Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 37551. |
The terminology of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum is given in the text. Use the formula E = hν (for energy of a quantum of radiation: photon) and obtain the photon energy in units of eV for different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. In what way are the different scales of photon energies that you obtain related to the sources of electromagnetic radiation? |
|
Answer» Solution :Photon ENERGY [for `lamda =1` m] `=(6.63xx10^(-34) xx3xx10^(8))/(1.6xx10^(-19)) eV=1.24 xx10^(-6) eV` Photon energy for other wavelengths in the figure for electromagnetic spectrum can be obtained by multiplying approximate POWERS of ten. Energy of a photon that a source produces indicates the SPACINGS of the relevant energy levels of the source. For example, `lamda = 10^(-12) m` corresponds to photon energy `= 1.24 xx 10^(6) eV = 1.24 MeV`. This indicates that nuclear energy levels (transition between which causes γ-ray emission) are typically spaced by 1 MeV or so. Similarly, a visible wavelength `lamda = 5 xx 10^(-7)` m, corresponds to photon energy = 2.5 eV. This implies that energy levels (transition between which gives visible radiation) are typically spaced by a few eV. |
|
| 37552. |
Identify the device X and write the expression for its rectance |
|
Answer» Solution :The AC Generator works on the principle of electromagnetic indunction When the magnetic flux through a coil CHANGES . An emf is induced in it. As the coil rotates in magnetic field the effective area of the loop (I.e. A` cos theta` ) exposed to the magnetic field KEEPS on changing ,hence magnetic flux changes and an emf is induced  When a coil is rotated with a constant angular speed `omega` the angle ` theta` between the magnetic field vector ` oversetto B` and the area vector ` oversetto A ` , of the coil at any instant .t. equal cot : (assuming ` theta =O^(@) at t =0) ` As a result , the effective area of the coil exposed to the magnetic ,field changes with time , the flux any instant .t. is given by `PHI _n=NBA cos theta =NBA cos theta` ` therefore`The induced emf `=-N(dphi )/( DT )` ` = NBA = ( d)/( dt) (cos omega t) ` e= NBA `omega sin omegat ` |
|
| 37553. |
A rectangular illuminated slit produces |
|
Answer» SPHERICAL WAVE front |
|
| 37554. |
(A): The power output of a practical trans- former is always smaller than the power input (R): A transformer works on the principle of mutual induction |
|
Answer» Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation |
|
| 37555. |
A device used to print large maps, drawings, graphs, etc is known as plotter. A plotter contains a printing head and a drum through which the paper comes out. The plotting pencil is held in a block which in turn is head by a system of four springs as shown. The spring constants of the four springs are k_(1) = 20 N//m, k_(2) = 30 N//m, k_(3) = 60 N//m and k_(4) = 30 N//m. Initialy, the pencil is in the middle i.e., at x = 0 and all the springs are in natural length. The velocity of paper coming out is v_(0) =0.2 m//s. The block is set up in motion by giving a velocity = 1m/s towards right. The mass of the pencil block with pencil is m_(1) = 0.7 kg. The friction is assumed to the absent in the system. Suppose the pencil block is in the mean position and moving towards left. A parrot of weight 2.1 kg sits gently on it. The parrot flies in upward direction when the block reaches extreme left. What is the distance moved by the parrot ? |
|
Answer» 0.01 m |
|
| 37556. |
An op[tician prescribes spectacles to a patient with a combination of a convex lens of focal length 40 cm and a concave lens of focal length 25 cm. The power of the spectacles is : |
|
Answer» -6.5 D |
|
| 37557. |
A device used to print large maps, drawings, graphs, etc is known as plotter. A plotter contains a printing head and a drum through which the paper comes out. The plotting pencil is held in a block which in turn is head by a system of four springs as shown. The spring constants of the four springs are k_(1) = 20 N//m, k_(2) = 30 N//m, k_(3) = 60 N//m and k_(4) = 30 N//m. Initialy, the pencil is in the middle i.e., at x = 0 and all the springs are in natural length. The velocity of paper coming out is v_(0) =0.2 m//s. The block is set up in motion by giving a velocity = 1m/s towards right. The mass of the pencil block with pencil is m_(1) = 0.7 kg. The friction is assumed to the absent in the system. What is the value of the amplitude A? |
|
Answer» 0.05 m |
|
| 37558. |
What is the field inside the core of the solenoid? |
| Answer» Solution :The field is uniform and is `B = mu_0nl` where .n. is the NUMBER of turns PER UNIT LENGTH and I intensity of CURRENT. | |
| 37559. |
Define 'drift velocity' of free electrons . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The average velocity with which the FREE electrons are drifted in a direction OPPOSITE to the APPLIED field called drift velocity | |
| 37560. |
A particle performs simple harmonic motion. The equation of motion is x=5sin(4t-pi/6), where x is the displacement. If the displacement of the particle is 3 units, then its velocity is, |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 37561. |
What is greenhouse effect ? Explain. |
Answer» Solution :The earth.s surface SOLAR radiations and gets heated up. Then like any other hot body, it starts emitting radiations. The radiations emitted by earth is mainly infrared radiations. These radiations are unable to cross the LOWER atmoshpere, which reflects them back. Low LYING clouds also prevent IR radiation from PASSING through and thus serve to keep the earth.s surface warm at night. This phenomenon is called .Greenhouse Effect..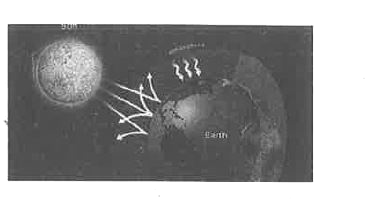
|
|
| 37562. |
A device used to print large maps, drawings, graphs, etc is known as plotter. A plotter contains a printing head and a drum through which the paper comes out. The plotting pencil is held in a block which in turn is head by a system of four springs as shown. The spring constants of the four springs are k_(1) = 20 N//m, k_(2) = 30 N//m, k_(3) = 60 N//m and k_(4) = 30 N//m. Initialy, the pencil is in the middle i.e., at x = 0 and all the springs are in natural length. The velocity of paper coming out is v_(0) =0.2 m//s. The block is set up in motion by giving a velocity = 1m/s towards right. The mass of the pencil block with pencil is m_(1) = 0.7 kg. The friction is assumed to the absent in the system. What is the force constant of SHM performed by the pencil ? |
|
Answer» 104.58 N/m |
|
| 37563. |
At t = 0, a flywheel has an angular velocity of 4.7 rad/s, a constant angular acceleration of -0.25rad//s^(2), and a reference line at theta_(0)=0 (a) Through what maximum angle theta_(max) will the reference line turn in the positive direction? What are the (b) first and ( c) second times the reference line will be at theta=1//2theta_(max)? At what (d) negative time and (e ) positive time will the reference line be at theta = 10.5 rad ? (f) Graph theta versus t, and indicate your answers. |
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 44 rad, (B) `q_(1)=22rad` is t = 5.5 s, ( C) `q_(1)=22rad` is t = 32 s, (d) t = -2.1 s, (e) t = -2.1s, (f) With radians and SECONDS understood, the graph of q versus t is shown below (with the points found in the previous parts INDICATED as small dots). 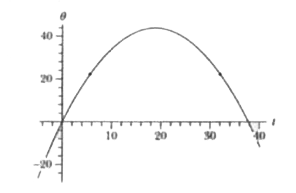
|
|
| 37564. |
What is an equipotential surface ? |
| Answer» Solution :An EQUIPOTENTIAL surface is a surface with CONSTANT VALUE of POTENTIAL at all points on the surface. | |
| 37565. |
Find (a) the average and (b) mis value for the Saw tooth voltage of peak value Vas shown in the figure |
|
Answer» Solution :As the equation of the Saw-tooth WAVE SHOWN in the figure will be `V=(2V_(@))/(T)t-V_(@)=V_(@)((2ty)/(T)-(1))` `So,(a)V_av=(int_(0)^(T//2)(Vdt)/(int_(0)^(T//2)=(2)/(T)int_(@)^(T//2)V_(@)(2t)/(T)-1)DT=|V_(@)/(2)` `and(B)V_(rms)[int_(@)^(T)V^(20dt)/(Int_(@)^(T)dt]]^(1//2)=(V_(@))/(sqrt3)` |
|
| 37566. |
Does the 'stopping potential' in photoelectric emission depend upon (i) the intensity of the incident radiation in a photocell.? (ii) The frequency of the incident radiation ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(i) No, (ii) Yes, increases on increasing the FREQUENCY of INCIDENT LIGHT. |
|
| 37567. |
Derive the formula for the electric potential energy of system of two charges. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider the charges `q_(1)` and `q_(2)` initially at infinity. Suppose, first the charge `q_(1)` is BROUGHT from infinity to the point by distance `r_(1)`. There is no extermal field against which work needs to be done, so work done in bringing `q_(1)` from infinity by distancer `r_(1)` is, `:. W_(1)=0` 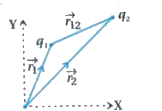 This charge `q_(1)` produces a POTENTIAL in SPACE is `V_(1)= (kq_(1))/(r_(1)p)` where `r_(1)p` is the distance of a point P in space from the location of `q_(1)` . Now work done in bringing charge `q_(2)` from infinity to the given point by distance `r_(2)` in theelectric field of `q_(1)` is `W_(2)=q_(2)V_(1)` `:. W_(2)=(kq_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))` where `r_(12)` is the distance between points 1 and 2 at distance `r_(1)` and `r_(2)` . Since electrostatic force is conservative this work gets stored in the form of potential energy of the system. Potential energy of system of two charges `q_(1)` and `q_(2)` is, `U= W_(1)+W_(2)` `:. U= (kq_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))` If `q_(2)` was brought first to its present location and `q_(1)` brought later the potential energy would be according to equation (2). Generally, the potential energy expression is unaltered whatever way the charges are brought to the specified locations because the path independence of work for electrostatic force. `:. U=k[0+(q_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))+(q_(1)q_(3))/(r_(13))+(q_(2)q_(3))/(r_(23))]` `:. U=k[(q_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))+(q_(1)q_(3))/(r_(13))+(q_(2)q_(3))/(r_(23))]` Equation (2) is true for any sign of `q_(1)`, and `q_(2)`. If `q_(1) q_(2) gt0` potential energy will be negative. And if `q_(1)q_(2) lt 0` potential energy will be negative . |
|
| 37568. |
A large negatively charged object was placed on an insulated table. A neutral metallic ball rolled straight toward the object but stopped before touching it. A second neutral metallic ball rolled along the same path as the first ball. Struck the first ball driving it a bit closer to the negatively charged object and stopped. After all stopped rolling, the first ball was closer to the negatively charged object than the second ball. At no time did either ball touch the charged object. which statement is correct concerning the final charge on each ball ? |
|
Answer» The FIRST BALL is POSITIVE and the second NEGATIVE |
|
| 37569. |
A bar of mass m=0.50kg lying on a horizontal plane with a friction coefficient k=0.10is attached to the wall by means ofa horizontal non- deformed spring. The stiffness of the spring is equal to x=2.45 N//cm, its mass is negligibl . The bar was displaced so that the spring was stretched by x_(0)=3.0 cm, and then released. Find : (a) the period of oscillation of the bar , (b) the total number os osciallations that the bar performs untial it stops completely. |
|
Answer» Solution :We shall denote the stiffness constant by `k. ` Suppose the spring is stretched by `x_(0)`. The bar in then subject to two horizontal forces `(1)` restoring force `- kx` and `(2)` friction `kmg` opposing motion. If `x_(0)gt (kgm)/(k )= Delta` the bar will come back. `(` If `x_(0) le Delta`, the bar will stay put . `)` The equation of the bar when it is moving to the left is `m ddot ( x) = - k x + k mg` This equation has the solution `x= Delta + ( x_(0)- Delta) cos sqrt((k)/(m))t` where we have used `x=x_(0), DOT(x)=0` at `t=0` . This solution is onely valid till the bar comes to rest. This happens at `t_(1)=pi//sqrt((k)/(m))` and at that time `x=x_(1)=2 Delta-x_(0)`. if` x_(0)gt 2 Delta` the TENDENCY of the rod will now be to move to the right. `(` if `Deltalt x_(0)lt 2 Delta`the rod will stay put now `)` Now the equation for rightward motion becomes `m ddot(x)=-k x - kmg` `(` the friction force has reversed `)`. We notice that the rod will move to the right only if `k ( x_(0)-2 Delta)gtk mg` `i.e.x_(0)gt3 Delta` In this case the solution is `x=-Delta+( x_(0)-3Delta)cos sqrt((k)/(m))t` Since `x=2 Delta- x_(0) `and `dot(x) =0` at `t=t_(1)=pi //sqrt((k)/(m))`. The rod will next come to rest at `t=t_(2)=2pi //sqrt((k)/(m))` and at that instant `x=x_(2)=x_(0)-4 Delta`. However the rod will stay put unless `x_(0)gt 5 Delta` Thus `(a)` time PERIOD of one full oscillation `=2pi //sqrt((k)/(m)).` `(b)` There is no oscillationif `0 lt x_(0) lt Delta` One half oscillation if `Delta lt x_(0) lt 3 Delta` 2 half oscillation if `3Delta lt x_(0) lt 5 Delta` etc We can say that the NUMBER of full oscillation is one half of the INTEGER`n` where `n=[(x_(0)-Delta)/(2 Delta)]` where`[x]=` smalles non- negative integer greater than `x`. 
|
|
| 37570. |
Monochromatic light of frequency 6 times 10^14 Hz is produced by laser. Each photon has an energy=……. |
|
Answer» `4 TIMES 10^-19` |
|
| 37571. |
Do magnetic forces obey Newton's third law. Verify for two current elements vec(dl_(1))=dl(hati) located at the origin and vec(dl_(2))=dl(hatj) located at (0, R, 0). Both carry current I. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :1. According to Biot-Savart law, direction of magnetic field is in the direction of `Ivec(DL)`. 2. Magnetic field for `dl_(2)`, element at (0, R, 0) is GIVEN by, `vecB=Ivec(dl_(2))xxvecr` = `Idl(hati)xxrhatj` = `Idlr(HATIXXHATJ)` `thereforevecB=Idlr(hatk)` That means, it is in z-direction. 3. Force on this element, `vecF_(2)=Ivec(dl_(2))xxvecB` = `Idl(hati)xxB(hatk)` = `IdlB(hatixxhatk)` = `IdlB(-hatj)` This force is in y-direction.  4. Magnetic force on `dl_(1)` element at origin, `Ivec(dl_(1))xxvecr=Idlhatjxxr(-hatj)` = 0 `vecr=r(-hatj)` because first element is at (0, R, 0) with respect to that this element is in y-direction. So, magnetic field is zero at this POINT. So, magnetic force on `vec(dl_(1))` due to `vec(dl_(2))` be zero. |
|
| 37572. |
Column I gives a list of possible set of parameters measured in some expermients. The varitions of the parameters in the form of graphs ar shownin Column II. Match the set of parameters given Column I with the graph given in Column II. Indicate your answer by darking the appropriate bubbles of the 4 xx 4 matrix given in the ORS. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37573. |
When ultraviolet rays incident on metal plate there photoelectric effect does not occur, it occurs by incident of |
|
Answer» INFRARED RAYS |
|
| 37574. |
Explain characteristics of nuclear binding force |
|
Answer» Solution :Nucleus contains protons and neutrons. The protons in the nucleus experience only the electrostatic force, then the nucleus would fly apart in an instant. There is a strong attractive force between protons to overcome the repulsive Coulomb.s force. This attractive force which holds the nucleus together is CALLED strong nuclear force. (i) The strong nuclear force is of very short range, acting only up to a DISTANCE of a few Fermi, nuclear force is the STRONGEST force in NATURE. (ii) The strong nuclear force is attractive and acts with an EQUAL strength between proton-proton, proton-neutron, and neutron - neutron. (iii) Strong nuclear force does not act on the electrons. So it does not alter the chemical properties of the atom. |
|
| 37575. |
Define magneticsusceptibilityof a material. Name two elements, one having positive susceptibilityand the other having negative susceptibility . What does negative susceptibility signify ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Magnetic susceptibility : Magnetic susceptibility of a material is defined as the ratio of the INTENSITY of MAGNETISATION (I) induced in the material to the magnetisation force (H) applied on it. Magneticsusceptibility is represented by `X_(m)=(I)/(H)`. `Diamagnetic substances like copper, lead etc. has NEGATIVE susceptibility. Paramagnetic substances like ALUMINIUM, calcium etc. has positive susceptibility. Negative susceptibilityof diamagnetic substance does not change with temperature. |
|
| 37576. |
An equiconvex lens of glass of focal length 0.1 metre is cut along a plane perpendicular to principle axis into two equal parts.The ratio of focal length of new lenses formed is: |
|
Answer» `1:1` |
|
| 37577. |
A vessel of depht 'x' is half filled with oil of refractive index mu_(1) and the other half is fillied with water of refractive index mu_(2) . The apparent depth of the vessel when viewed from above is |
|
Answer» `(X(mu_(1) + mu_(2)))/(2 mu_(1) mu_(2))` |
|
| 37578. |
A toroid has core (non-ferromagnetic ) of inner radius 25 cm and outer radius 26 cm, around which 3500 turns of a wire are wound. If the current in the wire is 11 A, what is the magnetic field (i) outside the toroid , (ii) insidethe core of the toroid, and (iii)in the empty space surrounded by the toroid. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :i. ZERO `II. B=mu_0 NI = (4pi xx 10^(-7) xx 3500 xx 11)/(2 pi xx 25.5 xx 10^(-2))=3.0 xx 10^(-2) T` iii. Zero |
|
| 37579. |
M_(1) and M_(2) are plane mirrors and kept parallel to each other . At point O , there will be a maxima for wavelength . Light from a monochromatic source S of wavelength lambda is not reaching directly on the screen . Then lambdais |
|
Answer» `(3D^(2))/D` |
|
| 37580. |
Which of the following statements regarding magnetic lines of force is correct ? |
|
Answer» Total magnetic FLUX linked a closed SURFACE is ALWAYS zero |
|
| 37581. |
The principle of photo cell is |
|
Answer» To CONVERT electrical energy into light energy |
|
| 37582. |
शुद्ध जल की मोलरता है |
|
Answer» 55.5 |
|
| 37583. |
A light of ray incidents normally on one side of equilateral prism. If refractive index of prism is 1.5, then deviation angle is ...... |
| Answer» SOLUTION : `45^@` | |
| 37584. |
A solenoid 60 cm long and of radius 4.0 cm has 3 layers of windings of 300 turns each. A 2.0 cm long wire of mass 2.5 g lies inside the solenoid (near its centre) normal to its axis, both the wire and the axis of the solenoid are in the horizontal plane. The wire is connected through two leads parallel to the axis of the solenoid to an external battery which supplies a current of 6.0 A in the wire. What value of current (with appropriate sense of circulation) in the windings of the solenoid can support the weight of the wire? |
Answer» Solution :1.  Magnetic FIELD inside a long current CARRYING solenoid is B then magnetic force exerted on current carrying wire placed perpendicular to axis of solenoid in the horizontal plane will be, `F=I.l.Bsin90^(@)` (Where, I. = current passing through wire) `thereforeF=I.l.(mu_(0)NI)""...(1)` (Where, I = current passing through the windings of solenoid) 2. Direction of above force is VERTICALLY upward (see the diagram). If it balances weight of wire then, F = mg `thereforeI.l.(mu_(0)nI)=mg` `therefore(6)(0.02)(4pixx10^(-7)XX(300xx3)/0.6xxI)=(2.5xx10^(-3))(9.8)` `thereforeI=108.36A` |
|
| 37585. |
The number of silicon atoms per m^(3) is5 xx 10^(28). This is doped simultaneously with 5 xx 10^(22) atoms per m^(3) of Arsenic and 5 xx 10^(20) per m^(3) atoms of Indium. Calculate the number of electrons and holes given that n_(i) = 1.5 xx 10^(16) m^(-3). Is the material n-type or p-type? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Arsenic is PENTAVALENT and Indium is trivalent. `n_(e) = 5 xx 10^(22) - 0.05 xx 10^(22) = 4.95 xx 10^(22)` but `""n_(i)^(2) = n_(e)n_(h)` `THEREFORE ""n_(h) = (2.25 xx 10^(22))/(4.95 xx 10^(22)) = 0.454 xx 10^(10)` `n_(h) = 4.54 xx 10^(9) `PER `m^(3)` since `n_(e) gt n_(h)`, the material is n type. |
|
| 37586. |
Zener diode has higher doping density as compared to ordinary p-n junction diode. How does if effect (i) the width of depletion layer and (ii) the junction field? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :[(i) `darr` (II) `uarr` as `E_(beta) = V_(B)/d`] | |
| 37587. |
A long straight wire is arranged along the symmetry axis of a toroidal coil of rectangular cross-section, whose dimensions are given in the figure. The number of turms on the coil is N, and permeability of the surrounding medium is unity. Fine the amplitude of the emf induced in this coil, if the current i=i_(m) cos omegat flows along the straight wire. |
Answer» 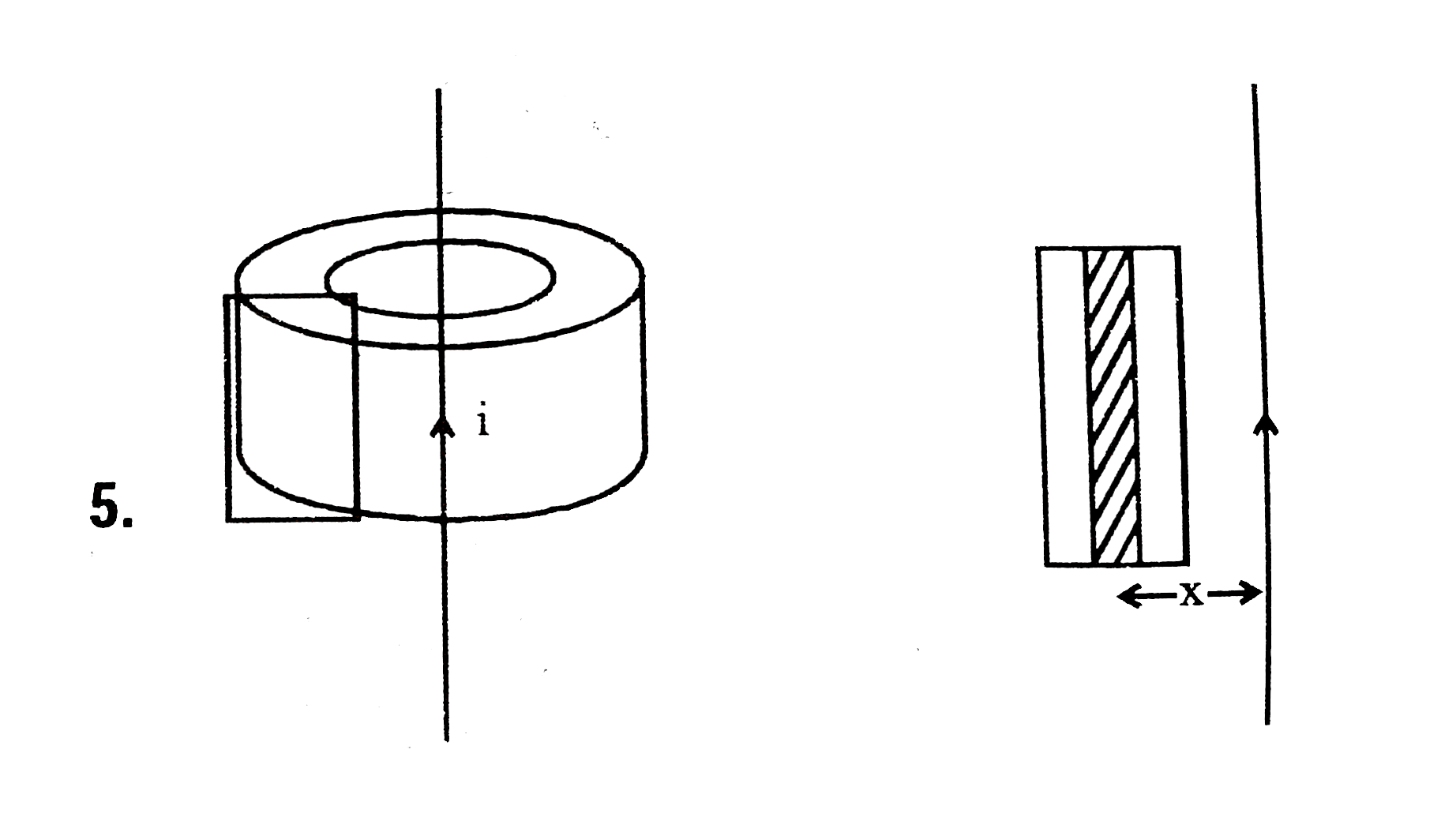 Flux through each loop `phi=int_(a)^(b) Bdx=int_(a)^(b)mu_(0)/2I/x hdx` `=mu_(0)/2Ih lnb/a` `e=-N(dphi)/(dt)=-ND/(dt)(mu_(0)/zhlnb/a)I` `=-(Nmu_(0)h)/2lnb/ad(dt)i_(m)cosomegat` `=(Nmu_(0)h)/2lnb/ai_(m)omegasinomegat` `=(Nmu_(0)homegai_(m))/2 ln b/a SINOMEGAT` `e_(0)=(Nmu_(0)homegai_(m))/2 ln b/a` |
|
| 37589. |
Static electricity is produced due to....... |
|
Answer» friction |
|
| 37590. |
To determine the quality of thermal insulation of a Dewar vessel, it is filled with ice at0^(@)C 42 g of ice have melted in 24 h. Usually liquid nitrogen at 78 K is kept in this flask. Assuming the quantity of heat entering the flask to be proportional to the difference in the internal and the external temperatures of the vessel, find the amount of liquid nitrogen that is going to evaporate in 24 h. The ambient temperature is 20^(@)C the heat of vapourization of liquid nitrogen at normal pressure is 1.8xx10^(5)J//K. |
|
Answer» Solution :The HEAT flowing to the Dewar vessel is `Q=alpha(T_("air")-T)`, . where `alpha` is a CERTAIN coefficient, and T is the temperature INSIDE the flask. For ice and liquid nitrogen we obtain the ratio `(Q_(1))/(Q_(2))=(T_("air")T_(1))/(T_("air")T_(2))` But for nitrogen `Q_(2)=m_(2)L`where L is its heat of evaporation, the respective value for ice being `Q_(1)=m_(1) LAMBDA`. HENCE `(m_(1)lambda)/(m_(2)L)=(T_("air")-T_(1))/(T_("air")-T_(2))`, from which `m_(2)=(m_(1) lambda(T_("air")-T_(2)))/(L(T_("air")-T_(1)))` |
|
| 37591. |
In the Bohr atom model, the frequency of transitions is given by the following expression v=Rc(1/n^(2)-1/m^(2)), where nltm, Consider the following transitions: Show that the frequency of these transitions obey sum rule (which is known as Ritz combination principle) |
|
Answer» Solution :In the Bohr ATOM model, the frequency of transition `upsilon = R_(c) ((1)/(N^(2)) - (1)/(m^(2)))n lt m ` `I^(st)` transition, m = 3 and n = 2 `upsilon_(3) to 2 = R_(c) ((1)/(2^(2)) - (1)/(3^(2))) = R_(c) ((1)/(4)- (1)/(9)) ` `= R_(c) ((9-4)/(36)) = R_(c) ((5)/(36))` `II^(nd)` transition , m = 2 and n = 1 `upsilon _(2) to 1 R_(c) ((1)/(1^(2))-(1)/(2^(2))) = R_(c) (1 - (1)/(4)) = R_(c) ((3)/(4))` `III^(rd)` transition m = 3 and n = 1 `upsilon _(3) to1 = R_(c) ((1)/(1^(2)) - (1)/(3^(2))) = R_(c)(1-(1)/(9)) = R_(c) ((8)/(9))` According to Ritz combination principle, the frequency transition of single STEP is the sum OFFREQUENCY transition in two steps. `upsilon_((3) to 2) + upsilon_((2) to 1) = upsilon_((3) to 1)` `R_(c) ((5)/(36)) + R_(c) ((3)/(4)) = R_(c) ((8)/(9))` `R_(c) ((8)/(9)) = R_(c) ((8)/(9))` `upsilon_((3) to 2)+ upsilon_((2) to 1) = upsilon_((3) to 1)` |
|
| 37592. |
The magnitude of the electric field on the surface of a sphere of radius r having a uniform surface charge density sigma is |
|
Answer» `sigma//epsi_(0)` |
|
| 37593. |
STATEMENT-1 Light can show interference. STATEMENT-2 Light can show diffraction. |
|
Answer» STATEMENT-1 is TRUE Statemetnt-2 is True,Statement -2 is a correct explanation for statement -1. |
|
| 37594. |
A body is sliding down an inclined plane have coefficient of friction 0.5. If the normal reaction is twice that of resultant downward force along the incline. Find the angle between the inclined plane and the horizontal. |
|
Answer» Solution :`MU =0.5`. `N=2mg(SIN theta - mu COS theta)` `mg cos theta = 2mg(sin theta-mu cos theta)` `cos theta = 2COS theta(tan theta - mu)` `(1)/(2)=tan theta-(1)/(2)` `rArr tan theta = 1 rArr theta = 45^(@)` |
|
| 37595. |
AssumingV_Cesat=0.2V =0.2and beta=50 ,Find the minium base current (I_B) required to drive transitor given in the figure to saturation. |
|
Answer» Solution :`V_(Cesat)=0.2V and beta=50` `V_(CE)=V_(C C)-I_cR_C` `0.2=3-I_C(1K)` `1110^(3)=2.8 A` `I_C=2.8mA` `I_B=(I_C)/(beta)=(2.8)/(50)xx10^(-3)` `=0.056xx10^(-3)=56xx10^(-6)` `I_B=56 muA` 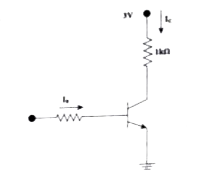
|
|
| 37596. |
In the figure three are three metallic large plates. The middle plates carries a total charge q. Plates 1 & 2 (which are uncharged) are connected by a wire. Find the charge induced on each surface of 1 & 2. Given l_(2) = 2l_(1) |
|
Answer» `RARR q_(3)-q_(1)+q_(1)-q+q_(3)=0` `rArr q_(3)=1//2` (1) & (2) have same potential `rArr (q_(1)l)/(A epsilon_(0))-((q-q_(1)))/(A epsilon_(0))2 l=0` `rArr -q_(1)+(q-q_(1))2=0` `rArr -3 q_(1)+(q-q_(1))2=0` `rArr -3q+2q =0` `q_(1)=-(2q)/(3)` Alternative Solution : Let the charge on ourter surface of plates (1) be x and on the inner (interfacing) surface of plate )1_ be y, then charge distribution on other plates is shown in figure (by using charge conservation and E = 0 INSIDE the metallic plates) For electric FIELD to be zero inside the plate 1  `=(x)/(2A epsilon_(0))=((q-x))/(2A epsilon_(0))` `rArr x=(q)/(2) & q-x =(q)/(2)` SINCE `V_(A) =V_(C) rArr V_(A) - V_(B) = V_(C) - V_(B)` `rArr E_(1) l_(1) = E_(2) l_(2)` `rArr = (y)/(A epsilon_(0)) l_(1) ((-q-y))/(A epsilon_(0)) 2 l_(1)` `y l_(1)=2ql_(1)-2yl_(1)rArr3yl_(1)=-2yl_(1)y =(-2q)/(3)` So, `-q-y=-q+(2q)/(3)=(-q)/(3)` So, charge on outer surface of plate 1 is `x = (-q)/(2)` Charge oninner (interfacing) surface of plate 1 is `y = (-2q)/(3)` Charge onouter surface of plate 2 is `q - x = (q)/(2)` Charge on inner (interfacing) surface of plate 2 is `(-q-y)=(-q)/(3)` `q_(1("outer"))=(1)/(2),q_(1("inner"))=(-2q)/(3)` `q_(2("outer"))=(q)/(2),q_(2("inner"))=(-q)/(3)`. |
|
| 37597. |
The critical angles of three transpararent media K, L & M are 30^(@), 60^(@)" and "45^(@) respectively. If K_(P), L_(P)" and "M_(P) are their polarising angles respectively, arrange them in increasing order |
|
Answer» <P>`K_(P), L_(P), M_(P)` |
|
| 37598. |
The length of a potentiometer wire is 1m and its resistance is 4Omega. A current of 5mA is flowing in it. An unknown source of e.m.f is the source. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`x=I rho=I=(R )/(L )=(5xx4)/(1)=20MV` `E=lx-0.40xx20=8mV` |
|
| 37599. |
In a cyclotron, a charge particle, |
|
Answer» UNDERGOES acceleration all the time. 2. INSIDE dees, there is no electric field due to shielding of charge or field. So, only magnetic force keeps the circular motion of charged particle inside. 3. So, the charged particle always accelerated. |
|
| 37600. |
The angle which the motion of the body makes with the horizontal is called ____ of motion of the body. |
|
Answer» |
|