Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 37151. |
From the platform edge located 10.0 m above the surface of the water, a high diver pushes off horizontally with a speed of 2.00 m/s. (a) At what horizontal distance from the edge is the diver 0.800 s after pushing off? (b) At what vertical distance above the surface of the water is the diver just then? (c) At what horizontal distance from the edge does the diver strike the water? |
|
Answer» Solution :The trajectory of the diver is a PROJECTILE motion. We are interested in the displacement of the diver at a later time. The initial velocity has no vertical component `(theta_0 =0 )`m but only an x component. ` x- x_0 = v_0 t` `y - y_0 = v_0 t -1/2 "gt"^2= - 1/2 "gt"^2` Where `x_0 = 0 , v_(0x) = v_0 = + 2.0 m//s and y_0 =+ 10.0 m `(taking the water surface to be at y = 0) . the setup of the problems is shown in the figure below . 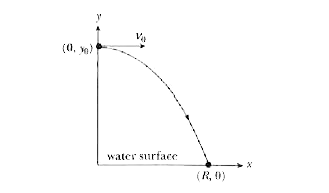 (a) At t = 0.80 s, the horizontal distance of the driver from the edge is ` x= x_0 + v_(0x) t =0 + (2.0m//s)(0.80s) = 1.60 m` (b) Similarly , USING the second equation for the vertical motion , we obtain `y = y_0 - 1/2 "gt"^2 = 10.0 m- 1/2 (9.90 m//s^2) (0.80s)^2 = 6.86 m` ( c) At the instant the diver STRIKES the water surface, y= 0. solving for t using the equation ` y = y_0- 1/2 "gt"^2` = 0 LEADS to `t = sqrt((2y_0)/(g)) = sqrt((2(10.0 m))/(9.80 m//s^2) ) = 1.43 s During this time , the x - displacement of the diver is R = x = (2.00 m/s) (1.34s) = 2.86 m |
|
| 37152. |
Current density in a cylindrical wire of radius R is given asJ={(J_(0)((x)/(R )-1)" for "0lex lt (R )/(2)),(J_(0)(x)/(R )" for "(R )/(2)le x le R):}. If the current flowing in the wire is (k)/(12)piJ_(0)R^(2), find the value of k. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37153. |
Number of electrons in one coulomb of charge will be : |
|
Answer» `5.46 XX 1029` |
|
| 37154. |
At absolute zero, Si acts as |
|
Answer» Non-metal |
|
| 37155. |
Light described at a place by the equation epsilon = (100 V/m)[sin(5 xx 10^(15)s^(-1))t + sin (8 xx 10^(15)s^(-1))t] falls on a metal surface having work function 2eV. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the photo electrons. |
|
Answer» 5.27 EV `v= omega/(2PI) = (8 xx 10^(15))/(2pi)s^(-1)` `K.E._("max") = hv - phi` `K.E_("max") =(6.6 xx 10^(-34) xx 8 xx 10^(15))/(1.6 xx 10^(-19) xx 2 xx 3.14)-2` `=5.27 -2 = 3.27 eV` |
|
| 37156. |
When the current through a solenoid increases at a constant rate, the induced current. |
|
Answer» Is constant and is in the direction of the instaneous current |
|
| 37157. |
The correctweaknuclear interactionis : |
|
Answer» `N tog + beta' + bar(V)` |
|
| 37158. |
Statement-1: Period of revolution of satellite in circular orbit around earth is inversely proportional to its orbital speed Statement-2: Period of revolution in uniform circularmotion is given by T=(2pir)/v where r is radius of orbit and v is speed. |
|
Answer» Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is correct EXPLANATION for statement-1. |
|
| 37159. |
How we define magnetic moment. |
| Answer» Solution :It is product of pole strength and VECTOR distance of either pole from SOUTH pole to noeth pole of the BAR magnet,given by `vec MU = 2 vecl m` where m is pole strenth `2 vecl` is the vector from S pole to N pole. | |
| 37160. |
Assertion: The pattern and position of fringes always remain same even after the introduction of transparent medium in a path of one of this slits. Reason: The central fringe is bright or dark does not depend uupon the initial phase difference between the two coherence sources. |
|
Answer» If both assertion and reason are true and reason correct explanation of assertion. Therefore, the zeroth fringe shifts to a NEW position where the two optical PATHS are equal. in such CASE fringe WIDTH unchraged. The centreal fringe is bright or dark depends upon the initial phase difference between the two conherent sources. |
|
| 37161. |
What is the 'door' of the soul? |
|
Answer» DEEPEST fear |
|
| 37162. |
An amplifier has voltage gain A = 1000 . The voltage gain in dB is ……….. . |
|
Answer» 30 dB |
|
| 37163. |
Radius of curvature of concave mirror is 40 cm and the size of image is twice as that of object, then the object distance is : |
|
Answer» Solution :(d) `f = (R )/(2) = 20 cm`, m = 2 For REAL IMAGE, m = - 2, By using m = `(f)/(f-u), - 2 = (-20)/(-20 - u) rArr u = - 30 cm` For virtual image , m = + 2 So, `+ 2 = (-20)/(-20 - u) = - 10 cm`. |
|
| 37164. |
The ratio of kinetic energy to the potential energy of a particle executing SHM at a distance equal to half its amplitude, the distance being measured from its equilibrium position is : |
|
Answer» `4:1` and `K.E.=(1)/(2)m omega^(2)(a^(2)-x^(2))` For `x=(a)/(2)` then the RATIO is `(K.E.)/(P.E.)=(1//2m omega^(2)(a^(2)-a^(2)//4))/(1//2m omega^(2)(a^(2)//4))` `(K.E.)/(P.E.)=(3a^(2)//4)/(a^(2)//4)=3:1` So CORRECT CHOICE is ( c ). |
|
| 37165. |
A ray of light originating in oil (n=1.21) is incident at the Brewster angle upon a flat surface of a quartz crystal (n=1.458). Determine the angle of incidence for this ray. |
|
Answer» `0.82^(@)` |
|
| 37166. |
A force of 20 dynes acts on a body of mass 5 gm. What is the acceleration produced ? If the body is initially at rest and the force acts on it for 5 s, how far the body will move during the time ? |
|
Answer» 30 cm |
|
| 37167. |
A 10 kg stone is suspended with a rope of breaking strength 30 kg-wt. The minimum time in which the stone can be raised through a height 10 m starting from rest is(Take g = 10 N/kg). |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 37168. |
What is virtual ampere ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Virtual ampere is the UNIT of virtual VALUE of A.C. which is given by `I_v = I_0/ sqrt 2` where `I_0= Peak value of AC. |
|
| 37169. |
Two cars 1 & 2 starting from rest are moving with speeds V_+(1) and V_(2) m/s (V_(1)gt V_(2)) .Car 2 is ahead of car '1' by 'S' metres when the driver of car '1' sees car '2' .What minimum retardation should be given to car '1' avoid collision |
|
Answer» `(V_(1)-V_(2))/(S)` |
|
| 37170. |
An n-type semi conductor can be formed by doping Si or Ge with |
|
Answer» III GROUP element |
|
| 37171. |
figure(a) shows three sheets that are large, parallel and uniformaly charged. Figure (b) gives the component of the net electric field along and x-axis through the sheets. The scale of the vertical axis is set by E_(s)= 6.0 xx10^(5)N//C what is the ratio of the charge density on sheet 3 to that on sheet 2? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37172. |
A projectile is projected at 10 ms -1 by making at an angle 60° to the horizontal. After some times its velocity makes an angle of 30° to the horizontal. Its speed at this instant is : |
|
Answer» `10/sqrt(3)` `:. Vcostheta=vcosalpha` `10xxcos60^@=vcos30^@` `:.V=(10xx1/2)/(sqrt(3)//2)` |
|
| 37173. |
A heavy nucleus at rest breaks into two fragments which fly off with velocities in the ratio 8:1. The ratio of the radii of the fragments (assumed spherical) |
|
Answer» `1:2` |
|
| 37174. |
Analyse the circuit shown in the figure in steady state |
|
Answer» Solution :`8i_(1)+13i_(1)+1(i_(1)+i_(2))-24=0` `22i_(1)+i_(2)=24`ldots (1) For RIGHT mesh,`5I_(2) +2i_(2) + 1 + i_(2) + 2i_(2) - 13I_(1)-8i_(1) = 0` or `10I_(2) - 2i_(1) + 1 = 0ldots(2)` From equations (1) and (2) `i_(1) = 1 amp` and, `i_(2) = 2 amp` Now, CONSIDERING current in different parts when capacitors were charging (e. when Lwwwisti 20 steady state was not reached) Current charging 2 muf CAPACITOR= current charging 1 muF capacitor + current charging 3 muF capacitor If steady state charges on 1 muF and 3 muF capacitors are a `q_(1)muC` and `q_(2)` `muC` respectively, then charge on` 2 muF` capacitor wil be`q_(1)+q_(2)` Hence, in steady state the circuit will be as shown in the figure . Applying Kirchoff.s voltage law on mesh BCKJB `5i_(2)+q_(2)/(3)-q_(1)/(1)-8i_(1)=0` `ldots(3) 512 +9 9 -81, = 0(3)` For mesh JKFGJ`q_(1)+(q_(2))/(3)-q_(1)/(1)-8i=0ldots(4)` In equations (3) and (4), substituting. `1_(1) = 1 amp. i_(2) = 2 amp` `q_(1)=4muC` `q_(2)=6muC` 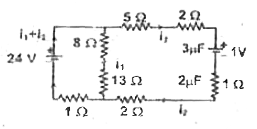 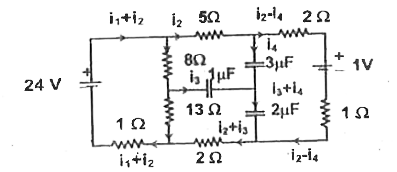 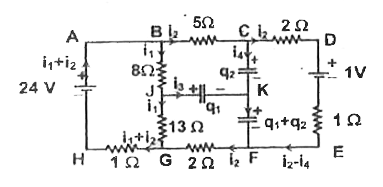
|
|
| 37175. |
Two gases have densities in the ratio 2:3 and their pressures are in the ratio 3:2 at same temperature. The ratio of their r.m.s. velocities is |
|
Answer» 2:3 |
|
| 37176. |
What is the maximum number of spectral line emitted by a hydrogen atom when it is in the fourth excited state? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :N=5 `N=(n(n-1))/(2)=(5xx4)/(2)` N=10 |
|
| 37177. |
Radius of a conducing wire r and its plane is perpendicular to magnetic field B. If the conductors is stretched and made in shape of square in its plane and in time t, then induced a emf epsilon is _____ |
|
Answer» `(piBr^2)/t(1-pi/10)` The length of side of square made is `l.=l/4=(2pir)/4=(pir)/2` Area `A_2=((pir)/2)^2` `therefore DeltaA=A_1-A_2` `=pir^2-((pir)/2)^2` `=pir^2-(pi^2r^2)/4=pir^2(1-pi/4)` `therefore` INDUCED EMF `|EPSILON|=(BDeltaA)/t=(Bpir^2)/t(1-pi/4)` |
|
| 37178. |
A charge particle after being accelerated through a potential difference V enters in a uniform magnetic field and moves in a circle of radius r. If V is doubled, the radius of the circle will become |
|
Answer» 2r |
|
| 37179. |
Obtain an expression for the impedance of a series LCR circuit. (using phasor diagram method). |
|
Answer» Solution :CONSIDER a resistance R, an inductor of self inductance L and a capacitance C CONNECTED in series across an AC source. The applied voltage is given by, `v=v_(0)sinomegat`  where, v is the instantaneous value, `v_(0)` is the peak value and `omega=2pif`, f being the frequency of AC. If i be the instantaneous current at TIME t, the instantaneous voltages across R, L and C are respectively `iR, iX_(L)andiX_(C)`. The vector sum of the voltage amplitudes across R, L, C EQUALS the amplitude `v_(0)` of the voltage applied. Let `v_(R),v_(L)` and `v_(C)` be the voltage amplitudes across R, L and C respectively and `I_(0)` the current amplitude. Then `v_(R)=i_(0)R` is in phase with `i_(0)`. `v_(L)=i_(o)X_(L)=i_(0)(omegaL)` leads `i_(0)` by `90^(@)` `v_(c)=i_(0)X_(C)=i_(0)((1)/(omegaC))` lags behind `i_(0)` by `90^(@)` The current in a pure resistor is phase with the voltage, whereas the current in a pure inductor lags the voltage by `(pi)/(2)` rad. The current in a pure capacitor leads the voltage by `(pi)/(2)` rad. For `v_(L)gtv_(C)`, phase angle `phi` between the voltage and the current is positive. From the RIGHT angled triangle OAP, `OP^(2)=OA^(2)+AP^(2)=OA^(2)+OB^(2)(becauseAP=OB)` `v^(2)=v_(R)^(2)+(v_(L)-v_(C))^(2)=(iR)^(2)+(iX_(L)-iX_(C))^(2)=i^(2)(R^(2)+(X_(L)-X_(C))^(2))` `i=(v)/(sqrt(R^(2)+(X_(L)-X_(C))^(2)))=(v)/(Z)andZ=sqrt(R^(2)+(X_(L)-X_(C))^(2))` Where Z is the impedance of the circuit. Phase angle between v & i. `tanphi=(v_(L)-v_(C))/(v_(R))=(X_(L)-X_(C))/(R_(L)),phi=tan^(-1)((X_(L)-X_(C))/(R))` 
|
|
| 37180. |
The circular scale of deflection magneto meter is divided into ........... Quadrants ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37181. |
Analog voltmeters and ammeters work b measuring the torque exerted by a megentic field on a current carrying coil. The reading is displayed by means of the deflection of a pointer over a scale. The adjacent figure shows the essentials of a galvanometer, on which both analog ammters and analog voltmeters are based. Assume that the coil is 2.1 cm high, 1.2 cm wide has 250 turns and is mounted so that it can rotate about an axis (into the page) in a uniform radial magnetic field with B = 0.23 T. for any orientation of the coil, the net magnetic field through the coil is perpendicular to the normal vector of the coil (and thus parallel to the plane of coil) A spring S_(P) provides a counter torque that balance the magnetic torque so that a given steady current I in the coil results in a steady angular diflection phi. The greater the current is greater the deflection is and thus greater the torque required of the spring is A current of 100 muA produces an angular deflection of 28^(@). If we reduce the value of this K ti half of its value then the delection would be |
|
Answer» `28^(@)` |
|
| 37182. |
Analog voltmeters and ammeters work b measuring the torque exerted by a megentic field on a current carrying coil. The reading is displayed by means of the deflection of a pointer over a scale. The adjacent figure shows the essentials of a galvanometer, on which both analog ammters and analog voltmeters are based. Assume that the coil is 2.1 cm high, 1.2 cm wide has 250 turns and is mounted so that it can rotate about an axis (into the page) in a uniform radial magnetic field with B = 0.23 T. for any orientation of the coil, the net magnetic field through the coil is perpendicular to the normal vector of the coil (and thus parallel to the plane of coil) A spring S_(P) provides a counter torque that balance the magnetic torque so that a given steady current I in the coil results in a steady angular diflection phi. The greater the current is greater the deflection is and thus greater the torque required of the spring is A current of 100 muA produces an angular deflection of 28^(@). If the value ofmagnetic field is put equal to 0.69 T and K= 15.6 xx 10^(-8) nm/degree. Then the deflection would be |
|
Answer» `LT 28^(@)` |
|
| 37183. |
Analog voltmeters and ammeters work b measuring the torque exerted by a megentic field on a current carrying coil. The reading is displayed by means of the deflection of a pointer over a scale. The adjacent figure shows the essentials of a galvanometer, on which both analog ammters and analog voltmeters are based. Assume that the coil is 2.1 cm high, 1.2 cm wide has 250 turns and is mounted so that it can rotate about an axis (into the page) in a uniform radial magnetic field with B = 0.23 T. for any orientation of the coil, the net magnetic field through the coil is perpendicular to the normal vector of the coil (and thus parallel to the plane of coil) A spring S_(P) provides a counter torque that balance the magnetic torque so that a given steady current I in the coil results in a steady angular diflection phi. The greater the current is greater the deflection is and thus greater the torque required of the spring is A current of 100 muA produces an angular deflection of 28^(@). What must be the torional conctant k of the spring ? |
|
Answer» `2.6 XX 10^(-8)` Nm/degree |
|
| 37184. |
In the question number 44, the phase difference between the voltage across the source and current is |
|
Answer» `80.2^(@)` PHASE DIFFERENCE `phi = TAN^(-1)((X_(L)-X_(C ))/(R ))` `therefore phi = tan^(-1)((3.6)/(6))=tan^(-1)(0.6)=31^(@)` |
|
| 37185. |
Two charges 2 C and 6 C are separated by a finite distance. If a charge of-4 C is added to each of them,the initial force of 12 xx 10^(3) N will change to |
|
Answer» `4 xx 10^(3)N` repulsion |
|
| 37186. |
Light with an energy flux of 18 W//cm^(2) falls on a non-reflacting surface at normal incidence. If the surface has an area of 20 cm^(2), find the average force exerted on the surface during a 30 minute time span. |
|
Answer» Solution :The total energy falling on the surface is `U=(18 W//cm^(2))xx(20 cm^(2))xx(30xx60 s)` `=6.48 xx10^(5) J` Therefore, the total momentum delivered (for complete absorption) is `p=(U)/(c )=(6.48xx10^(5) J)/(3xx10^(8) m//s)=2.16 xx10^(-3) KG m//s` The average force exerted on the surface is `F=(p)/(t) =(2.16 xx10^(-3)/(0.18xx10^(4))=1.2xx10^(-6) N` How will your result be modified if the surface is a perfect REFLECTOR? |
|
| 37187. |
What is a noise? What are their causes? |
|
Answer» Solution :The UNDESIRED electrical signals are termed as noise. The noises are of TWO TYPES. Internal noise : The undesired electrical signals arising due to thermal motion of electrons within the system (due to their RANDOM motion, recombination of diffusion are called inernal noise.(ii) External noise : The undesired electrical signals arising due to nearly radio frequency transmitters electrical CIRCUITS, sparks, fluroscent tubes are termed as external noise. |
|
| 37188. |
Speed of Electro Magnetic wave depends |
|
Answer» only upon the ELECTRIC properties of the MEDIUM |
|
| 37189. |
An object starts moving at an angle of 45^@ with the principal axis as shown in fig. in front of a biconvex lens of focal length + 10 cm. If A denotes the angle at which image starts to move with principal axis, then |
|
Answer» `THETA = (3PI)/(4)` |
|
| 37190. |
Two solid balls A and B having masses 200 g and 400 grespectively are moving in opposite direction with velocity of A equal to 0.3 m//s. After the collision the two balls come to rest. The velocity of B before collision is : |
|
Answer» `- 0.15 m//s` `m_(1)u_(1)+m_(2)u_(2)=(m_(1)+m_(2))0` `u_(2)=(-200xx0.3)/(400)=-0.15m//s` Hence correct choice is (a). |
|
| 37191. |
A point source of light moves in a straight line parallel to a plane table. Consider a small portion of the table directly below the line of movement of the source. The illuminance at this portion varies with its distance r from the source as |
|
Answer» `E PROP (1)/(r)` |
|
| 37192. |
As shown in the figure a rectangular loop of a conducting wire is moving away a constant velocity 'v' in a perpendicular direction from a very long straight conductor carrying a steady current 'I'. When the breadth of the rectangular loop is very small compared to its distance from the straight conductor, how does the e.m.f. 'E' induced in the loop vary with time 't' ? |
|
Answer» `E prop (1)/(t^(2))` `E=-(d phi)/(dt)RARR E=-(d(BA))/(dt)` `rArr E=-A(DB)/(dt)=-A(d)/(dt)(mu_(0)I)/(2PI(v t))` `rArr E=-Ai(mu_(0))/(2pi v)(d)/(dt)(t^(-1)) rArr E=Ai (mu_(0))/(2pi v)t^(-2)` `therefore E prop (1)/(t^(2))` |
|
| 37193. |
In the figure shown a massless spring of stiffness k and natural length l_(0) is rigidly attached to a block of mass m and is in vertical position. A wooden ball of mass m is released from rest to fall under gravity. Having fallen a height h the ball strikes the spring and gets stuck up in the spring at the top. What should be the minimum value of h so that the lower block will just lose contact with the ground later on ? Assume that l_(0) gt gt (4mg)/(k). Neglect any loss of energy. (Given k=mg//2) |
|
Answer» Solution :The minimum force needed to LIFT the lower BLOCK is equal to its weight. During upward motion the spring will get elongated. If elongation in the spring for just lifting the block is `x_(0)` then `kx_(0)=mg` `rArrx_(0)=(mg)/(k)`……`(i)` From `COE` `mg(l_(0)+h)=mg(l_(0)+x_(0))+(1)/(2)kx_(0)^(2)` `rArr mgh=mgx_(0)+(1)/(2)kx_(0)^(2)rArr mgh=((mg)^(2))/(k)+(1)/(2)(m^(2)g^(2))/(k)rArrh=(3mg)/(2k)` During down ward motion, SUPPOSE maximum compression in the spring is `X` From `COE` `mg(l_(0)+h)=mg(l_(0)-x)+(1)/(2)kx^(2)` `rArrmgh= -MGX+(1)/(2)kx^(2)rArrmg"(3mg)/(2k)= -mgx+(1)/(2)kx^(2)` `rArr 3(mg)^(2)= -2mgkx+k^(2)x^(2)` `rArr k^(2)x^(2)-2mgkx-3(mg)^(2)=0` `rArr x=(2mgk+-sqrt(4(mgk)^(2)+12k^(2)(mg)^(2)))/(2k^(2))=(2mgk+-4mgk)/(2k^(2))rArrx=(3mg)/(k)` |
|
| 37194. |
The velocities of sound in an ideal gas at temperature T_(1) and T_(2) K are found to be V_(1) and V_(2) respectively. If ther.m.s velocities of the molecules of the same gas at the same temperatures T_(1) and T_(2) are v_(1) and v_(2) respectively then |
|
Answer» `v_2 = v_1 (V_1/V_2)` |
|
| 37195. |
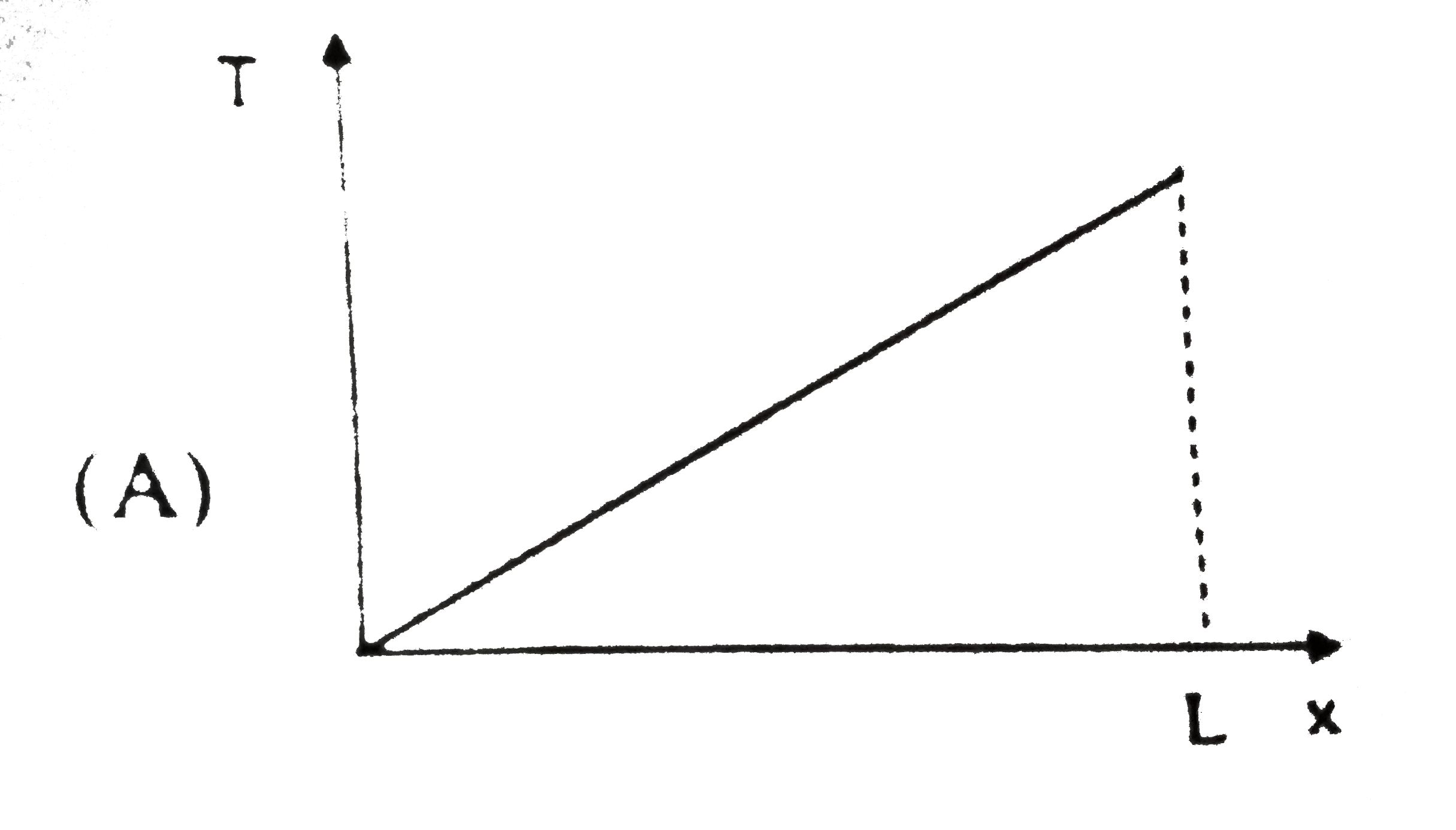
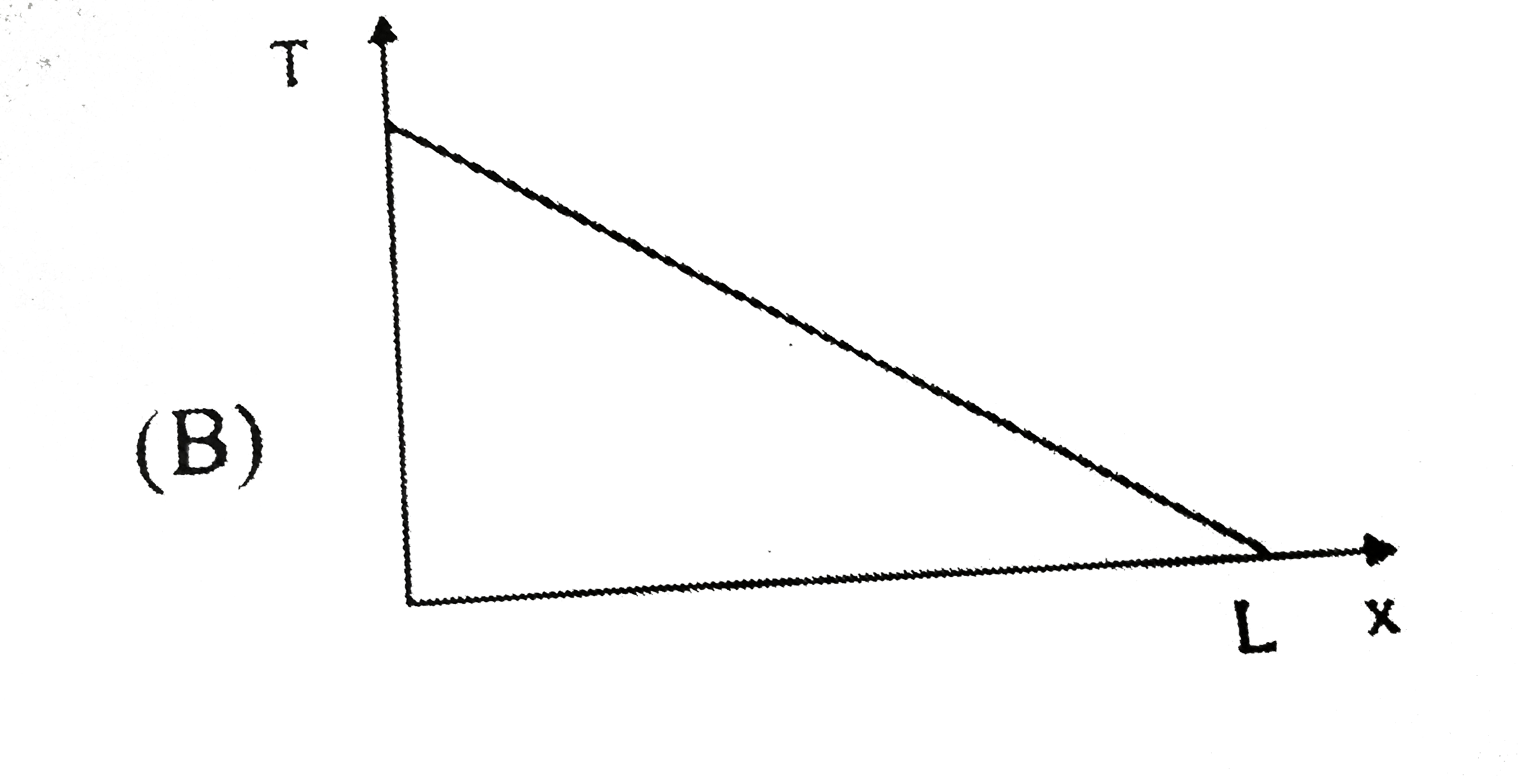
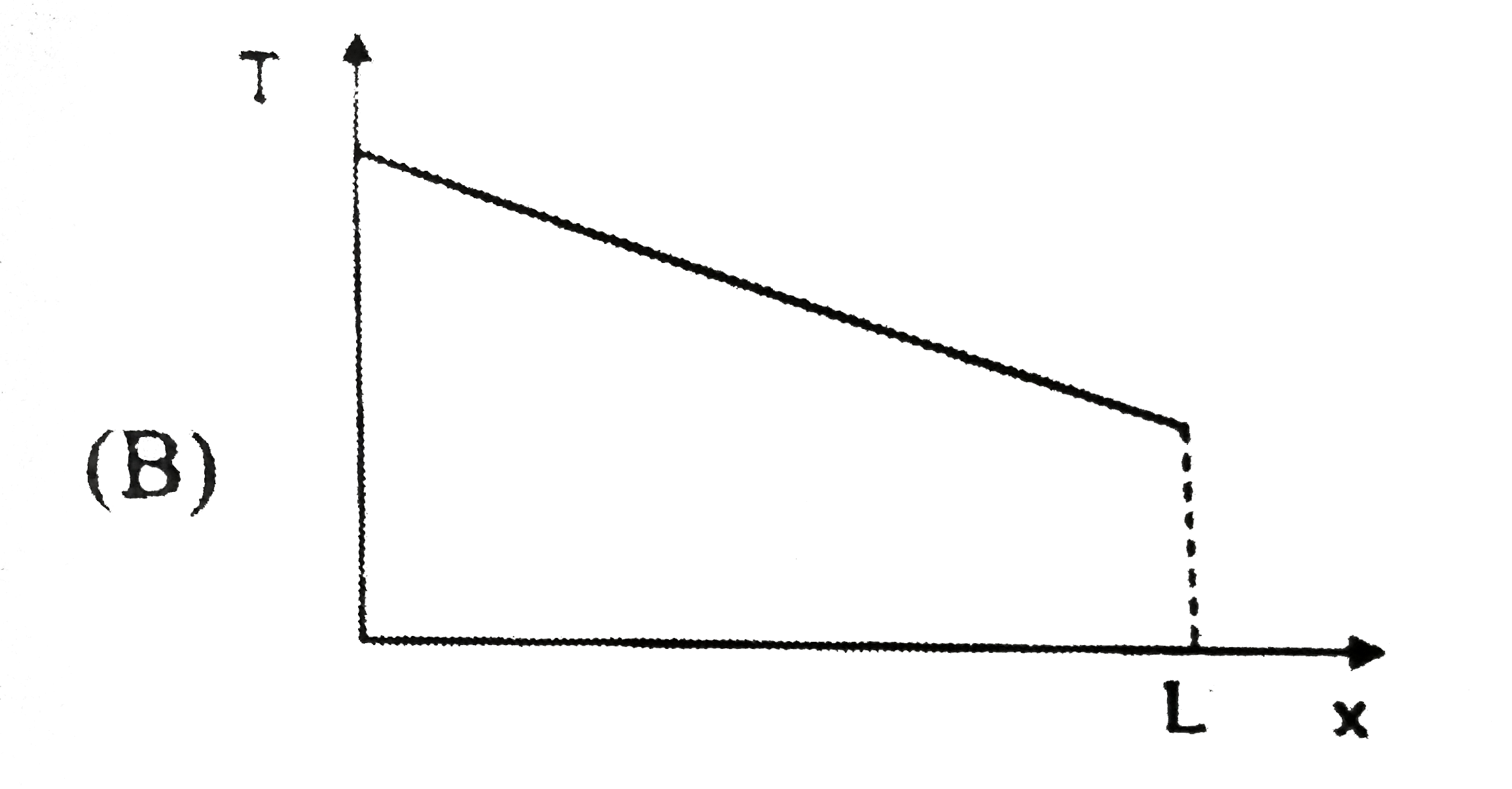
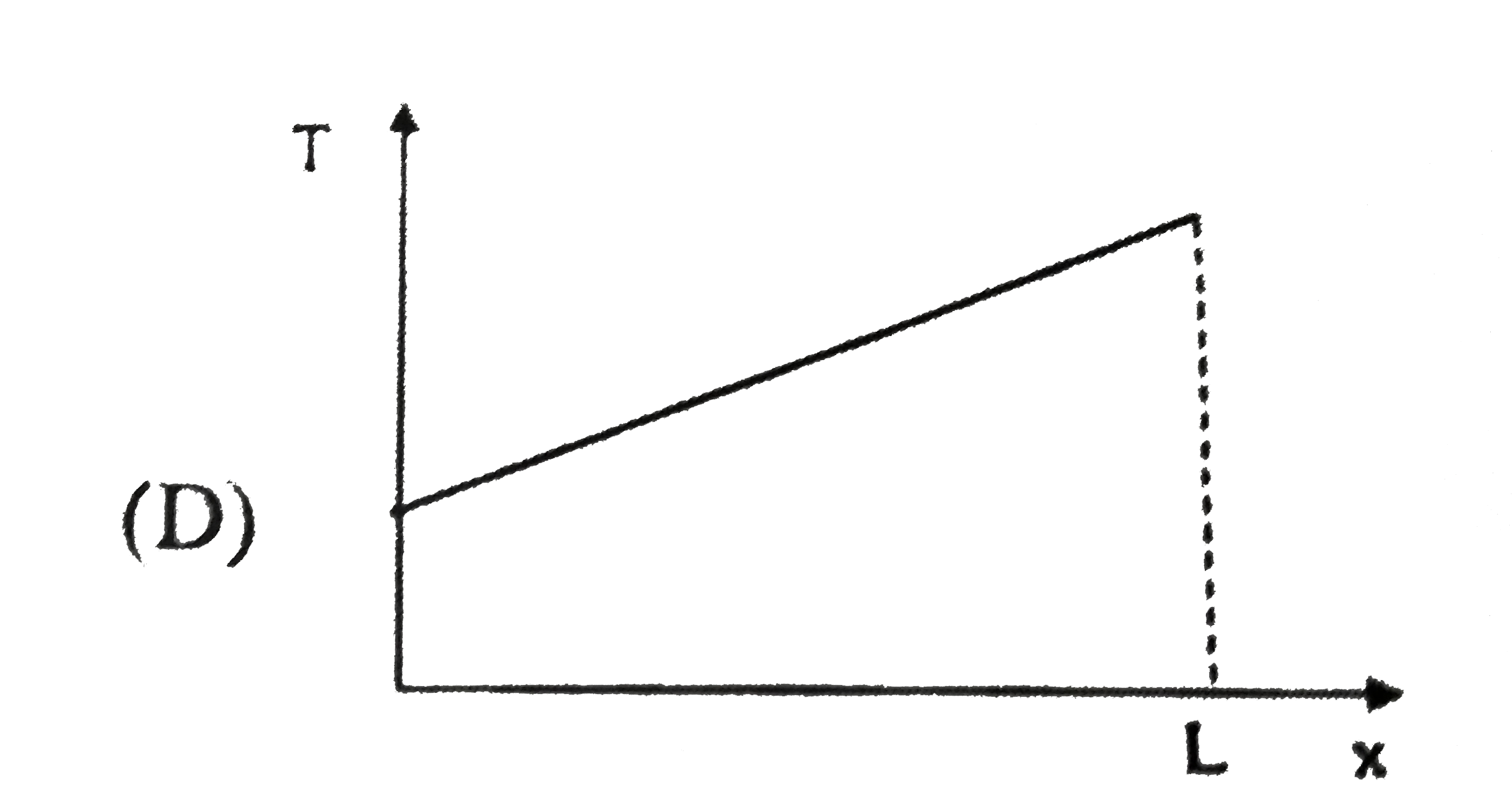
A uniform rope of mass (m) and length (L) placed on frictionless horizontal ground is being pulled by two forces F_(A) and F_(B) at its ends as shown in the figure. As a result, the rope accelerates toward the right. Which of the following graph best represents variation in tension at a point on the rope with distance x of the point from the end A ? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 37196. |
A uniform rope of mass (m) and length (L) placed on frictionless horizontal ground is being pulled by two forces F_(A) and F_(B) at its ends as shown in the figure. As a result, the rope accelerates toward the right. Expression T_(x) of tension at a point at distance x from the end A is |
|
Answer» `T_(X)=((F_(B)-F_(A))/(L))x+F_(A)` |
|
| 37197. |
Calculate the magnetic field at the point p (Refer figure ) due to straight wire XY carrying a current i. |
|
Answer» Solution :`B=(mu_0 in SIN THETA)/(4 PI R)` ans. `(sqrt(2) mu_0 i)/(8 pi a )` |
|
| 37198. |
Define the distance of closest approach. |
| Answer» Solution :It is the distance from nucleus at which an energetico-particles approaching directly TOWARDS the nucleus, retraces its path through 180". At distance of closest APPROACH speed of Q- PARTICLE is zero. | |
| 37199. |
A turtle in water (refractive index mu) looks at a stationary cloud vertically above in the air. If h is the height of the cloud and d is the depth of the fortle from the surface, then the distance of the clond as estimated by the turfle is |
|
Answer» `d+h(1+1/mu)` |
|