Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 3551. |
If L = (20pm 0.01 ) mand B = (10pm 0.02) m then L/B is |
|
Answer» `(2PM 0.03)m` |
|
| 3552. |
A mark at the bottom of a liquid appears to rise by 0.1 m. The depth of the liquid is 1m. The refractive index of the liquid is |
|
Answer» `1.33` |
|
| 3553. |
What was grandmother's view for music? |
|
Answer» It was for BEAUTIFUL people |
|
| 3554. |
Mention the function of the following used in the communication system (i) Transducer (ii) Transmitter |
| Answer» Solution :I) Transducer. The device that CONVERTS ONE form of energy in to another is called tranducer. II) TRANSMITTER- A transmitter transmits the infor | |
| 3555. |
If polarising angle of air glass interference is 56.3^@. What is the angle of refraction in glass ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :As `i_p+r_p=90^@`, `r_p=90-i_p=90-56.3^@=33.7^@` |
|
| 3556. |
Explainthe workingof a semiconductor diode when it is forward biased. Draw the I-V characteristics for both forward bias and reverse bias of a semiconductordiode. |
Answer» Solution :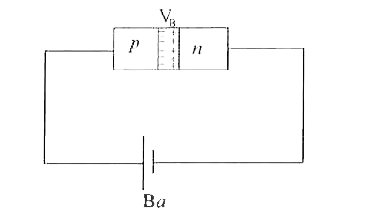 When the +ve terminal of a BATTERY is connected to the p regionand the -ve terminal battery is connected to the n-regionof the junctiondiode ,then the p-n junctionis SAID to be forward biased. When a batteryis connected across the p-n junction diode , a p.d of .v. volt is applied across the diode . The resistance of depletionregion is very high as it has no free charge carriers.As a RESULT of this ,the potentialbarrier height is reduced and width of deplectionlayer is decreased. The +ve potential of the p-regionattracts the electrons from the n-regions and the -ve potential of the n-region ATTRACTS the holes from the p-region. Due to these , the diffusionof majority carriers takes place across the junction . Thus an electric currentwill flow due to migrationof majoritycarriersacross the p-n junction, which is called forward CURRENT. 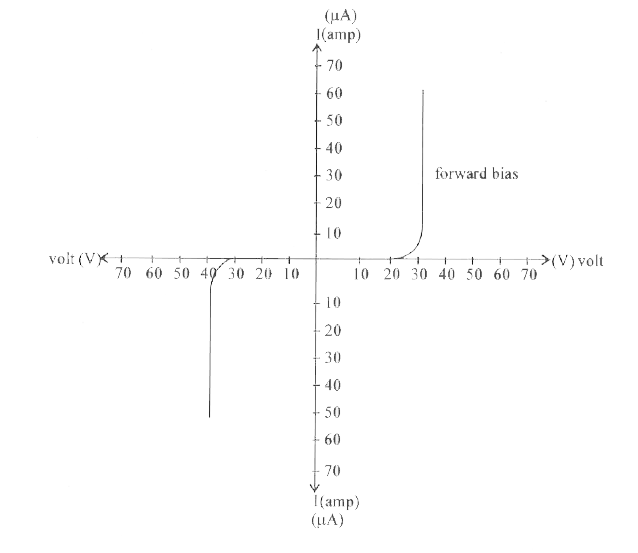
|
|
| 3557. |
The prism shown in the figure has one side silvered. The angle of the prims is 30^(@) and mu=sqrt(2). What should be the angle of incidence, if the incidence ray retraces its initial path? |
|
Answer» `50^(@)`  In `DeltaAED` `30^(@)+90^(@)+/_D=180^(@)` `/_D=60^(@)` ALSO `/_D+/_r=90^(@)` `/_r=90^(@)-60^(@)~=30^(@)` From shell's law `1 sin i =(sqrt(2))sin 30^(@)` `i=sin^(-1)(1/(sqrt(2)))` `i=45^(@)` |
|
| 3558. |
In the figure given below, the position - time graph of a particle of mass 0.1 kg is shown. Find impulse at t=2sec. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`v=(DX)/(dt)=4/2 = 2m//s ` velocity between t=0 sec to t =2 sec = 2 m/s velocity at 2 sec = 0 m/s Impulse = change in LINEAR momentum `=m(V_f - V_i) =0.1(0-2) = -0.2 kg ms^(-1)` 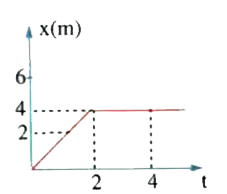
|
|
| 3559. |
On a hot summer night, the refractive index of air is smallest near the ground and increases with height from the ground. When a light beam is directed horizontally, the Huygens. principle leads us to conclude that as it travels, the light beam 1...... |
|
Answer» becomes narrower  Assume a PLANAR wavefront moving in horizontal direction. Its DIFFERENT PARTS will move with different SPEEDS during its motion. Speed in rarer medium will be more and that in denser medium will be less hence its shape will be as shown. |
|
| 3561. |
Consider the following statements in case of Young's double slit experiment.1. A slit S is necessary if we use an ordianry extended source of light. 2. A slit S is not needed if we use an ordinary but wellcollimated beam of light. 3. A slit S is not needed if we use a spatially coherent source of light Which of the above statements are correct? |
|
Answer» 1, 2 and 3 |
|
| 3562. |
Name the colors corresponding to the digits 4 and 7 in the color code scheme for carbon resistors. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`4 to ` YELLOW `7 to ` VIOLET |
|
| 3563. |
A particle has mass 10^(-27)kg. This is moving with a speed of 107 m//s. The wavelength associated with the particle is "__________". |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 3564. |
In the circuits shows in S_(1) and S_(2) are switches. S_(2) remains closed for a long time and S_(1) is opened. Now S_(1) is also closed. Just after S_(1) is closed, find the potential difference (V) across R and di//dt (with sign) in L. |
Answer»  For LEFT LOOP: `varepsilon = i_(1) R + L(di)//dt)` (i) For right loop: `varepsilon = i_(2)(2R) + L(di//dt)` (II) and `i_(1) + i_(2) = i` (iii) Solve to get `(di)/(dt) = (2varepsilon)/(3L)` p.d.across `R: V_(R) = i_(1)R = varepsilon - L(di//dt) = varepsilon - L ((2 E)/(3L)) = (varepsilon)/(3)` |
|
| 3565. |
Define mutual inductance of a pair of coils and write its SI unit. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3566. |
A parallel beam of white light falls on a convex lens. Images of blue,yellow and red light are formed on other side of the lens at a distance of 0.20 m, 0.205 m and 0.214 m respectively. The dispersive power of the material of the lens will be |
|
Answer» `619/1000` |
|
| 3567. |
A fully charged capacitor has a capacitance· C. Itis discharged through a small ,coil of - resistance wire embedded in a thermally insulated block of specific heat capacity s andmass. If the temperature of the block is raised by DeltaT, the potential difference V across the capacitance is ...... . |
|
Answer» `(msDeltaT)/(C)` `:. (1)/(2) CV^(2)= msDeltaT` `:. V^(2)= (2msDeltaT)/(C)` `:. V =sqrt((2msDeltaT)/(s))` |
|
| 3568. |
A convex lens is used to obtain a magnified image of an object on a screen . The object is at a distance 10 m from the lens . If the magnification is 19. the focal length of the lens is |
|
Answer» 9.5 CM |
|
| 3569. |
Find out the value of x so that the image will form on object itself. |
|
Answer» Solution :`1/f_(eq)=1/f_(m)-2 {(0.5) (1/10+1/10)}` `rArr 1/f_(eq)=1/oo-2/10` `rArr f_(eq)=-5 cm` The SYSTEM is equivalent to a CONCAVE mirror of focal length 5 cm Object must be at the centre of CUVATURE `:. x=2(5)=10` cm 
|
|
| 3570. |
Assertion : Binding energy per unit nucleon increase in atomic mass number . Reason : Density of nucleus increases with increase in mass number. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3571. |
A motorbike starts from the origin and moves over an xy plane with acceleration components a_(x)=6.0m//s^(2)anda_(y)=-3.0m//s^(2). The initial velocity of the motorbike has components v_(0x)=12.0m//sandv_(0y)=18.0m//s. Find the velocity of the motorbike, in unt-vector notation, when it reaches its greatest y coordinate. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`(48m//s)HATI` | |
| 3572. |
If the area of a square is (100+-0*2)cm^(2) then the side of the square is : |
|
Answer» `(10+-0*1)CM` `impliesA=100cm^(2)` and `DELTAA=0*2cm^(2)` `:.` Side of square `(l)=10cm` As `A=l^(2)` `(DeltaA)/(A)=2(DELTAL)/(l)` `Deltal=(DeltaA*l)/(2A)=(0*2xx10)/(2xx100)=0*01` cm. So the correct choice is `(c )`. |
|
| 3573. |
Vibrations are produced in a vertical tube of length 150cm closed at one end by a tuning fork of frequency 340 Hz. Now water is filled slowly in the tube. IF the speed of sound in air is 340 m//s then the minimum height of water required for resonance is: |
|
Answer» 90cm |
|
| 3574. |
Assertion :Lines of force are perpendicular to conductor surface. Reason : Generally electric field is perpendicular to equipotential surface. |
|
Answer» If both assertion and REASON are TRUE and reason is the CORRECT explanation of assertion. |
|
| 3575. |
Electrons are transferred from the material whose ……. Is …… to thematerial whose ………. Is …… . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3576. |
A solid cylinder of radius R and mass M, rolls down on inclined plane without slipping and reaches the bottom with a speed v. The speed would be less than v if we use? |
|
Answer» A CYLINDER of same mass but of SMALLER RADIUS |
|
| 3577. |
There is a positively charged ring of radius R whose plane in kept vertical in gravity free space. One electron is released at rest from a point on its axis at a distance x from its centre. Assume that the positive charge is uniformly distributed over ring. |
|
Answer» The electron performs S.H.M about the centre if x is very small in comparison to radius of the ring. Here a is the radius of the ring. If x < < a then `E approx (Qx)/(4piepsilon_0 a^3)` The acceleration of electron near the centre of ring on its axis can be written as Acceleration=`(eE)/m approx (eQx)/(4piepsilon_0ma^3)` We can SAY that the magnitude of acceleration is directly proportional to the distance from the centre of the ring if the electron is very CLOSE to the centre. Acceleration is in accordance with the requirement for S.H.M and moreover electric force is always directed towards the centre of the ring on electron on both sides of ring, hence it is restoring. Now we can say that the electron will perform S.H.M if it is released on the axis of a POSITIVELY charged ring at a very small distance from the centre of ring. Thus option (a) is CORRECT. If a is the radius of the ring then we know that electric field intensity of the ring is maximum on its axis at a distance `a/sqrt2` from its centre. We can say that the electron will attain maximum acceleration when it crosses the point of maximum electric field. So, option (b) is correct. We can see in the expression of electric field intensity due to a charged ring that electric field at its centre is zero. The acceleration of electron becomes zero at the centre and thus option (c) is correct. S.H.M is also a kind of idealised model of oscillatory motion but in option (a) we have discussed that it is only possible if the distance of electron from the centre of ring is lesser in comparison to radius of the ring. Here in general, the electron will oscillate about the centre even if it is released from a relatively large distance, but it will be just oscillatory motion and will not be S.H.M. So, option (d) is correct. |
|
| 3578. |
वायु मे प्रकाश की चाल 3xx10^8 मी/से है जबकि पदार्थ मे इसकी चाल 1.5xx10^8मी/से हो जाती है तो पदार्थ का अपवर्तनांक |
|
Answer» 3 |
|
| 3579. |
If an object is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, will the size of the image be magnified with respect to the size of the object? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3580. |
The circuit symbol of LED, p-n junctiondiode is ….. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3581. |
Calculate the back e.m.f of a 10H, 200 Omega coil 100 ms after a 100Vdc supply is connected to it. |
|
Answer» Solution :The VALUE of current at 100 ms after the switch is CLOSED is `I=I_(0)[1-e^((-t)/(T_(0)))]`, Here, `I_(0) =(100)/(200)` =0.5 amp, `tau_(0)=(L)/(R)=(10)/(200)=0.05` sec, t=0.1 sec `I=0.5(1-e^(-0.1//0.05))=0.5(1-e^(-2))=0.4325A` Now, `E=IR+L(dI)/(dt)`, or `100= 0.4325 xx 200+L(dI)/(dt)` Back `e.m.f=L(dI)/(dt) = 100 -0.4325 xx 200 = 13.5V` |
|
| 3582. |
Calculate the power developed by mass weighing 70 kg in climbing up a vertical staircase at the rate of 1 m/s. |
|
Answer» 686 Watt |
|
| 3583. |
A series combination of n_1 capacitors, each of value C_1 is charged by a source of potential difference 4V. When another parallel combination of n_2 capacitors each of value C_2 is charged by a source of potential difference V it has the same total energy stored in it as the first combination has. The value of C_2 in terms of C_1 is then |
|
Answer» `(16 C_1)/( n_1 n_2)` |
|
| 3584. |
The figure shows variation of R, X_(L) and X_(C) with frequency f in a series L, C, R circuit. Then for what frequency point, the circuit is inductive? |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 3585. |
A bar magnet with poles 25.0 cm apart and of pole strength 14.4 Am rests with its centre on a frictionless point. It is held in equilibrium at 60^(@) to a uniform magnetic field of induction 0.25T by applying a force F at right angle to the axes, 12 cm from its pivot. The magnitudeof the force is : |
|
Answer» `15sqrt(3)` N |
|
| 3586. |
The phenomena of light passes through sleet and bends at edges of slit is called ....... |
|
Answer» REFLECTION |
|
| 3587. |
A block of wood of mass 0.5 kg is placed on a plane making 30^(@) with the horizontal. If the coefficient of friction between the surfaces of contact of the body and the plane is 0.2. What force is required to keep the body sliding down with uniform velocity. |
|
Answer» Solution :FORCE REQUIRED to keep the body SLIDING down with constant velocity. Given, `m = 0.5 KG g = 9.8 ms^(-2)`, `theta = 30^(@)` `mu = 0.2` `F=mg(sin theta-mu cos theta)` `=1.6 N`. |
|
| 3588. |
Reflectance of a perfectly black body is |
|
Answer» zero |
|
| 3589. |
A series would dc motor has a total resistance of 1.5 ohm. When connected across a 115 volt and running at a certain speed it draws a current of 10 A. The back emf in the motor is |
|
Answer» 100 V `i=(epsilon-e_(b))/(R )`or`10=((115-e_(b))/(1.5))` `THEREFORE e_(b)=100 V`. |
|
| 3590. |
A beam of X-rays with wavelength lambda = 40pm falls normally on aplne rectangular array of scattering centres and produces a system of diffraction maxima (Fig.) on a plane screen removed from the array by a distance l = 10cm. Find the array periods a and b along the x and y axes if the distance between symmetrically located maxima of second order are equal to Deltax = 60mm (along the x axis) and Deltay = 40mm (along the yaxis). |
|
Answer» Solution :We given here a simple derivation of the condition for diffraction maxima, KNOWS as Laue equations. It is easy to see from the above figure that the path DIFFERENCE between waves scattered by nearby scattering centres `P_(1)` and `P_(2)` is `P_(2)A - P_(1)B = OVERSET rarr(r ).overset rarr(s_(0)) - overset rarr(e ). overset rarr(s)` `=overset rarr(r ). (overset rarr(s_(0))-overset rarr(s)) =overset rarr(r ). overset rarr(S)`. Here `overset rarr(r)` is the radius vector `overset rarr(P_(1))P_(2))`. For maxima this path difference must be an inyeger multiple of `lambda` for any two neighbouring atoms. In the present case of two dunensional lattice with `X`-rays incident normally `oversetrarr(r).oversetrarr(s) = 0`. Taking successively. nearest neighbours in the x-&y- directions We get equations `a cos alpha = h lambda` `b cos alpha = k lambda` Here `cos alpha` and `cos beta` ar the direction consines of the RAY with respect to the `x` & `y` axes of the two dimensional crystal. `cos alpha = (Deltax)/(sqrt((Deltax)^(2) + 4l^(2))) = sin (tan^(-1)(Deltax)/(2l)) = 0.28735` so using `h = k = 2` we get `a = (40 xx 2)/(28735)pm = 0.278nm` Similarly `cos beta = (Deltay)/(sqrt((Deltay)^(2) + 4l^(2))) = sin (tan^(-1)(Deltay)/(2l)) = 0.19612` `b = (80)/(cos beta)pm = 0.408nm` 
|
|
| 3591. |
The phase difference between two waves reaching a point 15 pi/2. What is the resultant amplitude .If the individual amplitude are 3 mm and 4 mm ? |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 3592. |
A battery of internal resistance 4Omega is connected to the network of the resistance as shown in figure . If the maximum power can be delivered to the network, the magnitude of resistance in Omegashould be |
|
Answer» `19//21 OMEGA` |
|
| 3593. |
Two events take place simultaneously at points A and B as seen in the lab. Frame. They also occur simultaneously in a frame moving with respect to the lab in a direstion |
|
Answer» parallel to AB |
|
| 3594. |
Block A of mass m rests on the plank B of mass 3m which is free to slide on a frictionless horizo-ntal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and plank is 0.2. If a horizontal force of magnitude 2 mg is applied to the plank B, the acceleration of A relative to the plank and relative to the ground respectively, are: |
|
Answer» `0,g/2` |
|
| 3595. |
Why a common emitter amplifier is preferred to a common base amplifier |
| Answer» Solution :Becausetehe current gain in a common EMITTER amplifier is GREAT than in common BASE amplifier | |
| 3596. |
The entire network shown here, has uniform wire having resistance per unit length as 1Omega//m. It is placed in a uniform but time varying magnetic field vecB(directed into the plane). If the strength of the magnetic field is increasing at 1T//s, the ratio I_(1)//I_(2) equals |
|
Answer» `2` `RARR 4I_(1)+3I_(2)=1`…..(`i`) `2I_(2)-I_(1)=1//2` `rArr-2I_(1)+4I_(2)=I`……(`ii`) By solving equations (`i`) and (`ii`) `(I_(1))/(I_(2))=(1)/(6)` 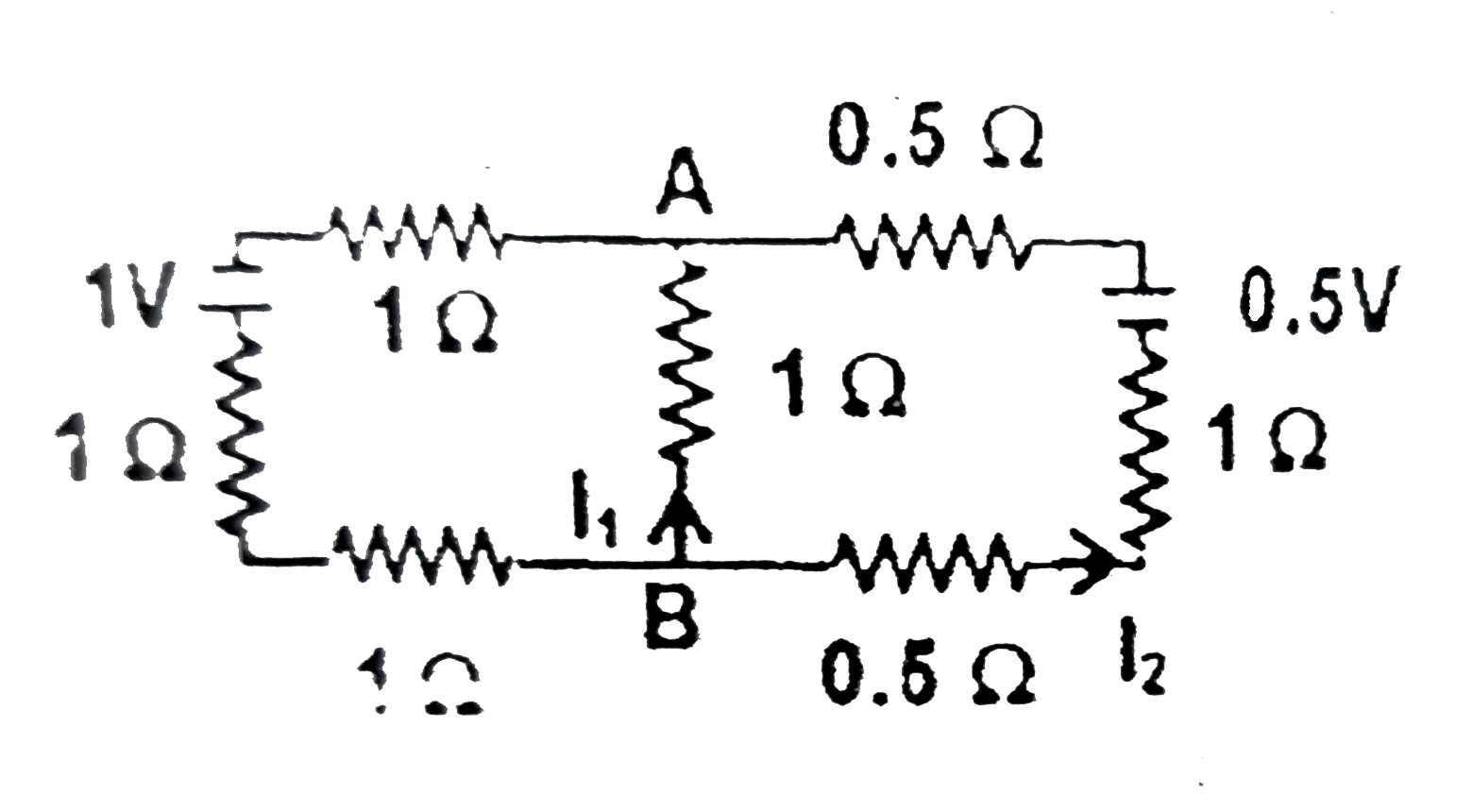
|
|
| 3597. |
An Earth starship has been sent to check an Earth outpost on the planet P1407, whose moon houses a battle group of the often hostile Reptulians. As the ship follows a straightline course first past the planet and then past the moon, it detects a high-energy microwaveburst at the Reptulian moon base and then, 1.10 s later, an explosion at the Earth outpost, which is 4.00xx10^(8) m from the Reptulian base as measured from the ship's reference frame. The Reptulians have obviously attacked the Earth outpost, and so the starship begins to prepare for a confrontation with them. The speed of the ship relative to the planet and its moon is 0.980c. What are the distanceand time interval between the burst and the explosion as measured in the planet-moon frame (and thus according to the occupants of the stations)? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :KEY IDEAS 1. This problem involves measurements made from two reference frames, the planet-moon frame and the starship frame. 2.We have two EVENTS: the burst and the explosion. 3. We need to TRANSFORM the given data as measured in the starship frame to the corresponding data as measured in the planet-moon frame. Starship frame: Before we get to the transformation, we need to carefully choose our notation. We begin with a sketch of the situation as shown in Fig. 36-12. There, we have chosen the ship.s frame S to be stationary and the planet-moon frame S. to be moving with positive velocity (rightward). (This is an arbitrary choice, we could, instead, have chosen the planet-moon frame to be stationary. Then we WOULD redraw `vecv` in Fig. 36-12 as being attached to the S frame and indicating leftward motion, v would then be a negative quantitiy. The results would be the same.) Let subscripts e and b represent the explosion and burst, respectively. Then the given darta, all in the unprimed (starship) reference frame, are `Deltax=x_(e )-x_(b)= +4.00xx10^(8)m` and `Deltat=t_(e )-t_(b)=+1.10s`. The relative motion alters the time intervals between events and maybe even their sequence.  Figure35-12 A planetand its moon in reference frame S. move rightward with speed v relative to a starship in reference frame S. Here, Deltax is a positive quantity becasuse in Fig. 36-12, the coordinate `x_(e )` for the explosion in greater than the coordinate `x_(b)` for the burst, `Deltat` is also a positive quantity because the time `t_(e )` of the explosion is greater (later) than the time `t_(b)` of the burst. Planet-moon frame: We seek `Deltax.` and `Deltat.`, which we shall get by transforming the given S-frame data to the planet-moon frame S.. Because we are considering a pair to events, we choose transformationequations from Table 36-2-namely, EQS. 1. and2.: M `Deltax.=gamma (Deltax-v Deltat)""`(36-27) and `Deltat.=gamma(Delta-(v Deltax)/(c^(2))).""`(36-28) Here, `v = +980c` and the Lorentz factor is `gamma=(1)/(sqrt(1-(v//c)^(2)))=(1)/(sqrt(1-(+0.980c//c)^(2)))=5.0252.` Equation 36-27 then becomes `Deltax.=(5.0252)[4.00xx10^(8)m-(+0.980c)(1.10s)]` `=3.86xx10^(8)m`, and Eq 36-28 becomes `Deltat.=(5.0252)[(1.10s)-((+0.980c)(4.00xx10^(8)m))/(c^(2))]` `= -1.04s`. |
|
| 3598. |
Two magnets of magnetic moments M_1 and M_2 are joined at their centres to form a cross (perpendicular to each other). The combination is suspended in a uniform magnetic field directed vertically upwards. It stands in equilibrium when either of them. makes an angle of 45^(@)with the vertical field. What is the ratio of their magnetic moments? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`M_1 : M_2 = 1:1` | |
| 3599. |
An Earth starship has been sent to check an Earth outpost on the planet P1407, whose moon houses a battle group of the often hostile Reptulians. As the ship follows a straightline course first past the planet and then past the moon, it detects a high-energy microwaveburst at the Reptulian moon base and then, 1.10 s later, an explosion at the Earth outpost, which is 4.00xx10^(8) m from the Reptulian base as measured from the ship's reference frame. The Reptulians have obviously attacked the Earth outpost, and so the starship begins to prepare for a confrontation with them. What is the meaning of the minus sign in the value for Deltat' ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Reasoning: We must be consistent with the notation we set up in part (a). Recal how we ORIGINALLY defined the time interval between burst and explosion: `DELTAT=t_(e )-t_(b)= +1.10s`. To ber consistent with that choice of notation, our definition of `Deltat. ` must be `t._(e )-t._(b)`, thus, we have found that `Deltat.=t._(e )-t._(b)= -1.04s`. The minus sign here tells US that `t._(b) gt t._(e )`, that is, in the planet-moon reference frame, the burst OCCURRED 1.04s after the explosion, not 1.10 s before the explosion as DETECTED in the ship frame. |
|
| 3600. |
State and explain Biot-Savart law for the magnetic field produced by a current element. Give the direction of magnetic field and define the unit of it. |
Answer» Solution :1. Biot-Savart Law : Magnetic field of position VECTOR of point relative to element "I`dvecl` which is current carrying element at `vecr` position vector is given by `dvecB=mu_(0)/(4pi)*(Idveclxxvecr)/r^(2)`.  2. According to Biot-Savart law, the magnitude of the field is `dvecB`. (1) Directly proportional to the current I through the conductor, `thereforedBpropI` (2) Directly proportional to the length `|dvecl|` of the current element, `thereforedBpropdl` (3) Directly proportional to `sintheta`, `thereforedBpropsintheta` (4) Inversely proportional to the square of the distance r of the point P from the current element, `thereforedBprop1/r^(2)` Combining all these four factors, we get `dBprop(Idlsintheta)/r^(2)` `dBprop(Idlrsintheta)/r^(3)` `dvecBprop(Idveclxxvecr)/r^(3)` `thereforedvecB=mu_(0)/(4pi)(Idveclxxvecr)/r^(3)""...(1)` 3. Where `mu_(0)/(4pi)` is proportionally CONSTANT. 4. Where `mu_(0)` is vacuum permeability. It.s value is `mu_(0)=4pixx10^(-7)(T*m)/A` `THEREFORE(mu_(0))/(4pi)=10^(-7)(T*m)/AorNA^(-2)` 5. Equation (1) is for magnetic field in vacuum. 6. Magnitude of electric field from equation (1) is given by, `|dvecB|=mu_(0)/(4pi)(Idlrsintheta)/r^(3)ormu_(0)/(4pi)*(|Idveclxxvecr|)/r^(3)` where `theta` is the angle between `Idveclandvecr`. `therefore|dvecB|=mu_(0)/(4pi)(Idlsintheta)/r^(2)""...(2)` 7. The direction of `dvecB` is the direction of the perpendicular to plane of cross PRODUCT of `Idveclandvecr` which is inside to plane of paper which is indicated as  near point P. |
|



