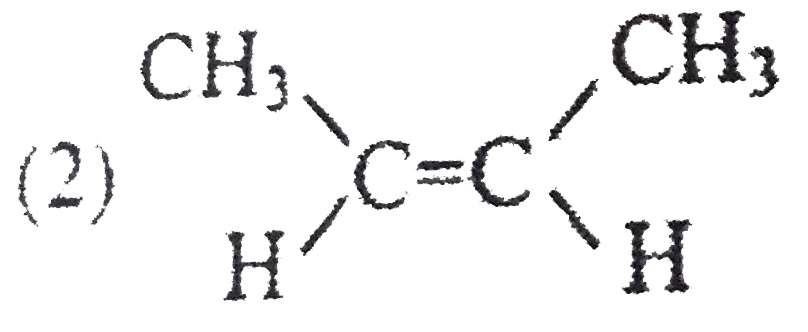Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 38951. |
A capacitor is used in the primary circuit of an induction coil. |
| Answer» Solution :A capacitor is used in the PRIMARY CIRCUIT of an INDUCTION coil because when the circuit is BROKEN, a large induced voltageis used up in charging the capacitor. So, the sparking or any damages are avoided. | |
| 38952. |
A spherical conducting shell of inner radius r_1 and outer radius r_2 has a charge Q. Is the electric field inside a cavity (with no charge) zero, even if the shell is not spherical, buthas any irregular shape ? Explain. |
| Answer» Solution :Electric FIELD inside a cavity (with no CHARGE) is ALWAYS zero whether the shell isspherical or of any other shape. It is in accordance with Gauss.s THEOREM in ELECTROSTATICS. As charge enclosed by the cavity is zero, hence total electric fluxand consequently, the electric field intensity inside a cavity must be zero. | |
| 38953. |
When monochromatic red light is used instead of blue light in a convex lens, its focal length will ...... |
|
Answer» not DEPEND on COLOUR in light. Now `1/f=(n-1)((1)/(R_1)-(1)/(R_2))` `1/f prop n` `therefore (f_2)/(f_b)=(n_b)/(n_r)` `therefore (f_r)/(f_b) gt 1 ""thereforef_r gt f_b` `therefore` Focal length will increase. |
|
| 38954. |
Mixotrophic nutrition is shown by |
|
Answer» diatoms |
|
| 38955. |
In case of a simple harmonic motion, if the velocity is plotted along the X-axis and the displacement (from the equilibrium position) is plotted along the Y-axis, the resultant curve happens to be an ellipse with the ratio =("major axis along X")/("minor axis along Y") = 20 pi What is the frequency of the simple harmonic motion? |
|
Answer» 100 Hz  `V^(2)/(OQ)^(2) + X^(2)/(OP)^(2) =1`…………..(i) Now, `OQ = AOMEGA[therefore v = ROMEGA = aomega]` and OP =a, where `omega` = angular velocity From eqn. (i) `v^(2)/(a^(2)omega^(2)) + x^(2)/a^(2) =1` Thus, major AXIS, `=2 xx aomega = 2aomega`, minor axis = 2a Given, that `("major axis along X")/("minor axis along Y") = 20pi, therefore (2aomega)/(2a) = 20pi` `f= 10Hz` |
|
| 38956. |
Object O is moving with a velocity 8m//s inside water and mirror is moving with a velocity of 6m//s as shown in the figure. Then find the velocity of image with respect to object in m//s |
|
Answer» Solution :VELOCITY of `v_(JG)=12-6=6m//s` Velocity of `v_(IW)`(VELOCITYOF image with RESPECT to observer who is in the water) `=6xx4//3=8m//s` So `v_(JO)=8-8=0` 
|
|
| 38957. |
A positron and a proton are accelerated by the same accelerating potential. Then the ratio of the associated wavelengths of the positron and the proton will be [M=Mass of proton, m=Mass of positron] |
|
Answer» `(M)/(m)` |
|
| 38958. |
Q.39, find t he loss of energyduring the collision. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`K_(1)` = Total KE before collision `=1/2mv^(2)+1/2(3m)v^(2).` `k_(2)=` Total KE after collision `=1/2(4m)V ^(2)` PUT the VALUE of V FOUND in Q. 39 `DeltaK=` loss of ` KE=K_(1)-K_(2)` `K_(1)` total KE before collision `=1/2mv^(2)+1/2(3m)v^(2)=2mv^(2)` `=2m5/8v^(2)asV=sqrt((5)/(8))v` `=5/4mv^(2)` `Deltak=` loss of KE during the collision `=K_(1)-K_(2)` `=2mv^(2)-5/4mv^(2)` `DeltaK=3/4mv^(2)` |
|
| 38959. |
Four point charges q_(A)=2 muC, q_(B)=-5 muC, q_(C)=2 muC and q_(D)=-5 muC are located at the corners of square ABCD of side 10 cm. What is the force on a charge of 1 muC placed at the centre of the square? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ZERO N | |
| 38960. |
Magnification at least distance of distinct vision is 25 cm of a simple microsope of focal length 5 cm is |
| Answer» Solution :`m = 1 + (25)/(F) = 1 + (25)/(5) = 6` | |
| 38961. |
A plane with a wing span of 18 m flies horizontally at a speed of 800 km/h. The vertical component of the Earth's magnetic field strength is about 40 A/m. Find the voltage across the tips of the wings. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38962. |
A metal sphere with its centre at A and radius R has a charge 2q on it. The field at a point B outside the sphere is E. If another metal sphere of radius 3R and having a charge -3q is placed with its centre at point B, find out the resultant electric field at a point mid way between A and B. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38963. |
As shown in the figure, a conducting rod of length I, mass m and resistance R falls through a magnetic field vecB in a plane perpendicular to plane of figure. Find terminal velocity of rod. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38964. |
Let us list some of the factors, which could possibly influence the speed of wave propagation: (i) nature of the source. (ii) direction of propagation. (iii) motion of the source and/or observer. (iv) wavelength. (v) intensity of the wave. On which of these factors, if any, does (a) the speed of light in vacuum, (b) the speed of light in a medium (say, glass or water), depend? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) The speed of light in vacuum is a universal constant independent of all the factors listed and anything else. In particular, note the surprising fact that it is independent of the relative motion between the source and the observer. This fact is a BASIC axiom of Einstein’s special THEORY of relativity. (b) Dependence of the speed of light in a medium: (i) does not depend on the nature of the source (wave speed is determined by the properties of the medium of propagation. This is also true for other waves, e.g., sound waves, water waves, etc.). (ii) independent of the direction of propagation for isotropic media. (iii) independent of the motion of the source relative to the medium but DEPENDS on the motion of the observer relative to the medium. (iv) depends on wavelength. (v) independent of intensity. [For high intensity beams, however, the SITUATION is more complicated and need not CONCERN us here.] |
|
| 38965. |
A sample of oxygen at NTP has volume V and a sample of hydrogen at NTP has the volume 4V. Both the gases are mixed. If the speed of sound in hydrogen at NTP is 1270 m/s, that in mixture is |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 38966. |
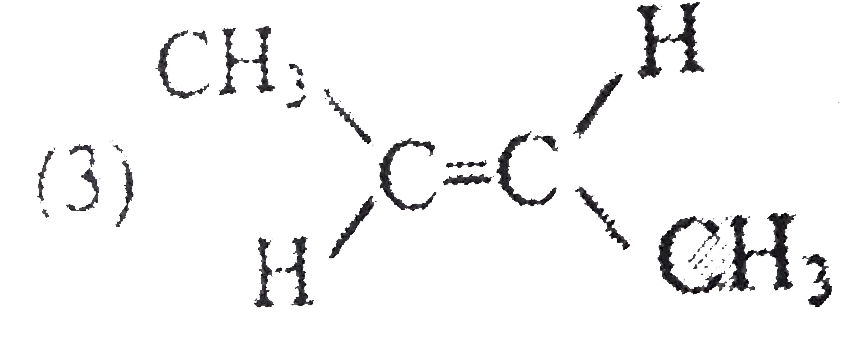
the major productof the reaction Is - {:(CH_(3)CH_(2)CHCH_(3) underset("heat")overset( AgOH)to),(|),((CH_(3))_(3)N^(o+)I^(Ө)):} |
|
Answer» `CH_(3)CH_(2)CH=CH_(2)` `CH_(3)-Ch_(2)-underset(I^(Ө))underset(""^(o+)N(CH_(3))_(3))underset(|)CH-CH_(3)overset(AgOH //Delta)to CH_(3)-CH_(2)-CH=CH_(2)` |
|
| 38967. |
State Gauss' law in electrostatic.. A thin straight infinitely long conducting wire of linear charge densitylambdais enclosed by a cylinder surface of radius 'r' and length ''l' ,its axis coinciding with the length of the wire . Qbtain the expressionn for the electric field, indicating its direction at a point on the surface of the cylinder. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider an infinitely long straight charged wire of linear charge desnsity `lambda`. To find electric field at a POINT P situated at a distance r from the wire by using Guass. law consider a cylinder of length l and radius r as the Gaussian SURFACE. From symmetry consideration electric field at each point of its curved surface is `vecE` and is point outwards NORMALLY . Therefore, electric flux over the curved surface. ` int vecE hatn ds = E 2 PI r l` 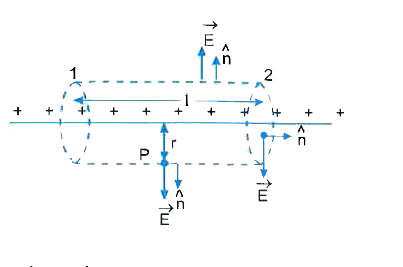 On the side face 1 and 2 of the cylinder normal drawn on the surface is perpendicular to electric field E and hence these surfaces do not contribute towards the TOTAL electric flux. `therefore ` Net electric flux over the entire Gaussian surface `phi_E = E. 2pi r l` By Gauss law electric flux `phi_E = 1/(epsi_0)` (charge enclosed)`= (lambda l)/(epsi_0)` Comparing (i) and (ii) , we have `E. 2 pi rl= (lambdal)/(epsi_0)` `impliesE = (lambda)/(2 pi epsi_0 r)` As `E prop 1/r` , hence E -r shown in fig. 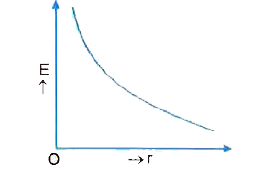
|
|
| 38968. |
Electrons are caused to fall through a potential difference of 1500 volts. If they were initially at rest. Then calculate their final speed. |
|
Answer» Solution :The electrical potential ENERGY is converted into KINETIC energy. If v is the final speed then `(1)/(2) mv^(2) =`eV ` v = sqrt((2eV)/(m)) = sqrt((2xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19)xx 1500)/(9.1xx 10^(-31))) = 2.3 xx 10^(7) ms^(-1)` |
|
| 38969. |
If C_1, C_2, C_3 are the velocities of 3 molecules thentheir mean square velocity is |
|
Answer» `(C_1^2+C_2^2+C_3^2)/3` |
|
| 38970. |
Answer the following : (a) Name the e.m. waves which are suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Write the range of frequency of these waves. |
| Answer» Solution :(a) Microwaves are SUITABLE for RADAR systems used in aircraft navigation and the frequency range of these WAVES VARIES from `10^(@) Hz" to "10^(12) Hz`. | |
| 38971. |
Light of the wavelength 5000Å is incident normally on a slit of width 2.5xx10^(-4)cm. The angular position of second minimum from the central maximum is |
|
Answer» a. `sin^(-1)(1/5)` |
|
| 38972. |
A positively charged point object is kept fixed at its location and another point mass with same charge is suspended in mid-air due to electric force of repulsion that equal to the weight of this suspended object The point mass in very slightly pushed down and then released |
|
Answer» The POINT mass will continue to move down |
|
| 38973. |
A system of two electric dipoles, each of dipole moment having magnitude P are arranged in the configuration shown in figure The electrostatic interaction energy of this systm of two dipoles is: |
|
Answer» `(5 kp^(2))/(4 a^(2))` |
|
| 38974. |
The tuned circuit of an oscillator in a simple AM transmitter employs a 250 micro henry coil and 1nF condenser. If the oscillator output is modulated by audio frequency upto 10 KHz. The frequency range occupied by the side bands in KHz is |
|
Answer» 210 to 230 |
|
| 38975. |
अनिषेक जनन सामान्यतः मिलता है |
|
Answer» अंगूर में |
|
| 38976. |
Which of the following statements is correct in relation to electromagnetic waves in an isotropic medium? |
|
Answer» Energy due to electric FIELD is equal to that due to MAGNETIC field |
|
| 38977. |
Show that the first few frequencies of light that is emitted when electrons fall to the n^(th) level from levels higher than n, are approximate harmonics (ie, in the ratio 1:2:3...) when n gt gt 1. |
|
Answer» Solution :In an atom of an ELEMENT with atomic no. 2, when an electron makes a transition from `(n + x)^(th)` ORBIT (where x = 1, 2, 3, ....) to `n^(th)` orbit, if FREQUENCY and wavelength of emitted radiation are respectively f and then, `(1)/(lambda)=RZ^(2)((1)/(n^(2))-(1)/((n+x)^(2)))` `:.(f)/(c)=RZ^(2){((n+x)^(2)-n^(2))/((n+x)^(2)(n)^(2))} ( :. c=flambda)` `:.f=RcZ^(2){(n^(2)+2nx+x^(2)-n^(2))/((n+x)^(2)(n^(2)))}` `:.f=RcZ^(2){(2nx+x^(2))/((n+x)^(2)(n^(2)))}` Here `n gt gt 1 and x = 1,2,3.... and so (n+x)= n( :. x lt lt n)`. Also we can neglecte `x^(2)` from the ADDITION. Thus, `r~~RcZ^(2)((2nx)/(n^(4)))` `:.f~~((2rCZ^(2))/(n^(3)))x` `:.f prop x` `:.f_(1):f_(2):f_(3)=x_(1):x_(2):x_(3)` `=1:2:3` |
|
| 38978. |
When an object is placed at a distance of 25 cm from a concave mirror, the magnification is m_1. Theobject is moved 15 cm farther away with respect to the earlier position, and the magnification becomes m_2. If m_1//m_2 = 4 the focal length of the mirror is (Assume that image is real and m_1,m_2are numerical values) |
|
Answer» 10cm |
|
| 38979. |
Two balls of masses are connected with a massless rod of length 1 meter and are given velocities on a horizontal surface parallel to surface as shown in the figure. Then the tension in the rod at the given instant is: |
|
Answer» As `OMEGA=(V_("rel"))/r=(5-3)/1=2rad//sec` `T+2(T/2)=(2xx2^(3))/1impliesT=4` NEWTON |
|
| 38980. |
The emissivity of black body is equal to |
|
Answer» 4 |
|
| 38981. |
Fill in the blanks Impedance : admittance………………………: conductance |
| Answer» SOLUTION :RESISTANCE | |
| 38982. |
One mole of an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure occupies 22.4 L (molar volume). IF the size of the hydrogent molecule is about 1A. What is the ratio of molar volume to the atomic volume of a mole of hydrogen? |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 38983. |
The material medium is not required for the propagation of heat in |
|
Answer» a)RADIATION |
|
| 38984. |
Refer to the circuit given below. Initially the switch S is in position 1 for 1.5 s. Then the switch is changed to position 2. After a time t (measured from the change over of the switch) the voltage across 5k Omega resistanceis found to be about 1.226 volt. Then, t is |
|
Answer» 330 ms |
|
| 38985. |
A particle of mass5 kg moving in the x-y plane has its potential energy given by U=(-7x+24y)J where x and y are in meter. The particle is initially at origin and has a velocity vec(i)=(14 hat(i) + 4.2 hat (j))m//s |
|
Answer» the particlehas a speed of 25 m/s at`t=4`s |
|
| 38986. |
State Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. Figure shows a rectangular conductor PQRS in which the conductor PQ is free to move in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane of the paper.The field extends from x=0 to x=b and is zero for x gt b.Assume that only the arm PQ posses resistance r.When the arm PQ is pulled outward from x=0with constant speed v, obtain the expressions for the flux and the induced emf. sketch the variations of these quantities with distance 0 le x le 2b. |
|
Answer» Solution :Part I:Farady's law of induction:It states that the `emf` induced in a coil of `N` turns is directly related to the rate of charge of flux through it. `therefore epsilon=-N(d phi_(B))/(dt)` Where `phi_(B)` is the flux linked with one turn of the coil.If the circuit is closed, a current `I=epsilon/R` is setup in it. Part II : Refer to Following Fig.(a) the arm `PQ` of the rectangular conductor is moved form `x=0` outwards, the uniform magnetic FIELD is perpendicular to the PLANE and extends from `x=0` at `x=b` and is zero these situation when the arm `PQ` passes substantial resistance `r`.Consider the situation when the arm `PQ` is pulled outwards from `x=0` to `x=2b`,and is then moved back to `x=0` with constant speed `V`. Let us first consider the forward motion from `x=0` to `x=2b` The flux `Phi_(B)` linked with the circuit `SPQR` is `Phi_(B)=Blx, 0lex lt b` =`Blbb LE x lt 2b` The induced `emf` is `epsilon=-(dPhi_(B))/(dt)` =`-Blv 0le x lt b` =`0 b le x lt 2b` When the induced `emf` is non-zero.the current `I` is (in magnitude) `l=(Blupsilon)/r` The FORCE required to keep the arm `PQ` in constant motion is `IiB`. its direction is to the left.In magnitude `F=(B^(2)l^(2)upsilon)/r0 ne x lt b ` `F=0 b le x lt 2b` The joule heating loss is `P=I^(2)r` `=(B^(2)l^(2)upsilon^(2))/r 0 ne x lt b ` `=0 b le x lt 2`  
|
|
| 38987. |
A man throws balls into air one after another throwing one the other is at the highest point. How high the balls rise , if he throws twice a second ? |
|
Answer» 2.45m |
|
| 38988. |
The momentum of a photon of an electromagnetic radiation is 3.3xx10^(-29) kg m/s. The frequcncy of the associated wave is (h=6.6xx10^(-34)Js,c=3xx10^(8)m//s) |
|
Answer» `3.0xx10^(3)HZ` `HV=(HC)/(lambda)pc, v=(pc)/(h)=(3.3xx10^(-29)xx3xx10^(8))/(6.6xx10^(-34))` `=1.5xx10^(13)Hz`. |
|
| 38989. |
What is the value of shunt which passes 10% of the main current through a galvanometer of 99 ohm? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :As shunt is a small resistance S in parallel with a galvanometer (of resistance G) as shown in FIG. `(I-I_(g))S=I_(G)G` i.e. `S=(I_(G)G)/((I-I_(G)))` And as here, `G=99Omega` and `I_(G)=(10/100)I=0.1IS=(0.1Ixx99)/((I-0.1I))=(0.1)/(0.9)xx99=11Omega` 
|
|
| 38990. |
The induced e.m.f. in a rod of length l translating at a speed v making an angle theta with length l and perpendicular to magnetic field B is |
|
Answer» B/v |
|
| 38991. |
Young's double slit experiment is carried out by using green, red and blue light, one colour at a time. The fringe widths recorded are beta_(G), beta_(R ) and beta_(B) respectively. Then, |
|
Answer» `beta_(G) gt beta_(B) gt beta_(R )` |
|
| 38992. |
In a hydrogen atom, the electron and proton are bound at a distance of about 0.53 Å : (a) Estimate the potential energy of the system in eV, taking the zero of the potential energy at infinite separation of the electron from proton. (b) What is the minimum work required to free the electron, given that its kinetic energy in the orbit is half the magnitude of potential energy obtained in (a)? (c) What are the answers to (a) and (b) above if the zero of potential energy is taken at 1.06 Åseparation ? |
|
Answer» Solution :If zero of POTENTIAL energy is taken at INFINITY, the potential energy of hydrogen atom system will be `u = (q_1q_2)/(4pi epsi_0r)` In present CASE `q_1 = +1.60 xx 10^(-19)C and R =0.53 Å = 5.3 xx 10^(-11) m` `:. u = ((1.60xx10^(-19))(-1.60 xx 10^(-19))xx9xx10^9)/(5.3xx 10^(-11))J=-((1.60xx10^(-19))^2xx9xx10^9)/(5.3 xx 10^(-11) xx 1.60 xx 10^(-19))eV = -27.2 eV` (b) K.E. of electron in its orbit `K =basu/2`[Because K.E. is always positive] `:. K = 27.2/2 = 13. 6 eV` `:.` Total energy of electron `= K + u= 13.6 - 27.2 = -13.6 eV` `:.` Minimum WORK required to free the electron = + 13.6 eV (c) If zero of potential energy is taken at `r_1 = 1.06 Å = 1.06 xx 10^(-10)m`, then the potential energy of the system for `r_2 = 0.53Å = 5.3 xx 10^(-11)m` is given by `u. = (q_1q_2)/(4pi epsi_0)[1/r_2- 1/r_1] J = (q_1q_2)/(4pi epsi_0e) [ 1/r_2-1/r_1]eV` `=((+ 1.60 xx 10^(-19))(-1.60 xx10^(-19))xx9xx10^9)/(1.60 xx 10^(-19))[1/(5.3xx10^(-11))-1/(1.06xx10^(-10))]eV` `=(13.6 - 27.2)eV = -13.6 eV` but kinetic energy of electron `K. = K =+13.6 eV` `:.` Total energy of electron `=K. + u. = 13.6 = 13.6 = 0` As an amount 13.6 eV [as calculated in case (b) above] has been used up in increasing the potential energy from - 27.2 eV to - 13.6 eV. Therefore, minimum work requred to free the electron = 0 - (13.6)eV = 13.6 eV. |
|
| 38993. |
Three resistances each of 4 Omega are connected to form a triangle. The resistance between any two terminals. is |
|
Answer» `12 OMEGA` |
|
| 38994. |
Choose the wrong option: |
|
Answer» interference |
|
| 38995. |
The potential difference that must be applied to stop the fastest photoelectrons emitted by a nickel surface, having work function 5.01 eV, when ultraviolet light of 200 nm falls on it, must be |
|
Answer» `-2.4V` `THEREFORE K_(max)=E-phi_(0)=6.21eV-5.01eV=1.2eV` `therefore` Stopping potential=-1.2eV. |
|
| 38996. |
A conducting loop in the shape of a right angled isosceles triangle of height 10cm is kept such that the 90^(@) vertex is very closed to an infinitely long conducting wire (see the figure). The wire is electrically insulated from the loop. The hypotenuse of the triangle is parallel to the wire. The current in the triangular loop is in counterclockwise direction and increased at a constant rate of 10As^(-1). Which of the following statement(s) is (are)true ? |
|
Answer» The magnitude of induced emf in the wire is `((mu_(0))/(pi))` VOLT |
|
| 38997. |
The binding energy per nucleon for C^(12)is 7.68MeV and that for C^(13)is 7.47 MeV. The energy required to remove a neutron from C^(13)is |
|
Answer» 0.21 MEV |
|
| 38998. |
When a thin transparent plate of Refractive Index 1.5 is introduced in one of the interfearing becomes, 20 fringes shift. If it is replaced by another thin plate of half the thickness and of R.I 1.7 the number of fringes that undergo displacement is |
|
Answer» 23 |
|
| 38999. |
A long charged cylinder of linear charged density à is surrounded by a hollow co-axial conducting cylinder. What is the electric field in the space between the two cylinders ? |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Let A be a long charged cylinder of linear charge density ^ and B be a hollow co-axial conductingcylinder. Charges are induced on B as shown in Fig. 2.08. Let us find electric field at a point P in the space between the TWO cylinders SITUATED at a distance r from axis of cylinders.To find `vecE` at point P consider a cylinder of length land radius r as the Gaussian surface. Obviously total electric FLUX over the surface `phi_E = int vecE.hatn ds = E pi rl...(i)` According to Gauss.s theorem, the electric flux `phi_E = 1/epsi_0` (charged enclosed) `= 1/epsi_0.(lambda I)`...(ii) Comparing the values of electric flux given by (i) and (ii), we have `E 2pi rl= (lambda I)/(epsi_0) rArr E = lambda/(2pi epsi_0 r)` Obviously, the electric field is radial i.e., field is directed outward perpendicular to the charged cylinder. 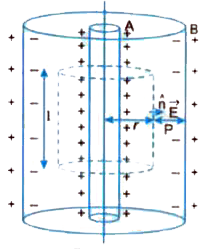
|
|
| 39000. |
Two copper cubes A and B composed of identical insulated plates are suspended from strings in between the pole pieces of an electromagnetic . Both cubes are rotating at the same angular velocity . The electro magnet is energise when we swithch on the electro magnet, the cube that will come to rest letter is . |
|
Answer» A |
|