Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 3401. |
An electron and a photon possess the same de-Broglie wavelength. If E_(e) and E_(ph) are respectively the energies of electron and photon and v and c are their respective velocities, then (E_(e))/(E_(ph))= |
|
Answer» `(v)/(C)` Also `lambda=(hc)/(E_(p)), But E_(e)=(1)/(2) MV^(2)` So `m=(2E_(e))/(v^(2))` `rArr 2E_(e)m=m^(2)v^(2)=(m^(2)v^(2))=(mv)^(2)=p^(2) [ :. P=((E_(p))/(c))]` `:.e[(2E_(e))/(v^(2))]E_(e)=(E_(p)^(2))/(c^(2))` SOLVING `(E_(e))/(E_(p))=(v)/(2c)` |
|
| 3402. |
In Young's double slit experiment, one of the slit is wider than other, so that the amplitude of the light from one slit is double of that from other slit. If I_(m) be the maximum intensity the resultant intensity I when they interface at phase difference phi is given by ....... |
|
Answer» `(I_(m))/(9)(4+5 COS phi)` `:.(I_(1))/(I_(2)=(A_(1)^(2))/(A_(2)^(2))=((2A_(2))^(2))/(A_(2)^(2))` `:.(I_(1))/(I_(2))=4 "" :.I_(1)=4I_(2)` and maximum intensity for constructive interference, `I_("max") =I_(m) (A_(1)+A_(2))^(2) ` (TAKING VALUE of proportionally constant =1) `:. I_(m)=(2A_(2)+A_(2))^(2)` [ as GIVEN `A_(1)=2A_(2)]` `:. I_(m)=(3A_(2))^(2)` `:. I_(m)=9A_(2)^(2) ""...(1)` but `I_(2)prop A_(2)^(2)` `:.I_(2)=A_(2)^(2)` [ Taking proportionally constant] `:. I_(m)=9I_(2)` [ From equation (1)] `:. I_(2)=(I_(m))/(9) ""...(2)` Now intensity of light at a point of both waves, `I=I_(1)+I_(2)+2sqrt(I_(1)I_(2)) cos phi` `=4I_(2)+I_(2)+2 sqrt((4I_(2))+(I_(2))) cos phi` `=5I_(2)+4I_(2) cos phi =I_(2)[1+4+4cos phi]` `=I_(2)[1+4(1+cos phi)]=(I_(m))/(9)[1+4xx"cos"^(2)(phi)/(2)]` `[ :. I_(2)=(I_(m))/(9),1+cos phi=2"cos"^(2) (phi)/(2)]` `=(I_(m))/(9)[1+8"cos"^(2)(phi)/(2)]` |
|
| 3403. |
A capillary tube is dipped in water and water rises to a height of 4cm above the surrounding liquid. If the angle of contact is zero and radius of tube is 0.4 mm, the surface of liquid is |
|
Answer» 78.4 N/m |
|
| 3404. |
A 12 kg bomb at rest explodes into two piece of 4 kg and 8kg . If the momentum of 4kg piece is 20Ns, the kinetic energy of the 8kg piece I |
|
Answer» `25J` `8xxv=20` `V=(20)/(8)=2.5ms^(-1)` K.E. of 8 kg piccc, `K=(1)/(2)mv^(2)=(1)/(2)xx8xx(2.5)^(2)=25J` |
|
| 3405. |
In the above question the radius of curvature of the curvature of the curved surface of plano-convex lens is : |
| Answer» Solution :N//a | |
| 3406. |
Assertion The spectral series 'Blamer' of the of the hydrogen atomlies in the visible region of theelectromagnetic spetrum Reason Wavelength of light inthe visible region lies in the range of 400 nm to 700 nm |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and REASON ar true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. |
|
| 3408. |
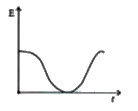
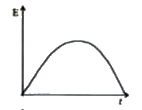
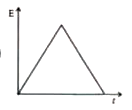
The variation of induced emf E with time t in a coil when a short bar magnet is moved along its axis with constant velocity as shown in below fig. which fig. is best represented as ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 3409. |
A splash is heard 3,12s after a stone is dropped into a well 45 m deep.The second of sound in air is [g=10 ms^(-2)] |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 3410. |
Consider the circuit shown in the figure. The value of the resistance X for which the thermal power generated in it is practically independent of small variation of its resistance is |
|
Answer» `X=R` ` R. = R+(RX )/( R+X )` the currentof thecircuitwill be ` (##MTG_WB_JEE_PHY_C13_E02_010_S01.png" width="80%"> `I = (V )/(R )=(E )/( R+(RX )/( R +X))` thepotentialdropacrossthe resistanceR and Xwill be ` i.e,V_(RX )= i R_(XR ) = ((E )/( R+(RX )/( R+X ) )) ((RX )/(R xx X )) = (EX )/( R + 2X )` the powergeneratedacrossresistanceX , ` P_X =(V^2 RX )/( X )= (E^2X )/( (R +2X)^2)` differtiatingwith RESPECT TOX `(dP_X )/( dX ) = (E^2(R - 2X ))/((R + 2X)^3 ):.(dP_X )/( dx)= 0` ` thereforeR-2X=0orX =(R )/(2 )`s |
|
| 3411. |
A string vibrates with one loop between the fixed points A and B. The ratio of magnitudes of maximum velocities of P and Q is [The shape of string when P and Q having zero speeds as shown in the figure. |
|
Answer» `2:3` |
|
| 3412. |
A plane light wave of intensity I = 0.20 W//cm^(2) falls on a plane mirror surface with reflection coefficient rho = 0.8. The angle of incidence is 45^(@). In terms of the corpuscular theory find the magnitude of the normal pressure extered by light on that surface. |
|
Answer» Solution :Suppose the mirror has a surtace AREA `A`. The incident BEAM then has a cross section of `A cos theta` and the incident enegry is `IA cos theta`: Then the momentum transferred per second `(=` FORCE) is from the lest PROBLEM `-(IA cos theta)/(c ) (1+rho)cos theta hatj +(IA cos theta)/(c ) (1-rho)sin theta hati` The normal pressure is then `p = (I)/(c)(1+rho)cos^(2)theta (hatj` is the unit vector `_|_^(r )` to the plane mirror). Putting in the values `p = (0.20xx10^(4))/(3XX10^(8)) xx1.8 xx (1)/(2) = 0.6nNcm^(-2)` 
|
|
| 3413. |
Statement-I: Power loss in ideal choke coil is zero. Statement-II: Ideal choke coil has zero resistance. |
|
Answer» If both Statement- I and Statement- II are true, and Statement - II is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of Statement– I. |
|
| 3414. |
In a transformer primary has 50 turns and secondary has 10 turns . The RMS voltage in the primary is 120V . Find the RMS secondary voltage in the open circuit .if the secondary has a load of 12 Omega . What are the currents in the primary and secondary ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`V_S/V_P= N_S/N_P = I_P/I_S` `N_P = 500 , N_S = 10 , V_P = 120 V` ` therefore V_S = N_S/N_P XX V_P = 10/500 xx 120= 2.4 V` by the ohm.s law current in the SECONDARY `I_S = V_S/R_S = (2.4)/(12) = 0.2A` Hence current in the primary `I_P = N_S/N_P xx I_S = 10/500 xx 0.2 = 4 xx 10^(-3) A ` `I_P = 4mA` |
|
| 3415. |
Sharp lines are present in the spectrum of a gas. What does this indicate ? |
| Answer» Solution :Sharp lines in the SPECTRUM of gas, indicates BRIGHT lines against DARK background. | |
| 3416. |
Pole strength of a magnet is 5 Am and the magnetic length of it is 10 cm. Calculate the magnetic dipole moment of it. |
|
Answer» `0.5 Am^(2)` `therefore m_(B) = 5 xx 10xx 10^(-2)` `=0.5 "Am"^2` `P=5 "Am"` `2L = 10 xx 10^(-2) m` |
|
| 3417. |
A particle is moving along x-axis under the action of a force, F which varies with its position (x) as F prop x^(-1//4). The variation of power due to this force with x is |
|
Answer» `X^(1//3)` |
|
| 3418. |
Four charges equal to Q are placed at the four comers of a square and a charge q is at its centre . If the system is in equilibrium , the value of q is |
|
Answer» `(-Q)/(4)(1+2sqrt(2))` Diagonal `AC=SQRT(a^(2)+a^(2))=asqrt(2)` `thereforeOA=OC=(asqrt(2))/(2)=(a)/(sqrt(2))` The systen is in equilibrium means the force experienced by each CHARGE is zero . It is clear that charge placed at centre would be at equilibrium for any value of q, so we are considering the equilibrium of charge placed at any comer (SAYA). 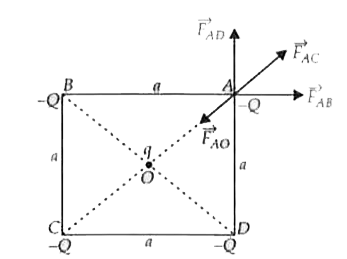 Hence, `vecF_(A)=vecF_(AB)+vecF_(AD)+vecF_(AC)+vecF_(AO)=vec0` `vecF_(AB)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(Q^(2))/(a^(2))` along `BA,vecF_(AC)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(Q^(2))/(2a^(2))`along CA `vecF_(AD)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(Q^(2))/(a^(2))`along `DA,vecF_(AO)=-(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(2Qq)/(a^(2))`along AO Resultant of `vecF_(AB)andvecF_(AD)=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(Q^(2))/(a^(2))-(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(2Qq)/(a^(2))=0` or `sqrt(2)Q+(Q)/(2)-2q=0` `2q=(Q)/(2)[2sqrt(2)+1]rArrq=(Q)/(4)[2sqrt(2)+1]` |
|
| 3419. |
Twoidentical thin bar magnets each l and pole strength m are placed at right angle to each otherwith north pole of one touching south of other the magnetic moment of the system is |
|
Answer» ML hence M=`mxxsqrt(2)`l 
|
|
| 3420. |
On your birthday, you measure the activity of the sample ""^(210)Bi which has a half - life of 5.01 days. The initial activity that you measure is 1muCi. (a) What is the approximate activity of the sample on your next birthday? Calculate (b) the decay constant (c) the mean life (d) initial number of atoms. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a)A YEAR of 365days is equivalent to `(365 d)/(5.01d) APPROX 73` half - lives. Thus , the activity will bereduced after one year to approximately `(1/2)^(73)(1.000 mu Ci) approx 10^(-22)mu Ci`. (b) Initial measure `R_(0) = 1.000 mu Ci` `= 10^(-6) xx 3.7 xx 10^(10)` ` = 3.7 xx 10^(4) Bq` After 1 year, the measure R = `10^(-22)mu Ci` ` = 10^(-22) xx 10^(-6) xx 3.7 xx 10^(10)` ` = 3.7 xx 10^(-18) Bq` decay constant `lambda = (1)/(t) In((R_(0))/(R)) = ((1)/(1 year)) In ((3.7 xx 10^(4))/(3.7 xx 10^(-18)))` `(1)/(3.156 xx 10^(7)) In(10^(22))` `lambda = (50.657)/(3.1567 xx 10^(7)) = 1.6 xx 10^(-6) s^(-1)` (c) Mean life `TAU = (1)/(lambda) = (1)/(1.6 xx 10^(-6))s [ 1s = (1)/(86400) days]` `tau = 7.24` days (d) Initial number of ATOMS `R_(0) = lambda N, N = (R_(0))/(lambda)` `= (3.7 xx 10^(4))/(1.6 xx 10^(6)), N = 2.31 xx 10^(10)` |
|
| 3421. |
The type of electromagnetic wave propagation which is effected as a result of reflection in the upper stratosphere of atmosphere is known as: |
|
Answer» AIR WAVE propagation |
|
| 3422. |
Assertion : Separation of isotope is possible because of thedifference in electron numbers of isotope. Reason : Isotope of an element can be separated by using a mass spectrometer. [AIIMS 1999] |
|
Answer» If both ASSERTION and reason are TURE and the reason is the CORRECT explanation of the assertion. |
|
| 3423. |
The work function of a metallic surface is 5.01 e V. The photoelectrons emitted when light of wavelength 2000 A^@ falls on it . The potential difference applied to stop the fastest photo electrons is : (h = 4.14 xx 10^(-15) e V) |
|
Answer» 2.24 V |
|
| 3424. |
A dielectric slab is placedbetween the plates of a parallel plates capacitor. Its capacitance |
|
Answer» BECOMES zero |
|
| 3425. |
Latent Heat of vaporisation of liquid is ………………. |
|
Answer» 20 KJ/Kg |
|
| 3426. |
-10mu C, 40 mu C and qare the charges on three identical conductors P,Q and R respectively, Now P and Q attract each other with a force F when they are separated by a distance d. Now P and Q are made in contact with each other and then separated . Again Q and R are touched and they are separated by a distance 'd' . The repulsive force between Q and R is 4F . Then the charge q is: |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 3427. |
(A): The magnitude of a physical quantity does not change when the system of units is changed from S.I system to C.G.S system. (R): The magnitude of a physical quantity is independent of system of units |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 3428. |
A certain airplane has a speed of 290.0 km/h and is diving at an angle of theta=30.0^(@) below the horizontal when the pilot releases a radar decoy. The horizontal distance between the release point and the point where the decoy strikes the ground is d = 700 m. (a) How long is the decoy in the air? (b) How high was the release point? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 10.0 s, (B) 897 m | |
| 3429. |
The triangular wedge shown in the figure is pulled towards left with an acceleration 1.5g. What is the acceleration of m_(1)? |
|
Answer» g DOWNWARDS |
|
| 3430. |
If the horizontal and vertical components of earth's magnetic field are equal at a place, what is the angle of dip ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`H = R cosdelta, V = R sindelta` But H = V . Thus, R `cosdelta = R sindelta` or `tandelta = 1 `or `DELTA = 45^@` |
|
| 3431. |
When a wave undergoes reflection at rarer medium then it undergoes a phase difference of : |
|
Answer» `PI` HENCE the correct choice Is (d) . |
|
| 3432. |
In the previous question, calculate the time required for the potential difference across capacitor to become equal to that across resistor. |
|
Answer» 13.86s `i= (dq)/(dt) = CV_(0) (0 + (1)/(RC) e^(-t//RC)) = (V_(0))/(R ) e^(-t//RC)` POTENTIAL difference across capacitor = Potential difference across resistor `rArr q//C = iR` `rArr V_(0) (1-e^(-t//RC)) = V_(0) e^(-t//RC)` `rArr e^(-t//RC) = (1)/(2) rArr e^(t//RC) = 2` `rArr (t)/(RC) = ln 2 rArr t = RC (ln 2)` `=(5 xx 10^(6)) (4 xx 10^(-6)) (0.693) = 13.86s` HENCE, option (a) is correct |
|
| 3433. |
A body of mass m falls from height h_0 on the ground. If e is the coefficient of restitution between body and the ground, then the height upto which it rises after ten collisions is |
|
Answer» `e^10` . `h_0` |
|
| 3434. |
Explain, how a CE transistor acts as a switch. |
|
Answer» Solution :Transistor as a switch Circuit DIAGRAM. The circuit daigram of an n-p-n transistor in CE mode is as shown in the figure. In this circuit, the emitter is forward biased by emitter base battery `V_("bb")` and the collector is reversed biased by emitter collector battery `V_("CC").R_(B)` and `R_(c)` are input and output resistance connected between emitter-base and collector-base respectively . Using Kirchhoff.s LAW, In emitter base circuit `V_("bb")=V_(be)+I_(b)R_(B)`.........`(i)`  In collector-base circuit, `V_(ec)=V_("cc")-I_(c)R_(c)`.......`(ii)` Here `V_("bb")=V_(i)` (input voltage and `V_("cc")=V_(0)` output voltage ) `:.V_(i)=V_(be)+I_(b)R_(B)` .................`(iii)` `V_(0)=V_("cc")-I_(c)R_(c)`............`(iv)` Equations `(iii)` and `(iv)` indicate how `V_(0)` changes, when `V_(i)` is increased slowly. (for Si n-p-n transistor) `(i)` If `V_(i) lt 0.6V`, the transistor is in cut off state and `I_(c)=0` and `V_(0)=V_("cc")`. `(ii)` If `0.6V ltV_(i) lt 1V` the transistor is in active state and `I_(c)` INCREASE linearly and `V_(0)` is less than the earlier value of `V_("cc")`. `(iii)` If `V_(i) gt 1V`, `I_(c)` increases non-linearly and hence `V_(0)` decreases non-linearly and when `I_(c)R_(c)` becomes maximum and transistor is said to be in saturation state tending to zero as shown in the figure.  Switching action. `(i)` When input voltage is very small, the transistor is in cut off region i.e., the transistor is not conducting and acts as if in open condition i.e. OFF state. `(ii)` When input voltage is large and the transistor is in saturation state, `V_(0)` is very small `(V_(0)-0)` , the transistor acts as a closed switch i.e. ON state. |
|
| 3435. |
A choke coil in series with a lamp is connected to a dc line. The lamp is seen to shine brightly. Insertion of an Iron core in the choke causes no change in the lamp's brightness. Predict the corresponding observations if the connection is to an ac line. |
|
Answer» Solution :When the choke coil is connected to dc, there is no change in the brightness. Because `f=0, X_(L)=0`. So, no change in the brightness. In Ac, the choke offers impedance, so, it glows DIM. As we insert an iron core the magnetic FIELD increases and hence inductance increases. `BA=LI = phi` `L PROP B` So, `X_(L)` also increases and the brightness of bulb decreases. |
|
| 3436. |
When a stream of electrons collides with a stream of photons in this collision which of the following is not conserved ? |
|
Answer» Linear momentum |
|
| 3437. |
What is the largest voltage youcan safely put across a resistor marked 196 Omega-1W? |
|
Answer» <P> Solution : ` P= (V^2)/(R ) , V^2=PR =1 xx 196= 196 `` V = 14`volt. |
|
| 3438. |
A square loop ABCD carrying a current i is placed near and coplanar with a long straight conductor XY carrying a current I. |
|
Answer» There is no NET force on the LOOP |
|
| 3439. |
An astronaut can hear his companion on the surface of the earth but can not do so on the surface of moon. Why is it so? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Sound is a LONGITUDINAL WAVE motion and requires a MEDIUM . Since, there is no atmosphere on the moon, sound cannot propagate from one point to the other on the moon. | |
| 3440. |
The work function of caesium metal is 2.14 eV. When light of frequency 6xx10^(14)Hz is incidennt on the metal surface, photoemission of electrons occus. What is the (a) maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, (b) stopping potential, and (c) maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here work function `phi_(0)=2.14eV,` and FREQUENCY of incident radiation `v=6xx10^(14)Hz` `therefore`Energy of light photon `E=hv=6.63xx10^(-34)xx6xx10^(14)J=(6.63xx10^(-34)xx6xx10^(14))/(1.6xx10^(-19))eV=2.48eV` `therefore`Maximum kinetic energy of the emitted ELECTRONS `K_(max)=E-phi_(0)=2.48-2.14=0.34eV` (b) Stopping potential `V_(0)=(K_(max))/(e)=0.34V` (c) As `K_(max)=(1)/(2)mv_(max)^(2)=0.34eV=0.34xx1.6xx10^(-19)J=5.4xx10^(-20)`J `impliesv_(max)=SQRT((2K_(max))/(m))=sqrt((2xx5.4xx10^(-20))/(9.1xx10^(-31)))=3.44xx10^(5)ms^(-1) or 344km" "s^(-1)`. |
|
| 3441. |
An electromagnetic wave is travelling in x-direction with electric field vector given by, vecE_y= E_Asin(kx= omega t) J . The correct expression for magnetic field vector is . |
|
Answer» `vecB =(E_a)/(C )SIN ( KX - omega t) J` |
|
| 3442. |
You are given two circuits as shown in Fig. 14.38, which consist of NAND gates. Identify the logic operation carried out by the two circuits. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) AND, (B) OR | |
| 3443. |
An inductor 20 mH, a capacitor 100 muF and a resistor 50 Omega are connected in series across a source of emf, V = 10 sin 314 t. The power loss in the circuit is. |
|
Answer» 1.13 W V=Vm sin Wt Vm=10 V, W=314 rad `s^(-1) , L=20xx10^(-3)`H, `C=100xx10^(-6) F , R=50Omega` `X_L=WL=314xx20xx10^(-3)=6.28 Omega` `X_C=1/(WC) =1/(314xx10^(-4))=31.85 Omega` `THEREFORE |z|=sqrt(R^2+(X_L-X_C)^2)` `=sqrt((50)^2+(6.28-31.85)^2)` `=sqrt(2500+(25.57)^2)` `=sqrt(2500+653.82)` `=sqrt3153.82` `therefore` |z|=56.16 `Omega` Now, Power `P=I_m I_(rm) cos theta` `=V_m/sqrt2xxV_m/(sqrt2xxZ)xxR/Z` `=(V_m^2R)/(2Z^2)` `=((10)^2xx50)/(2xx(56.16)^2)` = 0.79265 W `therefore P approx` 0.79 W |
|
| 3444. |
Vehicles are streamlined to reduce |
|
Answer» a. CONVERT static to dynamic friction |
|
| 3445. |
In the system shown in figure, the block A is released from rest. Find theacceleration of both blocks ‘A’ and ‘B’. |
Answer» 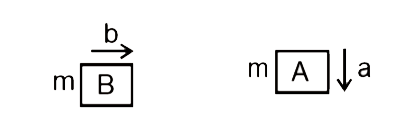 Takingboth blocks as a system `T=2mb . . . .. .. (i)` 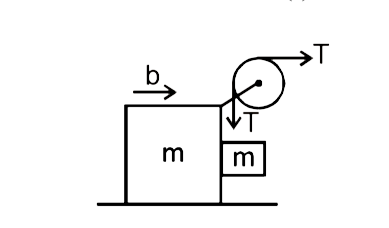 Taking A BLOCK : `mg – T = ma "" . . . . . . . . . (II)` From EQUATIONS (i) & (ii) , `ma + 2 mb = mg` ` a + 2 B = g"" .. . . . . . . . .(III)` From string constraint , `a=b"". . . . . . . . . . .(iv)` From equations (iii) & (iv), 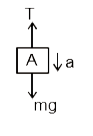 `a=b=(g)/(3)` hence, acceleration of block A `a_(A)=bhat(i)-ahat(j)""a_(A)=g/3hat(i)-g/3hat(j)` acceleration of block B `a_(B)=bhat(i)=(g)/(3)hat(i)` |
|
| 3446. |
Referring to Fig (i) and (ii0, match the following |
|
Answer» <P>`{:(P,Q,R,S),(2.3,2.4,2.3,2.4):}` |
|
| 3447. |
The force between two point charges in air is 100 N. If the distance between them is increased by 50%, then the force between two charges will be nearly equal to |
|
Answer» 50N |
|
| 3448. |
Two sound waves of equations y_1 = 3 sin ( 200pi - 2pix/5) cm and y_2 = 3 sin ( 210pit - 2pix/4.9) cm. Number of beats per second will be |
|
Answer» 10 |
|
| 3449. |
A capillary tube of radius r can support a liquid of weight 6.28 xx 10^(-4) N. If the surface tension of the liquid is 5 xx 10^(-2) N/m. The radius of the capillary must be: |
|
Answer» `2.5xx10^(-4)m` W=T.2`pi`R `rArrr=W/(2piT)=(6.28xx10^(-4))/(2x3.14xx5xx10^(-2))` `=1/5xx10^(-2)=2XX10^(-3)m` Thus the CORRECT choice is (d). |
|
| 3450. |
The resultant of two forces is 20 N when one of force is 20sqrt(3) N and angle between two forces is 30° then what is value of second force ? |
|
Answer» 10N `(20)^(2)=(20sqrt(3))^(2) +B^(2)+2xx20sqrt(3)Bxxsqrt(3)/2` `(20)^(2)=1200+B^(2)+20sqrt(9)B` `-800=B^(2)+60B` or `B^(2)+60B+800=0` SOLVING the quadratic equation B = 20 N |
|