Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 6251. |
In fig. each +q. arefixed at L and M.O is the point of distance LM.X and Y axes are as shown. Consider the situations given in Column - I and match with the information in Column - II |
|
Answer» <P> |
|
| 6252. |
The force oversettoF on a charged particle in an electric field is_____of velocity oversettov of the charged particle while entering the electric filed. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INDEPENDENT | |
| 6253. |
If four forces act at a point 'O' as shown in the figure and if O is in equilibrium then the value of 'theta' & 'P' are |
|
Answer» `15^(@),10sqrt2N` |
|
| 6254. |
A man who can swim at a speed v relative to the water wants to cross a river of width d, flowing with a speed u. The point opposite him across the river is P. |
|
Answer» The MINIMUM time in which he can cross the river is `(d)/(v)` |
|
| 6255. |
In the circuit shown in fig., the potential difference between the points C and D is balanced against 40cm length of potentiometer wire of total length 100cm. In order to balance the potential difference between the points D and E. The jockey be pressed on poten-tiometer wire at a distance of |
|
Answer» 16 cm |
|
| 6256. |
A conductor of length 20cm and mass 18 mg lies in a direction of 60^@N of E. If the horizontal component of earth's magnetic field is 36 mu T , the current to be passed in the conductor so that it is suspended in air is (g = 10 ms^(-2) ) |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 6257. |
What type of lens should be used in spectacles for the remedy of myopia ? |
|
Answer» concave LENS whose focal length is equal to the distance of the FAR point of the DEFECTIVE eye fromthe lens |
|
| 6258. |
A radioactive substance emit 100 beta particfles in the first 2 s and 50 beta particles in the next 2s. The mean life of the sample is |
|
Answer» 4 s `:.T_(1//2)=2s` Hence, mean life, `T=(t_(1//2))/(0.693)=(2)/(0.693)` |
|
| 6259. |
The focal lengths of the objective and the eyepiece of an astronomical telescope are 20 cm and 5 cm respectively. If the final image is formed at a distance of 30 cm from the eye piece, find the separation between the lenses for distinct vision: |
|
Answer» 32.4cm |
|
| 6260. |
S.T f=(R )/(2) in the caseof a spherical mirrorwhere symbols have theirusual notations |
Answer» Solution : From the figure `tan theta=(MD)/(CD)` For small ANGLES `tantheta^(@)= theta `(rad) `therefore theta("rad") =(MD)/(CD)"" `.........(1) Also, `tan 2theta=(MD)/(FD)` for small angles,`tan 2theta^(@)=2theta("rad")=(MD)/(FD)""`............(2) Using (1) and (2) we can WRITE `2((MD)/(CD))=(MD)/(FD)` i.e. `CD=2FD` i.e. `R=2f or f=(R)/(2)` |
|
| 6261. |
Figure 22-35 shows the d eflecting plates of an ink-jet printer, with superimposed coordinate axes. An ink drop with a mass m of 1.3xx10^(-10)kg anda negative charge of magnitude Q=1.5xx10^(-13)C enters the region between the plates, initially moving along the x axis with speed v_(x)=18 m//s. The length L of each plate is 1.6 cm. The plates are charged and thus produce an elecric field at all points between them. Assume that field vecE is downward directed, is uniform, and has a magnitude of 1.4xx10^(6)N//C. What is the vertical deflection of the drop at the far edge of the plates? (The gravitational force on the drop is small relative to the electrostatic force acting on the drop and can be neglected.) |
|
Answer» Solution :KEY IDEAS The drop is negatively charged and the electric field is directed downward. From Eq. 22-45, a constant electrostatic force of magnitude QE acts upward on the charged drop. Thus, as the drop travels parallel to the x axis at constant speed `v_(x)`, it ACCELERATES upward with some constant acceleration `a_(y)`. Calculations: Applying Newtons.s second law (F = ma) for components along the y axis, we FIND that `a_(y)=(F)/(m)=(QE)/(m). "" (22-47)` Let t represent the TIME required for the drop to pass through the REGION between the plates. During t the vertical and horizontal displacements of the drop are `y=(1)/(2) a_(y)t^(2) and L=v_(x)t,"" (22-48)` respectively. Eliminating t between these two equationsand substituting Eq. 22-47 for `a_(y)`, we find `y=(QEL^(2))/(2mv_(x)^(2))` `=((1.5xx10^(-13)C)(1.4xx10^(6)N//C)(1.6xx10^(-2)m)^(2))/((2)(1.3xx10^(-10)kg)(18m//s)^(2))` `=6.4xx10^(-4)m=0.64mm.` (Answer) |
|
| 6262. |
Explain in detail Coulomb 's law and its various aspects. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider two point charge `q_(1)` and `q_(2)` at rest in vacuum and separated by a distance of r . Accrording to Coulomb the force on the point charge `q_(2)` exerted by another point charge `q_(1)` is `vecF_(21)= k (q_(1)q_(2))/(r_(2)) hatr_(12)` where `hatr_(12)` is the unit vector directed from charge `q_(1)` to charge `q_(2)` and k is the proportionality constant . 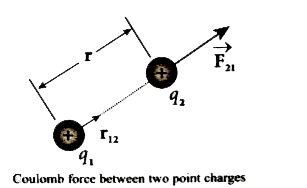 Important aspects of Coulomb .s law : (i) Coulomb.s law statres that the electrostatic force is directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of the two point charge and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two point charges. (ii) The force on the charge `q_(2)` exerted by the charge `q_(1)` always lies along the LINE joining the two charges `hatr_(21)` is the unit vector pointing from from charge `q_(1)` to `q_(2)` . Likewise the force on the charge `q_(1)` exerted by `q_(2)` is along -(i.e ., in the direction opposite to `hatr_(21))` . (iii) In SI units k =`(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))` and its value is `9XX10^(9) Nm^(2)C^(-2)` . Here `epsilon_(0)` is the permittivity of free space or vacuum and the value of `epsilon_(0)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))= 8.85xx10^(-12)C^(2)N^(-1)m^(-2)` (iv) The magnitude of the electrostatic force between two charges each of one coulomb and separated by a distance of 1 m is calculated as follows : `[F]=(9xx10^(9)xx1xx1)/(1^(2))`. This is a huge quantity almost equivalent to the weight of one million ton. We never come across 1 coulomb of charge in practice. Most of the electrical PHENOMENA in day - to -day life involve electrical charge of the order of `muC` ( micro coulomb ) or nC ( nano coulomb). (v) In SI units Coulomb.s law in vacuum takes the form `vecF_(21) = (1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(q_(1)q_(2))/(r^(2))hatr_(12)` . In a medium of permittivity `epsilon`, the force between two point charges is given by `vecF_(21)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(q_(1)q_(2))/(r_(2))hatr_(12)`. (v) In SI units Coulomb .s law in vacuum takes the form `vec_(21)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(q_(1)q_(2))/(r^(2))hat_(12)` . In a medium of permittivity `epsilon` the force between two point charge is given by `vecF_(21)= (1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(q_(1)q_(2))/(r^(2))hatr_(12)`. Sin since `epsilon gt epsilon_(0)` the force between two point charge in a medium other than vacuum is always less than in vacuum. We define the relative permittivity for a given medium as `epsilon=(epsilon)/(epsilon_(0))` . For vacuum or air `epsilon_(r)=1` and for all other media `epsilon_(r) gt 1` . (vi) Coulomb .s law has same structure as Newton.s law of gravitation . Both are inverselyproportional to the square of the distance btween the particles . The electrostatic force ios directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of two point charges and gravitational force is directly proportional to the product of two masses. (vii) The force on a charge `q_(1)` exerted by a point charge `q_(2)` is given by `vecF_(12)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(q_(1)q_(2))/(r^(2))hatr_(21)` Here `hatr_(21)` is the unit vector from charge `q_(2)` to `q_(1)` . But `hatr_(21)= -hatr_(12), vecF_(12) =(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(q_(1)q_(2))/(r^(2))(-hatr_(12))=-(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(q_(1)q_(2))/(r^(2))(hatr_(12)` (or ) `vecF_(12)=-vecF_(21)` Therefore the electrostatic force obeys Newton .s third law. (viii) The expression for Coulomb force is true only for point charges. But the point charge is an ideal concept . However we can apply Coulomb.s law for two charged objects whose sizes are very much smaller than the distance between them . In fact Coulomb discovered his law by considering the charged spheres in the torsion BALANCE as point charges . The distance between the two charge is much greater than the radii of the spheres. |
|
| 6263. |
Draw energy band diagram of p & n type semiconductors. Also write two differences between p and n type semiconductors. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 6264. |
The refractive indices of violet and red light are 13.54 and 1.52 respectively, If the angle of te prism is 10^@, the angular dispersion in degree is |
|
Answer» 0.02 |
|
| 6265. |
The part of communication system that extracts the signal at the output of the channel is |
|
Answer» transducer |
|
| 6266. |
A substance that attracts pieces of iron and steel is callled a magnet and this property what we call ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MANGNETISM | |
| 6267. |
Three concentric metallic spherical shell of radii R, 2R, 3R are given charges Q_(1), Q_(2), Q respectively, it is found that the surface charge densities on the outer surface of the shells are equal. Then the ratio of the charges give to the shells Q_(1) : Q_(2): Q_(3) is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 6268. |
The value of angle of dip is zero at the magnetic equator because on it |
|
Answer» V and H are equal Angle of DIP `delta = 0`, VERTICAL component V= 0 `I sin delta = 0` implies I sin delta = 0 implies sin delta = 0 implies delta = 0 |
|
| 6269. |
Two conductors of the same shape and size. One of copper and the other of aluminium (less conducting) are placed in an uniform electric field, the charge induced in aluminium |
|
Answer» will be LESS than in copper |
|
| 6270. |
A wire carrying a current of 16A and its cross-sectional area 10^(-5 )m^2. If the free electron density in wire is 4 xx 10^(28) m^(-3), the drift velocity is in 10^(-4) m/s) |
|
Answer» `1.6` |
|
| 6271. |
Charges can neither be created nor be destroyed is the statement of law of conservation of |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6272. |
The focal length of objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope are 1cm and 5cm. An object is placed at a distance of 1.1 cm from the objective and if the final image is formed at infinity the magnifying power and distance between the lenses are respectively |
|
Answer» 60, 16cm |
|
| 6273. |
A closed organ pipe of length 'L' and an open organ pipe contain gases of densities rho(1) and rho_(2)respectively . The compressibility of gases are equalin both the pipes . If the frequencies of their first overtones are same then, the length of the open organ pipe is |
|
Answer» Solution :Frequency of first overtone is closed pipe `F=(3)/(4l_(1)) SQRT((P)/(rho_(1)))`Frequency of first overtone in open pipe `f^(1)=(1)/(l_(2)) sqrt((p)/(rho_(2))) rArr l_(2)=(4)/(3)l_(1) sqrt((rho_(1))/(rho_(2)))` |
|
| 6274. |
What did he do when he reached the fence? |
|
Answer» He BEGAN to sleep |
|
| 6275. |
A rigid horizontal smooth rod AB of mass 0.75 kg and length 40 cm can rotate freely about a fixed vertical axis through its mid-point O. Two rings each of mass 1 kg initially at rest at a distance 10 cm from O on either side of the rod. The rod is rotated with angular velocity of 30 rad s^(-1). When the rings reach the ends of the rod, the angular velocity of the rod is : |
|
Answer» 5 or `((ML^(2))/(12)+2mr^(2))omega_(1)=((ML^(2))/(12)+2m(L^(2))/(4))omega_(2)` PUTTING the VALUES `=[(0.75xx(0.4)^(2))/(12)+2xx1xx(0.1)^(2)]2pixx30` `=[(0.75xx(0.4)^(2))/(12)+2XX(0.2)^(2)]xx2pin_(2)` `n_(2)=((0.01+0.02)30)/((0.01+0.08))=(30xx0.03)/((.09))=10r.p.s.` |
|
| 6276. |
The pressure of an ideal gas is Increased by keeping temperature constant . The kinetic energy of molecules |
|
Answer» DECREASES |
|
| 6277. |
The vibrations of a string of length 60 cm at both ends are represented by the equation. y =4 sin[(pix)/(15)] cos (96 pi t) where x and y are in cm and t is in sec. What is the maximum displacement Ilt x = 5 cm? |
|
Answer» Solution :For `x =5,y = 4 sin (5pi//15) COS (96PI t)` or `y = 2 sqrt3 cos (96 pi t)` So y will be MAXIMUM when `cos (96 pi t)= max =1, i.e,. (y_(max))_(x=5) =2 sqrt 3 cm` |
|
| 6278. |
If A = 1 and B = 0 , then in terms of Boolean algebra , A + B is equal to |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`A=1,B=0,barB=1,T=A+barB=1+1=1` | |
| 6279. |
Earth's magnetic field inside a closed iron box, as compared to that of outside is : |
|
Answer» more |
|
| 6280. |
The vibrations of a string of length 60 cm at both ends are represented by the equation. y =4 sin[(pix)/(15)] cos (96 pi t) where x and y are in cm and t is in sec. Write down the equations of component waves whose superposition gives the above wave. |
|
Answer» Solution :As `2 sin A cos B = sin (A +B) + sin (A -B)` So `y = 4sin [(PI x)/(15)] cos (96PI t)` `=2[sin((pi x)/15 + 96pi t) + sin ((PIX)/15 -96pit)]` ` y = 2sin [96pit+(pi x)/15] - 2 sin [96 pi t - (pix)/15]` `[as sin(-theta) = - sintheta]` `y = y_1 + y_2" with" y_1 = 2sin [ 96pi t +(pix)/(15)]` `y_2 = -2 sin [96 pi t - (pi x)/15]` |
|
| 6281. |
The energy flux of sunlight reaching the surface of the earth is 1.388xx10^(3)W//m^(-2). How many photons (nearly) perr square metre are incident on the earth per second ? Assume that the photons in the sunlight have an average wavelength of 550 nm. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here ENERGY of flux of photons per UNIT area `phi=1.388xx10^(3)Wm^(-2)`, and wavelength of sunlight `lamda=550nm=5.5xx10^(-7)m` `THEREFORE`Energy of each photon `E=(hc)/(lamda)=(6.63xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))/(5.5xx10^(-7))=3.6xx10^(-19)J` `therefore`Number of photons incident per square metre on earth per second `n=(phi)/(E)=(1.388xx10^(3))/(3.6xx10^(-19))=4XX10^(21)m^(-2)s^(-1)`. |
|
| 6282. |
Monoclinic crystal lattice has dimensions |
|
Answer» `alpha=beta=GAMMA` |
|
| 6283. |
A body slides down from rest along a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 45^(@) with the horizontal and takes time 'Y' to slide down the whole length of the plane. If the plane surface is rough the same body takes n.t time to slide down same length of the plane where n is a number greater than one. What is the value of coefficient of friction between the body and rough plane surface? |
|
Answer» `mu=1-(1)/(n^(2))` and putting u = 0, we get For smooth inclined plane `theta = 45^(@)` `|a|= G sin theta= g//SQRT/2` Now ` t_(1)=sqrt((2s)/(a))=sqrt((2sqrt(2))/(g))` For rough plane `a = g sin theta-mu g cos theta=g//sqrt2-(mu)/(sqrt2)` `=(g(1-mu))/(sqrt2)` and `t_(2)=sqrt((2S.sqrt2)/(g(1-mu)))=sqrt(2sqrtS)/(g(1-mu))` DIVIDING `(1)/(1-mu)=n^(2)` `:.1-mu=(1)/(n^(2))` or`mu=1-1//m^(2)` Hence (a) is the corect choice |
|
| 6284. |
If the vectors veca = 2hati -4hatj-2hatk and vecb = 3hati +2hatj+xhatk are at the right angles to each other, then the value of r should be |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 6285. |
What is the meaning of the term "transmuting"? |
|
Answer» God is granting wishes |
|
| 6286. |
A physiscist points out that glass is rarer than water. |
|
Answer» This STATEMENT is CORRECT in the case of sound |
|
| 6287. |
A nonconducting sphere is given a non zero net electric charge +Q, and then brought close to a neutral conducting sphere of the same radius. Which of the following will be true? |
|
Answer» An electric field will be induced WITHIN the conducting sphere.  . .
|
|
| 6288. |
निकोबारी कबूतर कौन-सी श्रेणी से संबंधित है? |
|
Answer» सुभेद्य |
|
| 6289. |
(A) : The magnetic field at the centre of a circular coil carrying current could be calculated using Amperes circuital law. (R) : Biot savart law could be derived from Amperes law. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the CORRECT explanation of 'A'. |
|
| 6290. |
Two magnetic poles of strengths 40Am and 10 Am areseparated by a distance of 20 cm in air. Find the force between them. If the distance is reduced to 10 cm, find the force. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :i) Pole strength of magnetic POLES , `m_1 = 40 Am and m_2= 10 Am` Distance between the poles , ` d=20 cm = 0.2 m` Force between the magnetic poles ,` (mu_0)/(4pi)(m_1m_2)/(d^(2))` `= (4 pi XX 10^(-7))/(4pi ) xx (40 xx 10)/((0.2)^(2)) = 10^(-3) N` ii) Distance between the poles , `d^(1) = 10 cm = 0.1 m` Forece between the magnetic poles . `F^(1) = (mu_0)/(4pi)(m_1 m_2)/((d^1)^(2))` `= ( 4pi xx 10^(-7))/(4 pi ) xx (40 xx 10)/( (0.1)^(2)) = 4 xx 10^(-3)N`. |
|
| 6291. |
What will be the dimensions of the ratio of electric intensity of the electric field E to the magnetic induction B of the magnetic field in case of electromagnetic wave propagation ? |
|
Answer» same as that of acceleration `x=(E)/(B)=(F//q)/(B)` `=(MLT^(-2))/([MT^(-2)A^(-1)][AT])=LT^(-1)=` velocity `:.(b)`is the correct choice. |
|
| 6292. |
The conduction current in ideal casc through a circuit is zero when charge on capacitor is: |
|
Answer» zero |
|
| 6293. |
The vector sum of two forces is perpendicular to their vector differences. In that case, the forces : |
|
Answer» are equal to each other in magnitude `vec(F_(s))=vec(F_(1)) + vec(F_(2))` and `vec(F_(d))=vec(F_(1))-vec(F_(2))` Now `vec(F_(s))` is `bot`R to `vec(F_(d)):.vec(F_(s)).vec(F_(d))=0` or `|vec(F_(1))|^(2)=|vec(F_(2))|^(2)` or `|vec(F_(1))|=|vec(F_(2))|` The forces are equal in magnitude. |
|
| 6294. |
What is the height to which a liquid rises between two long parallel plates, at d distance a part between them T and p are surface tension and density of liquid respectively and contact angle between plate and liquid is zero. |
|
Answer» `(4T)/(PGD)` |
|
| 6295. |
A lamp consumes only 50% of maximum power applied in an A.C. circuit. What will be the phase difference between applied voltage and circuit current ? |
|
Answer» `pi/6` RAD `THEREFORE cos delta =P/P_m =P_(m//2)/P_m=1/2` `therefore delta = pi/3` RADIAN |
|
| 6296. |
Complete the line : We'll finish the race, |
|
Answer» No MATTER the course |
|
| 6297. |
A screen is at a distance of 2 m from narrow slits that are illuminated with light of 6000 A^(0) .The first maximum lies at 0.005 m on either side of the central maximum , then the distance between the slits will be |
|
Answer» `0.024` MM |
|
| 6298. |
Plot a graph showing the variation of resistance of conducting wire as a function of it's radius keeping the length of a wire and temperature as constant. |
Answer» Solution : `R=rho=l/pi=rhol/(pir^2)` or `R prop1/r^2` HENCE, the graph of R VERSUS r is as SHOWN in the graph. |
|
| 6299. |
A conductor in the shape of a cylinder of length l and cross sectional radius r is connected to a cell of emf V. The resistivity of the material of the conductor is rho and does not change much with temperature. The emissivity of the curved surface of the conductor is e. [Take emissivity of the flat circular surfaces to be zero]. In steady state the temperature of the conductor is T when the environmental temperature is T_(0). The difference between T and T_(0) is much smaller than the environmental temperature. Stefan’s Constant is sigma. Find the steady state temperature T for the conductor. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6300. |
Five moles of an ideal monoatomic gas with an initial temperature of 150^@C expand and in the process absorb 1500 J of heat and does 2500 J of work. The final temperature of the gas in .^@C is (ideal gas constant R = 8.314 J K^(-1)mol^(-1)) |
|
Answer» 134 |
|