Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 37201. |
If three unit vectors are inclined at an angle of 60^@ with each other, then the magnitude of their resultant vector will be |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 37202. |
Find the resultant of the vectors shown in fig by the component method |
|
Answer» Solution :`vecR_(X) =lhati - 5COS 37^(@)hati -6cos 53hati` `vecR_(x) =1hati - 4hati -3.6hati, therefore vecR_(x), therefore vecR_(x) =-6.6hati` `vecR_(y) =3hatj + 5sin 37hatj - 6sin 53^(@)HATJ` `vecR_(y) = 3hatj + 3hatj - 4.8 hatj, therefore vecR_(y) = 1.2 hatj` `R=sqrt(R_(x)^(2) + R_(y)^(2)) =sqrt((-6.6)^(2) +(1.2)^(2)) = 6.7` |
|
| 37203. |
Obtain the relation between electric field and electric potential due to a point charge. |
Answer» Solution :Consider a point charge .+q.. Let .P. be a point initially at INFINITY. Let .A. be a point inside the field region. Let.+1C. be a unit POSITIVE charge moved from the point at infinity to point .A.. Let .A. be at a distance of .r from the given point charge. Let .B. be another point at distance of dr.. from .A. towards the point charge +q. 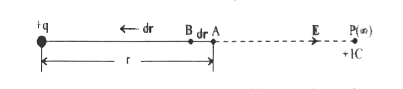 The work done in MOVING positive test charge from A to B, against the force of repulsion is dW= Fdr. The-ve sign indicates that the work is done against the direction of the force and dr is the displacement of +1 C Of test charge in the direction opposite to the electric field. But electric potential `dV=(dW)/(+q_0)` and electric field`E=E/(+q_0)` When `q_0`=+1C thendW=dV, E=F Hence dV=-Edr or `E=-(dV)/(dr)` i.e., Electric field intensity at a point is the negative potential gradient at that point and electric field intensity is in the direction of DECREASING ELECTROSTATIC potential. |
|
| 37204. |
How many percent of work done by a battery is consumed to fully charge a capacitor which is stored as electric potential energy in the capacitor ? |
|
Answer» 25 |
|
| 37205. |
List - IList -II a) spherical wave fronte) location of new wave front b) plane wave front f) line source c) cylindrical wave front g) point source at finite distance d) Huygen.s principle h) point source at infinite distance |
|
Answer» `A-G, B-H, C-F, D-E` |
|
| 37206. |
Which dilute solutionhavethe highervapours presure ? |
|
Answer» 0.002 M NaCl at `50^(@)C` |
|
| 37207. |
A steel wire of diameter 1 mm and length 2 m is stretched by a force of 2kg .wt , what is the increase in the length of wire ? (Y = 2 xx 10^11 N/m^2,g = 9.8m/s^2) |
|
Answer» a)`25 XX 10^(-5)m` |
|
| 37208. |
A sample of a radioactive element whose half-life is 30s contains a million nuclei at a certain instant of time. How many nuclei will be left after 10 s? |
|
Answer» `3.33 xx 10^(5)` `=(0.5)^(1//3)=0.7955` `N=0.7955 xx 10^(6)` `=7.955 xx 10^(5)` |
|
| 37209. |
6 ग्राम यूरिया 180 ग्राम जल में उपस्थित है तो यूरिया का मोल प्रभाज होगा |
|
Answer» `10/10.1` |
|
| 37210. |
Radioactive nuclei that are injected into a patient collect at certain sites within its body undergoing radioactive decay and emitting electromagnetic radiation. These radiations can then recorded by a detector. This procedure provides an important diagnostic tool called |
|
Answer» Gamma camera |
|
| 37211. |
Mean kinetic energy per degree of freedom for gas molecule is |
|
Answer» `(3KT)/(2)` |
|
| 37212. |
A plano-convex lens fits exactly into a plano-concave lens. Their surfaces are parallel to each other if the lenses are made of different materials. Will the combination act as a lens? If so, what is its focal length? Is it convergent or divergent ? |
|
Answer» Solution :LET R be the radius of curvature `(1)/(f_(1)) = - ((n_(1) - 1))/(R) and "" (1)/(f_(2)) = - ((n_(2) - 1))/(R)` `therefore (1)/(f) = (1)/(f_(1)) + (1)/(f_(2)) = (n_(2) - n_(1))/(R) ne 0"" because n_(2) ne n_(1)` Since F has finite VALUE, The combination ACTS as a LENS, It will be conversent if `n_(2) gt n_(1)` and divergent if `n_(2) lt n_(1)` |
|
| 37213. |
Show that it makes little sense placing the dees of a cyclotron into a uniform magnetic field. Specify a rational shape of the pole pieces capable of focusing a particle beam in the centre of the dees. |
Answer» Solution :An ion entering a uniform magnetic field at an ANGLE to the lines of induction will MOVE along a helix to one of the poles of the magnet, and after some time will strike the dees and leave the bunch. To prevent LOSSES, the magnetic field should be made slightly nonuniform (in the shape of a barrel) (FIG. 28.6). It is easily seen that such a field focusses the ions, CONCENTRATING them in the middle plane.
|
|
| 37214. |
Blue colour of sky is due to phenomenon of : |
|
Answer» Reflection |
|
| 37215. |
Two lenses of powers - 15 D and + 5D are in contact with each other. The focal length of combination is : |
|
Answer» `- 10 cm` `therefore "" F = (1)/(P) = (1)/(10) m = - 10 cm ` |
|
| 37216. |
A solenoid of resistance R and inductance L has a piece of soft iron inside it. A battery of emf E and of negligible internal resistance is connected across the solenoid as shown in Fig. At any instant, the piece of soft iron is pulled out suddenly so that inductance of the solenoid decrease to etaL(eta lt 1) with battery remaining connected. Assume t = 0 is the instant when iron piece has been pulled out, the current as a function of time after this is |
|
Answer» `i=E/R [1-(1-(1)/(eta))e^(-t/(LAMBDA))]` `E=IR+ETAL(dI)/(DT)implies int_(I_2)^(i) (dI)/(E-IR)= int_(0)^(t)(dt)/(etaL)` Solve to get: i=(E)/(R)[1-(1-(1)/(eta))e^(-t//lambda)]`. |
|
| 37217. |
A solenoid of resistance R and inductance L has a piece of soft iron inside it. A battery of emf E and of negligible internal resistance is connected across the solenoid as shown in Fig. At any instant, the piece of soft iron is pulled out suddenly so that inductance of the solenoid decrease to etaL(eta lt 1) with battery remaining connected. Power supplied by the battery as a function of time |
|
Answer» <P>`P=(E^(2))/R [1+(1-(1)/(ETA))e^(-t/(lambda))]` |
|
| 37218. |
A solenoid of resistance R and inductance L has a piece of soft iron inside it. A battery of emf E and of negligible internal resistance is connected across the solenoid as shown in Fig. At any instant, the piece of soft iron is pulled out suddenly so that inductance of the solenoid decrease to etaL(eta lt 1) with battery remaining connected. The work done to pull out the soft iron piece is |
|
Answer» `(eta LE^(2))/(2R^(2))` `IMPLIES I_(2)=(L_1)/(L_2)I_(1)=I_(1)//eta` `W=U_(f)-U_(i)=1/2 L_(2)I_(2)^(2)-1/2L_(1)I_(1)^(2)` `1/2etaL((I_1)/(eta))^(2)-1/2 LI_(1)^(2)=(LE^2)/(2etaR^(2))[1-eta]`. |
|
| 37219. |
(a) Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media. (b) Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30^(@). Find (i) Polarising angle, and (ii) refractive index of the medium. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37220. |
A wire kept along north-south direction is allowed to fall freely. Will an induced e.m.f be set up? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No, because there will be no CHANGE of MAGNETIC FLUX is this CASE. | |
| 37221. |
Five identical charges Q are placed equidistant on a semicircle as shown in the figure . Another point charge q is kept at the center of the circle of radius R. Calculate the electrostatic force experienced by the charge q. |
Answer» Solution :FORCE acting on q due to `Q_(1)` and `Q_(5)` are opposite direction so CANCEL to each other. 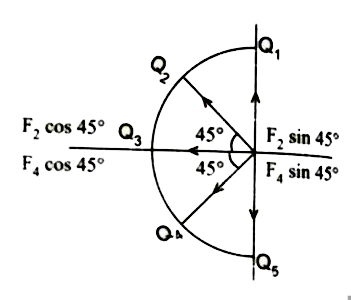 Force acting on q due to `Q_(3)` is `F_(3)= (1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(qQ_(3))/(R^(2))` Force acting on q due to `Q_(2)` and `Q_(4)` Resolving in two component method: (i) Vertical component : `Q_(2) " Sin" theta "and " Q_(4) " Sin" theta` are equal and opposite direction so they are cancel to each other. (ii) Horizontal Component : `Q_(2) "Sin" theta "and " Q_(4) "cos " theta ` are equal and same direction so they can get added. `F_(24)=F_(2q)+F_(4q)= F_(2) "cos " 45^(@)+ F_(4)"cos"45^(@)` `F_(24)= (1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(qQ_(2))/(R^(2))"cos" 45^(@)+ (1)/(4piepsilon_(0)) (qQ4)/(R^(2))"cos" 45^(@)` Resultant net force F `= F_(3)+F_(24)+F_(15)` `Q=Q_(1)=Q_(2)=Q_(3)=Q_(4)=Q_(5)` `"cos" 45^(@) = (1)/(sqrt(2))` `F=(QQ)/(4piepsilon_(0)R^(2))[1+(1)/(sqrt(2))+(1)/(sqrt(2))]` `=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(qQ)/(R^(2))[1+(2)/(sqrt(2))]` `F= (1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(qQ)/(R^(2))[1+sqrt(2)]N` Vector form : `vecF=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(qQ)/(R^(2))(1+sqrt(2))N hati` |
|
| 37222. |
There are two sources of light,each emitting with a power of 100W.One emits X-rays of wavelength 1 nm and the other visible light at 500 nm.Find the ratio of number of photons of X-rays to the photon of visible light of the given wavelength? |
|
Answer» Solution :Power`(E_(N))/(t)=(nhf)/(t)=(nhc)/(lambda)` `therefore P=n.(hc)/(lambda)` (where n.=no.of photons EMITTED PER unit time) `therefore n.=((P)/(hc))lambda` `therefore n.prop lambda` (`because` Here P,h,c are CONSTANT) `therefore (n.1)/(n._(2))=(lambda_(1))/(lambda_(2))` `=(1nm)/(500 nm)` `(n.1)/(n.2)=(1)/(500)` |
|
| 37223. |
Figure shows a siphon , which is a device for removing liquid from a container. Tube ABC must initially be filled , but once this has been done , liquid will flow through the tube until the liquid surface in the container is level with the tube opening at A . The liquid has density 1000 kg//m^(3) and negligible viscosity . The distances shown are h_(1) = 25 cm d = 12 cm and h_(2) = 40 cm Theoretically , what is the greatest possible height h_(1) that a siphon can lift water ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Since `p_(B) ge 0` , we must LET `p_(air) - rho g ( h_(1) + d + h_(2)) ge 0 ` which yields `h_(1) LE h_(1 , "max") = (p_("air"))/(rho g) - d - h_(2) = 10.3 `m |
|
| 37224. |
An electric field vecE and a magnetic field vecB exist in a region. The fields are not perpendicular to each other : |
|
Answer» This is not possible |
|
| 37225. |
Figure shows a siphon , which is a device for removing liquid from a container. Tube ABC must initially be filled , but once this has been done , liquid will flow through the tube until the liquid surface in the container is level with the tube opening at A . The liquid has density 1000 kg//m^(3) and negligible viscosity . The distances shown are h_(1) = 25 cm d = 12 cm and h_(2) = 40 cm If the atmospheric pressure is 1.0 xx 10^(5) Pa, what is the pressure in the liquid at the topmost point B ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Since `v_(B) = v_(C)` by equation of CONTINUITY , and `p_(C) = p_(air)` , Bernouli.s equation becomes `p_(B) = p_(C) + rho g (h_(C) - h_(B)) = p_(air) - rho g (h_(1) + h_(2) + d)` `= 10 xx 10^(5) Pa - (1.0 xx 10^(3)kg//m^(3)) (9.8 m//s^(2)) xx (0.25 m + 0.40 m + 0.12 m)` `= 9.2 xx 10^(4)` Pa |
|
| 37226. |
During which of the following orbits in which electrons makes transitions so that the lines Lyman series obtained in hydrogen atom ? |
|
Answer» From HIGHER ORBIT to FIRST orbit |
|
| 37227. |
Sketch the output Y from a NAND gate having inputs A and B given below: |
Answer» SOLUTION :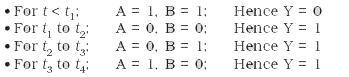 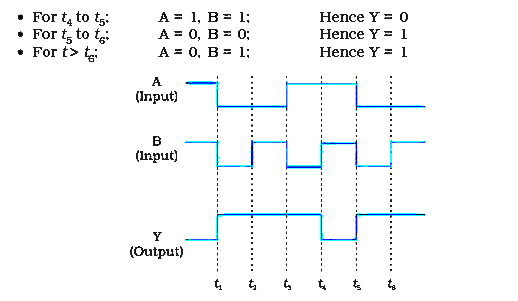
|
|
| 37228. |
A nucleuswithmass numberA =240and BE//A= 7.6 Me V breaksintotwofragmentseach ofA =120with BE//A=8.5 Me V .Calculatethe releasedenergy . |
|
Answer» Solution :Binding energy of nucleus with MASS NUMBER 240, `BE_1 = 240 xx 7.6 =1824 Me V` Binding energy of two fragments `BE_2 = 2 xx 120 × 85 = 2040 MeV` `:.` Energy released = `BE_2 – BE_1` = (2040 – 1824) MeV = 216 MeV |
|
| 37229. |
The circuit is shown in figure. The ratio of current i_(1) // i_(2) is |
|
Answer» `5//3` `- 16 i_(2) + 6= 16 i_(2) = 0 implies i_(2) = (3)/(16) A` In loop `hikjj` `-6 + 8 - 4 (4 i_(2) - i_(1)) = 0 implies 2 2 - 4 ((3)/(4) - i_(i)) = 0` `i_(1) = (1)/(4) A implies (i_(1))/(i_(2)) = (5)/(3)` 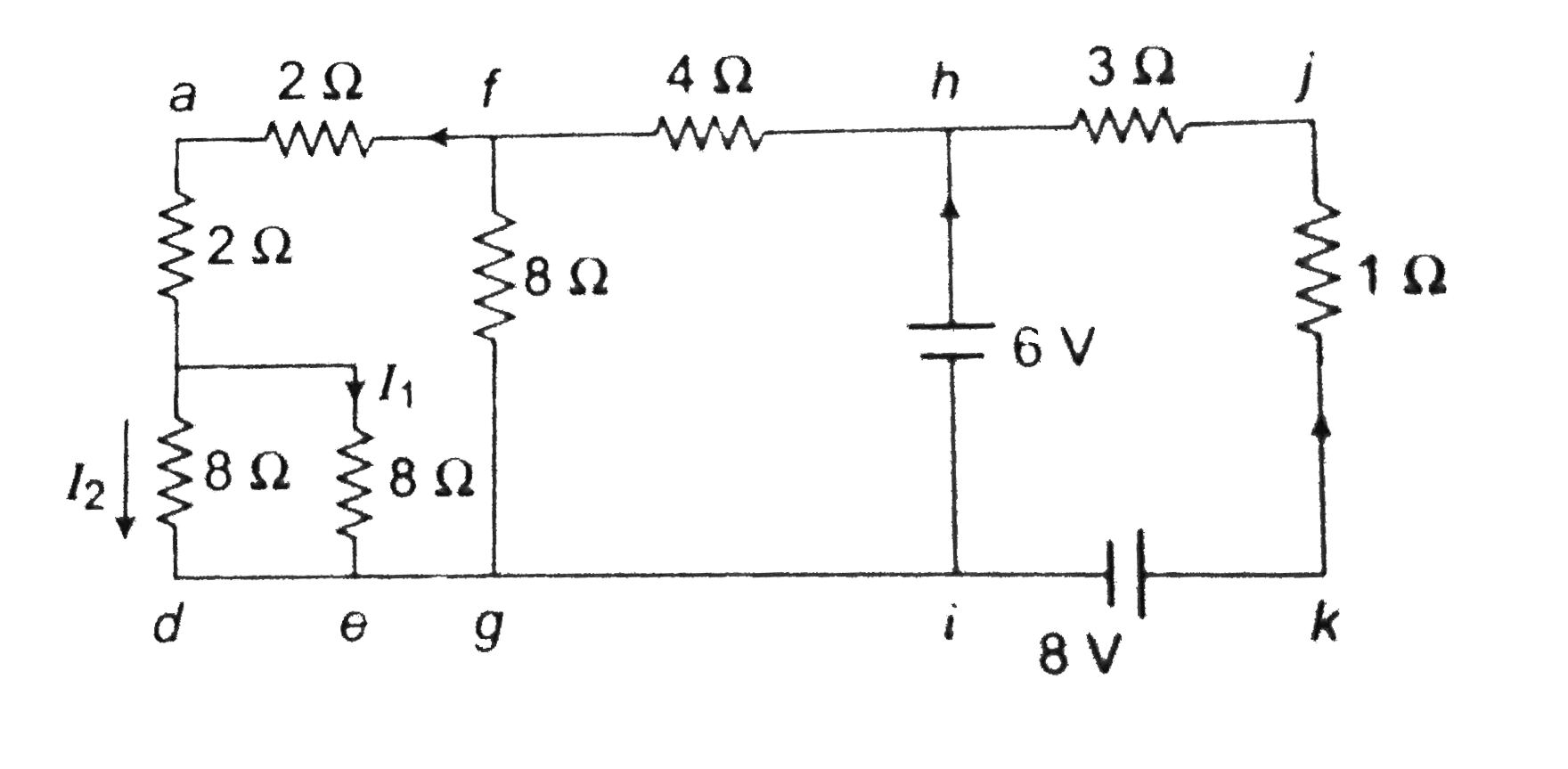
|
|
| 37230. |
Complete the following nuclear reaction equations_4Be^9+_2He^4to_0n^1+ ------ |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`_6C^12` | |
| 37231. |
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends only on |
|
Answer» INTENSITY of INCIDENT radiation |
|
| 37232. |
Explain Curie's law. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Experimentally it was found that the magnetisation of a PARAMAGNETIC material is inversely proportional to the absolute temperature T. Curie experienced that magnetization of paramagnetic substance is directly proportional to external magnetic FIELD `B_0` and inversely proportional to absolute room temperature. `therefore M= C(B_0)/( T) ""...(1) and M= chi H ""...(2)` and `B_0 = mu_0 H` `therefore M= (Cmu_0 H)/(T)` `therefore (M)/( H) = (C mu_0 )/( T)` `therefore chi = (Cmu_0)/( T) `[From equation (2) ] This is KNOWN as Curie.s law. The constant C is called Curie.s constant. For a paramagnetic material both `chi and mu_r` depend not only on the material but also on the absolute temperature. As the field `(B_0)` is increased or the temperature is lowered the magnetisation increases until it reaches the saturation value `M_S` at which point all the dipoles are perfectly ALIGNED with the field. Beyond this, Curie.s law is no longer valid. |
|
| 37233. |
An electric dipole is the combination of two equal and opposite charges q and -q, respectively, separated by distance 2a. There are different points where we can find electric field due to the electric dipole. In the given table, column 1 shows different positions of point where we have to find electricfield due to dipole, column 2 shows the figure of dipole with different positions of point where we have to find the electric field and column 3 shows the value or final formula of the electric field of different positions of the point. When point P lies on the equatorial plan of the electric dipole, electric field due to -q is ? |
|
Answer» (I) (i) (J) |
|
| 37234. |
An electric dipole is the combination of two equal and opposite charges q and -q, respectively, separated by distance 2a. There are different points where we can find electric field due to the electric dipole. In the given table, column 1 shows different positions of point where we have to find electricfield due to dipole, column 2 shows the figure of dipole with different positions of point where we have to find the electric field and column 3 shows the value or final formula of the electric field of different positions of the point. when point P lies on the equatorial plane of the electric dipole, electric field due to +q is ? |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 37235. |
An electric dipole is the combination of two equal and opposite charges q and -q, respectively, separated by distance 2a. There are different points where we can find electric field due to the electric dipole. In the given table, column 1 shows different positions of point where we have to find electricfield due to dipole, column 2 shows the figure of dipole with different positions of point where we have to find the electric field and column 3 shows the value or final formula of the electric field of different positions of the point. When point P lies on the axis of the electric dipole, electric field due to -q is ? |
|
Answer» (III) (ii) (L) |
|
| 37236. |
Statement -1: A horse can pull a cart on a horizontal surface only if it exerts force greater than limiting static friction. Statement-2: An external force exceeding limiting friction is required to make a block slide on rough horizontal surface |
|
Answer» Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is correct explanation for statement-1. |
|
| 37237. |
What is the ammeter's reading in prob. No. 41 ? |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 37238. |
A point charge + q is fixed at same height as centre of an uncharged sphere placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in figure. Neglect the induced charges on horizontal surface. Then conducting sphere is released from rest. Then the conducting sphere |
|
Answer» ROLLS TOWARDS left |
|
| 37239. |
Path difference between two wavefronts emitted from coherent sources is 2.1 mu m. Phase difference between the wavelength of light emitted by source will be |
|
Answer» 5385 Å |
|
| 37240. |
A horizontally kept cylindrical vessel closed at both ends is separated into two equal (42 cm each) parts by an adiabatic piston. Both parts contain gas having equal mass at a temperature of 27^@ C and a pressure of 1 atm. How much should the gas be heated in one part of the cylinder to shift the piston by 2 cm? Find the pressure p of the gas after shifting of the piston. |
|
Answer» Solution :Since the gas in both ends is having equal mass and the piston is in equilibrium, ` (V_2)/( V_1)= (T_2)/(T_1)` hence`T_2= (V_2)/(V_1)T_1` Considering I, and I, as the new lengths of the cylinder, ` V_2= pir^2 l_2andV_i = PI r^2l_1` Calculations: CALCULATING`T_2 ` ` T_2 = (V_2)/(V_1) T_i =(l_2 )/(l_1) T_i` `=(44 )/( 40 ) XX 27 ^@C =30 ^@C =330 K` applyingboyle.slawto thevolumeof thegaswhosetemperaturedoesnot change, weobtain ` p= (p_0 V_0)/(V_i)` usingthe values ` P_0 =1atm, V_0= 44 pir^2 ` and`V_i = 42pir^2 `we get ` p = (1 xx 44 pi r^2 )/( 42pir^2 ) = 1.05 atm` |
|
| 37241. |
IF a thermometer reads reads freezing point of water as 20^@C and boiling point as 150^@C, how much thermometer read went the actual temperature is 60^@C ? |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 37242. |
Define capacitive reactance. Write its SI units. |
| Answer» Solution :Capacitive REACTANCE of a capacitor is the OPPOSITION OFFERED by it for flow of a current through it. 1 Capacitive reactance `X_(C) =1/(C omega)` , where W is the angular frequency of current supply. SI unit of capacitive reactance is OHM `(Omega)`. | |
| 37243. |
Antenna is |
|
Answer» inductive |
|
| 37244. |
The diameter of the magnet of the Serpukhov synchrotron is 472 m. The protons enter the accelerating chamber with an energy of 100 MeV and leave it with an energy of 76.5 GeV. Find the initial and the final magnetic induction in the gap and the accelerating field frequencies. We |
|
Answer» <P> `B=(p)/(E B) =sqrt(K(2epsi+K))/(eeR)` and the frequency from the equation `u=(c sqrt(1-(epsi_(0))//epsi)^2)/(2pi R)` (see 41,6). Note that towards the end of the acceleration cycle the proton.s energy is so GREAT that `N= c//2piR` approximately. |
|
| 37245. |
For an HF molecule find the number of rotational levels located between the Zeroth and first excited vibrational levels assuming rorational states to be independent of vibrational ones. The natural vibration frequency of this molecule is equal to 7.79.10^(14) rad//s and the distance between the nuclie is 91.7p m. |
|
Answer» Solution :If the vibrational frequency is `omega_(0)` the EXCITATION energy of the FIRST vibrational level will be ` ħ omega_(0)`. Thus if there are `J` ratational LEVELS contained in the band between the ground STATE and the first vibrational excitation, then ` ħ omega_(0)=(J(J+1) ħ^(2))/(2I)` where as stated in the problem we have IGNORED any coupling between the two. For `HF` molecule `I=(m_(H)m_(F))/(m_(H)+m_(F))d^(2)= 1.336xx10^(-4) gm cm^(2)` Then `J(J+1)=(2I omega_(0))/( ħ)= 197.4` For `J=14, J(J+1)= 210`. For `J= 13,J(J+1_= 182`. Thus there lie `13` levels between the ground state and the first vibrational excitation. |
|
| 37246. |
If the width of the slit S in Young's double slit experiment is gradually increased |
|
Answer» Bright FRINGES become brighter and dark fringes become DARKER |
|
| 37247. |
At 10^(@)C tempreture ,de-Broglie wave length of atom is 0.4 Å.If temperatire of atom is increased by 30^(@)C ,What will be change in de-Broglie of atom? |
|
Answer» decreases `10^(2)Å` `T_(2)=40+273=313K` `lambda_(1)=0.4 Å` `lambda=(h)/(sqrt(2ME))` but,`E=(3)/(2)KT` so `lambda =(h)/(sqrt(3mKT))` `therefore lambda prop (1)/(sqrt(T))` `therefore (lambda_(2))/(lambda_(1))=sqrt(T_(1)/(T_(2)))` `therefore (lambda_(2))/(0.4xx10^(-10))=sqrt((283)/(313))` `therefore (lambda_(2))/(0.4xx10^(-10))=0.951` `therefore lambda_(2)=0.951xx0.4xx10^(-10)` `therefore lambda_(2)0.38 Å` `therefore "wavelength" =lambda_(2)-lambda_(1)` |
|
| 37248. |
The alluvial soil consists of: |
|
Answer» sand |
|
| 37249. |
Radius of circular path, followed by a charged particle is proportional to ______ . |
|
Answer» charge of a particle `(MV^(2))/r=Bqv` `therefore(mv)/r=Bq` `thereforer=p/(Bq)" "[becausemv=p]` `thereforerpropp" "[becauseBq" is same"]` |
|
| 37250. |
A galvanometer has a resistance of 96 Omega. If 4% of the main current is to be passed through the meter, what should be the value of the shunt? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`4 OMEGA` | |