Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39051. |
Find theinteraction forceof two coilswith magnetic momentp_(1m) = 43.0 mA.m^(2) and p_(2m) = 6.0 mA.m^(2) and coilnear axis if the separationbetweenthe coilsis equalto l = 20 cm which exceedsconsiderably theirlinear dimensions. |
|
Answer» Solution :`P = P_(2m) (DEL)/(del t) [(mu_(0))/(4PI) (3 vec(p_(1M)) . vec(r) vec(r) - vec(p_(1m)) r^(2))/(r^(2))]` `P_(2m) (del)/(del l) [(mu_(0))/(2pi) (P_(1m))/(l^(3))] = (-3)/(2) (mu_(0) P_(1m) p_(2m))/(pi l^(4)) = 9 nN` |
|
| 39052. |
When straight conductor moves in external magnetic field (LHP rule):- |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39054. |
A person, standing between two parallel hills, fires a gun. He hears the first echo after 1.5 s and the second after 2.5 s. If the speed of sound is 332 m/s, calculate the distance between the hills. When will he hear the third echo? |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :LET the person P be at a distance x from hill `H_1 and y " from " H_2` as shown in figure. The time interval between the original sound and echoes from `H_1 and H_2` will be respectively. So the distance between the hills `x + y =v/2 (t_1+t_2) = 332/2 [1.5 +2.5] = 664 m` Now as I ECHO will be from `H_1` after TIMES `t_1` while II echo from `H_2` after time `t_2`, III echo will be produced due to reflection of sound of I echo from `H_2` or of II echo from `H_1`, i.e., `t_3 =t_1 +t_2 =1.5 +2.5 = 4 sec`i.e., III echo will be produced after 4 sec. and in it sound from both I and II echoes will reach simultaneously. |
|
| 39055. |
Two identical sonometer wires have a fundamental frequency of 500 Hz when kept under the same tension. What fractional increase in the tension of one wire would cause an occurrence of 5 beats per sec, when both wires vibrate together? |
|
Answer» 0.01 |
|
| 39056. |
What is a wavefront ? |
| Answer» Solution :A wavefront is a surface or line in the PATH of a WAVE motion on which the disturbance at EVERY POINT has same PHASE. | |
| 39057. |
When forward bias is applied to a p-n junction, what happens to the potential barrier and the width of depletion region. |
|
Answer» RAISE the POTENTIAL barrier. |
|
| 39058. |
A slabof materialof dielectricconstantK hasthe sameareaastheplatesof aparallelplatecapacitorbuthas athickless(1/2)d.Whered isthe separationof theplates. Howis thecapacitancechangedwhentheslabisinsertedbetweenthe plates |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`V=V_0[(k+1)/( 2K)] ANDC= (2k)/(K+1) C_0` | |
| 39059. |
A projectile is traveling in a parabolic path for a total of 6 seconds. How does its horizontal velocity 1 s after launch compare to its horizontal velocity 4 s after launch ? |
| Answer» Solution :The only acceleration experienced by the projectile is DUE to gravity, which is purely vertical, so there's no HORIZONTAL acceleration. If there's no horizontal acceleration, then the horizontal velocity cannot CHANGE during flight, and the projectile's horizontal velocity 1 after it's launched is the same as its horizontal velocity 3 s later. | |
| 39060. |
Which law of thermodynamics leads as to conclude that it is not possible to convert whole of heat into work continuously ? |
|
Answer» SECOND law |
|
| 39061. |
The direction of induced emf during electromagnetic induction is given by |
|
Answer» Fareday's law. |
|
| 39062. |
A sample of a radioactive substance has 10^(6) radioactive nuclei. Its half life time is 20 s How many nuclei will remain after 10 s ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`4 XX 10^6` | |
| 39063. |
A rectangular loop of sides 25 cm and 10 cm carrying current of 15A is placed with its longer side parallel to a long straight conductor 2.0 cm apart carrying a current of 25A. What is the new force on the loop ? |
|
Answer» `F_2 = (mu_(0))/(4pi) (2I_1 I_2)/(r_2) xx l = (10^(-7) xx 2 xx 25 xx 15 xx 0. 25)/(0.12) = 1.56 xx 10^(-4)` N REPULSIVE Net `F= F_1 = F_2 = 7.82 xx 10^(-4)` N 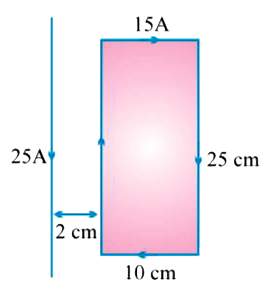
|
|
| 39064. |
A point source of 3000 lumen is located at the centre of a cube of side length 2 m . The flux through one side is |
|
Answer» 500 lumen |
|
| 39065. |
A simple pendulum of length 1 m with a bob of mass m swings with an angular amplitude 30°. Then (g = 9.8 ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» time period of pendulum is 2 s  Simle pendulum of LENGTH 1 m is CALLED second.s pendulum whose time period is T =2S. But this time period is for small oscillations. In this case, angular amplitude is `30^(@)`. Therefore, time period wil not be 2s. At angular displacement `15^(@)`. `T-mg cos 15^(@) =(mv^(2))/l` or `T gt mg cos 15^(@)` and tangential acceleration `a = g sin 15^(@)` = rate of change of speed. |
|
| 39066. |
A hemisphere is uniformly charged positively, The electric field at a point on a diameter away from the centre is directed |
|
Answer» perpendicular to the DIAMETER |
|
| 39067. |
If the depression d at the end of a loaded bar is given by d = (Mg l^3)/(3 yi) where M is the mass , lis the length and y is the young's modulus, then i has the dimensional formula |
|
Answer» `L^2` |
|
| 39068. |
If the amplitude ratio of two interfering choherent waves producing an interference pattern is 0.5, what is the ratio of the minimum intensity to maximum intensity? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`(I_("MIN"))/(I_("MAX")) = ((1-0.5)/(1+0.5))^(2) = ((1//2)/(3//2))^(2) = 1/9` | |
| 39069. |
A sytemconsistsofa longcylindricalanode ofradius a anda coxialcylindricalcylindricalcathodeof radiusb(b lt a). A filamentlocatedalong theaxis of the systemcarriesa heatingcurrentI producinga magneticfieldin the surroundingspace. FInd theleast potentilal differnce betweenthe cathodeandanode at which thetherimal electrons leavingthe cathodewithout intital velcitystart reaching the anode. |
|
Answer» Solution :When `a`CURRENT `I` flows along the axis, a magnetic field `B_(varphi) = (mu_(0) I)/(2pi p)` is set up where `rho^(2) = X^(2) + y^(2)`. In terms of COMPONENTS, `B_(x) = - (mu_(0) ly)/(2pi rho^(2)), B_(y) = (mu_(0) lx)/(2pi rho^(2))` and `B_(x) = 0` Suppose a p.d. `V` is set up between the inner cathode and the other anode. This mean a potential function of the form `varphi = V (In rho//b)/(In a//b), a gt rho gt b`, as one can check by solvingLaplace equaction , The electricfield correspondingto this is, `E_(x) = (Vx)/(rho^(2) In a//b), E_(y) = (Vy)/(rho^(2) In a//b), E_(x) = 0`. The equactions of motion are, `(d)/(dt) mv_(x) = + (|e|V_(z))/(rho^(2) In a//b) + (|e| mu_(0) I)/(2pi rho^(2)) x dotz` `(d)/(dt) mv_(y) = + (|e|V_(z))/(rho^(2) In a//b) + (|e| mu_(0) I)/(2pi rho^(2)) y dotz` and`(d)/(dt) mv_(x) = -|e| (mu_(0)I)/(2pi rho^(2)) (x dotx + y doty) = -|e| (mu_(0) I)/(2pi) (d)/(dt) In rho` `(-|e|)` is the charge on the electron. Intergrating the last equaction, `mv_(e) = -|e| (mm_(0) I)/(2pi) In rho//a = m dotz`.  since `v_(z) = 0` where `rho = a`. We know substitude this `dotz` in the other two equactions to get `(d)/(dt) ((1)/(2) mv_(x)^(2) + (1)/(2) mv_(y)^(2))` `= [(|e|v)/(In a//b) - (|e|^(2))/(m) ((mu_(0) I)/(2pi))^(2) In rho//b]. (x dotx + y doty)/(rho^(2))` `= [(|e|V)/(In a/b) - (|e|^(2))/(m) ((mu_(0) I)/(2pi))^(2) In rho/b]. (1)/(2RHO^(52)) (d)/(dt) rho^(2)` `= [(|e|V)/(In a/b) - (|e|^(2))/(m) ((mu_(0) I)/(2pi))^(2) In rho/b] (d)/(dt) In (rho)/(b)` Intergatingand using`v^(2) = 0`, at `rho = b`, we get, `(1)/(2) mv^(2)= = [(|e|V)/(In (a)/(b)) IN (rho)/(b) - (1)/(2m) |e|^(2) ((mu_(0) I)/(2pi))^(2) (In (rho)/(b))]` The `RHS` must be positive, for all `a gt rho gt b`. The condition for this is, `V ge (1)/(2) (|e|)/(m) ((mu_(0) I)/(2pi))^(2) In (a)/(b)` |
|
| 39070. |
What is lorentz force ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The combined electric and MAGNETIC force on a moving charge is called Lorentz force. | |
| 39071. |
A solenoid 60 cm long and of radius 4.0 cm has a layers of windings of 300 turns each. A 2.0cm long wire of mass 2.5 g lies inside the solenoid (near itscentre) normal to its axis, both the wire and the axis of the solenoid are in the horizontal plane. The wireis connected through two leads parallel to the axis of hte solenoid to an external battery which supplies a current of 6.0 A in the wire. What value of current (With appropriate sense of circulation) in the windings of the solenoid can support the weight of the wire ? g = 9.8 m s^(-2). |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `l = 60 cm= 0.6 m, ` total number of turns in SOLENOID coil `N = 3 xx 300 = 900`, HENCE number of turns per unit length `n = N/l = 900/0.6 = 1500 m^(-1)` , current FLOWING in coil = I, mass of wire `m = 2.5 g= 2.5 xx 10^(-3) kg`, current flowing in wire `I. = 6 A` and length of wire `l. = 2 cm = 2 xx 10^(-2) m` `:.` Magnetic field inside the solenoid near its CENTRE `B = mu_0 n I = 4 pi xx 10^(-7) xx 1500 xx I = 6 pi I xx 10^(-4) T` The magnetic field `vecB` acts along the axis of solenoid and is, thus, normal to the wire. Therefore, the force experienced by the wire is `F = B I. l. = (6 pi xx 10^(-4) I) xx (6) xx (2 xx 10^(-2)) = 72pi xx 10^(-6) I N` This force should just support the weight of the wire `:. 72 pi xx 10^(-6) I = (2.5 xx 10^(-3)) xx (9.8)` `I = (2.5 xx 10^(-3) xx 9.8)/(72 pi xx 10^(-6)) = 108.37 A ~~ 108 A` |
|
| 39072. |
An electron in a circular orbit of radius 0.05 mm performs 10^(16) revolutions per second. The magnetic moment due to this rotation of electron is ("in Am"^(2)) |
|
Answer» `2.16 xx 10^(-23)` `= 0.05 xx 10^(-9)m` Frequency, `v = 10^(16)rev//s` The electron moving in a orbit behaves as a CURRENT loop. The current due to orbit MOTION of electron is `I = ev` Area of the loop, `A = pir^(2)` `therefore` Magnetic moment of the loop, `M = IA = evpur^(2)` `therefore M = 1.6 xx 10^(-19) xx 10^(16) xx 3.14 xx (0.05 xx 10^(-9))^(2)` `= 0.0126 xx 10^(-21) Am^(2) = 1.26 xx 10^(-23)A m^(2)` |
|
| 39073. |
Two samples A and B of a gas are initially at the same temperature and pressure, are compressed from volume V to V/2 (A isothermally and adiabatically), then the final pressure of : |
|
Answer» A is greater than that of B |
|
| 39074. |
To get 2F capacitance, the area of each plate kept at separation of 2 mm is ...... . ' (epsilon_(0) = 8.85 xx 10^(-12) MKS) |
|
Answer» `4xx10^(5) m^(2)` `:. A = (Cd)/(epsilon_(0))= (2xx2xx10^(-3))/(8.85xx10^(-12))` `:. A = 0.4519xx10^(9)` `:. A = 4.519xx10^(8) m^(2)` |
|
| 39075. |
The critical velocity of a satellite, orbiting around the earth at a height equal to radius of the earth is,, (R) = 6400 km,(G=6.67xx10^-11Nm^2//kg^2,M=6xx10^24kg) |
|
Answer» a)`1.1xx10^11km` |
|
| 39076. |
If unit vectors vec(A) and vec(B) are inclined at an angle theta then |vec(A)-vec(B)| is: |
|
Answer» `2sin(theta/2)` `(hatA-hat(B))^(2)=(hatA-hatB).(hatA-hatB)` |
|
| 39077. |
Shape of ideal toroid is ____ |
|
Answer» cylindrical |
|
| 39078. |
Consider the given diagram. An ideal gas is contained in a chamber (left) of volume V and is at an absolute temperature T. It is allowed to rush freely into the right chamber of volume V which is initially vacuum. The whole system is thermally isolated. What will be the final temperature of the system after the equilibrium has been attained? |
|
Answer» `T ` Now , given , `P_(i) = P , V_(i) = V , P_(f) = P//2 , V_(f) = 2V, T_(i) = TP_(i) V_(i) = nRT rArr PV = nRT ` Now , `P_(f) V_(f) = n RT_(f) rArrP/2 xx 2V = nRT_(f)` `rArr PV = nRT_(f) rArr nRT = nRT_(f)` ` rArrT_(f) = T ` ` :. ` Initial and final TEMPERATURE of the system remains same after the equilibrium has been attained as the system is not doing any work at the time of free expansion `(i.e., Delta U = 0 )`. |
|
| 39079. |
At what condition atoms and molecules can be treated as electric dipoles ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :POSITIVE CHARGE CENTRE does not COINCIDE with charge centre. | |
| 39080. |
Which one of the following number (s) is/are rational? |
|
Answer» `SIN15^(@)` |
|
| 39081. |
A current I flows in a circular coil of radius r. If the coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field B with its plane parallel to the field, magnitude of the torque that acts on the coil is |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 39082. |
Explain resonance for an L-C-R series circuit and write its uses. In what kind of circuit will it possible ? |
|
Answer» Solution :For an L-C-R circuit DRIVEN with voltage of amplitude `V_(m)` and frequency `omega` the curren amplitude is given by, `I_(m) = ( V_(m))/( Z) = ( V_(m))/( sqrt( R^(2) + (X_(C ) - X_(L))^(2)))` where `X_(C ) = ( 1)/( omega C )` and `X_(L) = omega L `. `I_(m) = ( V_(m))/( sqrt(R^(2)+ (( 1)/( omega C) - omega L )^(2)))`....(1) Hence, if `omega` is varied so current amplitude is varied at a particular frequency `omega _(0) , X_(C ) = X_(L)` and the impedance is minimum. `Z = sqrt( R^(2) + O^(2))= R ` . The value of amplitude of current is maximum. This is called resonance. `:. ` If `X_(C ) = X_(L)`, then from equation (1), `I_(m) = ( V_(m))/( R )` at resonant frequency amplitude is maximum and `X_(C ) = X_(L)` or`(1)/( omega_(0) C ) \= omega_(0) L ` `:.omega _(0)^(2) =( 1)/( LC ) ` or `omega_(0) = ( 1)/( sqrt( LC ))` Hence, at resonance frequency amplitude of current becomes maximum and it is` I_(m) = ( V_(m)) /( R )`.  Resonant circuits have a variety of applications for EXAMPLE in the tuning mechanism of a raido or a TV set . The antenna of a radio accepts signals from manybroadcasting stations. The siglas pickedup in the antenna ACTS as a source in the tuning circuit of the radio, so the circuit can be driven at many frequencies. But , to hear one particular radio station, we tune the radio. In tuning, we vary the CAPACITANCE of a capacitor in the tuning circuit such that the resonant frequency of the circuit becomes nearly equal to the frequency of the radio signal received. Hence, resonance occurs and amplitude of current becomes maximum. The resonance phenomenon is exhibited by a circuit only if both L and C are present in the circuit. Only then do the voltages across L and C cancel each other and the current amplitude is `I_(m) = ( V_(m))/( R )` the total source voltage appearing across R `:` This means that we cannot have resonance in a RL and RC circuit but resonance L and C both should be in circuit. |
|
| 39083. |
A block of mass 'm' is attached to a spring. Block is released from rest, when spring is in natural length. Block is along the pricipal axis of concave mirror and size of block is very small. When spring is in natural length then block is at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror, distance (in cm) in which the image formed by mirror oscillates is (mass of the block =5xx10^(-2) kg, spring constant k=20 N//m) |
|
Answer» `1/v=1/f-1/u` `1/v=1/(-10)-1/(-20)=(-2+1)/20` `v=-20` cm `d_(1)=20` cm (initial distance of image from mirror) `1/v=1/(-10)-1/(-15)=(-3+2)/30` `v=-30` cm `d_(2)=30` cm (final distance of image from mirror) `d_(2)-d_(1)=10` cm(distance in which the image oscillates) |
|
| 39084. |
A coil of 20 turns of area 8 xx 10^(-2) cm^2 with its plane parallel to the magnetic field of intensity 3000G and carrying a certain current experiences a torque 2.4 xx 10^(-3) Nm .Calculate the value of current. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`50 A (1 G = 10^(-4) T)` | |
| 39085. |
If a lens of focal length 20 cm, made of glass of refractive index 1.5, is placed in a liquid of refractive index 1.25, the focal length of the lens becomes ___________. |
|
Answer» Solution :`(1)/(20)=((15)/(1)-1)((1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2)))=0.5 ((1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2)))` and `(1)/(F)=((1.5)/(1.25)-1)((1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2)))=(0.25)/(1.25)((1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2))) RARR f=(0.5xx1.25)/(0.25)xx20=50cm` |
|
| 39086. |
in the question number 63, the frequency of emitted photon due to the given transition is (h=6.64xx10^(-34)Js,1eV=1.6xx10^(-19)J) |
|
Answer» `2.46xx10^(10)Hz` `hupsilon=E_2=-E_1=10.2eV therefore upsilon=(10.2)/(h)EV` Here, `10.2eV=10.2xx1.6xx10^(-19)J,h=6.64xx10^(34)J_s` `therefore upsilon=(10xx1.6xx10^(-19))/(6.64xx10^(-34))=2.46xx10^(15)Hz`. |
|
| 39087. |
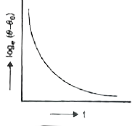
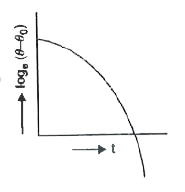
A liquid in a beaker has temperature phi(t) at time t and theta_(0) is temperature of surroundings, then according to Newton's law of cooling the correct graph between log_(e)(theta-theta_(0)) and t is |
|
Answer»
`int_(theta_(0))^(theta)(d theta)/(theta-theta_(0))=-Kint_(0)^(t)dt` `lntheta_(0)-theta_(0)=-Kt+C` The above EQUATION shows that graph is a STRAIGHT line Correct CHOICE is (b). |
|
| 39088. |
Curie's law states I = C _____ |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`[B_0/T]` | |
| 39089. |
A ray incident at an angle of incidence 60^@ enters a glass sphere of refractive index mu = sqrt3. This ray is reflected and refracted at the farther surface of the sphere. The angle between reflected and refracted rays at this surface is |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 39090. |
Distinguish between isotopes and isobars, giving one example for each. |
|
Answer» Solution :Isotopes of an element are NUCLIDES having same atomic number Z but different mass number A (or different neutron number N). Isotopes have identical ELECTRONIC configuration and, hence, identical chemical properties. `" "_(1)^(1)H, " "_(1)^(2)H, " "_(1)^(3)H and " "_(6)^(11)C, " "_(6)^(12)C, " "_(6)^(14)C` etc., are isotopes. Nuclides having same mass number A but different atomic number Z are called isobars. Isobars REPRESENT different chemical elements. In isobars number of protons as well as number of neutrons differ but total nucleon (or mass) number is the same. `" "_(1)^(3)H, " "_(2)^(3)He and " "_(6)^(14)C, " "_(7)^(14)N` are examples of isobars. |
|
| 39091. |
Define photoelectric work function. How in it relaterd to threshold frequency ? |
| Answer» Solution :The minimum amount of radiation energy needed to PULL an electron (without imparing it any KINETIC energy) from a METALLIC SURFACE is called work function of the METAL. The relation between work function `W_0` and threshold frequency `v_0` is `W_0` = h`v_0`. | |
| 39092. |
(A): When an electric motor is started, a variable resistance (that decreases with time) is used in series. This resistance is known as motor starter. (R): The back emf in the beginning, when motor starts, is very small. |
|
Answer» Both A and R are TRUE and R is the correct EXPLANATION |
|
| 39093. |
A coil of inductance 4//pi H is joined in series with a resistance of 30 Omega. Calculate the current flowing in the circuit when connectedto a.c. mains of 200 V and frequency 50 Hz. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39095. |
The electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to the |
|
Answer» a) SUM of the charges |
|
| 39096. |
A 100 turn closely wound circular coil of radius 10 cm carries a current of 3.2 A. (a) What is the field at the centre of the coil? (b) What is the magnetic moment of this coil? The coil is placed in a vertical plane and is free to rotate about a horizontal axis which coincides with its diameter. A uniform magnetic field of 2T in the horizontal direction exists such that initially the axis of the coil is in the direction of the field. The coil rotates through an angle of 90^@ under the influence of the magnetic field. (c) What are the magnitudes of the torques on the coil in the initial and final position?(d) What is the angular speed acquired by the coil when it has rotated by 90^@? The moment of inertia of the coil is 0.1 kg m^2. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) From eq. `B = (mu_0 NI)/(2 R)` Here , N = 100 , I = 3.2 A, and R = 0.1 m . Hence `B = (4pi xx 10^(-7) xx 10^2 xx 3.2)/(2 xx 10^(-1)) = (4 xx 10^(-5) xx 10)/(2 xx 10^(-1)) `( using `PI xx 3.2 = 10` ) The direction is given by the right-hand thumb rule. (b) The magnetic moment is given by Eq. `m = NIA = NI pi r^2 = 100 xx 3.2 xx 3.14 xx 10^(-2) = 10 A m^2` The direction is once again given by the right-hand thumb rule (C ) ` tau = | m xx B| ` `= m B sin theta ` Initially, ` theta = 0`. Thus , initial torque `tau_1 = 0` . finally , `theta = pi//2 ( or90^@)` Thus final torque `tau_f = mB = 10 xx 2 = 20 Nm` (d) From newton.s SECOND law `(d omega)/(DT)= mB sin theta ` Where `omega`is the moment of inertia of the coil . from chain rule , `(d omega)/(dt) = (d omega)/(dtheta)( d theta)/(dt) = (d omega)/(d theta) omega` using this , `omega d omega=m B sintheta d theta ` Integrating from ` theta = 0 ` to ` theta =pi//2` `g int_(0)^(omega_f) omega d omega = m B int_(0)^(pi//2) sin theta d theta` `g (omega_f^2)/(2 ) = - mB cos theta ]_0^(pi//2) = mB` `omega_f = ( (2m B)/( g) )^(1//2) = ((2 xx 20)/(10^(-1)))^(1//2) = 20 s^(-1)` |
|
| 39097. |
Two satellites of earth, S_(1) and S_(2) are moving in the same orbit. The mass of S_(1) is four times the mass of S_(2). Which one of the following stetements is true ? |
|
Answer» The potential energies fo earth and satellite in the two cases are equal. `:.` Kinetic ENERGY of a satellite, `K=(GM m)/(2r )""`..(i) Potential energy of a satellite, `U=(-GM m)/(r )""`.. (ii) Orbit speed of satellite , `v=sqrt((GM)/(r ))""`...(iii) Time-period of satellite, `T=[(((4pi^(2)))/(GM))r^(3)]^(1//2)""`...(iv) GIVEN `m_(S_(1))=4_(m_(S_(2))` Since M, r is same for both the satellites `S_(1)` and `S_(2)`. `:.` From equation (ii), we get `U PROP m` `:. (U_(S_(1)))/(U_(S_(2)))=(m_(S_(1)))/(m_(S_(2)))=4" or ",K_(S_(1))=4K_(S_(2))` HENCE option (c ) is wrong. From (iv), since T is independent of the mass of a satellite, time period is same for both the satellites `S_(1)` and `S_(2)`. Hence option (d) is is wrong. |
|
| 39098. |
how many time constants will elapse before the power delovered by the battery drops to half of its maximum value in an RC circuit ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`POWER = CV^2 = q xx V` ` Now, QV/2 = qV xx e^(-t/rc)` ` rArr1/2 = e^(-t/rc)` ` rArr t/rc = - In (0.5) ` ` = -(-0.69) = 0.69.` |
|
| 39099. |
Match the statement in Column I with the statements in Column II. One or more than one choice from Column II can match with a statement from Column I. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39100. |
What is the de-Broglie wavelength associated with an electron ,accelerated through a potential difference of 10K volts? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`LAMBDA`=0.01227 NM or =0.1227 Å | |