Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 7351. |
A convex lens is placed in contact with a plane mirror. An axial point object at a distance of 20 cm from this combination, has its image coinciding with itself. What is the focal length of the convex lens ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The focal length of the lens = 20 cm Explanation: As the image of this combination coincides with the object itself, the rays from the object, after refraction from the lens should FALL normally on the PLANE mirror, so that they retrace their PATH. So the rays from the point object after refraction from the lens MUST form parallel beam. For CLARITY, mirror has been placed at a small distance from the lens. 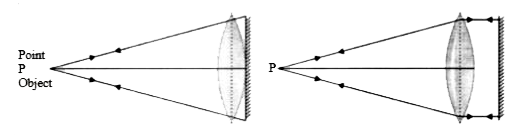
|
|
| 7352. |
Two electrons separated by distance 'r' experience a force F between them. The force between a proton and a singly ionized helium atom separated by distance 2r is |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 7353. |
Derive the expression for the self inductance of a long solenoid of cross sectional area A and length l, having n turns per unit length. |
|
Answer» Solution :Magnetic field at a point inside the SOLENOID is `B=(mu_(0) NI)/(t)` where N is the total NUMBER of turns of the solenoid and L is its length. B is constant throughout the length of the solenoid. Magnetic flux through each turn `=B xx ` area of each turn. `therefore phi_(1)= mu_(0)(N)/(l) I xx A` where, A is the area of each turn. `therefore` Total magnetic flux linked with the solenoid `= PHI= mu_(0) (N)/(l)IA xx N` But from thedefinition of self inductance `(L), phi= LI`. `therefore LI=mu_(0)(N)/(l) IAxxN implies L=(mu_(0)N^(2)A)/(l)=mu_(0)n^(21A)` Henry. 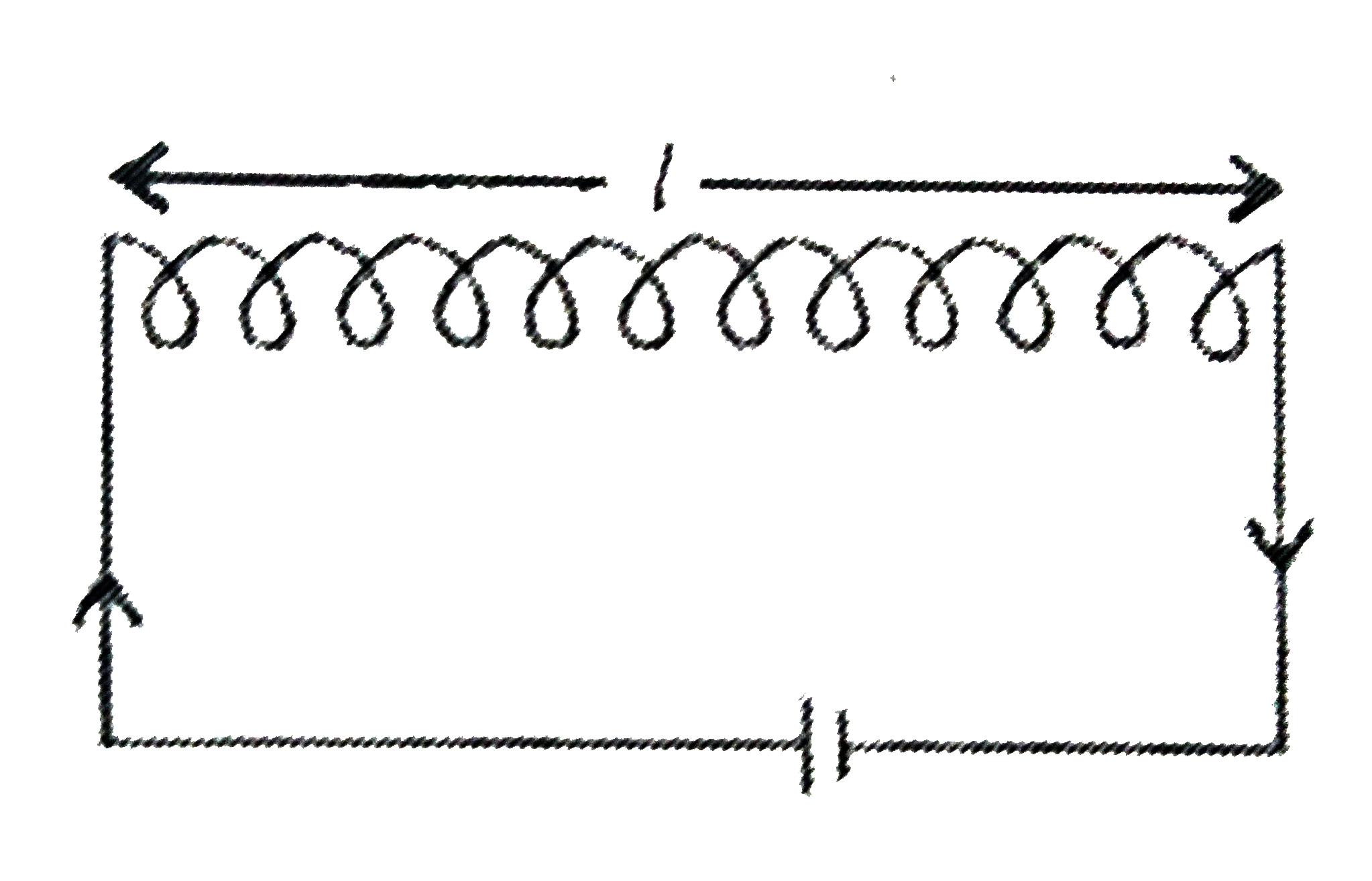
|
|
| 7354. |
A bus starts moving with an acceleration2 ms? A cyclist 96 m behind the bus starts simultaneously towards the bus at 20 m s-, after what time will he able to overtake the bus? |
|
Answer» 4 s ALSO total distance covered bythe cylist =20.t `:. 20.t=(1)/(2)xx2t^(2)+96` or `t^(2)-20t+96` `t=(20pmsqrt(400-384))/(2)` `t=(20pm4)/(2)=12sec,8sec` Minimum time =8 sec |
|
| 7355. |
Find the speed of two objects if when they move uniformly towards each other, they get 4.0 metres closer each second and when they move uniformly in the same direction with original speeds, they ger 4.0 metres closer each 10 sec |
|
Answer» Solution :LET their speeds be `v_(1) and v_(2)` and let `v_(1) gt v_(2)` In first Case In SECOND Case: Relative velocity `v_(1)-v_(2)=(4)/(10)=0.4""....(2)` Solving eqns. (1) and (2) we get `v_(1)=2.2 m s^(-1), v_(2) 1.8m s^(-1)` |
|
| 7356. |
A body of 5 kg mass is raised vertically to a height of 10 m by a force of 120 N. Find the final velocity of the body using two methods: Newton's second law and the law of conservation of energy. The initial speed is zero. |
|
Answer» (b) According to the law of conservation of energy the work per FORMED by a FORCE is equal to the change in energy `A = DeltaU+K , "or " Fh = MGH +(mv^2)/2` HENCE `v=sqrt(2h(f/m-g))` |
|
| 7357. |
(A) : The quantity L//R possesses dimension of time. (R) : To reduce the rate of increase of current through a solenoid, we should increase the time constant (L//R) |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are true and 'R' is the correct EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 7358. |
One end of a string of length 7 is connected to a particle of mass m and the other to a small peg on a smooth horizontal table. If the particle moves in a circle with speed upsilon the net force on the particle (directed towards the centre) is |
|
Answer» T |
|
| 7359. |
An electron of mass m_e, revolves around a nucleus of charge +Ze. Show that it behaves like a tiny magnetic dipole. Hence, prove that the magnetic moment associated with it is expressed as vec(mu) = - e/(2 m_e) vecL, where vecL is the orbital angular momentum of the electron. Give the significance of negative sign. |
|
Answer» Solution :We KNOW that a revolving electron constitutes an electric current GIVEN by `I = e/T = (ev)/(2 pi r)` where `T = (2 pi r)/v` = peroid of revolution of electron revolving in a circular orbit of radius r with a speed v. `:.` Magnetic moment `(mu_l)` associated with this circulating current, `mu_l = I CDOT A = (ev)/(2pi r) cdot pi r^2 = (evr)/(2)` As an electron revolving is an anticlockwise direction is equivalent to current in clockwise direction, hence in accordance with right hand rule the magnetic moment is in a direction perpendicular to plane of paper (or plane of orbit) directed inward. The above relation may also bewritten as : `mu_l = (e v rm)/(2m ) = e/(2m) cdot l` and in vector notation, `vec(mu)_(l) = -e/(2m) cdot vecl ,` where `l = m v r` = orbital ANGULAR momentum of the electron around the nucleus . The -ve sign applied here INDICATES that the angular momentum of the electorn is opposite in direction to the magnetic moment. 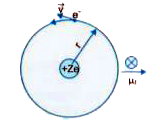
|
|
| 7360. |
Obtain Gauss'Law for magnetism and explain it. |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) According to Gauss's law for magnetism, the net magnetic flux `(phi_(B))` through any closed surface is always zero. (2) The law implies that the no. of magnetic FIELD lines LEAVING any closed surface is always equal to the number of magnetic field lines entering it. (3) Suppose a closed surface S is held in a uniform magnetic field B. Consider a SMALL vector area element `Delta S` of this surface as SHOWN in figure. (4) Magnetic flux through this area element is defined as `Delta phi_(B) = B. Delta S`. Then the net flux `phi_(B)`, is, `phi_(B) = UNDERSET("all")sum Delta phi_(B) = underset("all")(sum)B. Delta S = 0`. (5) If the area elements are really small, we can rewrite this equation as `phi_(B) = oint B. ds = 0` - (1) (6) Comparing this equation with Gauss's law of electrostatics i.e., electric flux through a closed surface S is given by `phi_(E) = oint E. Delta S = (q)/(epsilon_(0))` - (II) Where q is the electric enclosed by the surface. (7) In an electric dipole were enclosed by the surface equal and opposite charges in the dipole add upto zero. Therefore, `phi_(E)` would be zero. (8) The fact that `phi_(B) = 0` indicates that the simplest magnetic element is a dipole or current loop. (9) The isolated magnetic poles, called magnetic monopoles are not known to exist. (10) All magnetic phenomena can be explained interms of an arrangement of magnetic dipoles and/or current loops. (11) Thus corresponding to equation (II) of Gauss's theorem in electrostatics, we can visualize equation (I) as `phi_(B) = underset(S)intB.dS = mu_(0) (m) + mu_(0) (-m) = 0` where m is strength of N - pole and -m is strength of S - pole of same magnet. (12) The net magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero. 
|
|
| 7361. |
Why are Si and GaAs are perferred materials for solar cells? |
Answer» Solution :The solar radiation spectrum is shown below.  1.5 eV has the maximum intensity of radiation. To obtain the electrical ENERGY in a solar CELL the energy of the incidentphoton must be `hv gt E_(g)` (where `E_(g)` is band gap energy). So the band gap for solar cell which is about 1.5 eV or less, works at maximum capacity for solar energy conversion. Siliconhas `E_(g)` about 1.1 eV while for GaAs it is about 1.53 eV. In fact GaAsis better than Si because of its relativer higher absorptioncoefficient. The band gap `E_(g)` of CdS or CdSe is about2.4 eV and if we USE such materials in solar cell then only the high energy part of the solar energy can be convertedinto light energy and a significant part of energy will be no use. The question arises, why we do not use material like PBS `(E_(g)=0.4eV)` which satisfy the condition `hv gt E_(g)` for v maxima corresponding to the solar radiation spectra. It we do so, most of the solar radiation will be absorbed on the top layer of solar cell and will not reach in or near the deplection region. For effective electron hole seperation, due to the junction field, we want the PHOTO generation (formation of e and h occuring after lightincident)to occur in the junction region only. |
|
| 7362. |
Through a series of thermodynamic processes, the internal energy of a sample of confined gas is increased by 560 J. if the net amount of work done on the sample by its surroundings is 320 J, how much heat was transferred between the gas and its environment? |
|
Answer» 240 J absorbed |
|
| 7363. |
Two identical point particles A and B are placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm, at distances 10 cm and 30 cm respectively. The particles oscillate perpendicular to the principal axis, such that the displacement equation for both the particles is given by Y_A=Y_B = 0.1 sin(pit) cm . Find the maximum separation between the images of A and B measured perpendicular to the principal axis in mm. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7364. |
Define threshold frequency and on which factor threshold frequency depend? |
|
Answer» Solution :Minimum incident FREQUENCY required to emit electron from metal surface is CALLED threshold frequency.IT is DENOTED by `V_(0)` . Value of threshold frequency depends on type of metal. Value of threshold frequency depends on type of metal. For most metals like zinc cadmium,magnesium threshold frequencies lie in ultraviolet region which have short short wavelength. |
|
| 7365. |
A steel ball of mass m_(1)=1kg moving with velocity 50ms^(-1) collides with another ball of mass m_(2)=200g lying on the ground. Due the collision, the KE is lost and their internal energies change equally and T_(1) and T_(2) are the temperature changes of masses m_(1) and m_(2) respectively. If the specific heat of steel is unity and J="4.18 J cal"^(-1), then |
|
Answer» `T_(1)=7.1^(@)C and T_(2)=1.47^(@)C` |
|
| 7366. |
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted is doubled when the wavelength of light incident on the photosensitive surface changes from lambda_(1)to lambda_(2). Deduce expressions for the threshold wavelength and work function for the metal surface in terms of lambda_(1) and lambda_(2). |
|
Answer» Solution :In terms of WAVELENGTH `LAMBDA`, the photoelectric equation may be expressed as: `HC((1)/(lambda)-(1)/(lambda_(0)))=K_("max")`, where `lambda_(0)` is the THRESHOLD wavelength. As per question for incident light of wavelength`lambda_(1), K_("max")=`K(say) and for light of wavelength `lambda_(2), K_("max")=2K`. Hence, we have `hc((1)/(lambda_(1))-(1)/(lambda_(0)))=K and hc((1)/(lambda_(2))-(1)/(lambda_(0)))=2K` `rArr 2((1)/(lambda_(1))-(1)/(lambda_(0)))=(1)/(lambda_(2))-(1)/(lambda_(0)) rArr (1)/(lambda_(0)) =(2)/(lambda_(1))-(1)/(lambda_(2)) rArr lambda_(0)=(lambda_(1)lambda_(2))/((2lambda_(2)-lambda_(1)))` and work function of the metal `phi_(0)=(hc)/(lambda_(0))=(hc(2lambda_(2)-lambda_(1)))/(lambda_(1)lambda_(2))` |
|
| 7367. |
An object is located in a fixed position in front of a screen. Sharp image is obtained on the screen for two positions of a thin lens separated by 10 cm. The size of the images in two situtation are in the ratio 3 : 2. What is the distance between the screen and the object? |
|
Answer» 124.5 CM 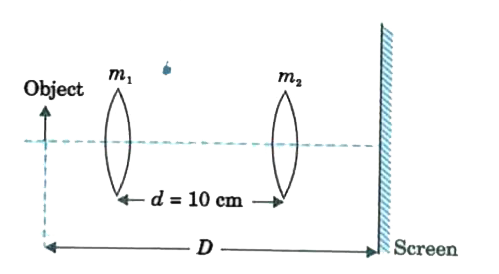 `implies (m_1)/(m_2) = ((D + d)/(D - d))^(2)` `implies 3/2 = ((D + 10)/(D - 10))^(2)` `3(D - 10)^2 = 2 (D + 10)^2` `3(D^2 + 100 - 20D) = 2(D^2 + 20 D + 100)` `D^2 - 100 D + 100 = 0` `D = 99 cm` |
|
| 7368. |
Sketch the emergent wavefront. |
Answer» SOLUTION :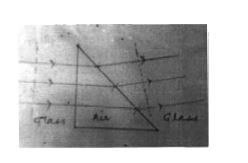
|
|
| 7369. |
Briefly explain Malus law about the intensity of polarised light. |
|
Answer» Solution :Let intensity of plane POLARISED obtained, when UNPOLARISED light passes through a polaroid A, be `I_(0)`. Now a second polaroid B is held in the PATH of polarised light beam such that pass axis of B makes an angle `theta` from the pass axis of A as SHOWN figure (a) and (b). If amplitude of vibration of electric field vector along the pass axis of polaroid A be E, then its component passing along the pass axis of polaroid B will be `E.=Ecostheta`. `therefore` Intensity of light passed through the polaroid `I=kE^(2) and I.=kE^(.2)`, where k is a constant of proportionality. `therefore I.=kE^(.2)=k(Ecostheta)^(2)=kE^(2)cos^(2)theta=Icos^(2)theta` The relation `I.=Icos^(@)theta` is known as Malus law. (i) If `theta=0^(@)`, then `I=Icos^(2)0^(@)=I` (ii) If `theta=(pi)/(2)`, then `I.=Icos^(2)90^(@)=Ixx0=0`.  . .
|
|
| 7370. |
Explain the term nuclear binding energy and express it in terms of mass defect. What is binding energy per nucleon? Write the expression for it |
|
Answer» Solution :In the atomic nucleus, the protons and the neutrons are bound together by a strong, short RANGE and charge-independent, attractive force expression for it. called the nuclear force. The minimum energy required to separate a nucleus into its free constituents, i.e., protons and neutrons, is known as the nuclear BINDING energy. It is the mass energy of the nucleons MINUS the mass energy of the nucleus. The mass defect of a nucleus, of mass M, mass number A and PROTON number Z, is `Deltam=(Zm_(v)+Nm_n)-M` where N=A- Zis the neutron number, `m_(p)` is the proton mass and `m_(n)` is the neutron mass. Thus, it is the DIFFERENCE between the sum of the masses of all the individual nucleons in a nucleus and the mass of the nucleus. From Einstein's mass-energy relation,nuclear binding energy where c is the speed of light in free space. In calculations using the above equatios, m, is replaced by m, (mass of the hydrogen atom). M is taken to the atomic mass and not nuclear mass because the electron masses Cancel out, and the difference in electronic binding energies is ignored as these are about 10 times smaller than the nuclear binding energy. `therefore ` Nuclear binding energy `cong [(Zm_(H)+Nm_(n))-M_("atom")]c^(2)` The minimum energy regúired on the average to separate a nucleon nucleon for thatnucleus. It is the nuclear binding energy for a nucleus divided by its mass number. It indicates the stability of the nucleus. `=(Deltamc^(2))/(A)` `=[(Zm_(v)+Zm_(n))-M] (c^(2))/(A)` `approx [(Zm_(H)+Nm_(n))-M_("atom")] (c^(2))/(A)` |
|
| 7371. |
A spherical mirror is placed 10 cm below the level of water. A point oject is placed in air 30 cm above the water surface on the axis of the mirror such that two images seen by an observer above the water surface coincide. The images are formed by partialreflection at the water surface and due to emerging light after feflection from the mirror. Find the focal length of the mirror. (mu_("water")=(4)/(3)) |
|
Answer» `(100)/(3)CM` |
|
| 7372. |
The magnetic induction due to the electron revolving in the first Bohr orbit of hydrogen atom at the centre of the orbit is B. If the electron is revolving in the second Bohr orbit the magnetic induction at the centre will be |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`B=(mu_(0)i)/(2r)RARRB=(mu_(0))/(2r)RARR(qv)/(2pir)` According Bohr.s theory of HYDROGEN atom, `Bpropv/(r^(2))}_(vprop1/n)^(rpropn^(2))` |
|
| 7373. |
In a radioactive series, ""_(92)^(238)Uchanges to""_(82)^(206)Pbthrough n_(1) alpha -decay processes and n_(2)beta -decay processes. |
|
Answer» `n_(1) = 8 , n_(2)=8` |
|
| 7374. |
White light is sent downward onto a horizontal thin film that is sandwiched between two materials. The indexes of refraction are 1.80 for the top material, 1.65 for the thin film, and 1.50 for the bottom material. The film thickness is 5.00 xx 10^(-7) m. Of the visible wavelengths (400 nm to 700 nm) that result in fully constructive interference at an observer above the film, which is the (a) longer and (b) shorter wavelength? The materials and film are then heated so that the film thickness increases. (c) Does the light resulting in fully constructive interference shift toward longer or shorter wavelengths? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 550 NM, (B) 413 nm, (c) longer wavelength | |
| 7375. |
मान लीजिए कि U = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 , 7 , 8 , 9, 10 } और Auu B = { 2, 4, 5, 7, 8} है तोAnnB होगा |
|
Answer» {3, 5, 7} |
|
| 7376. |
Show that net force acting on an electric dipole held in a uniform electric field is zero. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider an electric dipole AB held in a uniform electric field held at an ANGLE ` theta` with the direction of electric field ` oversetto E . ` Now force acting on +q charge `F_1 =qE ` along direction of ` OVERSET to E ` and force acting on -q charge `F_2=qE ` in a direction opposite to that of ` oversetto E` Since `F_1 and F_2 ` are equal but in mutually opposite direction, HENCE the net translational force acting on the electric dipole will be zero. ` (##U_LIK_SP_PHY_XII_C01_E09_028_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 7377. |
The relation between half-life (T) and decay constant (lambda) is: |
|
Answer» `lambdaT=1` The time in which the final amount becomes half of its INITIAL value is called half-life (T) of that radioactive element. Relation between half-life and distintegration (decay) constant is given by `T=(0.6931)/(lambda)` `rArr T=(log_(e)2)/(lambda)` So, `lambdaT=log_(e)2`. |
|
| 7378. |
Calculate the number of half lives elapsed, the end of which, the activity of a radioactive sample decrease by 90%. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The change in activity with time follows the same was that of number of radioactive atoms. `THEREFORE`PERCENTAGE of radioactive atoms LEFT undecayed. 100-90%=10% i.e., `N/N_0=1/10` From `(N/N_0)=(1/2)^n` [where n=no. of half lives elapsed ] `(1/2)^n =1/10` or, `2^n=10` or , n log 2 = log 10 or , `n=1/0.3010`=3.3 Thus, at the end of 3.3 half lives, the activity and hence the number of atoms) would have DECREASED by 90%. |
|
| 7379. |
The rectangular components of a vector lying in xy plane are (n+1) and 1. If coordinate system is turned by 60^@. They are n & 3 respectively the value of 'n' |
|
Answer» 2 |
|
| 7380. |
The path followed by a projectile is called _____. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7381. |
An object of length 10 cm is placed at right angles to the principal axis of a mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm such that its image is virtual, erect and has a length 6 cm. What kind of mirror it is and also determine the position of the object? |
|
Answer» CONCAVE 20 CM from the mirror |
|
| 7382. |
Energy levels A, B, C of a certain atom corresponding to increasing values of energy are E_A lt E_(B) lt E_(C) lambda_(1),lambda_(2),lamda_(3) are the corresponding wavelengths of the radiations corresponding to the transitions C to B, B to A and C to A respectively. Which of the following statements is true ? |
|
Answer» `lambda_(3)=lambda_(1)+lambda_(2)` `or (hc)/(lambda_(1))+(hc)/(lambda_(2))=(hc)/(lambda_(3))` `or (1)/(lambda_(1))+(1)/lambda_(2)=(1)/(lambda_(3))` `lambda_(3)=(lambda_(1).lambda_(2))/(lambda_(1)+lambda_(2))` |
|
| 7383. |
Some ratioisotopes are used for medical imaging . A radioisotope is injected into th blood of a person. Malignant tissue absorb and retian this isotope much more efficiently than other healthy tissues. A sample of radio isotope having half life of 5 hour and activity of 22mCi is injected into the blood aof a patient. the isotope enters into thyroid glnads through the blood streams. The isotope radiates gamma photons each having energy of 2xx10^(-8)muJ. (a) Qualitatively sketch the amount of radio isotope in the thyroid glands as a function of time. (b) Sometime after the injection a scan of the glands is taken over a period of 20 minute. The total energy emitted by the glands was found to be 6xx10^(-4)J. Assume that the thyroid glands are quickly saturated (with isotopes) after the injection and almost 50% of the injected isotopes are absorbed by the glands. Make an estimate of the time after the injection when the scan was performed. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7384. |
An RC-circuit , with R=600kOmega and C=10muF , is connected toa 5.0-V battery until the capacitor is fullycharged .Then , the battery is suddenly replaced with a new 3.0-V battery of opposite polarity .At what time (in seconds)after this replacement will the energy stored in the capacitor be zero ? (given that e~~8/3) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7385. |
Assertion: Gauss's law shows diversion when inverse square law is not obeyed Reason:Gauss's law is a consequence of conser vation of charges |
|
Answer» Both ASSERTION and Reason are TRUE and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion |
|
| 7386. |
Which substance hasthe highestmeltingpoint? |
|
Answer» <P>NaCI |
|
| 7387. |
If deviation by a prism with small prism angle with refractive index 1.6 is 3.6^@, then prism angle is …..... |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`DELTA=A(n-1)` `therefore A=(delta)/(n-1)=(3.6)/(1.6-1)=(3.6)/(1.6)=6^@` |
|
| 7388. |
Two wires of equal length, one of aluminium and the other of copper have the same resistance.Which of the two wires is lighter ? Hence, explain why aluminium wires are preferred for overhead power cables.(rho_(Al) = 2.63 xx 10^(-8) Omegam, rho_(Cu) = 1.72 xx 10^(-8) m, relative density of Al = 2.7 , of Cu = 8.9) |
|
Answer» Solution :We KNOW that`R = (rho l )/(A)` As resistance and LENGTH of both wires are same, hence it means that `(rho_(AL))/(A_(Al)) = (rho_(Cu))/(A_(cu))` ` rArr (A_(Al))/(A_(Cu)) = (rho_(Al))/(rho_(Cu)) = (2.63 xx 10^(-8))/(1.72 xx 10^(-8)) = (2.63)/(1.72)` As relative density of Al, `d_(Al)` = 2.7 and of Cu, `d_(Cu) = 8.9` `(m_(Al))/(m_(Cu)) = (A_(Al))/(A_(Cu)) xx (d_(Al))/(d_(Cu)) = (2.63)/(1.72) xx (2.7)/(8.9) = 0.47 ` (APPROX) Thus, aluminium wire is lighter than copper wire. Due to this very reason aluminium wire is preferred for overhead POWER cables because its mass and hence the cost will be comparatively less. |
|
| 7389. |
Find the energy of the reaction .^(14)N(alpha, p) .^(17)O, if the kinetic energy of the incoming alpha-particle is T_(alpha) = 4.0 MeV & the proton outgoing at an angle theta = 60^(@) to the motion direction of the alpha-particle has a kinetic energy T_(p) = 2.09 MeV. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7390. |
A long straight wire carries a current of 35 A. What is the magnitude of the field vecB at a point 20 cm from the wire? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here `l = 35 A ` and `R = 20 cm = 0.2 m` `:. "" B = (mu_0 I)/(2 PI R) = (4 pi xx 10^(-7) xx 35)/(2 pi xx 0.2) = 3.5 xx 10^(-5)T`. |
|
| 7391. |
Find the ratio of de-Broglie wavelengths associated with two electron beams accelerated through 25 V and 36 V respectively. |
|
Answer» Solution :de-Broglie wavelength associate with potential DIFFERENCE `lambda PROP (1)/(sqrt(V))` `(lambda_(1))/(lambda_(2)) = sqrt((V_(2))/(V_(1))) = sqrt((36)/(25)) = (6)/(5)""rArr lambda_(1) : lambda_(2) = 6 : 5` |
|
| 7392. |
The sun delivers 10^(3) W // m^(2) of electromagnetic flux to the earth's surface. The total power that is incident on a roof of dimensions 8 m xx 20 m, will be: |
|
Answer» `2.56 xx 10^(4) W` `=1.62 xx 10^(5) W`. |
|
| 7393. |
Compare (a) current sensitivity and (b) voltage sensitivity in the following moving coil galvanometers. Meter A : N = 30A = 1.5 xx 10^(-3) m^2 B = 0.25 T R= 20 Ω Meter , B :N = 35 A=2 xx 10^-3 m^2 B=0.25 T R= 30 Ω You are given that the springs in the two meters have the same torsional constant . |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 0.643(B) 0.964 | |
| 7394. |
Draw phasor diagrams showing phase relationship between voltage and current in an a.c. circuit containing (a) a pure inductor only, and (b) a pure capacitor only. Also show graphs of V and I versus time t |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Phasor DIAGRAM for a PURE inductive a.c. circuit has been shown in FIG. 7.15. Here CURRENT I lags behind the voltage V by a phase angle `pi/2`. (b) Phoasor diagram for pure capacitive a.c. circuit has been shown in fig. Here current/leads the voltage V by a phase angle `pi/2`. 
|
|
| 7395. |
Assume earth to be a solid sphere of uniform density and radius 6.4 x 10^6 m and having a mass6.4 x 10^24 kg. the rotational K.E. is |
|
Answer» `2.6 X 10^29 J` |
|
| 7396. |
Draw an arrangement for winding of primary and secondray coils in a transformer with two coils on a separate limb of the core. State the underlying principles of a transformer. Deduce the expression for the ratio of secondary voltage to the primary voltage in terms of the ratio of the number of turns of prrmary and secondary winding. For an ideal transfomer, obtain the ration of primary and secondary currents in terms of the ratio of the voltage in the secondary and primary voltages. Write any two reasons for the energy losses which occur in actual transformers. |
Answer» Solution :Transformer : A transformer is an electrical device for CONVERTING an ALTERNATING current at low volatage into that at high voltage or vice veras. If it increases the input voltage, it is called step up transformer and if it decreases the input voltage, it is called step down transformer.  PRINCIPLE : It works on the principle of mutual induction, i.e., when a charging current is passed through one of the two inductively coupled coils, an induced emf is set up in the other coil. Consider the situation when no load is connected to the secondary i.e., its terminals are open. Let `N_(1)andN_(2)` be the number of turns in the primary and secondary respectively. Then, Induced emf in the secondary coil, `epsi_(1)=-N_(1)=(dphi)/(dt)` Induced emf in the secondary coil, `epsi_(2)=-N_(2)=(dphi)/(dt)` where `phi` is the magnetic flux linked with each turn of the primary or secondary at any instant. Thus, `(epsi_(2))/(epsi_(1))=(N_(2))/(N_(1))`. Let `(epsi)` be the emf applied to the primary. By Lenz's law, self-induced emf `(epsi_(1))` opposes `(epsi)` in the primary coil. `:.` RESULTANT emf in the primary `epsi-epsi_(1)` This emf SENDS current `I_(1)` through the primary coil of resistance R. `:.epsi-epsi_(1)=RI_(1)` But R is very small, so the term `RI_(1)` can be negelcted. Then `epsi=epsi_(1)` Thus, `epsi_(1)` may be regarded as input emf and `epsi_(2)` as the output emf. `(epsi_(2))/(epsi_(1))=("output emf")/("Input emf")=(N_(2))/(N_(1))` Assuming the transformer to be ideal one so that there are no energy losses, then Input power = Output power or `epsi_(1)I_(1)=epsi_(2)I_(2)` where `I_(1)andI_(2)` the currents in the primary and secondary respectively. Hence, `(I_(2))/(I_(1))=(epsi_(2))/(epsi_(1))=(N_(2))/(N_(1))`. Two losses are : (i) Flux leakage. (ii) Eddy current loss. |
|
| 7397. |
The aperture of a lelescope is increased to : |
|
Answer» GET HIGH resolving power |
|
| 7398. |
To know the resistance G of a galvanometer by half deflection method , a battery of emf V_Eand resistance R is used to deflect the galvanometer by angle theta . If a shunt of resistance S is needed to get half deflection then , G,R and S related by the equation : |
|
Answer» `S(R+G)=RG` |
|
| 7399. |
A resistor of 200 Omegaand a capacitor of 15.0 mu F are connected in series to a 220V , 50Hz ac source . (a) Calculate the current in the circuit, (b) Calculate the voltage (rms) across the resistor and the capacitor . Is the algeraic sum of these voltages more than source voltage ? if yes, resolve the paradox. |
|
Answer» Solution :` R= 200Omega, C = 15.0 muF = 15.0 xx 10^(-6) F, V= 220V, v = 50Hz` a. In order to calculate the current, we need the impedance `Z = sqrt(R^2 + X_C^2) = sqrt(R^2 + (2pi v C)^(-2) )` ` = sqrt( (200)^2 + (2 xx 3.14 xx 50 xx 10^(-6) )^(-2) ) = sqrt( (200)^2 + (212)^2)= 291.5 Omega` Therefore, the current in the circuit is, `I= V/Z = (220)/(291.5) = 0.755 A` B. Since, the current is the same throughout the circuit, we have `V_R = IR = (0.755)(200) = 151 V` `V_C = IX_C = (0.755) (212.3) = 160.3 V` The algebraic sum of the two voltages, `V_R`and `V_C ` is 311.3 V which is more than the source voltage of 220V. You have LEARNT that, the two voltages are not in the same phase. Therefore, they cannot be added like ordinary numbers. The two voltages are out of phase by ninety degrees. Therefore, the TOTAL of these voltages must be obtained using the Pythagorean theorem:`V_(R_+C) = sqrt(V_R^2 + V_C^2) = 220V` Thus, if the phase difference between two voltage is properly taken into account, the total voltage across the resistor and the capacitor is equal to the voltage of the source. |
|
| 7400. |
A 1mu F capacitor is connected to 220 V - 50 Hz a.c. source Find the virtual value of current through the circuit. What is the peak voltage across the capacitor ? |
|
Answer» |
|