Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 4901. |
Explain Rutherford's argument for scattered alpha-particles. |
|
Answer» Solution :Rutherford argued that since large number of Cl-particles are scattered at very SMALL angles, atoms must be LARGELY hollow. If a large part of the mass of atom is tightly concentrated at its centre and it has a positive charge, then Coulomb repulsive FORCE may act between this positive charge and positive charges of d-particles. If so, then the incoming a particle could get very close to the positive charge without penetrating it and it will deflected. This argument supported the hypothesis of the nuclear atom. This is why Rutherford is credited with the discovery of the NUCLEUS. He argued that the electron is a short distance from the nucleus. As the planets orbit the Sun, the electrons will orbit around the nucleus in a fixed orbit. Rutherford.s experiments suggested the size of the nucleus to be about `10^(-15)` m to `10^(-14) `m. From kinetic theory, the size of an atom was KNOWN to be `10^(-10)` m about 10,000 to 1,00,000 times larger than the size of the nucleus. |
|
| 4902. |
A.C. adaptor converts household ac into low voltage dc. A stepdown transformer is a essential part of ac adapterWhat is the use of step down transformer? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :To DECREASE VOLTAGE | |
| 4903. |
The expression 1/lamda=R(1/p^2-1/n^2) after the Balmer's work is known as R=((me^4)/(8h^3c(epsilon_0)^2)) |
|
Answer» BALMER's formula |
|
| 4904. |
The force required to row a boat at constant velocity is proportional to square of its speed. If a speed of v km/h requires 4 kW, how much power does a speed of 2v km/h require? |
|
Answer» 8 kW |
|
| 4905. |
In a biprism experiment, the distance between the slit and eye-piece is 1 m. If the convex lens is interposed at a distance of 30 cm from the slit then the size of the magnified image is 0.7 mm. The distance between the two virtual images of the slits will be: |
|
Answer» 0.1 mm |
|
| 4906. |
Explain dispersive and non-dispersive medium. |
|
Answer» Solution :The variation of refractive index with wavelength MAY be more pronounced in some media than the other. In vacuum of course, the speed of light is independent of wavelength. Thus, vacuum (or air approximately) is a non dispersive medium in which all colours travel with the same speed. This also follows from the fact that sunlight reaches US in the FORM of WHITE light and not as its components. On the other hand, GLASS is a dispersive medium. |
|
| 4907. |
A body cools from 60^(@)C to 50^(@)C in 10 minutes, when kept in air at 30^(@)C. In the next 10 minutes, its temperature will be : |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 4908. |
What are Optoelectronic devices? |
| Answer» Solution :OPTOELECTRONICS deals with devices which CONVERT electrical ENERGY into LIGHT and light into electrical energy through SEMICONDUCTORS. | |
| 4909. |
An electron is not deflected, while moving through a certain region of space. Can we say that there is no magnetic field in the region? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No. The ELECTRON may be MOVING PARALLEL to the direction of MAGNETIC field. | |
| 4910. |
A solid sphere is rolling down on inclined plane from rest and a rectangular block of same mass is also slipping down simultaneously from rest on the same plane. Then- |
|
Answer» both of them will REACH the bottom simultaneously |
|
| 4911. |
An alpha particle of velocity 1.6xx10^(7) ms^(-1) approaches a gold nucleus (Z=79). Calculate the distance of the closestapproach. Mass of an alpha particle is 6.6xx10^(-27) kg. What is the significance of this closest approach? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4912. |
Which of the following statements is correct in the given figure? Infinitely long wire at E kept perpendicular to paper carrying current inwards: |
|
Answer» Net force on LOOP is zero |
|
| 4913. |
The 0.8 kg collar slides freely on the fixed vertical circular rod. Calculate the velocity v of the collar as it hits the stop at B if it elevated from rest at A by the actionof the constant 40N force in the cord. The cord is guided by the small fixed pulleys. |
|
Answer» `40 m//s` `40xx(0.5-0.1)-0.8xx10xx0.4` `=1//2mv^(2)-0` |
|
| 4914. |
Two plane mirrors are combined to each other such that one is in y-z plane and the other is in X-z plane. A ray of light travelling along a vector hati+ hati+ hatk is incident on the first mirror. Find the unit vector in the direction of emergent ray after successive reflections through both the mirrors. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`-(1)/( SQRT(3)) hati- (1)/( sqrt(3))HATJ+ (1)/( sqrt(3)) hatk` | |
| 4915. |
How can you ascertain that the drift is steady and not accelerated? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :An ACCELERATED CHARGE GIVES out RADIATION. Here there is no radiation. | |
| 4916. |
A particle A havinga charge of 5.0 xx 10^(-7)C is fixed in a vertical wall. A second particle B of mass 100g and having equal charge is suspended by a silk thread of length 30 cm from the wall. The point of suspension is located 30 cm vertically above the first particle. Find the angle of the thread with the vertical when it stays in equilibrium. |
|
Answer» Solution :The situation is show in the figure. Let the point of suspension be O, where the thread makes an angle `theta` with the vetical. FORCES on the particle B are (1) weight mg acting downward. (2) tension, T alongthe thread, (3) electric force of repulsion F along AB. At equilibrium sum of all these forces becomes ZERO. From the given figure, OA=OB, `angleOAB = angleOAB =(90^(@)-theta/2)` Considering the components along BX, we get `F cos theta/2 = mg cos (90^(@)-theta)= mg sin theta= 2mg sin theta/2 cos theta/2` or `sin theta/2 = F/(2mg)` Now, `F=1/(4pi epsilon_(0)).(q_(1)q_(2))/(AB^(2))` and AB = 2(OA) `sin theta/2` `therefore sin theta/2 = 1/(4pi epsilon_(0)).(q_(1)q_(2))/(4(OA)^(2) sin^(2) theta/2). 1/(2mg)` 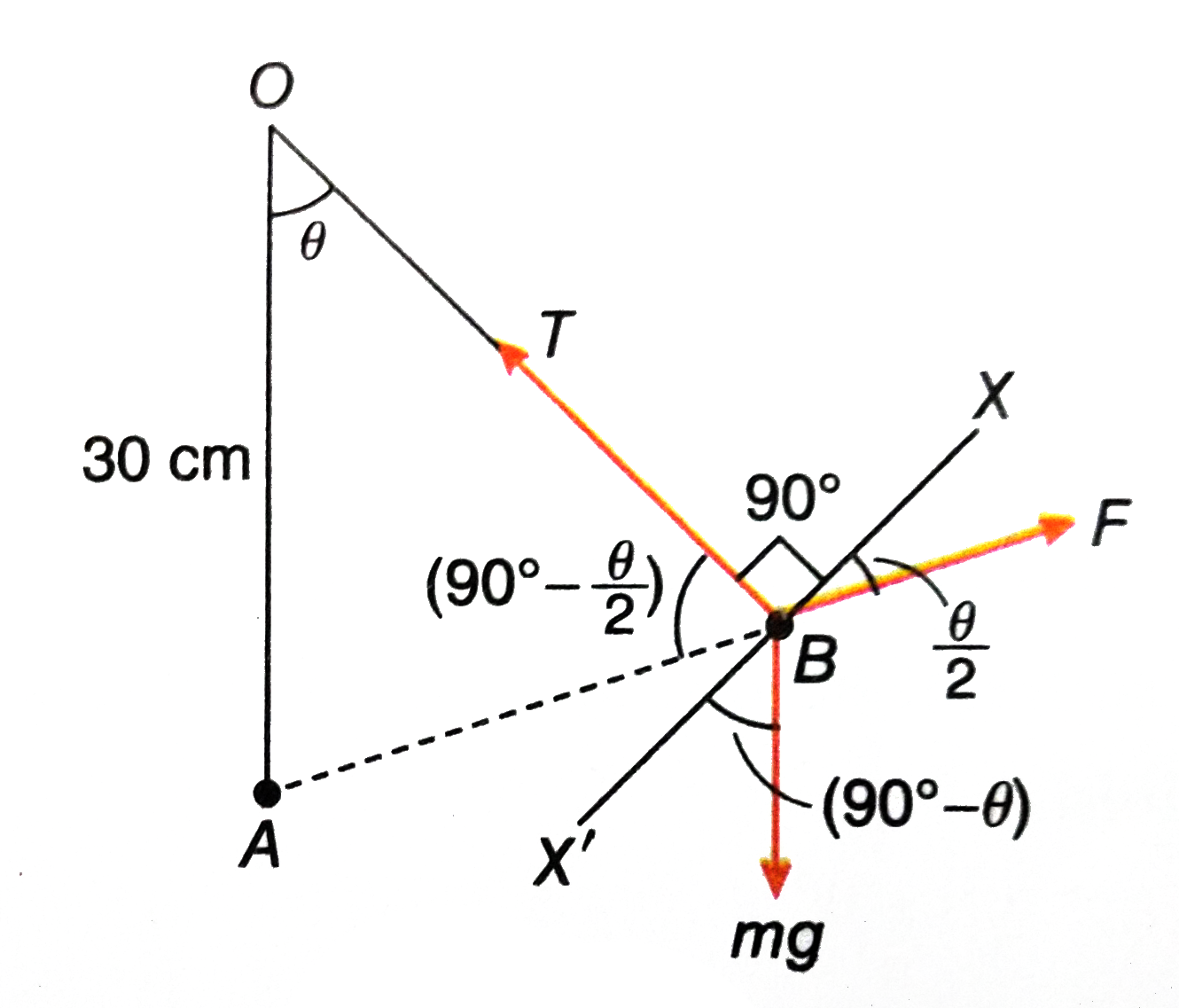 or `sin^(3) theta/2 =1/(4pi epsilon_(0)).(q_(1)q_(2))/(4(OA)^(2) sin^(2)theta/2). 1/(2mg)` `=(9 XX 10^(9)) xx ((5 xx 10^(-7))^(2)/(4 xx (30 xx 10^(-2))^(2))) xx 1/(2 xx (100 xx 10^(-3)) xx 9.8)` =0.0032 or, `sin theta/2 = 0.15` `therefore theta = 17^(@)` |
|
| 4917. |
What amount of heat in micro joule will be generated in the circuit , after the switch is shifted from position 1 to position 2? (C=C_(0) =2muF, E = sqrt6V) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4918. |
The threshold frequcney for a certain metal is 3.3xx10^(14) Hz. If light of frequency 8.2xx10^(14) Hz is incidenton the metal, predict the cut-off voltage for the photoelectric emission. |
|
Answer» Solution :`upsilon_(0)=3.3xx10^(14)HZ, upsilon=8.2xx10^(14)Hz` `(1)/(2)mv_("MAX")^(2)=h(upsilon-upsilon_(0))`, But `eV_(0)=(1)/(2)mv_("max")^(2)` `eV_(0)=h(upsilon-upsilon_(0))=6.6xx10^(-34)[8.2xx10^(14)-3.3xx10^(14)]` `V_(0)=(6.6xx10^(34)xx4.9xx10^(14))/(1.6xx10^(-19))=20.2xx10^(-1)V=2V` |
|
| 4919. |
The value of |vecA+vecB-vecC+vecD| canbe zero if:- |
|
Answer» `|vecA|=5,|vecB|=3,|vecC|=4,|vecD|=13` |
|
| 4920. |
In Bohr's theoryof hydrogenatom ,calculate theenergy of thephoton emitted duringa transitionof theelectron from thefirstexcitedstateto itsground state . Writein whichregionof the electromagneticspectrum thistransition lies . Given Rydbergyconstant R = 1.03 xx 10^(7) m^(-1) . |
|
Answer» Solution :When in a hydrogen atom a transition takes place from the first excited state (n = 2) to its GROUNDSTATE (n = 1), we have ` (1)/(lambda) = R [(1)/((1)^(2)) - (1)/((2)^(2))] = (3R)/(4)` `therefore ` Energyof photon`E= hv = (hc)/(lambda) = (hc.3R)/(4) J = (3hcR)/(4 e)eV` `rArr "" E= (3xx 6.63 xx 10^(-34) xx 3xx 10^(8) xx 1.03 xx 10^(7))/(4 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-9)) eV = 9.6 eV` The transition lies in the ULTRAVIOLET region of electromagnetic spectrum and corresponds to first line of Lyman series. |
|
| 4921. |
The wave theory of light, in its original form was first postulated by |
|
Answer» ISAAC Newton |
|
| 4922. |
The polarising angle depends upon the |
|
Answer» ORIENTATION of the plane of vibration |
|
| 4923. |
Transistor can be used as a A) Oscillator B) amplifier C) Rectifier D) Modulator |
|
Answer» Only B is true |
|
| 4924. |
In a two dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v_0 is a positive constant. Then which of the following are necessarily true? |
|
Answer» The ACCELERATION of the particle is zero |
|
| 4925. |
In doppler effect of light, term red shift represents ...... |
|
Answer» DECREASE in FREQUENCY |
|
| 4926. |
A frequently used device to measure the speed of bullets is the ballistic pendulum. It comprises of a heavy block of wood of mass M suspended by two long chords. A bullet of mass m is fired into the block horizontally. The block, with the bullet embedded in it, swings upwards. The centre of mass of the combination rises through a vertical distance h before coming to rest momentarily. In a particular experiment, a bullet of mass 40 gm is fired into a wooden block of mass 10 kg. The block is observed to rise by a height of 20.0 cm.Fraction of initial energy lost in the collision |
|
Answer» `0.9880` Initial `K.E. = (1)/(2)m U^(2)=(1)/(2)xx(40)/(1000)xx502^(2)=5040.08 J` Fractional loss of K.E. = 0.9960 `therefore` (B) |
|
| 4927. |
जब कई छोटी-छोटी नदियां बड़ी नदी में मिल जाती है तो उसे क्या कहते है ? |
|
Answer» नदी तंत्र |
|
| 4928. |
(A): At rest, radium is decayed into Radon and an a-particle. They both moves back to back of each other. (R) : Splitting of radioactive particles is based on conservation of linear momentum |
|
Answer» Both .A. and .R. are TRUE and .R. is the CORRECT explanation of .A. |
|
| 4929. |
A frequently used device to measure the speed of bullets is the ballistic pendulum. It comprises of a heavy block of wood of mass M suspended by two long chords. A bullet of mass m is fired into the block horizontally. The block, with the bullet embedded in it, swings upwards. The centre of mass of the combination rises through a vertical distance h before coming to rest momentarily. In a particular experiment, a bullet of mass 40 gm is fired into a wooden block of mass 10 kg. The block is observed to rise by a height of 20.0 cm.If the bullet penetrates the block to a depth of 3.0 cm, the approximate average force of resistance by the block of wood is |
|
Answer» `8.2xx10^(4)N` `RARR 0-502^(2)=2xx a XX(3)/(100)` `rArr a=-(502^(2)xx100)/(2xx3)~=4.2xx10^(8)m//s` `vec(F)=vec(m)vec(a)=(40)/(1000)xx4.2xx10^(6)=16.8xx10^(4)N` `THEREFORE` (D) |
|
| 4930. |
Assertion : When a capacitor is charged by a battery. Half of the energy supplied by the battery is stored in the capacitor and rest half is lost. Reason : If resistance in the circuit is zero, then there will be no loss of energy. |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and Reason are TRUE and Reason is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of Assertion. |
|
| 4931. |
STATEMENT-1 In young's double slit experiment if whole set up is immersed in a liquid then fring is decrease STATEMENTS-2 Wavelength of light entering in a liquid increases |
|
Answer» Statement-1 is true Statemetnt-2 is True,Statement -2 is a correct EXPLANATION for statement -1. |
|
| 4932. |
What is the de Broglie wavelengthof a nitrogen molecule in air at 300 K ? Assume that the molecule is moving with the root-mean square speed of molecules at this temperature. (Atomic mass of nitrogen = 14.0076 u) |
|
Answer» Solution :`T =300K "" LAMBDA=?` `m=14.0076u=14.0076xx1.6xx10^(-27)kg ` `K_("max")=(3)/(2)KT=(3)/(2)xx1.38xx10^(-23)xx300=6.21xx10^(-21)J` `p=sqrt(2mK_("max"))=sqrt(2xx14.0076xx1.6xx10^(-27)xx6.21xx10^(-21))=1.7xx10^(-23)kg ms^(-1)` `lambda=(h)/(p)=(6.6xx10^(-34))/(1.7xx10^(-23))=3.9xx10^(-11)m` |
|
| 4933. |
Lenz's law gives us the direction of current induced in a circuit. According to this law, the polarity of induced e.m.f is always such that is opposes the change in magnetic flux responsible for its production. It means if e.m.f. is induced due to increase in magnetic flux, the direction of e.m.f. induced is such as to oppose the increase in magnetic flux. The reverse is also true. Read the above passage and answer the following questions : (i) Does Lenz's law violate the principle of conservation of energy ? (ii) Name any other rule for finding the direction of induced current. (iii) What does Lenz's law imply in day to day life? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) No, Lenz's law does not violate the principle of conservation of energy. (ii) FLEMING's Right HAND rule is yet another rule for finding the direction of induced current. (iii) In day to day life, Lenz's law implies that you cannot ge something out of nothing. When we do MECHANICAL work in moving the magnet towards/away from the coil, we obtain ELECTRICAL energy in the form of induced current/e.m.f. The moment we stop moving the magnet, induced current/e.m.f. disappears. If we IGNORE stray losses, energy obtained is always equal to energy spent or work done. |
|
| 4934. |
Specific resistance of material of one wire is rho. Its volume is 3 m^(3) and its resistance is 3 Omega. Its length would be ..... . |
|
Answer» `SQRT((1)/(rho)) ` volume V = AREA A `xx ` LENGTH L `therefore A= (V)/(l)= (3)/(l) ""` ... (1) `rArr R = (rho l)/(A) = (rho l)/((3)/(l))"" [ because " from equation (1)" ] ` `therefore 3 = (rho l^(2))/(3) "" [ because R= 3 Omega ] ` `therefore l^(2)= (9)/(rho)` `therefore l = (3)/(sqrt(rho))` |
|
| 4935. |
The crrors due to imperfect design or calibration of the measuring instrument are |
|
Answer» RANDOM ERRORS |
|
| 4936. |
What is average value of a.c. over a complete cycle and why ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Average VALUE of a.c. over a complete CYCLE is zero, because a.c. is positive during one half cycle and equally NEGATIVE during the other half cycle. | |
| 4937. |
Capacitor C_3 in the circuit is a variable capacitor (its capacitance can be varied). C_1 and C_2 are of fixed values. Graph is plotted between potential difference V_1 (across capacitor C_1)versus C_3. Electric potential V_1 approches on asymptote of 10 V as C_3 prop oo. , Relation between C_1and C_2 is |
|
Answer» `C_1 = C_2` Fromgraphs when `C_(3)=0,V_(1)=2V. So C_(3)` will act like open switch `C_(1)` and `C_(2)` will be in series potential different across `C_(2)` is `V_(2)=10-V_(1)` `=8V` `q=C_(1)V_(1)=C_(2)V_(2)` or `C_(12)=C_(28)` or `C_(1)=4C_(2)` `V_(1)=4V,V_(2)=10-4=6V` `q=C_(1)V_(1)=(C_(2)+C_(3))V_(2)` or `C_(14)=(C_(2)+C_(3))6` or `16C_(2)=6C_(2)+6C_(3)` or `C_(3)=5C_(2//3)` |
|
| 4938. |
Capacitor C_3 in the circuit is a variable capacitor (its capacitance can be varied). C_1 and C_2 are of fixed values. Graph is plotted between potential difference V_1 (across capacitor C_1)versus C_3. Electric potential V_1 approches on asymptote of 10 V as C_3 prop oo. , When V_1 = 4Vm then C_3 is equal to |
|
Answer» `5C_2//2` Fromgraphs when `C_(3)=0,V_(1)=2V. So C_(3)` will act LIKE open switch `C_(1)` and `C_(2)` will be in series potential DIFFERENT across `C_(2)` is `V_(2)=10-V_(1)` `=8V` `q=C_(1)V_(1)=C_(2)V_(2)` or `C_(12)=C_(28)` or `C_(1)=4C_(2)` `V_(1)=4V,V_(2)=10-4=6V` `q=C_(1)V_(1)=(C_(2)+C_(3))V_(2)` or `C_(14)=(C_(2)+C_(3))6` or `16C_(2)=6C_(2)+6C_(3)` or `C_(3)=5C_(2//3)` |
|
| 4939. |
Capacitor C_3 in the circuit is a variable capacitor (its capacitance can be varied). C_1 and C_2 are of fixed values. Graph is plotted between potential difference V_1 (across capacitor C_1)versus C_3. Electric potential V_1 approches on asymptote of 10 V as C_3 prop oo. , The electric potential V across the battery is equal to |
|
Answer» 10V Fromgraphs when `C_(3)=0,V_(1)=2V. So C_(3)` will act like open SWITCH `C_(1)` and `C_(2)` will be in series potential different across `C_(2)` is `V_(2)=10-V_(1)` `=8V` `q=C_(1)V_(1)=C_(2)V_(2)` or `C_(12)=C_(28)` or `C_(1)=4C_(2)` `V_(1)=4V,V_(2)=10-4=6V` `q=C_(1)V_(1)=(C_(2)+C_(3))V_(2)` or `C_(14)=(C_(2)+C_(3))6` or `16C_(2)=6C_(2)+6C_(3)` or `C_(3)=5C_(2//3)` |
|
| 4940. |
जल का विद्युत - अपघटन करने पर H_2तथा O_2 गैसों के मोलों काअनुपात होता है- |
|
Answer» 1:1 |
|
| 4941. |
A conducting ring of radius r is placed in a varying magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the ring. If the rate at which the magnetic field varies is x, the electric field intensity at any point of the ring is |
|
Answer» RX `therefore epsi = E(2pi r)`.....(i) Also , the induced emf is `epsi = (dphi)/(dt) = pi r^2 (dB)/(dt) = pi r^2 x `......(ii) Equating (i) and (ii) , we get`E = (rx)/(2)` |
|
| 4942. |
The altractive forces which hold the constituent particles of substance together are called |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4943. |
Interference of light from two sources can be observed if |
|
Answer» The SOURCE are independent |
|
| 4944. |
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show image fromation when theconcave mirror produces a real, inverted and magnified image of the object (b) Obtain the mirror formula and write the expression for theliner magnification. (c) Explain two advantages of a reflectingtelescope over a refracting telescope. |
Answer» Solution :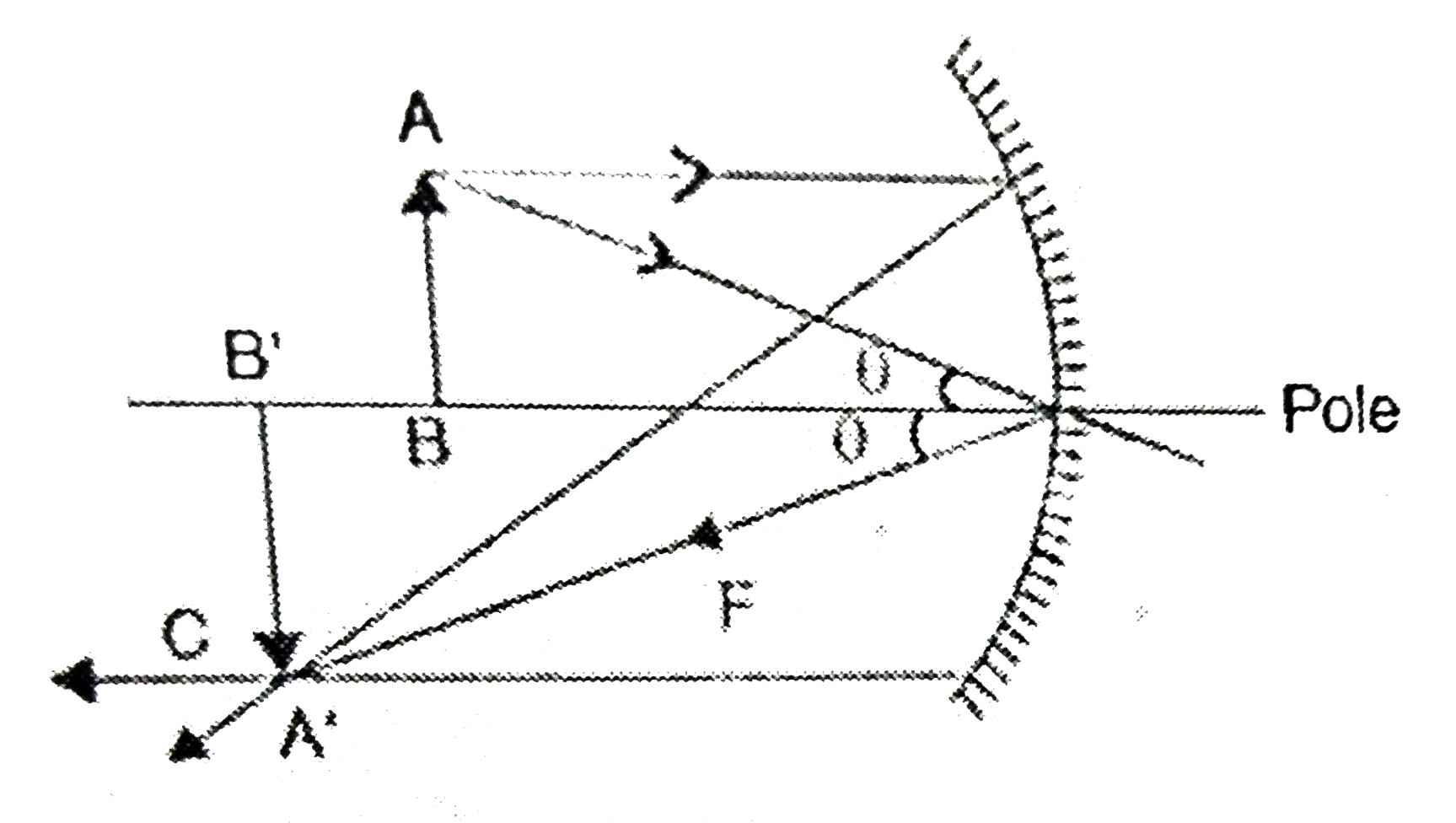 (b) `Delta A'B'F'` andMPF are similar So, `(A'B')/(MP) = (B'F')/(FP)""…(i)` `Delta ABF` and `A'B'P'` are similar `(A'B')/(BP)=(B'P)/(BP)""....(ii)` `MP = AB ""("by gemoetry")` `(A'B')/(AB) = (B'F')/(ER) ""...(iii)` EQUATE (ii) and (iii) `(B'P)/(BP) = (B'F)/(FP) ""(-v)/(-mu) = (B'P - FP)/(EP)` `(V)/(mu) = ((-V)-(-f))/(-f)""(-vf)/(Uvf)=(-Uv + Uf)/(U v f)` `-(1)/(f)=-(1)/(v) + (1)/(U) ""(1)/(f) = - (1)/(v) + (1)/(U)` Form equation (ii), `(A'B)/(AB) = (B'P)/(BP) ""(-h')/(h)= (-v)/(-U)` `m = (-h')/(h) = (-v)/(U)""m = v//U` (c) (i) Reflectingtelescope have higher resolvingpowerdue to the LARGE aperture of mirror. (ii) Due to AVAILABILITY of paraboloidal mirror the IMAGE is FREE from chromatic and spherical aberration. 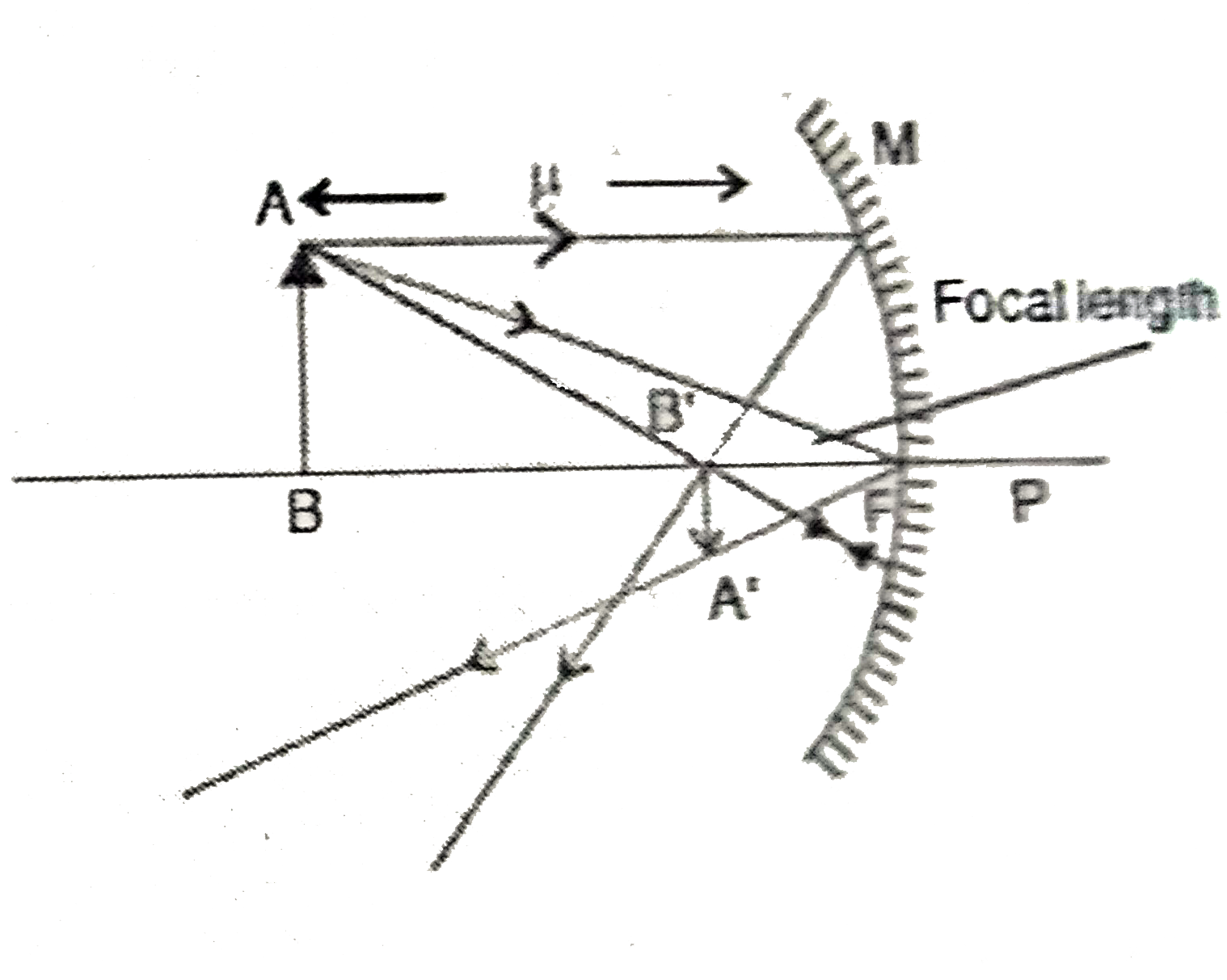
|
|
| 4945. |
When a voltage measuring device is connected to AC mains, the meter shows the steady input voltage of 220V. This means |
|
Answer» input voltage cannot be AC voltage, but a DC voltage. `therefore V_"rms"=V_m/sqrt2` The voltmeter connected to AC mains read MEAN value `ltV^2gt` (AVERAGE value) and is calibrated in such a way that it GIVES value of `ltV^2gt`. This is obtained by dividing `sqrt2` to maximum voltage `V_m`. |
|
| 4946. |
What is the meaning of "treacherous"? |
|
Answer» trustworthy |
|
| 4947. |
A light bulb and an open coil inductor are connected to an ac source through a key as shown in the figure. The switch is closed and after sometime, an iron rod is inserted into interior of the inductor. The glow of the light bulb (a) increases , (b) decreases , (c ) is unchanged, as the iron rod is inserted. Given your answer with reasons. |
| Answer» Solution :As the iron ROD is INSERTED, the magnetic field inside the coil magnetizes the iron increasing the magnetic field inside it. Hence, the inductance of the coil increases. Consequently, the inductive reactance of the coil increases. As a result, a larger fraction of the applied AC voltage appears across the inductor, LEAVING less voltage across the bulb. Therefore, the glow of the light bulb DECREASES. | |
| 4948. |
In anomalous expansion of water at what temperature, the density of water is maximum ? |
|
Answer» `4^(@)C` So, correct CHOICE is (a). |
|
| 4949. |
A ray of light, incident on an equilateral glass prism (mu_(g) = sqrt(3)) moves parallel to the base line of the prism inside it. Find the angle of incidence for this ray. |
|
Answer» Solution :As the REFRACTED light MOVES parallel to the base line of the prism inside it, the prism is set in minimum DEVIATION condition. `angleA = 60^(@)`for an equilateral prism and REFRACTIVE index of glass `n_(g) = sqrt(3)` `therefore sqrt(3) =((sini 60^(@) + D_(m))/2)/(sin 60^(@)/2) =(sin(60^(@) + D_(m))/2)/(1/2)` `rArr (sin(60^(@) + D_(m))/2) = sqrt(3)/2 rArr (60^(@) + D_(m))/2 = sin^(-1) (sqrt(3)/2) = 60^(@) rArr D_(m) = 60^(@)` In minimum deviation condition angle of INCIDENCE `i=(A+D_(m))/2 =(60^(@) + 60^(@))/2 = 60^(@)` |
|