Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 40501. |
Frequency range used in down linking in satellite communication is |
|
Answer» `0.896` to `0.901 GHZ` |
|
| 40502. |
What is the meaning of “fright"? |
|
Answer» Happy |
|
| 40503. |
A particle of mas 70g, moving at 50cm//sis acted upon by a variable force opposite to its direction of motion. The force F is shown as a function of time t. |
|
Answer» Its SPEED will be `50 cm//s` after the force stops acting |
|
| 40504. |
To identify whether the transistor is working or not using multimeter, which statement serves the purpose? |
|
Answer» The common lead of multimeter is connected to a base and other lead to FIRST emitter and then to collector only `1ST` CONNECTIONS SHOWS the continuity |
|
| 40505. |
The crystal with metal deficiency defect is....... |
|
Answer» NaCl |
|
| 40506. |
What is the function of a choke coil in a fluorescent tube? |
| Answer» Solution :It DECREASES CURRENT in the circuit WITHOUT wastage of electrical energy in the FORM of heat. | |
| 40507. |
What is quantisation of energy ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Electrons can have only certain ORBITAL radii, thus have only certain VALUES of ENERGY called energy LEVELS. | |
| 40508. |
A point luminous object (O) is at a distance h from front face of a glass slab of width d and of refractive index mu. On the back face of slab is a refracting plane mirror. Anobserver sees the imageof object in mirroras shown in figure. Distance of image from front face as seen by observerwill be |
|
Answer» `h+ (2d)/(mu)` Now asa plane mirror formsimage behind the mirrorat the samedistanceas the objectis in forntof it, the DISTANCEOF imageI form `mm'`will be `h + (d/u)` and as thedistance of vir tualmirror from the front face as seen by observer `=[h+(d)/(mu)] + (d)/(mu) = h + (2d)/(mu)` 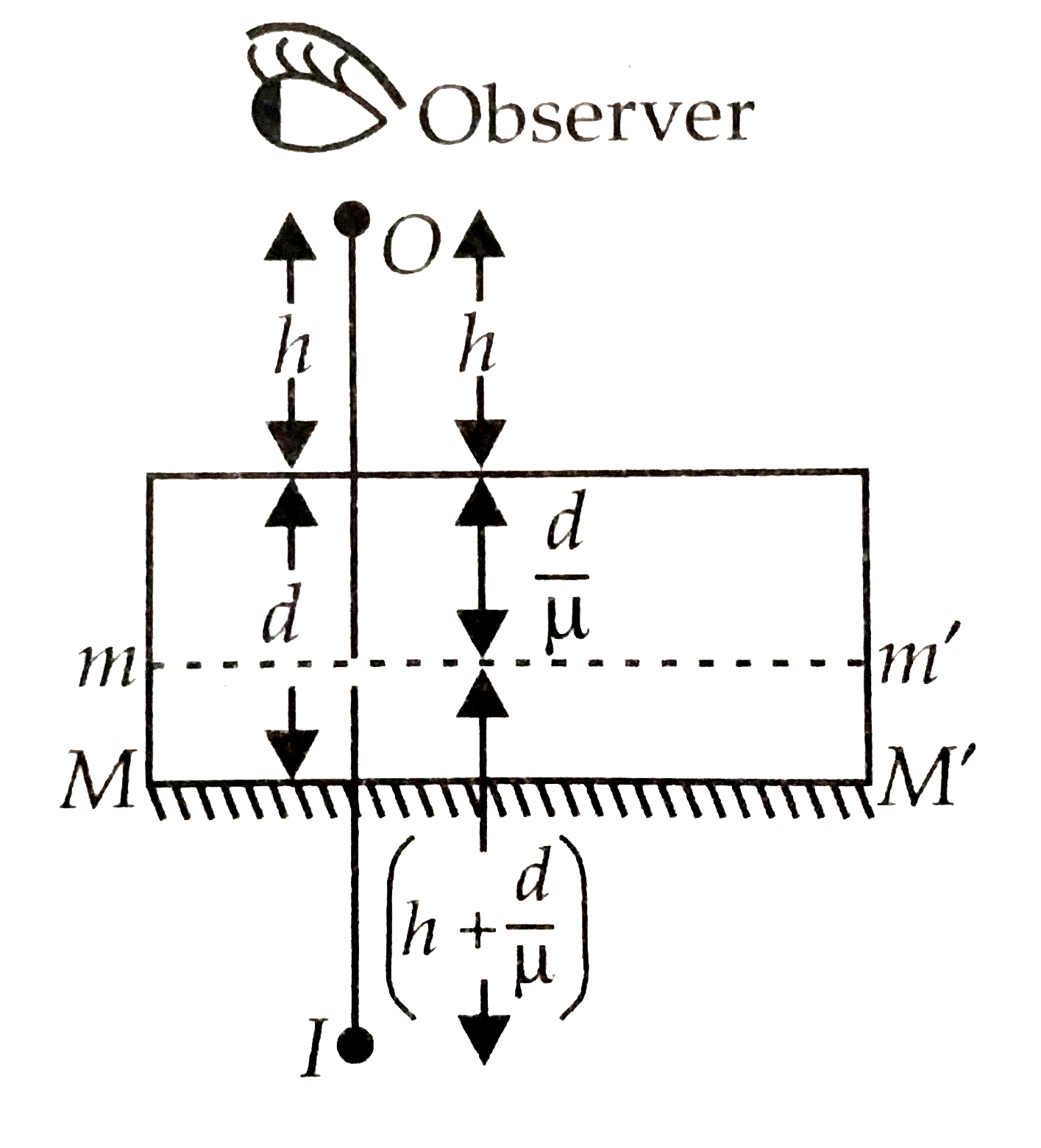
|
|
| 40509. |
Assertion : NH3 is liquidities more easily than CO_(2). Reason : Critical temperature of NH3 is more than CO_(2). |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and reason are true and reason is the correct EXPLANATION of assertion. |
|
| 40511. |
A very long magnet of pole strength 4A-m is placed vertically with its one pole on the table. At what distance from the pole, will there be a neutral point on the table? [B_H = 4 xx 10^(-5)Wbm^(-2)] |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`0.1 m` | |
| 40512. |
When light is refracted, which of the following does not change? |
|
Answer» frequency |
|
| 40513. |
A piece of copper and another of germanium are cooled from room temperature to 77 K, the resistance of ………. |
|
Answer» the resistance of each INCREASES. The resistance of copper decreases with temperature while resistance of SEMICONDUCTOR germanium increases with DECREASING temperature. |
|
| 40514. |
An artificial satellite of the Moon revolves in a circular orbit whose radius exceeds the radius of the Moon eta times. In the process of motion the satellite experiences a slight resistance due to cosmic dust. Assuming the resistance force to depend on the velocity of the satellite as F=av^2, where alpha is a constant, find how long the satellite will stay in orbit until it falls onto the Moon's surface. |
|
Answer» Solution :For a satellite in a circular orbit about any MASSIVE body, the following relation holds between kinetic, potential & total energy: `T=-E`, `U=2E` (1) Thus since total mechanical energy must decrease due to RESISTANCE of the cosmic dust, the kinetic energy will increase and the satellite will 'fall', We see them, by work energy theorem `dT=-dE=-dA_(f r)` So, `mvdv=alphav^2vdt` or, `(alphadt)/(m)=(dv)/(v^2)` Now from NEWTON's law at an arbitrary radius r from the moon's centre. `v^2/r=(gammaM)/(r^2)` or `v=sqrt((gammaM)/(r))` (M is the mass of the moon). Then `v_i=sqrt((gammaM)/(etaR))`, `v_f=sqrt((gammaM)/(R))` where R=moon's radius. So `underset(v_1)overset(v_f)int(dv)/(v^2)=alpha/m underset(0)overset(tau)intdt=(alphatau)/(m)` or, `tau=m/alpha(1/v_i-(1)/(v_f))=(m)/(alphasqrt((M)/(gammaR)))(sqrteta-1)=(m)/(alphasqrt(gR))(sqrteta-1)` where g is moon's gravity. The averaging IMPLIED by Eq. (1) (for noncircular orbits) makes the result approximate. |
|
| 40515. |
Assertion: Five charges +q each are placed at five vertices of a regular pentagon. A sixth charge - Q is placed at the centre of pentagon. Then net electrostatic force on -Q is zero Reason:Net electrostatic potential at the centre is zero. |
|
Answer» Both Assertion and REASON are TRUE and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion |
|
| 40516. |
Unpolarized light of intensity I_0 is incident on surface of a block of glass at Brewster.s angle. In that case, which one of the following statements is true? |
|
Answer» TRANSMITTED LIGHT is partially polarized with INTENSITY `I_(0)"/"2` |
|
| 40517. |
A plane EM wave travelling along z - direction is desctribed vec(E )=E_(0)sin(kz - omega t)hat(i)andveC(B)=B_(0)sin (kz - omega)hat(j). Show thatThe time averaged intensity of the wave is given by I_(av)=(1)/(2)c in_(0)E_(0)^(2). |
|
Answer» Solution :Radiant flux density, `S=(1)/(mu_(0))(vec(E )xx vec(B))` `therefore S=c^(2)in_(0)(vec(E )xx vec(B)) "" …(1) [because c=(1)/(sqrt(mu_(0)in_(0)))]` Let electromagnetic WAVES propagate in X - DIRECTION. Electric field vector in y - direction and magnetic field vector in z - direction. Hence, `vec(E )=vec(E )_(0)cos(K x-omega t)` `vec(B)=vec(B)_(0)cos(kx - omega t)` `vec(E )xx vec(B)=(vec(E )_(0)xx vec(B)_(0))cos^(2)(kx-omega t)` `S=c^(2)in_(0)(vec(E )xx vec(B))` [`because` From equation (1)] `c^(2)in_(0)(vec(E )_(0)xx vec(B)_(0))cos^(2)(kx-omega t)` Average value of magnitude of radiant flux density over complete cycle is, `S_("average")=c^(2)in_(0)|vec(E )_(0)xx vec(B)_(0)|(1)/(T)int_(0)^(T)cos^(2)(kx-omega t)dt` `c^(2)in_(0)E_(0)B_(0)xx(1)/(T)xx(T)/(2) "" [because |vec(E )_(0)xx vec(B)_(0)|=E_(0)B_(0)sin 90^(@)=E_(0)B_(0)]` and`int_(0)^(T)cos^(2)(kx-omega t)dt=(T)/(2)` `therefore S_("average")=(c^(2))/(2).in_(0)E_(0)((E_(0))/(c )) "" [because c=(E_(0))/(B_(0))rArr B_(0)=(E_(0)^(2))/(c )]` `=(c )/(2)in_(0)E_(0)^(2)` `=(c )/(2)xx(1)/(c^(2)mu_(0))xx E_(0)^(2) "" [because c=(1)/(sqrt(mu_(0)in_(0)))rArr in_(0)=(1)/(c^(2)mu_(0))]` `=(E_(0)^(2))/(2mu_(0)c)` |
|
| 40518. |
The amount of work done to form a spherical soap bubble of radius 0.05 m and of surface tension 0.03 N/m is |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 40519. |
Explainzenerdiode as votltage regulator . |
Answer» Solution :ZENER diode as a voltage regulator: A Zener diode working in the break down repin can serve as a voltage regulator. It maintains a CONSTANT output voltage even when input voltage `V_1`. or load current `I_L` varies. Here, in this circuit the input voltage `V_i` is regulated at a constant voltage. `V_z`. (Zener voltage) at the output represented as Vousing a Zener diode. The output voltage is maintained constant as long as the input voltage does not FALL below `V_z` Circuit to study voltage regulation by Zener diode When the potential developed across the diode is greater than `V_z` the diode moves into the Zener BREAKDOWN region. It conducts and draws relatively large current through the series resistance `R_i` The total current I passing through Requals the sum of diode currently and load current `I_L(I=I_Z+I_L)`. It is to be noted that the total current is ALWAYS less than the maximum Zener diode current Under all conditions `V_o=V_z` Thus, output voltage is regulated. |
|
| 40520. |
If a liquid rises to a height of 9cm in a glass capillary of radius 0.02 cm. What will be the height of liquid column in a glass capillary of radius 0.03 cm? |
|
Answer» 4 cm |
|
| 40521. |
What is principle of a meter bridge ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :BASED on WHEATSTONE .s BRIDGE. | |
| 40522. |
If the current sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer is increased by 20% and its resistance also increased by 50% then how will the voltage sensitivity of the galvanometer be affected? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :25% DECREASE | |
| 40523. |
(a) Assuming that Eq. holds, find how last you would have to go through a red light to have it appear green. Take 620 nm as the wavelength of red light and 540 nm as the eavelength of green light. (b) What would the emission wavelength be if you went twice that speed? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 40524. |
Draw the intensity patten for single slit diffraction and double slit interference. Hence , state two differences between interference and diffraction patterns. |
Answer» SOLUTION :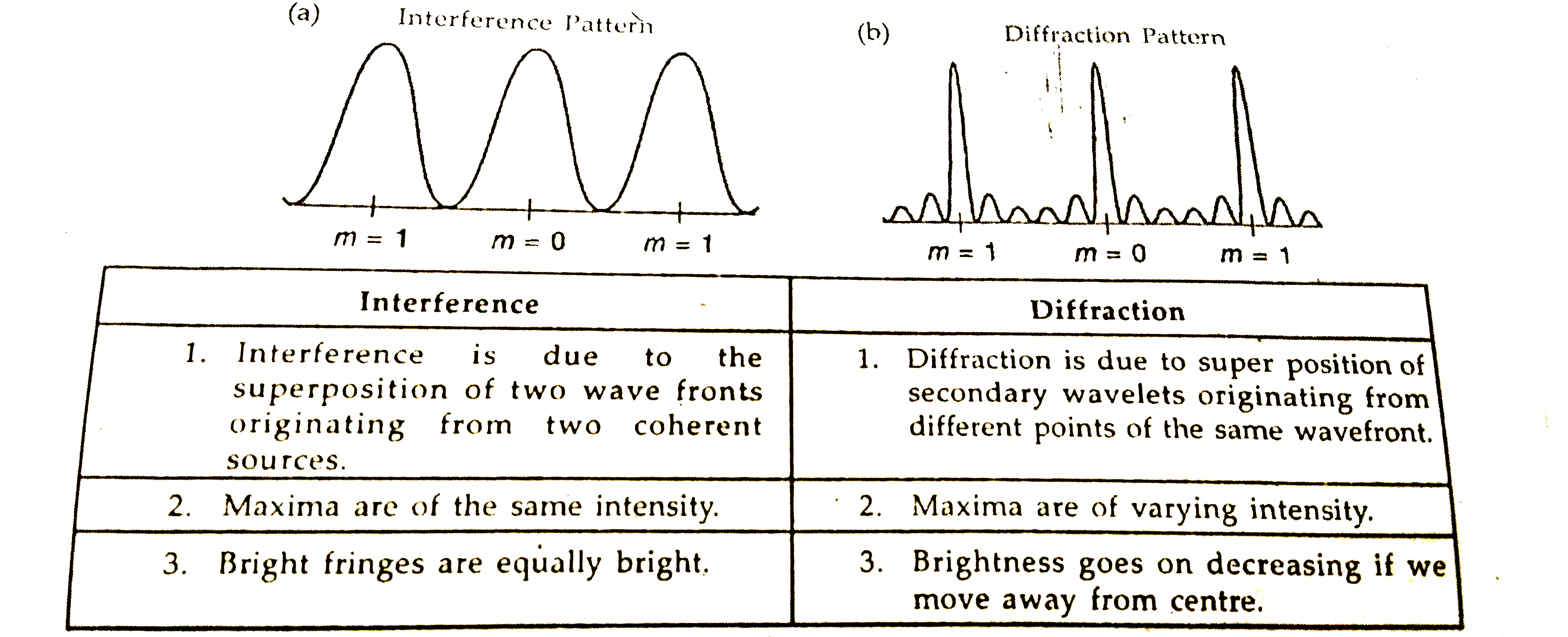 . .
|
|
| 40525. |
The young's modulus of steel is 20 xx 10^(10) N/m^(2) . If the density of steel is 7.7xx10^(3) kg/m^(2), the velocity of longitudinal wave in steel is nearly : |
|
Answer» 50 m/s. ` = sqrt((20 xx 10^(10))/(7.7 xx 10^(3))) = 5345 ms^(-1) = 5000` m/s `hence the correct choice is (C). |
|
| 40526. |
If |vecAxxvecB|=sqrt3(vecA.vecB), then the value of |vecAxxvecB| is : |
|
Answer» `(A^(2)+B^(2)+AB)^(1//2)` HENCE, `AB sin THETA = sqrt3AB cos theta` `"or"tan theta = sqrt3` `theta=60^(@)` `|vecAxxvecB|=(A^(2)+B^(2)+2ABcos 60^(@))^(1//2)` `=(A^(2)+B^(2)+2AB cos 60^(@))^(1//2)` `=(A^(2)+B^(2)+2AB XX(1)/(2))^(1//2)` `=(A^(2)+B^(2)+AB)^(1//2)` |
|
| 40527. |
Define self-inductance and is it's SI unit ? |
| Answer» Solution :Self- inductance is defined as the magnetic flux linked through a coil DUE to FLOW of ONE AMPERE current in it. | |
| 40528. |
In the displacement method, a convex lens is placed in between an obect and a screen. If the magnification in the two positions are m_(1) and m_(2) and the displacement of the lens between two positions is x, then the focal length of the lens is: |
|
Answer» `(X)/(m_(1)+m_(2))` `(1)/(f) = (u-v)/(UV)` `(1)/(f)=((u-v)(v+u))/(uv(v+u))` `f = (uv(v+u))/(u^(2)-v^(2))` `therefore "" f=(v+u)/(u^(2)/(uv)-(v^(2))/(uv))=(u+v)/((u)/(v)-(v)/(u))` `therefore "" f = (x)/(m_(2) - m_(1))`. |
|
| 40529. |
The huge advantage of using the conservation of energy instead of Newton's laws of motion is that we can jump from the initial state to the final state without considering all the intermediate motion. Here is an example. In Fig. 8-25, a child of massm is released from rest at the top of a water slide, Assuming that the slide is frictionless because of the water on it, find the child's speed at the bottom of the slide. |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) We cannot find her speed at the bottom by using her acceleration along the slide as we might have in earlier chaptersbecause we do not know the slope (angle) of the slide. However, because that speed is related to her KINETIC energy, perhaps we canuse the principle of conservation of mechanical energy to get the speed . Then we would not need to know the slope. (2) Mechanical energy is conserved in a systemif the system is isolted and if only conservative forces cause energy transfers within it. Let.s CHECK. Forces: Two forces act on the child. The gravitational force, a conservative force, does work on her. The normal force on her from the slide does no work because its direction at anypoint during the descent is always perpendicular to the direction in which the child moves. 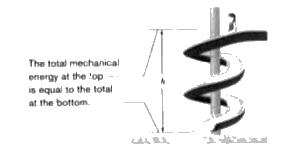 Figure 8-25 A child slides down a water slide as she descends a height h. System: Because the only force doing work on the child is the gravitational force, we choose the child-Earth system as our system, which we can take to be isolaed. Thus, we have only a conservative force doing work in an isolated system, so we can use theprinciple of conservation of mechanical energy. Calculations: Let the mechanical energy be `E_("mec.t)` when the child is at the top of the slide and `E_("mec.b")` when she is at the bottom. Then the conservation principle tells us `E_("mec.b")=E_("mec.t")` To show both KINDS of mechanical energy, we have `K_(b) +U_(b) =K_(t)+U_(t)`, or `1/2 mv_(b)^(2) + mgy_(b)=1/2 mv_(t)^(2)+mgy`. Dividing by m and rearranging yield `v_(b)^(2)=v_(t)^(2)+2g(y_(t)-y_(b))`. Putting `v_(t)=0` nd `y_(t)-y_(b)=h` leads to `v_(b)=sqrt(2gh)=sqrt((2)(9.8 m//s^(2))(8.5 m))` `=13m//s`. This is the same speed that the child would REACH if she fell 8.5 m vertically. On an actual slide, some frictional forces would act and the child would not be moving quite so fast. Comments: Although this problem is hard to solve directly with Newton.s laws, using conservation of mechanical energy makes the solution much EASIER. However, if we were asked to find the time taken for the child to reach the bottom of the slide, energy methods would be of no use, we would need to know the shape of the slide, and we would have a difficult problem. |
|
| 40530. |
A freshly prepared radioactive source of half life 2 hours emits radiations of intensity, which is 64 time the permissible safe level. The minimum time after which it would be possible to work safely with this source is: |
|
Answer» 6 hrs `t/T=6, t=6T=6 XX 2` =12hrs. |
|
| 40531. |
Velocity of electromagnetic wave having wavelength 5000 Å in medium of refractive index 2 is ..... |
|
Answer» `2XX10^(8)` `:.v=(c)/(v)=(3xx10^(8))/(2)=1.5xx10^(8)m//s` |
|
| 40532. |
A straight wire of length 2m carries a current of 10A. If this wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.15T making an angle of 45^(@) with the magnetic field, the applied force on the wire will be |
|
Answer» 1.5N `|VEC(F)| = |I (vec(l) xx vec(B))| or F= IlB SIN theta` Here, I=10A, l=2M, B= 0.15T, `theta= 45^(@)` `:.` Force, `F= (10A) (2m) (0.15T) sin 45^(@) = (3)/(sqrt2)N` |
|
| 40533. |
A box contains L,C and R When 250V dc is applied to the terminals of the box a current of 0.1 A flows in the circuit When an ac source of 250V rms at 2250 rad//sec is connected a current of 1.25 A rms flows it is observed that the current rises with frequency and becomes maximum at 4500rad/sec Find the value of L,Cand R Draw the circuit diagram . |
|
Answer» Solution :When dc source is applied current `=1A` In dc circuit inductor offers ZERO resistance and capacitor offers infinite resistance `R` and `C` cannot be in series `I = (V_(dc))/ (R ) implies 1 = (250)/R` ` R = 250 Omega` Force source IMPEDANCE `Z = (V_(rms))/(i_(rms)) = (250)/(1.25) = 200 Omega` As `Z lt R, R L C` cannot be in series `R` cannot be in series with `C` as explained earlier As current is maximum at resonance and current increases with frequency `R` cannot be in series with `L` In fact `L` and `C` must be in series `i_(1) = (250)/(250) =1` A in phase with voltage Impedance of lower branch `Z' = | (omegaL -(1)/(omegaC))|` `i_(2) = (250)/(Z)` The phase difference between `i_(2)` and voltage is `pi//2` The angle between `i_(1)` and `i_(2)`i is `90^(@)` `i_(1)^(2) + i_(2)^(2) = i^(2)` `(1)^(2) + i_(2)^(2) = (1.25)^(2)` `i_(2)^(2) = (1.25)^(2) -(1)^(2) = (2.25) (0.25)` `i_(2) = 1.5 xx 0.5 =0.75 A` `i_(2) = (V)/(Z')` `Z' = (V)/(i_(2))` `|omegaL - (1)/(omegaC)| = (250)/(0.75)` `|(omega^(2) LC -1)/(omegaC)|= (1000)/(3) ` `|((2250)^(2) LC -1)/(2250C)|= (1000)/(3)` At resonance `i_(2)` is maximum `Z` is minimum `Z' = omegaL - (1)/(omegaC) =0` `(1)/(LC) = omega^(2) = omega_(r)^(2) = (4500)^(2)` Solving (i) and (ii) we get `|(((2250)/(4500))^(2) -1)/(2250 C)|= (1000)/(3)` `C = (3//4)/(2250)X (3)/(1000) = 10^(-6) F = 1mu F` `LC = (1)/((4500)^(2)` `L = (1)/((4500)^(2) xx 10^(-6)) = (100)/(45 xx 45) =(4)/(81)H` `R = 250 Omega, L = 4//81 H ,C =1 MUF`   . .
|
|
| 40534. |
How are infrared waves produced ? What is the range of their wavelength ? |
| Answer» Solution :Infrared waves are produced by hot BODIES and molecules on account of VIBRATIONS in atoms and molecules. Their wavelength RANGES from 1 mm to 700 nm. | |
| 40535. |
The tungsten filament of an electric lamp has a length l = 0.25m and diameter d = 0.04 mm. The power rating is P = 100 W. Assuming the radiation from the filament to be eta=80% of that of a black body radiator at the same temperature, estimate the temperature of the filament. Stefan constant = 5.7 xx 10^(-8)W//m^(2)K^(4). |
|
Answer» |
|
| 40536. |
Electric field lines provide information about |
|
Answer» FIELD strength |
|
| 40537. |
A nuclear explosion is designed to deliver MW of heat energy. The explosion is designed with a nuclear fuel ""^(235)U to run the reactor to ...This power level if 200 MeV of energy is released for each fission event, then |
|
Answer» Energy per fission is joule is `3.2xx10^(-11)` |
|
| 40538. |
During the Doppler principle, as apparent frequency increases louder is heard because |
|
Answer» the LOUDNESS is proportional to the FREQUENCY of SOUND |
|
| 40539. |
What forces the children to live a life of exploitation? |
|
Answer» Greed |
|
| 40540. |
If P represents radiation pressure, C represent speed of light and Q represents radiation energy striking a unit area per second, then the non-zero integers, x,y and z such that P^(x)Q^(y)C^(z) is dimensionless are : |
|
Answer» `x=1,y=1,z=1` `c=[LT^(-1)]` and `Q=("ENERGY")/("area" xx "time")=(ML^(2)T^(-2))/(L^(2)T)=[ML^(0)T^(-3)]` Now `P^(x)Q^(y)C^(z)=[M^(x)L^(-x)T^(-2x)][M^(y)T^(-3y)][L^(z)T^(-z)]` `P^(x)Q^(y)C^(z)=M^(x+y)L^(-x+z)T^(-2x-3y-z)` `P^(x)Q^(y)C^(z)` to be DIMENSIONLESS. `x+y=0,-x+z=0,-2x-3y-z=0` Also it is given that `x,y,z` are to be non-zero `i.e` least value of `x` should be. `1`. Thus if `x=1,` then `y=-1` and `z=1` will satisfy the above equations. Therefore, we get `x=`,`y=-1` and `z=1`. Hence correct choice is `(d)`. |
|
| 40541. |
To demonstrate the phenomenon of interference, we require two sources which emit radiation ...... |
|
Answer» of NEARLY the same frequency. |
|
| 40542. |
A galvanometer has resistance G and Current I_g produces full scale deflection. S_1 is the value of the shunt which converts it into an ammeter of range 0 - 1 and S_2 is the value of shunt for the range 0 - 21. The ratio of S_1 and S_2 is |
|
Answer» `1/2 ((I-I _g)/ (2I - I_g))` |
|
| 40543. |
The respective number of significant figures for the numbers 23.023, 0.0003 and 2.1xx10^(-3) are : |
|
Answer» `4,4,2` `0.0003` only `1` significant digit. [ zero after decimal is INSIGNIFICANT if there is not NON - zero digit before decimal place ] `2.1xx10^(-3)` only `2` significant digits. Hence correct choice is `(b)`. |
|
| 40544. |
A coil has self inductance L = 0.04 H and resistance R = 12 Omega. When it is connected to 220 V, 50 Hz supply, what will be current flowing through the coil ? |
|
Answer» 12.7 A `|Z|=SQRT(R^2+X_L^2)` `=sqrt((12)^2 + (12.56)^2)` `=sqrt(301.75)=17.37 Omega` `therefore |I|=V/"|Z|"=220/17.37= 12.6655 APPROX` 12.7A |
|
| 40545. |
The correct order in which the ratio of SI unit to CGS unit increases is (a) Power(b) Surface tension (c) Pressure(d) Force |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 40546. |
A glass prism has a refracting angle of 60^@ , if a ray undergoes minimum deviation of 30^@ . What is the refractive index of the prism material? |
|
Answer» `SQRT(4/3)` |
|
| 40547. |
A message signal of frequency is superposed on a carrier wave of frequency omega_(c). to get an amplitude modulated wave (AM). The frequency of the AM wave will be |
|
Answer» `omega_(m)` |
|
| 40548. |
Consider a simple circuit shown in figure stands for a variable resistance R. R can very from R_(0) to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r lt lt R lt lt R_(0)) . (a) Potential drop across AB is nearly constant as R' is varied. (b) Current through R' is nearly a constant as R' is varied. (c) Current I depends sensitively on R'. (d) I ge (V)/(r + R) always. |
|
Answer» Potential drop across AB is nearly constant as R' is varied. In parallel connection of resistors equivalent resistance is smaller than smallest VALUE of resistance. Potential difference is obtained across AB and r. Equivalent resistance of R and R. is always smaller than R. HENCE , I `ge (V)/(r + R)` and as equivalent of parallel connection of R. and R is less than R and nearly EQUAL to R. Hence, variation in R. won.t CHANGE p.d. across AB . |
|
| 40549. |
An object of length 2.5 cm is placed at a distance of 1.5 f from a concave mirror where f is the magnitude of the focal length of the mirror The length of the object is perpendicular to the principle axis. The length of the image is: |
|
Answer» 5 cm, erect `therefore 1/(+2.5)=(-f)/(-f-(-1.5f))implies I=-5cm` (NEGATIVE sign INDICATES that image is inverted.) |
|
| 40550. |
A car with a horn of frequency 620 Hz travels towards a large wall at a speed of 20 ms^(-1)the frequency of echo of sound as heard by the driver is x xx10^2Hz , what is the value of x (velocity ofsound -330m/s |
|
Answer» |
|