Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 7301. |
The focal lengths of the objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope are 11 cm and 2 cm, respectively and the separation between them is 15 cm. At what distance should an object be placed so that the final image is formed at a distance of 25 cm from the eyepiece. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7302. |
If force =(X)/(density)+C is dimensionally correct, the dimensions of X are : |
|
Answer» `MLT^(-2)` `:.X=`Force `XX` density or `X=[MLT^(-2)xxML^(-3)]` `=[M^(2)L^(-2)T^(-2)]` `:.(d)` is correct. |
|
| 7303. |
The way the fringe pattern changes when the screen is moved away from the slits is |
|
Answer» WIDTH of FRINGS increases |
|
| 7304. |
A round cone with half-angle alpha=30^@ and the radius of the base R=5.0cm rolls uniformly and without slipping over a horizontal plane as shown in fiugre. The cone apex is hinged at the point O which is one the same level with the point C, the cone base centre. The velocity of point C is v=10.0cm//s. Find the moduli of (a) the vector of the angular velocity of the cone and the angle it forms with the vertical, (b) the vector of the angular acceleration of the cone. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Let the axis of the cone (OC) rotates in anticlockwise sense with constant angular VELOCITY `vecomega` and the cone itself about it's own axis (OC) in clockwise sense with angular velocity `vecomega_0`(figure). Then the resultant angular velocity of the cone. `vecomega=vecomega+vecomega_0` (1) As the rolling is pure the magnitudes of the vectors `vecomega` and `vecomega_0` can be easily found from figure. `omega'=(v)/(Rcot alpha)`, `omega_0=v//R` (2) As `vecomega_|_vecomega_0` from Eq. (1) and (2) `omega=sqrt(omega^('^2)+omega_0^2)` `sqrt(((v)/(Rcotalpha))^2+(v/R)^2)=(v)/(Rcosalpha)=2*3rad//s` (B) Vector of angular acceleration `vecbeta=(dvecomega)/(dt)=(d(vecomega+vecomega_0))/(dt)`(as `vecomega=` constant.) The vector `vecomega_0` which rotates about the `OO^'` axis with the angular velocity `vecomega`, retains i magnitude. This increment in the time interval dt is equal to `|dvecomega_0|=omega_0*omega^'dt` or in vector from `dvecomega_0=(vecomegaxxvecomega_0)dt`. Thus `vecbeta=vecomegaxxvecomega_0` The magnitude of the vector `vecbeta` is equal to `beta=omega^'omega_0` (as `vecomega_|_vecomega_0`) So, `beta=(v)/(Rcotalpha)(v)/(R)=v^2/R^2 tan alpha=2*3rad//s` 
|
|
| 7305. |
You are asked to construct a capacitor having a capacitance near 1 n F and a breakdown potential in excess of 10,000 V. You think of using the sides of a tail pyrex drinking glass as a dielectric lining the inside and outside curved surfaces with aluminium foil to act as the plates. The glass is 10cm tall with an inner radius of 3.6 cm and an outer radius of 3.8 cm What are the (a) capacitance and (b) breakdown potential of this capacitor? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`a) 0.48 NF B) 28 KV` | |
| 7306. |
When is Wheatstone Bridge most sensitive ? |
| Answer» Solution :Wheatstone BRIDGE is most sensitive when the valueof resistances of the FOUR ARMS of the bridge P, Q, R and S are of the same magnitude. | |
| 7307. |
What is the required condition, if the light incident on one face of a prism, does not emerge from the other face? |
|
Answer» `n LT "COSEC "((A)/(2))` |
|
| 7308. |
The potentiometer wire AB is 600cm long. At what distance (in cm) from A should the jockey J touch the wire to get zero deflection in the galvanometer? |
|
Answer» ` V_(AJ) = (E )/(2), iR_(AJ) = (E )/(2) ,((E )/( 15 r +r)) ((15R)/(600)) AJ = (E )/(2)` ` AJ =320CM` |
|
| 7309. |
At a pointin an interference pattern, the two interfering coherent waves of equal intensity I_(0) have phase difference 60^(@). What will be the resultant intensity at that point? |
|
Answer» Solution :RESULTANT INTENSITY, `I=2I_(0)(1+cos phi)` `=2I_(0)(1+cos60^(@)) = 2I_(0)(1+1/2) = 3I_(0)` |
|
| 7310. |
In mu-particle scattering experiment, the expression of distance of closest approach (r_0)is (symbols have their usual meanings) |
|
Answer» `1/(4πepsilon_0) × (Ze^2)/E` |
|
| 7311. |
The electrical conductivity of a semiconductor increases when electromagnetic radiation of wavelength shorter than 2480 nm is incident on it. The band gap (in eV) for semi-conductor is |
|
Answer» 0.9 Here, `lamda = 2480 nm = 2480 xx10^(-9) m = 248 xx10^(-8)m` `:.E_g=(6.6xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))/(248xx10^(-8))=7.984xx10^(-20)J` `=(7.984xx10^(-20))/(1.6xx10^(-19))eV=0.499eV = 0.5 eV` |
|
| 7312. |
A ball rolls of the top of a stair way with a horizontal velocity u m s^(-1). If the steps are h metre high and b metre wide, the time taken by the ball to hit the edge of n^(th) step, is |
|
Answer» `(hu)/(gb)` ALSO , `nh=1/2 g t^2 = 1/2 g XX (b^2n^2)/u^2, therefore n=(2u^2H)/(gb^2)` Time taken to travel vertical distance nh is `t=sqrt((2nh)/g)=sqrt((2h)/gxx(2u^2h)/(gb^2))=(2uh)/(gb)` |
|
| 7313. |
Spectra are produced due to electronic transitions from higher energy level to lower energy level,: Name the series spectra produced by hydrogen. |
| Answer» Solution :LYMAN series, BALMER series, Paschen series, Brackett series, PFUND series | |
| 7314. |
The group of limited number of lines of force forming a tube like structure in dielectric medium is : |
|
Answer» TUBE of FORCE |
|
| 7315. |
A cylindrical copper conductor AB length L areaaof cross-section a has large number of free electrons which at mean temperature move at random within the body of the conductorlike the molecules of a gas. The averagethermal motion at room temperature is of the enter of 10^(5)ms^(-1) where a potential difference V is applied free electronic in the condictior experience , the free electrons in the conductorexperience force and are accelerated towards the positive emf of the condutor on their gained kinetic energy After each collision the free electronic are angle acceleration due of the electric field , towards the positive end the conductor andnext collision with the ions/atoms of the electrons The average speed of the free electrons with which they drift toward the positive and of the conductor under theeffect of applied electric field is called drift of the electrons When the potential difference is applied the two ends of the conductors , an electric field exists |
|
Answer» outside the CONDUCTOR |
|
| 7316. |
A ray of light is incident at an anlgge of 60^(@) on a sqrt(3) cm thick palte (mu=sqrt(3)). The shift in the path of the ray as it emerges out from the plate is (incm) |
|
Answer» 1 |
|
| 7317. |
Three particles each of mass 'm' can slide on fixed frictionless circular track in the same horizontal plane as shown in the figure. Particle m_(1) moves with velocity v_(0) and hitsparticle m_(2),the coefficient of restitutionbeing theta=1//2. AsSigmae m_(2) and m_(3) are initially in rest andlie along a radial line before impact and the spring is initially Unstretched. Then, The velocity of m_(3) when extension in the spring is maximum |
|
Answer» `(1)/(10)v_(0)` |
|
| 7318. |
A cylindrical copper conductor AB length L areaaof cross-section a has large number of free electrons which at mean temperature move at random within the body of the conductorlike the molecules of a gas. The averagethermal motion at room temperature is of the enter of 10^(5)ms^(-1) where a potential difference V is applied free electronic in the condictior experience , the free electrons in the conductorexperience force and are accelerated towards the positive emf of the condutor on their gained kinetic energy After each collision the free electronic are angle acceleration due of the electric field , towards the positive end the conductor andnext collision with the ions/atoms of the electrons The average speed of the free electrons with which they drift toward the positive and of the conductor under theeffect of applied electric field is called drift of the electrons The drift speed of the electrons depends on |
|
Answer» dimension of the CONDUCTOR Which is independent of DEMENSIONS and number density of free electrons in the conductor. |
|
| 7319. |
In practice principle of uncertainty is applied |
|
Answer» only for MICRO particles |
|
| 7320. |
The energy of an electron in the first orbit of hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV. The energy of electron in the 4th orbit is_______ eV. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`-0.85eV`[ENERGYIN 4TH ORBIT `E_(u) = - (13.6)/((4)^(2)) ` V = - 0.85 eV]. | |
| 7321. |
A cylindrical copper conductor AB length L areaaof cross-section a has large number of free electrons which at mean temperature move at random within the body of the conductorlike the molecules of a gas. The averagethermal motion at room temperature is of the enter of 10^(5)ms^(-1) where a potential difference V is applied free electronic in the condictior experience , the free electrons in the conductorexperience force and are accelerated towards the positive emf of the condutor on their gained kinetic energy After each collision the free electronic are angle acceleration due of the electric field , towards the positive end the conductor andnext collision with the ions/atoms of the electrons The average speed of the free electrons with which they drift toward the positive and of the conductor under theeffect of applied electric field is called drift of the electrons The motion of electronsin between two successive collisions with the atoms/ions follows |
|
Answer» a STRAIGHT path |
|
| 7322. |
The mass of electron varies with |
|
Answer» electron velocity |
|
| 7323. |
A galvanometer is connected as shown in figure. It has resistance 100Omega. What should be the resistance connected to it in parallel so that its deflection is reduced to half? |
|
Answer» `100OMEGA` |
|
| 7324. |
A cylindrical copper conductor AB length L areaaof cross-section a has large number of free electrons which at mean temperature move at random within the body of the conductorlike the molecules of a gas. The averagethermal motion at room temperature is of the enter of 10^(5)ms^(-1) where a potential difference V is applied free electronic in the condictior experience , the free electrons in the conductorexperience force and are accelerated towards the positive emf of the condutor on their gained kinetic energy After each collision the free electronic are angle acceleration due of the electric field , towards the positive end the conductor andnext collision with the ions/atoms of the electrons The average speed of the free electrons with which they drift toward the positive and of the conductor under theeffect of applied electric field is called drift of the electrons The speed of electrons in a conductor is small (= 10^(-4) ms^(-1)) when the switch is closed, the bulb at a distance glows immediately. It is so because |
|
Answer» drift velocity of electrons INCREASE when swich in CLOSED |
|
| 7325. |
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light? |
| Answer» Solution :(i) The light from a clear blue portion of the sky shows a RISE and fall of intensity when viewed through a polaroid which is rotated. (ii) This is because of sunlight, which has changed its direction (having been scattered) on encountering the molecules of the earth's atmosphere. (iii) The incident sunlight is unpolarised. The electric field of light interact with the electrons PRESENT in the AIR molecules. (IV) Under the influence of the electric field of the incident wave the electrons in the molecules acquire components of motion in both these directions. (v) An OBSERVER looking at `90^@`to the direction of the sun. Clearly, charges accelerating parallel do not radiate energy towards this observer since their acceleration has no transverse component. (vi) The radiation scattered by the molecule is therefore polarized perpendicular to the plane. This explains the reason for polarisation of sunlight by scattering. | |
| 7326. |
The diameter of telescope lens is 0.61 m, the A wavelength of light is 5000 Å, then resolving power of telescope will be ...... |
|
Answer» `2xx10^(4)` `=(D)/(1.22 LAMBDA)` `=(0.61)/(1.22xx5xx10^(-7))=10^(6)` |
|
| 7327. |
Light of frequency 7.21xx10^(14)Hz is incident on a metal surface. Electrons with a maximum speed of 6.0 xx 10^(5) m/s are ejected from the surface. What is the threshold frequency for photoemission of electrons? |
|
Answer» Solution :`upsilon=7.21xx10^(14)HZ, v=6xx10^(5)ms^(-1)` `(1)/(2)mv_("max")^(2)=h(upsilon-upsilon_(0))=hupsilon-h upsilon_(0)` `h upsilon_(0)=h upsilon-(1)/(2)mv_("max")^(2)` `upsilon_(0)=upsilon-(1)/(2)(mv_("max")^(2))/(h)=7.21xx10^(14)-(1)/(2)XX(9.1xx10^(-31)xx(6xx10^(5))^(2))/(6.6xx10^(-34))=4.73xx10^(14)Hz` |
|
| 7328. |
A telescope (f_0=140 cm,f_e=5cm) is used to view a distant tower 100 m high situated at a distance 3 km. The tower is made of iron channels consisting rectangular grades of approximate size 2 xx2 m each in the image formed by telescope's objective , each square channel will appear to be of area |
|
Answer» `100 cm^2` |
|
| 7329. |
If both the length and radius of a metallic wire are doubled then its resistance remainsunchanged. |
|
Answer» Solution :False - In LENGTH and radius both are doubled then L. = 2L and A. = 4A and HENCE resistance `R. = (RHO l.)/(A.) = (rho (2l))/((4A)) = 1/2 (rhol)/(A) = R/2` |
|
| 7330. |
A telescope objective lens has a focal length of 100 cm . When the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision, the distance between the lenses is 105 cm. Calculate the focal length of eye piece and magnifying power of telescope. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7331. |
Speed of light is: |
|
Answer» the same in medium-1 and medium - 2 |
|
| 7332. |
What did the grandmother do when the author comes back to his home? |
|
Answer» She COLLECTED the women of the neighbourhood |
|
| 7333. |
An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit around the earth with a speed equal to 3/8 times of the magnitude of escape velocity from the earth. If the satellite is stopped suddenly in its orbit and allowed to fall freely onto the earth . Then the speed with which it hits the surface of the earth is sqrta . find a (take g=10 m/s and R_e=6400 km) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7334. |
What is the relation between critical angle and RI ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`MU`= `1/sini_c` where `mu` and C critial ANGLE | |
| 7335. |
A potentiometer is an accurate and versatile device to make electrical measurements of E.M.F. because the methods involves: |
|
Answer» A combination of CELLS, galvanometer and RESISTANCES |
|
| 7336. |
How does the resistance of a conductor vary with the increaseof temperature ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :INCRESES. | |
| 7337. |
The bends during flight. Anyone who scuba dives is advised not to fly within the next 24 h because the air mixture for diving can introduce nitrogen to the bloodstream. Without allowing the nitrogen to come out of solution slowly, any sudden air-pressure reduction (such as during airplane ascent) can result in the nitrogen forming bubbles in the blood, creating the bends, which can be painful and even fatal. Military special operation forces are especially at risk. What is the change in pressure on such a special-op soldier who must scuba dive at a depth of 25 m in seawater one day and parachute at an altitude of 8.1 km the next day? Assume that the average air density within the altitude range is 0.87 kg/m^(3). |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`~~ 1.8 XX 10^(5)` PA | |
| 7338. |
A wavefront AB passing through a system C emerges as DE (As shown in the following figure). The system C could be |
|
Answer» A slit |
|
| 7339. |
Solve the same problem for the case of a weight suspended from a thin rod of negligible mass. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7340. |
A stone falls freely under gravity.It covers distance h_(1),h_(2) and h_(3) in the first 5 seconds.the next 5 second and the next 5 seconds respectively.The relation between h_(1),h_(2)and h_(3) is |
|
Answer» `h_(2)=3h_(1)` and `h_(3)=3h_(2)` |
|
| 7341. |
Two simple pendulums of lengths 0.5 m and 2 m respectively are given small linear displacements in one direction at the same time. They will again be in phase when the pendulum of shorter length has completed : |
|
Answer» 5 |
|
| 7342. |
When the medium moves and the source and observer^are stationary: |
|
Answer» `LAMBDA` CHANGES |
|
| 7343. |
In the above problem, find the focal lengths if the lens is a negative meniscus. |
|
Answer» (80 CM, 160 cm, -160 cm) |
|
| 7344. |
Monochromatic rays of intensity I are falling on a metal plate of surface area A placed on a rough horizontal surface at certainn angle theta as shown in figure. Choose correct statement (s) based on above information |
|
Answer» There is a VALUE of `theta` for which plate will not move however high the intensity of RADIATION is |
|
| 7345. |
A block of mass 2M is attached to a massless spring with spring-constant k. This block is connected to two other blocks of masses M and 2M using two massless pulleys and strings. The accelerations of the blocks are a_(1)a_(2) and a_(3) as shown in the figure. The system is released from rest with the spring in its unstretched state. The maximum extension of the spring is x_(0) Which of the following option(s) is(are) correct? [g is the acceleration due to gravity. Neglect friction] |
|
Answer» `a_(2)-a_(1)=a_(1)-a_(2)` `2Mg-T=3Ma_(3)`...(2) `2T-Kx=2Ma_(1)`...(3) From (1) and `M(a_(2)+a_(3))="Mg-T+Mg"(-T)/(2)=2Mg-(3T)/(2)|` implies`ubrace(2Ma_(1)=2Mg-(3T)/(2))_(xx(4)/(3)) implies(8Ma_(1))/(3)=(3Ma)/(3)=(3Ma)/(3)-2T` ...(4) `(3)+(4)implies(8Mg)/(3)-kx=(2M+(8M)/(3))a_(1)` `implies(14M)/(3)a_(1)=-K[x-(8Mg)/(3K)]impliesa_(1)=-(3K)/(14M)[x-(8Mg)/(3K)]` `omega=sqrt((3K)/(14M))`,`A=(8Mg)/(3K)(x_(0))/(2)=2A`[Maximum elongation=2A] `V_(max)=Aomega=(8Mg)/(3K)sqrt((3K)/(14M))``a_(1)atx=(x_(0))/(4)=-(3K)/(14M)xx(4Mg)(3K)=(2g)/(7)` Correct answer is (A) 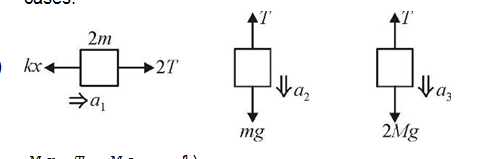 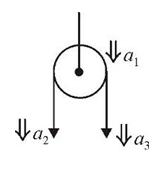
|
|
| 7346. |
Referring to the previous illustration find the energy stored in the inductor when the current l is dropped to a value of 5A . |
|
Answer» Solution :REQUIRED energy = `(1)/(2) LI^(2)` ` = (1)/( 5 xx 10^(-3)) (5)^(2) = 62.5 mJ.` |
|
| 7347. |
Three sinusoidal waves of the same frequency travel along a string in the positive direction of x axis. Their amplitudes are y_1, y_1/2 and y_1/3, and their phase constants are 0, pi/2, and pi respectivey, What are (a) the amplitude and (b) the phase constant of the resultant wave ? |
Answer» Solution :Phasor DIAGRAM WAVE || `phi_2 =pi/2` `A_R =sqrt(((2y_1)/3)^2 +(y_1/2)^2) =y_1sqrt(4/9 +1/4) =5/6 y_1` `phi_R = tan^(-1) ((y_1//2)/(2y_1 //3)) = tan^(-1) (3//4) =37^@` The phase CONSTANT of the RESULTANT wave with respect to first wave is `37^0`. |
|
| 7348. |
A uniform disc of mass m and radius R is given a velocity v_(0) and angular velocity omega_(0) as shown and released of a fixed horizontal surface. Only the x length of the surface is rough. Find the minimum value of x (in metres) so that disc starts pure rolling. Use (omega_(0)^(2)R^(2))/(72mug)=1m |
|
Answer» `impliesomega_(0)=3/2omegaimpliesomega=(2omega_(0))/3` `implies v=omegaR=2/3omega_(0)R=(4v_(0))/3` `=(16v_(0)^(2))/9=v_(0)^(2)+2mugx` `2mugx=(7v_(0)^(2))/9impliesx=(7v_(0)^(2))/(18mug)=(7omega_(0)^(2)R^(2))/(72mug)=7m` 
|
|
| 7349. |
A convex lens is used to obtain a magnified image of an object on a screen 10 m from the lens. If the magnification is 19, find the focal length of the lens. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, DISTANCE of screen from the lens v = 10 m and magnification of image m = 19As image is being formed on the screen, the image is a real image and v is + ve. As `m=v/u`, hence `u=v/m = (10M)/19` and `-ve` As `m=v/u`, hence, `u=v/m = (10 m)/19` and `-ve` Using lens FORMULA `1/v -1/u = 1/f`, we have `1/(+10) -1/(-10/19) = 1/f rArr 1/f = 1/10 + 19/20 = 20/20 =2 `or `f=1/2 m = 0.5 m` or 50 CM |
|
| 7350. |
When a body is projected vertically up, its PE is twice its KE when it is at a height h above the ground. At what height will its K.E. be twice the PE. |
|
Answer» `H'=h//2` |
|