Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 4251. |
The magnetic induction due to a short magnetic dipole of moment 0.1 Am^2 at an equatorial point 10 cm away from the centre of dipole is : |
|
Answer» `1 xx 10^(-5) (WB)/(Am)` |
|
| 4252. |
if speed of electron is ground state energy level is 2.2xx10^(6)ms^(-1), then its speed in fourth excited state will be |
|
Answer» `6.8xx10^(6)ms^(-1)` Here,`v_A=2.2xx10^(6)ms^(-1)`,`n_A=1,n_B=4` `therefore v_B=v_Axx(n_A)/(n_B)=2.2xx10^(6)xx(1)/(4)=0.55xx10^(6)` `=5.5xx10^(5)ms^(-1)` |
|
| 4253. |
A 2 kg weight is attached to the lower end of a spring which is hanging vertically producing in it an elongation of 4xx10^(-2)m. Then potential energy of the stretched spring is |
|
Answer» 0.392 J `=(1)/(2) XX 2 xx 9.8 xx 4 xx 10^(-2) = 39.2 xx10^(-2)` `=0.392J.` |
|
| 4254. |
A ray of light travelling in air is incident at grazing angle (incident angle = 90^@) on a large rectangular slab of a transparent medium of thickness t = 1 m. The point of incidence js the origin A (0, 0). The medium has a refractive index of n (y) given n(y)= (9ky^(3/2)+ 1)^(1/2)Where K = ("meter")^((-3)/2), The refractive index of air is 1. Obtain the equation for the trajectory y(x) of the ray of the medium. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :If `theta` be the incident angle, the slope of the curve (TRAJECTORY) at any point, `m=tan(90^@-theta)=cot theta` Since, `(sintheta_(1))/(sintheta_(2)) = n_(2)/n_(1) implies n_(1) sintheta_(1)= n_(2)sintheta_(2)` If the RAY is incident from the air on the medium at an angle `theta_(1)=90^@` then `sintheta_(1)=1` and `n_(1)=1` `implies n_(2)sintheta_(2) =1 implies sintheta_(2)= 1/n` Putting `theta_(2)=theta` we obtain, `implies SIN theta=1/n implies cot theta = sqrt(n^(2)-1)` Since `m= dy/dx = cottheta implies dy/dx = sqrt(n^(2)-1)` Since `n= sqrt(ky^(3//2) +1)` we obtain `dy/dx = sqrt(ky^(3//2))` `4y^(1//4) = k^(1//2)x` 
|
|
| 4255. |
Calculate the rms and the average value of the voltage wave shown Fig. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4256. |
4 g of a radioactive substance is kept in a store for 15 years. Its half life is 10 years. How much material is decayed? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4257. |
A parallel beam of light of wave length 6xx10^(-7)m falls normally on a straight slit of width 0.2 mm. Find the totalk angular width of the central diffraction maximum and also its linear width as observed on a screen placed 2 m away. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4258. |
In equtaion y= 5 sin(0.05t + 0.05) y represents the displacement at the instant t .Then which one of the following gives the frequency ? |
|
Answer» 5 |
|
| 4260. |
Construct a truth table for the following logic circuit |
Answer» SOLUTION :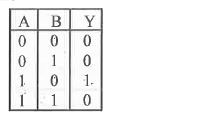
|
|
| 4261. |
An object lying inside a pond is viewed by a man from above (air) along horizontal plane. Now if the man moves away from the object keeping his along the same horizontal plane, how will the apparent depth of the object change? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4262. |
Give relation between focal length and radius of curvature for spherical mirror. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let C be the centre of curvature of the mirror. Consider a ray parallel to the principal axis striking the mirror at M. Then CM will be PERPENDICULAR to the mirror at M. Let `theta` be the angle of incidence and MD be the perpendicular from M on the principal axis. Then `angleMCP = theta" and "angleMFP = 2theta` Because, `DeltaMCP` is an obtuse angle for `angleMCP" and "angleMCF" and "angleCMF` are its internal angles. `DeltaMDC" and "DeltaMDF` are equiangular. [D `~~` P] `therefore tan theta=(MD)/(CD)" and "tan2theta=2theta` For small `theta`,which is true for paraxial rays, `tan theta ~~ theta" and "tan 2theta ~~ 2theta` `therefore theta=(MD)/(CD)" and "2 theta=(MD)/(FD)` ... (1) Now, for small 8, the point D is very close to the point P. Therefore, CD = CP = R and FD = FP = f From equation (1), `2theta=(MD)/(FD)` `therefore 2 theta=(MD)/(f)`... (2) and `theta=(MD)/(CD)` `therefore theta=(MD)/(R)`... (3) `therefore` From equation (2) and (3), `2xx(MD)/(R)=(MD)/(f)` `therefore 2f=R` `therefore` R=2f or f=`R/2` This relation is true for both CONCAVE and convex mirrors. |
|
| 4263. |
The velocity - time graph for two bodies A and B are in the ratio |
|
Answer» tan 25 to tan50 `:. (a_(A))/(a_(B))=(tan25^(@))/(tan50^(@))` |
|
| 4264. |
A stone is dropped from the top of a tower of height h. After 1 second, another stone is dropped from the balcony 20m below the top . Both reach the button simultaneously . Whatis the value of h ? |
|
Answer» 3125m. |
|
| 4265. |
A force between two protons is same as the force between proton and neutron. The nature of the force is |
|
Answer» WEAK NUCLEAR FORCE |
|
| 4266. |
The relative rates of effusion of O_(2) to CH_(4) througha containe containing O_(2) and CH_(4) in 3 : 2 mass ratio will be- |
|
Answer» `(3sqrt(2))/(4)` `(r_(O_(2)))/(r_(Ch_(4)))= ((3)/(32sqrt(32)))/((2)/(16sqrt(16)))=3/(4sqrt(2))` |
|
| 4267. |
Why are alkali metals most salted for photosensitive metals ? |
| Answer» Solution :Alkali metals have LOW WORK function. Even visible radiation can eject out ELECTRONS from them. So, alkali metals are most suitable PHOTOSENSITIVE materials. | |
| 4268. |
A conducting sphere of radius R= 20cm is given a charge Q= 16 mu C what is bar(E ) at centre. |
|
Answer» `36 XX 10^(6)N//C` |
|
| 4269. |
A current of 0.1 A circulates around a coil of 100 turns and having a radius equal to 5cm. The magnetic field set up at the centre of the coil is (mu=4pixx10^(-5) "weber"//"amp-metre") |
|
Answer» `2XX10^(-5)` TESLA |
|
| 4270. |
A stretched wire of length 114 cm is divided into three segments whose frequencies are in the ratio 1 : 3 : 4, the length of the segments must be in the ratio : |
|
Answer» `18 : 24 : 72` |
|
| 4271. |
Thermodynamic temperture is measured in |
|
Answer» Celsius |
|
| 4272. |
North Pole of a bar magnet is moved towards a metal ring. What is the direction of induced current in the ring when viewed from magnet side ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ANTICLOCKWISE. | |
| 4273. |
A side wall of a wide open tank is provided with a narrowing tube (figure) through which water flows out. The cross-sectional area of the tube decreases from S=3.0cm^2 to s=1.0cm^2. The water level in the tank is h=4.6m higher than that in the tube. Neglecting the viscosity of the water, find the horizontal component of the force tending to pull the tube out of the tank. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Suppose the radius at A is R and it decreases uniformly to r at B where `S=piR^2` and `s=piR^2`. Assume also that the semi vectical angle at 0 is `alpha`. Then `(R)/(L_2)=(r)/(L_1)=y/x` So `y=r+(R-r)/(L_2-L_1)(x-L_1)` where y is the radius at the point P distant x from the vertex O. Suppose the velocity with which the liquid flows out is `V` at A, v at B and u at P. Then by the equation of continuity `piR^2V=pir^2v=piy^2u` The velocity v of efflux is given by `v=sqrt(2gh)` and BERNOULLI's theorem gives `p_p+1/2rhou^2=p_0+1/2rhov^2` where `p_p` is the pressure at P and `p_0` is the atmospheric pressure which is the pressure just outside of B. The force on the nozzle tending to pull it out is then `F=int(p_(rho)-p_0)sintheta2piyds` We have subtracted `p_0` which is the force due to atmospheric pressure the factor `sintheta` gives horizontal component of the force and `ds` is the length of the element of nozzle SURFACE, `ds=dxsectheta` and `tantheta=(R-r)/(L_2-L_1)` Then `F=underset(L_1)overset(L_2)int 1/2(v^2-u^2)rho2piy(R-r)/(L_2-L_1)dx` `=pirhounderset(r)overset(R)intv^2(1-(r^4)/(y^4))ydy` `=pirhov^2 1/2(R^2-r^2+(r^4)/(R^2)-r^2)=rhogh((pi(R^2-r^2)^2)/(R^2))` `=rhogh(S-s)^2//S=6*02N` on putting the values. Note: If we try to calculate F from the momentum change of the liquid flowing out will be wrong even as REGARDS the sign of the force. There is of course the effect of pressure at S and s but quantitative derivation of F from Newton's law is DIFFICULT. 
|
|
| 4274. |
A function y=f(x) satisfiesf"(x)=-(1)/(x^(2))-pisin(pix),f(2)=pi+(1)/(2)andf(1)=0. then |
|
Answer» `F((1)/(2))=1-ln2` |
|
| 4275. |
Calculate the magnetic induction produced by a short magnetic dipole having a moment 2 Am^2 at a distance of 0 cm from either pole : |
|
Answer» `1.6 XX 10^(-6) Wb/m^2` |
|
| 4276. |
The electric potential (V) in volts varies with x (in metre) according to the relation V = 5 + 4x^(2). The force experienced by a negative charge of 2 mu C located at x = 0.5 m is |
|
Answer» ` 2XX 10^(-6) N` |
|
| 4277. |
Two charge 3 xx 10^(-8)C and -2 xx 10^(-8)C are located 15 cm apart. At what point on the line joining the two charges the electric potential zero? Take the potential at infinity to be zero. |
Answer» Solution :Let P be the required point on the x-axis where the potential is zero. We have 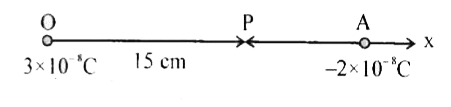 `1/(4PI epsi_(0)) [(3 xx 10^(-8))/(x xx 10^(-2)) -(2 xx 10^(-8))/((15-x) xx 10^(-2))]=0` where x is in cm. That is `3/x-(2)/(15-x)=0" which gives x=9cm"` If x lies on the extended line OA, the required condition is `3/x -(2)/(x-15)=0` which gives x=45 cm. The electric potential is zero at 9cm and 45 cm AWAY from the positive charge on the side of the negative charge. |
|
| 4278. |
A planet is moving in an elliptical path around the sun as shown in figure. Speed of planet in positions P and Q are V_(1) and V_(2) respectively with SP=r_(1) and SQ=r_(2) , then v_(1)//v_(2) is equal to |
|
Answer» `(r_(1))/(r_(2))` |
|
| 4279. |
In an electron microscope, the electrons are accelerated by a voltage of 14kV. If the voltage is changed to 224 kV, then the de Broglie wavelength associated with the electrons would |
|
Answer» INCREASE by 2 times de-Broglie wavelength of ELECTRON, `lambda=(12.3)/SQRT(14000) Å=0.104 Å` At voltage, V=224kV `lambda.=(12.3)/sqrt(224000) Å=0.026Å` `lambda/(lambda.)=(0.104)/(0.0260)=4 RARR 4lambda. rArr lambda.=lambda/4` |
|
| 4280. |
In Bohr model of hydrogen atom Which of the following is quantised? |
|
Answer» LINEAR MOMENTUM of the electron |
|
| 4281. |
Which of the following is the weakest kind of the bonding in solids? |
|
Answer» Ionic |
|
| 4282. |
A body moves along a circular path of radius 1m & mu = 0.4. The maximum angular velocity in rad/sec of the body so that it does not slide is (g = 10ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 4283. |
When a charged particle moves in a transverse magnetic field, its path is |
|
Answer» parabolic |
|
| 4284. |
Two point charges q_(A)= 5mu C and q_(B)= -5muC are located at A and B separated by 0.2m vacuum. What is the electric field at the midpoint O of the line joining the charges? If a negative test charges of magnitude 2mC is placed at O, what is the force experienced by the test charge? |
|
Answer» Solution :`q_(A)= 5 xx 10^(-6)C, q_(B)= -5 xx 10^(6)C, AB= 0.2m, r= OA = OB= 0.1m` ELECTRIC field at O due to charge at A `E= (1)/(4pi in_(0)) ((q_(A))/(r^(2)))` `E_(A)= 9 xx 10^(9) [(5 xx 10^(-6))/(10^(-2))]= 45 xx 10^(5) NC^(-1)` Electric field at O due to charge at B `E = (1)/(4pi in_(0)) ((q_(B))/(r^(2)))` `E_(B)= 9 xx 10^(9) [(5 xx 10^(-6))/(10^(-2))] = 45 xx 10^(5)NC^(-1)` Resultant electric field `E= E_(A) + E_(B)= 9 xx 10^(6)NC^(-1)` `F=Q E=2 xx 10^(-9) C xx 90 xx 10^(5) NC^(-1)` `F= 18 xx 10^(-3)N` |
|
| 4285. |
The focal length of a convex mirror is obtained by using a convex lens The following observations are recorded during theexperiment . {:("objectopsition",,=5cm),("lens",,=35.4cm),("Image",,=93.8cm),("Mirror",,=63.3cm),("Bencherror",,=-0.1cm):} then the focal length of mirror will be . |
|
Answer» `7.5` |
|
| 4286. |
In a T.G. experiment , for two different values of current , the deflections are 45^(@) " and " 30^(@)respectively , then the ratio of the current is |
|
Answer» Solution :`I_1=tan theta_1` `I_2=tan theta_2` `I_1/I_2=(tan 45^@)/(tan 30^@) =1/(1/sqrt3)=sqrt3/1` |
|
| 4287. |
A ring of mass m and radius a is connected to an inextensible string which passes over a frictionless pulley. The other end of string is connected to upper end of a massless spring of spring constant k. The lower end of the spring is fixed. The ring can rotate in the vertical plane about hinge without any friction. If horizontal position of ring is equilibrium position then find time period of small in oscillations of the ring. |
|
Answer» Solution :When displacement of the ring is `theta`, then extension in spring `= (2a theta + x_(0))` Energy of system `E = (1)/(2) k (2a theta + x_(0))^(2) - MG a theta + (1)/(2)l ((d theta)/(dt))^(2)` `E = (1)/(2) k (2a theta + x_(0))^(2) - mg a theta + (1)/(2) ((1)/(2) ma^(2) + ma^(2)) ((d theta)/(dt))^(2)` `RARR (dE)/(dt) = k (2a theta + x_(0)) 2a (d theta)/(dt) - mg a (d theta)/(dt) + (3)/(2) ma^(2) ((d theta)/(dt)) (d^(2) theta)/(dt^(2))` As `(dE)/(dt) = 0, k (2 a theta + x_(0)) 2a - mg a = - (3)/(2) ma^(2) (d^(2) theta)/(dt^(2))` `4ak theta + 2a k x_(0) - mg a = - (3)/(2) ma^(2) (d^(2) theta)/(dt^(2))` `:. (8)/(3) (k)/(m) theta = - (d^(2) theta)/(dt^(2))` `:. omega = sqrt((8K)/(3m))` `:. T = 2PI sqrt((3m)/(8k))` 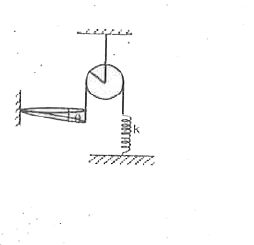
|
|
| 4288. |
(a) Differentiate between three segments of a transistor on the basis of their size and level of dopping. (b) How is a transistor biased to be in active state? (c) With the help of necessary circuit diagram, describe briefly how n-p-n trnasistor in Ce configuration amplifies a small sinusoidal input voltage. Write the expression for the ac current gain. |
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) Emitter (E) : It is the left hand side thick layer of the transistor, which is heavily doped. 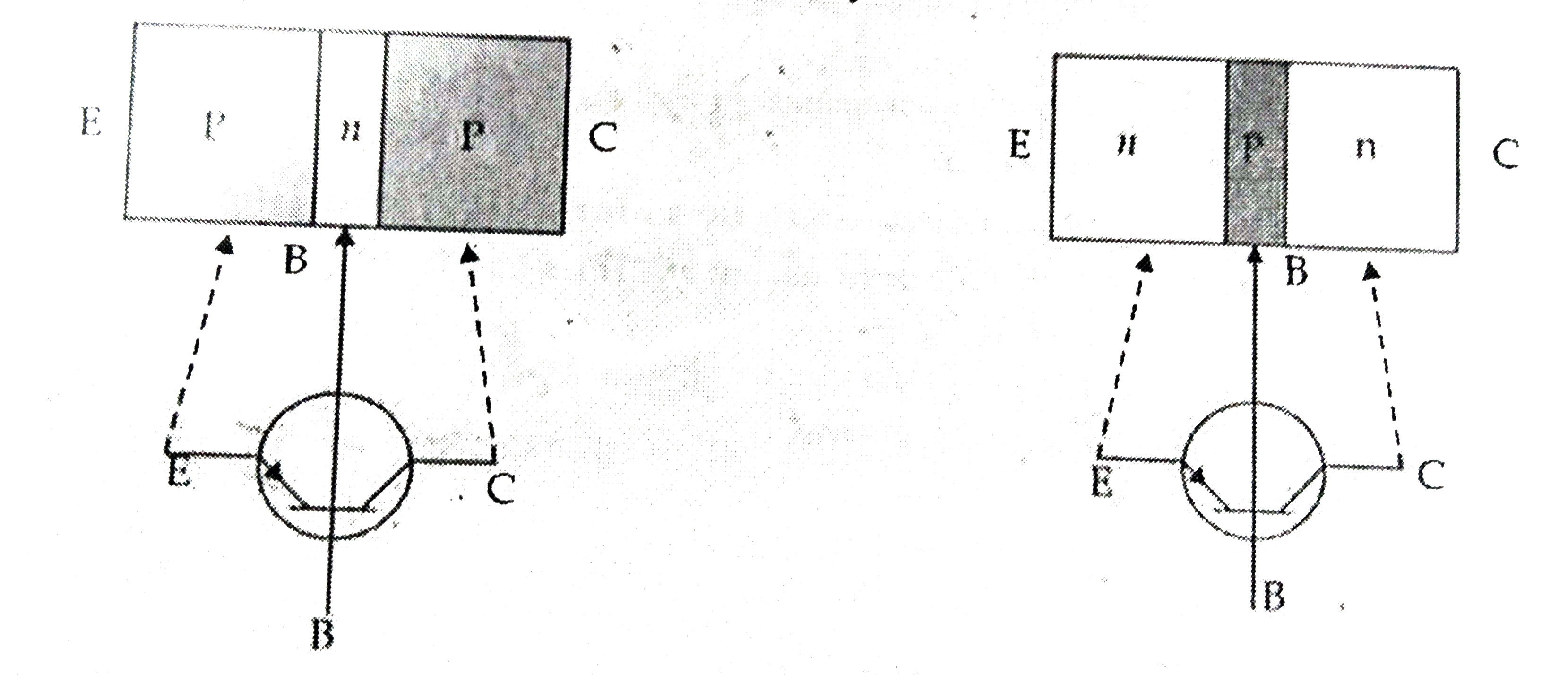 BASE (B) : It is the central thin layer of the transistor, which is lightly doped. Collector (C) - It is the RIGHT hand side thick layer of the transistor, which is moderately dope. (b) There are two conditions for a transistor to be into an active region. 1. The input circuit should be forwed biased by using a low voltage battery. 2. The OUTPUT circuit should be reverse biased by using a high voltage battery. (c) C.E. configuration (Transistor as an Amplifier). The current diagram of a common emitter amplifier using n-p-n transistor is shown in Figure. 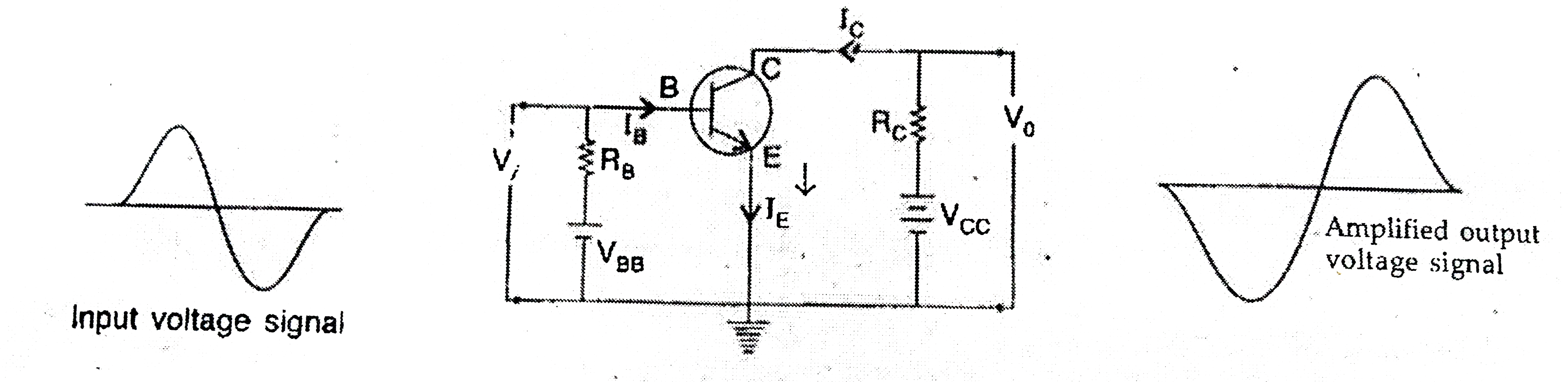 The input (base-emitter) circuit is forwed biased and the output (collector-emiiter) circuit is reverse blased. When no a.c. signal is applied, the potential difference `V_("CC")` between the collector and emitter is given by `V_("CC")=V_(CB)+I_(C)R_(C)`. When an a.c. signal is fed to the input circuit, the forward bias increases during the positive half cycle of the input. This results in increases in `I_(C)` and decrease in `V_("CC")`. Thus, during positive half cycle of the input, the collector becomes less positive. During the negative half cycle of the input, the forward bias is decreased resulting in decrease in `I_(E)` and hence `I_(C)`. Thus `V_("CC")` would increase making the collector more positive. Hence in a common-emitter amplifier, the output voltage is `180^(@)` out of phase with the input voltage. (i) Input signal voltage `V_(i)=I_(B)R_(B)`. (ii) Output signal voltage `V_(0)=I_(C)R_(C)`. (iii) Voltage gain `(A_(V))` of the amplifier is `A_(V)=(V_(0))/(V_(i))=(I_(C)R_(C))/(I_(V)R_(B))=beta((R_(C))/(R_(B)))...[becausebeta=(I_(C))/(I_(B))]` |
|
| 4289. |
Two metal strip , eahc of lenght l , are clamped parallel to each other on a horizontal floor with a seperation b between them. A wire of mass m ies on them perpendicular as shown i figure. A vertically upward magnetic field of strenght B exists in the space. The metal strips are smooth but the coefficient of frication between wire and the floor is mu . A current i is established when the switch S is closed at the instant t=0.Discuss the motion of the wire after the switch is closed. How far away from the strips will the wire reach ? |
|
Answer» Solution :When current starts flowing in the wire, it experiences a force, F =Bibof CONSTANT MAGNITUDE due to which it accelerates on the metal strips. There after when wire falls on the floor, it retards due to friction and finallystops. Thus `a = (F)/(m) = (Bib)/(m)` The velocity gained by the wire on the strips `v^2 = 0 + 2al = 2 (Bib l)/(m)` Let x be the distance MOVED by the wire on the floor. Its final velocity becomes zero, and so `= v^2 -2a.x or x = (v^2)/(2a.)` Here ` a. = (mu mg)/(m) = mu g` `thereforex = ([(2Bib l)/(m)])/(2mug) = (Bib l)/(mu mg)` Note : TRY usiing work - energy theorem |
|
| 4290. |
In series LCR circuit, at resonance. a) The circuit behaves as a pure resistor. b) Potential difference across inductor and capacitor are equal and opposite. c) Current in the circuit is maximum. |
|
Answer» Only a, B are CORRECT |
|
| 4291. |
Electrons can revolve in _____ orbits in Bohr's atom model. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :STATIONARY | |
| 4292. |
An alpha -particle having energy 10MeV collides with a nucleus of atomic number 50. Then distance of closest approach will be |
|
Answer» `14.4 XX 10^(-16)m` |
|
| 4293. |
When a light of frequency9xx 10^(14) Hz is incident on a metal surface, photoelectrons are emitted with a maximum speed of 8 xx 10^(5) ms^(-1) . Determine the threshold frequency of the surface. |
|
Answer» Solution :According to Einstein.s photoelectrc equation `(1)/(2) mv_(max)^(2) = h(upsilon - upsilon_(0))` `upsilon_(0) = upsilon - (mv_(max)^(2))/(2h)` `= 9 xx 10^(14) - ((9.11 xx 10^(-31) xx (8 xx 10^(5))^(2))/(2. xx 6.6 xx 10^(-34)))` `= 9 xx 10^(14) - ((583.04 xx 10^(-21))/(13.2 xx 10^(-34))) = 9 xx 10^(14) - 44.169 xx 10^(13)` `= 9xx 10^(14) - 4.4 xx 10^(14)` `upsilon_(0) = 4.6 xx 10^(14)` Hz |
|
| 4294. |
The phase difference between two waves, represented by y_(1) = 10^(-6) sin [100t +(x//50) + 0.5] m y_(2) = 10^(-6) cos[100t +(x//50)]m where x is expressed in metres and t is expressed in seconds, is approximately. |
|
Answer» 1.07 radians and `y_(2) = 10^(-6) COS [100t + (x//50)]` `=10^(-6)sin[100t + (x//50) + 1.57]` [ USING `cos x = sin(x + pi//2)]` The PHASE difference `=1.57 -0.5 = 1.07` radius. [Also using `sinx = cos(pi//2 -x)`, we can get the same result] |
|
| 4295. |
Particle of masses m, 2m,3m,…,nm grams are placed on the same line at distance l,2l,3l,…..,nl cm from a fixed point. The distance of centre of mass of the particles from the fixed point in centimeters is : |
|
Answer» `((2n+1)L)/(4)` |
|
| 4296. |
A person with vibrating tuning fork of frequency 338 Hz is moving towards a vertical wall with speed of 2 ms^(-1)Velocity of sound in air is 340 ms^(-1)The number of beats heard per second is |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 4297. |
Intensity of electromagnetic wave is 0.02 "wattmeter"^(-2) and its velocity in space is 3xx10^(8)ms^(-1) then energy density of radiation is ….. Jm^(-2) |
|
Answer» `6.67xx10^(11)` |
|
| 4298. |
A ball of mass m is fired vertically upwards from the surface of the earth with velocity nv_e, where v_e is the escape velocity and n < 1. Neglecting air resistance, to what height will the ball rise ? (Take radius of the earth as R) :- |
|
Answer» `R//n^2` `=(GMmh)/(R(R+h))` `THEREFORE 1/2 mv^2 =(mghR)/(R+h)` Since , `v=nv_e` and `v_e=sqrt(2gR)` , HENCE `h=(Rn^2)/((1-n^2))` |
|
| 4299. |
Relation between the magnetic field vectorvec(B) and magnetic intensityvec(H) at a point in a magnetic field vec(B)=muvec(H) wheremuis the mangnetic permeability of the medium in which the point is situated . Magnetic permeability of vacuum mu_(0)=4pixx10^(-7)H.m^(-1) . Thus the relative magnetic permeability of the mediummu_(r)-(mu)/(mu_(0)) . To define the magnetic field at a point in a medium another vector needs mention , which is magnetisationvec(M). The magnetic field is known as the magnetisation of the point . In most cases vec(M)propvec(H) "or,"vec(M)=kvec(H),this k is called the magnetic susceptibility of the medium . The relation among these vectors is expressed as vec(B)=mu_(0)(vec(H)+vec(M)). Magnetisation at a point in the medium is0.002A.m^(-1). The intensity at the point is (inA.m^(-1) ) |
|
Answer» `2.52xx10^(-9)` |
|
| 4300. |
What is ground wave communication? On what factors does the maximum range of propagation in this mode depend? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The amplitude modulated radiowaves having frequency 1500 KHz upto 40 MHZ (or wavelength between 7. 5 m to 200 m) which are travelling directly FOLLOWING the surface of earth are known as ground waves. The short wave COMMUNICATION over long distance is only possible via sky waves. It is not possible via ground waves because the ground waves can bend round the corner of the objects on earth and hence, their intensity falls with distance. Moreover, the ground waves transmission becomes weaker as frequency increases. | |