Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1901. |
The focal length of a thin biconex lens is 20 cm. When an object is moved from a distance of 25 cm in front energy stored in the wire is |
|
Answer» 6 |
|
| 1902. |
What is the effect on the interference fringes in a Young.s double-slit experimental due to each of the following operations : The width of the source slit is increased. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Same as in (d). As the source slit width increases, fringe pattern gets less and less sharp. When the source slit is so wide what the CONDITION `s"/"S le lambda"/"d` is not satisfied, the INTERFERENCE pattern DISAPPEARS. | |
| 1903. |
What is the effect on the interference fringes in a Young.s double-slit experimental due to each of the following operations : The monochromatic source is replaced by a source of white light? |
|
Answer» Solution :The INTERFERENCE patterns due to different COMPONENT COLOURS of WHITE light overlap (incoherently). The central bright fringes for different colours are at the same position. Therefore, the central fringe is white. For a point P for which `S_(2)P-S_(1)P= lambda_(b)"/"2`, where `lambda_(b)(= 4000 dotA)` represents the wavelength for the blue colour, the component will be absent and the fringe will appear red in colour. Slightly farther away where `S_(2)Q-S_(1)Q= lambda_(b)= lambda_(r )"/"2` where `lambda_(r )(approx 8000 dotA)` is the wavelength for the red colour, the fringe will be PREDOMINANTLY blue. Thus, the fringe closest on either side of the central white fringe is red and the farthest will appear blue. After a few fringes, no clear fringe pattern is seen. |
|
| 1904. |
What is the effect on the deflection of a galvanometer attached to a coil, if a magnet is moved closer to the coil? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1905. |
What is the effect on the interference fringes in a Young.s double-slit experimental due to each of the following operations : The screen is moved away from the plane of the slit. |
| Answer» Solution :Angular separation of the fringes remains CONSTANT `(lambda"/"d)`. The ACTUAL separation of the fringes increases in proportion to the DISTANCE of the SCREEN from the plane of the TWO slits. | |
| 1907. |
The presence of gravitational firld is required for the heat transfer by : |
|
Answer» STIRRING of liquids Correct CHOICE is (B). |
|
| 1908. |
Write a short note on electrostatic shielding . |
| Answer» Solution :During LIGHTNING ACCOMPAINED by a thunderstorm, it is always safer to SIT inside a bus than in open ground or under a tree. The metal body of the bus provides electrostatic shielding, since the electric FIELD inside is ZERO. During lightning the charges flow through the body of the conductor to the ground with no effect on the person inside that bus. | |
| 1909. |
What is the moment of inertia of a solid sphere of radius R and density rho about it's diameter ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`I=2/5(MR^2)=2/5(4/3(piR^3xxrho)R^2=8/15(piR^5rho)` | |
| 1910. |
An electric bulb, a capacitor, a battery and a switch are all in series in a circuit. How does the intensity of light vary when the switch is turned on? |
|
Answer» Continues to increase gradually MAXIMUM charge on capacitor = `C xx epsi ` HENCE equations of charge and current are as given below. `q= epsi[1- e^(-t//RC)]` ` i= ( dq )/( d t) = ( epsi)/(R) e^(-t //RC )` ` :. ` intensityof light` propI^2R.` 
|
|
| 1911. |
Energy required for the electron excitation in Li^(++) from the first to the third Bohr orbit is : |
|
Answer» 36.3 eV `E_(L^(++))=-13.6xx(9)/(1)=-122.4eV` `E_(L^(++))=-13.6(9)/(9)=-136eV` `Delta=-13.6-(-122.4)` `=108.8eV` |
|
| 1912. |
If the current gain alpha of a transistor is 0.98, what is the value of beta of the trnasistor ? |
|
Answer» `0.49` |
|
| 1913. |
A transparent slab of thickness d has a refractive index n(z) that increases with z. Here z is the vertical distance inside the slab, measured from the top. The slab is placed between two media with uniform refractive indices n_(1) and n_(2) (gtn_(1)), as shown in the figure. A ray of light is incident with angle theta_(i), from medium 1 and emerges in medium 2 with refraction and theta_(f), with a lateral displacement l. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true ? |
|
Answer» l is independent of `n_(2)` Using Snell.s law `mu sin theta= const`, we can understand that option (b) is correct. Bending of LIGHT in medium will depend on how n(z) varies with the height. Hence, option (c) is wrong. We can understand that if option (b) is correct then (d) cannot be correct. Option (d) is wrong. Only options (a) and (b) are correct. |
|
| 1914. |
Show, on a plot, variation of resistivity of (i) a conductor, and (i) a typical semiconductor as a function of temperature. Using the expression for the resistivity in terms of number density and relaxation time between the collisions, explain how resistivity in thc casce of a conductor increases while it decrcases in a semiconductor, with the rise of temperature. |
|
Answer» Solution :Variation of resistivity `rho`T of (i) a conductor, and (II) a typical semiconductor as a function of temperature T has been shown here. The resistivity of a material is given by the relation ` rho = (m)/(n e^(2) tau)` When the temperature rises, the number density of conduction electrons (n) in a conductor does not materially change but amplitude of atomic/molecular vibrations increases and, consequently, frequency of collisions with electrons increases. As a RESULT, relaxation period decreases and consequently resistivity of the conductor increases. The resistivity of a semiconductor decreases on increasing the temperature. In semiconductors, the number density of electrons (n) increases rapidly with rise in temperature due to TRANSFER of electrons from valence level to conduction level on ACCOUNT of high kinetic energy of free electrons. However, the EFFECT of decrease in relaxation period is not of much consequence. Due to increase in value of n, the resistivity decreases. 
|
|
| 1915. |
Find the de Broglie wavelength of relaativistic electrons reaching the anticathode of an X-ray tube if the short wavelength limit of the continous X-rays spectrum is equal to lambda_(sh)= 10.0p m? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :For relativistic elelctrons, the formula for the short wavelength LIMIT is `X`-rays will be `(2pi ħc)/(lambda_(sh))=m_(0)c^(2)((1)/(sqrt(1-beta^(2)))-1)=csqrt(P^(2)+m^(2)c^(2))-mc^(2)` or `((2pi ħ)/(lambda_(sh))+mc)^(2)=P^(2)+m^(2)c^(2)` or `((2piħ)/(lamda_(sh)))((2piħ)/(lambda_(sh))+2MC)=P^(2)` or `p=(2piħ)/(lambda_(sh))sqrt(1+(mc lambda_(sh))/(piħ))` HENCE `lambda_(sh)=lambda_(sh)//sqrt(1+(mc lambda_(s h))/(piħ))-3.29p m` |
|
| 1916. |
Two resistors are connected in series with 5V battery of negligible internal resistance. A current of 2A flows through each resistor. If they are connected in parallel with the same battery of current of 25/3AA flows through combination. Calculate the value of each resistance. |
Answer» SOLUTION :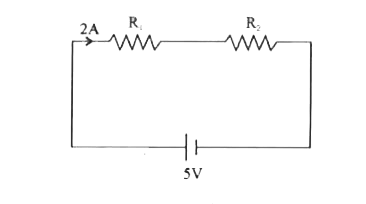 `I_g=(IS)/(G+S)`….(I) `I_gG=(I-I_g)S` or `S=(I_gG)/(I-I_g) ""I_gG=IS-I_gS` `thereforeI_g=(IS)/(G+S)` `I_gG+I_gS=IS , "" (G+S)I_g=IS` from EQUATION (1) `I_g PROP I` Since S and G are CONSTANTS, the scale can be graduated to give the main CURRENT directly. |
|
| 1917. |
A current loop in a magnetic field |
|
Answer» can be in equilibrium in ONE orientation |
|
| 1919. |
A polarizer analyzer set is adjusted such that the intensity of ligth coming out of the analyzer is just 10% of the original intensity. Assuming that the polarizer analyzer set does not asorb any light, the angle by which the analyzer needs to be rotated further to reduce the output intensity to be zero is |
|
Answer» `60^(@)` `I=I_(0) COS^(2) theta` `0.1 I_(0)=I_(0)cos^(2) theta [ :. I=10% of I_(0)]` `:. cos^(@) theta =0.1` `:.cos theta=sqrt(0.1)` `=cos theta=0.3162` `:. Theta=71.6^(@)` Angle of ROTATION `=90^(@)-theta` `=90^(@)-theta` `=18.4^(@)` |
|
| 1920. |
If i_p is the polarising angle, then the refractive index (n) of the reflecting material is given by : |
|
Answer» SIN `i_p` |
|
| 1921. |
A monochromatic beam of light is travelling from medium A of refractive index n_(1) to a medium B of refractive index n_(2). In the medium A, there are x number of waves in certain distance. In the medium B, there are y number of waves in the same distance, Then, refractive index of medium A with respect to medium B is : |
|
Answer» `(x)/(y)` `s = xlambda_(1) = ylambda_(2)` or "" `(x)/(y) = (lambda_(2))/(lambda_(1)) = (n_(1))/(n_(2))` `therefore (n_(1))/(n_(2)) = (x)/(y)`. |
|
| 1922. |
The spectral line of lambda=5000 Å in the light coming from a distant star is observed at 5200 Å . Determine the recession velocity of the star. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1923. |
Two protons are situated at a distancer r apart in free space. The ratio of the magnitude of electric force to the gravitational force between them is of the order of ___________, |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1924. |
What will an ammeter measures when it is connected in parallel with a circuit? Will it still measure the current through the circuit? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :It MEASURES the CURRENT FLOWING through it only and not the current in the CIRCUIT. | |
| 1926. |
Define Bohr magneton using Bohr's first hypothesis. |
|
Answer» Solution :1. It is DEFINED as the magnetic moment associated with an electron due to its orbital motion in the first orbit of hydrogen atom. 2. BOHR hypothesised that the angular momentum assumes a discrete set of values namely `l=n(h/(2pi))` where n is a natural NUMBER. n = 1, 2, 3, ... and h is a constant which is KNOWN as Planck constant. `h=6.625xx10^(-34)Js` 3. We know that, `(mu_(l))_(min)=e/(2m_(e))(l)` = `e/(2m_(e))((nh)/(2pi))` 4. Taking n = 1 `(mu_(l))_(min)=(e/(2m_(e)))h/(2pi)` = `((1.6xx10^(-19))(6.63xx10^(-34)))/(4xx3.14xx9.11xx10^(-31))` `(mu_(l))_(min)=9.27xx10^(-24)Am^(2)` 5. Where .min. is minimum value. Minimum value of `(mu_(l))` is known as Bohr magneton. |
|
| 1927. |
A cyclist is riding with a speed of 27kmh^(-1) As he approaches a circular turn on the road of radius 80m, he applies brakes and reduces his speed at the constant rate of 0.50ms^(-1) cvery second. The net acceleration of the cyclist on the circular turn is |
|
Answer» `0.68 MS^(-2)` |
|
| 1928. |
Assuming the expression for drift velocity, derive the expressionfor conductivityof a materialsigma="ne"^2 tau//m. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :We KNOW that drift velocity `V_d =(eE tau)/m` We have CURRENT `I="NE" AV_d`…(1) Substitute `V_d` in eqn.(1) `I="ne"A(eEtau)/m =("ne"^2 A E tau)/m` `I/A=("ne"^2 Etau)/m rArr j=("ne"^2 E tau)/m` We know that `j=sigmaE` `therefore sigma cancelE=("ne"^2 cancelE tau)/m` `sigma=("ne"^2 tau)/m` 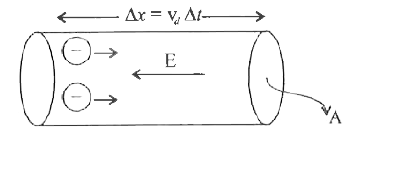
|
|
| 1929. |
(c) Must every magnetic configuration have a north pole and a south pole ? What about the field due to a toroid ? |
| Answer» Solution :(C)It is not necessary that every MAGNETIC configuration should have north pole and south pole. If the source of magnetic field has some net magnetic MOMENT then only it has magnetic north pole and magnetic south pole, otherwise not. For EXAMPLE : toroid, current carrying ring, infinitely long current carrying STRAIGHT thin wire do not possess magnetic north pole and magnetic south pole. | |
| 1930. |
Copper and silicon is cooled from 300K to 60K, the specific resistance. |
|
Answer» DECREASE in COPPER but INCREASE in silicon |
|
| 1931. |
A person row a boat across a river making an angle 60^@ with down stream. Find the percentage of time he would have saved had he crossed the river in shortest possible time |
|
Answer» 0.47 |
|
| 1932. |
The ability of a material to retain magnetism even after removal of the magnetising field is known as ______________ , |
| Answer» SOLUTION :RETENTIVITY | |
| 1933. |
{:("(i) Horizontal component"B_(H),(a) l_(g) prop theta ),("(ii) vertical component"B_(v ),(b) B_(E) cos I ),((iii) "Galvanometer to a ammeter",(c ) l_(g) prop v ),("(iv) Galvanometer to a voltmeter",(d) B_(e) sin l):} |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1934. |
A long straiht telephone cable contains six wires , each carrying a current of 0.5 A. The distance between the wires can be neglected. a. If the current in all six wires are in the same direction, what is the magnitude of the magnetic field 10 cm from the cable ? b. If four wires carry current in one direction and the other two in opposite directions, what is the field magnitude at 10 cm from the cable ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`6 xx 10^(-6) T b. 2 xx 10^(-6)` T | |
| 1935. |
The potentiometer is bestfor measuringvoltageas . |
|
Answer» It HASA sensitivegalvnometer |
|
| 1936. |
A projectile can have the same range 'R' for two angles of projection. If t_(1) and t_(2) be the times of flight in the two cases, then product of the two times of flights is proportional to : |
|
Answer» Solution :As RANGE for `theta` and (90° - `theta`) is the same, the times of flight are given by `t_(1)=(2usintheta)/g` and `t_(2)=(2ucostheta)/g` `t_(1).t_(2)=(2u^(2)sin2theta)/g=(2R)/g` or `t_(1).tpropR` |
|
| 1937. |
A bar magnet of magnetic moment M is cut into two parts of equal length. The magnetic moment of either part is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 1938. |
A rectangular loop, in edge view, as shown in the following figure, is rotating in a horizontal magnetic field. The axis of rotation is perpendicular to the page and is shown by a black dot in the middle of the figure. The parts of the loop perpendicular to the page are moving at a velocity v as shown in the figure. At the instant depicted, the normal to the loop makes an angle of 30° with the east direction. Which of the following statements, about the magnetic flux phi through the loop and the induced emf in the loop, are true, at the instant depicted? |
|
Answer» `PHI` is INCREASING and EMF is increasing |
|
| 1939. |
An astronaut in a spaceship sees the sky as |
|
Answer» blue |
|
| 1940. |
In Young's double slit experiment, the central bright fringe can be identified |
|
Answer» as it is narrower than other bright fringes |
|
| 1941. |
Two materials X and Y are magnetised, whose intensity of magnetisation are 500 A m^(-1) and 2000 A m^(-1), respectively. If the magnetising field is 1000 A m. then which one among these materials can be easily magnetized ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The susceptibility of material X is `X_(m) x= |(vec(M))/(vec(H))| = (500)/(1000) = 0.5 ` The susceptibility of material Y is `X_(m) Y = |(vec(M))/(vec(H))| = (2000)/(1000) = 2` Since, susceptibility of material Y isgreater than of material X. material Y can be EASILY magnetized than X. |
|
| 1942. |
Which of the following experiment proved that ..There is no ether.. in the universe |
|
Answer» Foucault.s experiment |
|
| 1943. |
Infinite number of masses, each of mass 3 kg are placed along the y-axis at y = 1 m, 3 m, 9 m 27 m ... The magnitude of resultant gravitational potential in terms of gravitatinal constant at the origin (y = 0) is |
|
Answer» 4.5 G unit |
|
| 1944. |
A Car is travelling at (v//10) ms^(-1) and sounds horn of frequency 990 Hz. The apparent frequency heard by a police chasing the car at (v//9) ms^(-1) where V is velocity of sound |
|
Answer» 990 Hz |
|
| 1945. |
The diameter of the sun is several hundred times larger than the moon still at a time of the solar eclipse, the sun is covered entirely by the moon, How? |
| Answer» Solution :The distance of the sun from the EARTH is 1000 times larger than the distance of moon from the earth. During SOLAR eclipse, moon comes in between sun and Earth. Both the sun moon subtend nearly equal ANGLES at our eyes. Hence, the entire sun gets covered by the moon. | |
| 1946. |
What is maximum number of electron in an atom whose highest energy electrons have principle quantum number n=5. [Divide your answer by 23] |
| Answer» Solution :`[Ra]7s^(2)5f^(14)6d^(10)7P^(6)8S^(2)5g^(18)` | |
| 1947. |
What is the net flux of the uniform electric field of Q.15 thorugh a cube of side 20cm oriented so that its facesare parallel to the co-ordinate planes ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :NET flux over the cube is zero, becausethe numberof LINES enteringthe cube is the same as the numberof lines leavingthe cube. | |
| 1948. |
In the circuit shown R_(1)=R_(2)=10Omega and resitance per unit length of wire PQ=1Omega//cm andlength PQ=10Omegacm. If R_(2) is made 20Omega then to get zero deflection in galvanometer S is midpoint of wire PQ |
|
Answer» The jockey at `P` can be moved towards right `2 cm` (hence Wheatstone will be balanced) 
|
|
| 1949. |
Calculate the electric field intensity E which would be just sufficient to balance the weight of an electron. If this electric field is produced by a second electron located below the first one what would be the distance between them? [Given: e= 1.6 xx 10^(-19)C, m= 9.1 xx 10^(31) kg adn g= 9.8 m//s^(2)] |
|
Answer» Solution :As FORCE on a charge in an electric field E `F_(e)= eE` So according to given problem `F_(e) = W` i.e., eE= mg `E= (mg)/(e ) = (9.1 XX 10^(-31) xx 9.8)/(1.6 xx 10^(-19)) = 5.57 xx 10^(-11) (V)/(m)` As this intensity E is produced by another electron B, located at a distance r below A  `E= (1)/(4pi in_(0)) (e )/(r^(2)) "i..e, " r= sqrt((e)/(4pi in_(0)E))` So, `r= [(9 xx 10^(9) xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19))/(5.57 xx 10^(-11))]^(1//2)= 5m` |
|
| 1950. |
A lead bullet penetrates a board, its speed being reduced as a result from 400 m/s to 200 m/s. What fraction of the bullet will melt? Neglect the heating of the board. The initial temperature is about 30 ^@C. |
|
Answer» |
|