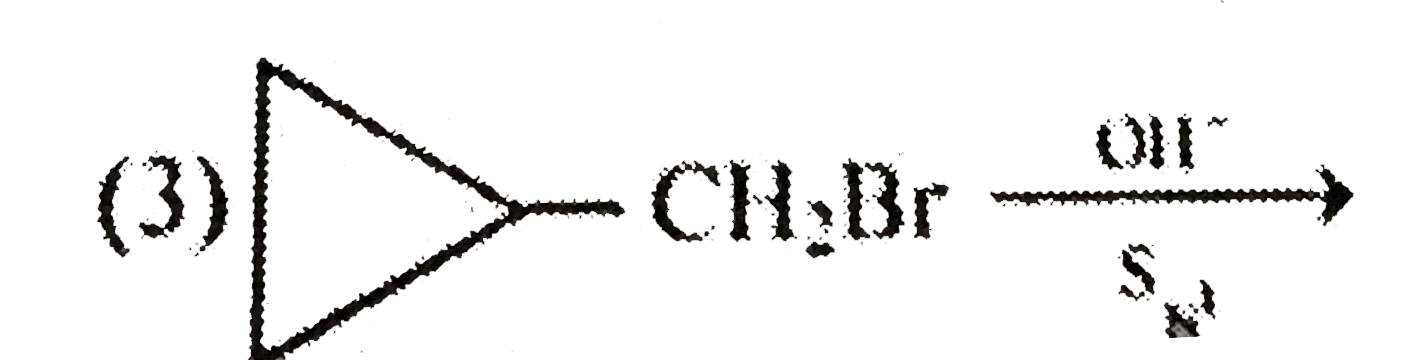Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 37651. |
A block of mass 1kg lies on a horizontal surface in a truck. The coefficeint of friction between the block and surface is 0.5. If the acceleration of the truck is 6ms^(-2) the acceleration of the block relative to ground is |
|
Answer» `6 m//s^(2)` |
|
| 37652. |
If E is an electric field and B is the magnetic induction then the energy flow per unit area per unit time in an electromagnetic field is given by |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 37653. |
Draw a circuit diagram to study characteristics of a transistor (pnp or ppn) in common emitter configuration. Draw the sketch of (i) input characterisitics and (ii) output characteristics for this configuration. |
Answer» Solution :Common emitter characteistics. The circuit diagram for common emitter p-n-p transistor is shown in fig.(a). The input is applied across the emitter and base and output is taken across collector and emitter. Here emitter is common to both input and output circuits. The most important characteristics of common base connections are input characteristic and output characteristics.  `(i)` Input Characteristics A graph showing the RELATIONSHIP between base-emitter voltage and base-current and constant collector-emitter is called input characteristics of the transistor. To obtain input characteristic , the emitter is forward biased by base emitter voltage `V_(be)` and the collector is reverse biased by collector emitter voltage `V_(ce)`. The collector voltage `V_(ec)` is kept constant at a suitable value. The base voltage `V_(be)` is varied in SMALL steps and the base current `I_(b)` is noted corresponding to each value of the base-emitter voltage. A curve is then plotted between `V_(BC)` and `I_(b)` for a given value of `V_(ce)`. This is one characteristic. Similar characteristic CURVES can be drawn for different fixed values of `V_(ce)("SAY"-2V,-4V"etc)` as shown in fig. (b) .  `(ii)` Output characteristics . A graph showing the relationship between the collector base voltage and collector current at constant output characteristic of the transistor. To obtain output characterisitics the base current is kept constant at a suitable value the collector emitter voltage `V_(ce)` is varied in small steps and the collector current `I_(c)` is noted corresponding to each value of the base current `I_(b)` . A curve is then plotted between `V_(ce)` and `I_(c)` for a given value `I_(b)`. This is one characteristic. Similar characteristic curves can be drawn for different fixed  values of `I_(b)` (say `10muA`, `15muA`, `20muA` etc. as shown in fig.(c) |
|
| 37654. |
Explain the processes of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion by using the plot of binding energy per nucleon(BE/A) versus the mass number A |
|
Answer» Solution :(a)Nuclear fission:BINDING energy per nucleon for heavier nuclei is about 7.6 MEV and for lighter nuclei it is about 8.4 MeV . So the heavier nuclei are less stable and theheavier nucleus splits into lighter nuclei which results in release of energy. This phenomenon is called nuclear fission. (B) Nuclear fission :The binding energy per nucleon for nuclei having MASS number A lt 12 is small and so they are less stable . Hence two such nuclei can combine to from a slightly heavier nucleus , which has higher binding every per nucleon Therefore , energy is released in this process and it is called nuclear FUSION. |
|
| 37655. |
We know how by neglecting the air resistance, the problems of projectile motion can be easily solved and analysed. Now we consider the case of the collision of a ball with a wall. In this case the problem of collision can be simplified by considering the case of elastic collision only. when a ball collides with a wass we divide its velocity into two components, one perpendiclar to the wall and other parallel to the wall. If the collision is elastic then the perpendicular component of velocity of the ball gets reversed with the same magnitude. The other parallel component of velocity will remain constant if wall is given smooth. Now, let us take a problem. Three balls A, B, and C are projected from ground with same speed at same angle with the horizontal. The ball A,B and C collide with the wall during their flilght in air and all three collide perpendicularly with the wall as shown in figure. If the total time taken by the ball A to fall back on ground is 4 seconds and that by ball B is 2 secons. Then, the maximum height attained by ball B from ground will be |
|
Answer» `15m` Time taken by `B` to TOUCH the inclined roof is 1 second. Hence, `S=20t- 1/2 "gt"^(2)=20xx1-5xx1^(2)=15m` 
|
|
| 37656. |
A 100 W sodium lamp radiates energy uniformly in all directions .The lamp located at the centre of a large sphere the absorbs allthe sodium light which is incident on it.The wavelength of the sodium light 589 nm.(a) what is the energy per photo assosciated with the sodium light? (b)At what rate are the photons delivered to the sphere. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here P=100 W, `lambda=589 nm=589xx10^(-9)m` `h=6.63xx1-^(-34)Js,c=3xx10^(8)ms^(-1)` (a) Energy of each photon, E=hv `therefore E=(hc)/(lambda)=(6.63xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))/(589xx10^(-9))` `therefore E=0.033769xx10^(-17)` `E~~3.38xx10^(-19)J` `therefore E=(3.38xx10^(-19))/(1.6xx10^(-19))eV` `therefore` E=2.11 eV (b)Rate of photon incident on sphere. `N=(P)/(E)=(100)/(3.38xx10^(-19))` `therefore N=29.58xx10^(+19)` `therefore N~~3.0xx10^(20)`photon/second |
|
| 37657. |
A 220 V, 50 Hz a.c. source is connected an inductance of 0.2 H and a resistance of 20 Omegain series. What is the current in the circuit ? |
|
Answer» `10A` `=sqrt(400+2500xx0.04)` `I=V/"|Z|"` `=sqrt(400+100)` `=220/22.36` `=sqrt500` `THEREFORE` I=9.84 A `APPROX` 10.0 A `therefore |Z|=22.36 Omega` |
|
| 37658. |
We know how by neglecting the air resistance, the problems of projectile motion can be easily solved and analysed. Now we consider the case of the collision of a ball with a wall. In this case the problem of collision can be simplified by considering the case of elastic collision only. when a ball collides with a wass we divide its velocity into two components, one perpendiclar to the wall and other parallel to the wall. If the collision is elastic then the perpendicular component of velocity of the ball gets reversed with the same magnitude. The other parallel component of velocity will remain constant if wall is given smooth. Now, let us take a problem. Three balls A, B, and C are projected from ground with same speed at same angle with the horizontal. The ball A,B and C collide with the wall during their flight in air and all three collide perpendicularly with the wall as shown in figure. The vertical component of velocity of balls wiht which they are projected is |
|
Answer» `20m//s` |
|
| 37659. |
Which of the following is most unsymmetrical lattice........ |
|
Answer» Monoclinic |
|
| 37660. |
Findout the equivalent focal length of the combenation of lenses shown in the figure. Surrounding medium is air. |
|
Answer» Solution :`1/f_(1)= (mu_(l)/mu_(s)-1)(1/R_(1)-1/R_(2))` `=(1.5-1)(-1/10-1/10)` `=0.5 xx(-2)/10` `rArr f_(1)=10/(0.5xx-2)=-10` cm `1/f_(2)=(mu_(l)/mu_(s)-1)(1/R_(1)-1/R_(2))` `=(4/3-1)(1/10+1/10)` `rArr 1/f_(1)=1/3 (2/10)` `rArr f_(2)=(30/2)=15` cm `f_(3)=-10` cm `1/f_(eq)=1/f_(1)=1/f_(2)+1/f_(3)` `=1/15-2/10` `rArr f_(eq) =150/(-20)=-7.5` cm |
|
| 37661. |
Findout the equivalent focal length of the combenation of lenses shown in the figure. Surrounding medium is air. |
|
Answer» Solution :`h_(1)/h_(0)=v/u` `RARR h_(i)/h_(0)=v/u` `rArr (d h_(i))/(d t)=v/u (d h_(0))/(d t)` `rArr 30/(-15)xx2 =-4` cm/sec (DOWNWARDS) |
|
| 37662. |
A shell has mass 3 kg and radius 1m. Its moment of inertia about the tangent is : |
|
Answer» `2kgm^(2)` `I_(T)=(5)/(3)MR^(2)=(5)/(3)xx3xx1^(2)=5kgm^(2)` |
|
| 37663. |
A linear conductor with current I_(1) is placed along the axis of a circular conductor, which caries current I_(2). The magnetic force acting on each of the conductoris : |
|
Answer» Zero |
|
| 37664. |
Findout the equivalent focal length of the combenation of lenses shown in the figure. Surrounding medium is air. |
|
Answer» Solution :`1/f =1/v-1/u` `rArr 1/10=1/v+1/15` `rArr 1/v=1/10-1/15` `rArr v=150/5=30` `1/f=1/v-1/u` By differentating : `0=(dv)/(v^(2) dt)-(du)/(dt u^(2))` `rArr 0=- (dv)/v^(2)+(du)/u^(2)` `rArr (du)/u^(2)=(dv)/v^(2)` `rArr (dv)/(du)=v^(2)/u^(2)` `rArr dv =((30)^(2))/((15)^(2))xx(1-2)=-4(1)` `rArr (v_(I)-v_(L))=v^(2)/u^(2) (v_(E)-v_(L))` `rArr (v_(I)-2)=4xx-1` `rArr v_(I)=-2` |
|
| 37665. |
If c is the velocity of light in vacuum, then find the time taken by the light to travel through a glass plane of thickness t and having refractive index mu. |
|
Answer» `(t/(muc))` or `c'=c/(mu)` Time TAKEN `=("DISTANCE")/("velocity")=t/((c/(mu)))=(muf)/c` |
|
| 37666. |
nA small block is given a velocityv along the inclined palne in the downward direction at the highest point on an inclined plane in the downward direction at the highest point on an inclined plane. Then block moves with constant velocity. After reaching at lowest point, block is given same speed v up the incline. find time to reach the block again at lowest point (Assume vle2sqrt(gl sin theta)) |
|
Answer» `(2l)/(V)` `mg sin theta=f` When BLOCK is projected up the plane. It will STOP at some point. At that MOMENT v=0 and net-acceleration along the plane will be zero so it will not return. |
|
| 37667. |
A nonconducting sphere has radius R = 2.31 cm and uniformly distributed charge q = +3.50 fC. Take the electric potential at the sphere's center to be V_0= 0. What is V atradial distance (a) r = 1.45 cm and (b) r = R. ( c) If, instead, V_(0)=0 at infinity, what is V at r= R? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `-0.268 MV,` (B) `-0.681 mV,` (C ) `+1.36 mV` | |
| 37668. |
a. For what kinetic energyof a neutron will the associated de Broglie wavelength be 1.40xx10^(-10)m? b. Also find the de Broglie wavelengthof a neutron, the thermal equilibrium with matter, having an average kinetic energyof (3/2) k T at 300 K. |
|
Answer» Solution :`lambda=1.4xx10^(-10)m` a. `K_("max")=(1)/(2)mv^(2)=(p^(2))/(2m)=(h^(2))/(2m lambda^(2))=((6.6xx10^(-34))^(2))/(2xx1.67xx10^(-27)XX(1.4xx10^(-10))^(2))=6.65x10^(-21)J` b.`lambda=(h)/(sqrt(3mKT))=(6.6xx10^(-34))/(sqrt(3xx1.6xx10^(-27)xx1.38xx10^(-23)xx300))=(6.6xx10^(-34))/(sqrt(1987.2)xx10^(25))=(6.6)/(44.5)xx10^(-9)` `=0.148xx10^(-9)m=0.148nm` |
|
| 37669. |
A plane electromagnetic wave traveling in the positive direction of an x axis in vacuum has components E_(x)=E_(y)=0and E_(z) = (4.0V//m) cos [(pixx10^(15)s^(-1)) (t-x//c)] . (a) What is the amplitude of the magnetic field component ? (b) Parallel to Which axis does the magnetic field oscillate ? (c ) When the electric field component field oscillate ? (c ) When teh electric field component is in the the positive direction of the z axis at a certain point P what is the direction of the magnetic field component there ? (d) In what direction is the wave moving ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 13 NT , (n) y , (c ) NEGATIVE direction of y , (d) positive direction of x | |
| 37670. |
The wheels of an automobile are locked as it slides to a stop from an initial speed of 30.0 m/s. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.600 and the road is horizontal, approximately how long does it take the car to stop? |
|
Answer» `4.22s` |
|
| 37671. |
The transmitter is a RADAR is a high power __________ |
|
Answer» CYCLOTON oscillator |
|
| 37672. |
A machine gun is mounted on a flat rail car. The gun is firing bullets at the rate of 10 bullets per second each of mass 10 g. The bullets come out with velocity 500 ms^(-1) from the rear. Calculate the acceleration of the car at the instant when its mas is 200 kg. Also calculate the force at that instant. |
|
Answer» `0.25 m//"SEC"^(2) , 100 N ` |
|
| 37673. |
There is a uniformly charged non-conducting solid sphere. A small spherical cavity is made inside it. Distance of the centre of cavity is x from the centre of sphere |
|
Answer» Electric FIELD intensity inside the cavity is zero if x=0 
|
|
| 37674. |
This question has S-1 and S-2. Of the four choices given after the statements, choose the one that best describes the two statements. An insulating solid sphere of radius R has a uniformly positive charge density rho. As a result of this uniform charge distribution there is a finite value of electric potential at the centre of the sphere, at the surface of the sphere and also at a point out side the sphere. The electric potential at infinity is zero S-1: When a charge 'q' is taken from the centre to the qр surface of the sphere, its potential energy changes by (q rho)/( 3 epsi_0) S-2: The electric field at a distance r (r |
|
Answer» S-1 is TRUE, S-2 is true, S-2 is not the CORRECT explanation of statement - 1 |
|
| 37675. |
In a charged capacitors energy is stored |
|
Answer» POSITIVELY CHARGED plate |
|
| 37676. |
A spherical equipotential surface is not possible |
|
Answer» for a POINT chargge |
|
| 37677. |
Find an expression for loss of electrical energy when two capacitors (or conductors ) maintained at different potential are allowed to share their charges . |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider two capacitors having capacitances `C_1` and `C_2` and maintained at the potentials `V_1` and `V_2` respectively . Their TOTAL initial electrostatic energy is `U_(1) = (1)/(2) C_(1) V_(1)^(2) + (1)/(2) C_(2) V_(2)^(2)""... (i) ` On BRINGING them in electric constant potential acquired by them will be `V = (C_1 V_1 + C_2 V_2)/(C_1 + C_2)` `therefore` Net final electrostatic energy of the two capacitors `U_(2) = (1)/(2) (C_1 + C_2) V^(2) = (1)/(2) ((C_(1) V_1 + C_2 V_2)^(2))/((C_1 + C_2))` `therefore` LOSS of electrostatic energy on account of sharing of charge `Delta U = U_(1) - U_2 = 1/2 C_1 V_(1)^(2) + (1)/(2) C_(2) V_(2)^(2) - (1)/(2) ((C_(1) V_(1) + C_(2) V_(2))^(2))/((C_(1) + C_(2)))` `= (C_(1)^(2) V_(1)^(2) + C_(1) C_(2) V_(1)^(2) + C_(1) C_(2) V_(2)^(2) + C_(2)^(2)- (C_(1)^(2) + V_(1)^(2) + C_(2)^(2) V_(2)^(2) + 2 C_(1) C_(2) V_(1) V_(2)))/(2 (C_(1) + C_(2)))` `= (C_(1) C_(2) (V_(1)^(2) + V_(2)^(2) - 2V_(1) V_(2)))/(2 (C_(1) + C_(2))) = (C_(1) C_(2))/(2 (C_(1) + C_(2))) (V_(1) - V_(2))^(2)` This is term is always positive irrespective of the fact whether `V_(1) gt V_(2)` or `V_(1) lt V_(2)` |
|
| 37678. |
A body weighing 20 kg just slides down a rough plane that rises 5 in 12. What is the coefficient offriction? |
|
Answer» 0.458 |
|
| 37679. |
The switch in Fig. 30-28 is closed on a at time t = 0. What is the ratio E_(L)//E of the inductor's self-induced emf to the battery's emf (a) just after t = 0 and (b) at t = 2.00 tau_(L)? (b) At what multiple of tau_(L), will E_(L)//E = 0.500? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 1.00, (B) 0.135, (0.693) | |
| 37680. |
A copper bar ofmass m sides under gravity on twosmooth parallel rails l distance apart and set at angle alphato thehorizontal . At the lop , the rails arejoinedby a resistorR. Calculate the steady velocity of thebar then when there is a unifrom magnetic field B perpedicularto the plane of the rails . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37681. |
A coil with self inductance of 2.4H and resistance 12Omegais suddenly switched across a 120V direct current supply of negligible internal resistance. Determine (i) the time constant of the coil and (ii) the final steady current |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 37682. |
Electric field due to an infinite sheet of charge having surface charge density omega is E. Electric ficld due to an infinite conducting sheet of same surface density of charge is |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 37683. |
A 220 V ac supply is connectedbetween points A and B [Fig.1.51]. What will be the potential difference V across the capacitor?(##CHY_DMB_PHY_XII_P2_U09_C01_E04_003_Q01.png" width="80%"> |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 37684. |
In given RC circuit, capacitance of capacitor C_(1) = 3 mu F and C_(2) = 1 mu F.It is given that time constant of circuit between A and B is 3 millisecond.Value of R will be |
|
Answer» `1 OMEGA` 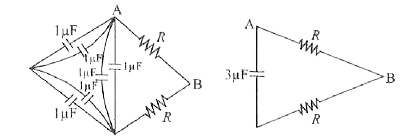 `RC = 3 XX 10^(-3) SEC` `R xx 3 xx 10^(-6) = 3 xx 10^(-3)` `R = 1000 Omega` |
|
| 37685. |
In which case racemisation takes place ? |
|
Answer» `H_(3)C-underset(H)OVERSET(C_(2)H_(5))overset(|)C-CH_(2)Brunderset(S_(N^(1)))overset(OH^(-))to` |
|
| 37686. |
How can you enhance the range of a voltmeter? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :By INCREASING the value of resistance ADDED in SERIES with the galvanometer. | |
| 37687. |
Unpolarised light falls first on polarizer Pan then on analyzer A. If the intensity o transmitted light from the analyzer is (1)/(8) th the incident unpolarized light what will be th angle between optic axis of P and A? |
|
Answer» `45^(@)` `(I_(0))/(8)=(I_(0))/(2)cos^(2) theta "" (1)/(2)=cos theta` `(1)/(4)=cos^(2) theta "" :. theta=60^(@)` |
|
| 37688. |
if accidentily the calorimeter remained open to atmosphere for same time during the experiment due to which the steady state temperature comes out to be 30^(@)C then total heat loss to surrounding during the experiment is (Use the specific heat capacity of the liquid from previous question) (A) 20 kcal (B) 15kcal (C) 10kcal (D) 8kcal . |
|
Answer» Solution :Heat given by the SPHERE `= (1000) (1//2) (80-30) = 25,000cal` Heat absorbed by the water calorimeter system `= (9000 (1) (40 -30) + (200) (1//2) (40 -30)` `10,000cal` So heat loss to SURROUNDING `= 15,000 CAL` . |
|
| 37689. |
(i)Draw a neat labelled ray diagram of an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment. Explain briefly its working. (ii) An astronomical telescope uses two lenses of powers 10 D and 1 D. What is its magnifying power in normal adjustment ? |
|
Answer» Solution :An astronomical telescope consists of an objective lens O of LARGE focal length (`f_0`) and large aperture and an eyepiece E of small focal length (`f_e`) and small aperture. In normal adjustment the distance between the two lenses is `L =f_(0) + f_(e)` . A labelled ray diagram is shown in Fig. 9.83. A parallel beam of light coming from a distant astronomical object, after refraction from the objective lens, FORMS a real, inverted and highly diminished image A.B. in the focal plane of the objective lens. The image A.B. behaves as an object for the eyepiece lens E, which again renders the emergent light as a parallel beam. Thus, final image in normal adjustment is formed at infinity and is an inverted and magnified image. The angular magnification (or MAGNIFYING power) of a telescope is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended by the final image (B) at the eye to the angle subtended (`alpha`) by the object at the eye. The angular magnification (or magnifying power) of a telescope is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended by the final image (`beta`) at the eye to the angle subtended (`alpha`) by the object at the eye. Angular magnification of the image in normal adjustment is `m=-f_(0)/f_(e)`  (ii) GIVEN that power of objective lens `P_(0) =1 D` and power of eyepiece lens `P_( e) =10 D` `therefore` Magnifiying power of telescope `m=-f_(0)/f_(e) =-P_(e)/P_(0) =-10/1 = -10` The -ve sign signifies that the final image is an inverted image. |
|
| 37690. |
If the pressure amplitude in a sound wave is tripled then the intensity of sounds is increased by : |
|
Answer» 9 `THEREFORE` when amplitude is TRIPLED then intensity becomes 9 times Hence the correct CHOICE is (a) |
|
| 37691. |
Starting from origin at t=0, with initial velocity 5 hat(j) m//s, a particle moves in the x-y plane with a constant acceleration of (10 hat(i) - 5hat(j))m//s^(2). Find the coordinates of the particle at the moment its y-coordinate is maximum. |
|
Answer» (5m, 5m) `y_(y) = u_(y) + a_(y) t rArr 0= 5- 5t rArr t= 1` `x= u_(x) t + (1)/(2) a_(x) t^(2) = 0 + (1)/(2) (10) (1)= 5` `y= u_(y) t + (1)/(2) a_(y) t^(2) = 5(1) + (1)/(2) (-5) (1) = 2.5` |
|
| 37692. |
The minimum distance between an object and its real image is |
|
Answer» f |
|
| 37693. |
A gardener is watering plants at the rate 0.1 litre/sec using a pipe of cross-section 1 cm_2. What additional force he has to exert if he desires to increase the rate of watering two times ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`F= Adv^(2) =((Av)^(2)d)/A`If rate of WATERING plant (Av) is doubled, it means AMOUNT of water poured /sec is doubled which is possible only if velocity is doubled. Hence force is to be made 4 times. `therefore`additional force = 3 times initial force `=3Adv^(2) =3(Av)^(2)/A d = (3 XX 0.1 xx 0.1 xx 10^(3))/10^(-4) = 3 xx 10^(5)` N |
|
| 37694. |
In an electrical circuit, R, I, C and AC voltage source are all connected in series. When L is removed from the circuit, the phase difference between the voltage and current in the circuit, is (pi)/(3). Instead, if C is removed from the circuit, the phase difference is again (pi)/(3). The power factor of the circuit is |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 37695. |
A curved surface of radius R separates two medium of refractive indices mu_1 and mu_2 as shown in figure Choose the correct statement(s) related to the virtual image formed by object O placed at a distance x, as shown in figure. |
|
Answer» Virtual image is formed for any position of O if `mu_2 LT mu_1` |
|
| 37696. |
If unpolarised light of intensity I_(0) is incident on the polarising plate, intensity of emerging light will be ...... |
|
Answer» ZERO Intensity of light not COMING out `I=-(I_(0))/(2)=(I_(0))/(2)` |
|
| 37697. |
A soap bubble is given a negative charge, then its radius |
|
Answer» Decreases |
|
| 37698. |
In above problem, if coefficient of friction for both the spheres is same and let t^(1)and t^(2)be the times when pure rolling of solid sphere and of hollow sphere is started. Then : |
|
Answer» `t_(1) = t_(2)` `a=(mumg)/(m) = mugtherefore v=at` or `t=v/a = omega_(0)/(mug(1/R + (mR)/I)` Again `I_("SOLID") lt I_("hollow") therefore t_("solid") lt t_("hollow")` or `t_(1) lt t_(2)` |
|
| 37699. |
Discuss the types of electric charges by rubbing appropriate non-conductors. Which scientists gave their names ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`-` Any matter is mainly made up of two particles : Electron and proton. - Charge on electron is considered as negative and charge on proton is considered as positive. Charge is scalar quantity. - When two non-conductors are rubbed, electrons are TRANSFERRED from one body to another body due to its less mass. The body which GAINS the electrons becomes negatively charged and the body which donates the electrons becomes positively charged. - Positive and negative names of charges were given by American SCIENTIST Benjamin Franklin. -The body which has charge is called charged body and the body which has no charge is called neutral body. - When two bodies of opposite charges are BROUGHT in contact, both bodies become neutral. - Examples of what type of charge will object have by rubbing two non-conducting OBJECTS are given in pair in following table : |
|
| 37700. |
Potential at a point by the relation V=4x^(2) +5y^(2)+6z^(2). Calculate the magnitude of field of components at (1,-2,2) |
|
Answer» |
|