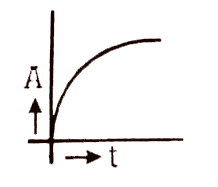Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 201. |
At the initial moment the activity of a certain radionuclie totalled 650 particles per minute.What will be the activity of the preperation after half its half-life period? |
|
Answer» Solution :The ACTIVITY is proprotional to the number to the number of parent nuclei(assuming that the daughter is not radioactive). In half its half-life period, the number of parent nucli decrease by a factor `(2)^(-1//2)=(1)/(SQRT(2))` So activity decreases to `(650)/(sqrt(2))= 460` particles per minute. |
|
| 202. |
After time 't' the height ‘y ’ of projectile is y = 8t - 5t^(2) and horizontal distance x = 6t if g=10 ms^(-2)1 , velocity of projectile at this instant is : |
|
Answer» 10m/s `x=ucosthetat` `6t=ucosthetatimplies ucostheta=6impliesu_(x)=6ms^(-1)` Similarly `y=usinthetat-1/2g t^(2)` `8T - 5t^(2)=usinthetat-1/2g t^(2)` `implies usintheta=8impliesu_(y)=8MS^(-1)` Now `u=sqrt(u_(x)^(2)+u_(y)^(2))=10ms^(-1)` |
|
| 203. |
Compare the intensities of maxima and minima in terms ofamplitude ratio |
|
Answer» Solution :a. INTENSITY (maximum or minimum) `prop` BANDWIDTH B. Intensity (maximum) `I_("MAX")prop(a_(1)+a_(2))^(2)` Intensity (minimum) `I_("minimum")prop(a_(1)-a_(2))^(2)` `:.(I_("max"))/(I_("min"))=((a_(1)+a_(2))^(2))/((a_(1)-a_(2))^(2))` |
|
| 204. |
(A) : Range is the largest distance between a source and a destination upto which the signal is received with sufficient strength (R) :Use of repeater station to increase the range of communication |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 205. |
A short linear object of length b lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length f at a distance u from the pole of the mirro. The size of the image is approximately equal to |
|
Answer» `B((u-F)/f)^(1//2)` |
|
| 206. |
A source emitting light of wavelength 480 nm and 600 nm is used in a double slit interference experiment. The separation between the slits is 0.25 mm and the interference is observed on a screen placed at 150 cm from the slits. Find the linear separation between the first maximum (next to the central maximum) corresponding to the two wavelengths. |
|
Answer» 0.36 mm |
|
| 207. |
Which one of the following is the property of a monochromatic, plane electromagnetic wave in free space ? |
|
Answer» Electric and magnetic fields have a phase DIFFERENCE of `(PI)/(2)` |
|
| 208. |
A ball is rising through a liquid with constant speed. The ratio of density of liquid to that of material of ball is 3 : 1. The ratio of viscous force to the weight of the ball is: |
|
Answer» `1:3` `=4/3pir^(3)3.p.g` or `6pietarv=4/3pir^(3)g(3p-p)` `F=6pietarv` `=4/3pir^(3)xx2p.g=8/3pir^(3)pg` Ratio `F/W=(8/3pir^(3)pg)/(4/3pir^(3)pg)=2/1` `therefore` CORRECT CHOICE is (B). |
|
| 209. |
A metallic square loop PQRS is moving in its own plane with velocity v in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to its plane as shown in Fig. If V_(P), V_(Q), V_(R) and V_(S) are the potentials of points P, Q, R and S then which of the following is an incorrect statement? |
|
Answer» `V_(P)=V_(Q)` so, `V_(P)=V_(Q), V_(S)=V_(R), V_(P)gtV_(S), V_(P)` `gtV_(R), V_(Q)gtV_(R`). 
|
|
| 210. |
Assertion : A galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter by connecting hight resistance (Rh) in series with the galvanometer . Reason : The high resistance , R_(h) = V/I_(g) - R_(g) where , I_(g) tocurrent through galvanometer R_(g) toResistance of the galvanometer |
|
Answer» ASSERTION and REASON are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion . |
|
| 211. |
A black body at a temprature of 227^@C radiates heat at the rate of 5 cal/cm^2 sec. At the temperature of 727^@C the rate of heat radiated in cal/cm^2 sec is |
|
Answer» 20 |
|
| 212. |
In oscillator circuit, presence of .........are necessary |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 213. |
Show a plot of variation of alternating emf versus time generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. |
Answer» SOLUTION :MAGNETIC FLUX VERSUS TIME 
|
|
| 214. |
What amount of heat is needed to raise the temperature of 2xx 10^(-2) kg of nitrogen at room temperature to raise itstemperature by 45^(@)C at constant pressure ? (Given molecular mass =28 and R=8.3" J mol"^(-1)K^(-1),C_(p)=7//2 R): |
|
Answer» `9.33 CAL` `C_(p) =(7)/(2) R=(7)/(2) xx8.3 J" mole"^(-1) K^(-1)` `Delta Q =n C_(p) XX Delta T` `=0.714xx(7)/(2)xx8.3 xx45 J` `=933.4 J`. `therefore` Correct CHOICE is (c ). |
|
| 215. |
Modern telescopes prefer using suitable mirrors over using suitable lenses. Give two reasons for this preference. |
|
Answer» Solution :Modern telescopes prefer using concave mirror of large APERTURE as the objective instead of convex lens due to the following reasons : (1) There is no chromatic aberration in a mirror. (2) If the mirror is a parabolic mirror then even spherical aberration is also removed. (3) Mechanical support of reflecting type telescope is easy to design and install because mirror weigh much LESS than a lens of equivalent optical quality. (4) It is possible to have telescope objective mirror of larger aperture. In this way we can design telescopes of HIGHER RESOLVING power and greater viewing RANGE. |
|
| 216. |
Mass of photon moving with speed v is ……,m_(0) is rest mass of photon. |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 217. |
The wavefront of a distant source of unknown shape is approximately |
|
Answer» Spherical |
|
| 218. |
One concave and one convex lens have same focal length. If they are kept in contact, combination behaves as ....... |
|
Answer» CONCAVE lens `1/f_1=(1)/(-f)+1/f`[`because` For concave lens f is NEGATIVE and for convex lens f is positive] `therefore 1/f_1=0``thereforef_1=infty` `therefore` Transparent plane plate. |
|
| 219. |
Figure shown a particle P of mass m moving on a smooth circular wire of radius 5 cm beingacted upon by attractiveforce ( conservative in nature) directed towards O which is 3cm from C as shown in the figure and having magnitude 4/3 (m)/((OP)^(2)) dynes, find the minimum velocity which should be given to the particle at A so that it may complete the circle successfully . Neglect gravity. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 220. |
The distance between an object and its image produced by a converging lens is 0.72 m. The magnification is 2. What will be the magnification when the object is moved by 0.04 m towards the lens ? |
|
Answer» 2 `THEREFORE "For a real image" (1)/(f) = (1)/(v) + (1)/(u)` `or "" 1 + (1)/(m) = (u)/(f)` `rArr "" 1+ (1)/(2) = (u)/(f)` `rArr (3)/(2) = (0.72)/(f)` `or "" f = (0.72 xx 2)/(3) = 0.16m` As the object is moved by 0.04 m towards the LENS, the new `mu_(1) = 0.72 - 0.04 = 0.68 m` Again real image is formed `rArr "" 1 + (1)/(m) = (u_(1))/(f)` `rArr "" (1)/(m) = (0.04)/(0.16)` `rArr "" m = 4`. |
|
| 221. |
The magnetic moment of a bar magnet is 45 Am^(2) and its length is 10 cm. Calculate the magnetic field induction at a point 10 cm away from the centre of the magnet on the axial line. |
|
Answer» Solution :Length of the magnet , 2l = 10 cm `= 10 xx 10^(-2)` m `implies l =5 xx 10^(-2) m` Distance of the POINT on axial line , d=10 cm `= 10 xx 10^(-2) m ` Magnetic moment, `M=45 Am^(2)` `:.` Magnetic induction on the axial line of the BAR magnet is `B = (mu_0)/( 4 PI ) (2MD)/((d^(2)-l^(2))^(2))` `B = (4 pi xx 10^(-7))/(4 pi) ( 2 xx 45 xx 10 xx 10^(-2))/([(10 xx 10^(-2))^(2) - ( 5 xx 10^(-2))^(2)]^(2))` ` = 16 xx 10^(-3) T ` |
|
| 222. |
If the components of A are A_(x)=2 and A_(y)=3, and the components of B are B_(x)=-4 and B_(y)= 2, compute the components of each of the following vectors. (i) A+B (ii) A- B (iii) 2A (iv) A+ 3B |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Using unit vector notation, `A= 2i - 3j and B= - 4I + 2j`. Adding COMPONENTS, we see that `A + B= (2+[-4])i+ ([-3]+2)j= 2i-j`. Therefore, the X COMPONENT of the sum is `-2` and the y - components is `-1`. (ii) `A- B= (2i-3j)-(-4i+2j)=(2-[-4])i+(-3-2)j=6i-5j`. The x-component is 6 and the y-component is `-5`. (iii) `2A=2(2i-3j)=4i-6j`. 4 and `-6` are the x- and y-components, respectively. `(iv) A+3B=(2i-3j)+3(-4i+2j)=(2+3[-4])i+(-3+3[2])j=-10i+3j. -10 and 3` are the x- and y-components, respectively. |
|
| 224. |
A 100 V battery, a 5.00 Vresistor, and a 10.0 H inductor are connected in series. After the current in th circuit has reached its maximum value. |
|
Answer» the power being supplied by the BATTERY is `20.0 W` |
|
| 225. |
A ring of mass m and radius r rotates about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with angular velocity omega. Its kinetic energy is |
|
Answer» `1/2mr^(2)OMEGA^(2)` |
|
| 226. |
A bar magnet of magnetic moment M is kept in a uniform magnetic field of strength B makingan anglethetawith its direction the torque acting on it is |
|
Answer» `MB COS THETA` |
|
| 227. |
The incient light photon involved in the photoelectric emission phenomenon |
|
Answer» COMPLETELY disappears. |
|
| 228. |
In a betatron the magnetic flux across an equilibrium orbit of radiusr = 25 cmgrowsduringthe acceleration time at paractically constantrate Phi = 5.0 Wb//s. In the process, theelectrons acquire an energy W = 25 MeV. Findthe numberof revolutionsmade by theelectronduring the acedeleration time andthe correspondingdistancecovered by it. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The increment is ENERGY per revoltion is `E Phi`, sothe NUMBER of revoltutions is, `N = (W)/(e Phi)` The distancetraversed is, `s = 2pi rN` |
|
| 229. |
A copper rod of length 2m is rotated with a speed of 10 rps, in a uniform magnetic field of 1 tesla about a pivot at one end. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of rotation. Find the emf induced across its ends |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`e = 1/2 B omega l^2 = 1/2 B (2pi n)l^2 =PI Bn l^2` ` e = 3.14 XX 1 xx 10 xx 2 xx 2 = 125.6 `volt |
|
| 230. |
Nanukaka had tied a huge ............. turban around his head. |
|
Answer» red |
|
| 231. |
Consider a sphere of radius R with charge density distributed as : rho( r) =kr, r le R =0 for r gt R (a) Find the electric field at all points r. (b) Suppose the total charge on the sphere is 2e where e is the electron charge. Where can two protons be embedded such that the force on each of them is zero. Assume that the introduction of the proton does not alter the negative charge distribution. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) Let us consider a sphere S of radius R and two hypothetic spheres of radius r < R and r > R. Electric field intensity for point r < R, `ointvecE.dvecS = 1/epsilon_(0) int rho dN` But volume, `V = 4/3 pir^(3)` `dV = 4/3 pi xx 3r^(2) dr` `dV = 4pir^(2)dr`  `therefore ointvecE.dvecS = 1/epsilon_(0) 4pikint_(0)^(r)r^(3)dr |rho =kr|` `therefore E=1/(4epsilon_(0)).kr^(2)` As charge density is positive it means the direction of `vecE` is radially outwards. Electric field intensity for point `r gt R`. `ointvecE.dvecS = 1/epsilon_(0)intrho dV` `therefore E=(kR^(4))/(4epsilon_(0)r^(2))`.........(1) Here, also the charge density is again positive. So, the direction of `vecE` is radially outward. (b) The two PROTONS must be placed symmetrically on the opposite sides of the centre along a diameter. This can shown by the figure GIVEN below.  Charge on sphere, `q = int_(0)^(R)rho dN = int_(0)^(R)(kr)4pir^(2)dr` `therefore q=4pik R^(4)/4=2e` `therefore k = (2e)/(piR^(4))`........(2) The protons 1 and 2 are embedded at distance r from the centre of the sphere as shown, then attractive force on proton 1, due to charge distribution is, `F_(1) = eE = (-EKR^(2))/(4epsilon_(0))`.........(3) And REPULSIVE force on proton 1 due to proton 2 is, `F =F_(1) + F_(2)` `therefore F=[(-er^(2))/(4epsilon_(0)).(Ze)/(piR^(4)) + e^(2)/(16 pi epsilon_(0)r^(4))]` Thus, net force on proton 1 will be zero, when `therefore (er^(2)2e)/(4epsilon_(0)piR^(4)) = e^(2)/(16piepsilon_(0)r)` `therefore r=R/(8^(1//4))` Hence, the protons must be at a distance r from the centre. |
|
| 232. |
A cylindrical disc of a gyroscope of mass m=15kg and radius r=5.0cm spins with an angular velocity omega=330rad//s. The distance between the bearings in which the axle of the disc is mounted is equal to l=15cm. The axle is forced to oscillate about a horizontal axis with a period T=1.0s and amplitude varphi_m=20^@. Find the maximum value of the gyropscopic forces exerted by the axle on the bearings. |
|
Answer» Solution :The MOMENT of inertia is `1/2mr^2` and angular momentum is `1/2mr^2omega`. The axis oscillates about a horizontal axis making an INSTANTANEOUS ANGLE. `varphi=varphi_m"sin"(2pit)/(T)` This MEANS that there is a variable precession with a rate of precession `(dvarphi)/(dt)`. The MAXIMUM value of this is `(2pivarphi_m)/(T)`. When the angle between the axle and the axis is at the maximum value, a torque `IomegaOmega` `=1/2mr^2omega(2pivarphi_m)/(T)=(pimr^2omegavarphi_m)/(T)` acts on it. The corresponding gyroscopic force will be `(pimr^2omegavarphi_m)/(lT)=90N` |
|
| 234. |
What is sharpness of resonance ? Derive equation of Q-factor |
|
Answer» Solution :Frequency of resonance is independent to resistance R but sharpness of resonance is inversely proportional to R. Sharpness of resonance `= ( omega_(0))/( 2 DELTA omega)` `= ( omega_(0) 2 L )/( 2 xx R ) = ( omega_(0) L ) /( R )`but `( omega_(0) L )/( R ) ` is CALLED the quality factor Q of a circuit. `:.` Quality factor `Q = ( omega_(0) L )/( R )` `:. ( omega_(0))/( 2 Delta omega ) = Q = ( " Resonant frequency ")/( "BANDWIDTH") = ( omega_(0))/( omega_(2) - omega_(1))` `:. 2 Delta omega = ( omega_(0))/( Q)` where `omega_(2)` and `omega_(1)` are the frequency at the current amplitude of `(I_("rms") )_("max")` with a value of `(1)/( sqrt(2))`. So, larger the value of Q the smaller is value of `2 Delta omega` or bandwidth and SHARPER is the resonance. Putting`L = ( 1)/( omega^(2) C 0` `Q = ( omega_(0) xx 1 )/( R xx omega_(0)^(2) C )` `:. Q = ( 1)/( omega_(0) RC )` (1) For series LCR circuit, Q-factor, `Q = ( 1)/( R ) sqrt(( L )/( C )) = ( omega_(0) L )/( R ) = ( 1)/( omega_(0) CR )` (2) For parallel LCR circuit, `Q = ( V_(L ))/( V_(R )) ` or `( V _(C ))/( V_(R ))` If the resonance is less sharp not only is the maximum current less the circuit is close to resonance for a larger range `Delta omega` of frequencies and the tuning of the circuit will not be good. So, less sharp the resonance, less is selectivity of the current or vice versa. If quality is larger, means R is low or L is large the circuit is more sleective. |
|
| 235. |
Two sinusoidal currents are given by i_1 = 2 sin (omegat + pi/6) and i_2 = 10 sin (omegat - pi/4)The phase difference between them is : |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 236. |
If the electric flux entering and leaving an enclosed surface respectively is phi_(1) and phi_(2), the electric charge inside the surface will be |
|
Answer» `(phi_(2)-phi_(1))epsilon_(0)` |
|
| 237. |
An electron and a proton have same speed. How are their wavelength related? |
| Answer» Solution :We KNOW de BROGLIE `LAMBDA=(H)/(mv)`.i.e., `lambda prop (1)/(m)`. As PROTON is heavier than electron, wavelength of proton is less than that of electron. | |
| 238. |
Find the magnetic induction at the point O of the following figures if the wire carrying a current I = 15A has the shapes shown here. The radius of the curved part R=5cm, the linear parts of the wire are very long. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 239. |
When Sunita, a class XII student, came to know that her parents are planning to rent out the top floor of their house to a mobile company she protested. She tried hard to convince her parents that this move would be a health hazard. (i) Ultimately her parents agreed. (1) In what way can the setting up to transmission tower by a mobile company in a residential colony prove to be injurious to health? (2) By objective to this move the parents, what value did Sunita display? (3) Estimate the range of e.m. waves which can be transmitted by an antenna of height 20m. (Given radius of the earth = 6400 km). |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) A transmitting TOWER makes use of electromagnetic waves such as microwaves, exposure to which can cause sever health hazards like tumour and cancer. Also, the transmitting antenna operates on a very high power, so the risk of someone GETTING severely burnt in a residential area increases. (2) By OBJECTING to this move to her parents, Sunita has DISPLAYED awarness towards the health and environment of her society. (3) Range of the transmitting antenna, `d=sqrt(2hR)` Here, h is the height of the transmitting antenna and R is the radius of the Earth. `R=6400km=64xx105m` `d=sqrt(2xx20xx64xx10^(5))=16,000m` `16km` |
|
| 240. |
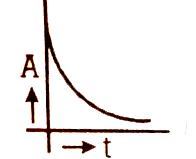
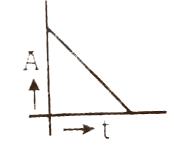
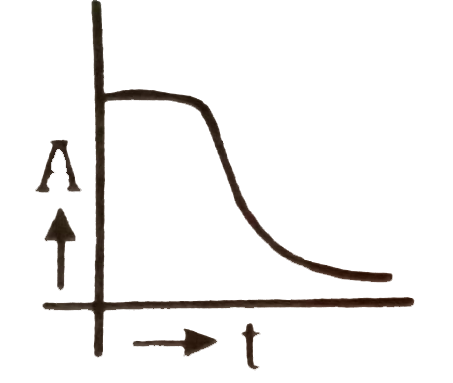
Which of the following graphs represents the variation of activity (A) of a radioactive substance with time (t). |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 241. |
Light of certain frequency and intensity incident on a photosensitive material causes photoelectric effect. If both the frequency and intensity are doubled, the photoelectric saturation current becomes |
|
Answer» halved |
|
| 242. |
A circular coil of closely wound N terns and radius r carriers a current I. Write the expressions for the following : (i) the magnetic field at its centre (ii) the magnetic moment of this coil |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) At centre `B_(C)=(mu_(0)Ni)/(2R).` Here, current in the coil is anticlockwise and the direction of magnetic field is PERPENDICULAR to the plane of coil upward, but if the current in the coil is clockwise, then the direction of magnetic field will be perpendicular to the plane of coil downward. (ii) The magnetic field DUE to a circular coil of radius R, carrying current I at its centre is `B=(mu_(0) I)/(2r)` The direction of magnetic field is perpendicular to plane of coil, directed outward if current is anticlock wise and inward if current is clockwise. |
|
| 243. |
A cord is wound round the circumference of a wheel of radius r. The axis of the wheel is horizontal and its moment of inertia about this axis is I. A weight mg is attached to the end of the cord and is allowed to fall from rest. The angular velocity of the wheel, when the weight has fallen through a distance h, is |
|
Answer» `[(2gh)/(l+mr)]^(1//2)` |
|
| 244. |
Assertion: Electromagnetic radiations are regarded as waves. Reason: Because they exhibit interference, diffraction and polarization under some suitable circumstances. |
|
Answer» ASSERTION and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. |
|
| 245. |
A negatively charged oil drop is prevented from failing under gravity by applying a vertical electric field 100 Vm^(-1). If the mass of the drop is 1.6 xx 10^(-3)g the number of electrons carried by the drop is (g=10 ms^(-2)) |
| Answer» | |
| 246. |
In a p - n junction diode , not connected to any circuit |
|
Answer» the potential is the same everywhere 
|
|
| 247. |
In the output characteristics, curve of an NPN transistor , ……….is about to be a constant near knee point . |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 248. |
निम्नलिखित में से कोनसी संक्रियाएँ क्रम-विनिमय नियम का पालन नहीं करती है |
|
Answer» योगफल |
|
| 249. |
What fraction of hydrogen atoms is in the state with the principle quantum number n=2 at a temperature T=3000K? |
|
Answer» Solution :By Boltzmann formula `(N_(2))/(N_(1))=(g_(2))/(g_(1)) e^(DeltaE//kT)`. Here `DeltaE=` energy difference between `N=1` and `n=2` STATES `=13.6(1-(1)/(4))eV=10.22eV` `g_(1)=2` and `g_(2)=8` (counting `2s` & `2P` states).Thus `(N_(2))/(N_(1))=4e^(-10.22xx1.602xx10^(-19)//1.38xx10^(-23)xx3000)=2.7xx10^(-17)` Explicity `ETA=(N_(2))/(N_(1))=n^(2)e^(-DeltaE//kT),DeltaE_(n)= ħR(1-(1)/(n^(2)))` for the nth excited state beacuse teh degeneracy of the state with principle quantum number `n is 2n^(2)`. |
|
| 250. |
Light of wavelength 589 nm is used to view an object under a microscope. The aperture of the objective has a diameter of 0.900 cm. Find What is the maximum limit of rewolution for this microscope Unsing visible light of any wavelength you desire. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :To obtain the smallest angle corresponding to the maximum limit of resolution, we have to use the shortest wavelength `(lambda= 400 NM)` in the visible SPECTRUM. Limiting angle of resolution `triangle THETA = 1.22((400xx10^(-9)m)/(0.900xx10^(-2)m)) rad` `= 5.42xx 10^(-5)rad` |
|