Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 351. |
Assertion: Polaroids are used to polarise as well as analyse place polarised light. Reason: Polaroids reduce the intensity of light to zero. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ASSERTION is CORRECT but reason is false. A polaroid allows those light VIBRATIONS to pass through it which are parallel to its AXIS. | |
| 352. |
Statement-I: Average of sinusoidal A.C. can never be zero for half cycle. Statement-II: Impedance given by inductance does not depends on frequency |
|
Answer» If both STATEMENT- I and Statement- II are TRUE, and Statement - II is the correct EXPLANATION of Statement– I. |
|
| 353. |
Which combination of resistance gives maximum current ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :PARALLEL COMBINATION. | |
| 354. |
The de Broglie wavelength associated with an electron accelerated by a potential of 64 V is |
|
Answer» a)1.227 NM |
|
| 355. |
When a dielectric medium is introduced between the plates has a capacitance 'C', If the oil is removed, then its capacitor becomes |
|
Answer» REMAINS constant |
|
| 356. |
Find the wavlength of the K_(alpha) line in copper (Z=29) if the wavelength of the K_(alpha) line in iron (Z=26) is known to be equal to 193 p m. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :From Moseley's LAW `omegak_(alpha)=(3)/(4)R(Ƶ-1)^(2)` or `lambdak_(alpha)=(4)/(3R)(1)/((Ƶ-1)^(2))` Thus `(lambdak_(alpha)(Cu))/(lambdak_(alpha)(Fe))=((25)/(28))^(2)=((Ƶ_(Fe)-1)/(Ƶ_(cu)-1))^(2)` Substitution gives `lambdak_(alpha)(Cu)= 153.9p m` |
|
| 357. |
A wave travelling along the x-axis is described by the equation y(x,t) = 0.005cos(alphax - betat) . If the wavelength and the time period of the wave are 0.08m and 2.0s, respectively, then alpha/beta = n xx 5, then the value of n is ……………….. (where alpha, beta are in appropriate units). |
|
Answer» |
|
| 358. |
The electric field for p-n junction is 1xx10^(6) V/m and depletion region is 5000 Å wide then the potential barrier = …… V. |
|
Answer» 0.05 `E=(V)/(d)` `THEREFORE V=Ed=1xx10^(+6)xx5000xx10^(-10)` `therefore V=0.5V` |
|
| 359. |
A block of mass 0.1 kg is connected to an elastic spring of spring constant 640" Nm"^(-1) and oscillates in a medium of constant 10^(-2)" kg s"^(-1). The system dissipates its energy gradually. The time taken for its mechanical energy of vibration to drop to half of its initial value, is closest to : |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 360. |
Find out the value of current through 2Omega resistance for the given circuit. |
| Answer» Solution :RESISTANCE of `2Omega` does not belong to any CIRCUIT where in a SOURCE of emf is CONNECTED. Hence no current FLOWS through it. | |
| 361. |
(a) Write two distinguishing features of nuclear forces. (b) Complete the following nuclear reactions for a and B decay: (i) " "_(92)^(238)Uto ? +" "_(2)^(4)He +Q (ii) " "_(11)^(22)Na to " "_(10)^(22)Ne +?+nu |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Two distinguishing features of nuclear forces are as follows : 1. Nuclear forces are extremely short range forces. 2. Nuclear forces are charge independent. (b) The COMPLETED nuclear reactions are as given below : (i) `" "_(92)^(238)Uoverset(-ALPHA)(to) " "_(90)^(234)Th +" "_(2)^(4)He +Q` (II) `" "_(11)^(22)Na overset(-BETA^(+))(to) " "_(10)^(22)Ne +" "_(+1)^(0)e+nu` |
|
| 362. |
The energy of a photon of light of wavelength 66 eV is |
|
Answer» `4.4 XX 10^(-19)` |
|
| 363. |
When you have learned to integrate derive the formula to calculate the work of expansion of a gas at constant temperature. |
|
Answer» <P> SOLUTION :The work DONE by a gas expanding by a gas expanding at constat temperature is`W = int_(v_1)^(v_2) p DV = m/M RT int_(v_1)^(v_2) (dV)/(V) = m/M RT ln (V_2)/(V_1) = p_1V_1 ln (V_2)/(V_1)`. |
|
| 364. |
e) When viewing through a compound microscope, our eyes should be positioned not on the eyepiece but a short distance away from it for best viewing. Why? How much should be that short distance between the eye and eyepiece ? |
|
Answer» Solution :e) The IMAGE of objective lens in eye pie is called 'eye ring' All the rays from the object REFRACTED by the objective go through the eye ring. Therefore, ideal position for our eyes for VIEWING is this eye ring only. When eye is too close to the eye piece, field of view reduces and eyes do not collect much of the light. The precise. location of the eye ring WOULD depend upon the separation between the objective and eye piece, and also on focal length of the eye piece. |
|
| 365. |
Draw an OR gate using two diode and explain its operation. Write the truth table and logic symbol of OR gate. |
Answer» Solution :OR Gate `:` It has two input terminals and one output terminal.If both inputs are low the output is low. If one of the inputs is high, or both the inputs are high then the output of thegate is high.The truth tables of OR gate. In truth table logicfunction is written as A or B 'OR' logic function is represented by the symbol 'plus' `Q = A+B ` Logic gate 'OR' is shown given below . Implementation of OR gate using diode `:` Let `D_(1)` and `D_(2)` be two DIODES. A potential of 5V represents the logical value 1 A potential of 0V REPRESENTES the logicalvalue 0. When A=,B=0 both the diodes are reverse BIASED and there is no current through the resistance .So, the potential at Q is zero i.e., Q = 0 . When A=0 or B =0 and the other equal to a potential of 5Vthe diode whose anode is at a potential of 5V is forward-biasedand that diode behaves like a closed switch. The output potential then becomes5V i.e., Q =1.When both A and B are 1, both the diodes are forward -biased and the potential at Q is same as that at A and Bwhcih is 5V i.e., Q =1 . The output is same as that of the OR gate. 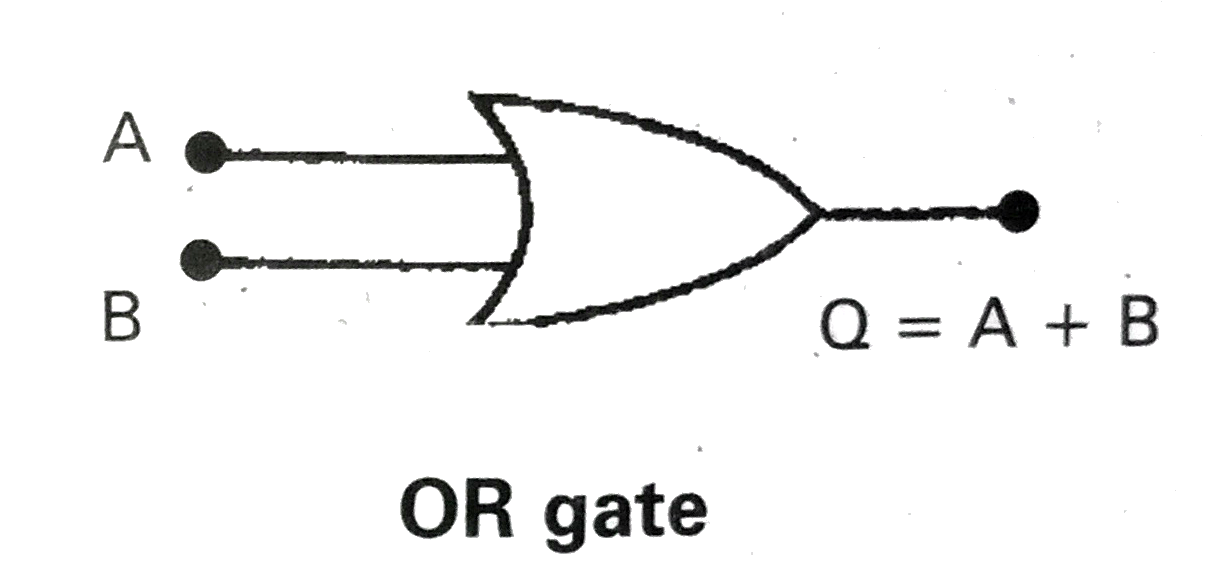 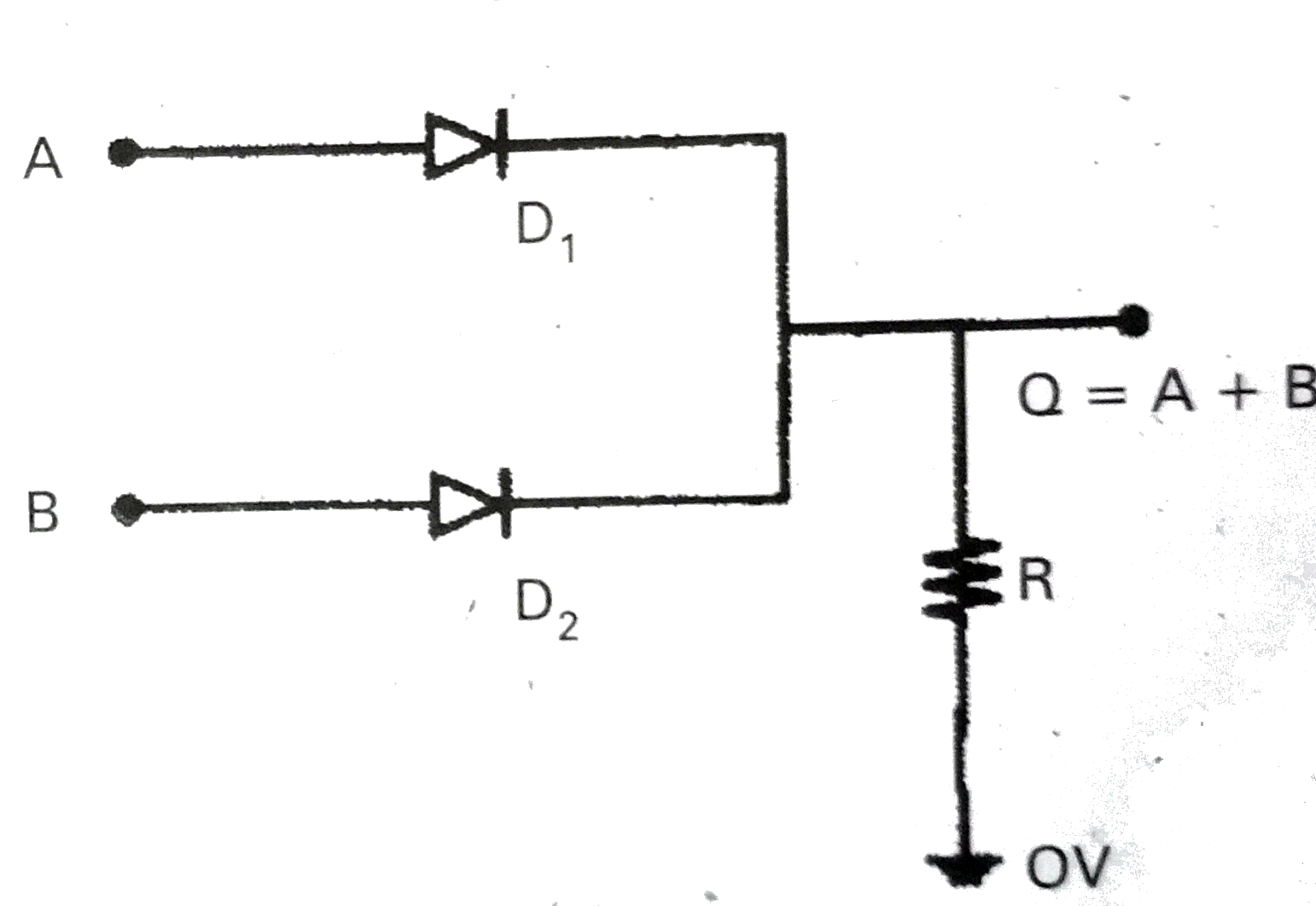
|
|
| 366. |
Which is more efficient mode of transmission FM or AM? |
| Answer» Solution :FM TRANSMISSION is more efficient because all the transmitted power is USEFUL but in AM transmission most of the power GOES waste in transmitting the carrier ALONE. | |
| 367. |
Is ohm's law true for all conductors ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :No. it is only true for metallic CONDUCTORS provided physical CONDITIONS does not CHANGE. | |
| 368. |
The relation between mu_r andX_m is mu_r=1+X_m How will you arrive at this relation ? Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :We have total MAGNETIC INDUCTION `B=B_0+B_m` where `B_0` - magnetic induction in FREE SPACE. `B_0=mu_0H,B_m=mu_0I and B=muH "":. muH=mu_0H+mu_0I` But `MU =mu_rmu_0 "":.mu_rmu_0H=mu_0H+mu_0I` `mu_rH=H+I=(H+I)/H=1+I/H=1+X_m:.mu_r=1+X_m` |
|
| 369. |
A constant horizontal force of 20N acts on a body on a smooth horizontal plane. The body starts from rest and is observed to move 20 m in two seconds. The mass of the body is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 370. |
Which of the following are polynomials- |
|
Answer» `F(X)=X^2-3X+2` |
|
| 371. |
In a magnetic field vecB=hati+yhatj+3hatk a charge particle (q, m) is moving with velocity vecV=2hati+3hatj+zhatk experiences a force vecF=-hati+2hatj+hatk. The value of y and z may be |
|
Answer» y=4, z=2 |
|
| 372. |
Arrange the following electromagnetic radiations per quantum in the order of increasing energy :A : Blue lightB : Yellow lightC : X - rayD : Radiowave |
|
Answer» D, B, A, C `= (hc)/(LAMBDA)` (hc = CONSTANT) `prop (1)/(lambda)` Arranging in decreasing order of wavelength Radiowaves `gt` Yellow light `gt` Blue light `gt` X - rays Hence quantam energy `THEREFORE`Arrange quantum energy in increasing order. Radiowaves `gt` Yellow light `gt` Blue light `gt` X - rays `D gt B gt A gt C`. |
|
| 373. |
The current in the primary circuit of a potentiometer wire is 0.5 A. Specific resistance of wire is 4 xx 10^(-7) Omega m and area of cross section of wire is 8 xx 10^(-6) m^(2). The potential gradient on the wire would be |
|
Answer» 2.5 m V/m POTENTIAL gradient `sigma= (I rho)/(A) = (0.5 xx 4 xx 10^(-7))/(8 xx 10^(-6))` `therefore sigma = 0.25 xx 10^(-1) = 25 xx 10^(-3)` `therefore sigma = 25 ` m V/m |
|
| 374. |
When the electrical conductivity of a semi-conductor is only due to the breaking of its covalent bonds, then the semiconductor is said to be |
|
Answer» Donor |
|
| 375. |
The following fusion reaction take place 2_1^2Ararr_2^3B+n+3.27MeV. If 2 kg of ._1^2Ais subjected to the above reaction,the energy released is used to light a100 Wlight a lamp, how long will the lamp glow ? |
|
Answer» `7xx10^(3)` years |
|
| 376. |
Obtain the formula for the electric field due to a long thin wire of uniform linear charge density lambda without using Gauss's law. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let us consider a long thin wire of linear charge density `lambda`. We have to find the RESULTANT electric field due to this wire at point P. Now, consider a very small element of length dx at a distance x from C. 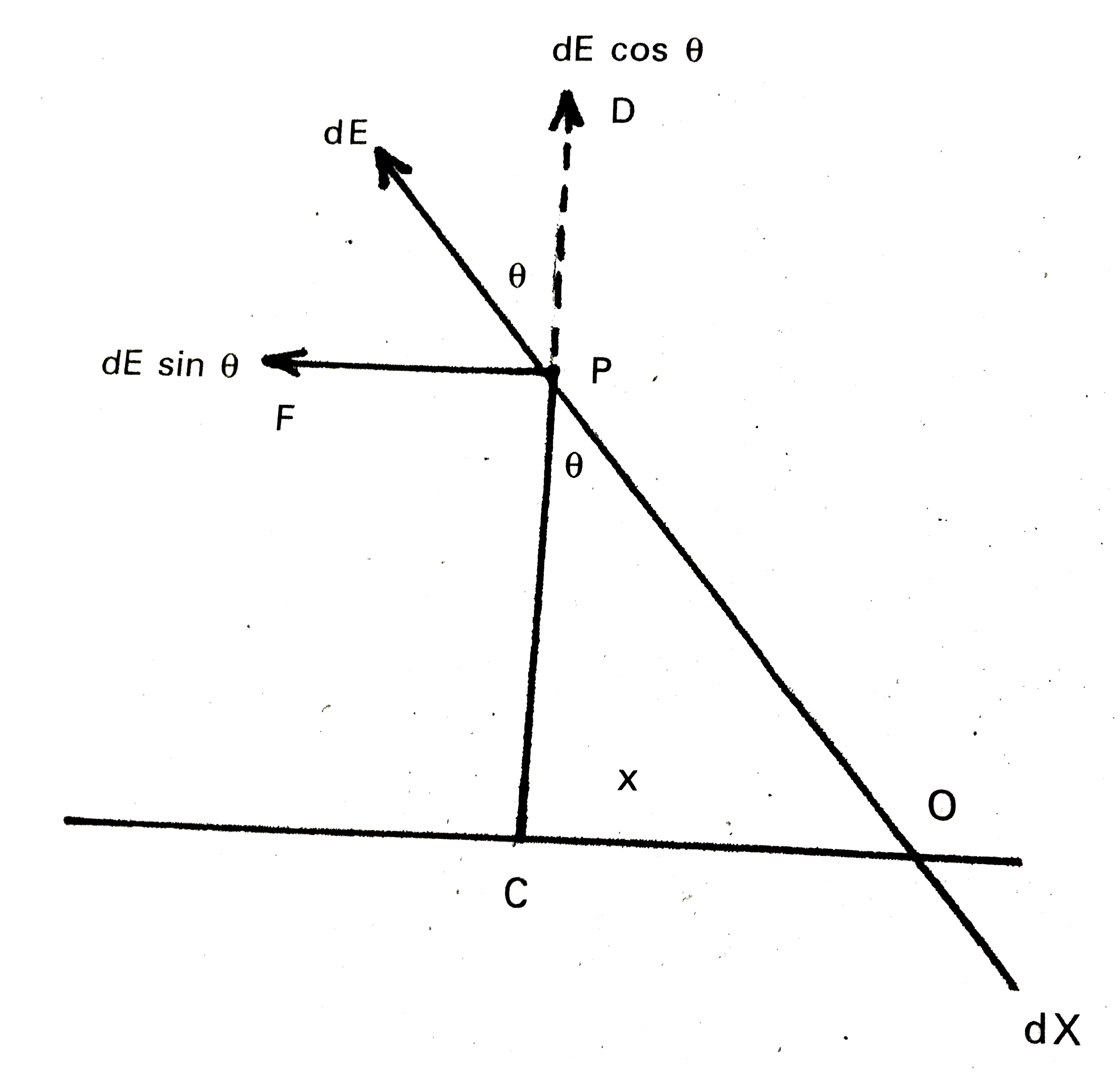 The charge on this ELEMENTARY portion of length dx `q = lambda dx` ...(1) Electric field intensity at point P due to the elementary portion `DE=1/(4pi epsi_(0)). q/((OP)^(2))=1/(4pi epsi_(0)) (lambda dx)/((OP)^(2))` [` :'` from (1)] Now, in `Delta PCO""(PO)^(2)=(PC)^(2)+(CO)^(2)` `(OP)^(2)=r^(2)+x^(2)` `dE=1/(4pi epsi_(0)) (lambda dx)/((x^(2)+r^(2)))` ...(2) The components of dE are `dE cos theta` along PD and `dE sin theta` along PF. Here, there are so many elementary portion. So all the `dE sin theta` components balance each other. the resultant electric field at P is due to only `dE cos theta` components. The resultant electric field due to elementary component, `dE'=dE cos theta` `dE'=1/(4pi epsi_(0)). (lambda d x)/((x^(2)+r^(2))) cos theta` ...(3) In `Delta OCP tan theta=x/r implies x =r tan theta` Differentiation with respect to `theta`, we get `dx= r sec^(2) theta d theta` Putting in equation (3), we get `dE'=1/(4pi epsi_(0)) (lambda.r sec^(2) theta d theta cos theta)/((r^(2)+r^(2) tan^(2) theta))` `dE'=1/(4pi epsi_(0)) (lambda.r sec^(2) theta d theta cos theta)/(r^(2) sec^(2) theta)` `dE'=1/(4pi epsi_(0)). lambda/r cos theta d theta` As the wire os of infinite length, so integrate WITHIN the limits `-pi/2` to `pi/2`, we get `E'=int dE'=1/(4pi epsi_(0))lambda/r underset(-pi//2)overset(pi//2)(int)cos theta d theta` `E'=1/(4pi epsi_(0)).lambda/r[sin theta]_(-pi//2)^(pi//2)=1/(4pi epsi_(0)) lambda/r ["sin"pi/20sin(-pi/2)]` `E'=1/(4pi epsi_(0)) lambda/r [1+1]` `E'=(2 lambda)/(4pi epsi_(0) r)` `:. E'=lambda/(2pi epsi_(0) r)` |
|
| 377. |
Show thatn=(sin((A+D)/(2)))/(sin((A)/(2))) where symbols have their usual notations. |
|
Answer» Solution :BC - Base of the prism AB and AC - Refracting sides representing the planes ABC - Principle section of prism. PQ - incident ray. RS - emergent ray `d_(1)` - angle of deviation `d_(1)=i_(1)-r_(1)` `d_(2) ` - angle of deviation`d_(2)=i_(2)-r_(2)` `u hatTS `- d - total angle of deviation or net deviation i.e., `d=d_(1)+d_(2)` (exterior angle = sum of two opposite interior angles) 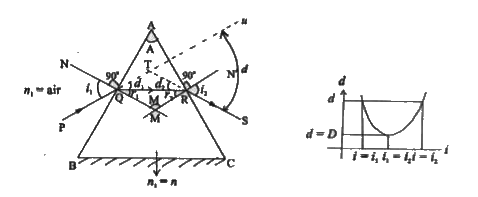 NM is normal to AB at Q N.M is normal to AC at R `i_(1)`- angle of incidence `i_(2)` - angle of emergence. D = angle of minimum deviation, From figure (1) From the quadrilateral AQMR, `A hatQM~=A hatRM=90^(@)` (Nm, N.M are normal to AB and BC) So that `A+M=180^(@)""` ......(1) `THEREFORE `AQMR is a cyclic quadrilateral. From the triangle QMR `r_(1)+r_(2)+hatM=180^(@)("Property of a "Delta) "" `......(2) From (1) and (2) `A+M=r_(1)+r_(2)+M` i.e.,`A=r_(1)+r_(2)""`.......(3) For non-symmetric condition `i_(1) ne i` `d_(1) ne d_(2)` also net deviationd. `d=d_(1)+d_(2)` `d=i_(1)-r_(1)+i_(2)-r_(2)` `therefored=i_(1)+I_(2)-(r_(1)+r_(2))` using (3) we write, `d=i_(1)+i_(2)-A""`.......(4) from the fig., we note that for non-symmetric condition for two angles of incidence, angle of net deviation is the same. However for a symmetric condition, `i_(1)=i_(2)=i and r_(1)=r_(2)=r` net deviation becomes the minimum angle of deviation. In this case the refracted ray will be parallel to the base. `therefore` for symmetric condition, (4)can be written as `D=2i-A` i.e., `i=((A+D)/(2))""` ......(5) (3) can be written as, `A=2r` or`r=((A)/(2))"" ` ......(6) From Snell.s law of refraction at AB, |
|
| 378. |
A battery of emf 10 V internal resistance 3 Omega is connected to a resistor R. (i) If the current in the circuit is 0.5 A. calculate the value of R. (ii) What is the terminal voltage of the battery when the cirucit is closed. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`I=(E)/(R+r)or` `R=(E)/(I)-r-(10)/(0.5)-3=17Omega` `V=IR=0.5xx17=8.5V`. |
|
| 379. |
A radio active isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to 3.125% |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 5 T YEARS (B) 6.65 T years | |
| 380. |
The quantities of heat required to raise the temperatures of two copper spheres of radii r_(1) and r_(2) (_(1)=1.5 _(2)) through 1 Kare in the ratio of |
|
Answer» Solution :REQUIRED heat, `Q prop ^(2)` where R is the radius. `therefore (Q_(1))/(Q_(2))=(r_(1)^(2))/(r_(2)^(2))` `(Q_(1))/(Q_(2))=((1.5)^(2))/((1)^(2))` `(Q_(1))/(Q_(2))=(9)/(4)`. So, CORRECT choice is (b). |
|
| 381. |
A vessel of capacity V_0 contains n molecules. Calculate the probability of all the molecules assembling in a part of the vessel V lt V_0. |
|
Answer» `p = V/(V_0) , q = 1 - p = (V_0 - V)/(V_0)`  In the present problem k = n, i.e. all the molecules are contained inside V. The answer is obtained from the solution of Problem 18.5. For a large number of molecules the probability of such an event is negligible. Second method. The problem may be solved without the binomial distribution, bul directly on the basis of the THEOREM for compound probability. Spocificully, the probability of finding a molecule inside the given volume is `p = V//V_0)`. The probability of finding simultaneously all the n molecules in it is the PRODUCT of the INDIVIDUAL probabilities : `w = p^n = (V//V_0)^n` |
|
| 382. |
The magnetic flux linked with a coil varies with time as phi=5t^2-4t+16 weber The induced emf in the circuit of t=0.2s is |
|
Answer» 0.4V |
|
| 383. |
Draw circuit diagram for a full wave rectifier and show input output voltages. |
|
Answer» Solution :Rectification. Rectification is the process of converting alternating voltage/current into direct voltage/current. A device used for this purpose is called rectifier and this phenomenon is called rectification. Principle. It is based on the principle that a p-n junction diode conducts when it is forward biased and does not CONDUCT when it is reverse biased. Construction. The apparatus for rectification consists of TWO diodes `D_(1)` and `D_(2)` connected to two ends of the secondary of a step down transformer. Output is TAKEN out from mid point of the secondary and common point N of two diodes. Ouput is taken out from ends of the load R.  Working. During the positive HALF of input `AC,D_(1)` is forward biased and `D_(2)` reverse biased. Hence the current FLOWS through the upper circuit as shown. During negative half, lower portion `(D_(2))` is forward biased and upper `(D_(1))` is reverse biased. Thus during each half, we get the current either from `D_(1)` or from `D_(2)`. The output voltage is unidirectional having ripple contents. Ripple factor of a rectifier `=("r.m.s of a.c.component")/("value of d.c. component")` To smoothen the output electric filters are used. The electric filters are combination of inductors are capacitors. Some of the useful filters are L-filter and `pi`-filter. |
|
| 384. |
A shell fired a cannon with speed v m/s at angle theta with horizontal explodes into three pieces of equal masses at the highest point of trajectory. One piece falls down vertically while the other retraces its path. What is speed of the third piece ? |
|
Answer» Solution :If .m. is mass of SHELL, at highest point, INITIAL momentum `= m(v COS theta)`, along horizontal given, momentum of one fragment `=(m)/(3)(-v cos theta)` momentum of second along horizontal = 0 If `.v_(1).` is speed of third fragment, from momentum conservation `-(m)/(3)v cos theta +(m)/(3)v_(1)+0=m(v cos theta)`, `v_(1)=4v cos theta` |
|
| 385. |
What is the effect on the current measuring range of a galvanometer when it is shunted? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INCREASED. | |
| 386. |
If vecP and vecQ denote the sides of parallelogram and its area is (1)/(2)PQ, then the angle between vecP and vecQ is |
|
Answer» `0^(@)` or sin `theta=(1)/(2) or theta =30^(@)` |
|
| 387. |
A dynamo converts |
|
Answer» a. MECHANICAL ENERGY into thermal energy |
|
| 388. |
A proton and a deutron are acclerated through the same accelerating potential. Which one of the two has (a) Greater value of de-Broglie wavelength associated with it, and (b) Less momentum ? Given reason to justify your answer. |
|
Answer» Solution :For an ACCELERATION potential V the de-Broglie WAVELENGTH of a charged particle of CHARGE q and mass m is given by `lamda=(h)/(sqrt((2mqV)))` and momentum of particle `p=sqrt(2mqV)`. As mass of DEUTRON is greater than that of proton i.e., `m_(D) gt m_(P)`, hence we conclude that (a) de-Broglie wavelength of proton is greater than that of deutron, and (b) momentum of proton is less than that of deutron. |
|
| 389. |
The electrical resistance of pure platinum increases linearly with increasingtemperature over a small range of temperature . This property is used in a Platinum resistance thermometer. The relation between R_(theta) (Resistance at theta K) and R_(0) (Resistance at theta_(0)K) is given by R_(theta)=R_(0)[1+a(theta-theta_(0))], where alpha= temperature coefficient of resistance. Now, if a Platinum resistance thermometer reads 0^(@)C when its resistance is 80Omega and 100^(@)C when its resistance is 90 Omega find the temperature at which its resistance is 86Omega. |
|
Answer» Solution :Using the GIVEN relationship we have `(90-80)OMEGA=alpha(80 Omega)(100)`………..(i) `(86-80)Omega=alpha(80 Omega)(theta)`………..(ii) where `theta` is the desired TEMPERATURE. TAKING the RATIO of (i) and (ii) `10/6=100/(theta)impliestheta=60K` |
|
| 390. |
The maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons from a surface depends on the ____ of incident radiation as well as the _____of the given surface. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :FREQUENCY, WORK FUNCTION (or NATURE). | |
| 391. |
Find the potential difference between and N in the given branch of a circuit figure. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let us have a closed CIRCUIT by joining to N with dotted lines. Let the potentials at M and N be `V_(M)` and `V_(N)` respectively. Following counter clockwise direction and applying Kirchhoff.s SECOND LAW, we get `(V_(N)-V_(M))-4+(0.4xx1)+(0.4xx2)-6(0.4xx1)+(0.4xx6)=0` `(V_(N)-V_(M))-10+0.4+0.8+0.4+2.4=0` `V_(N)-V_(M)=6V` |
|
| 392. |
For any particular medium the refractive index is greater if the wavelength of light is _________ [Fill in blank]. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 393. |
A message signal of frequency 10 kHz and peak voltage of 10 volts is used to modulate a carrier of frequency 1 mHz and peak voltage of 20 volts Determine (a) modulation index, (b) the side bands produced. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) modulation INDEX = `10//20=0.5` (b) The side BANDS are at (1000+10 KHZ) = 1010 kHz and (1000-10 kHz) = 990 kHz. |
|
| 394. |
Two beams P and Q of light of the same wavelength fall upon the same metal surface causing photoemission of electrons. The photoelectric current produced by P is four times that produced by Q. Which of the following gives the ratio ("wave amplitude of beam P")/("wave amplitude of beam Q")? |
| Answer» Solution :`("WAVE amplitude of beamP")/("Wave amplitude of beam Q")=(("CURRENT of P")^(1//2))/(("Current of Q")^(1//2))=((4)/(1))^((1//2))=2` | |
| 395. |
Establish a relation for electric potential due to short dipole at a point distance r from the dipole along a line inclined at an angle theta from the dipole axis . Hence obtain value of electric potential at a point lying along (i) axial line , (ii) equatoral line of the dipole . |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Consider a short electric dipole AB consisting of two charges of `-Q` and `+q` separated by a small distance AB = 2a . The dipole has a dipole moment `vecp` whose magnitude is q (2a) and which points along AB .Let P be a point at a distance r from mid-point O of electric dipole and line OP subtends an angle `theta` from the dipole axis . Then electric potential at point P is given by `V = V_(A) + V_(B) = (q)/(4 pi in_(0) (AP)) + (q)/(4 pi in_(0) (BP))` Draw normals BC and AD from points B and A respectively on extended line PO. As dipole is a short dipole , hence as shown in fig. 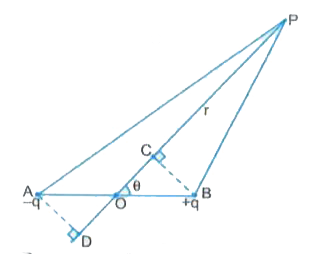 `BP = CP = OP - OC = r - a cos theta` and `AP = DP = OP + OD = r + a cos theta` `therefore V = (q)/(4 pi in_(0) (r + a cos theta)) + (q)/(4 pi in_(0) (r - a cos theta)) = (q)/(4pi in_(0)) [ (1)/((r - a cos theta)) - (1)/((r + a cos theta))]` `= (q)/(4pi in_(0)) (2 a cos theta)/((r^(2) - a^(2) cos^(2) theta)) = (p cos theta)/(4 pi in_(0) (r^(2) - a^(2) cos^(2) theta)) = (vecp * vecr)/(4 pi in_(0) (r^(2) - a^(2) cos^(2) theta))` As `a lt lt r` hence the TERM `a^(2) cos^(2) theta` may be neglected as compared to `r^(2)` and so we have `V= (p cos theta)/(4 pi in_(0) * r^(2)) = (vecp * vecr)/(4pi in_(0) r^(2))` Important cases to be remembered are (i) If point P lies along axial line of dipole towards `+q` charge , then `theta = 0^(@)` and hence `V= (p)/(4 pi in_(0) * r^(2))` (ii) If point P lies along axial line of dipole towards `-q` charge , then `theta = 180^(@)` and hence `V = (p)/(4 pi in_(0) r^(2))` (iii) If point P lies along equatoral line of dipole then `theta = 90^(@)` and hence V = 0 |
|
| 396. |
The S.I. unit of latent heat is |
|
Answer» `JKG^(-1)` |
|
| 397. |
How we define wave optics ? |
| Answer» Solution :The branch of OPTICS concerned with the nature of light and primarily the THEORY of WAVES is called WAVE optics. | |
| 398. |
A narrow slit is illuminated by a parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength lamda equals to 6000 Å and the angular width of the central maxima in the resulting diffraction pattern is measured. When the slit is next illuminated by light of wavelength lamda, the angular width decreases by 30%. calculate the value of the wavelength lamda. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 399. |
When a coil is connected to a D.C source of emf 12V, a current of 4 amp flows in it. If same coil is connected to 12V, 50Hz AC source, the current is 2.4 A. The self inductance of the coil is |
|
Answer» `(1)/(20pi)` |
|
| 400. |
Which radiation in sunlight, causes heating effect |
|
Answer» Ultraviolet |
|