Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 6051. |
Two cancave refracting surfacwe of equal radii fo curvature face each other in air as shown in figure. A point objectO is placed midway between the centreand oneof the poles. Then the separation between the images of O formed by each refracting surface is |
|
Answer» `11.4` R  `I_(1)` DUETO refraction at surface (1) `(1.5)/(V)-(1)/(R//2)=(1.5-1)/(R)` `(1.5)/(V)=(2)/(R)+(0.5)/(R)` `(1.5)/(V)=(2.5)/(R)` `V=(15)/(R)` `rArr(3)/(5)R=0.6R` `I_(2)` DUE to refraction at surface (2) `(1.5)/(V)=(2)/(-3R//2)-(1.5-1)/(-R)` `(1.5)/(V)=-(2)/(3R)-(0.5)/(R)` `(1.5)/(V)=(-3.5)/(3R)` `V=(+4.5)/(3.5)R` `rArr-(9)/(7)R` `rArr-1.285R`  DISTANCE between `I_(1)&I_(2)=0.114R` |
|
| 6052. |
A force of constant magnitude starts acting on a moving particle when it is at some point 'P'. Depending on the orientation of the force, the particle may(a) pass through point P at some time later(b) not return to point P(c ) describe a circular path(d) describe a parabolic path |
|
Answer» a is CORRECT |
|
| 6053. |
Determine the number of electrons flowing per second through a conductor, when a current of 32A flows through it. |
|
Answer» Solution :`I=32A, t=1s` Charge of an ELECTRON, `c=1.6xx10^(19)C` The number of electrons FLOWING per SECOND, `n =? ` `I=(q)/(t)=(n e)/(t)` `n=(I t)/(e )=(32xx1)/(1.6xx10^(-19)C)=20xx10^(19)=2xx10^(20)` electrons |
|
| 6054. |
lA fixed wedge ABC is an the shape of an equilateral triangle of side l initially, a chain of length 2l and mass m rests the wedge as shown. The chain is slowly being pulled down by the application of a force F as shown. Work done by gravity till the time the chain leaves the wedge will be: |
|
Answer» `-(((SQRT(3)+1)mgl)/(2))` `(Deltah)=(l(cos30^(@))/(2))+l` work done by GRAVITY `=MG Delta=+mg((lsqrt(3))/(4)+l)` 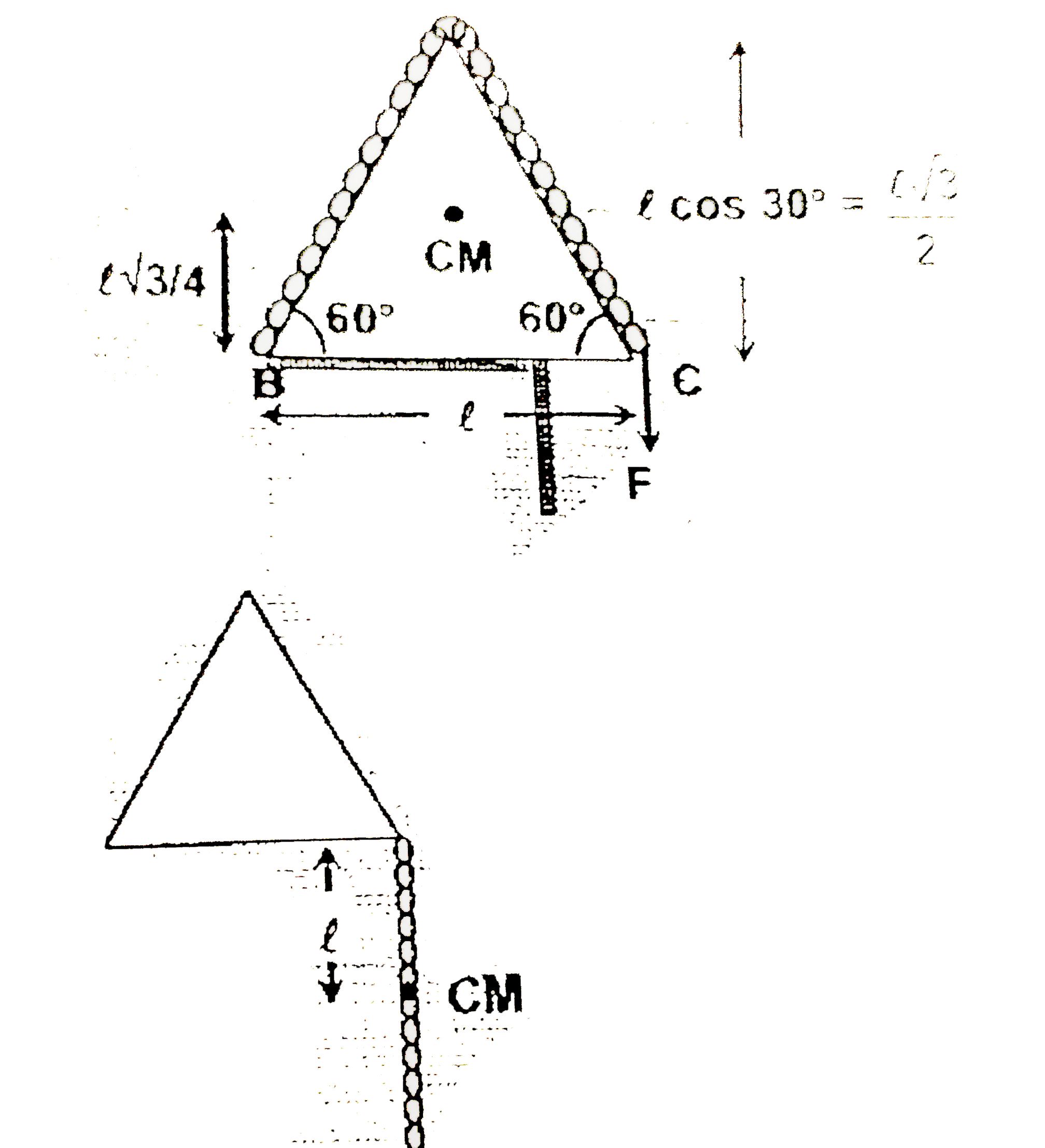 `=+mg(l(sqrt(3)+4)/(4))` |
|
| 6055. |
The total electric flux emanating from a closed surface enclosing an alpha-particle (e- electronic charge) is |
|
Answer» `(2e)/(epsi_(0))` |
|
| 6056. |
The resistance of a copper wire of length 5 m is 0.5 Omega. If the diameter of the wire is 0.05 cm, determine its specific resistance. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`rho = (RA)/(L )` or ` R = (rho l )/(A)` `A = PI r ^(2) = 3. 14 xx (2. 5 xx 10 ^(-4))^(2)` ` = 1. 96 25 xx 10 ^(-7) m ^(2)` `rho = (0.5 xx 1. 9625 xx 10 ^(-7))/( 5)` `rho = 1. 9625 xx 10 ^(-8) Omega -m` |
|
| 6057. |
Imagine that a charge .q. is situated at the centre of a hollow cube. What is the electric flux through one side of the cube? |
|
Answer» `Q/(6epsilon_0 )x10^-6` |
|
| 6058. |
A researcher studying the properties of ions in the upper atmosphere wishes to construct an apparatus with the following charateristics: Using an electric field, a beam of ions, each having charge q, mass m , and initial velocity vhati, is turned through an angle of 90^@ as each ion undergoes displacement Rhati + Rhatj. The ions enter a chamber as shown in figure and leave through the exit port with the same speed they had when they entered the chamber. The electric field acting on the ions is to have constant magnitude. Suppose the electric field is produced by two concentric cylindrical electrodes not shown in the diagram, and hence is radial. What magnitude should the field have? |
|
Answer» `(mv)^2/(2qR)` centered at A `qE=(mv^(2))/(R)` or `E=(mv^(2))/(qR)` As final velocity along x-axis BECOMES zero and finally the ions starts moving towards y direction the electric field should have component towards x-and y-directions, respectively. for x-component of electric field (using `v_(x)^(2)=u_(x)^(2)+2a_(x)trianglex)` `0=v^(2)-2((qE_(x))/(m))R` or `E_(x)=(mv^(2))/(2qR)` for y-component of electric field (again using `v_(y)^(2)=u_(y)^(2)+2atriangley)` `v^(2)=0+2((qE_(y))/(m))R` or `E_(y)=(mv^(2))/(2qR)` ltbr. Hence net electric field is `vecE=-(mv^(2))/(2qR)HATI+(mv^(2))/(2qR)hatj=(mv^(2))/(2qR)(-hati+hatj)` |
|
| 6059. |
200 Mev of energy may be obtained per fission of U^(235)A reactor is generating 1000 KW of power the rate of nuclear fission in the reactor is |
|
Answer» 1000 |
|
| 6060. |
A researcher studying the properties of ions in the upper atmosphere wishes to construct an apparatus with the following charateristics: Using an electric field, a beam of ions, each having charge q, mass m , and initial velocity vhati, is turned through an angle of 90^@ as each ion undergoes displacement Rhati + Rhatj. The ions enter a chamber as shown in figure and leave through the exit port with the same speed they had when they entered the chamber. The electric field acting on the ions is to have constant magnitude. If the field is produced by two flat plates and is uniform in direction, what value should the field have in this case? |
|
Answer» `(mv^2)/(2QR) (hati+hatj)` `qE=(mv^(2))/(R)` or `E=(mv^(2))/(qR)` As final velocity along x-axis becomes zero and finally the ions STARTS moving towards y direction the electric field should have component towards x-and y-directions, respectively. for x-component of electric field (using `v_(x)^(2)=u_(x)^(2)+2a_(x)trianglex)` `0=V^(2)-2((qE_(x))/(m))R` or `E_(x)=(mv^(2))/(2qR)` for y-component of electric field (again using `v_(y)^(2)=u_(y)^(2)+2atriangley)` `v^(2)=0+2((qE_(y))/(m))R` or `E_(y)=(mv^(2))/(2qR)` ltbr. Hence net electric field is `vecE=-(mv^(2))/(2qR)hati+(mv^(2))/(2qR)hatj=(mv^(2))/(2qR)(-hati+hatj)` |
|
| 6063. |
Astronomers have observed that light coming from far away starts do not show the same spectrum as observed on Earth. Each wavelength is shifted slightly towards the red end of the spectrum. It is observed that the 1^(st) line of Lyman series shows 121 nm on Earth, but from the star it shows 122nm. The speed of the star with respect to Earth is close to |
|
Answer» `2.5xx10^(6)MS^(-1)` |
|
| 6064. |
A person stands in contact against a wall of cylindrical drum of radius r, rotating with an angular velocity omega. If mu is the coefficient of friction between the wall and the person, the minimum rotational speed which enables the person to remain stuck to the wall is |
|
Answer» `SQRT(g//mur)` |
|
| 6065. |
Two converging glass lenses A and B have focal lengths in the ratio 2:1. The radius of curvature of first surface of lens A is 1/4 th of the second surface where as the radius of curvature of first surface of lens B is twice that of second surface. Then the ratio between the radii of the first surfaces of A and B is |
|
Answer» `5:3` |
|
| 6066. |
At what temperature is the r .m.s.velocity of a hydrogen molecule equal to that of an oxygen molecule at 47° C? |
|
Answer» 80 K `rArrsqrt((3RT)/(M_(H)))=SQRT((3R(47+273))/(M_(o)))` `rArrT/I=320/16rArrT=20K` So correct choice is (d). |
|
| 6067. |
A thin prism of angle 6^(@) made of glas of recfractive index 1.5 is combined with another prism made of glas of mu=175 to produce dispersion without deviation. The angel of second prism is |
|
Answer» `7^(@)` `:. delta_(1)-delta_(2)=0` or `(mu_(1)-1)A_(1)-(mu_(2)-1)A_(2)=0` or `(1.5-1)7^(@)=(1.75-1)A_(2)` or `7/2=3/4A_(2)` `:. A_(2)=7/2xx4/3` `=14/3=4.67^(@)` |
|
| 6068. |
A big drop of a liquid of radius 2 cm splits into 1000 small droplets. Then surface area of 1000 droplets will be |
|
Answer» GREATER then the S.A. of BIG drop |
|
| 6069. |
The current in self inductance L = 40 mH is to be increased uniformly from 1 amp to 11 amp in 4 milliseconds. The e.m.f. induced in inductor during process is |
|
Answer» 100 VOLT GIVEN that, `L=40xx10^(-3)H`, `di=11 A-1A=10 A` and `dt=4XX10^(-3)s` `therefore |epsilon|=40xx10^(-3)XX((10)/(4xx10^(_3)))=100 V` |
|
| 6070. |
Why can't we take one slab of p-type semiconductor and physically join it to another slab of 1-type semiconductor to get p-n junction ? |
| Answer» Solution :A slab of p-type or n-type semiconductor, howsoever FLAT, will have roughness much larger than the interatomic crystal SPACING. Hence, on joining p- and n-type slabs continuous contact at the atomic level is not possible and the TWO will notjoin together. In fact the junction will BEHAVE as a disconti- nuity. | |
| 6071. |
A railroad train is travelling at 30.0 m/s in still air. The frequency of the note emitted by the trainwhistle is 262 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. |
|
Answer» Frequency heard by a passenger on ANOTHER TRAIN moving in the opposite direction to the first at18.0 m/s and approaching the first is 302 HZ |
|
| 6072. |
An ideal heat engine works between the temperature 327^(@)C (source) and 27^(@)C (sink). What is its efficiency? |
|
Answer» 1 =75%. |
|
| 6073. |
In Young.s double slit experiment is used to demonstrate interference of light.If one of the slits is closed still dark and brightbands are observed on the screen. This is due to |
|
Answer» interference |
|
| 6074. |
.... can't be explained by ray optics. |
|
Answer» REFLECTION |
|
| 6075. |
What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point B ? |
|
Answer» `3.3xx10^(-5)` T, CLOCKWISE |
|
| 6076. |
A ray of light of wavelength of 5400AU in air is refracted in a medium of R.I. 1.5 The wavelength of light in a second medium is : |
|
Answer» 5000 AU |
|
| 6077. |
What is hydrogen spectral series? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The frequencies of the light emitted by a particular element WOULD exhibit some regular pattern. Hydrogen is the simplest atom, the frequency (wavelength) of lines of emitted radiation ADJUSTING progressively then spectrum is obtained and hydrogen has the simplest spectrum. A specific set of lines can be formed according to their frequency or wavelength of lines obtained in the atom.s spectrum and such a group is called the spectral series. The lines in some of the hydrogen spectrum sets are SHOWN in the figure.  The spacing between lines within CERTAIN sets of the hydrogen spectrum decreases in a regular way. Each of these sets is called a spectral series. |
|
| 6078. |
A solid sphere, a hollow sphere and a ring are released from top of an inclined plane (frinctionless) so that they slide down the plane. Then maximum acceleration down the plane is for (no rolling) : |
|
Answer» solid sphere |
|
| 6079. |
Find the r.m.s value of load current based on data given in the question no 10. |
|
Answer» `100xx10^(-3)A` Max. load current, `I_(0)=(V_(0))/(r+R)` Mean load current, `I_(m)=(2I_(0))/(PI)` `I_(r.m.s)=(I_(0))/(SQRT2)` |
|
| 6080. |
A metal rod of length 2 m is rotating with an angular velocity of 100 rad/sec in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.3T. The potential difference between the ends of the rod is |
|
Answer» 30V |
|
| 6081. |
When resonance takes place in series LCR A.C. circuit, |
|
Answer» current is minimum. `therefore tan delta =0` (`because` At RESONANCE , `X_L=X_C`) `therefore delta=0` |
|
| 6082. |
How many cells each marked (6V-12A) should be connected in mixed grouping so that it may be marked (24V-24 A) |
|
Answer» 4 |
|
| 6083. |
Obtain equation of electric energy of a single charge . |
|
Answer» Solution :The external ELECTRIC field `vecE` and the corresponding external POTENTIAL V may vary from point to point. According to definition of electric potential V at a point P is the WORK done in BRINGING a unit positive charge from infinity to the point P (We assume the potential at infinity to be zero.) Thus, work done in bringing a charge q from infinity to the point P in the external field is W =qV. This work is stored in the form of potential energy of q , `:. U =qV` If the point P has position vector `vecr` relative to ORIGIN, then potential energy at point P `U(vecr)=qV(vecr)` Means potential energy in an external field = electric charge `xx` electric potential in external field. |
|
| 6084. |
Eight dipoles of charges of magnitude e are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 6085. |
A sound wave travels from air to water. The angle of incidence is alpha_1, and the angle of reflection is alpha_2. If the Snell.s law is valid, then ...... |
|
Answer» `alpha_1 = alpha_2` Angle of reflection r = `alpha_2` Here Snell.s LAW will be obeyed. `therefore n_A sin alpha_1=n_w sin alpha_2` `therefore (sinalpha_1)/(sin alpha_2)=(n_w)/(n_A)`….......(1) Now `(n_w)/(n_A)=(C//v_w)/(C//v_A)=(v_w)/(v_A) lt 1` `v_A lt v_w` .......(2) (The velocity of sound in WATER is more than th velocity of sound in air) From equation (1) and (2), `(sin alpha_1)/(sin alpha_2) lt 1 = sin alpha_1 lt sin alpha_2` `therefore alpha_1 lt alpha_2` (sin function is increasing function) |
|
| 6086. |
Seperated p-type semiconductor is electrically ……… |
|
Answer» POSITIVELY CHARGED |
|
| 6087. |
Name the electromagnetic wave that have frequencies greater than those of ultraviolet light by less than those of gamma-rays. |
| Answer» Solution :The WAVELENGTH RANGE for the VISIBLE part of a electromagnetic SPECTRUM is `3900^@ A` to `7600^@ A` | |
| 6088. |
Find the total flux due to charge q associated with the given hemispherical surface |
|
Answer» `(a) Q/(2 in_0) , (B) 0, (c) q/(in_0), (d) 0, (e) 0` |
|
| 6089. |
When CdCl_2, is added to AgCl, it shows |
|
Answer» Impurity |
|
| 6090. |
In the given figure, the radius of curvature of curved surface for both the plano-convex and plano-concave lens is 10 cm and refractiveindex for both is 1.5. The location of the final image after all the refractions through lenses is |
|
Answer» Solution :The focal length of the plano-convex lens is `1/f = (1.5-1)(1/(+10)- (1)/(oo)) = 1/20` Focal length of plano-concave lens is `1/f =(1.5-1) (1/oo - 1/10) = (-1)/(20)` SINCE parallel beams are incident on the lens, its image from plano-concave lens will be formed at `+20` cm from it (at the FORCUS) and will act as an object for the plano-concave lens. Since the two lens are at a distance of `10 cm` fromeach other, therefore, cor the next lens`u= +10cm`. `:.V = (uf)/(u+f) = (10 xx 20)/(10 - 20) = 20 cm` |
|
| 6091. |
Maxwell from his studies concluded that an electric field and a magnetic field changing with time in a direction perpendicular to each other produce a diusturbance which propagets in a direction perpendicular to both the fields. This disturbance is called electromagnetic wave. The em wave is of transverse nature. The velocity of em wave in vacuum is c=1/(sqrtmu_0in_0) where mu_0= magnetic permiability of free space and in_0 =electric permittivity of free space. The wavelength of e.m. wave varies over a wide range from 10^(-14) to 10^3m. The em wave of different wavelengths travel with same speed in vacuum but move with different speeds in any medium. (i) What are the various e.m wave invisible to eye whose wavelength is lower than the smallestwavelength of visible light? (ii) How do you conclude that white lighttravels in vacuume with a speed 3xx10^8ms^-1? (iii) What do you learn from the above study? |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The invisible e.m. WAVE whose wavelength is LESS than the smallest wavelength of VISIBLE light are ultraviolet radiations, x-rays and `gamma`-rays. (II) The white light is an e.m. wave. The speed of e.m. wave in vacuum is given by `c=1/(sqrtmu_0in_0)`, where mu_0 =4pixx10^-7TmA^-1 and in_0=1/(4pixx9xx10^9)C^2N^-1m^-2` `:. c=1/(sqrt((4pixx10^-7) 1/((4pixx9xx10^9))))=3xx10^8ms^-1` (iii) From the above study, we find that nature/God that created all human beings alike. When they are exposed to DIFFERENT environments of the world and family, their thinking/views/speeds become different. God wants us to live in peace treating everyone as equal. |
|
| 6092. |
A charge q kept in front of a neutal metallic sphere. Find the electric field at the centre of sphere due to the induced charges on the surface of the sphere shown. The net electric field inside the conductor is zero. This is produced by induced charged and the external charge. |
| Answer» Solution :`E_("induced") + E_(q) = 0 RARR E_("indcued") = (q)/(4 PI epsilon_(0)d^(2))` | |
| 6093. |
Ampere second is the unit of |
|
Answer» power |
|
| 6094. |
An atom possesing the total angular momentumħvv6 is in the state with spin quantum number S=1. In the corresponding vector model the angle between the spin momentum and the total angular momentum is theta= 73.2^(@).Write the spectral symbol for the term that state. |
|
Answer» Solution :Total angular momentum ` ħsqrt(6)` means `J=2`. It is gives that `S=1` This means that `L=1,2 or 3`. From vector model RELATION `L(L+1) ħ^(2)=6 ħ^(2)+2 ħ^(2)sqrt(6)sqrt(2) COS 73.2^(@)` `=5.998 ħ^(2)~~6 ħ^(2)` THUS `L=2` and the spectral symbol of the STATE is `.^(3)D_(2)` |
|
| 6095. |
(a) (i) 'Two independent monochromatic sources light cannot produce a sustained interference pattern.' Give reasons. (ii) Light waves each of amplitude "a" and freuency "omega", emanating from two coherent light sources superpose at a point. If the displacement due to these waves is given by y_(1)=acosomegat and y_(2)=acos(omegat+phi) where phi is the phase difference between the two, obtain the expression for the resultant intensity at the point. (b) In Young's double-slit experiment, using monochromatic light of wavelength lamda, the intensity of light at a point on the screen where path difference is lamda, is K units. Find out the intensity of light at a point where path difference is lamda//3. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) (i) To produce a sustained interference pattern the SOURCES of light must be COHERENT sources. HOWEVER, two independent monochromatic sources of light can never be coherent and so cannot produce a sustained interference pattern. | |
| 6096. |
मानाf_k (x)=1/{k(sin^k x +cos^k x),जहा x in R.तथा kge1 तबf_4(x)-f_6(x) बराबर है |
|
Answer» `1/4` |
|
| 6097. |
Which of the following is best metal for photoelectric emission? |
|
Answer» Sodium |
|
| 6098. |
Gravitation is universally applicable as it does not depend on nature of weight or the medium, |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6099. |
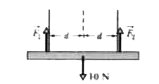
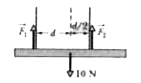
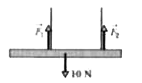
A horizontal uniform bar of weight 10 N is to hang from a ceiling by two wires that exert upward forces vec(F)_(1) and vec(F)_(2) on the bar. The figure shows four arrangements for the wires. Which arrangements, if any, are indeterminate (so that we cannot solvet for numerical values of vec(F)_(1) and vec(F)_(2)) ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 6100. |
Suppose you have three resistors each of value 30OmegaList all the different resistances you can obtain. |
| Answer» Solution :`10 OMEGA , 20 Omega, 45 Omega, 90 Omega` | |