Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 3601. |
An Earth starship has been sent to check an Earth outpost on the planet P1407, whose moon houses a battle group of the often hostile Reptulians. As the ship follows a straightline course first past the planet and then past the moon, it detects a high-energy microwaveburst at the Reptulian moon base and then, 1.10 s later, an explosion at the Earth outpost, which is 4.00xx10^(8) m from the Reptulian base as measured from the ship's reference frame. The Reptulians have obviously attacked the Earth outpost, and so the starship begins to prepare for a confrontation with them. Did the burst cause the explosion, or vice versa? |
|
Answer» Solution :KEY IDEA The sequence of events measured in the planet-moon reference FRAME is the reverse of that measured in the ship frame. In either situration, if there is a causal RELATIONSHIP between the two events, information MUST travel from the location of one event to the location of the other to cause it. Checking the speed: Let us check the required speed of the information. In the ship frame, this speed is `v_("info")=(Deltax)/(Deltat)=(4.00xx10^(8)m)/(1.10s)=3.64xx10^(8)m//s, ` but the speed is impossible because it exceeds c. In the planet-moon frame, the speed comes but to be `3.70xx10^(8)m//s`, also impossible. Therefore, neither event could POSSIBLY have caused the other event, that is, they are unrelated events. Thus, the starship should STAND down and not confront the Reptulians. |
|
| 3602. |
A conducting rod of length l is kept parallel to a uniform magnetic field vecB. It is moved along the magnetic field with a velocity vecv. What is the value of emf inducedin the conductor? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Zero (because `l, VECB and vecv` are all in same DIRECTION. | |
| 3603. |
Find the rms and the average values of the saw tooth wave form shown in fig. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3604. |
A tuning fork of frequency 340 Hz is vibrated just above a cylindrical tube of length 120 cm. Water is slowly poured in the tube. If the speed of sound is 340 ms^(-1) then the minimum height of water required for resonance is: |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 3605. |
Statement I: The wavelength of K_(prop) X-ray line of an anticathode element of atomic no. Z is proportional to ((1)/(Z-1))^(2) Statement II: The frequency of Kg X-ray line equals the sum of the frequencies of K and La X-ray lines of same anticathode element. |
|
Answer» A. Statement-I is FALSE, statement-II is true. |
|
| 3606. |
(a) Why photoelectric effect cannot be explained on the basis of wave nature of light ? Give reasons. (b) Write the basis features of photon picture of electromagnetic radiation on which einstein's photoelectric equation is based. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Wave nature of light fails to explain photoelectric effect due to the following reason: (i) In wave nature, the energy carried by a light beam is measured by its intensity. Thus, by increasing intensity of light (irrespective of wavelength or frequency) we can increase the energy of light beam and accordingly energy of photoelectrons should increase. However, experimentally, K.E. of photoelectrons is found to be independent of the intensity of incident light. (ii) Again as per wave nature photo-emission should take place from a metal surface for all frequencies but in reality it is not to be so. (iii) According to wave nature photoelectric emission cannot be an instantaneous process. (b) The basis features of photon picture of electromagnetic radiation are as follows: (i) Each photon travels in vacuum (or air) with a constant speed c, the speed of light, having a value `c=3xx10^(8)ms^(-1)`. this speed does not depend on frequency or energy/MOMENTUM of photon or on relative motion of source and observer ETC. (ii) Each photon having a frequency v has energy `E=hv and` momentum `p=(hv)/(c)=(H)/(lamda)`, where `lamda` is the wavelength. thus, all photons of light of a particular frequency have the same energy and momentum, irrespective of the intensity of light. the intensity of light indicates the number of photons striking per unit area of given surface per second. (iii) When a photon of appropriate energy interacts with an electron in a metal, it may transfer its energy to eelectron and electron may be EJECTED from the metal surface giving rise to phenomenon of photoelectric emission. |
|
| 3607. |
A spring-block system lies inside the horizontal frictionless tube as shown in figure. At t=0, tube starts rotating with uniform angular velocity 'omega'. Initially spring was in its natural length. If the block collides with the other end of tube and the collision is perfectly elastic, then find the magnitude of block's velocity after the collidon with respect to ground. ( take k = m omega^(2) ) |
|
Answer» `sqrt(2) OMEGA L` |
|
| 3608. |
The heat capacity per mole of water is (R is universal gas constant) |
|
Answer» 9R `U=3xx3k_(B)TxxN_(A)=9RT""[because k_(B)=(R)/(N_(A))]` `THEREFORE` Heat capacity per mole of water is `C=(DELTAQ)/(DeltaT)=(DeltaU)/(DeltaT)=9R` |
|
| 3609. |
A cylinder of radius R, made up of a material (thermal conductivity k_1) is surrounded by a cylindrical sheet of inner radius R and outer radius 2R (thermal conductivity k_2). The two ends of the combined system are maintained at two different temperatures. There is no loss of heat across the cylindrical surface and the system is in steady state. Calculate the effective thermal conductivity of the system. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3610. |
Explain the intensity of the point of superposition of the waves emanating from it by explaining the coherent and incoherent sources. |
|
Answer» Solution :If light sources having constant initial phase difference or their phase difference does not change with time, then this sources is called coherent sources. In the interference pattern intensity at any point does not change with time. This type of interference is known as stationary interference. There should be TWO coherent sources for stationary interference and the amplitude should also be the same. The position of the MAXIMUM and minimum in the stationary interference will not change with time. When the phase difference between the two vibrating sources changes very rapidly over time then this sources is known as incoherent source. The light intensities is added into each other DUE to superposition of the waves emanating from incoherently sources hence two different light sources illuminate the wall. When the path difference of the two sources is not constant, the interference pattern also changes with time. If the path difference changes very rapidly with time, the position of maximum and minimum will also change rapidly with time and we will see the average distribution of intensity with time. This average intensity is given by, `ltIgt==4I_(0)ltcos^(2)((phi)/(2))gt` where `ltcos^(2)((phi)/(2))gt`represent time averaging term. If `phi(t)` varies randomly with time, the time averaged quantity `ltcos^(2)((phi)/(2))gt` will be `(1)/(2)` and the resulting intensity at all point, `I=4I_(0)ltcos((phi)/(2))gt` `=4I_(0)xx(1)/(2)` `:.I=2I_(0)` at all points. |
|
| 3611. |
The distance between an object and the screen is 100cm. A lens produces an image on the screen when the lens is placed at either of the positions 40 cm apart. The power of the lens is nearly |
|
Answer» 3 diopter |
|
| 3612. |
Write any one application of the cyclotron. |
| Answer» Solution :CYCLOTRON is used to accelerate the CHARGED particles or IONS to HIGH ENERGIES. | |
| 3613. |
Four very long straight wires carry equal electric currents in the +z direction. They intersect the x-y plane at (x,y)=(-a,0),(a,0),(0,a),(0,-a).The magnetic force exerted on the wire at position (-a,0) is along |
|
Answer» `+y`  `because""|vecF_(1)|=|vecF_(2)|` `therefore` Their resultant will be ALONG `vecF_(3)` i.e.X-axis So net force on WIRE sis along `+X` DIRECTION |
|
| 3614. |
A mass of 1kg attached to one end of a string is first lifted up with acceleration 4.9 m//s^(2) and then lowered with same acceleration. What is the ratio of tension in string in two cases |
|
Answer» Solution :When MASS is LIFTED up with ACCELERATION `4.9 m//s^(2), T_(1)=m(9.8+4.9)` When mass is LOWERED with same acceleration, `T_(2)=m(9.8-4.9)` `therefore (T_(1))/(T_(2))=(14.7)/(4.9)=3:1` |
|
| 3615. |
The density, of mercury in cgs system is 13.6 g cm". Its value in SI is |
|
Answer» 136 KG/`M^(3)` |
|
| 3616. |
Find the (i) angular momentuum (ii) velocity of the electron in the 5^(th) orbit of hydrogen atom (h = 66 xx 10^(-34) Js, m = 9.1 xx 10^(-31) kg) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) Angular momentum is given by `l = nh = (nh)/(2 pi)` `= (5 XX 6.6 xx 10^(-34))/(2 xx 3.14) = 5.25 xx 10^(-34) kgm^(2)s^(-1)` (II) Velocity is given by `Velocity v = (l)/(mr)` ` = ((5.25 xx 10^(-34) kgm^(2)s^(-1)))/((9.1 xx 10^(-31) kg)(13.25 xx 10^(-10) m))` `v = 4.4 xx 10^(5) ms^(-1)` |
|
| 3617. |
The kinetic energy needed to project a body of mass m from the surface of earth (radius R ) to infinity is |
|
Answer» `(mgR)/(4)` |
|
| 3618. |
Coenocytic dimorphic vegetative mycelium is found in |
|
Answer» Neurospora |
|
| 3619. |
Delta V measured between B and C is |
|
Answer» `(rho I)/(pi ALPHA)-(rho I)/(pi(alpha - B))` |
|
| 3620. |
Electric field is directed along the direction in which rate of electric potential is ....... |
|
Answer» decrease fastest |
|
| 3621. |
A proton and an electron are placed 1.6cm apart in free space. Find the magnitude of electrostatic force between them. The nature of this force. |
|
Answer» `9 XX 10^(-25)` REPULSION |
|
| 3622. |
What meaning would you give to the capacitance of a single conductor ? |
| Answer» Solution :Capacitance of a single conductor means its CAPABILITY to HOLD CHARGE with respect to another conductor situated at INFINITY and maintained at ZERO potential. | |
| 3623. |
(A): The average and instantaneous velocities have same value In a uniform motion (R ):In uniform motion ,the velocity of an object increases uniformly. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3624. |
If plane electromagnetic wave of momentum p and E are collied with the surface of any object then the value of p and E will be ….. |
|
Answer» <P>p = 0, E = 0 |
|
| 3625. |
An electrons moves along the line AB. Which lies in the same plane as a circular loop of conducting wires as shown in the diagram. What will be the direction of current induced if any, in the loop? |
|
Answer» No current will be induced |
|
| 3626. |
In Bohr's model of hydrogen atom, the total energy of the electron in nth discrete orbit is proportional to |
|
Answer» n [Hint: Total ENERGY E of ELECTRON in nth discrete orbit in a hydrogen ATOM is: E =`-(13.6)/(n^(2))eV`. THUS `absEprop1/(n^(2))`] |
|
| 3627. |
A wire is stretched as to change its diameter by 0.25%. The percentage change in resistance is |
|
Answer» `4.0%` |
|
| 3628. |
Let the angle between two nonzero vector vecA and vecB be 120^(@) and its resultant be vecC |
|
Answer» C must be equl to `|A-B|` |
|
| 3629. |
An infinite sheet carrying a uniform surface charge density sigma1lies on the xy - plane . The work done to carry a charge q from the point vecA=a(hati-2hatj+6hatk)to the point vecB=a(hati-2hatj+6hatk)(where a is a constant with the dimension of length and epsilon_(0)is the permittivity of free space) is |
|
Answer» `(3sigmaaq)/(2epsilon_(0))` DISPLACEMENT VECTOR `vecr` from POINT A to B is `vecr=vecr_(B)-vecr_(A)` `=a(hati-2hatj+6hatk)-a(hati+2hatj+3hatk)=a(-4hatj+3hatk)` Electric field due to an infinite plane sheet of uniformsurface charge density `SIGMA` is `vecE=(sigma)/(2epsilon_(0))hatn`where `hatn`is a unit vector normal to the plane. Here ,`hatn=hatk` `thereforevecE=(sigma)/(2epsilon_(0))hatk` Work done in moving a charge q from A to B is `W=vecF*vecr=qvecE*vecr ""(becausevecF=qvecE)` `=q((sigma)/(2epsilon_(0))hatk)*a(-4hatj+3hatk)=(3sigmaaq)/(2epsilon_(0))` |
|
| 3630. |
O_(2) molecule consists of two oxygen atoms. In the molecule, nuclear force between the nuclei of the two atoms |
|
Answer» is not important because nulear forces are short-ranged |
|
| 3631. |
A. A device to store electrical charge is called a. Transformer b. Capacitor c. Resistor d. Inductor B. What is meant by energy density of a parallel plate capacitor? C. Derive an expression for the energy stored in a parallel plate capacitor. D. What is the area of the plates of a 0.1muF parallel plate air capacitor, given that the separation between the plates is 0.1 mm. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3632. |
A convex lens is dipped in a liquid whose refractive index is equal to the refractive index of the lens. Then its focal length will ......... |
|
Answer» become zero `(1)/(f_1)=(n_g/n_L-1)(1/R_1-1/R_2)` `n_g=n_1` `THEREFORE(1)/(f_L)=(1-1)(1/R_1-1/R_2)` `therefore (1)/(f_L)=0` `thereforef_L`=Infinite |
|
| 3633. |
Carbon, silicon and germaniumn have same lattice structure. But charbon is an insulator, silicon and germanium are semiconductors because |
|
Answer» number of free electrons for conduction in CHARBON is negligibly small |
|
| 3634. |
A carrier wave is modulated by a number of sine waves with modulation indices 0.1, 0.2, 0.3. The total modulation index (m) of the wave is |
|
Answer» 0.6 |
|
| 3635. |
The natural vibration frequency of a hydrogen molecule is equal to 8.25.10^(14)S^(-1), the distance between the nuclei is 74 p m, Find the ratio of the number of these molecules at the first excited vibrational level (v=1) to the number of molecules at the first excited rotational level (J=1) at a temperature T= 875K. It should be remembered that degeneracy of rotational levels is equal to 2J+1. |
|
Answer» Solution :The energy of the molecule in the first roatational level will be `( ħ^(2))/(I)`. The ratio of the NUMBER of molecule at the first excited vibrational level to the number of molecule at the first excited rataional level is `(e^(- ħ omega//kT))/((2J+1)e^(- ħ^(2)J(J+1)//2IkT))` `(1)/(3)e^(- ħ omega//kT)=(1)/(3)e^(- ħ(omega-2B)//kT)` where `B=ħ//2I` For the hudrogen molecule `I=(1)/(2)m_(H)d^(2)` `=4.58xx10^(-41)gm cm^(2)` Substitution GIVES `3.04xx10^(-4)` |
|
| 3636. |
A galvanometer gives full scale deflection with 0.006 A current . By connecting it to a 4990Omega resistance , it can be converted into a voltmeter of range 0-30 V. If connected to a (2n)/(246)Omega resistance , it becomes an ammeter of range 0-1.5A. Thevalue of n is |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3637. |
If the earth suddenly contracts to half its radius,what would be the length of the day? |
|
Answer» 6 hrs |
|
| 3638. |
A transverse wave is tranvelling in a string at any moment a small element 'dx' is at inclination 30^@with the direction of propagation of the wave. After some time interval its inclination changes to 60^@with direction of propagation. Potential energy of this small element is initially U_0and finally it is KU_0, value of K is |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 3639. |
A student performs an experiment on photoelectric effect,using two materials A and B.A plot V_("stop")vs v is given in figure. (i)Which material A or B has a higher work function? (ii)Given the electric charge of an electron=1.6xx10^(-19)C,find the value of the h obtained from the experiment for both A and B.Comment on whether it is consistent with Einstein's theory: |
|
Answer» Solution :(i)Work function ,`phi_(0)=hf_(0)` (where `f_(0)`=threshold frequency) `therefore phi_(0)propf_(0)` ……..(1) From the figure , `f_(0)A=5XX10^(14)`Hz `f_(0)B=10xx10^(14)Hz` `impliesf_(0)Bgtf_(0)A` `IMPLIES` From relation(1), `phi_(0)Bgtphi_(0)A` (ii)We know that slope of graph of |`V_(0)|tof` Gives us value of `((h)/(e))`.HENCE Slope of graph for A, `tantheta_(1)=(PQ)/(QR)` `therefore (h)/(e)=(2)/(5xx10^(14))=0.4xx10^(-14)` `therefore h=0.4xx10^(-14)xxe` `therefore h=0.4xx10^(-14)xx1.6xx10^(-19)` `therefore h=6.4xx10^(-34)JS` .......(2) Slope of graph for B, `tantheta_(2)=(ST)/(QT)` `therefore (h)/(e)=(2.5)/(5xx10^(14))=0.5xx10^(14)` `therefore h=0.5xx10^(-14)xxe` `=0.5xx10^(-14)xx1.6xx10^(19)` `h=8xx10^(-34)Js` ..........(3) Thus ,here value of h are obtained different from the graphs for A and B.Hence ,above experimental observations are not consistent with Einstein.s theory. |
|
| 3640. |
When tube length of compound microscope is increased, then its magnifying power ...... |
|
Answer» INCREASES `THEREFORE m prop L` Hence, magnifying power increases with INCREASE in tube length. |
|
| 3641. |
In Nicol Prism Canada balsam acts as an………medium for the extra ordinary ray |
|
Answer» OPTICALLY rarer |
|
| 3642. |
The equation of sound wave is y=0.0015 sin.(64.4 x +316 t) Find the wavelength of the wave |
|
Answer» 0.2 unit |
|
| 3643. |
A source of sound emitting a frequency 660 Hz is moving counter-clockwise in a circular path of radius 2 metres with an angular velocity 15 rad/s. A recorder at a distance from the source is moving simple harmonically along a straight line with an amplitude 2 metres. The frequency of SHM is 15/(2pi)per second. The arrangement is shown in figure. When the source is at point A the detector is at D. Find the maxium and minimum frequencies recorded. Velocity of sound in air at this temperature can be taken as 300 m/s |
|
Answer» 870 HZ, 480 Hz |
|
| 3644. |
Figure shows a particle mass m = 100g attaches with four identical spring , each of length l = 10 cm . Initial tension in each spring is F_(0) = 25 N. Neglecting gravity , Calculate the period of small oscillation of the particle along a line perpendicular to the plane of the figure . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3645. |
Two converging glass lenses 'A' and 'B' have focal lengths in the ratio 2:1. The radius of curvature of first surface of lens 'A' is 1/4th of the second surface where as the radius of curvature of first surface of lens 'B' is twice that of second surface. Then the ratio between the radii of the first surfaces of A and B is |
|
Answer» `5:3` |
|
| 3646. |
A block of mass m rests on a platform. Theplatform is given up and down S.H.M. withan amplitude d. What can be themaximum frequency so that the block never leaves the platform ? |
|
Answer» `sqrt(g//d)` `:.""OMEGA^(2)d=gimplies4pi^(2)vd=g` `v=(1)/(2pi)sqrt(g//d)` Hence correct CHOICE is (B). |
|
| 3647. |
A: Magnification for convex lens is always positive where it may be positive or negative for concave lens.R: It depends on our choice of sign convention |
|
Answer» Both ASSERTION and REASON are TRUE and the reason is CORRECT EXPLANATION of the assertion. |
|
| 3648. |
Use Kirchhoff's rules to obtain the balance condition in a Wheatstone bridge. |
Answer» SOLUTION :Circuit arrangement for a Wheatstone bridge is being shown in the adjoining Fig. In balancecondition of bridge no CURRENT flows through galvanometer and it GIVES no deflection. Currents in various branches of network as per Kirchhoff.s first law are, thus, represented in figure.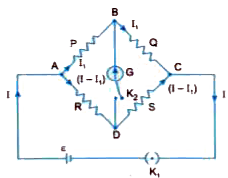 Applying Kirchhoff.s second law to mesh ABDA, we have `-P.I_1 + R. (I - I_1) = 0` or` PI_1 = R (I - I_1)`...(i) again for mesh BCDB , we have `-Q.I_1 +S.(I - I_1)= 0 ` or`QI_1 = S .(I- I_1) ` or`QI_1 =S (I - I_1) `...(ii) DIVIDING (i) by (ii) , we get `P/Q = R/S` which is the balance CONDITION of Wheatstone.s bridge. |
|
| 3649. |
A rocket with a lift-off mass 3.5 xx 10^(4) N kg is blasted upward with an initial acceleration of 10 m//s^(2). Then the initial thrust of the blast is: |
|
Answer» `1.75 xx 10^(5) N` `= 3.5 xx 10^(4) (10 + 10) = 70 xx 10^(4) = 7.0 x 10^(5)N` Hence CHOICE is (C). |
|
| 3650. |
Explain the working principle of a photodiode. Or Explain briefly how a photodiode operates. |
| Answer» Solution :A photodiode is a SPECIAL purpose p-n junction diode designed to detect and measure the intensity of LIGHT. It is fabricated with a transparent window so that light is allowed to FALL on it. A photodiode operates under reverse bias and hence its own current is NEGLIGIBLE. When light photons having energy greater than the energy gap `E_(g)`of semiconductor are incident at the junction, the electron - hole pairs are generated due to absorption of these photons. The diode is fabricated such that electron-hole pairs are generated in or near the depletion region. Due to strong electric field of the junction, electrons and holes are separated before recombining. Due to reverse bias electrons reach n-side of junction and holes reach p-side. This leads to an emf. When an extermal load is connected, a weak current flows. Value of photocurrent is directly proportional to intensity of incident light. | |