Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39101. |
The maximum value of magnitude of (vecA-vecB)is |
|
Answer» A-B |
|
| 39102. |
Give the empirical formula for observed wavelengths of Balmer series lines |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :WAVELENGTHS of Balmer SERIES lines are given by the EMPIRICAL formula. `(1)/(lambda) = R[(1)/(2^(2)) - (1)/(N^(2))] `, where n=3,4,5, .......... and R is Rydberg.s constant. |
|
| 39103. |
Three resistors R_1, R_2 and R_3 are to be combined to form an electrical circuit as shown in the figure. It is found that when R_1 R_2 and R_3 are put respectively in positions A, B and C, the effective resistance of the circuit is 70 OmegaWhen R_2, R_3 and R_1 are put respectively in position A, B and C the effective resistance is 35Omega and when R_3, R_1 and R_2 are respectively put in the position A, B and C, the effective resistance is 42 OmegaIf R_(1), R_(2 )and R_(3) are all connected in parallel, the effective resistance will be |
|
Answer» `37Omega` `(R_(2)R_(3)+R_(3)R_(1)+R_(1)R_(2))/(R_(2)+R_(3))35ldots(2)` `(R_(3)R_(1)+R_(1)R_(2)+R_(2)R_(3))/(R_(3)+R_(1))=42ldots(3)` `(R_(1)R_(2)+R_(2)R_(3)+R_(3)R_(1))=k` Then the system of three equation transforms to`R_(1)+R_(2)=(k)/(70)` `R_(2)+R_(3)=(k)/(35)R_(3)+R_(1)=(k)/(42)` SOLVING, this we get`R = k//210, R = k//105, R = 2k//105` implies`R_(1): R_(2): R_(3) = 1:2:4` So, let `R_(1) = X, R_(2) = 2x` and `R_(3) = 4X` Putting these valued in equation 1, we get`X = 15` `R_(1) = 15, R_(2) = 30, R_(3) = 60` |
|
| 39104. |
Three resistors R_1, R_2 and R_3 are to be combined to form an electrical circuit as shown in the figure. It is found that when R_1 R_2 and R_3 are put respectively in positions A, B and C, the effective resistance of the circuit is 70 OmegaWhen R_2, R_3 and R_1 are put respectively in position A, B and C the effective resistance is 35Omega and when R_3, R_1 and R_2 are respectively put in the position A, B and C, the effective resistance is 42 OmegaIf R_(1), R_(2) and R,_(3)are put in series, the effective resistance will be |
|
Answer» `210Omega` `(R_(2)R_(3)+R_(3)R_(1)+R_(1)R_(2))/(R_(2)+R_(3))35ldots(2)` `(R_(3)R_(1)+R_(1)R_(2)+R_(2)R_(3))/(R_(3)+R_(1))=42ldots(3)` `(R_(1)R_(2)+R_(2)R_(3)+R_(3)R_(1))=k` Then the system of three equation transforms to`R_(1)+R_(2)=(k)/(70)` `R_(2)+R_(3)=(k)/(35)R_(3)+R_(1)=(k)/(42)` Solving, this we get`R = k//210, R = k//105, R = 2k//105` implies`R_(1): R_(2): R_(3) = 1:2:4` So, let `R_(1) = x, R_(2) = 2X` and `R_(3) = 4x` PUTTING these VALUED in equation 1, we get`X = 15` `R_(1) = 15, R_(2) = 30, R_(3) = 60` |
|
| 39105. |
Three resistors R_1, R_2 and R_3 are to be combined to form an electrical circuit as shown in the figure. It is found that when R_1 R_2 and R_3 are put respectively in positions A, B and C, the effective resistance of the circuit is 70 OmegaWhen R_2, R_3 and R_1 are put respectively in position A, B and C the effective resistance is 35Omega and when R_3, R_1 and R_2 are respectively put in the position A, B and C, the effective resistance is 42 Omega The resistance R_(1): R_(2): R_(3 )are in the ratio |
|
Answer» 0.04380787037037 `(R_(2)R_(3)+R_(3)R_(1)+R_(1)R_(2))/(R_(2)+R_(3))35ldots(2)` `(R_(3)R_(1)+R_(1)R_(2)+R_(2)R_(3))/(R_(3)+R_(1))=42ldots(3)` `(R_(1)R_(2)+R_(2)R_(3)+R_(3)R_(1))=k` Then the SYSTEM of three equation transforms to`R_(1)+R_(2)=(k)/(70)` `R_(2)+R_(3)=(k)/(35)R_(3)+R_(1)=(k)/(42)` Solving, this we get`R = k//210, R = k//105, R = 2k//105` `impliesR_(1): R_(2): R_(3) = 1:2:4` So, let `R_(1) = x, R_(2) = 2x` and `R_(3) = 4x` Putting these valued in equation 1, we get`X = 15` `R_(1) = 15, R_(2) = 30, R_(3) = 60` |
|
| 39106. |
The path of a charged particle projected into a uniform transverse electric field is |
|
Answer» circle |
|
| 39107. |
A block of mass 2 kg is hanging over a smooth and light pulley through a light string. The other end of the string is pulled by a constant force F=40N. The kinetic energy of the particle increase 40 J in a given internal of time. Then |
|
Answer» tensionin the string is 40 N `(40-20)S=40 rArr S= 2m` Work done by gravity `=(-20)xx2=-40 J` Work done by tension `=40xx2=80 J` `:.` (A, B, D) 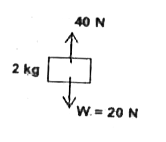
|
|
| 39108. |
A radioactive nucleus undergoes a series of decay according to the scheme. Aoverset(alpha)toA_(1)overset(beta)toA_(2)overset(alpha)toA_(3)overset(gamma)toA_(4). If the mass number and atomic number aer 180 and 72 respectively, the mass number (x) and atomic and atomic number (y) of A_(4) are |
|
Answer» x= 172: y = 72 |
|
| 39109. |
Figure shows a battery circuit with an unknown resistance x. If the value of x for maximum power dissipation in unknown resistance is 5/n Omega (n is an integer), find n |
Answer» 
|
|
| 39110. |
Define magnetic flux. |
|
Answer» Solution :The NUMBER of magnetic field LINES crossing per unit AREA is called magnetic FLUX `phi_(B)` . `phi_(B) = vec(B) vec(A) `= BA `cos THETA = B bot A ` |
|
| 39111. |
How many electrodes are there, in a transistor ? |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 39112. |
In optical fiber the refractive index of the material of the core is………. That of the cladding. |
|
Answer» HIGHER than |
|
| 39113. |
An isolated pole is _____ |
| Answer» SOLUTION :IMPOSSIBLE | |
| 39114. |
A prism object is placed 30 cm in front of an equiconvex lens of radius of curvature 15 cm and made of glass of refractive index (3)/(2). On placing a convex mirror of radius of curvature 15 cm behind the lens on image side, the final image is found to coincide with the object. The possible distance between convex lens and convex mirror is |
|
Answer» DEVIATION produced by FIRST prism is `(THETA)/(omega_(1))` |
|
| 39115. |
If the electric current flowing in wire BA is increasing, then what will be the direction of induced current in the loop shown in Fig. 6.17? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39116. |
There are four concentric spherical shells A, B, C and D of radii R, 2R, 3R and 4R respectively. Net charge on all the spherical shells are same and equal to Q. If V_(A), V_(B), V_C ) and V_(D) represent electric potentials of A, B, C and D respectively, the magnitude of V_(D)=V. |
|
Answer» `{:(P,Q,R,S),(1,3,2,4):}` In this given situation, the net charge on each spherical shell is Q, but due to induction phenomenon different charges will appear on both the inner and outer SURFACES of sphere but net charge is not going to change. We need not pay attention to induction of charge becausepotential depends only on the net charge. Total electric potential of sphere D can be written as follows: `V_(D)=(1)/(4pi epsilon_(0))[(Q)/(4R)+(Q)/(4R)+(Q)/(4R)+(Q)/(4R)]=(1)/(4pi epsilon_(0)) (Q)/(R )=V "" ...(i)` We can see that in the above case of sphere D, it is outside all the other spheres, so distance 4R is used due to all these spheres. But we should note that in case of other spheres it is not so. `V_(A)=(1)/(4pi epsilon_(0))[(Q)/(R )+(Q)/(2R)+(Q)/(3R)+(Q)/(4R)]` `=(25)/(12)(1)/(4pi epsilon_(0)) (Q)/(R )=(25)/(12)V "" ...(ii)` `V_(B)=(1)/(4pi epsilon_(0))[(Q)/(2R)+(Q)/(2R)+(Q)/(3R)+(Q)/(4R)]` `=(19)/(12)(1)/(4pi epsilon_(0)) (Q)/(R )=(19)/(12)V "" ...(iii)` `V_(C )=(1)/(4pi epsilon_(0))[(Q)/(3R)+(Q)/(3R)+(Q)/(3R)+(Q)/(4R)]` `=(5)/(4) (1)/(4pi epsilon_(0)) (Q)/(R )=(5)/(4)V "" ...(iv)` `V_(A)-V_(B)=(25)/(12)V-(19)/(12)V=(V)/(2)=(6V)/(12)` We can see that option (c ) is correct. |
|
| 39117. |
The focal lengths of objective and eye peace of a microscope are 1.25 cm and 5 cm respectively find the position of the object relative to the objective in order to obtain an angular magnification of 30 in normal adjustment |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :In NORMAL ADJUSTMENT `m_e=d/f_e=25/5=5` `m=m_0m_e` `m_0=m/m_e=30/5=6` `m_0=V_0/u_0=-6` `V_0=-6u_0` `1/v_0-1/u_0=1/f_0` `1/(-6u_0)-1/u_0=1/f_0` `f_0=1.25 CM` `u_0=-1.46 cm` |
|
| 39118. |
A capacitor with capacitance C and a coil with active resistance R and inductance L are connected in parallel to a source of sinusoidal voltage of frequency omega. Find the phase difference between the current fed to the circuit and the source voltage. |
|
Answer» Solution :We use the METHOD of complex voltage `V=V_(0)e^(iomegat)` Then `I_(C)=(V_(0)e^(iomegat))/( (1)/( iomegaC))=iomegaCV_(0)e^(iomegat)` `I_(L,R)=(V_(0)e^(iomegat))/( R+iomegaL)` `I=I_(C)+I_(L,R)=V_(0)(R-iomegaL+i omegaC(R^(2)+omega^(2)L^(2)))/(R^(2)+omega^(2)L^(2))e^(iomegat)` Then taking the REAL part `I=(V_(0)sqrt(R^(2)+{omegaC(R^(2)+omega^(2)L^(2))-omegaL}^(2)))/(R^(2)+omega^(2)L^(2))cos(omegat-varphi)` where` TAN varphi=( omegaL-omegaC(R^(2)+omega^(2)L^(2)))/(R)` 
|
|
| 39119. |
The magnetic susceptibility of a paramagnetic material at is 0.0075 and its value at will be |
|
Answer» 0.0075 |
|
| 39120. |
Two non-viscous, incomoressible and immiscible liquids of densities rho and 1.5 rho are poured into the two limbs of a circules tube of radius R and small cross-section kept fixed in a vertical plane as shown in fig. Each liquid occupies one-fourth the cirumference of the tube. (a) Find the angle theta the radius to the interface makes with the vertical in equilibrium position. (b) If the whole liquid column is given a small displacement from its equilibrium position, show that the resulting oscillations alre simple harmonic. Find the time period of these oscillations. |
|
Answer» Therefore `P_(1) = P_(2)` or `P + (1.5 p g h_(1)) = P + (rho g h_(2))` (`p =` pressure of gas in empty part of the tube) `:. 1.5 h_(1) = h_(2)` `1.5 [ R costheta - R SINTHETA] = rho (R costheta + R sintheta)` or `3 costheta - 3 sintheta = 2 costheta + 2 sintheta` or `5 TANTHETA = 1` `theta = tan^(-1)((1)/(5))` 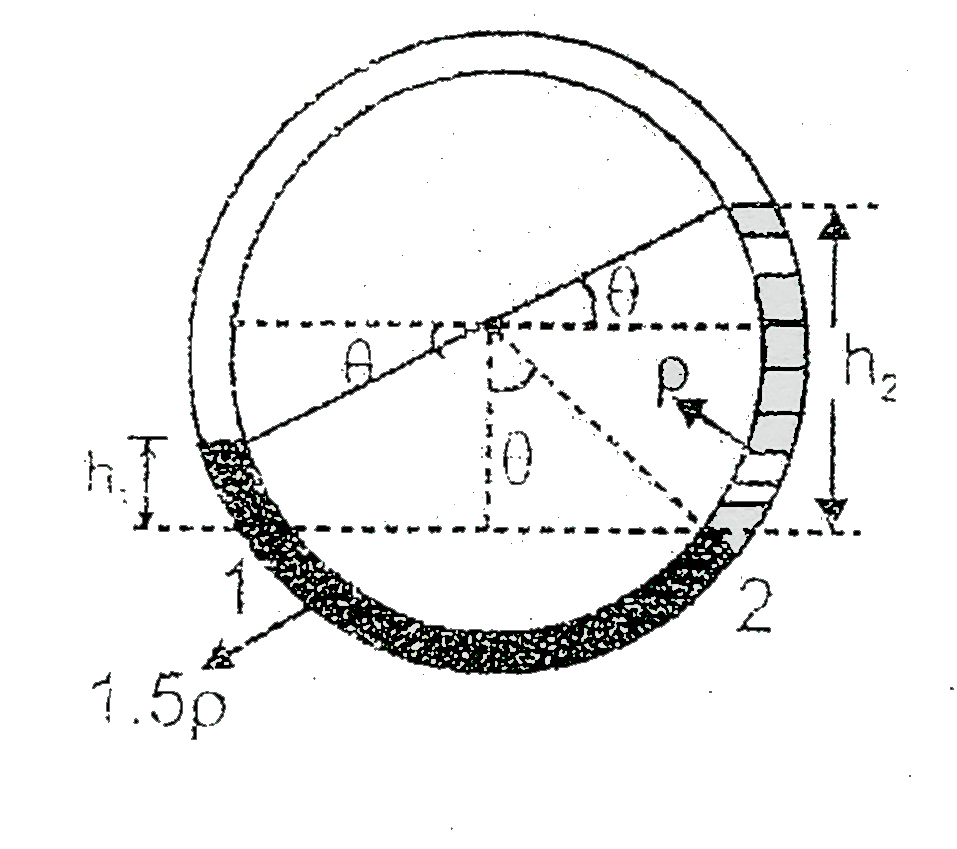 (b) When liquid are slightly disturbed by an angle `beta`. Net restoring pressure `DeltaP = 1.5 rhogh + rhogh` this pressure will be equal at all sections of the liquid. Therefore, net restoring torque on the whole liquid.  `h = R sin (theta + beta) - Rsintheta` or, `tau = -(DeltaP) (A) (R)` `tau = -2.5rhogh AR` `= - 2.5rhog AR [R sin (theta + beta) - R sintheta]` `= -2.5 rhog AR^(2) [ sintheta COSBETA + sinbeta costheta - sintheta]` Assuming `cos beta = 1` and `sinbeta = beta` (given, `beta` is small) `:. tau = -(2.5 rhoA gR^(2) costheta)beta` or `Ialpha = -(2.5 rhoAgR^(2) costheta)beta ....(1)` Here, `I = (m_(1) + m_(2))R^(2)`  `= [((piR)/(2).A)rho + ((piR)/(2)).A (1.5 rhop) ]R^(2)` `= (1.25 piR^(3)rho)A` and `costheta = (5)/(sqrt(26)) = 0.98` Substituting in equation `(1)`, we have `alpha = -((6.11)beta)/(R) rArr` angular acceleration `prop-`angular displacement As angular acceleration is propotional to `-beta`, motion is simple harmonic in nature. `T = 2pisqrt(|(beta)/(alpha)|) = 2pisqrt((R)/(6.11))` |
|
| 39121. |
The maximum force of static friction upto which body does not move is called |
|
Answer» NORMAL reaction |
|
| 39122. |
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction , it |
|
Answer» raises the potential barrier. |
|
| 39123. |
The image formed by a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm is one quarter of the size of object. The distance of object from the mirror is : |
|
Answer» 30 cm |
|
| 39124. |
A non-reletivistic proton enters a half-space along the normal to the transverse unifrom magnetic field whose induction equals B = 1.0 T. Find the raatio of the enrgy lost by the proton due to radiation during its motion in the field to its initial kinetic energy. |
|
Answer» Solution :For the semicicirular PATH on the right `(mv^(2))/(R ) = Bev` or `v = (BeR)/(m)`. THUS `K.E. = T = (1)/(2)mv^(2) = (B^(2)e^(2)R^(2))/(2m)` Power radiated `= (1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(2)/(3C^(3)) ((ev^(2))/(R ))^(2)` hence energy radiated `= DeltaW` `= (1)/(4piepsilon_(0)) (2)/(3c^(3)) ((B^(2)e^(3)R)/(m^(2)))^(2).(PIR)/(BeR)m = (B^(3)e^(5)R^(2))/(6epsilon_(0)m^(3)c^(3))` So `(DeltaW)/(T) = (Be^(3))/(3epsilon_(0)c^(3)m^(2)) = 2.06 xx 10^(-18)` (neglecting the change in `v` due to radiation, CORRECT if `DeltaW//T lt lt 1`). 
|
|
| 39125. |
Two point charges each of 5 muC but oppositein sign are placed 4cmfrom the mid pointon the axialline of dipole. |
|
Answer» `2a = 4cm = 4xx10^(-2)m, E = ?` `r = 4 cm = 4xx10^(-2) m`. `E_("axial") = (2 PR)/(4 pi in_(0) (r^(2) - a^(2))^(2)) = (2 (q) (2a) r)/(4PI in_(0) (r^(2) - a^(2))^(2))` `= (9xx10^(9)xx2(5xx10^(-6))(4xx10^(-2)) xx4xx10^(-2))/([0.04^(2) - 0.02^(2)]^(2))` `E_("axial") = 10^(8) NC^(-1)` |
|
| 39126. |
The height y and the horizontal distance x for a projectile at any instant t after it is projected at an angle theta with horizontal are given by eq. 2y = 16t - 10t^(2) and x = 6t metre when t is in sec. the velocity with which the projectile projected is : |
|
Answer» `6ms^(-1)` `implies ucostheta=6`…(i) and `2y=16t - 10T^(2)implies y=8t-5t^(2)` or `usintheta t-1/2g t=8t-5t^(2)` `impliesusintheta=8`…(II) Squaring and adding (i) and (ii) gives u=10m/s |
|
| 39127. |
Why average value of a.c is zero ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :As because a.c. is +ve during ONE HALF CYCLE and -ve during other half cycle. | |
| 39128. |
Consider the L-C-R circuit shown in the fiure. Find the net current I and the phase of i. Show that i=V/Z. Find the impedance Z of this circuit. |
|
Answer» So, we can write `i=i_(1)+i_(2)` `V_(m)SINOMEGAT=Ri_(1)`(from the circuit diagram) `i_(1)=(V_(m)sinomegat)/(R)`.............(i) If `q_(2)` is charge on the CAPACITOR at any time t, then for series combination of C and L. APPLYING KVL inthe Lower circuit as shown.  `q_(2)/C + (Ldi_(2))/(dt) - V_(m)sinomegat=0` `rArr q_(2)/C + (Ld_(2)q_(2))/(dt)^(2) = V_(m)sinomegat``[therefore i_(2)=(dq_(2))/(dt)]`......(ii) Let `q_(2) = q_(m) sin (omegat+phi)`..............(iii) `(dq_(2))/(dt) = q_(m)cos(omegat+phi)` `rArr (d^(2)q_(2))/(dt^(2))=-q_(m)omega^(2)sin(omegat+phi)` Now putting the values in Eq. (ii), we GET `q_(m)[1/C+l(-omega^(2))]sin(omegat+phi)=V_(m)sinomegat` If `phi = 0` and `(1/C-Lomega6(2)) gt 0,` then `q_(m)=v_(m)/(1/C-Lomega^(2))`..............(iv) From Eq. (iii), `i_(2) = (dq_(2))/(dt) = omegaq_(m)cos(omegat+phi)` Using Eq. (iv), `i_(2) = (omegaV_(m)cos(omegat+phi))/(1/C-Lomega^(2))` Taking `phi =0, i_(2)=(V_(m)cos(omegat))/(1/(omegaC)-Lomega)` From Eqs. (i) and (v), we find that `i_(1)` and `i_(2)` are out of phase by `phi/2` Now, `i_(1)+ i_(2) = (V_(m)sinomegat)/R + (V_(m)cosomegat)/(1/(omegaC)-Lomega)` Put `V_(m)/R = A = C cosphi` and `V_(m)/(1/(omegaC)-Lomega)=B = C sinphi` `therefore i_(1) + i_(2) = C cos phisinomegat+ C sinphi cos omegat` `= C =sqrt(A^(2) + B^(2)` and `phi=tan^(-1)B/AC = [V_(m)^(2)/R^(2) + (V_(m)^(2))/(1/(omegaC)-Lomega)]^(1//2)` and `phi = tan^(-1) =R/(1/(omegaC)-Lomega)` Hence, `i=i_(1)+i_(2)= [V_(m)^(2)/R^(2) + V_(m)^(2)/(1/(omegaC)-Lomega)^(2)]^(1//2)sin(omegat+phi)` or `i/V_(m)=1/Z =[1/R^(2)+1/(1/(omegaC)-Lomega)^(2)]^(1//2)` This is the expression for impedance Z of the circuit. |
|
| 39129. |
Direction : The questions 62 and 63 are based on following paragraph : de-Broglie wave associated with electron forms a standing wave when distance (d) between atoms of the array of material is 2Å. A similar standing wave is again formed, when distance is increased to 2.5Å. Least value of distance (d) for which standing wave can be formed is |
|
Answer» `0.2Å` `d=(nlambda)/(2)` `d_(1)=(nlambda)/(2),d_(2)=(n+1)lambda//2` `:. lambda//2=d_(2)-d_(1)` `rArr lambda=2(d_(2)-d_(1))` `rArr lambda=2(2.5-2)Å=1Å` `:.d_("min")=lambda//2=(1)/(2)Å=0.5Å` |
|
| 39130. |
Direction : The questions 62 and 63 are based on following paragraph : de-Broglie wave associated with electron forms a standing wave when distance (d) between atoms of the array of material is 2Å. A similar standing wave is again formed, when distance is increased to 2.5Å. Then energy of electron is |
|
Answer» 92.51 eV `=(1)/(2M)(h^(2))/(lambda^(2))=150.95eV` |
|
| 39131. |
Three capacitors each of capacity 10muF are connected in parallel. This combination is connected to a capacitor of capacity C in series so that the effective capacity is 12muF. Find the value of C. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39132. |
IfE_abe the electric field of a short dipole at a point on its axial line and E_e that on the equatorial line at the same distance ,then |
|
Answer» `E_(a)= 2E_e` |
|
| 39133. |
A conducting rod PQ of length L = 1.0m is moving with a uniform speed v= 2.0 m/s in a uniform magnetic field B = 4.0 T directed into the paper. A capacitor of capacity C = 10 mu Fis connected as shown in the figure. Then what are the charges on the plates A and B of the capacitor. |
|
Answer» Solution : The motional emf is `e = Blv` `therefore ` p.d across the capacitor ` = Blv = 4 xx 1 xx 2 = 8V` `q = CV= 10 xx 8 = 80 MU C` A is + Ve w.r.t B (from fleming right hand rule) The CHARGE on PLATE A is `q_A = + 80 mu C` The charge on plate B is `q_B = -80muC` |
|
| 39134. |
Demonstratethat thelaw of electriccharge conservation, i.e.,grad. J = -del rho//del t, follows fromMaxwell's equactions. |
|
Answer» Solution :From the equction `CURL vec(H) - (del vec(D))/(del t) = vec(j)` we get on takingdivergence of both sides `- (del)/(del t)` DIV `vec(D) = di v vec(j)` But div `vec(D) = rho` and hence div `vec(j) + (del rho)/(del t) = 0` |
|
| 39135. |
V_(1) and V_(2) are the stopping potentials for the incident radiations of wave lengths lamda_(1) and lamda_(2) respectively are incident on a metallic surface. If lamda_(1)=3lamda_(2) then |
|
Answer» `V_(1)gt3V_(2)` |
|
| 39136. |
Given the graph of velocity of material point as a function of time. The plot of acceleration of the particle as a function of time is given as: |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39137. |
Longitudinal progressive wave . |
| Answer» Solution :A PROGRESSIVE WAVE in which the VIBRATION of the individual particles of the medium is ALONG the line of propagation of the wave is called a longitudinal progressive wave . | |
| 39138. |
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in order in increasing frequency : gamma -rays, microwaves, infrared rays and ultraviolet rays. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MICROWAVES `lt` INFRARED rays `lt` Ultraviolet rays `lt``gamma`-rays. | |
| 39139. |
What are the different types of message signals used in a communication system? |
| Answer» Solution :The different type of MESSAGE signals are VOICE, MUSIC, PICTURE and computer data | |
| 39140. |
An alternating current can be converted into direct current by a |
|
Answer» RECTIFIER |
|
| 39141. |
A student has studied the use of Ampere’s law in calculation of magnetic field (B) due to a straight current carrying conductor of infinite length. Now she used similar arguments for calculation of B due to a current carrying conductor (AB) of finite length. She assumes a closed circular path (C) of radius r with the conductor along the axis (see fig.). She argues that because of symmetry the field (B) shall be tangential to C and must have same magnitude at all points on C. Therefore she writes B =(mu_(0)I)/( 2pir)Do you support the answer? Give reasons. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39142. |
The enrgy The energy reqduired to accelerate a car from 10 m/s to 20 m/s compared with that required to accelerate from 0 to 10 m/sec in the same interval of time overcoming same resistance is : |
|
Answer» twice |
|
| 39143. |
A doubly ionized lithim atom is hydrogen like with atomic number 3. Find the wavelength of the radiation required to excite the electron inLi^(2+) from the first to the third Bohr orbit. The ionization energy of the hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV. (Take hc=1240 eV nm) |
|
Answer» 11.4nm For ` Li^(2+) , Z =3 , E_(n) = (122.4)/(n^(2))eV` ` E_(1) = (122.4)/(I)^(2) = -122.4e V and E_(3) = - (122.4)/((3)^(2)) =-13.6 eV` ` thereforeDelta E = E_(3)-E_(1) = 108.8 eV` THe correspondingwavelength is ` lamda = (hc)/(Delta E) = (1240 eV nM)/( 108.8 eV) = 11.4 nm` |
|
| 39144. |
A particle of mass m and charge + q enters horizontally with speed V_(0) midway between the horizontal plates of a parallel plate capacitor at time t = 0. Separation between the capacitor plates is ‘d’ and it starts getting charged, by a constant current source, at time t = 0. Plate area of the capacitor is A. It was found that the particle just misses (to hit) the lower plate. Assume that the plates are quite long and acceleration due to gravity is g. (a) Give a rough sketch of the path of the particle. (b) Find the constant current (i_0) supplied by the source to the capacitor. Consider no magnetic force on the charge |
|
Answer» (B) `i_(0)=(2mgAin_(0))/(q)sqrt((g)/(3d))` |
|
| 39145. |
Explain experiment which represents the total internal reflection. |
|
Answer» Solution :Take a glass beaker with clear water in it. Stir the water a few times with a piece of soap, so that it becomes a little turbid. Take a laser pointer and shine its BEAM through the turbid water. You will find that the path of the beam inside the water shines brightly.  Shine the beam from below the beaker such that it strikes at the upper water surface at the other end it undergoes partial reflection which is seen as a spot on the table below and partial refraction which comes out in the air and is seen as a spot on the roof figure (a). Now direct the laser beam from ONE side of the beaker such that it strikes the upper surface of water more obliquely figure (b). Adjust the direction of laser beam until you find the ANGLE for which the refraction above the water surface is totally absent and the beam is totally reflected back to water. This is total internal reflection at its simplest. Pour this water in a long test tube and shine the laser light from top as shown in figure (C). Adjust the direction of the laser beam such that it is totally internally reflected EVERY time it strikes the walls of the tube. This is similar to what happens in optical fibres. Note: Take care not to look into the laser beam directly and not to point it at anybody.s face. |
|
| 39146. |
भोजन विषाक्तता (food poisoning) के लिए निम्नलिखित में से कौन उत्तरदायी है ? |
|
Answer» जैन्थोमोनस सिट्री |
|
| 39147. |
A non-conducting charged ring of charge q. mass m and radius r is rotated with constant angular speed omega. Find the ratio of its magnetic moment with angular momentum is ............. . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`q/(2m)` | |
| 39148. |
Simplify Y=AB+ABC+barAB+AbarBC using Boolean Algebra. Draw the resultant simplified logic circuit. |
|
Answer» Solution :GIVEN `Y=AB+ABC+barAB+AbarBC` `Y(A+barA)+AC(B+barb)Y=B+AC(because B+barb=1)` LOGIC CIRCUIT is shown below. 
|
|
| 39149. |
What is Sardar Kishan Singh careful about? |
|
Answer» About his wife |
|
| 39150. |
Preferential filtering of light consisting of different wavelengths can be done using total internal reflection. The concept of filtering lies in the fact that different wavelengths have different refractive indices in a medium The beam of light with different wavelengths are made incident on an isosceles right angled prism as shown in the figure. The wavelength or wavelengths which satisfy the condition of totai internal reflection, theta sin ge(1/mu), get reflected Others get refracted, hence gets separated. G is the angle of incidence and u. is the refractive index .of the particular wavelength in that particular medium. Thus, by changing the medium and by changing the angles of the prism we can satisfy the condition df total internal reflection for a particular wavelength, which gets separated out. QWhich of the following does not affect the filtering process? |
|
Answer» MATERIAL of the prism |
|