Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 6701. |
The surface energy of a liquiddrop is u . If it is split into 1000 equal droplets , then itssurface energy becomes . |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 6702. |
Assume that temperature varies linearly with height near the Earth.s surface. Considering temperature at the surface of the Earth T_(1)and T_2 at a height h above the surface, calculate the time / needed for a sound wave produced at a height x to reach the Earth.s surface. Velocity of sound at the Earth.s surface is c. |
|
Answer» `t = (2h)/c sqrt(T_(1))/(T_(2)-T_(1))[sqrt(T_(1)) - sqrt((T_(2)-T_(1))/H) xx + T_(1)]` |
|
| 6703. |
In the previous question, the directions of the curent flow in the ring when M is above R and below R will be |
|
Answer» the same in all cases |
|
| 6704. |
A coil of inductance 0.50 H and resistance 100 Omega is connected to a 240 V, 50 Hz AC supply. (a) What is the maximum current in the coil ? (b) what is the time lag between the voltage maximum and current maximum ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION : (a) For LR circuit inductance, L = 0.50 H Resistance, R = 100 `Omega` RMS value of voltage , `E_(rms ) = 240 `V Freqeuency, f = 50 Hz angular frequency,` omega = 2 pi` f `I_(0) = (E_(0))/(sqrt(R^(2) + L^(2) omega^(2)))= (sqrt(2) xx E_(rms))/(sqrt(R^(2) + L^(2) (2 pi v)^(2)))` = ` (sqrt(2) xx 240)/(sqrt(10^(4) + (0.5)^(2) xx 4 pi^(2) xx 2500)) ` = 1.82 A (b) RL circuit, instantaneous voltage is ` E = E_(0) cos omega t` Instantaneous current is `I - I_(0) cos (omega t - phi) ` at t = 0 `E = E_(0) ` (maximum voltage ) Att ` = (phi)/(omega)` I = `I_(0)` (maximum current ) THEREFORE, time lag BETWEN maximum voltage and maximum current instant is `(phi)/(omega)` Now tan `phi = (omega L)/(R)` = `(2pi xx 50 xx 0.5)/(100) `1.571 `or"" phi = tan^(-1) ( 1.571) = 57.5 ` time lag = `(phi)/(omega) = (57.5 pi)/(180 xx 2 pi xx 50) = 3.2 ` ms |
|
| 6705. |
राजस्थान के बीकानेर फलोदी और बाड़मेर में पीने का पानी संग्रहित करने के लिए लोग इनमें से कौन से तरीके अपनाते हैं? |
|
Answer» टांका |
|
| 6706. |
(A) : An inductor and a capacitor are called low pass filter and high pass fileter respecitvley. (R): Reactance of an inductor is low for low frequency signals and that of a capacitor is high for high frequency signals. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 6707. |
A ray of light incident on a prism of angle 60^(@), does not emerge out. Refractive index of material of prism may be |
|
Answer» `1.50` |
|
| 6708. |
Let S_(1) and S_(2) be the two slits in Young.s doubleslit experiment. If central maxima is observedat P and angle angleS, P_(2)= thetathen the fringe width for the light of wavelength lambda will be (assume thetato be a small angle ) |
|
Answer» `lambda//theta ` |
|
| 6709. |
To know the presence of charge on a substance......is used. |
|
Answer» stethoscope |
|
| 6710. |
A telescope of diameter 2 m uses light of wavelength 5000 Å for viewing stars. The minimum angular separation between two starts, whose image is just resolved by this telescope, is |
|
Answer» `4.0xx10^(-4)RAD` |
|
| 6711. |
The potential energy function for the force between two atoms in a diatomic molecule is approximately given by U(x)=a/(x^(12))-b/(x^(6)), where a and b are constants ans x is the distance between the atoms. If the dissociation energy of the molecule is D = [U(x = oo) - U_(at) equilibrium], D is : |
|
Answer» `(b^(2))/(6a)` `F=(DU)/(DX)=0` (at equilibrium) `rArrx^(6)=2a//b` or `D=(b^(2))/(4a)` So correct choice is (d). |
|
| 6712. |
The dimensions of thermal resistance are : |
|
Answer» `ML^(2)T^(-2)K^(-2)` `R_(H)=((T_(1)-T_(2)))/((DQ)/(dt))=(K)/("ML"^(2)T^(-3))=[M^(-1)L^(-2)T^(3)K]` correct choice is (d). |
|
| 6713. |
(a) Why do the 'free electrons' , in a metal wire , flowing by themselves' not cause any current flow in the wire ? Define drift velocity' and obtain an expression for the current flowing in a wire, in terms of the 'drift velocity of the free electrons. (b) Use the above expression to show that the 'resistivity ' of the material of a wire is inversely proportional to the 'relaxation time' for the 'free electrons ' in the metal. |
|
Answer» Solution :At room temperature, free electrons move with velocities of the order of `10^5ms^-1`. However , these velocities are distributed randomly in all directions. There is no preferred direction of motion. On the average, number of electrons travelling in any direction will be equal to number of electrons travelling in the opposite direction. If `vecu_1,vecu_2,....vecu_N` are the randsom velocities of N free electrons, then average velocity of electrons will be `vecu=(vecu_(1)+vecu_2+......vecu_N)/(N)=0`. It may be defined as the average velocity gained by the free electrons of a CONDUCTOR in the opposite direction of the externally applied electric field. Suppose a potential difference V is applied across a conductor of length l and of uniform cross-sectionA. The electric field E set up inside the conductor is given by `E=(V)/(I)` Let the number of electrons per unit volume of electron density =n Change on an electron =e 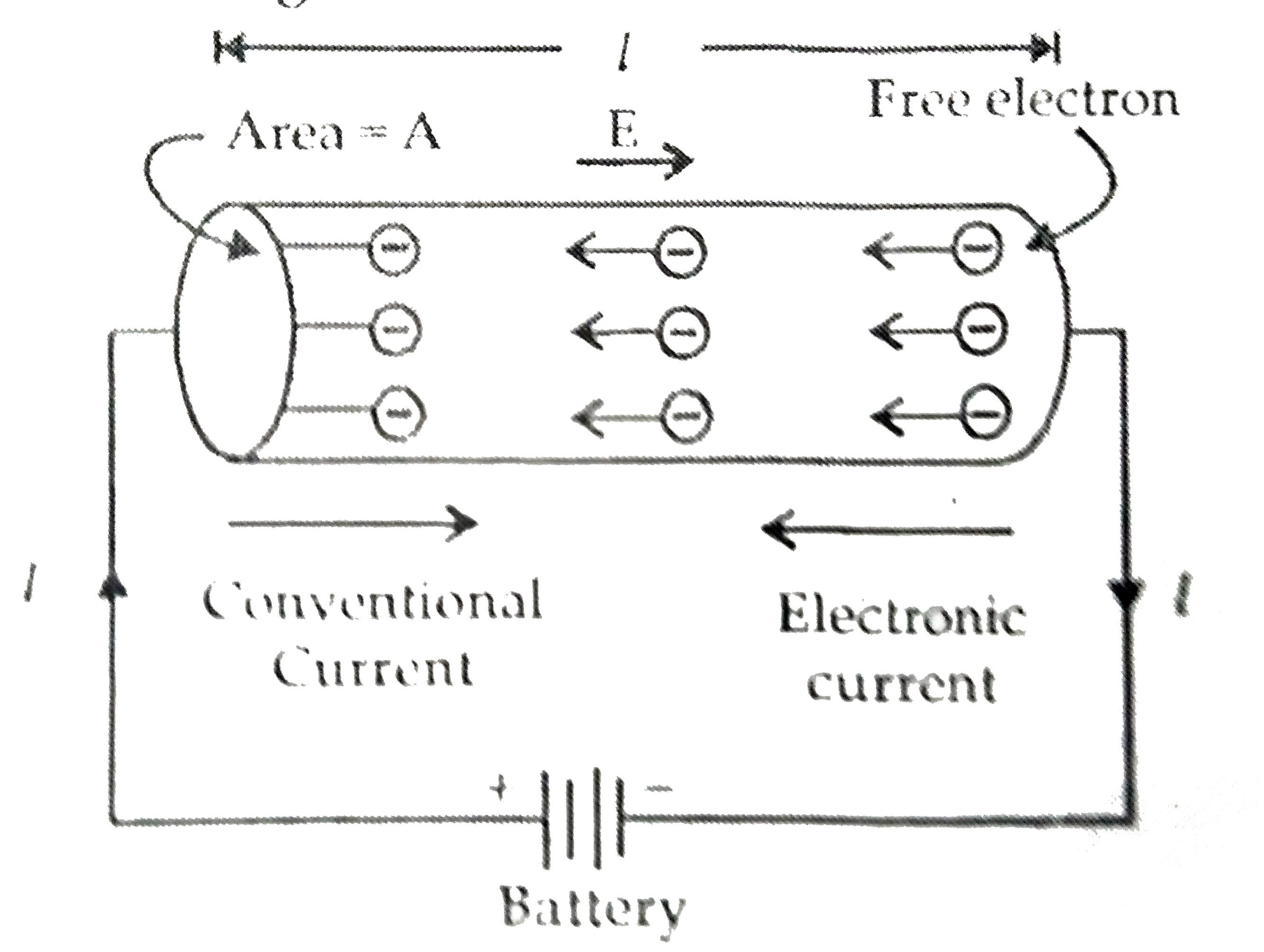 (b) Number of electrons in length l of the conductor `nxx ` volume of the conductor is Total CHARGE contained in length l of the conductor is ` q=` en Al All the electrons which enter the conductor at the right end will pass through the conductor at the left end in time, `t= ("distance")/("velocity")=(l)/(upsilon_d)` ` therefore" Current" I=(q)/(t)=(enAl)/(l//epsilon_d) or I=enAv_d` or `(V)/(I) =(ml)/(ne^2tauA)` At a fixed temperautre , the quantities `m,l,e,tau, and A`, all have constant values for a given conductor. Therefore , `(V)/(I)=` a constant, R This proves Ohm's law for a conductor and here `R=(ml)/(ne^2tauA)` is the resistance of the conductor. Resistivity in terms of electron density and relaxation time. The resistance R of a conductor of length l, area of cross-section A and resistivity `RHO` is given by `R=rho(l)/(A)`. But `R=(ml)/(ne^2tauA)` where, `tau` is the relaxation time. Comparing the above two equations, we GET `rho=(m)/(ne^2tau)`. |
|
| 6714. |
A short magnetic dipole of pole strength 200 Am and dipole moment 10 Am^2 has length of : |
|
Answer» 5 cm |
|
| 6715. |
Give Einstein's explanation of photoelectric effect. |
|
Answer» Solution :Einstein assumed that one photoelectron is liberated from a metal surface when one photon of suitable frequency is incident on it. Consider a photon of frequency v and energy hv incident on a photo sensitive metal. The energy of photon is spent in liberating electrons. (i) Since the collision between an electron and a photon is treated as the collision between two particles, the process is instantaneous. (ii) If `E = hv` represents the incident photon energy and .w. is the minimum energy required to just liberate the electron from the surface and K.E. is the kinetic energy of electron then `E= w + K.E. ` or `hv = hv_(0) + "K.E." rarr (1)` This is known as the P.E. equation. For K.E.`= 0, hv = hv_(0) = w.` Therefore for every metal surface there exists minimum energy of the electron above which electron is liberated. The CORRESPONDING frequency is called the threshold frequency and the minimum energy corresponding to v is known as the work function. (III) K.E. `=1/2mv^(2)` `1/2mv^(2) = hv - hv_(0)` `11/2 mv^(2) = H(v-v_(0))` 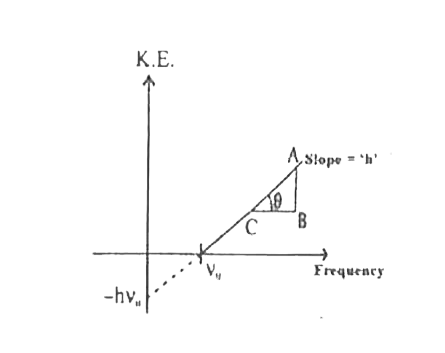 `therefore` K.E. and hence velocity of photoelectron depends on the frequency of incident radiation above the threshold frequency `(v_(0))` but not on the intensity of incident radiation. (iv) For a particular negative potential of the anode, photoelectrons do not reach the anode. Hence P.E. current`= 0`. This -ve potential of the anode for which PEI` = 0` is known as stopping potential. 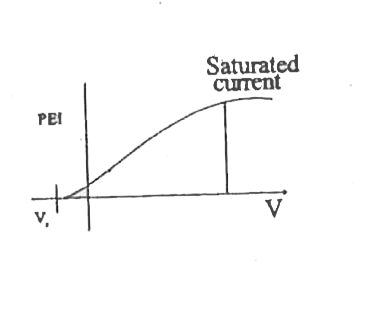 (v) For `vlt v_(0) , 1/2 mv^(2) = -ve ` which is absurd `therefore` P.E.E. cannot TAKE place for a frequency less than the threshold frequency. (vi)Photo electrons will be ejected in large numbers when intense radiation is incident because intense radiation contains more photons resulting in more INTERACTIONS. |
|
| 6716. |
Assertion (A) : An induced emf is generated across the two ends of a solenoid coil when a magnet is withdrawn from the solenoid coil. Reason (R) : The relative motion between magnet and the solenoid coil induces an emf. |
|
Answer» If both assertion and reason are TRUE and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. |
|
| 6717. |
A system is shown in figure. Blocks 2 & 3 kg are at rest then co-efficient of friction between 2 kg & incline is |
|
Answer» `2//sqrt(3)` |
|
| 6718. |
A capillary tube of the radius 0.5 mm is immersed in a beaker of mercury . The level inside the tube is 0.8 cm below the level in beaker and angle of contact is 120^@. What is the surface tension of mercury , if the mass density of mercury is rho= 13.6 xx 10^3 kg m^3and acceleration due togravity is g = 10 m s^(-2) ? |
|
Answer» `0.225 "N m"^(-1)` |
|
| 6719. |
Why are short waves used in long distance broadcasts? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The short wves (wavelength less than 200 m and greater than 1500 KHz) are absorbed by earth due to their high FREQUENCY but are effectively reflected by F layer in ionosphere. After reflection from ionosphere, the SHORTWAVES REACH the surface of the earth BACK only at a large distance from the transmitter. For this reason, shortwaves are used in long distance transmission. | |
| 6720. |
(c) If magnetic monopoles existed, how would the Gauss's law of magnetism be modified ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(c) If magnetic monopoles WOULD have existed then Gauss.s law for magnetism COULD have been written as `oint OVERSET(to) (B) . overset(to) (d) a = mu_(0)(sum_(q_(m) ) )` (Where `sum_(q_m) =` net pole strength, enclosed by considered Gaussian surface) (Note : Above law is analogous to Gauss.s law `oint overset(to) (E) . overset(to) (d) a = (sum_(q) ) /( in_0)` for electrostatics) |
|
| 6721. |
An accelerated charge can produce electromagnetic waves . why ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :An ACCELERATED CHARGE has both TIME varing ELECTRIC. | |
| 6722. |
The velocity of the wave v depends uponthe wave length, density of water 'd' and acceleration due to gravity g Then : |
|
Answer» `v^(2)=Klambda^(-1)G^(-1)d^(-1)` `M^(0)L^(1)T^(-1)=[L^(1)]^(a)XX[L^(1)T^(-2)]^(b)xx[ML^(-3)]^(c )` `=M^(c )L^(a+b-3c)T^(-2b)` THUS `c=0,-2b=-1` or `b=(1)/(2)` `a+b-3c=1` or `a=1-(1)/(2)=(1)/(2)` Hence `v=Klambda^(1/2)g^(1/2)d^(0)` `v^(2)=Klambdag` Hence correct choice is `(c )`. |
|
| 6723. |
Obtain the amount of " "_(27)^(60)Co necessary to provide a radioactive source of 8.0 mCi strength. The half-life of " "_(27)^(60)Co is 5.3 years. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here activity R= 8.0 mCi =`8.0 xx 10^(-3) xx 3.7 xx 10^(10)` BQ=`2.96 xx 10^(8)`Bq and disintegration constant `lambda=0.6931/T_(1/2)=0.6931/(5.3xx3.154xx10^(7))s^(-1)` From the relation R=`lambda`N, we find `N=R/lambda = (2.96xx10^(8) xx5.3xx3.154 xx 10^(7))/0.6931 =7.14 xx 10^(16)` atoms `therefore` Amount of `" "_(27)^(60)CO approx=(Nxx60)/(6.023xx10^(23))g=(60xx7.14xx10^(16))/(6.023xx10^(23))g = 7.126 xx 10^(-6)`g |
|
| 6724. |
In order that a thin oil film on the surface of water may show the changes in color, its thickness should be of the order of : |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 6725. |
A charged capacitor of capacitance C is discharged through a resistance R. A radio active sample decays with an average life t. Find R interns of C and t in order that the ratio of the electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor to the activity of the radio active sample remains constant with time |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 6726. |
In a two tourmalines experiment, the polariser and analyser are crossed with each other. At what angle should the analyser be rotated so that 25% of light passes through analyser ? |
|
Answer» `60^(@)` `I=I_(0) cos^(2) theta"" [ I=I_(0),25%=(I_(0))/(25)]` `(I_(0))/(4)=I_(0) cos^(2) theta` `(1)/(2) cos theta :. theta=60^(@)` `:.` Analyswer should be ROTATES at `(90^(@)-60^(@))=30^(@)` angle. |
|
| 6727. |
Find the time constant (in mu s) for the given RC circuits in the given order respectively. R_(1) = 1 omega, R_(2) = 2 omega, C_(1) = 4muF, C_(2) = 2mu F |
|
Answer» `18, 4, (8)/(9)` (i) `tau_(1) = (2 + 1)(2 + 4) = 18 mus` (ii) `tau_(2) = ((2xx 1)/(2 + 1)) ((2 XX 4)/(2 + 4)) = (8)/(9)mus` (iii) `tau_(3) = ((2 xx 1)/(2 + 1)) xx (4 + 2) = 4 MU s` |
|
| 6728. |
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity due to the presence of- |
|
Answer» LONE PAIR of electrons |
|
| 6729. |
A string is stretched between fixed points separated by 75 cm. It is observed to have a resonant frequencies of 420 Hz and 315 Hz. There are no other resonant frequences between these two. Then the lowest resonant frequency for this string is : |
|
Answer» 105 Hz `rArr"" v_(1) = (315)/(3) = `105HZ. so correct choice is (a) . |
|
| 6730. |
A moving particle of mass m makes a head on elastic collision with a particle of mass 2 m which is initially at rest. What fraction of energy of the colliding particle is lost after collision ? |
|
Answer» `8//9` `mu+0=mv_1+2 mv_2` or `u-v_1=2 v_2` ALSO by conservation ENERGY `1/2"mu"^2=1/2mv_1^2+1/2(2m)v_2^2` or `u^2=v_1^2=2v_2^2` or `(u-v_1)(u+v_1)=2 v_2^2` From these eqns.`u+v_1=v_2`.Now eliminating `V-2`, we GET `v_1=1//3u` Fraction LOST =`(1/2"mu"^2-1/2mv_1^2)/(1/2mu^2)` =`(u^2-(-1//3u)^2)/(u^2)=(1-1/9)=8//9` |
|
| 6731. |
Calculate the smallest angle resolved by a telescope with an objective of 5.0m diameter. What minimum magnification is needed to enable the human eye to utilize the resolution? (Aperture of the eye =2.5 mm, lambda= 5500 dotA). |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, `lambda 5500 dotA= 5500xx 10^(-10)m` apertureof objective `a_(0) = 5.0m` Aperture of eye, `a_(a)= 2.5mm = 2.5xx 10^(-3)m` `triangle theta = 1.22(lambda)/(a)= 1.22((5500xx10^(-10)m)/(5M))= 1.34xx 10^(-7)RAD` Minimum MAGNIFICATION needed, `M_(0)= ("aperature of the objective "(a_0))/("aperature of the eye "(a_a))= (0.5m)/(2.5xx 10^(-3)m)=2000`. |
|
| 6732. |
A beam of unpolarised light is incident, on the boundary between two transparent media, at an angle of incidence =i_B,the Brewester's angle. At what angle does the reflected light get polarised ? |
| Answer» Solution :When reflected WAVE is PERPENDICULAR to refracted wave it is COMPLETELY POLARIZE. | |
| 6733. |
When the voltage applied to and X-ray tube is increases from V_(1)=10KV "to" V_(2)=20kV, the wavelength difference between the K_(alpha) line and short wavelengthlimit of the continuous X-ray spectrum increases by a factor 3. The atomic number of the element of which the tube anticathode is made will be |
|
Answer» 62 `:. (12375)/(10.2 (Z-1)^(2))-(12375)/(20xx10^(3))=3[(12375)/(10.2(Z-1)^(2))-(12375)/(10xx10^(3))]` Solving , we get =29 |
|
| 6734. |
Find the resultant of the vectors shown in figure. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`vecR = vec(OA) + vec(AB) + vec(BC)` `vecR = (5cos 37 hati + 5 sin 37 hatj) + 3HATI + 4hatj` `vecR = 4hati + 3hatj+ 4hatj` `vecR = 7hati + 7hatj, THEREFORE R = 7sqrt(2)` cm and `alpha = 45^(@)` with horizontal. |
|
| 6735. |
A small block of mass m and a concave mirror of radius R fitted with a stand, lie on la smooth horizontal table with a separation d between them. The mirror together with its stand has a mass m. The block is pushed at t=0 towards the mirror so that it starts moving towards the mirror at a constant speed V and collides with it. The collides is perfectly elastic. Find the velocity of the image (a) at a time tltd//V (b) at a time tgtd//V. |
|
Answer» `(-R^(2)V)/([2(d-Vt)-R]^(2)),V[1+(R^(2))/([2(Vt-d)-R]^(2))]` |
|
| 6736. |
If solar constant is equal to 2 cal ("minute")^(-1) cm^(-2), itsvalue in S.I. system is |
|
Answer» `1400 WM^(2)` |
|
| 6737. |
COLUMN-I (A) Angle of projection (B) Angle of velocity horizontal after 4 s (C) Maximum height (D) Horizontal range COLUMN-II (P) 20 m (Q) 80 m (R) 45^@ (S) tan^(-1)(0.5) |
|
Answer» Given `y-x^(2)/(80)," comparing it with y"=x TAN THETA-(qx^(2))/(2u^(2) cos^(2) theta)" we have tan theta=1 rArr theta=45^(@)` We have `(2u^(2) cos^(2) theta)/(g)=80 rArr (2u^(2) (1//2))/(10)=80. ("where "theta " angle of projection & U: velocity of projection")` `rArr u^(2)=800 rArr u=20sqrt2m//s rArr u_(x)=u cos theta=20m//s and u_(y)=u sin theta =20m//s` `rArr" after 4 sec ", v_(y)=u_(y)+a_(y)t=20-40=-20m//s` `rArr` angle made by velocity vector with horizontal `=tan^(-1)""(v_(y))/(u_(x))=45^(@)`below horizontalMaximum height `=(u_(y)^(2))/(2g)=20m"Horizontal range "=(2u_(x)u_(y))/(g)=(2 XX 20 xx 20)/(10)=80` |
|
| 6738. |
Two persons A and B are located in X-Y plane at the points (0,0) and (0,10) respectively, The distances are measured in MKS unit. At a time t = 0, they start moving simultaneously with velocities vec v_(A) = 2hatj ms^(-1) and vec v_(B) = 2hat i ms^(-1) respectively. The time after which A and B are at their closest distance is |
|
Answer» (a) 2.5 s Distance `d =sqrt((0 - V_(B)t)^(2) + (V_(A)t - 10)^(2))` `RARR d =sqrt((2t^(2) + (2t - 10)^(2))` ` rArrd^(2) = 4T^(2) + 4t^(2) - 40t + 100` `rArr d^(2) = l = 8t^(2) - 40t + 100` `rArr dl/(dt) = 16t - 40` `dl/(dt) = 0` `rArr 16t - 40 = 0` `:. t = 40/(16) = 2.5 s` 
|
|
| 6739. |
Two convex lenses of focal lengths 2f and f are arranged to from an eye-piece and are spaced by f. The first lens is to be used as field lens and the second one as eye-lens. Find (a) equivalent focal length. (b) See whether it is positive or negative eye-piece. (c) Whether it is free from spherical aberration and chromatic aberration? (d) What will be the disadvantage it f is used as field lens? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6740. |
A person sits near the edge of a circular platform revolving with a uniform angular speed. What will be the change in the motion of the platform ? What will happen when the person starts moving from the edge towards the centre of the platform ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The SYSTEM tends to keep it.s ANGULAR momentum constant. When the person sits NEAR the edge of the platform. | |
| 6741. |
On the basis of the uncertainty particle ,it can be proved that …. |
|
Answer» ELECTRON EXIST INSIDE the nucleus. |
|
| 6742. |
An aluminium cube with 1 cm edge is subjected to hydrostatic stress. What force acts on each face if the decrease in the volume is 1 percent? |
|
Answer» `F = KS epsilon = KS |(DeltaV)/V|` . |
|
| 6743. |
Find the equivalent resistance between A & B in the given network |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`R(r+3R)/(4(R+r))` | |
| 6744. |
Dimensions of in_(0)mu_(0) are : |
|
Answer» `[LT^(-1)]` `:. mu_(0)epsilon_(0)=(1)/(C^(2))=L^(-2)T^(2)` Hence CORRECT CHOICE is `(d)`. |
|
| 6745. |
माना एक फलन f: RrarrR में f(x) = x-2द्वारा परिभाषित है तब f^(-1)(x)होगा |
|
Answer» `x-2` |
|
| 6746. |
What are the types of biasing in a diode ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :TWO, FORWARD and REVERSE BIASING. | |
| 6747. |
Assertion: Coulomb force is a long range force. Reason:Coulomb force acts between two charged bodies only |
|
Answer» Both Assertion and Reason are TRUE and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion |
|
| 6748. |
Consider four independent trials in which an event A occurs with probability 1/3 in any single trial. The event B occurs with probability 1 if the event A occursat least twice,it cannotoccur if the event A does not occur and it occurs with probability 1/2 if the event A occurs onlyonce. If the probability p of the occurrence of event 'B' can be expressed as m/n ,then the least value of (m + n), where m, n in N, is |
|
Answer» <P> P(B)=0 if the event'A' does not occur `P(B)=1/2` If 'A' occurs once `P(B)=.^4C_1(1/3)(2/3)^2(1/2)+(.^4C_2(1/3)^2(2/3)^2 + .^4C_3(1/3)^3 (2/3)^1 + .^4C_4(1/3)^4)(1)` `=49/81` |
|
| 6749. |
The number of turns of a solenoid are doubled without changing its length and area of cross-section. The self-inductance of the solenoid will become .......times. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6750. |
A tuned amplifier circuit is used to generate a carrier frequency of 2MHz for the amplitude modulation. The value of sqrt(LC) is |
|
Answer» `(1)/(2 PI xx 10^(6))` |
|