Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in Current Affairs.
This section includes 7 InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your Current Affairs knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1. |
A wire is bent to form a semicircle of the radius a. The wire rotates about its one end with angular velocity omega . Axis of rotation is perpendicular to the plane of the semicircle . In the space , a uniform magnetic field of induction B exists along the aixs of rotation as shown in the figure . Then - |
|
Answer» <P>potential DIFFERENCE between p and Q is equal to` 2 B omega a^2` |
|
| 2. |
A massless non conducting rod AB of length 2l is placed in uniform time varying magnetic field confined in a cylindrical region of radius (R gt l) as shown in the figure. The center of the rod coincides with the centre of the cylin- drical region. The rod can freely rotate in the plane of the Figure about an axis coinciding with the axis of the cylinder. Two particles, each of mass m and charge q are attached to the ends A and B of the rod. The time varying magnetic field in this cylindrical region is given by B = B_(0) [1-(t)/(2)] where B_(0) is a constant. The field is switched on at time t = 0. Consider B_(0) = 100T, l = 4 cm(q)/(m) = (4pi)/(100) C//kg. Calculate the time in which the rod will reach position CD shown in the figure for th first time. Will end A be at C or D at this instant ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 3. |
A concave lens with equal radius of curvature both sides has a focal length of 12 cm. The refractive index of the lens is 1.5. How will the focal length of the lens change if it is immersed in the liquid of refractive index 1.8 ? |
| Answer» Solution :Focal LENGTH will BECOME `+36 CM` | |
| 4. |
If the tempearture of black body is raised by 5%, the heat energy radiated would increases by : |
|
Answer» `5%` `(E_(2))/(E_(1))=((T_(2))/(T_(1)))^(4)` `(E_(2))/(E_(1))=((105)/(100))^(4)=1*2158` `:.""(E_(2))/(E_(1))-1=1*2155-1` `rArr(E_(2)-E_(1))/(E_(1))xx100=*2155xx100=21*55%` Thus CORRECT choice is (c ). |
|
| 5. |
What are the co-ordinates of the image of S formed by a plane mirror as shown in figure? |
|
Answer» (4 CM, 0) |
|
| 6. |
The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by PQ in Fig. The direction in which the ray would travel after reflection is shown by four rays marked 1, 2, 3 and 4. Which of the four rays correctly shows the direction of reflected ray? |
|
Answer» 1 |
|
| 7. |
What is meant by polarisation ? |
| Answer» Solution :POLARISATION is the phenomenon of restricting the WAVES in OSCILLATIONS to PARTICULAR plane. | |
| 8. |
Two concentric coils each of radius equal to 2πcm are placed right angles to each other. If 3 A and 4 A are the currents flowing through the two coils respectively. The magnetic induction( in Wb m^(-2) )at the center of the coils will be |
|
Answer» `7 xx 10^(-5)` `B_(1)= (mu_(0))/(2) (3)/(2pi xx 10^(-2))= 3 xx 10^(-5)T` `B_(2)= (mu_(0))/(2) (4)/(2pi xx 10^(-2))= 4 xx 10^(-5)T` `B= sqrt(B_(1)^(2))+ B_(2)^(2)= 5 xx 10^(-5)T` |
|
| 9. |
Assertion: Out of ""_(1)He^(3) and ""_(7)He^(3), the binding energy of ""_(1)He^(3)is greater than ""_(2)He^(8). Reason: Inside the nucleus of""_(1)H^(3), there is more repulsion than inside the nucleus of ""_(2)He^(4). |
|
Answer» If both assertion and reason are CORRECT and reason is a correct EXPLANATION o F the assertion. |
|
| 10. |
In which accelerated motion, K.E of the particle is constant |
|
Answer» NON. U.C.M. |
|
| 11. |
60 W, 100 W and 1000 W bulbs are connected in parallel to the mains. The bulb that will be brightest is (all of them have same specified voltage) |
|
Answer» 60W |
|
| 12. |
Demonstarate that electronsmove in a betatronalong around orbitof constantradiusprovidedthe magnetic induction on the orbitof constantradiusprovidedthe magnetic inductionon the orbitis equalto halfthe meanvalue of that indide the orbit (the betatron condition). |
|
Answer» Solution :On the one hand, `(dp)/(dt) = eE = (e)/(2pi r) (d Phi)/(dt) = (e)/(2pi r) (d)/(dt) int_(0)^(r) 2pi r' B (r') dr'` On the other, `p = B (r) er, r` = constant. so, `(dp)/(dt) = er (d)/(dt) B(r) = er dotB (r)` Hence, `er dotB (r) = (e)/(2 pi r) pi r^(2) (d)/(dt) LT B gt` So, `dotB (r) = (1)/(2) (d)/(dt) lt B gt` This is most EASILY SATISFIED by taking`B(r_(0)) = (1)/(2) lt B gt` . |
|
| 13. |
A wire of length L is fixed at both ends such that F is tension in it. Its mass per unit length varies from one end to other end as mu=mu_0x, where mu_0 is constant. Find time taken by a transverse pulse to move from lighter end to its mid point. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 14. |
A light ray travels through four adjacent media of refractive indices mu_(1), mu_(2), mu_(3), mu_(4) as shown in the Fig. 2.83. The bases of the media are parallel. If emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray AB then |
|
Answer» `mu_(1) = mu_(2)` |
|
| 15. |
Combination of two convex lenses works always as ....... |
|
Answer» concave lens In `F=(f_1f_2)/(f_1+f_2)` for concave lens. `f=((f_1)(f_2))/(f_1+f_2)` `therefore f=`positive `therefore` WORKS as convex lens. |
|
| 16. |
Consider the following reactions, The end product 'S' is - |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 17. |
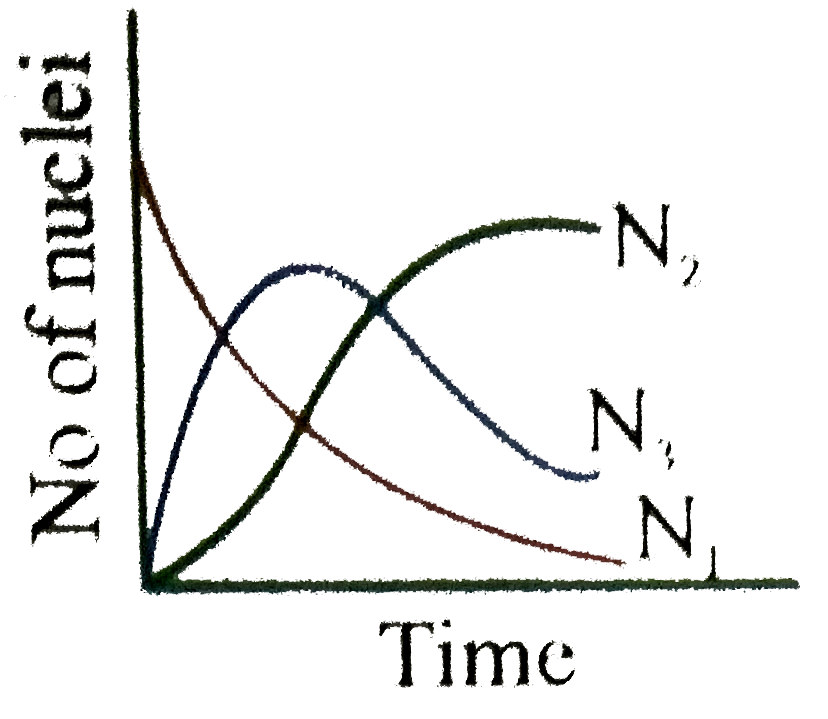
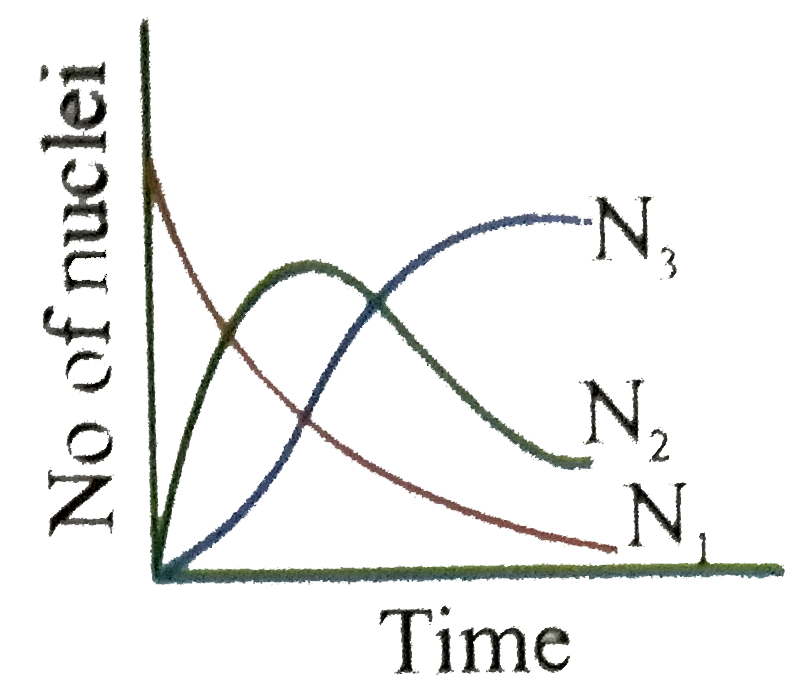
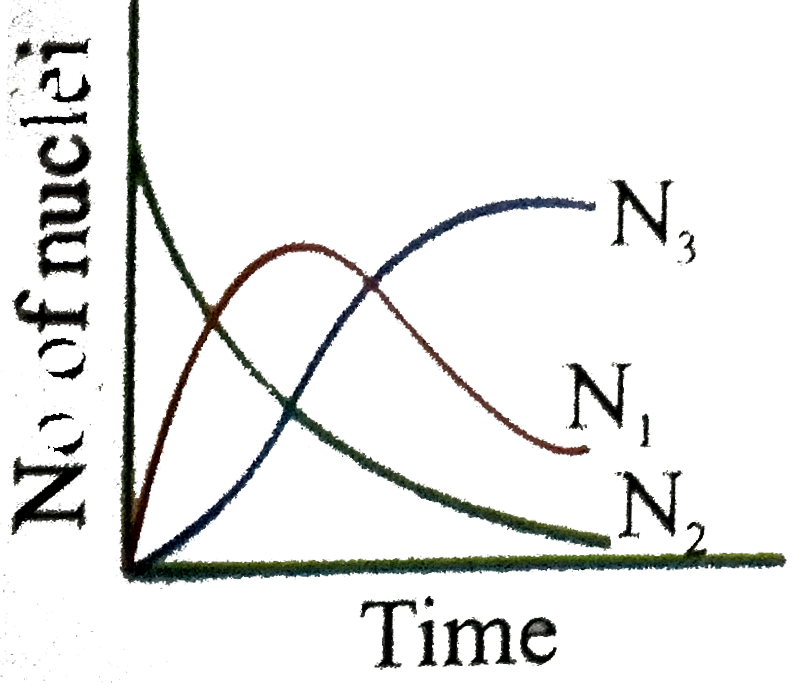
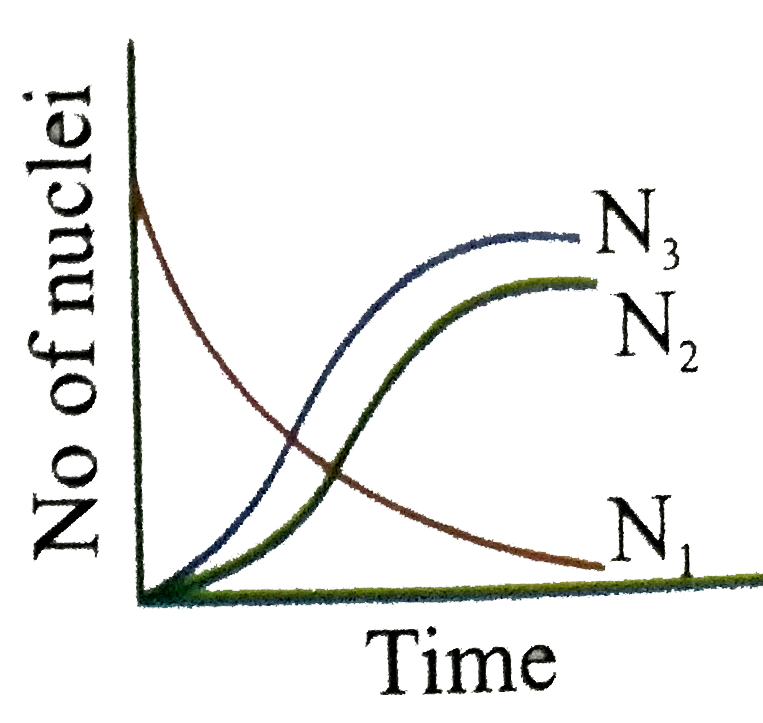
Uranium ._(92)^(238)U is an ustable nucleus. It decays to Thorium ._(92)^(238)Th, which is again an unstable nucleus which further decays to ._(91)^(234)Pa. Let ._(92)^(238)U be called A of decay constant lambda_(1) and ._(90)^(234)Th is called as B of decay constant lambda_(2) and stable nuclei ._(91)^(234)Pa be called as C. Here A is called parent nucleus and B is called daughter nucleus of A. Any two adjacent nuclei may be consider parent or daughter nuclei A, B and C respectively at time 't'. Then we can write Aoverset(lambda_(1))rarrBoverset(lambda_(2))rarrC Rate of disintergration of A=(dN_(1))/(dt)=lambda_(1)N_(1) Rate of disintergration of B=(dN_(2))/(dt)=lambda_(1)N_(1)-lambda_(2)N_(2) Rate of formation of nuclei C is equal to (dN_(3))/(dt)=lambda_(2)N_(2) If at t=0, there are N_(0) number of nuclei of A where as nuclei B and C are absent in the sample Answer the following questions The graph N_(1), N_(2) and N_(3) with time can be best represent by |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 18. |
Explain the laws of photoelectric effect from the Einstein photoelectric equation. |
|
Answer» Solution :Einstein’s explanation of photoelectric effect. Photoelectric effect is the phenomenon of emission of ELECTRONS by certain substances, chiefly metals, when these are illuminated by radiations like X-rays, ultraviolet rays and even visible light. The electrons ejected from a. substance in this manner are called photoelectrons.  According to quantum theory, light consists of bundles of energy, called photons, each of energy hv, where h is the Planck’s constant and V is the frequency of the light. When a photon of energy hv is incident on the surface of a PHOTOSENSITIVE substance, a part of its energy `W_(0)` is used up in liberating the electrons from the surface and the rest of the energy is given to the ejected electron to impart it is a velocity v and hence a kinetic energy `1/2 mv^(2)`. Work Function. The part of the incident photon WQ which is used up in liberating an electron from the surface is called the work function and depends upon the nature of the surface. Einstein’s photoelectric equation Einstein assumed that one incident photon can eject only one electron. The photon energy is utilised in two ways : (i) A part of energy of photon is used for electron free from the atom and away from the metal surface. This energy is called photoelectric work function WQ. (ii) The balance of the photon energy is used up in giving the electron a kinetic energy `1/2 mv^(2)`. `therefore`Energy of incident photon = Work function + K.E. of electron or `hv =W_(0) +1/2mv^(2)`...........(i) If `v_(0)`is the threshold frequency which is just sufficient to eject an electron with zero velocity, i.e. v = 0. So, `W_(0) =hv_(0)`...............(ii) Putting (ii) in (i) we get `hv = hv_(0) + 1/2mv^(2)` or `1/2 mv^(2) = h(v-v_(0))`...........(iii) This equation is called Einstein.s photoelectric equation.  From Eqn. (iii), it is clear that (i) v depends only upon v, m and h are constants. Thus the velocity of the photoelectron ejected depends upon the frequency of light. From equation (iii), it is seen that greater is the frequency v, greater is the velocity of the photoelectrons ejected. This is the first LAW of photoelectric emission. (ii) If the intensity of light is increased, the number of incident photons increases which RESULTS in an increase in the number of photoelectrons ejected. This is the second law. (iii) If `v lt v_(0), v^(2)`is negative, i.e., v is imaginary. In other words, if the frequency of the incident photon is less than `v_(0)` no photoelectric effect is POSSIBLE. This is the third law of photoelectric emission. (iv) The phenomenon of photoelectric emission has been conceived as an effect of collision between a photon and an electron in metal. Hence there should be no time lag between the incidence of photon and ejection of the photoelectrons. This is the fourth law. |
|
| 19. |
Blue light can eject photo electron from a photo sensitive surface while orange light cannot. Then |
|
Answer» Violet light can EJECT electron |
|
| 20. |
A photocell is illuminated by a small bright source placed 1m away. When the same source of light is placed (1/2)m away, the number of electrons emitted by photocathode would |
|
Answer» INCREASE by a FACTOR 2 |
|
| 21. |
A current carrying loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The torque acting on it does not depend upon ______ . |
|
Answer» Shape of the LOOP |
|
| 22. |
A sensor to find liquid level in a tank is a cylindrical capacitor of length with outer and conductor radii R_(0)and R_(i) respectively. When a liquid fills the tank up to height h, (h le l)tank.s bottom the dielectric in lower part is liquid (K_l)and dielectric in upper part is vapour liquid (K_r) Value of capacitance of capacitor when tank is completely empty is |
|
Answer» `2.5 xx10^(-9)F` |
|
| 23. |
The position - time graph for a particle is shown in fig. Then in the time interval of (0, 6sec) |
|
Answer» Particle RECEIVES two identical impulses |
|
| 24. |
Name the experiment in which nucleus was first discovered. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 25. |
A nucleus with Z =92 emits the following in a sequence alpha, beta, alpha,alpha,alpha,alpha,alpha,beta^(-),beta^(-),alpha,beta^(+),beta^(+),alpha. The Z of the resulting nucleus is : |
|
Answer» 78 New atomic no. =92-14=78 |
|
| 26. |
A wire of resistance 8R is bent in the form of a circle. What is the effective resistance between the ends of a diameter AB ? |
Answer» Solution :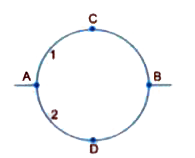 TOTAL RESISTANCE of wire bent in the form of a circle = 8R Resistance of each half ACB or ADB =`(8R)/(2) = 4R` The two half lengths are connected in PARALLEL across AB `R_(eff) = (4R xx 4R)/(4R + 4R) = 2R` |
|
| 27. |
For steady interference, the two sources of light must be : |
|
Answer» coherent |
|
| 28. |
Which of the following can be expressed in coulomb : |
|
Answer» `oint vecB . VEC(dl)` |
|
| 29. |
A negatively charged oil drop is prevented from falling under gravity by applying a vertical electric field 100 V m^(-1). If the mass of the drop is 1.6 xx 10^(-3)g, the number of electrons carried by the drop is (g = 10 ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» `10^(18)` FORCE on the drop DUE to electric field = Weight of the drop qE = mg `:. q = (1.6 xx 10^(-6) xx10)/(100) = 1.6 xx 10^(-7) C` Number of electrons carried by the drop is `N = (q)/(e) = (1.6 xx 10^(-7)C)/(1.6 xx 10^(-19)C) = 10^(12)` |
|
| 30. |
A wavefront AB moving in air is incident on a plane glass surface XY as given in figure.Its position CD after refraction through the glass slab is shown along with normals A to D. The refractive index of glass w.r.t. Air will be equal to : |
|
Answer» `(BD)/(AC)` `therefore mu= (sin theta)/(sin phi)` |
|
| 31. |
A wavefront AB moving in air is incident on a plane glass surface XY as given in figure.Its position CD after refraction through the glass slab is shown along with normals A to D. The refractive index of glass w.r.t.air is given by : |
|
Answer» `(BD)/(AC)` `therefore mu= (sin theta)/(sin phi)` |
|
| 32. |
A sensor to find liquid level in a tank is a cylindrical capacitor of length with outer and conductor radii R_(0)and R_(i) respectively. When a liquid fills the tank up to height h, (h le l)tank.s bottom the dielectric in lower part is liquid (K_l)and dielectric in upper part is vapour liquid (K_r)When liquid fills the tank up to height h, the capacity of capacitor is |
|
Answer» `(2piepsilon_0l)/(LN(R_0lR_i)){(K_f-K_v)h/l+K_v}` |
|
| 33. |
A sensor to find liquid level in a tank is a cylindrical capacitor of length with outer and conductor radii R_(0)and R_(i) respectively. When a liquid fills the tank up to height h, (h le l)tank.s bottom the dielectric in lower part is liquid (K_l)and dielectric in upper part is vapour liquid (K_r)If l=2m , R_(0) = 5mm, K_l=1.4K_v =1.0 . Then , capacitance of capacitor when tank is fully filled is |
|
Answer» `4.5 xx10^(-9)F` |
|
| 34. |
A uniform resistance wire of resistance 10Omega is bent in the form of a circle.The resistance between any two diameterically opposite points will be |
|
Answer» `5OMEGA` |
|
| 35. |
A particle of mass 3 xx 10^(-6) g has the same wavelength as an electron moving with a velocity 6 xx 10^(6) ms^(-1). The velocity of the particle is…………………… |
|
Answer» `1.82 xx 10^(-18) ms^(-1)` `lambda = (h)/(mv) = (6.63 xx 10^(-34))/(9.1 xx 10^(-31) xx 6 xx 10^(6)) = 1.214 xx 10^(-10)`m Velocity of the PARTICLE `v = (h)/(m lambda) = (6.63 xx 10^(-34))/(3 xx 10^(-9) xx 1.214 xx 10^(-10)) = 1.8204 xx 10^(-15) ms^(-1)` |
|
| 36. |
In photoelectric emission process from a metal of work function 1.8 eV, the kinetic energy of most energetic electrons is 0.5 eV. The corresponding stopping potential is |
|
Answer» 1.8 V |
|
| 37. |
A conducting rod of length l is higed at point O. It is free to rotate in a vertical plane. There exists a uniform magnetic field vec(B) in horizontal direction. The rod is released from the position shown in figure. Potential difference between the two ends of the rod is proportional to |
|
Answer» `L^(3//2)` From energy conservation : `MG.(1)/(2)sin theta =(1)/(2)I omega^(2)`, where `I=(ml^(2))/(3)` `rArr omega prop (sin theta)^(1//2)rArr E prop omega rArr e prop (sin theta)^(1//2)` Also `e prop l^(2)`. |
|
| 38. |
In the above problem . What is the least distance from the central maximum where the bright fringe due to both the wavelength coincide ? |
|
Answer» 0.32 cm |
|
| 39. |
An iron block of mass m = 500 kg is kept at the back of a truck moving at a speed v_(0)=90km h^(-1). The driver applies the brakes and shows down to a speed of v=54km h^(-1) in 10s. What constant force acts on the block during this time if the block does not slide on the truck-bed? |
|
Answer» Solution :The acceleration, `a=(v-v_(0))/(t)` `=(54 km h^(-1)-90kmh^(-1))/(10s)` `=(15ms^(-1)-25ms^(-1))/(10s)` `=-1m//s^(2)` or, Force F = ma `=500kg (-1 ms^(-2))` `=-500N` -ve sign INDICATES that the force ACTS opposite to the VELOCITY of the block. The magnitude of force is 500 N. |
|
| 40. |
The magnetic fields at two pointslying at same distance from an isolated poleare |
|
Answer» the samebothin magnitude and direction |
|
| 41. |
Define Snell's Law. Using a neat labelled diagram derive an expression for the refractive index of the material of an equilateral prism. |
|
Answer» Solution :Snell's law : The ratio of the sine of the ANGLE of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is constant, called the refractive index of the medium. `(sini)/(sinr)=mu"(constant)".` Let ABC be the glass prism. Its angle of prism is A. The refractive index of the material of the prism is `mu`. Let AB and AC be the two refracting surfaces PQ = incident ray, RS = EMERGENT ray. `"Let angle of incidence "= r_(1)"angle of emergence "=i_(2)` `"angle of refraction "=r_(1)"angle of refraction at R"=r_(2)` After travelling through the prism it falls on AC and emerges as RS. The D = angle of deviation. From the `DeltaQRT` `r_(1)+r_(2)+angleT=180^(@)"..................(1)"` From the quadrilateral AQTR `angleA+angleT=180^(@)` `angleT=180^(@)-A."..............(2)"` From the equations (1) and (2) `r_(1)+r_(2)+angleT=180^(@)" we get "` `r_(1)+r_(2)+180^(@)-A=180^(@)` `r_(1)+r_(2)=A."...............(3)"` from the `DeltaQUR` `i_(1)-r_(1)+i_(2)-r_(2)+180^(@)-D=180^(@)` `i_(1)+i_(2)-(r_(1)+r_(2))=D` `i_(1)+i_(2)-A=D""[because r_(1)+r_(2)=A]` `i_(1)+i_(2)=A+D"....................(4)"` 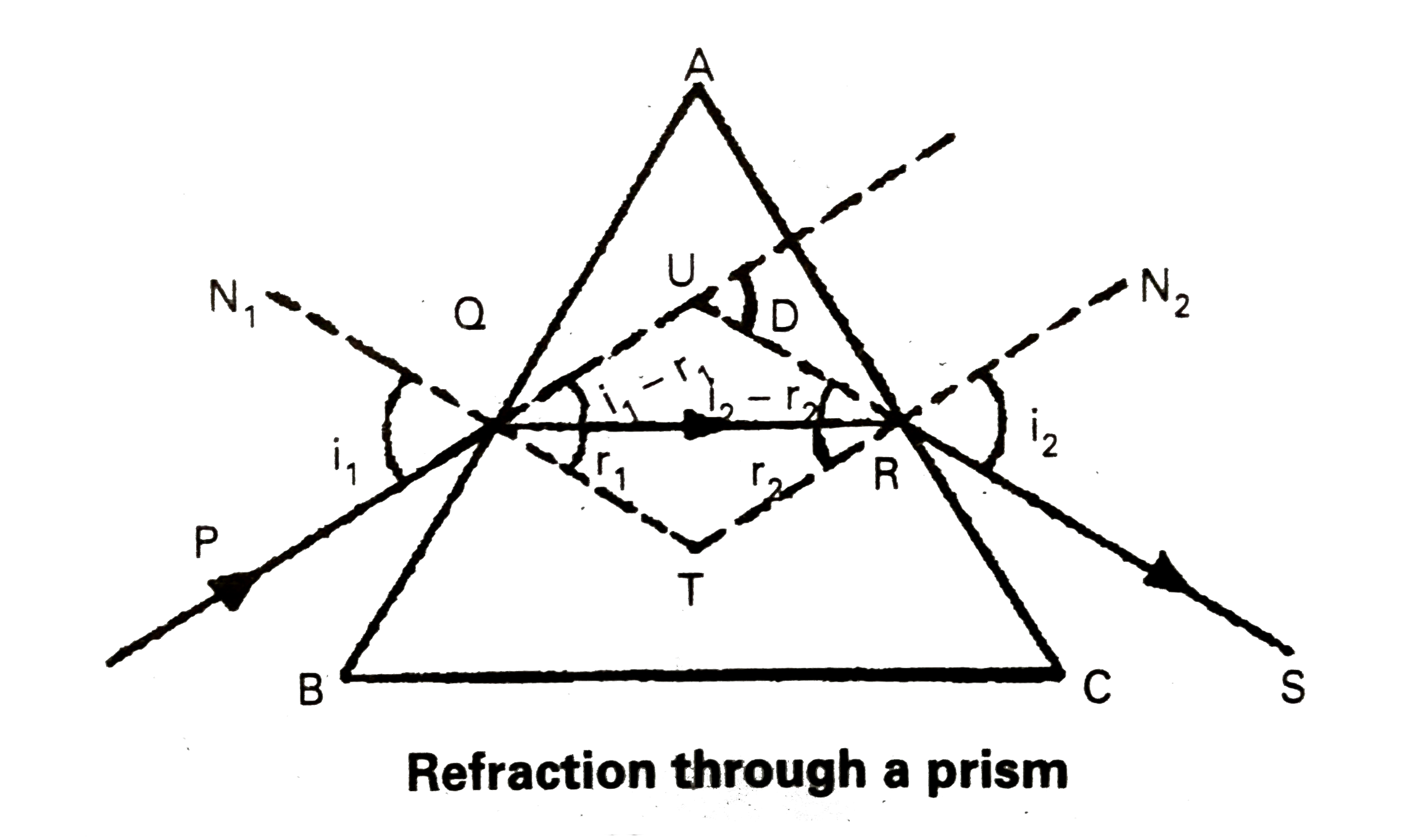 MINIMUM deviation : Experimentally it is found that as the angle of incidence increased the angle of deviation decreases till it reaches a minimum value and then it increases. This least value of deviation is called angle of minimum deviation `'delta'` as shown in the fig. When D decreases the two angles `i_(1) and i_(2)` become closer to each other at the angle of minimum deviation, the two angles of incidence are same i.e., `i_(1)=i_(2)` As `i_(1)=i_(2), r_(1)=r_(2)` `therefore i_(1)=i_(2)=i, r_(1)=r_(2)=r,` substituting this in (1) and (2) we get `"2r = A"rArr r=A//2` `i+i=A+delta rArr i=(A+delta)/(2)` According to Snell's law `mu=("Sin i")/("Sin r")` `mu=("sin"((A+delta)/(2)))/("Sin A/2")` 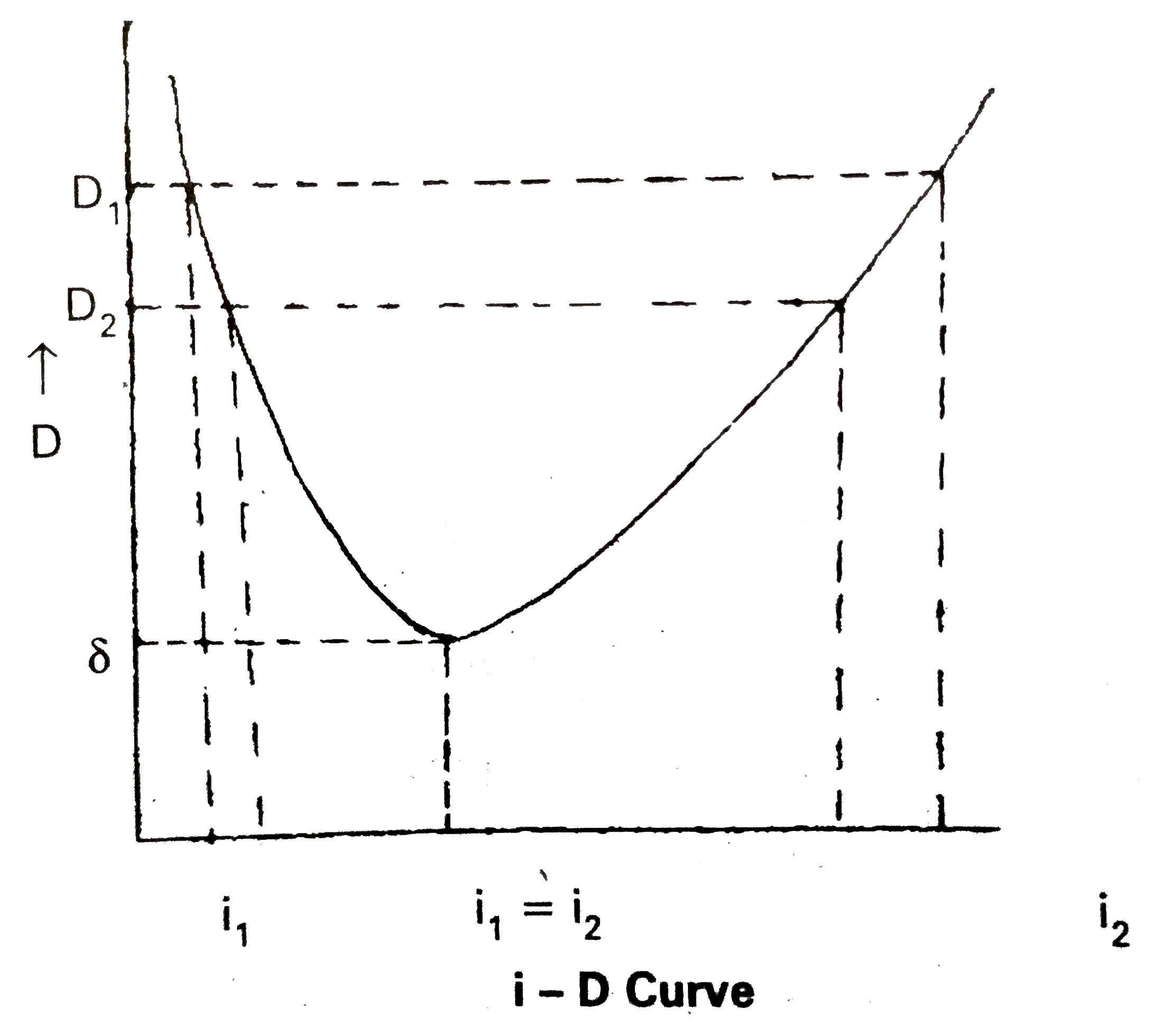
|
|
| 42. |
A conductor has got different areas of cross sections. Are the currents same at different cross sections? What conservation law helps you to decide the answer? |
| Answer» Solution :CONDUCTOR may be having different cross SECTIONS at different POINTS along its LENGTH. But the current i will be the same for all cross sections of the conductor. This is a consequence of the law of CONSERVATION of charge. | |
| 43. |
The capacity of each condenser in the following fig. is .C.. Then the equivalent capacitance acrossA and B is |
|
Answer» C/4 |
|
| 44. |
How many times in succession should the light fraction be separated in the centrifuge to obtain a mixture containing 80% of light uranium isotope? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 45. |
Non-transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of the came flower due to a mechanical barrier is |
|
Answer» Dichogamy |
|
| 46. |
A solid sphere rolls down on an inclined plane of 30^(@) inclination. Ratio of acceleration when it rolls and slides is : |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here `a_(R)=(5)/(7)gsinthetaanda_(s)=gsintheta` `a_(r):a_(s)::5:7` |
|
| 47. |
A carbon resistor is shown in the Fig. Using colour code, write the value of the resistance. |
| Answer» Solution : The VALUE of RESISTANCE `47 XX 10^2 Omega = 4.7 K Omega` . | |
| 48. |
Write the condition of destructive interference in terms of path difference. |
|
Answer» path difference =`n LAMBDA` |
|
| 49. |
Obtain the expression for the equivalent resistance for 3 resistors connected in parallel and also write the expression of equivalent resistance for connection of' n' resistors. |
Answer» Solution :`rArr "" R_(1) ,R_(2) and R_(3)` are connected between a and b points as shown in figure.  `rArr` By connecting terminals of BATTERY of voltage V with a and b, I current will be passed through `R_(1) , R_(2), R_(3) " are " I_(1), I_(2) , I_(3)` respectively. `rArr` According to Ohm.s law, p.d. ACROSS `R_(1), R_(2), R_(3)` is V. `rArr V = I_(1) R_(I) rArr I_(1) = (V)/(R_(1)) "" `....(1) `V = I_(2) R_(2) rArr I_(2) = (V)/(R_(2)) "" ` ....(2) and V = `I_(3) R_(3) rArr I_(3) = (V)/(R_(3)) ` ... (3) `rArr` At point .a. , `I = I_(1) + I_(2) + I_(3) ""` ... (4) By substituting values of equation (1), (2) and (3) in equation (4), `I = (V)/(R_(1)) + (V)/(R_(2)) + (V)/(R_(3))` `therefore (I)/(V) = (1)/(R_(1)) + (1)/(R_(2)) + (1)/(R_(3)) "" `[ Dividing by V] `rArr " If"(I)/(V) = (1)/(R_(eq)) , ` then `(1)/(R_(eq) ) = (1)/(R_(1)) + (1)/(R_(2)) + (1)/(R_(3)) ` If `R_(eq) ` is represented as `R_(p)`, then `(1)/(R_(p)) = (1)/(R_(1)) + (1)/(R_(2)) + (1)/(R_(3))` `rArr` For EQUIVALENT resistance of .n. unequal resistors in parallel, `(1)/(R_(eq))= (1)/(R_(1)) + (1)/(R_(2)) + (1)/(R_(3)) + ...+ (1)/(R_(n))` `rArr` For equivalent resistance of .n. equal resistors of resistance R in parallel, `(1)/(R_(eq)) = (n)/(R)` `therefore R_(eq) = (R)/(n)` |
|
| 50. |
A milliammeter of range 10 mA has a coil of resistance 1Omega. To use it as a voltmeter ofrange 10 V, the resistance that must be connected in series with it is |
|
Answer» `999Omega` |
|