Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 5001. |
A glass slab of thickness 4 cm contains the same number of wavs as 5 cm of water when both are traversed by the same monochromatic light. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, then that of glass is |
|
Answer» 43954 |
|
| 5002. |
For which one of the following input combinations , the given logic circuit gives the output Y = 1 ? |
|
Answer» a) A = 0 , B = 0 , C = 0 b) A = 0 , B = 1 , C = 1 |
|
| 5003. |
A planar structure of length L and width W is made of two different optical media of refractive indices n_(1)=1.5 and n_(2)=1.44 as shown in figure. If L gt gt W. a ray entering from end AB will emerge from end CD only if the total internal reflection condition is met inside the structure. For L=9.6m, if the incident angle theta is varried, the maximum time taken by ray to exit the plane CD is t x 10^(-9) S, where t is ___ [Speed of light c=3xx 10^(8) m/s] |
|
Answer» |
|
| 5004. |
A 120V, 60 HzA.C. is connected across a non - inductive resistace of 400 Omega an un-known capacitor joined in series. The voltage across resistance is 66.3 V. The voltage drop across capacitor is |
|
Answer» 120 V `therefore V_(C )=100` VOLT |
|
| 5005. |
An insect of negligible mass is sitting on a block of mass M, tied with a spring of force constant k. the block performs simple harmonic motion with amplitude A in front of a plane mirror placed as shown in the figure the maximum speed of insect relative to its image will be |
|
Answer» `Asqrt((k)/(m))` |
|
| 5006. |
A coil having n turns and resistance ROmegais connected with a galvanometer of resistance 4 ROmega . This combination is moved in time t seconds from a magnetic field W_1 Weber to W^2 Weber. The induced current in the circuit is ____ |
|
Answer» `(W_2-W_1)/(5Rnt)` `therefore I=-(n(W_2-W_1))/((R+4R).t) [ because phi=W]` `therefore I=-(n(W_2-W_1))/((R+4R).t)[ because N=n]` `therefore I=-(n(W_2-W_1))/(5Rt) [ because Delta t=t]` |
|
| 5007. |
Electric lines of force always leave an equipotential surface |
|
Answer» at any ANGLE to the surface |
|
| 5008. |
(A): If there exists coulomb attraction between two bodies, both of them may not be charged. (R ): In coulomb attraction two bodies are oppositely charged |
|
Answer» Both .A. and .R. are TRUE and .R. is the CORRECT explanation of .A. |
|
| 5009. |
A certain prism is found to produce a minimum deviation of 38^(@). It produces a deviation of 44^(@) when the angle of incidence is either 42^(@) or 62^(@). What is the angle of incidence when it is undergoing minimum deviation? |
|
Answer» `49^(@)` |
|
| 5010. |
If the 3v battery is replaced by an AC source with the key closed, what will be observation? Justify your answer |
| Answer» Solution :When AC is CONNECTED the BRIGHTNESS of BULB will be decreased. This is due to the BACK emf in the circuit. | |
| 5011. |
Velocity of light wave in air is : |
|
Answer» far GREATER than that in vacuum |
|
| 5012. |
Potential energy of a magnetic dipole of dipole strength vecm placed in a uniform magnetic field vecB is given as _______ |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`U =-VECM . VECB` | |
| 5013. |
Deuteron and alpha - particle are put 1A^@ apart in Air. Magnitude of intensity of electric field due to deuteron at alpha - particle is (N/ C) |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 5014. |
The total power content of an AM signal is 3000 w. For 100% modulation, the power of CW and that of each side band are, |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 5015. |
Name the em. Waves which are used for the treatment of certain forms of cancer. Write their frequecny range. |
| Answer» Solution :OZONE LAYER absorbs ultraviolet RADIATION from thr sun and prevent it from REACHING the earth and casusing damage to life. | |
| 5016. |
In a young 's double slit experiment, 12 fringes are observed to be formed in a certain segment of the screen, when light of wavelenght 600 nm is used. If the wavelenght of light is changed to 400 nm. Number of fringes observed in the same segment of the screen is given by |
|
Answer» 12 |
|
| 5017. |
Three condensers of same capacity connected in series has effective capacity 2mF. If they are connected in parallel and charged using a battery of emf 12V, the total energy stored in the combination is |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 5018. |
Draw a schematic arrangement of Geiger-Marsden experiment showing the scattering of C-particles by a thin foil of gold. Why is it that most of the O-particles go right through the foil and only a small fraction gets scattered at large angles ? |
|
Answer» Solution :A schematic arrangement of the Geiger-Marsden EXPERIMENT is shown in Fig. 12.11. In their experiment it was OBSERVED that most of the alpha-particles pass through the gold foil without any appreciable deflection. Some a particles are scattered through different angles and a very small number of particles suffers large angle scattering of about `180^(@)` Large angle scattering can be EXPLAINED if we consider the entire positive CHARGE and almostwhole mass of gold foil atom to be concentrated in a tiny central core of the atom. When an `alpha`-particle with kinetic energy K approaches the gold nucleus DIRECTLY along itscentral line it slows down, as it approaches the a-particles gold nucleus, due to coulombian repulsion force between nucleus and `alpha`-particle. The `alpha` -particle can come up to a certain minimumdistance is calledthe distanceof closed approach . Obviously valueof distanceof closest approach provides the upperlimit onthe size of thenucleus . 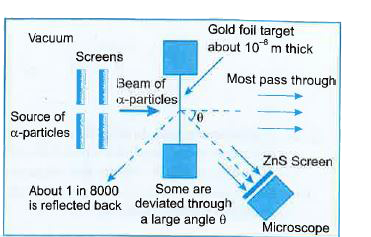
|
|
| 5019. |
Two ideal Carnot engines operate in cascade (all heat given up by one engine is usedby the other engine to produce work) between temperatures, T_(1) and T_(2). The temperature of the hot reservoir of the first engine is T_(1) and the temperature of the cold reservoir of the second engine is T_(2). T is temperature of the sink of first engine which is also the source for the second engine. How is T related to T_(1) and T_(2), if both the engines perform equal amount of work? |
|
Answer» `T=(2T_(1)T_(2))/(T_(1)+T_(2))` |
|
| 5020. |
Two fixed charges 4Q (positive) and Q (negative) are located at A and B. the distance AB being 3 m. |
|
Answer» The point P where the resultant field due to both is zero is on AB. |
|
| 5021. |
One end of a long string of linear mass density 8.0 xx 10^(-3) kgm^(-1) is connected to an electrically driven tuning fork of frequency 256Hz. The other end passes over a pulley and is tiedto a pan containing a mass of 90 kg. The pulley end absorbs all the incoming energy so that reflected waves at thisend have negligible amplitude. At t=0, the leftend ( fork end )of the string x=0 has zero transverse displacement ( y = 0 ) and is moving along positive y-direction. The amplitude of the wave is 5.0 cm.Write down the transverse displacement y as function of x and t that describes the wave on the string. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here , `mu= 8.0 xx 10^(-3) kg//m,v = 256Hz, T = 50 kg= 90 xx 9.8 = 882 N`. Amplitudeof wave, r= 5.01m = 0.05m . As the wave propagation along the string isa transverse travelling wave, the velocity of the wave is given by `v= sqrt((T)/(mu)) = sqrt((882)/( 8.0 xx 10^(-3))) = 3.32 xx 10^(2)m//s ` `omega = 2piv =2 xx(22)/(7) xx 256= 1.61 xx10^(3 ) rad//s` `lambda =(v)/(v) = ( 3.32 xx10^(2))/(256) m`. Propagation constant `k = ( 2pi)/( lambda)` `= ( 2 xx 3.142 xx 256)/( 332 xx 10^(2)) = 4.84m^(-1)` As the wave is propagating along x direction, the equation of the wave is`y ( x,t) = r sin ( omega t - kx) ` `=0.05 sin ( 1.61 xx 10^(3) t- 4.84x)` Here x,yare in mt & t in SEC. |
|
| 5022. |
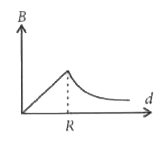
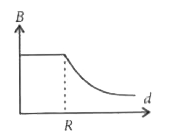
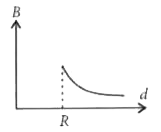
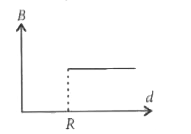
A uniform current is flowing along the length of an infinite, straight, thin, hollow cylinder of radius 'R'. The magnetic field 'B' produced at a perpendicular distance 'd' from the axis of the cylinder is plotted in a graph. Which of the following figure looks like the plot? |
|
Answer»
`:. mu_(0)I= oint vec(B).d vec(l)= oint Bdl = B underset(0)OVERSET(2pi r)INT dl [ :. theta= 0^(@)]` `=B 2pi R` ( `:.`B= constant) `:.` Using Ampere.s law, `B 2pi R= mu_(0)I` `:. B= (mu_(0)I)/(2pi R)` For `d lt R [ :. theta= 0^(@)]` `:. B 2pi r= MU I_("in") or B= (mu I_("in"))/(2pi r) rArr B=0 ( :. I_("in")= 0)` 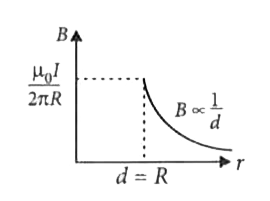
|
|
| 5023. |
On two hollow spheres (shells) charges -q and +q are placed, so the flux on each is phi. Now, both are connected as shown in the figure, so total flux is………… (a) phi/2 (b) 2phi (c) zero(d) Uncertain |
|
Answer» `phi/2` `sumQ = +Q + (-q)` `THEREFORE sumQ =0` Therefore, `phi =(sumQ)/epsilon_(0)` (Gauss.s LAW) `therefore phi =0` |
|
| 5024. |
A,B,C,D,P and Q are points in a uniform electric field. The potentials at these points are V (A) = 2 volt. V (P) = V (B) = V (D) = 5 volt. V (C ) = 8 volt. The electric field at P is |
|
Answer» `10 VM^(-1)` along PQ |
|
| 5025. |
Answer the following questions : (a) The angle subtended at the eye by an object is equal to the angle subtended at the eye by the virtual image produced by a magnifying glass. In what sense then does a magnifying glass provide angular magnification ? (b) In viewing through a magnifying glass, one usually positions one's eyes very close to the lens. Does angular magnification change if the eye is moved back ? (c) Magnifying power of a simple microscope is inversely proportional to the focal length of the lens. What then stops us from using a convex lens of smaller and smaller focal length and achieving greater and greater magnifying power ? (d) Why must both the objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope have short focal lengths ? (e) When viewing through a compound microscope, our eyes should be positioned not on the eyepiece but a short distance away from it for best viewing. Why ? How much should be that short distance between the eye and eyepiece ? |
|
Answer» Solution : (a) Although the actual angle subtended at the eye by the virtual image produced by a magnifying glass is exactly same as the angle subtended by the object, EVEN then we say that the magnifying glass produces angular magnification. It is on account of the fact that if the object is seen directly without using magnifying glass, it must have been put at near point (25 cm) of eye and angle subtended by the object must have been less. However, with magnifying glass, the object is placed at a shorter distance from the eye and subtends a greater angle at the eye. THUS, EFFECTIVELY angular magnification has been achieved. (b) Yes, the angular magnification slightly decreases if the viewer moves his eye away from the magnifying glass. It is due to this reason that we keep our eye very very close to magnifying glass. (c) We cannot produce a convex lens of extremely short wavelength because grinding of such a lens is extremely difficult. Moreover, with decrease in focal length, the lens becomes more and more thick at the middle and it results in increase in spherical and CHROMATIC aberrations. This, puts a upper limit on magnifying power of a simple microscope. (d) The magnifying power of a compound microscope may be expressed as : `m=-L/f_(0) (1+ D/f_(0))`,when the final image is formed at near point of eye. where L is the length of microscope tube. From the relation, it is clear that for higher magnifying power the focal lengths of both the objective and eyepiece should be as small as possible. (E) The image of the objective lens formed by the eyepiece of microscope is called .eye-ring.. All the rays from the object, after being refracted from the objective lens pass through it. The eye would receive all the rays from object, if it is placed at the position of the eye-ring, provided the area of the pupil of the eye is greater than or at least equal to the area of the eye-ring. In case, eye is placed very close to the eyepiece, then it would not be able to collect all the rays from the object. Moreover, the field of view will be reduced. |
|
| 5026. |
Which of the following statement is not true for a photon a photon? |
|
Answer» PHOTON produces pressure |
|
| 5027. |
Two point charages placed at a distance r. in the air experiene a certain force. Then the distance at which they will experience the same force in the medium of dielectric constant K is |
|
Answer» KR |
|
| 5028. |
The magnetic flux in a closed circuit of resistance 20ohm, varies with time (t) according to equation phi =8t^2-6t+5. What is the magnitude of induced current at time t = 1 sec? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`E =(dphi)/DT` = d(8t^2-6t+5)/dt` `THEREFORE e = 16t-6 = 16xx1-6 = 10V` `therefore I = e/R = 10/20 = 0.5V` |
|
| 5029. |
If in an A.C. circuit voltage V and current is then the power dissipated in the circuit is ……. |
|
Answer» VIcosx `=VI cos delta` from this `lt P gt` depends on `delta` |
|
| 5030. |
A fighter plane flying horizontally at an altitude of 1.5 km with speed 720 km/h passes directly overhead an antiaircraft gun. At what angle from the vertical should the gun be fired for the shell with muzzle speed 600 ms to hit the plane? At what minimum altitude should the pilot fly the plane to avoid being hit ? (Take g= 10 ms^(-2)). |
|
Answer» `sin^(-1) (1/3), 16 km ` |
|
| 5031. |
Derive formula for fringe width using Young's double slit method for interference of light. What will happen if the distance between the two slits becomes nearly zero ? |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Fringe Width. It is the distance between any two successive fringes in interference pattern.Let `S_(1), S_(2)` be the two fine slits illuminated by a monochromatic sources of wavelength `lambda`. Intensity of light at any point P on the screen at a distance D from the slit depends upon the path difference between `S_(2)P` and `S_(1)P`. 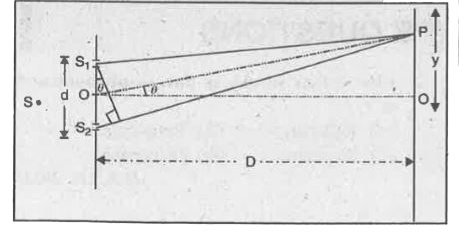 From `S_(1)` draw `S_(1)A` perpendicular to `S_(2)P`. Since `/_S_(2)S_(1)A to theta` [D is very LARGE as compared to d], therefore, `/_S_(1)AS_(2) to 90^(@)` and `AP ~~ S_(1)P`. `:. "Path difference" = S_(2)P-S_(1)P = (S_(2)A + AP) - S_(1)P` or `"Path difference" = S_(2)A = d sin theta` Since `theta` is very small, `sin theta` can be replaced by `tan theta` . `:. "Path difference" = d tan theta = d(y)/(D)` Constructive interference [Bright Fringes). For bright fringes, the path difference should be equal to an even multiple of`lambda // 2`. `:. (DY)/(D)=2n(lambda)/(2)=n lambda` or `y=n(lambda D)/(d)` If n = 0, `y_(0)=0`, which is the POSITION of central maxima. If n = 1, `y_(1)=(D)/(d)lambda`, which is the position of first maxima. If n = 2, `y_(2)=(2D)/(d)lambda`, which is the position of Similarly `y_(n-1)=(n-1)(D)/(d)lambda` and `y_(n)=n(D)/(d)lambda` Fringe width `beta=y_(n)-y(n-1)=(D)/(d)lambda[n-(n-1)]` `beta=(D)/(d)lambda` ...(i) Destructive interference [Dark Fringes]. For dark fringes, the path difference should be an old multiple of `1 // 2`. `(d)/(D)y=(2n-1)(lambda)/(2)` or `y=(D)/(d)(2n-1)(lambda)/(2)` If n = 1, `y_(1)=(D)/(d)(lambda)/(2)`, which is the position of 1st minima. If n = 2, `y_(1)=(D)/(d)(2lambda)/(2)`, which is the position of 2nd minima. If n = 3, `y_(1)=(D)/(d)(3lambda)/(2)`, which is the position of 3rd minima. `:.` Fringe width, `beta=y_(3)-y_(2)=(D)/(d)lambda` or `beta=(D)/(d)lambda` ...(ii) From (i) and (ii), we CONCLUDE that bright and dark fringes have equal fringe width. `beta prop D` `prop lambda` `prop (1)/(d)` If d = 0, `beta= infty` i.e. dark and bright bands will be infinitely well spaced and there will be uniform illumination. |
|
| 5032. |
only the central fringe will be white, all other will look colourful. - Using B = 10 43) In Young's experiment, yellow light of wavelength 5890 Å is used. The angular width of the fringes is 0.2^(@). How much do you need to change the wavelength to increase the angular width by 10% ? |
|
Answer» Increase of `589Å` Widht of frings `2(d sin theta)=2(1) lambda` `:. 2 theta=(2lambda)/(d)` [ for SMALL angle `sin theta- theta`] In this forumula if d is CONSTANT than `theta prop lambda` `:. (theta_(2))/(theta_(1))=(lambda_(2))/(lambda_(1))` `theta_(2)=theta_(1)+10% theta_(1)` `=1.1 theta_(1)` `:.(theta_(2))/(theta_(1))=(lambda_(2))/(lambda_(1))` `:. (1. theta_(1))/(theta_(1))=(lambda_(2))/(5890Å)` `:. lambda_(2)=6479Å` `:.` Increase in wavelength `=lambda_(2)-labda_(1)` `=6479-5890` `=589Å` |
|
| 5033. |
Lead-199 has a half-life of 1.5 hours. If a researcher begins with 2 grams of lead-199, how much will remain after 6 hours? |
|
Answer» 0.125 grams |
|
| 5034. |
Match the statement in Column I with the statements in Column II. One or more than one choice from Column II can match with a statement from Column I.{:(,"Column I",,"Column II"),((a),"If the wire is pulled at its ends",(p),"Young's"),(,"by equal and opposite forces of",,"modulus (Y)"),(,"magnitude F so that it undergoes an",,),(,"elongation x, according to Hooke's",,),(,"law, F=-kx, where k is the force",,),(,"constant, Force constant (k) of the",,),(,"wire will depend on",,),((b),"Let us suspend the wire vertically",(q),"elongation (x)"),(,"from a rigid support and attach",,),(,"a mass m at its lower end. If the",,),(,"mass is slightly pulled down and",,),(,"released, it executes SHM of a time",,),(,"period that will depend on",,),((c ),"If the given wire is fixed between",(r ),"length (l)"),(,"two rigid supports and its",,),(,"temperature is decreased, then the",,),(,"thermal stress that develops in the",,),(,"wire will depend on",,),((d),"Work done in stretching the wire",(s),"area of cross-"),(,"to a length l + x will depend on",,"section (a)"):} |
| Answer» Solution :(a) `to` (p), (R ), (s), (B) `to` (p), (r ), (s),(C ) `to` (p), (d) `to` (p), (q), (r ), (s) | |
| 5035. |
Two cell with unequal emfs of 2V and 3V are connected as shown in the figure. If each cell has an internal resistance r = 0.45Omega and external resistance is of 4Omega. Then, Potential drop across resistor 4Omega is |
|
Answer» 5.32V |
|
| 5036. |
In a potentiometer experiment the balancing length with a cell is 560 cm. When an external resistance of 10 Omega is connected in parallel to the cell, the balancing length changes by 60 cm . Find the internal resistance of the cell. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`R= 10 Omega,` BALANCING length `l_1 = 560 CM` Change in balancing length `(l_1 - l_2) = 60 cm` internal resistance= r= ? `l_1 - l_2 = 60 , 56 - l_2 = 60` `therefore l_2 = 500 cm` `r= R((l_1 - l_2)/(l_2)) = 10 xx (60)/(500) = 6/5 = 1.2 Omega` |
|
| 5037. |
Match the statement in Column I with the statements in Column II. One or more than one choice from Column II can match with a statement from Column I.{:(,"Column I",,"Column II"),((a),"Young's modulus",(p),(-Delta V)/(rho V)),((b),"Bulk modulus",(q),(Fl)/(A Delta l)),((c ),"Compressibility",(r ),(-Delta d//d)/(Delta Dl//l)),((d),"Poisson's ratio",(s),"(-rho V)/(Delta V)):} |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(1) `to` (b), (2) `to` (d), (3) `to` (c ) | |
| 5038. |
An alternating current of frequency 200 "rad"//sec" and peack value of 1A as shown in the figure in applied to the primary of a transformer. If the coefficient of mutual induction between the primary and the secondary is 1.5 H, the voltage induced in the secondary will be |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 5039. |
he radioactivity of given sample of whisky due to tritium (Half life=12 yrs) was found to be only 3.125% of that measured in a recently purchased bottle marked "10 years old". By how many years ago the sample must have been prepared? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`m/m_0=1/2^n rArr 3.125/100=1/2^n` `n=5=t/T` t=5T = 5 X 12 = 60 YEARS. `therefore` Total AGE of SAMPLE = 60+10 =70 years |
|
| 5040. |
Using the diagram from the previous example, assurme that m=2 kg, M= 10 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the small block and the tabletop is 0.5. What is the acceleration of the blocks ? |
Answer» SOLUTION :Once again, draw a free-body diagram for each object. Notice that the only difference between these diagrams and the ones in the previous EXAMPLE is the INCLUSION of friction, `F_(f)` that acrs on the block on the table. As before, we have TWO equations that contain two unknowns `(a and F_(T))`. `F_(T)-F_(f)= ma(1)` `Mg- F_(T)=Ma(2)` We add the equations (thereby eliminating `F_(T))` and solve for a. Notice that, by DEFINITION, `F_(f)= mu F_(N)` and from the free body diagram for m, we see that `F_(N)= mg`, so `F_(f)= mu mg` : `Mg-F_(f)= ma+Ma` `Mg- mu mg= a(m+M)` `(M-mu m)/(m+M) g= a` Or, using our shorter method :  Substituting in the numberical values given for m, M, and `mu_(k)`, we find that `a= (3)/(4)g` ( or `7.5 m//s^(2))`. |
|
| 5041. |
An iron bar of length l and cross-section A is heated from 0°C to 100°C. If the rod is so held that it is not permitted to expand or bend, the force developed in it is : |
|
Answer» directly PROPORTIONAL to length Stress = `F/A` and STRAIN= `(Deltal)/l` Now Y =`F/Axxl/(Deltal)=F/Axxl/(alphalDeltaT)` Clearly F does not depend upon length. Hence the correct CHOICE is (C). |
|
| 5042. |
A light planet is revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T, if the gravitational force of attraction between the two varies as R^(-5//2), then T^(2) is proportional to : |
|
Answer» `R^(3)` Now `T=(2PI R)/(v) therefore T^(2)=(4pi^(2)R^(2))/(v^(2))` `T^(2)=(4pi^(2)R^(2)xxR^(3//2))/(GM) rArr T^(2)prop R^(7//2)` Thus correct choice is (b). |
|
| 5043. |
Two carts A and B, are placed on an air track. They are made of same material and look identical. B is given a constant speed and collides elastically with A at rest. After the collision, both carts move in same direction. One concludes that: |
|
Answer» A is hollow |
|
| 5044. |
What is a nuclear fusion reaction ? Why is nuclear fusion difficult to carry out for peaceful purpose ? |
| Answer» Solution : For fusion, temperature REQUIRED is from`10^6 "to" 10^7`K. So, to carry out fusion for PEACEFUL purposes we need some system which can create and bear such a HIGH temperature. | |
| 5045. |
What is real image ? |
| Answer» Solution :It is foormed when the REFLECTED or REACTED rays interset at a POINT. | |
| 5046. |
A point source S is placed at a height h from the bottom of a vessel of height H(lt h) and area A. The vessel is polished at the base. Water is gradually filled in the vessel at a constant rate alpham^3//s. Find how the distance d of image of the source from the bottom of the vessel varies with time t. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`d=mu H -((mu-1) 0 a)/(A)` | |
| 5047. |
How does the rest energy of a nucleus compare to the sum of the rest energies of the individual nucleons when they are apart from the nucleous? |
|
Answer» It is greater than the sum |
|
| 5048. |
Anelectron falls throgh a distance of 1.5 cm in a uniform electric field of magnitude2.0 xx10^(4) N c^(-1)the direction of the fieldis reversed keeping its magnitude unchangedandaproton falls throughthe same distance computethe time of falls in each case contrastthe situation with that of free fall under gravity |
|
Answer» Solution :The field is upward so the negatively charged the magnitude of the electricof the ELECTRON is`a_(e )=eE//m_(e )` where `m_(e )` is the mas of the electron distanceh is given by `t_(e )=sqrt(2h)/(a_(e ))=sqrt(2hm_(e ))/(e E)` For e=`1.6 xx10^(-19) C, m_(e )=9.11 xx10^(-31)` kg `t_(e )=2.9n xx10^(-9)` S where `m_(p)` is the mass of the proton `m_(p)=1.67 xx10^(-27)` kg the time of fall for the proton is `t_(p)=sqrt(2h)/(a_(p))=sqrt(2hm_(p))/(eE)=1.3 xx10^(-7)` S `a_(p)=(eE)/(m_(p))` `=1.9xx10^(12) ms^(-2)` which is enormous compared to the value of g (9.8 `ms^(-2)`)the acceleration DUE to GRAVITY thethus the effect of acceleration due to gravity can be ignored in this example |
|
| 5049. |
(a) Define mutual inductance and write its SI units. (b) Derive an expression for the mutual inductance of two long co-axial solenoids of same length wound one over the other. (c) In an experiment, two coils C_(1) and C_(2) are placed close to each other. Find out the expression for the emf induced in the coil C_(1) due to a change in the current through the coil C_(2). |
|
Answer» Solution :For part (a) and part (b), see Short Answer Question Number 50. (c) Let CURRENT in coil `C_(2)` be changing at a rate `(dI_(2))/dt`. As a result of it magnetic flux linked with coil `C_(2)` and CONSEQUENTLY the coil `C_(1)` CHANGES. If the coils are placed close to each other then magnetic flux PER turn of both coils will be same and hence INDUCED emf `varepsilon_(1)` in coil `C_(1)` will be given as: `varepsilon_(1) = -M (dI_(2))/dt`, where M = Mutual inductance of the given pair of coils. The -ve sign indicates the direction of induced emf. |
|
| 5050. |
A radio can tune over the frequency range of a portion of MW broadcast band : (800 kHz to 1200 kHz). If its LCcircuit has an effective inductance of 200 mu H, what must be the range of its variable capacitor ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`V=(1)/(2pi) sqrt((1)/(LC)), i.e., C=(1)/(4pi^(2)v^(2)L)` For `L=200muH, v=1200kHz, C=87.9pF`. For `L=200muH, v=800kHz, C=197.8pF`. The variable capacitor should have a RANGE of about 88 pF to 198 pF. |
|