Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39001. |
For what distance is ray optics a good approximation when the aperture is 3 mm wide and the wavelength is 500 nm? |
|
Answer» Solution :`Z_(F)=(a^(2))/(lambda)=((3XX10^(-3))^(2))/(5xx10^(-7))=18m` This example shows that even with a small APERTURE, diffraction spreading can be neglected for rays MANY metres in length. Thus, ray optics is valid in many COMMON situations. |
|
| 39002. |
If the relation between range R and time of flight T is given by R = 5 T^(2) , the angle of throw of the projectile is : (g = 10 m s^(-2) ) |
|
Answer» 45° or `tantheta=1` if `g=10ms^(-2),` and `theta=45^@` |
|
| 39003. |
If the earth were to suddenly contract to (1)/(n)th of its present radius without any change in its mass, the duration of the new day will be nearly |
|
Answer» `(24)/(n)h` `(2)/(5)MR^(2)((2PI)/(T_(1)))=(2)/(5)M((R )/(n))^(2)(2pi)/(T_(2))` `rArr T_(2)=(T_(1))/(n_(2))=(24)/(n^(2))h""`(`:. T_(1)=24`hours) |
|
| 39004. |
A bi-convex lens is placed between a light source and a concave mirror as shwon such that image of the light source coincides with itself. Then, |
|
Answer» light, after being REFRACTED, may fall NORMALLY on the mirror |
|
| 39005. |
The height at which the acceleration due to gravity becomes g/9. (Where g = acceleration due to gravity) in terms of R. Where R is the radius of earth |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`G=(GM)/R^2` and g'=(GM)/(R+h)^2 THEREFORE g'//g=^1//9=GM/((R+h)^2)xxR^2/(GM)=R^2/((R+h)^2) thereforeR^2=(R+h)^2 therefore3R=R+h=2R` |
|
| 39006. |
A string of mass per unit length "0.2 kg m"^(-1) and length 0.6 m is fixed at both ends such that it has a tension of 80 N. If the string is vibrating in its second overtone mode, then the frequency of the string is |
|
Answer» 40 Hz |
|
| 39007. |
What does the story teach us? |
|
Answer» It gives us an INSIGHT into disabled PEOPLE's lives |
|
| 39008. |
Increasing reverse bias voltage applied to p-n junction diode …….. |
|
Answer» depletion capacitance and resistance of diode of diode INCREASES. On incresing REVERSE bias VOLTAGE in p-n junction diode the width of depletion barrier increases. Therefore according to formula `C prop (1)/(d)` value of capacitance increases. Now according to `V=(Q)/(C )` as C decreases V increases. So resistance in reverse bias from `(r_(RB)=(DeltaV)/(DeltaI))` increases. |
|
| 39009. |
Two point objects of masses 1.5 g and 2.5 g respectively are at a distance of 16 cm apart, the centre of gravity is at a distance x from the object of mass 1. 5 g where x is |
|
Answer» 10 CM  TAKING the moment of FORCES about centre of gravity G (1.5)g `XX` = 2.5g (16-x) `rArr3x=80-5x` or `8x=80` or x=10 cm |
|
| 39010. |
The greatest height to which a man can throw a stone is 100 m. The greatest distance to which he can throw it will be: |
|
Answer» Solution :`H_(MAX)=100m` `R_(max)/H_(max)=2impliesR_(ma)=200m` |
|
| 39011. |
When electron in hydrogen is in minimum excited state then its radius will become ...... radius of first orbit. |
|
Answer» double For first excited state n = 2 radius be `r_(2)` Now `r_(n)alphan^(2)` `:.(r_(2))/(r_(1))=((n_(2))/(n_(1)))^(2)` `=((2)/(1))^(2)"":.(r_(2))/(r_(1))=4` `:.` Radius will become four times. |
|
| 39012. |
Which of the following is true about solid ? |
|
Answer» They are compressible |
|
| 39013. |
Unpolarised light of intensity 32 "Wm"^(-2) passes through three polarisers such that the transmissionaxisof the last polariser s crossed with first . If the intensity of the emerging lightis 32 "Wm"^(-2) , the anglebetween the axes of the first two polarisers is |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 39014. |
In an a.c. circuit the current lags behind the voltagle by pi/3. The compounds of the circuit are |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 39015. |
Three materials A, B and C have electrical conductivities sigma , 2 sigma and 2 sigma respectively. Their numbers densities of free electrons are 2 n, n and 2n respectively. For which material is a average collision time of free electrons maximum? |
|
Answer» Solution :CONDUCTIVITY `SIGMA=1/rho = (n E^(2) tau)/m` Relaxation TIME, `tau = (m sigma)/(n e^(2)`. i.e., `tau prop sigma/n` `:. tau_(A) : tau_(B):tau_(C) = sigma/2n : 2sigma/n : 2sigma/2n = sigma/2n : 2sigma/n : sigma/n` Thus, `tau_(B) gt tau_(C ) gt tau_(A)`. So average collision time for material B is maximum. |
|
| 39016. |
If B is the magnetic Induction, at the centre of a circular coil of radius 't' carrying a current is 1 T, · then its value at a distance of sqrt3 r on the axis from the centre of the coil is |
|
Answer» `1/8T` |
|
| 39017. |
An intrinsic semiconductor, at the absolute zero temperature, behaves like a/an |
|
Answer» INSULATOR |
|
| 39018. |
An alpha-particle of energy 5 Mev is scattered through 180^(@) by a fixed uranium nucleus the distance of closest approach is of the order of |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 39019. |
A plane mirror is on y-z plane facing positive x-axis. A point object is present at (10,5). The mirror is translated by 2 units along positive x and 3 units along positive y-direction. Final image of the point object is at |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 39020. |
A sonometer wire is in unison with atuning fork of frequency 107 Hz when it is stretched by a certain weight. When the weight is completely immersed in water , 7 beats are heard per second . Find the specific gravity of the material of the weight. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`n_(2) = n_(1) -7 = 107 -7= 100 HZ` `n_(1)/n_(2) = SQRT(s/(s-1)) "" sqrt(s/(s-1)) = 107/100 = 1.07` `s/(s-1) = (1.07)^(2) = 1.145` ` s/(s-(s-1)) = 1.145)/(1.145-1)"" 1.145/0.145 = 897` The specific gravity (RELATIVE density ) of the material is 7.897 |
|
| 39021. |
A long copper wire carries a current of 10 ampere . Calculate the magnetic flux per metre of the wire for a plane surface S inside the wire as shown in the figure. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39022. |
Write any three experimental observations of photoelectric effect |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) The photoelectric emission is an instantaneous process without any apparent time lag (`~10^(-9)` s or less), EVEN when the incident radiation is made exceeding by dim. (ii) For every photo emissive surface there is a certain MINIMUM frequency of the incident radiation below which there is no photoelectric effect, called threshold frequency and the corresponding wavelength is called threshold wavelength no matter how intense the incident LIGHT is. Threshold frequency is different for different materials. (iii) For a frequency greater than the threshold frequency, the strength of the photoelectric current is DIRECTLY proportional to the intensity of the incident radiation. |
|
| 39023. |
A fly wheel rotation about an axis has a kinetic energy of 225J when it's angular speed is 30 rad/sec. What is the moment of inertia of the fly wheel about it's axis of rotation? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`E=1/2Iomega^2 THEREFORE I=2E/omega^2=2xx225//3xx300=1/2` |
|
| 39024. |
A sinusoidal wave is propagating along a stretched string that lies along the x-axis. The displacement of the string as a function of time is graphed in figure for particles at x = 0 and x = 0.09 m. These two points are with in one wave length of each other. The speed of the wave, if the wave is moving in positive x-direction. [Take sin^(-1)(3/4) = 0.589 (radians)] |
|
Answer» 3 m/s |
|
| 39025. |
The period of a simple pendulum for large deflection angles may be determined from the approximate formula T=2pisqrt((l)/(g))(1+(1)/(4)sin^(2)""(alpha_(0))/(2)) Compare with the result of numerical calculations for the previous problem. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39026. |
If 5J of work is needed to shift 10C of charge from one plane to another.The potential difference between the places should be |
|
Answer» 0.5V |
|
| 39027. |
Find the equivalent capacitance of the given figure. |
|
Answer» Solution :`1/(DC)=(y)/(epsi_(0)k_(1)BDX)+(d_(0)-y)/(epsi_(0)k_(2)bdx)` `1/(dc)=(d_(0)k_(1)+y(k_(2)-k_(1)))/(epsi_(0)k_(1)k_(2)bdx)` `dx=(epsi_(0)k_(1)k_(2)bdx)/(d_(0)k_(1)+y(k_(2)-k_(1)))` All these capacitors (SMALL) are parallel So, `C_(eq)=underset(0)OVERSET(C_(eq))int dC=underset(0)overset(a)int (epsi_(0)k_(1)k_(2)bdx)/(d_(0)k_(1)+y(k_(2)-k_(1)))` Now, `d_(0)/a=y/x rArr C_(eq)=underset(0)overset(a)int (epsi_(0)k_(1)k_(2)bdx)/(d_(0)k_(1)+d_(0)/AX(k_(2)-k_(1)))` `C_(eq)=(a epsi_(0)k_(1)k_(2)b)/(d_(0)(k_(2)-k_(1)))ln [((k_(2)-k_(1)))/(k_(1))]` 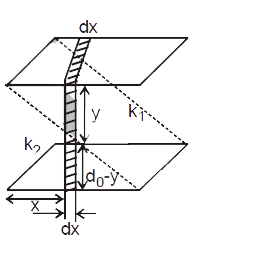
|
|
| 39028. |
(A): When an algebraic equation has been derived, it is advisible to check it for dimensional consistancy. (R): Dimensional correctness of an equation guarantees that it is correct. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A) |
|
| 39029. |
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is - 4.2 xx 10^(-6). Name the type of magnetic materials it represents. |
| Answer» Solution :As the SUSCEPTIBILITY of given MAGNETIC MATERIAL `(x = -4.2 XX 10^(-6) )` is extremely small and negative, the material is a DIAMAGNETIC material. | |
| 39030. |
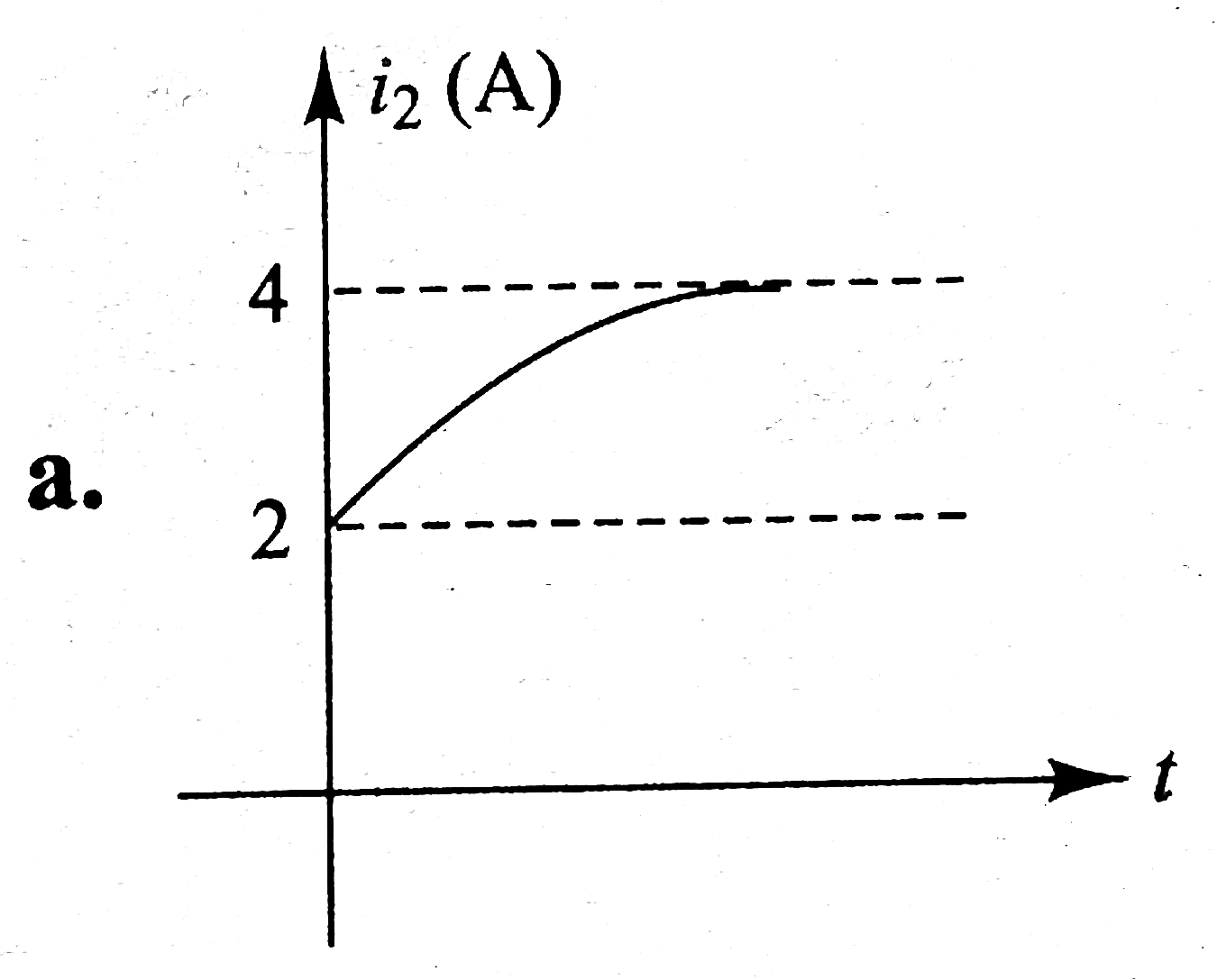
In Fig i_(1) = 10e^(-2t) A, i_(2) = 4 A, and V_(C) = 3e^(-2t) V. The variation of current in the inductor with time can be represented as |
|
Answer»
`q = CV_(C) = (2)(3e^(-2t)) = 6e^(-2t) A` Current, `i_(C) = (dq)/(dt) = - 12e^(-2t)A` This current flows from `B` to `O`. From `KVL`, we have `i_(L) = i_(1) + i_(2) + i_(C) = 10e^(-2t) + 4 - 12e^(-2t)` `= (4 - 2t^(-2t)) A = [2 + 2(1 - e^(-2t))]A` `i_(L) vs`. time graph is as shows in Fig lt `i_(L)` increases from `2 A` to `4 A` expontially.  `V_(L) = L(di_(L))/(dt)` `= (4)(d)/(dt) (4 - 2e^(-2t)) = 16e^(-2t) V` `V_(L)` decreases exponentially from `16 A` to `0` as shows in Fig To determine `V_(AC)`, we begin from `A` and at `C`. From `KVL`, we have  `V_(A) - i_(1)R_(1) + i_(2)R_(2) = V_(C)` `V_(A) - V_(C) = i_(1)R_(1) - i_(2)R_(2)` Substituting the values, we have `V_(AC) = (10 e^(-2t))(2) - (4)(3)` 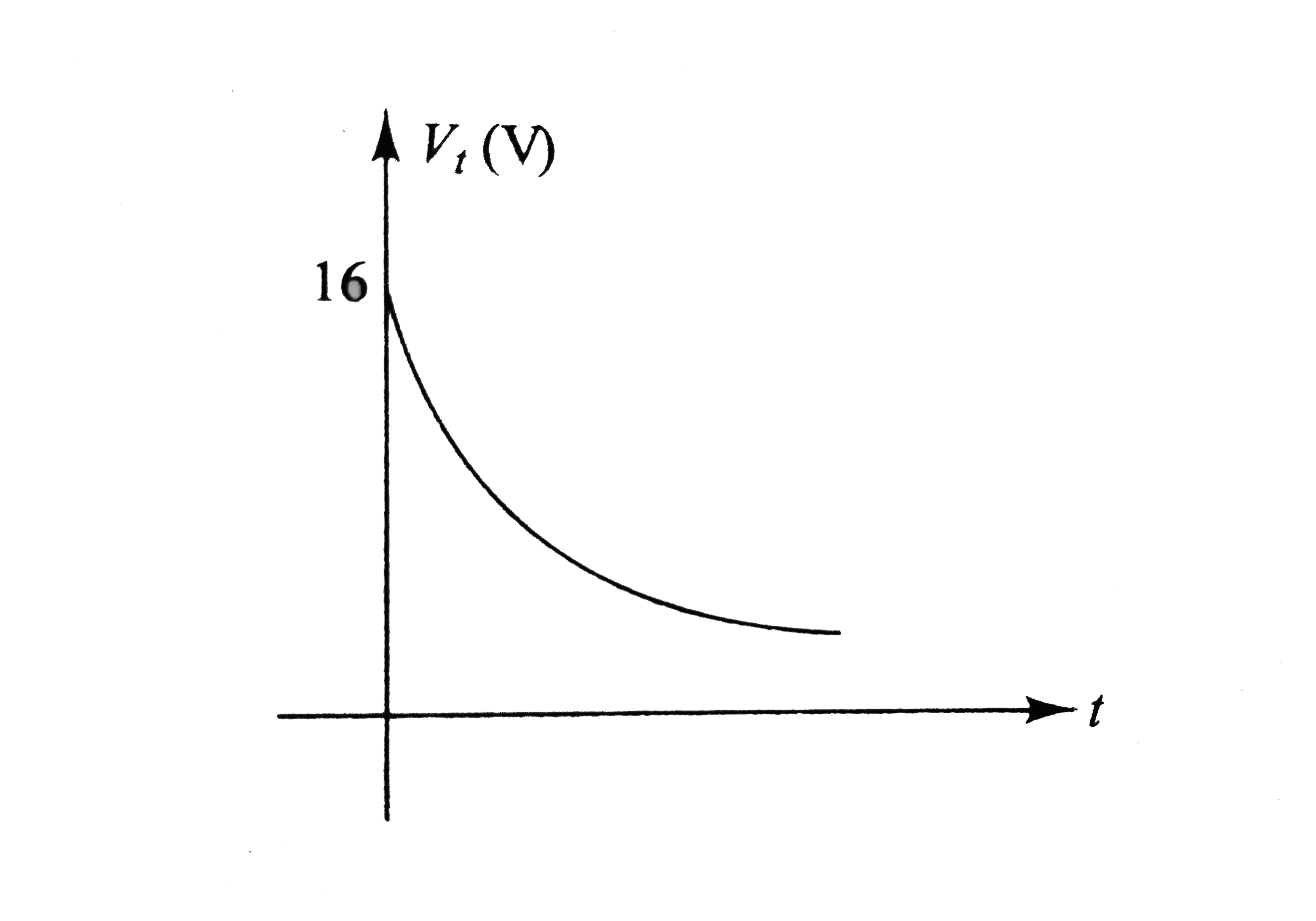 `V_(AC) = (20e^(-2t) - 12) V` At `t = 0`, `V_(AC) = 8V` At `t = oo`, `V_(AC) = - 12 V` Therefore, `V_(AC)` DECREASE exponentially from `8 V` to `12 V`. Similarly, we have from `A` to `B` `V_(A) - i_(1)R_(1) + V_(C) = V_(B)` `V_(AB) = V_(A) - V_(B) = i_(1)R_(1) - V_(C)` 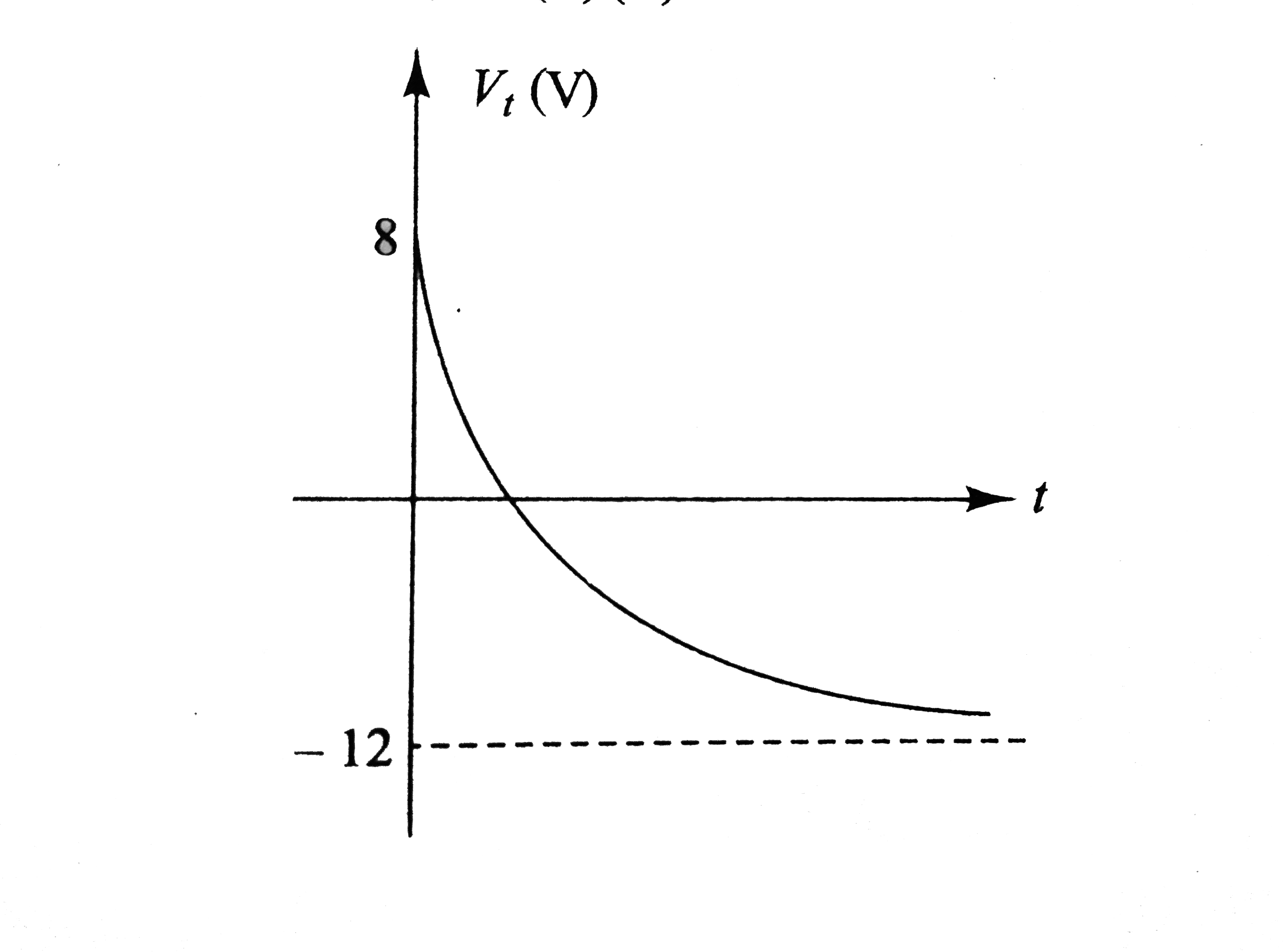 Substituting the values, we have `V_(AB)=^((10e^(-2t)))(2)-3e^(-2t)` `V_(AB) =^(17e^(-2t))V` THUS, `V_(AB)` decreases exponentially from `17 V` to `0`. As we move from `C` to `D`, `V_(C) - i_(2)R_(2) - V_(L) = V_(D)` `V_(CD)= V_(C) - V_(D) = i_(2)R_(2) + V_(L)` Substituting the values we have, `V_(CD)= (4)(3) + 16e^(-2t)` 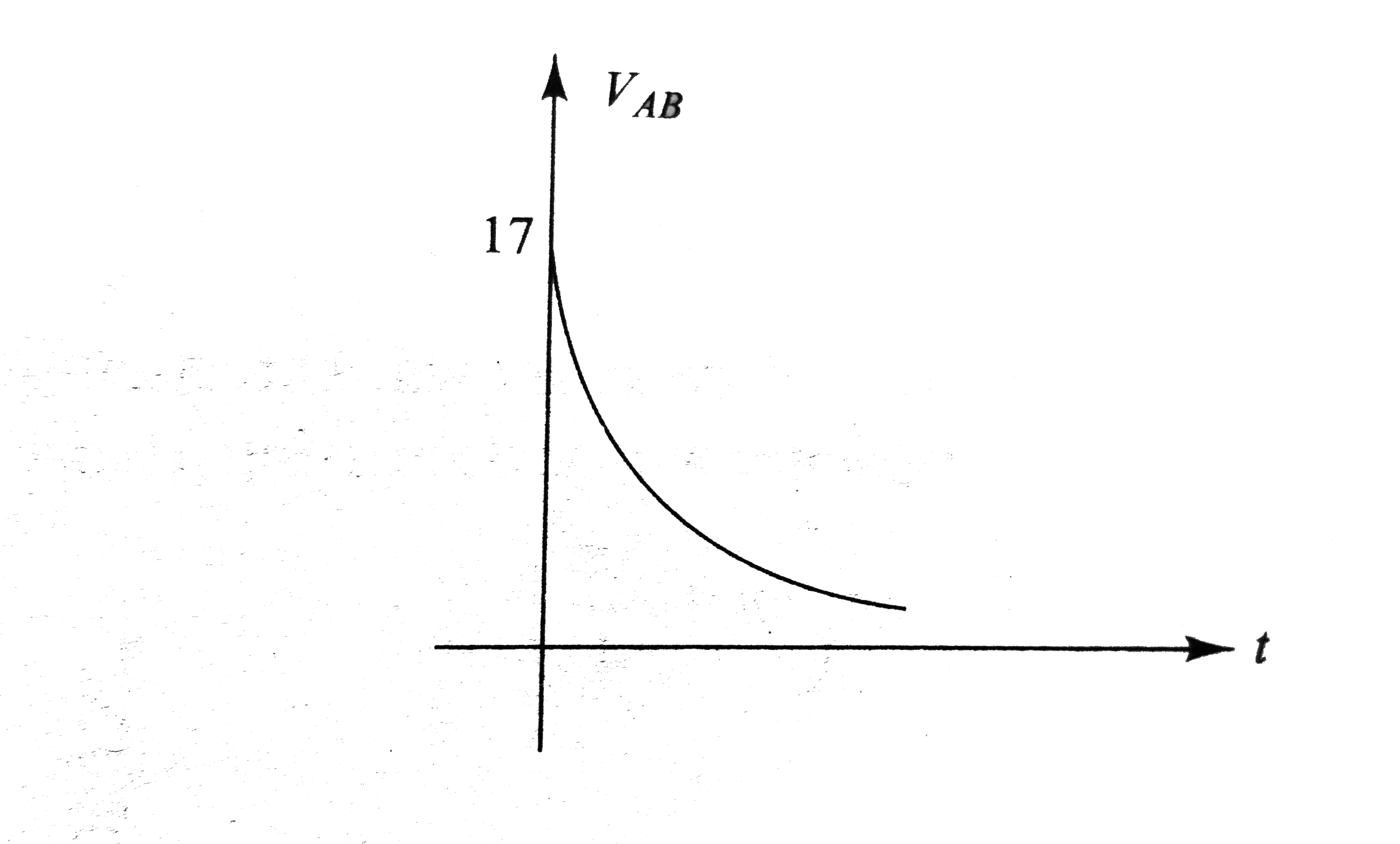 `V_(AD) = (12 + 16e^(-2t))V` At `t = 0, V_(CD) = 28 V` and at `t = oo, V_(CD) = 12 V` i.e., `V_(CD)` decreases exponentially from `28 V` to `12 V`. |
|
| 39031. |
Theinternationally accepted frequency deviation for the purpose of FM broadcasts. |
|
Answer» 75kHz |
|
| 39032. |
A radioactive isotope has a life of T years. The time after which its activity is reduced to 6.25% of its initial activity is |
|
Answer» 8T years |
|
| 39033. |
Show that the electric field at the surface of a charged conductor is given byoversetto E = ( sigma )/( 60 ) hat n, wheresigmais the surface charge density andhatnis a unit vector normal to the surface in the outward direction. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider a charged conductor whose surface charge density is ` sigma . ` To derive electric field at its surface consider a short cylinder (pill box)as the Gaussian surface about a given point . The cylinder is partly inside and PARTY outside the surface of the conductor. It has a small area of cross section ` delta S ` and NEGLIGIBLE height. Just inside the surface , the electric field is ZERO but just outside the field has a magnitudeE and is directed normal to the surface. Thus , the contribution to the electric flux comes only from the outside circular cross-section of the cylinder. ` therefore phi_in =oversetto E . oversetto (delta S) = E.delta S ` As per Gauss theorem. ` phi _in =(1)/( in_0)` (charged close)`=(1)/( in_0).(delta sigma S) ""...(II) ` Comparing (i) and (ii) we get `E =( sigma)/( in_0)rArr ""oversetto E =(sigma)/( in_0)hatn ` 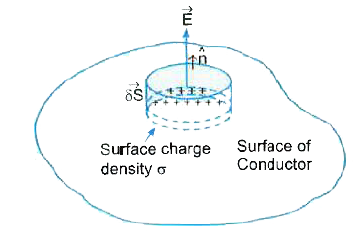
|
|
| 39034. |
Let E_a be the electric field due to a dipole in its axial plane at distant r and let E_q be the field in the equatorial plane at distant r. The relation between E_a and E_q is |
|
Answer» `E_a = E_q` |
|
| 39035. |
Represent graphically the variation of photoelectric current with the intensity of incident radiation for a given photo sensitive material. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 39036. |
What is a transformer? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :A transformer is a device USED for stepping up or stepping down the AC VOLTAGES. | |
| 39037. |
Water is flowing at a speed of 1.5ms^(-1) through a horizontal tube of cross-sectional area 10^(-2)m^(2) and you are trying to stop the flow by your palm. Assuming that the water stops immediately after hitting the palm, the minimum force that you must exert should be (density of water = 10^3 kgm^(-3)). |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 39038. |
An aeroplane requires a speed of 72 kmph for a take off with 150m run on the ground. The mass of the plane is 1500kg and the coefficient of friction between the aeroplane and the ground is 0.4. Assuming that the aeroplane acceleration uniformly during take off, find the minimum force exerted by the engine of the aeroplane for take off. |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 39039. |
(a) The refractive index of glass is 1.5. what is the speed of light in glass ? (Speed of light in vacuum is 3.0xx10^(8)ms^(-1)) (b) Is th speed of light in glass independent of the colour of light ? If not, which of the two colours red and violet travels slower in a glass prism ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :(a) Here `c=3.0xx10^(8)MS^(-1) and n=1.5` `THEREFORE`Speed of light in glass `v=(c)/(n)=(3.0xx10^(8))/(1.5)=2xx10^(8)ms^(-1)` (b) The speed of light in glass depends upon the COLOUR of light. Speed of light in glass in maximum for red colour and least for VIOLET colour. |
|
| 39040. |
What percentage of original radioactive atom is left after four half lives : |
|
Answer» 0.2 |
|
| 39041. |
A gymnast does a one - arm handstand. The humerus, which is the upper arm bone between the elbow and the shoulder joint, may be approximated as a 0.30 - m - long cylinder with an outer radius of 1.0xx10^(-2)m and a hollow inner core with a radius of 4.0xx10^(-3)m. Excluding the arm, the mass of the gymnast is 63 kg. What is the compressional strain of the humerus ? |
|
Answer» `4.9xx10^(-4)` |
|
| 39042. |
Define mobility of charge carriers in a conductor. Mention the units of mobility. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Mobility : The mobility of a charge CARRIER is the average drift velocity RESULTING from the application of unit electric FIELD strength. It is represented by `mu` |
|
| 39043. |
The speed of a wave on a string is 150 m/s when the tension is 120 N . The percentage increase in the tension in order to raise the wave speed by 20% is |
|
Answer» 0.44 |
|
| 39044. |
Figure 25-35 shows a variable "air gap" capacitor for manual training Alternate plates are connected together, one group of plates is fixed in position, and the other group is capable is rotation. Consider a capacitor of n=8 plates of alternating polarity, each plate having area A=1.50 cm^2 and separated from adjacent plates by distance d=3.40mm. What is the maximum capacitance of the device? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`2.73 TIMES 10^-12 F` | |
| 39045. |
A hypothetical experiment conducted to determine Young's modulus, gave the formula, Y = (cos theta T^x tau)/l^3 If T=time period , tau = torque and l=length , then the value of x is |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 39046. |
A body of mass m is raised through a distance equal to the radius of the earth from earth's surface. The change in P.E. will be : |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 39047. |
Who was Alexander Aris? |
|
Answer» SON OF SAN SUU KYI |
|
| 39048. |
A satellite orbiting around earth of radius R is shifted to an orbit of radius 2R. How many times the time taken for one revolution increase? |
|
Answer» `2*5` times `T^(2)prop r^(3) therefore (T_(2))/(T_(1))=((r_(2))/(r_(1)))^(3//2)` `T_(2)=T((2R)/(R ))^(3//2)` `RARR T_(2)=2sqrt(2)T=2xx1.41T=2.82T` Thus correct choice is (c ). |
|
| 39049. |
How many electrons must be added to one plate and removed from the other so as to store 25.0 J of energy in a 5.0 nF parallel plate capacitor? |
|
Answer» Solution :`C=5 xx 10^(-9) F, U=25J` `U=Q^(2)//2C` `Q^(2)=2UC=2 xx 25 xx 5 xx 10^(-9)` `Q=5 xx 10^(-4)C` `Q=ne` `n=Q/e=3.125 xx 10^(15)"ELECTRONS".` |
|
| 39050. |
A plot of magnetic flux (phi) versus current (I) is shown in the Fig. 6.20 for two inductors A and B. Which of the two has larger value of self-inductance ? |
|
Answer» |
|



