Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 8101. |
Find graphically the position of the observer’s eye, which will allow him to see in a plane mirror of finite dimensions, the image of the straight line arranged as shown. |
Answer» Solution : A ’B ’ is the reflected IMAGE of AB by CD. The reflected rays EA2 and FA1 must reach the eye so that the whole image CANBE seen. 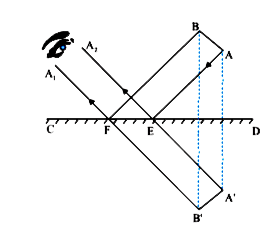
|
|
| 8102. |
A particle moves so that position vector is given by vecr=cosomegathatx+sinomegathaty. Where omega is a constant. Which of the following is true? |
|
Answer» VELOCITY and ACCELERATION both are perpendicular to `vecr`. |
|
| 8103. |
Match the Column-I with Column -II |
|
Answer» |
|
| 8104. |
Read the following (1) Refractive index can be less than one (2) Maximum usable frequency of sky wave is always less than critical frequency |
|
Answer» 1 is TRUE 2 is false |
|
| 8105. |
Draw a graph showing the variation of decay rate (-(dN)/(dt)) with number (N) of radioactive nuclei. |
Answer» Solution :SINCE `-(dN)/(dt)propN`, hence GRAPH is a straight LINE graph as shown in FIG. 13.02. 
|
|
| 8106. |
LEDS are advantageous over conventional incandescent low power lamps.a) Emitted light is nearly monochromatic b) Less power c) Slow in action |
|
Answer» a,B,c are CORRECT |
|
| 8107. |
Find the force experienced by a pole of strength 100 Am at a distance of 20 cm from a short bar magnet of length 5 cm and pole strength of 200 Am on its axial line. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`0.025N` | |
| 8108. |
A rocket of initial mass m_(0) moving with a velocity of upsilon discharges a jet of gases of mean density rho and effective area A. The minimum value of v of fuel gas which enables the rocket to rise vertically above is nearly : |
|
Answer» `((rhog)/(m_(0)A))^(1//2)` `:.F=(dm)/(dt)upsilonrho.upsilon=A.upsilon.rho` LEAST force REQUIRED `= m_(0)g` `:. m_(0)g = A.upsilon^(2)rho` or `upsilon^(2)=(m_(0)g)/(Arho)`or`upsilon=((m_(0)g)/(A rho))^(1)/(2)` (c) is the choice |
|
| 8109. |
Complete the reaction : " "_(72)^(180)A overset(-alpha)(to)A_(1)overset(-beta^(-))(to)A_(2) |
| Answer» Solution :`" "_(72)^(180)Aoverset(-alpha)(to)" "_(70)^(176)A_(1)OVERSET(-beta^(-))(to)" "_(71)^(176)A_(2)` | |
| 8110. |
There is an infinite straight chain of alternating charges q and -q. The distance between neighbouring charges is equalto d. Find the interaction energy of each chargewith all the other charges. |
|
Answer» Solution :The interaction energy of CHARGE at C due to charges on one SIDE (right or left) is `U=(1)/(4pi in_(0)) {(q(-q))/(a)+(q(q))/(2a)+(q(-q))/(3a)+(q(q))/(4A) +…..oo}` `=(q^(2))/(4pi in_(0) a){-1+(1)/(2)-(1)/(3)+(1)/(4)…….} =(-q^(2)ln2)/(4pi in_(0)a)` So, total interaction energy is 2U 
|
|
| 8111. |
A spherical mirror gives real image 3 times greater than object. If distance between object and image is 100 cm, then its focal length is |
|
Answer» 15 cm `therefore 3=v/u` `therefore 3=v/u` `therefore v=3u` Now u+v=100 `therefore u+3u=100` `therefore 4u=100` `therefore u=25 cm` `therefore` Now m=`(F)/(f-u)` `3=(f)/(f-(-25))` `therefore3 =(f)/(f+25)` therefore 35 -75 =f` `therefore 2F =-75` `therefore f=-37.5` cm |
|
| 8112. |
If the r.m.s. velocity of hydrogen gas at a certain temperature is c, then the r.m.s. velocity of oxygen gas at the same temperature is |
|
Answer» `(C )/(8)` For a given value of `T, v_(rms)prop(1)/(sqrt(M))` `((v_(rms))_(H_(2)))/((v_(rms))_(O_(2)))=sqrt((M_(O_(2)))/(M_(H_(2))))` `(v_(rms))_(H_(2))=C` `M_(O_(2))=32G,M_(H_(2))=2g,(v_(rms))_(O_(2))=?` `(c)/((v_(rms))_(O_(2)))=sqrt((32)/(2))=sqrt(16)=4therefore(v_(rms))_(O_(2))=(c)/(4)` |
|
| 8113. |
A transformer on a utility pole operates at V_p=8.5 kV on the primary side and supplies electrical energy to a number of nearby houses at V_s=120V , both quantities being rms values. Assume an ideal step-down transformer, a purely resistive load , and a power factor of unity. (a) What is the turns ratio N_p//N_s of the transformer ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The turns ratio `N_p//N_s` is related to the rms primary and secondary voltages `(V_s=V_p N_s//N_p)`. Calculation : We can write as `V_S/V_p = N_S/N_p` `N_p/N_S=V_p/V_S=(8.5xx10^3 V)/(120V)=70.83 approx71.` (b) The average rate of energy consumption (or dissipation) in the houses served by the transformer is 78 kW. What are the rms currents in the primary and secondary of the transformer? For a purely resistive LOAD, the power factor cos `phi` is unity, thus, the average rate at which energy is supplied and dissipated `(P_(avg)=EI=IV)`. Calculations : In the primary circuit, with `V_p`=8.5 kV, `I_p=P_(avg)/V_p = (78xx10^3W)/(8.5xx10^3 V)=9.176A approx 9.2 A` SIMILARLY , in the secondary circuit, `I_S=P_(avg)/V_S=(78xx10^3W)/(120V)`=650 A. You can check that `I_s=I_p(N_p//N_s)` as required by Eq. 31-74. (c) What is the resistive load `R_s` in the secondary circuit? What is the corresponding resistive load `R_p` in the pri mary circuit? One way: We can use V= IR to RELATE the resistive load to the rms VOLTAGE and current. For the secondary circuit, we find `R_S=V_S/I_S=(120V)/(650A)=0.1846Omega approx` 0.18 `Omega` Similarly , for the primary circuit we find `R_p=V_p/I_p =(8.5xx10^3 V)/(9.176A)=926 Omega approx 930 Omega`. Second way: We use the fact that `R_p` equals the equivalent resistive load "seen” from the primary side of the transformer, which is a resistance modified by the turns ratio and given by Eq. 31-76 `(R_(eq)= (N_p//N_s)^2R)` . If we SUBSTITUTE `R_p` for `R_(eq)`and `R_s` for R , that equation yields `R_p=(N_p/N_S)^2 R_S=(70.83)^2 (0.1846Omega)` `=926Omega approx 930 Omega`. |
|
| 8114. |
In the shown figure mass of the pulley is m and radius 2R. A light concentric spool of radius R is rigidly attached with the pulley. Two blocks A and B having masses m & 4m respectively are attached with the pulley by means of light strings. Lower surface of the block B is attached to a spring of stiffness ka and block B rests on a smooth inclined plane inclined 30^(@) with horizontal. Other end of the spring is fixed to the ground. The block A is stretched a small distance and released then find the frequency of the oscillation of block B. (The strings do not slip on the pulley). |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`2PI SQRT((10M)/(K))` | |
| 8115. |
Bichromatic light is used in YDSE having wavelengths, lamda_1 = 400nm and lamda_2 = 700nm. Find minimum order of lamda_1which overlaps with lamda_2 |
Answer» Solution : LET `n_1` bright FRINGE of `lamda_1` overlaps with `n_2` bright fringe of `lamda_2` Then `(n_1 lamda_1 D)/(d) = (n_2lamda_2 D)/(d)` `n_1/n_2 = lamda_2/lamda_1 = 700/400 = 7/4` The ratio `n_1/n_2 = 7/4`implies that 7th bright fringe of`lamda_1`will OVERLAP with 4th of `lamda_2` . SIMILARLY 14th of `lamda_1` will over lap with 8th of `lamda_2`and so on. So the minimum order of `lamda_1` which overlaps with `lamda_2` is 7. |
|
| 8116. |
For a radioactive material, is activity A and rate of change of its activity R are defined as A=(dN)/(dt) and R=(dA)/(dt). Two radioactive sources P (mean life tau ) Q (mean life 2tau ) have the same activity at t = 0. Their rates of change of activities at t=2tau are R_(P) and R_(0) respectively. if (R_(p))/(R_(0))=(n)/(e), then the value of n is |
|
Answer» |
|
| 8117. |
The resistivity of semiconductors is of the order of ………………… . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`10^(-2)-10^(2)OMEGA m` | |
| 8118. |
Vegetative reproduction in fungi takes place by |
|
Answer» Fragmentation |
|
| 8119. |
Derive the formula for the electric potential energy of system of three charges. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let charge `q_(1),q_(2)` and `q_(3)` are bring from infinity distance to at the point `P_(1), P_(2)` and `P_(3)`, located at distance `r_(1),r_(2)` and `r_(3)` respectively. All three charges are brought as shown in FIGURE. 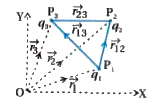 To bring `q_(1)` first from infinity to `P_(1)`, the work done`W_(1)=0` because there is no external force to bring `q_(1)` to `P_(1)` Electric potential at `P_(2)` due to charge `q_(1)` `V_(1)= (kq_(1))/(r_(12))` Now work done to bring charge `q_(2)` at point `P_(2)` `W_(2)=V_(1)xxq_(2)` `:. W_(2)=(kq_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))` Electric potential at Pz due to charge `q_(1) + q_(2)` `V_(2)=(kq_(1))/(r_(13))+(kq_(2))/(r_(23))` `:.` Work done to bring charge `q_(3)` to `P_(3)` `W_(3)` potential at `P_(3)` due to `q_(1)+q_(2)xxq_(3)` charge `=k[(q_(1))/(r_(13))+(q_(2))/(r_(23))]xxq_(3)` `=k[(q_(1)q_(3))/(r_(13))+(q_(2)q_(3))/(r_(23))]` `:.` OTAL potential energy of charges `q_(1)+q_(2)+q_(3)` `U=W_(1)+W_(2)+W_(3)` `[ because` Electric force is conservative and hence W U] `:. U=k[0+(q_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))+(q_(1)q_(3))/(r_(13))+(q_(2)q_(3))/(r_(23))]` `:. U=k[(q_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))+(q_(1)q_(3))/(r_(13))+(q_(2)q_(3))/(r_(23))]` Equation (3) is true for any sign of `q_(1)` and `q_(2 )` If `q_(1) q_(2) gt 0 ` potential energy will be positive. And if `q_(1)q_(2) lt 0`potential energy will be negative. |
|
| 8120. |
Light from a hydrogen discharge tube is made incident on the cathode of photoelectric cell. The work function of the cathode surface is 3.1 eV. In order to reduce the photoelectric current to zero value, the minimum potential applied to anode with respect to cathode should be |
|
Answer» `-3.1` VOLT |
|
| 8121. |
A particle starts moving from rest with uniform acceleration .It travels a distance x in the first 2 sec and a distance y in the next 2 sec.Then |
|
Answer» y=x |
|
| 8122. |
Calculate the normal or standard pressure at standard place. |
| Answer» Solution :The standard place is at `45^@` latitude and sea level where the value of 'g' is 9.806m/s and standard or NORMAL pressure is at pressure DUE to 76CM of mercury. The density of mercury is 13.6gm/`cm^3`. | |
| 8123. |
In Young's experiment , the width of fringe obtained with light of wavelength 6000overset@A is 2 mm. What will be the fringe width if entire apparatus is immersed in a liquid of R.I, 1.33 : |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 8124. |
What is magnifying power of a simple microscope ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`M=1+(D/f)` | |
| 8125. |
What has been personified in the poem? |
|
Answer» tiger |
|
| 8126. |
One solid sphere A and another hollow sphere B are of same mass and same outer radii. Their moment of inertia about their diameters are respectively I_(A) and I_(B) such that : |
|
Answer» `I_(A) = I_(B)` `I_(H)=(2)/(3)MR^(2)=0.66MR^(2)` `therefore I_(S)ltI_(H)` or `I_(A)ltI_(B)` |
|
| 8127. |
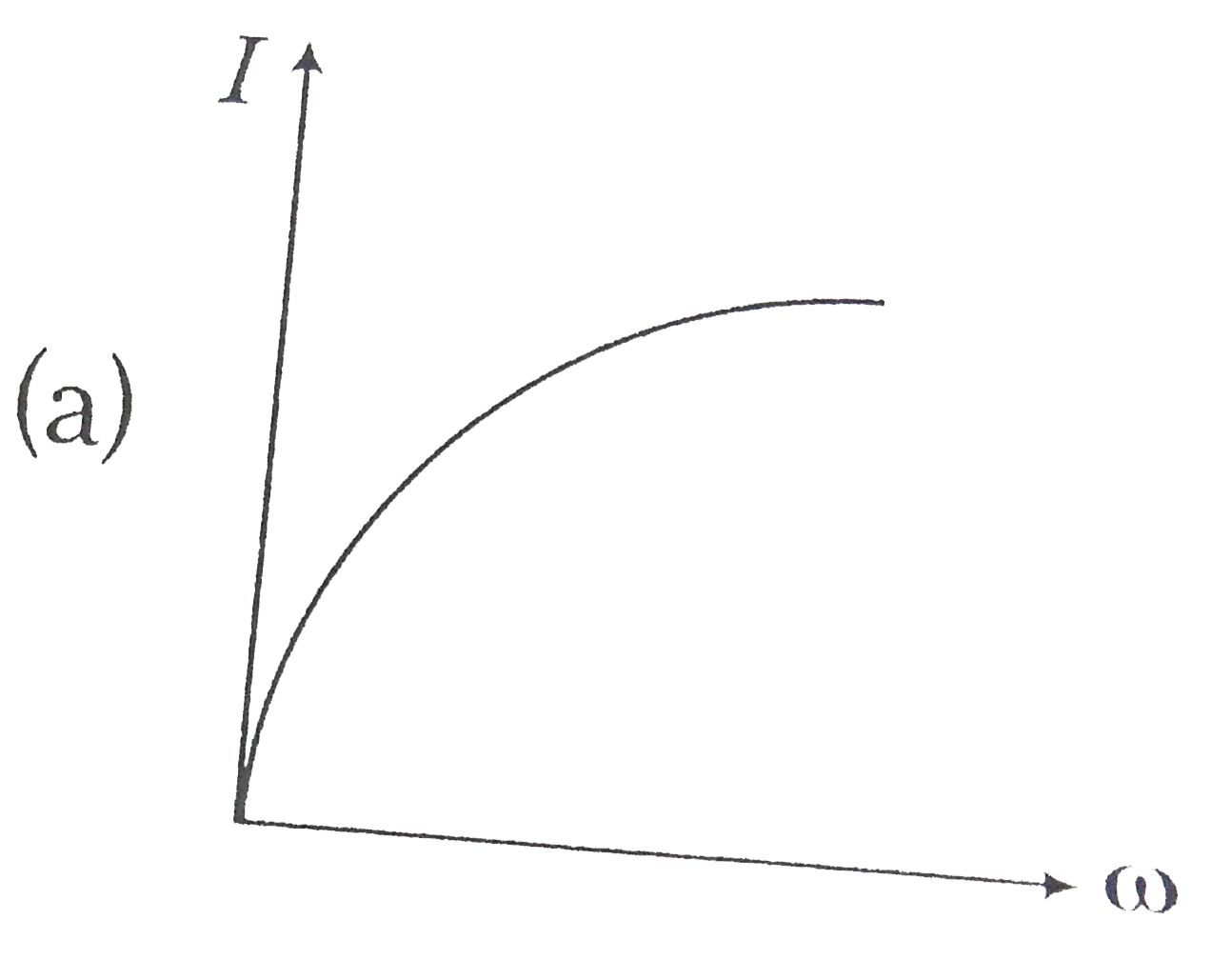
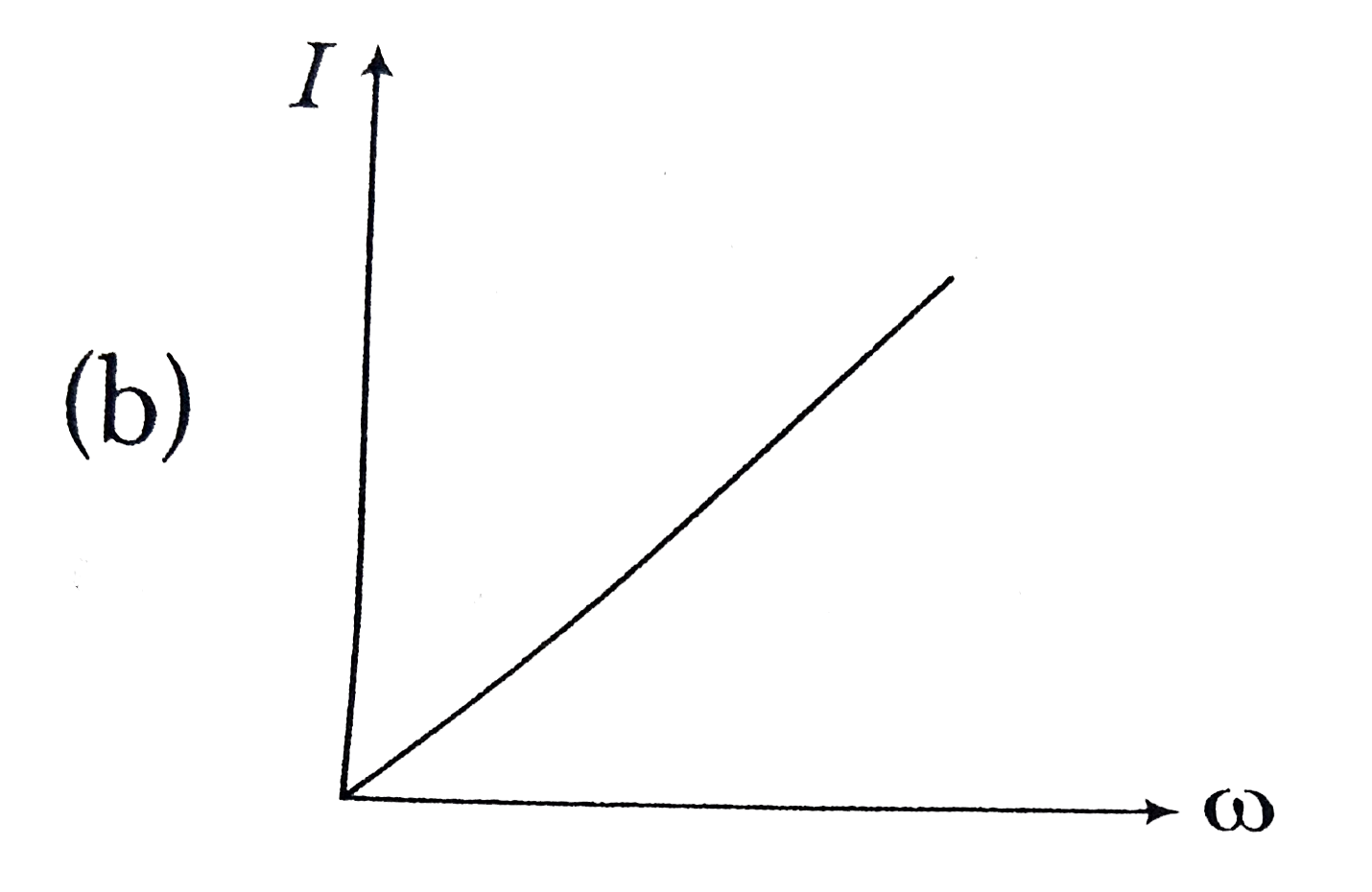
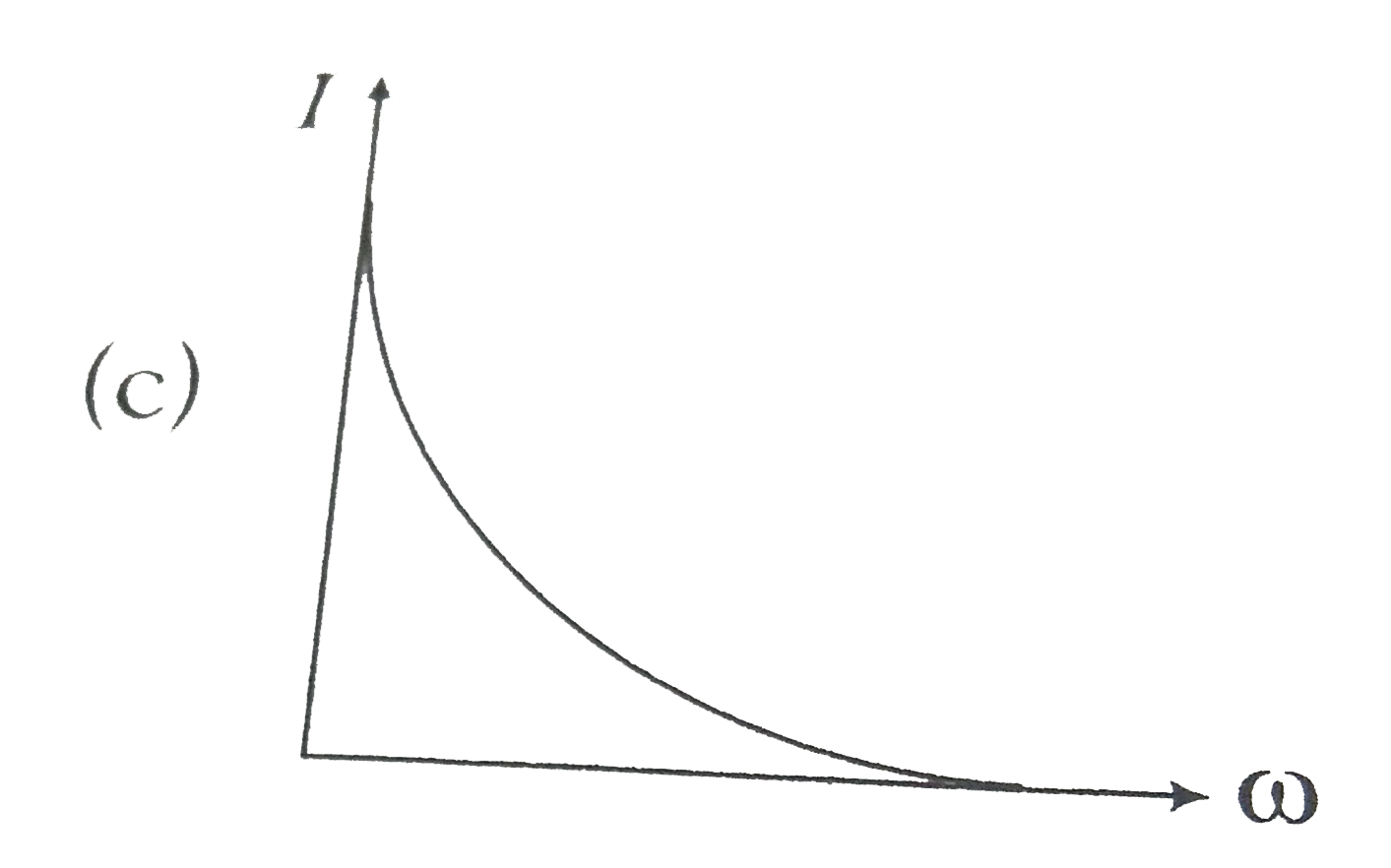
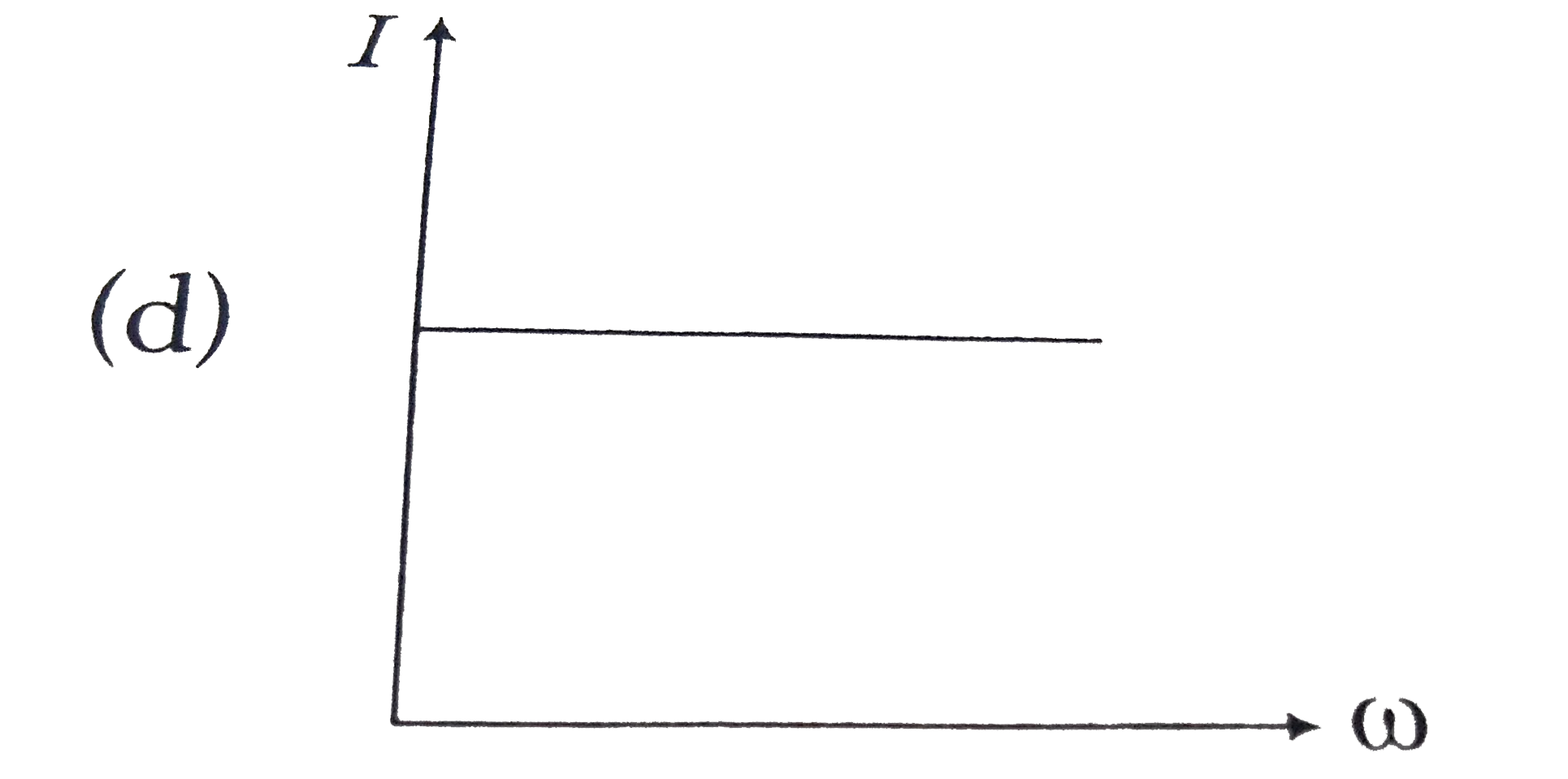
A constant voltage at different frequencies is applied across a capacitance. C as shown in the figure. Which of the following graphs correctly depicts the varitaion of current with frequency? |
|
Answer»
`I=1/(LC) = 1/(sqrt(10^(-3) XX 10 xx 10^(-6))` `omega = 1/(sqrt(10)^(-8))=10^(4)` `THEREFORE X_(L) = omegaL=10^(4)xx 10^(-3)= 10 Omega` |
|
| 8128. |
Two bar magnet oscillating of periodic time is 2:1. If interial of mass is constant then the ratio of magnetic dipole moment ....... |
|
Answer» `1:2` `(T_2)/( T_1) = sqrt((m_(1) B)/( m_(2) B)` `(T_2)/( T_1) = sqrt((m_1)/( m_2))` `THEREFORE (1)/(2)= sqrt((m_1)/( m_2) ) ""[because (T_1)/( T_2) = (2)/(1) ]` `therefore (1)/(4) = (m_1)/(m_2)` `therefore (m_1)/(m_2) = 1:4` |
|
| 8129. |
A charge of 5 C is placed at the centre of a spherical Gaussian surface of radius 5 cm. The electric flux through it is: |
|
Answer» 0.1 C |
|
| 8130. |
An object reaches a maximu m vertical height of 23.0 m when thrown vertically upward on the earth.How high would it travel on the moon where the acceleration due to gravity is about one sixth that on the earth?Assume that initial velocity is the same. |
|
Answer» 138 m |
|
| 8131. |
What is the unit of magnetic field strength in cgs system and SI? State the relation between them. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Unit of magnetic FIELD is cgs system is GAUSS and in SI is TESLA or `NA^-1m^-1` or weber `m^-2`. `1 tesla=10^4 gauss`. | |
| 8132. |
Assertion In diffraction phernomenon different maximas have different intensities Reason In interference different maximas have same intensities |
|
Answer» |
|
| 8133. |
Derive the expression for lateral shift produced when a ray of light passes through a parallel sided slab. |
Answer» SOLUTION :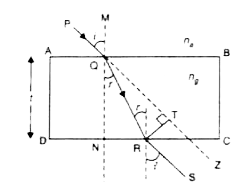 From `DELTA QTR`,`sin ( i-r) = ( R T )/( QR )` From `Delta QNR `, `cos r = ( QN )/( QR )` LATERAL shift `= QR xx sin ( i - r) `and `QR = ( QN )/ ( cos r )` Lateral shift ` = ( QN )/( cos r ) sin ( i - r)` Lateral shift `= ( t )/( cos r ) sin ( i - r )` |
|
| 8134. |
Sun is a very powerful source of ultraviolet rays.But we do not receive much ultraviolet rays onthe surface of the earth. Why? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :OZONE PREVENTS the UV RAY | |
| 8135. |
A L-C-R circuit connected to an A.C. source of frequency f. If current in phase leads by 45^@ then voltage, the capacitance of capacitor ………. |
|
Answer» `1/(2pif(2pifL-R))` `therefore tan 45^@ =(omegaL-1/(omegaC))/R` `therefore R=omegaL-1/(omegaC)` `therefore 1/(omegaC)=omegaL-R` `therefore omegaC=1/(omegaL-R)` `therefore C=1/(omega(omegaL-R))` `therefore C=1/(2pif(2pifL-R))` |
|
| 8136. |
बिना निषेचन फल के विकास को कहते है : |
|
Answer» अषेक जनन |
|
| 8137. |
Three coherent sources generating waves in the same phase are placed as shown. The wave length of the wave is 40 xx 10^7m. The minimum distanced (in M-in), such that intensity at point D is 9 times the intensity of each source will be .............. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 8138. |
A constant current of 1.5.A is maintained in a resistance of 5Omega. Has its r.m.s. value ? |
|
Answer» `1.5/SQRT2 A` |
|
| 8139. |
When an a.c. source is connected across an ideal inductor,show on a graph the nature of variation of the voltage and the current over one complete cycle. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 8140. |
In a biprism experiment, the distance between the two virtual images of the slits in the magnified and diminished position are 2.4 mm and 0.6 mm respectively. The distance between the two virtual images of the slit is : |
|
Answer» 1 mm |
|
| 8141. |
(a) Why do welders wear special glass goggles or face masks with glass windows ? (b) Why are ultraviolet rays used in LASIK eye surgery? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Welders wear special glass goggles or face masks with glass windows to protect their eyes from large amount of ultraviolet rays produced by welding arcs because these are absorbed by glass goggles/masks. (b) DUE to its shorter WAVELENGTHS, ultraviolet radiations can be focussed into very narrow beams for high precision applications. Accordingly UV rays are used in LASIK EYE surgery. |
|
| 8142. |
In davision -Germer experiment electron emitted from filament is accelerated by V volt.Its de-Broglie wavelength will be…….. |
|
Answer» <P>`(sqrt(H))/(2Vem)` `2Vem=m^(2)v^(2)` 2Vem=`p^(2) [because mv=p]` `therefore =sqrt(2Vem)` Now de-Broglie WAVELENGTH `lambda=(h)/(p)` `therefore lambda=(h)/(sqrt(2Vem))` |
|
| 8143. |
The tube of a mercury thermometer has an inside diameter of 0.120mm.The bulb has a voluem of 0.250cm^(3). How far will the thread of mercury move when the temperature changes from 10.0^(@)C to 20.0^(@)C? Take inot account expansion of the glass (Pyrex). b. Determined a formula for the length of the mercury column in terms of relavant variables. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 8144. |
The viscosity eta of a gas depends on the long - range attractive part of the intermolecular force, which varies with molecular separation r according to F=mur^(-n) where n is a number and mu is a constant. If eta is a function of the mass m of the molecules, their mean speed v, and the constant mu than which of the following is correct- |
|
Answer» `ETA PROP m^(N+1)v^(n+3)MU^(n-2)` |
|
| 8145. |
During sunrise and sunset light has to travel greater distance, why ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :SCATTERING . | |
| 8146. |
A : Standard optical diffraction gratings cannot be used for discriminating between different X-ray wavelengths. R : The grating spacing is not of the order of X-ray wavelengths. |
|
Answer» Both A and R are TRUE and R is the CORRECT explanation of A |
|
| 8147. |
Explain electric field and its source as well as magnetic field and its source. |
|
Answer» Solution :1. Source of electric FIELD is charge. 2. If Q charge is static, then electric field produce around it is, `vecE=(kQ)/r^(2)*hatrorvecE=(Qhatr)/(4piepsi_(0)r^(2))` where `hatr` is unit vector of position vector `vecrandvecE` is electric field which is vector. 3. Force on charge particle in electric field is given by `vecF=qvecE` = `(kQq)/r^(2)hatror(Qq)/(4piepsi_(0)r^(2))*hatr` 4. It can convey energy and momentum and is not established instantaneously but takes finite time to propagate. 5. It DEPENDING on each point in space, it can also vary with time. i.e. be a function of time. 6. In this chapter, we will assume that the fields do not change with time. 7. The field at a particular point can be due to one or more charges. If there are more charges the fields add vectorially. This is called the principle of superposition. 8. The force on a test charge is given by `vecF=vecEq_(0)` where `q_(0)` is known as test charge. 9. Static charges produces an electric field and moving charges produce electric field and magnetic field in addition which is denoted by `vecB(vecr)`. 10. Magnetic field is a vector quantity and it is DEFINED at each point in space and it depend on time. 11. The magnetic field of several sources is the vector addition of magnetic field of each individual source. It obey the superposition principle. |
|
| 8148. |
To know the resistance of a galvanometer by half deflection method, a battery of emf V and resistance R is used to deflect the galvanometer by angle theta . If a shunt of resistance is needed to get half deflection then, G, R and S are related by the equation : |
|
Answer» `2S (R + G) = RG` 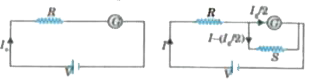 In first case Resistance R is connected in series with the galvanometer and CURRENT `(I_(g))`FLOWING through it can be written as follows: `I_(g) = V/(R + G) ` ....(i) In second case shunt S is connected in parallel to the galvanometer. TOTAL current (I) drawn from the battery can be written as follows: `I = V/(R + (GS)/(G + S)) ` ....(ii) Shunt is adjusted in such a manner that deflection in the galvanometer becomes half to that in first case. Hence `I_(g)/2` current passes through the galvanometer and`(I - I_(g)/2)`current passes through the shunt. For the same potential difference across galvanometer and shunt we can write the following equation. ` I_(g)/2 G = (I - I_(g)/2)S` ` rArr"" I_(g)/2 (G + S) = IS` Substituting values from equation (i) and (ii) we can rewrite the above expression as follows: `rArrV/(2(R+G))(G+S) = V/(R+(GS)/(G+S)) S` `rArr((G + S))/(2(R + G)) = (S(G + S))/(RG + RS + GS)` `rArrRG + RS + GS = 2RS + 2GS` ` RG = S (R + G)` Hence option (b ) is correct. |
|
| 8149. |
In optical fibres, the refractive index of the core is |
|
Answer» GREATER than that of the cladding |
|
| 8150. |
A square loop of side length L carries a current which produces a magnetic field B_(0) at the centre (O) of the loop. Now the square loop is folded into two parts with one half being perpendicular to the other (see fig). Calculate the magnitude of magnetic field at the centre O. |
|
Answer» |
|