Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 7451. |
Light from a source emitting two wavelengths lambda_(1) and lambda_(2) is made tyo fall on Young's double slit appratus after filtering one of the wavelengths.The position of interference pattern is noted.When filter is removed, both the wavelength are incident.It is found that maximum intentsity is produced where the fourth maxima occured intially. If the other wvaelength is filtered, at the same location, the third maxima is found. What is the ratio of wavelengths? |
|
Answer» `4/3` For first wavelengths `(x_(4)) lambda_(1)= (4lambda_(1)D)/(d)` This must be EQUAL to `(x_(3))lambda_(2) = (3lambda_(2)D)/(d)` SINCE ` (x_(4))lambda_(1) = (x_(3))lambda_(2)` `therefore (4lambda_(1)D)/(d) = (3 lambda_(2)D)/(d)` `therefore (lambda_(1))/(lambda_(2)) = 3/4` |
|
| 7452. |
In an ammeter 4% of the main current is passed through a galvanometer .If the galvanometer is shunted with a 5Omega resistance, what is the resistance of the galvanometer? |
|
Answer» `4 OMEGA` |
|
| 7453. |
A rayof light in air is incident on a glass plat at polarising angleof incidence /It suffers a deviationof 22^(@) on entering glass . The angle of polarisation is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 7454. |
Two planets at mean distances d_(1) and d_(2) from the sun have their frequencies n_(1) and n_(2) respectively. Then |
|
Answer» `n_(1)^(2)d_(1)^(2)=n_(2)^(2)d_(2)^(2)` or `(T^(2))/(R^(3))`=CONSTANT We know `T=(l)/(n),Rd` given `(T^(2))/(R^(3))=(1)/(n^(2)).(1)/(d^(3))`=constant or `n^(2)d^(3)`=constant For the two PLANETS,` n_(1)^(2)d^(3),=n_(2)^(2)d_(2)^(3)` |
|
| 7455. |
Analyse the figure and match the columns given below. ( ## EXP_SPS_PHY_XII_C04_E05_022_Q01 .png" width="80%"> |
| Answer» Solution :Low ENERGY ELECTRONS - B, High energy ELECTRON - C, POSITRON - A | |
| 7456. |
An antenna is |
|
Answer» inductive |
|
| 7457. |
In the minimum deviation position the refracted the refracted ray in the prism is ________ to the base of prism. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7458. |
A 50kg man is standing at one end of 3,25m long boat. He starts running towards the other end. On reaching the other end his velocity is 2ms^(-1) . If the mass of the boat is 200 kg, final velocity of the boat is ( in ms^(-1) ) |
|
Answer» `2/5` |
|
| 7459. |
Electrical current is the flow of charged particles. The electric current flows through a wire the same way as how water moves in a river. The electricity is nothing but the flow of electrons. What does the graph signify? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7460. |
An optical bench has 1.5 m long scale having four equal divisions in each cm. While measuring the focal length of a convex lens, the lens is kept at 75 cm mark of the scale and the object pin is kept at 45 cm mark. The image of the object pin on the other side of the lens overlaps with image pin that is kept at 135 cm mark. In thisexperiment, the percentage error in the measurement of the focal length of the lens is___ |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7461. |
When light travels from glass to air, there is no change in its |
|
Answer» wavelength |
|
| 7462. |
In Fig (b) , the magnetic needle has magnetic moment 6.7 xx10^(-2) "Am"^2 and moment of inertia I=7.5xx10^(-6)"kgm"^2 . It performs 10 complete oscillations in 6.70s. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The TIME period of OSCILLATION is , `T=(6.70)/10=0.67s ""B=(4pi^I)/(mT^2)=(4XX(3.14)^2xx7.5xx10^(-6))/(6.7xx10^(-2)xx(0.67)^2)=0.01T` |
|
| 7463. |
Three thin rods of mass m and length a each are joined to form a triangle ABC in vertical plane. The triangle is pivoted at the vertex A such that it can rotate in the vertical plane. It is released from rest when the side AB is horizontal as shown. As the triangle rotates, the maximum velocity of the vertex B,v_("MAX"), is given by: |
|
Answer» `v_("MAX")^(2)=(4ga)/(sqrt(3))` `I_(A)=2((1)/(3)ma^(2))+((1)/(12)ma^(2)+m((sqrt(3)a)/(2))^(2))=(3)/(2)ma^(2)` If the angular velocity of the triangle at any instant is `omega`, the velocity of the vertex B at that instant is `a omega` Therefore, the velocity of B is maximum at the instant the angular velocity is maximum, i.e. when the side BC becomes horizontal Let the angular velocity at this instant be `omega_("MAX")` Then, by conservation of energy Gain in KINETIC energy = LOSS in POTENTIAL energy `(1)/(2)I_(A)omega_("MAX")^(2)=3mg` (Loss in height of CM of triangle) `(1)/(2)((3)/(2)ma^(2))omega_("MAX")^(2)=3mg((a)/(sqrt(3))-(a)/(2sqrt(3)))=(sqrt(3))/(2)mga""implies""omega_("MAX")^(2)=(2g)/(sqrt(3)a)` Therefore, the maximum velocity of the vertex B is given by `v_("MAX")^(2)=omega_("MAX")^(2)a^(2)=(2ga)/(sqrt(3))` |
|
| 7464. |
Suppose India has a target of producing by 2020AD, 200 GW of electric power, ten precent of which is to be obtained from nuclear power plants. Suppose the efficiency remained at 25%, what amount of fuel may be required per year by 2020? Take the heat energy per fission of .^(235)U to be about 200 MeV. |
|
Answer» Solution :Nuclear power to be generated `=10% "of 200 hw=20 GW"` At `25%` efficiency actual required `=(100)/(25)xx20GW=80GW` Total energy required for 1 YEAR production of power `=80xx10^(9)xx365xx8.64xx10^(4)J` `"i.e.," E=2.523xx10^(18)J` Energy per fission `=200 MeV` `=200xx1.6xx10^(-13)J` `=320.0xx10^(-13)J` `E=3.2xx10^(-11)J` Total number of fission atoms required `=(2.523xx10^(18))/(3.2xx10^(-11))=7.884xx10^(28)` But `6.023xx10^(23)` atoms of Uranium have a mass of `235g`. `therefore 7.884xx10^(30)` atoms of Uranium have a mass of xg. `"i.e.," x=(235xx7.884xx10^(28))/(6.023xx10^(23))` `x=307.6xx10^(5)` Hence,`m=307.6xx10^(2) KG` `=3.076xx10^(4)kg` or`m=30.76`tons. |
|
| 7465. |
What is half wave rectification? Explain the working of a half wave rectifier. Indicate the waveforms of input and output voltage. |
|
Answer» Solution :The circuit of a HALF wave rectifier using a semiconductor DIODE is shown in figure below. The diode in series with a load resistor is connected to the secondary of a transformer. The AC VOLTAGE to be rectified is applied to the primary of the transformer. This produced induced voltage across the secondary of the transformer. During the positive half cycles of transformer output i.e., when A is positive, diode D is forward biased and hence it conducts. During negative half cycles, the diode D is reverse biased and hence does not coduct. CURRENT flows through the diode circuit only during positive half cycles. the current flowing through load resistance `R_(L)` produces the rectified voltage. 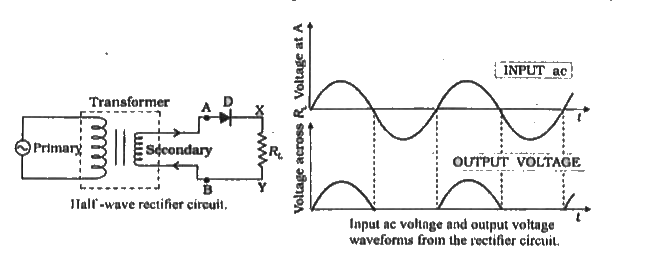
|
|
| 7466. |
An electric field vecE=10xhai i exists in a certain region of space. Then the potential difference V=V_(0)-V_(A) , where V_(0) is the potential at the origin and V_(A) is the potential at x =2 m is …….. . |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 7467. |
In a cyclotron a charged particle |
|
Answer» speeds up in DEE |
|
| 7468. |
निम्नलिखित मे से कौन सा परिमेय है |
|
Answer» `SIN15^(@)` |
|
| 7469. |
(a) What happens if a bar magnet is cut into two pieces: (i) transverse to its length, (ii) along its length ? |
Answer» Solution :(a) Consider a bar magnet with POLE strength `q_m` and magnetic length `2 overset(to) (l)` as shown below.  Magnetic dipole moment of magnetic dipole (or bar magnet) is defined as follows: `{:("Magnetic"),("dipole moment"):}=({:("Magnitude of"),("pole strength"):})({:("Magnetic"),(" length"):})` `therefore m= (q_m) (2l)` Considering directions, `overset(to) (m) = q_m (2 overset(to) (l) )` Above direction is from south pole to north pole. Here, straight line passing through magnetic poles of a bar magnet is called its magnetic axis and perpendicular bisector of this axis is called its magnetic equator. (i) When a bar magnet is cut into two equal pieces, transverse to its length (means it is cut through its equator), we get two identical half sized bar MAGNETS. Here, pole strength remains constant but magnetic dipole moment BECOMES half (because magnetic length becomes half) See the figure given below.  (Note : Above figures are drawn in two dimension for the sake of simplicity and ease. ACTUALLY, bar magnets are three dimensional objects) (ii) When a bar magnet is cut ALONG its axis, we get two identical half sized bar magnets. Here, magnetic length remains constant but magnetic dipole moment becomes half (because pole strength becomes half) See the figure given below.  `m= (q_m) (2l)` `m. = ((q_m)/( 2) ) (2l)` `= (q_m) (l)` `therefore m. = (m)/(2)` |
|
| 7470. |
Two resistances 300 ohm and 400 ohm are connected in series with a 60 volt supply. voltmeter connected across 400 ohm reads 30V. The same voltmeter when connected across the other resistance will read. |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 7471. |
The average path difference between two waves coming from third and fifth frenel zones of wave front at the centre of the screen is |
|
Answer» `LAMBDA/2` |
|
| 7472. |
An alternating voltage is connected in series with a resistor R and an inductor L. If the potential drop across the resistor is 200 V and across the inductor is 150 V, then what is the applied voltage ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`V^2=V_R^2 +V_L^2` `THEREFORE V=sqrt(V_R^2 +V_L^2)` `=sqrt((200)^2 + (150)^2)` `=sqrt(40000+22500)` `=sqrt62500` `therefore` V=250 V |
|
| 7473. |
Derive referaction formula (for objectin air and image in the denser medium ) for refraction of light at a spherical surface |
Answer» Solution :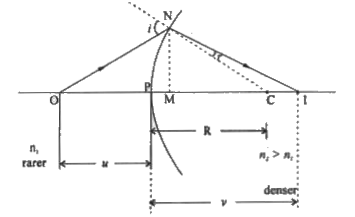 From the FIGURE, `tan angleNOM=(MN)/(OM)` `tan angle NCM=(MN)/(MC)` where, `angle NOM and angle NCM` are interior angles similarly, `angleNCM=r+angleNIM` i.e., `r=angleNCM-angleNIM` For small angles`tan angleNCM=angleNCM` in rad similarly `i=(MN)/(OM)+(MN)/(MC)"" ` .....(1) and `r=(MN)/(MC)-(MN)/(MI)""` .......(2) From snell.s law, `n_(1)SIN i = n_(2) sin r` for small anglesin i = i(rad) and sin r = r (rad) i.e., `n_(1)i = n_(2)r ""`.......(3) using (1) and (2) in (3) we write, `n_(1)((MN)/(OM)+(MN)/(MC))=n_(2)((MN)/(MC)-(MN)/(MI))` or `(n_(1))/(OM)+(n_(1))/(MC)=(n_(2))/(MC)-(n_(2))/(MI)` i.e.,`(n_(1))/(OM) +(n_(2))/(MI)=(1)/(MC)(n_(2)-n_(1))` where, OM = -u, MI = +v, MC = +R by using SIGN conventions. `(n_(1))/(-u)+(n_(2))/(v)=(1)/(R)(n_(2)-n_(1))` `therefore (n_(2))/(v)-(n_(1))/(u)=(1)/(R) (n_(2)-n_(1))` |
|
| 7474. |
At a given instant there are 25% of undecayed radio- active nuclei in a sample. After 10S, the number of undecayed nuclei reduces to 12.5%. The time in which the number of undecayed nuclei will further reduced to 6.25% of the reduced number is, |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 7475. |
A body rotates about a stationary axis. If the angular deceleration is proportional to square root of angular speed, then the mean angularspeed of the body, givenomega_0 as the initial angular speed, is |
|
Answer» `(omega_0)/(sqrt2)` angular deceleration `prop sqrt("angular SPEED")` i.e.,` (- d omega)/(DT) prop sqrt (omega) ` or`(-d omega )/(dt) = K sqrt(omega )` where, k is constant or` - int_(omega_0)^(omega) (d omega)/(sqrt (omega)) = k int_(0)^(t) dt ` `- [2 sqrt(omega)]_(omega_0)^(omega) = k [t]_(0)^(t) ` `rArr - 2[ sqrt(omega) - sqrt(omega_0) ] =kt ` `sqrt(omega) - sqrt(omega_0) =- (kt)/(2)` `rArrsqrt(omega) = sqrt(omega_0) - (kt)/(2) "" ...(i)` When then the total TIME of rotation, ` tau = t = (2 sqrt( omega_0) )/(k)` ` therefore ` Mean angular speed, `< baromega > = (int omega dt )/(int dt) = ( int_(0)^(2 sqrt(omega_0) // k) ( omega_0 + (k^2 t^2)/(4) - kt sqrt(omega_0) dt ))/(2 sqrt(omega_0) // k )` ` = ( [ omega_0 t + (k^2 t^3)/(12) - k/2 sqrt(omega_0) t^2 ]_(0)^(2sqrt(omega_0) // k) )/(2 sqrt(omega_0) // k ) ` After SOLVING , we get ` = (omega_0)/(3)` |
|
| 7476. |
In the given circuit, each resistance is r = 18.75Omega. The current(in A) in the resistance connected across A and B is '………..'A. . |
|
Answer» `(y-x)/R + (y-x-100)/r + (y-50)/r + (y/r) + (y -50)/r = 0` ` 5y - 2x = 200`………….(i) 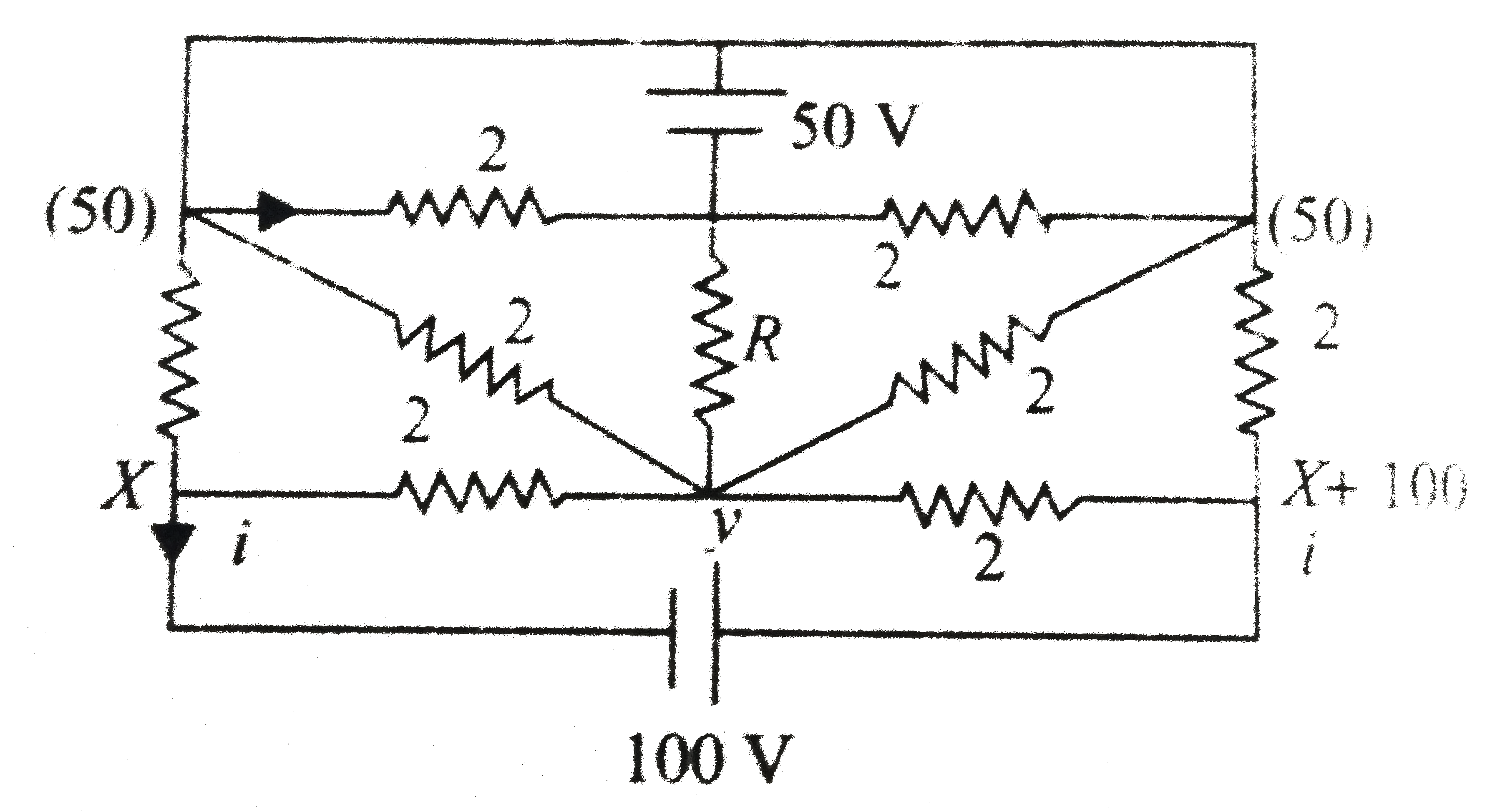 Similarly at x, `i = (50-x)/r + (y-x)/r`……..(ii) At x + 100, `i = (x + 100 - 50)/r + (x+100-y)/r` .......(III) From eqs. (ii) and (iii), we GET `y - 2x = 50`........(iv) From eqs. (i) and(iv), y = 37.5 V. So, CURRENT through R is `37.5//18.75 = 2A`. |
|
| 7477. |
The series and parallel circuits shown in figure have the same impedance and the same power factor If R = 3 Omega and X =4Omega find the valuse of R_(1) andX_(1)Also find the impedance power factor . . |
|
Answer» Solution :Impedance: `Z = sqrt(R^(2) + X^(2)) =5 Omega` Power factor: `cos phi = R/(Z) = (3)/(5) implies phi = cos^(-1) (0.6)` `TAN phi = (X)/R = (4)/(3)` `(i_(R1))_(1) = (V_(0))/(R_(1)) , (iX_(1))_(0) = (V_(0))/(X_(1))` `i_(0)= sqrt((i_(R1))_(0)^(2) + (i_(X1))_(0)^(2) ) = sqrt(((V_(0))/(R_(1)))^(2) + ((V_(0))/X_(1)^(2))^(2))` `(V_(0))/(Z) = V_(0)sqrt((1)/(R_(1)^(2)) + (1)/X_(1)^(2))` `Z =(1)/(sqrt((1)/R_(1)^(2) + (1)/(X_(1)^(2))))=5` `tan phi = (i_(X_1))_(0)/((i_(R_1))_(0)) = (V_(0)//X_(1))/(V_(0)//R_(1)) = (R_(1))/(X_(1)) = tan phi = (4)/(3) ` `X_(1) = (3)/(4) R_(1) ` in `(1)/(R_(1)^(2) ) + (1)/((3/(4) R_(1))^(2)) = (1)/(5^(2))` `(1)/(R_(1)^(2)) (1 + (16)/(9)) =(1)/(25) implies (1)/(R_(1)^(2) ) = (9)/((25)^(2))` `R_(1) = (25)/(3) Omega` `X_(1) = (3)/(4) R_(1) = (25)/(5)Omega` . 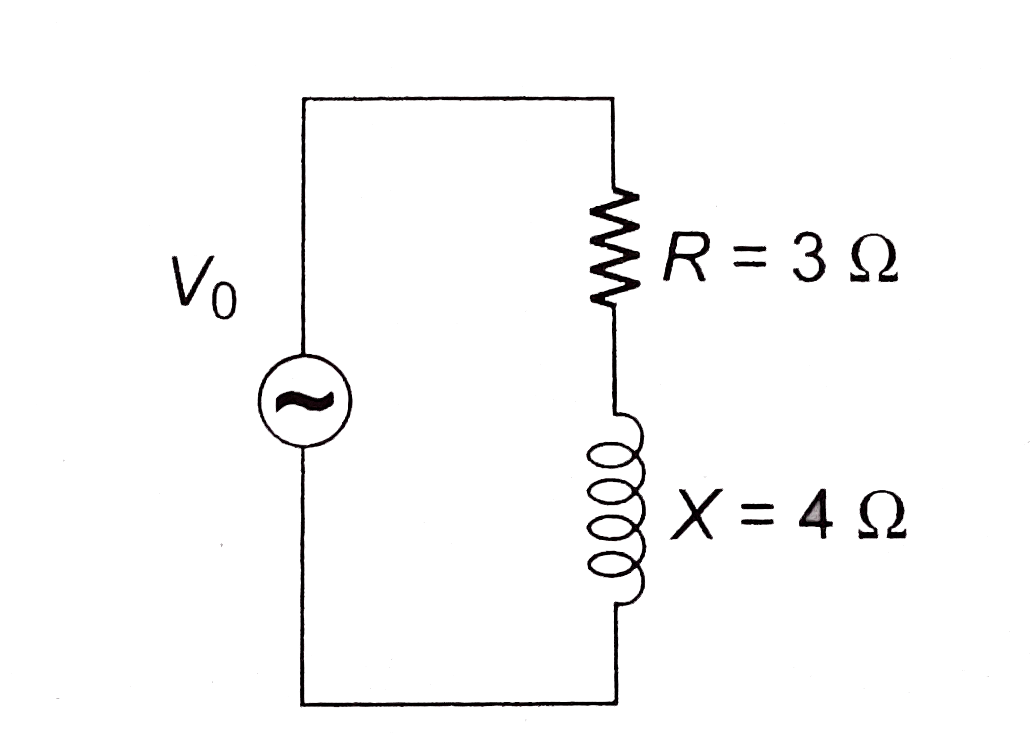 ` <br> <img src=) . .
|
|
| 7478. |
In SI system the fundamental units are |
|
Answer» meter, kilogram, second, ampere, Kelvin, mole and candela |
|
| 7479. |
A coil of effective area 0.45 m^(2) is placed in a field-free region. Subsequently, a uniform magnetic field that increases uniformly from zero to 1.25 T in 015 s is applied perpendicular to the plane of the coil. What is the magnitude of the emf inducted in the coil? |
|
Answer» Solution :Data: `NA= 0.45 m^(2), B_(f) = 1.25 T, B_(i) = 0, Deltat= 0.15s` Initial MAGNETIC flux, `Phi_(i) =0 (therefore B_(i)=0)` FINAL magnetic flux, `Phi_(f) = NAB_(f)` `E= - (DeltaPhi)/(Deltat) = -(Phi_(f)-Phi_(i))/(Deltat) = -(NAB_(f)-0)/(Deltat) = -(NAB_(f))/(Deltat)` `=-(0.45 xx 1.25)/(0.15)= -3.75 V` `therefore` The magnitude of the induced emf, `|E| = |(DeltaPhi)/(Deltat)|= 3.75` V |
|
| 7480. |
According to Moseley 'a' and 'b' are |
|
Answer» INDEPENDENT of the material |
|
| 7481. |
If an electron moving with a speed of 2.5xx10^(7)ms^(-1) is deflected by an electric field of 1.6k(V)m^(-1) perpendicular to its circular path, then (e)/(m) for the electron will be (given radius of circular path =2.3m): |
|
Answer» `1.67xx10^(11)Ckg^(-1)` `:.(e)/(m)=(v^(2))/(Er)=1*7xx10^(11)C Kg^(-1)` |
|
| 7482. |
Sometimes a radioactive nucleus decays into a nucleus which inself is radioactive . An example is : ""^38"Sulphur" underset"=2.48 h"overset"half-life"to ""^38 Cl underset"=0.62 h"overset"half-life"to ""^38 Ar (stable) Assume that we start with 1000 ""^38S nuclei at time t=0 . The number of ""^38Cl is of count zero at t=0 and will again be zero at t=oo . At what value of t, would the number of counts be a maximum ? |
|
Answer» 1.65 H |
|
| 7483. |
The equation of S.H.M. with amplitude 5m and period 0.5 sec is |
|
Answer» `y= 5 sin 4 PI t` |
|
| 7484. |
Three identical conductors of same material and dimension A, B and C are fixed at O as shown in figure. The conductorthrough which minimum heat flow is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 7485. |
What is meant by dielectric ? |
| Answer» Solution :A dielectric is a non-conducting material and has no free electrons. The electrons in a dielectric are bound WITHIN the atoms. Ebonite, GLASS and mica are some EXAMPLES of DIELECTRICS. | |
| 7486. |
A man is at a distance from the bus: when the bus begins to move with a constant acceleration 'a', with what minimum velocity the man should run towards the bus so as to catch it? |
|
Answer» `SQRT(2ax)` Distancecovered by the man=vt `:. X+(1)/(2)at^(2)-vt+x=0` or `t=(vpmsqrt(v^2-2ax))/(a)` Now t is real when `sqrt(v^(2)-2ax)` is +ve and its minimum VALUE is Zero. `:. V^2-2ax=0` or `v=sqrt(2ax)` |
|
| 7487. |
Uncertainty in position of a particle is 0.1587xx10^(-10) m what will be uncertainty in its momentum in kg ms^(-1)? |
|
Answer» `4xx10^(-23)` `Deltax DELTAP=(h)/(2pi)` `therefore Deltap=(h)/(2pix)` `=(6.625xx10^(-34))/(6.28xx0.1587xx10^(-10))` `=6.64736xx10^(-24)~~6.6xx10^(-24)KG ms^(-1)` |
|
| 7488. |
A cell of emf 2V and internal resistance 0.1 Omega is connected with a resistance of 3.9Omega . The voltage across the cell terminals will be |
|
Answer» a) 0.5 V |
|
| 7489. |
The photoelectric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is 1.5 V. What is themaximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`V_(0)=1.5V` `K_("max")=(1)/(2)mv_("max")^(2)=eV_(0)=1.6xx10^(-19)xx1.5=2.4xx10^(-19)J` |
|
| 7490. |
A charged particle experiences magnetic force in the presence of magnetic field. Which of the followingstatement is correct ? |
|
Answer» The PARTICLE is moving and magnetic FIELD is PERPENDICULAR to the velocity |
|
| 7491. |
The threshold frequency of a certain metal is v_(0). When frequency of incident radiation is 2v_(0), the maximum velocity of photoelectrons is found to be 3 xx 10^(6) m//s. If the frequency of radiataions is increased to 10v_(0), the maximum velocity of photoelectrons will be |
|
Answer» `(3)/(10)xx10^(6) m//s` `KE_(2)=h(10v_(0))-hv_(0)=9hv_(0)` `(KE_(2))/(KE_(1))=9rArr(v_(2))/(v_(1))=3` |
|
| 7492. |
Thick and thin wires give rise to 3 different squares x,y and z as shown in figure. The magnetic field at the centre of |
|
Answer» X, y and Z is zero |
|
| 7493. |
(a) Write symbolically the beta^(-) decay process of " "_(15)^(32)P. (b) Derive an expression for the average life of a radionuclide. Give its relationship with the half-life. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) The `BETA^(-)` decay process of `" "_(15)^(32)P` is symbolically written as : `" "_(15)^(32)Pto" "_(16)^(32)S+" "_(-1)^(0)e+bar(nu)` Here `e^(-)` is the `beta^(-)` PARTICLE and `bar(nu)` is antineutrino particle. (b) Let in a given radioactive sample INITIALLY we have `N_(0)` nuclei. At time t the number of nuclei intact is `N= N_(0)e^(-lambdat)`. The number of nuclei which decay in the time interval f to t + dt is `(-(dN)/(dt)).dt=lambdaNdt=lambdaN_(0)e^(-lambdat)dt`. Each of them has lived for time t. Hence, the total life of all these nuclei would be `tlambdaN_(0)e^(-lambdat)dt`. To obtain the average life of a RADIONUCLIDE we have to integrate this expression over all times from 0 to `oo` and divide by the total number `N_(0)` of nuclei at the beginning. `therefore` Average life period `tau = (lambdaN_(0)int_(0)^(oo)(t.e^(-lambdat)dt))/N_(0)=lambdaint_(0)^(oo)(te^(-lambdat)dt)=lambda[{(t.e^(-lambdat))/(-lambda)}_(0)^(oo)-int_(0)^(oo)(e^(-lambdat)/(-lambda)dt)]=lambda[(t.e^(-lambdat))/(-lambda)-e^(-lambdat)/(lambda)^(2)]_(0)^(oo)=1/(lambda)` `therefore` Half-life period `T_(1/2) = (ln2)/(lambda)= 0.693/(lambda)=0.693tau` |
|
| 7494. |
Define bBandwidth of transmission system |
| Answer» Solution :The range of FREQUENCIES required to transmit a piece of SPECIFIED information in a particular channel is CALLED channel bandwidth or the bandwidth of the transmission SYSTEM. | |
| 7495. |
For the telescope described in Exercise 9.3 (a), what is the separation between the objective lens and the eyepiece ? |
| Answer» Solution : 145 cm | |
| 7496. |
A series LCR circuit is connected to a DC source. The magnitude of inductive reactance is…………………. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :DIAMAGNETIC MATERIAL - MEISSNER EFFECT | |
| 7497. |
A direct vision spectroscope is made of two crown glass prisms each of which hasan angle of 5^(@) and two flint glass prisms. The dispersive powers of crown and flint glasses are 0.03. and 0.06 and their mean indices of refraction are 1.500 and 0.600 respectively. Calculate the dispersion produced by teh compound prism. What is the advantages of using two of each? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 7498. |
What is photo electric effect ? |
| Answer» Solution :EMISSION of ELECTRONS from a metal surface when illuminated by LIGHT. | |
| 7499. |
A current carrying coil in a uniform magnetic field behaves like a |
|
Answer» magnetic POLE |
|
| 7500. |
The magnitude of vectors vec(A), vec(B) and vec(C) are 12, 5 and13 units and vec(A) + vec(B) = vec(C) . The angle between A and B is : |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Since `(13)^(@)=(12)^(2) + (5)^(2)` `implies C^(2) =A^(2) + B^(2)` `:.` `vec(A)` and `vec(B)` are PERPENDICULAR to each other. |
|