. |
Calculate the magnetic moment of an atom (in Bohr magnetons) (a) in .^(1)F state, (b) in .^(2)D_(3//2) state, (c ) in the state in which S=1, L=2, and Lande factor g=4//3. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) For the `(1)F` states `S=0,L=3=J` `g=1+(3xx4-3xx4)/(2xx3xx4)=1` HENCE `mu=SQRT(3xx4) mu_(B)=2sqrt(3)mu_(B)` (b) For the `.^(2)D_(3//2)` state `S=(1)/(2),L=2,J=(3)/(2)` `g=1+((15)/(4)+(3)/(4)-6)/(2xx(15)/(4))=1+(18-24)/(30)=(4)/(5)` Hence `mu=(4)/(5)sqrt(15//4)mu_(B)=(2)/(5)sqrt(15)mu_(B)=2sqrt((3)/(5))mu_(B)` (C ) We have `(4)/(3)=1+(J(J+1)+2-6)/(2J(J+1))` or `(4)/(3)J(J+1)=J(J+1)-4` or `J(J+1)=12implies J=3` Hence `mu=(4)/(3)sqrt(12)mu_(B)=(8)/(sqrt(3))mu_(B)`. |
|
| 1738. |
[M^(1)L^(-2)T^(-2)] represents dimensional formula of which of the following physical quantities ? |
|
Answer» energy We have `=(ML^(1)T^(-2))/(L^(2)xxL^(1))=("Pressure")/("length")` `:.` Pressure gradient `i.e` (`d)` is CORRECT choice. |
|
| 1739. |
The intemal resistance of a 2.1 V cell which gives a current of 0.2 A through a resistance of 10Omega is |
|
Answer» `0.2Omega` |
|
| 1740. |
A good mirror reflects 80% of light incident on it. Which of of the following is correct ? (a) Energy of each reflected photon decreases by 20% (b) Total no. of reflected photons decreases by 20% . Justify your answer. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Total no. of REFLECTED PHOTONS decreases by 20% | |
| 1741. |
If magnetic lines of force are drawn by keeping magnet vertical, then number of neutral points will be |
|
Answer» One |
|
| 1742. |
If L,C,V,I respectively denote coefficient of self inductance, capacitance, electric potential and electric current, then the expression ((1/2cv^2) is consistent with that of |
|
Answer» `1/2LI^2` |
|
| 1743. |
A person runs along a circular path of radius 5 m. If he completes half of the circle find the magnitude of the displacement vector, How far the person ran? |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 1744. |
वाहनों में पीछे के दृश्य को देखने के लिए लगे दर्पण द्वारा आवर्धन: |
|
Answer» एक से कम होता है |
|
| 1745. |
The angle of deviation delta for a thin prism is given by |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`d=(mu-1)/A` | |
| 1746. |
A choke coll has |
|
Answer» LOW INDUCTANCE HIGH resistance |
|
| 1747. |
नर्मदा बचाओ आंदोलन तथा "टिहरी बांध आंदोलन "जैसे सामाजिक आंदोलन काकारण है? |
|
Answer» परंपरा बांध |
|
| 1748. |
The instantaneous current in an A.C. circuit is given by i = 2 sin (omegat + theta) ampere . The r.m.s. value of the current is : |
|
Answer» 2 AMPERE |
|
| 1749. |
A crown glass prism of angle 5^(@) is to be combined with a flint prism in such a way that the mean ray passes undeviated. Find (a) the angle of the flint glass prism needed and (b) the angular dispersion produced by the combinatino when white light goes through it. Refractive indices for red, yellow, and violet light are 1.541, 1.517 and 1.523, repectively, for crown flass and 1.613, 1.620 and 1.632 for flint glass. |
|
Answer» Solution :The deviation produced by the crown prism is `delta=(MU-1)A` and by the flint prism is `delta^(')=(mu^(')-1)A^(')` The prisms are placed with their angles inverted with respect to each other. The deviations are also is OPPOSITE directions. Thus, the net deviation is `delta_(n et)= delta-delta^(')=(mu-1)A-(mu-1)A^(')` (i) a. If the net deviation for the mean ray is ZERO, `(mu-1)A=(mu^(')-1)A^(')` or `A^(')=((mu-1))/((mu^(')-1))A=(1.517-1)/(1.620-1)xx5^(@)` B. The angular dispersion produced by the crown prism is `delta_(V)-delta_(r)=(mu_(v)-mu_(r))A` and that by the flintprism is `delta_(v)^(')-delta_(r)^(')=(mu_(v)^(')-mu_(r)^('))A` The net angulart dispersion is `(delta _(v)-delta_(r))A-(mu_(v)^(')-mu_(r)^('))A` `=(1.523-1.514) xx 5^(@)-(1.632-1.613)xx4.2^(@)` `=-0.0348^(@) ` . The angular dispersion has magnitude `0.0348^(@) `. a. If the net deviation for the mean ray is zero, `(mu-1)A=(mu^(')-1)A^(')` or `A=((mu^(')-1))/((mu^(')-1))A=(1.517-1)/(1.620-1)xx5^@` b. The angular dispersion produced by the crown prism is `delta _(v)-delta _(r)=(mu_(y)-mu_(r))A` and that by the flint prism is `delta_(v)^(')-delta_(r)^(')=(mu_(v)^(')-mu_(r)^('))A` The net angular dispersion is `(mu_(v)-mu_(r))A- (mu_(v)^(')-mu_(r)^('))A` `=(1.523-1.514)xx5^(@)- (1.632-1.613)xx4.2^(@)` `=-0.0348^(@)`. The angular dispersion havs magnitude `0.034^(@)`. |
|
| 1750. |
A point charge of 2.0 muC is at the centre of a cubic Gaussian surface 9.0 cm on edge. What is the net electric flux through the surface ? |
|
Answer» Solution :NET electric FLUX passing through any closed Gaussian surface is, `phi = q/epsilon_(0)` (where q= net charge ENCLOSED) `=(2 xx 10^(-6))/(8.85 xx 10^(-12))` `phi = 2.26 xx 10^(5) Nm^(2)//C^(2)` There is no change in flux due to dimensions of cube and position of charge inside cube. |
|



