Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 4801. |
The distance of closest approach of alpha particle to the nucleus was taken as a measure of |
|
Answer» ATOMIC radius |
|
| 4802. |
The three graphs shwon here show the total energy output of four different stars per second plotted against the wavelength that they radiate. All the four stars are behaving like black bodies. They can be assumed to be spherical bodies. Study the graphs below and answer the following questions. Take b=3xx10^(-3) mK. Which of the following statements correctly describes star C? |
|
Answer» It APPEARS to be red in COLOR and has temperature of 8000 K |
|
| 4803. |
What is meant by 'remote sensing' ? Mention any two applications of remote sensing. |
|
Answer» Solution :Remote sensing is a technique of obtaining information about an object/area from a distance without having any physical contact. Two types of satellites are USED for remote sensing. `(i)` Passive satellites. A passive satellite is not equipped with electronic devices to process or amplify the signal. The signal is simply reflected BACK to earth, hence a very powerful transmitter is required. `(ii)` Active satellite. Active satellites have high resolution cameras, infrared SCANNERS etc. These devices can record the information and them beamed down to earth in digital form which is them converted into maps and PICTURES by the computers. Applications `(i)` Remote sensing is used for geological surveys, water resource surveys, urban land USE survey and natural disaster surveys. `(ii)` Remote sensing data is used in monitoring climate changes. `(iii)` Remote sensing can be used to assess the damage caused by floods. |
|
| 4804. |
y=cosec^(-1) X का परिसर है - |
|
Answer» `(-pi/2,pi/2)` |
|
| 4805. |
The three graphs shwon here show the total energy output of four different stars per second plotted against the wavelength that they radiate. All the four stars are behaving like black bodies. They can be assumed to be spherical bodies. Study the graphs below and answer the following questions. Take b=3xx10^(-3) mK. Which of the following is the correct order of the radius of star A , Star C and Star D? |
|
Answer» `R_(A) GT R_(C) gt R_(D)` |
|
| 4806. |
The fig shows a network consisting of an infinite number of pairs of resistors R_(1) = 2 Omega and R_(2) = 1 Omega. Since the network is infinite, removing a pair of R_(1) and R_(2) from either end of the network will not make any difference. Using this calculate the equivalent (R) across points A and B. (b) Prove that I_(n)=(I_(n-1)R_(2))/(R_(2)+R)=(I_(n-1))/(sqrt(3)+2) ltbr Where I_(n) and I_(n-1) represent the current through R_(1) in n^(th) and (n-1)^(th) segment respectively (see Fig) (c) If a 20 V battery is connected across A and B find I_(10) |
|
Answer» (C) `(20)/((sqrt(3)-1)(sqrt(3)+2)^(9))` |
|
| 4807. |
A metal plate is getting heated. It can be because |
|
Answer» a direct CURRENT is passing through the plate. |
|
| 4808. |
Derive formula for mutual inductance for two very long coaxial solenoids. Also discuss reciprocity theorem. |
Answer» Solution :Consider figure which shows two long coaxial solenoids each of length L. We denote the radius of the inner solenoid `S_1` by `r_1` and the number of turns per unit length by `n_1`. The corresponding quantities for the outer solenoid `S_2` are `r_2` and `n_2` respectively. Let `N_1` and `N_2` be the total number of turns of coils `S_1` and `S_2` respectively. 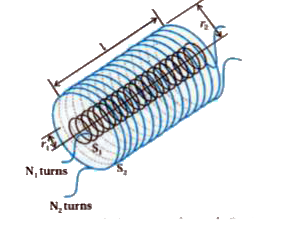 When a current `I_2` is SET up through `S_2`, it in turn sets up a magnetic flux through `S_1`. Let us denote it by `Phi_1`. The corresponding flux linkage with solenoid `S_1` is `therefore N_1 Phi_1 = M_12 I_2` ....(1) `M_12`is called the mutual inductance of solenoid `S_1` with RESPECT to solenoid `S_2`. It is also referred to as the coefficient of mutual induction. `N_1 Phi_1=N_1A_1B_2` `N_1 Phi_1=(n_1l)(pir_1^2)(mu_0n_2I_2)` `=mu_0n_1n_2 pir_1^2 pi_2`...(2) Where `n_1l` is the total number of thuns in solenoid `S_1` . Thus, from equation (1) and (2) , `M_12=mu_0 n_1n_2 pir_1^2l`...(3) Note that we neglected the edge effects and considered the magnetic field `mu_0n_2I_2`to be uniform throughout the length and width of the solenoid `S_2`. We now consider the reverse case. Current `I_1` is passed through the solenoid `S_1` and the flux linkage with coil `S_2` is, `N_2 Phi_2=M_21 I_1`..(4) `M_21` is called the mutual inductance of solenoid `S_2` with respect to solenoid `S_1`. The flux due to the current `I_1` in `S_1` can be assumed to be confined solely inside `S_1` since the solenoids are very long. Thus, flux linkage with solenoid `S_2` is `N_2 Phi_2=N_2A_1B_1` `N_2Phi_2 =(n_2I)(pir_1^2)(mu_0n_1I_1)` `=mu_0 n_1n_2pir_1^2 pi_1`....(5) Where `n_2I` is the total number of turns of `S_2`. From equation (4) to (5), `M_21=mu_0n_1n_2pir_1^2l`...(6) Using equation (3) and (6), we get `M_12=M_21=M` (say)...(7) Equation (7) is known as RECIPROCITY theorem. We have considered air as a medium in solenoid. Instead of air medium of relative permeability `mu` is considered then `M=mun_1n_2pir^2l` `mu=mu_0mu_r=(mu_0mu_r)n_1n_2pir^2l` |
|
| 4809. |
After switch S_(2) is closed and S_(1) is opened, the maximum value of current through the inductor is: |
|
Answer» `(sqrt(C/L))E` |
|
| 4810. |
Light of wavelength 6400overset@A incident normally on a plane paralled glass slab thickness 5 cm and mu = 1.6. The beam takes the same time to travel from source to the incident surface as it takes to travel through the slab. The distance between the source and incident surface and wavelength of ligt in glass is : |
|
Answer» `8 CM 4000overset@A` |
|
| 4811. |
Two physical pendulums (not simple pendulums) are made from meter sticks that are suspended from the ceiling at one end. They are identical, except that one is made of wood and the other of metal. They are set into oscillation and execute simple harmonic motion. The wood and metal pendulums have masses of 0.17 and 0.85kg, respectively. Determine the period of wood pendulum. |
|
Answer» 1.64s |
|
| 4812. |
Determine the balance point of the above bridge if X and Y are interchanged. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :60.5 cmfrom A | |
| 4813. |
A basic communication system consists of (a) Transmitter (b) Information source (c) User of information (d) Channel (e) Receiver The correct sequence of the arrangement is |
|
Answer» a, B, C, d and E 
|
|
| 4814. |
A conducting bar of sufficient length is pulled with a constant velocity in a conducting shaped rail as shown in the figure . Inward magnetic field of induction B is present inside the area bounded by the bar & the rail. Find the external powerdelivered in moving the rail with constant velocity v at time t ( A= area of cross section of the bar rho= resistivity of the bar ) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4815. |
A charge of 2 X 10-7 C is acted upon by a force of 0.1N. Determine the distance to the other charge of 4.5 X 107 C, both the charges are in vacuum |
|
Answer» 0.03 |
|
| 4816. |
The most commonly employed analog modulation technique in satellite communication is the |
|
Answer» AMPLITUDE modulation |
|
| 4817. |
Two balls are dropped from the same height at two different places A and B where the acceleration due to gravities are g_A and g_B. The body at 'B' takes 't' seconds less to reach the ground and strikes the ground with a velocity greater than at 'A' by upsilon m//s. Then the value of upsilon//t is |
|
Answer» `1/(SQRT(g_A g_B))` |
|
| 4818. |
A truck weighing 1000 kg changes its speed from 36 km/h to 72 km/h in 2 minutes. Thus , the work done by the engine on the truck is |
|
Answer» `2.5 XX 10^5 J` |
|
| 4819. |
Object is placed 60 cm away from convex mirror. If magnification is 0.5, image distance = ….... |
|
Answer» -30 `therefore1/2=-(v)/(-60)` [`because` u=-60 cm] `THEREFORE (60)/(2)`=v `therefore` v = 30 cm |
|
| 4820. |
Using mass (M), Length (L) , time (T) and electric current (A) as fundamental quantities the dimensions of permittivity will be |
|
Answer» `MLT^(-1) A^(-1)` |
|
| 4821. |
A ray of light travels in medium of refractive index mu. It incidents at a surface in contact with air at 45^@. For what value of mu, this ray will undergo total internal reflection ? |
|
Answer» `MU`=1.33 `mu ge (1)/(SINC) ge sqrt2 ge 1.414` `therefore mu=1.50` |
|
| 4822. |
A converginglensof focallength5.0cm isis placed incontactwitha diverginglensof focallength10.0 cmfindthe combinedfocallengthof thesystem . |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here`f_1= + 5.0cmf_2 =- 10.0cm` thereforethe COMBINED focallengthF isgivenby `(1)/(F) = (1)/(f_1 )+(1)/(f_2) =(1)/( 5.0 ) -(1)/(10.0 ) = + (1)/( 10.0)` ` thereforeF = + 10.0 CM `i.e.,the combinationbehaesas aconverginglensoffocallength10.0 cm |
|
| 4823. |
{:("(i) Electric dipole","(a)Ebonite"),("(ii) Dielectric ","(b)"H_(2)),("(iii)Polar molecules","(c) Ammonia"),("(iv)Non-polar molecules","(d)"H_(2)O):} |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4824. |
A ball weighing 1 kg is moving horizontally at 12 ms^(-1). It collides head on with another of double the mass moving in oppssite direction with double the speed. If the coefficient of restitution is 2/3, the energy lost in the collision is given by : |
|
Answer» Solution :According to conservation of momnetum, `1xx12+2xx(-24)=1xxv_(1)+2xxv_(2)`. ` impliesv_(1)+2v_(2)=36` …..(i) ALSO `E=(v_(2)-v_(1))/(u_(1)-u_(2))implies 2/3=(v_(2)-v_(1))/(12-(-24))` `implies v_(2)-v_(1)=24` Adding (i)&(ii), `3v_(2)=60 impliesv_(1)=20 m//s`. LOSS of energy=`1/2xx1xx12^(2)+1/2xx2(-34)` `-(1/2xx1xx(-4)^(2)+1/2xx2xx(20)^(2))` =72+576-(8+400) =240 J. |
|
| 4825. |
The block of mass 3M is attached to the pulley system as shown in the figure. At t = 0, particle M falling vertically , strikes the block 3 M with velocity 8 m s^(-1)and sticks to it. The speed of the combined mass just after the collision is |
|
Answer» `8 MS^(-1)` |
|
| 4826. |
A planet of mass m is moving around a star of mass M and radius R in a circular orbit of radius r. The star abruplly shrinks to half its radius without any loss of mass. What change will be there in the orbit of the planet ? |
|
Answer» The planet will escape from the star |
|
| 4827. |
In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic fields are 100 V/m and 0.265 A/m. The maximum energy flow will be: |
|
Answer» `79 W/m^2` |
|
| 4828. |
n identical condensers are joined in parallel and are charged to potential so that energy stored in cach condenser is . If they are seperated and joined in series, then the total energy and total potential difference of the combination will be |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 4829. |
A thin biconvex lens is prepared from glass of refractive index mu_(2)=3/2. Thetwo convex surfaces have equal radii of 20 cm each. One of the surfaces is silvered from outside to make it reflecting. It is placed in a medium of refractive index mu_(1)=5/3. It acts as a |
|
Answer» converging mirror |
|
| 4830. |
The tangents deflectionproduced in tan A and Bpositionsby a short magnet at equal distancesareinthe ratio . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4831. |
An object of mass m is travelling at constant rate b in a circular path of radius r. how much work is done by the centripetal force during one half of a revolution? |
|
Answer» `pimv^(2)` |
|
| 4832. |
Suposse the surface charge density over a sphere of radius R dendendson a polarangletheta as sigma = sigma_(0) cos theta, where sigma_(0) is a positiveconstant. Show that such a charge distribution can be represented as a resultof a small relative shift of two uniformly charge balls of radiusR whosechargesare equalin magnitudeand oppositein sign. Restoringto thisrepresentation, find teh electricfield strength vector inside the given spehre. |
|
Answer» Solution :We START from two charged SPHERICAL balls each of radius `R` with equaland opposite charge densities`+ rho` and `-rho`. The CENTRE of the balls are at `+ (vec(a))/(2)` and `- (vec(a))/(2)` respectively so the equaction of their surfaces are `|vec(r ) - (vec(a))/(2)| = R` or`r - (a)/(2) cos theta= R` and `r + (a)/(2) cos theta = R`, considering `a` to be small. The distance between the two surface in the radial direction at angle `theta` is`|acos theta|` and does not dependon TEH azimuhal angle. It is seen from the diagram that the surface of the sphere has in effect a surface density `sigma = sigma_(0) cos theta` when `sigma_(0) = rho a`. Insideany uniformlychargedspherical ball, the field is radial and has the magnitudegiven by Gaussain's theorem `4pi r^(2) E = (4pi)/(3) r^(3) rho//epsilon_(0)` or`E = (rho r)/(3 epsilon_(0)` In vector notation, using the fact the `V` myst be measured from the centre of the ball, we get, for the present case `vec(E) = (rho)/(3 epsilon_(0)) (vec(r ) - (a)/(2)) - (rho)/(3 epsilon_(0)) (vec(r ) + (vec(a))/(2))` `= -rho vec(a)//3 epsilon_(0) = (sigma_(0))/(3 epsilon_(0)) vec(k)` When `vec(k)` is teh unit vector along the polar axis from which`theta` is measured. 
|
|
| 4833. |
What is phase of a wave? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Phase is a paricular point in time on the CYCLE of a wavefrom, measured as a ANGLE in DEGRESS. | |
| 4834. |
(A) : A loosely wound helix made of stiff wire is suspended vertically with the lower end just touching a dish of mercury. When a current is passed through the wire, the helical wire, the helical wire executes oscillatory motion with the lower end jumping out of and into the mercury. (R) : Like current carrying wires attract each other. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 4835. |
Figure shows a long potentiometer wire AB having a constant potential gradient. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs epsi _(1) and epsi _(2) connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of l _(1) = 120 cm and l _(2) = 300 cmfrom the end A. Determine (i) epsi _(1) //epsi _(2) and (ii) position of null point for the cell epsi _(1) only. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) `(epsi _(1) - epsi _(2))/( epsi _(1) + epsi _(2)) = (120)/( 300 ) = 2/5` `(epsi _(1))/( epsi _(2)) = 7/3` (II) `(epsi _(1) + epsi _(2))/( epsi _(1)) = (300 )/(x ) IMPLIES ( 300 )/( x ) = (10)/(7)` `implies x = 210 cm` (where x is the position of null point with cell `epsi _(1)`). |
|
| 4836. |
A small test charge is released at rest at a point in an electrostatic field configuration. Will it travel along the field line passing through that point ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Electric field lines GIVE the direction of ACCELERATION of +ve CHARGE. If the electric field line is linear then the test charge will move along the line. If the field line is a curve (non-linear line), the charge will not move along the line. In other words, an electric field line gives the direction of electric field (or furce or acceleraliun) bul does not necessarily predicts the direction of motion (i.e., direction of velocity). | |
| 4837. |
A bar magnet is pulled through a conducting loop along its axis with its south pole entering the loop first. Draw the graphs of the induced current |
Answer» Solution :When the south pole of the magnet moves TOWARDS the conducting loop along its axis, then according to Lenz's LAW, the induced current will be clockwise when viewed along the motion of the magnet. According to the given question, induced current is positive in this CASE. Again, when the magnet goes to the other SIDE ACROSS the loop, the direction of the induced current will be anticlockwise. In this case, induced current is negative. Variation of induced current with time is shown in. 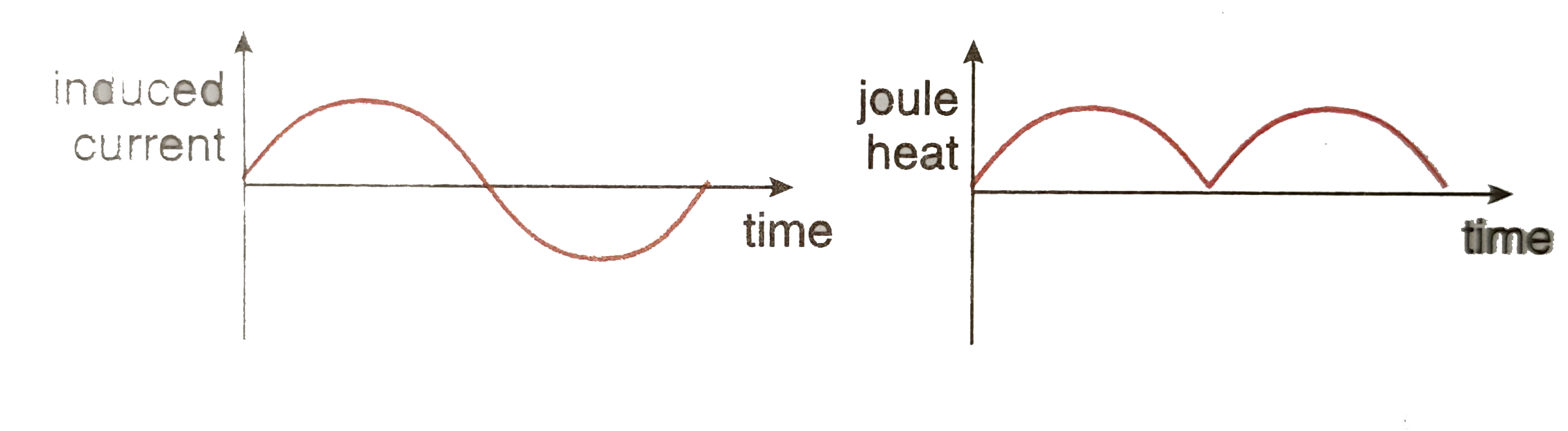
|
|
| 4838. |
A bar magnet is pulled through a conducting loop along its axis with its south pole entering the loop first. Draw the graphs of joule heating as a function of time. Take the induced current to be positive, if it is clockwise when viewed along the path of the magnet. |
| Answer» Solution :Joule heat PRODUCED is DIRECTLY proportional to the square of the current. Hence, heat produced will ALWAYS be POSITIVE and will be independent of the direction of current. Variation of heat produced with time is shown in. | |
| 4839. |
If an electron and an alpha - particle are accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 100 volt. The ratio of their momenta will be |
|
Answer» <P>`SQRT((M_(e)/(M_(alpha)))` `p="mu" = sqrt(2meV)` `(P_(e))/(P_(alpha))=sqrt((M_(e))/(M_(alpha)))` |
|
| 4840. |
In the case of bar magnet, lines of magnetic induction |
|
Answer» Start from the NORTH pole and END at the south pole |
|
| 4841. |
What is space wave propagation? Give two examples of communication system which use space wave mode. A TVtower is 80 m tall. Calculate the maximum distance upto which the signal transmitted from the tower can be received. |
|
Answer» Solution :Space wave PROPAGATION is the propagation of waves WHOSE FREQUENCIES lie above 40 MHz. Examples of communication system which use space wave MODE are : (i) Television broadcast (ii) Satellite communication NUMERICAL : Here `h=80 m=0.80km, R=6400 km` `therefore` Coverage range, `d=sqrt(2Rh)` `therefore d =sqrt(2xx6400 xx 0.080)` ` =sqrt(6400x 0.16)` ` =80xx 0.4=32 km` 
|
|
| 4842. |
Out of the following functions representing motion of a particle which represents SHM :(A) y = sin omegat - cos omegat (B) y = sin^(3) omegat(C )y = 5 cos ((3pi)/(4) - 3omegat) (D) y = 1 + omegat + omega^(2)t^(2) |
|
Answer» Only (A) and (B) |
|
| 4843. |
What is the dimensional formula of h/(mv) ? |
| Answer» Solution :`lambda= H/(mv),lambda` is WAVELENGTH and hence DIMENSIONAL formula is [L]. | |
| 4844. |
Find current through the cell and potential difference between A and D in the circuit shown in the figure |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4845. |
For air at room temperature the atmospheric pressure is 1.0 xx 10^(5) Nm^(-2)and density of air is 1.2 kg m^(-3). For a tube of length 1.0 m closed at one end the lowest frequency generated is 84 Hz. The value of y (ratio of two specific heats) for air is |
|
Answer» 2.1 `P_(0) =1.0 xx 10^(5) Nm^(-2)` `rho = 1.2 kg m^(-3)` `u_(0) = 84 Hz, gamma =?`  For FUNDAMENTAL FREQUENCY, `l = lambda/4 rArr lambda = 4l = 4m` Also, `u_(0) = v/lambda rArr 84 = v/4 rArr v = 336 ms^(-1)` Also `v=sqrt((gammaP_(0))/rho) rArr gamma =(v^(2)rho)/P_(0)` `gamma =((336)^2 xx 1.2)/(1 xx 10^(5)) = 1.35 = 1.4` |
|
| 4846. |
Some laws processes are given in column I. Match these with the physical phenomena given in column II. |
|
Answer» <P>`{{:(,,"Column I","Column II"),(,(a),"Transition between two atomic energy","(p) Characteristic X-rays"):}` |
|
| 4847. |
A block B of mass 5kg rests on a rough horizontal surface (mu=0.2),A block A of mass 2kg rests on block B(mu=0.4). If a horizontal force of 21 N be applied to the block B, what is force ("in N") of friction acting between the blocks A and B ? (g=10ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» 1 `because 21Ngtf_(2"MAX")=14Nimplies5kg"moves on ground"` `THEREFORE ""f_(2)=f_(k)=14N` `a_("Amax")=(f_(1"max"))/(2)=(0.4xx20)/(2)=4m//s^(2)` If both are to move together, COMMON acceleration, `a=(21-14)/(7)=1m//s^(2)lta_(Amax)` `therefore` both will move together with `1m//s^(2)implies f_(1)=f_(s)=2a=2N` 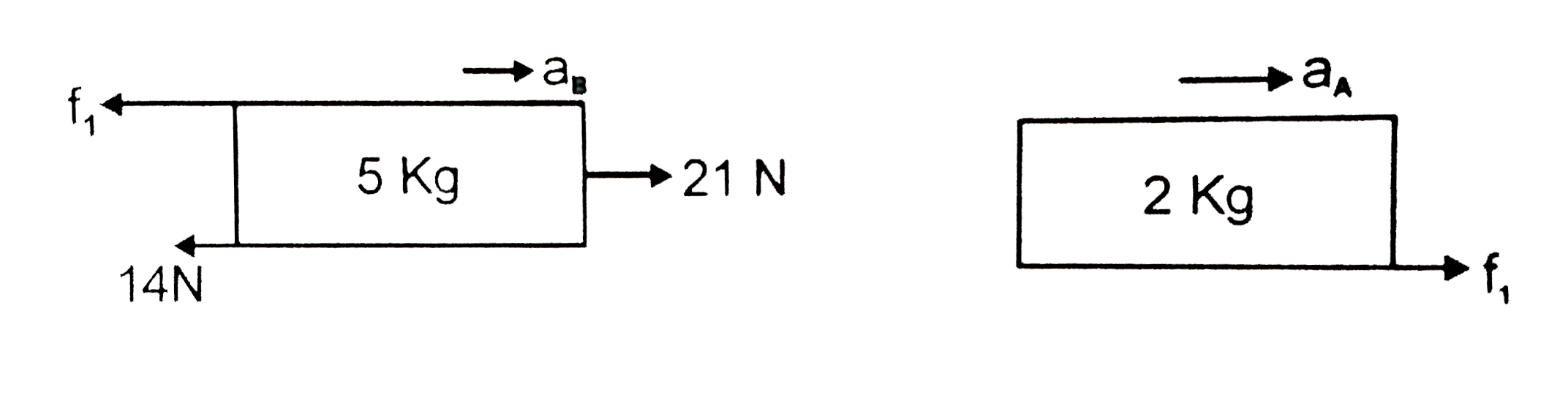
|
|
| 4848. |
The image obtained with a convex lens is erect and its length is four times the length of the object. If the focal length of the lens is 20 cm, calculate the object and image distances. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here f = 20 cm , m = + 4 for a virtual IMAGE. To CALCULATE u, we have `m=(f)/(u+f)rArr4=(20)/(u+20)rArr=-15cm` To calculate v, wehave `m = (f-v)/(f) rArr 4 = (20 - v)/(20) rArr v = - 60 cm` |
|
| 4849. |
The concept of stationary orbits was proposed by |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 4850. |
The range of frequencis alloted to FM radia is : |
|
Answer» 88 to 108 KHZ |
|