Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 1051. |
Assume a planet is a uniform sphere of radius R that (somehow) has a narrow radial tunnel through its center (Fig. 13-8). Also assume we can position an apple anywhere along the tunnel or outside the sphere. Let F_R be the magnitude of the gravitational force on the apple when it is located at the planet's surface. How far from the surface is there a point where the magnitude is 1//3F_R if we move the apple (a) away from the planet and (b) into the tunnel? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `R = Rsqrt3,` (B) r = R/3 | |
| 1052. |
The time period of a large fluid star may depends upon its mean radius R, its mean density (p) and the gravitation constant G. Using dimensional consideration the value of T is : |
|
Answer» `kpRG` `=[L^(1)]^(x)[ML^(-3)]^(y)[M^(-1)L^(3)T^(-2)]^(z)` `M^(y-z)L^(x-3y+3z)T^(-2z)` `:.y-z=0` Solving we get `-2z=1x=0,y=-(1)/(2),z=-(1)/(2)` `x-3y+3z=0` HENCE correct choice is `(C )`. |
|
| 1053. |
If a strong diffraction peak is observed when electrons are incident at an angle i from the normal to the crystal planes with distance d between them (see figure), de-Broglie wavelength lamda_(dB) of electrons can be calculated by the relationship (n is an integer) |
|
Answer» ` d SIN i= n lamda_(dB)` |
|
| 1054. |
The output of a step down transfomer is measured to be 24V when connected to a 12W light bulb. The value of the peak current is……..A |
|
Answer» `1/SQRT2` `therefore I_2=12/V_2=12/24=1/2A` Now according to formula, `I_(RMS)=I_m/sqrt2` `therefore I_m=sqrt2 I_(rms)=sqrt2 times 1/2=1/sqrt2 A` |
|
| 1055. |
The escape velocity from the earth’s surface is 11.2 km//s The .escape velocity from the surface of the moon is ? Given that the mass of the earth is 80 times that of the moon and radius of the earth is 4 times that of the moon, |
|
Answer» a)`59.6km//s` |
|
| 1056. |
The radii of curvature of the faces of a double convex lens are 10 cm and 15 cm. If focal length is 12 cm. What is the refractiveindex of glass? |
|
Answer» Solution :`f = + 12CM , R_(1) = 10 cm , R_(2) = - 15 cm , n = ?` `As "" (1)/(f) = (n-1)((1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2)))` `(1)/(12)=(n-1)((1)/(10)+(1)/(15))=(n-1)XX(5)/(30)` `(n-1) = (6)/(12)= 0.5` n = 0.5 + 1 n = 1.5 |
|
| 1057. |
Compound microscope was invented by |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Galilleo,1990 | |
| 1058. |
A long straight wire along the z-axis carries a current 'i' in the negative z direction. The magnetic vector field vecB at a point having coordinates (x,y) in the z = 0 plane is |
|
Answer» `(mu_(0)i(yhati-xhatj))/(2PI(X^(2)+y^(2)))` |
|
| 1059. |
If a moving particle have linear momentum bar P and position vector bar r then choose the correct relation between bar r,bar p and angular momentum bar Lof particle about the origin. |
|
Answer» ` bar R . bar L =0` |
|
| 1060. |
Does the value of polarising angle i_(p) for a transparent medium depend upon the wavelength of the light? |
| Answer» Solution :Yes, the value of polarising ANGLE varies with the wavelength of light. | |
| 1061. |
The primary winding of a transformer has 100 turns and its secondary winding has 400 turns. The primary is connected to an a.c. supply of 120 V and the current flowing in it is 10 A. The voltage and the current in the secondary coil, assuming transformer to be an ideal one, are ................. respectively. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1062. |
How did the grandmother spend her afternoon everyday? |
|
Answer» by feeding HUNDRED of sparrows |
|
| 1063. |
A sphere is made of an alloy of Metal A (density 8 g//cm^(3)) and Metal B (density 6g//cm^(3)). The sphere floats in mercury (density 13.6 g//cm^(3)) with half its volume submerged. The percentage of the total volume of the sphere that is occupied by metal A is ___________ . |
|
Answer» Let the TOTAL VOLUME of the SPHERE be V Then,Weight = Buoyant force `IMPLIES[8x+6(1-x)]Vg=(1)/(2)(13.6)Vgimpliesx=0.4` |
|
| 1064. |
A magnetic substance is placed in magnetic fields of different intensity . Does it produce same effect ? |
| Answer» Solution :The MAGNETIC OFA MATERIAL depends on the strength of the external FIELD (or magnetising field) GREATER the external field strength , greater the response. | |
| 1065. |
In short wave communication, waves of which of the following frequencies will be reflected back by the ionospheric layer having electron density 10^(11)m^(-3) |
|
Answer» 2 MHz =`9(10^(11))^(1//2)=2.8xx10^(6)Hz`=2.8MHz The wave of frequency 2 MHz will be reflected by the IONOSPHERE. |
|
| 1066. |
The first diffraction minimum due to a single slite diffraction is seen at theta = 30^(@) for a light of wavelength 5000 Å falling perpendicularly on the slit. The width of the slit is: |
|
Answer» `5 XX 10^(-5)` cm `d sin30 = 1 xx 5000 xx 10^(-10)` `d= 10^(-6) m= 10^(-4)` cm |
|
| 1067. |
(a) describe briefly three experimentally observed features in the phenomenon of photoelectriceffect. (b) Discuss briefly how wave theory of light cannot explain these features. OR (a) Writethe important properties of photons which are used to establish Eintein's photoelectric equation . (b)Use this equationto explain the concept of (i) threshouldfrequencyand (ii) stopping potential .3. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Einstein's photoelctric equation is `E_(k) =hv-W` for single photon. (i)Explanation of frequency Law :when frequency of incident photon (v). Incceases, the kinetic energy of emitted electron increases. Intensity has no effect on kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (ii) Explanation of Intensity Law :when intensity of incidentlight increases, the number of incident photons increases, as one photon ejects on electron , the increases in intensity will increase the number of ejected electrons. in other words, photocurrent will increase of intensity.Frequencyhas no effect on photocurrent . (iii) Explaantion of no time Lag Law : When the energy of incident photon is greater than work function, the photoelectron is immediately ejected. Thus, there is no time between incidence of light and emission of photoelectrons. (b) The wave theory of light could not explain the observed characteristics of photolectric effect. Einstein EXTENDED plank's quantum idea of light of explain photoelectric effect. OR (a) Importnt properties of photon which are used to establish Einstein's photoectric equation are : (i) it is a STABLE elementary paraticle of zero charge and spin equal to one. (ii)It travels with the speed of light. (iii) it is the exchange paraticle in electromagetic force. (iv) Absorption of photons by atoms and molecules can CAUSE excitation and ionisation. Ithas particle nature. (b) Einstein's photoelectric equation is . `hv= W + E_(k)` where, hv= energy of incident photon. W= Work function of PHOTOMETAL. `E_(k)`= K.E. of photoelectrons. For threshold frequency and stopping potential. The equation `K_(max) = 1/2 m V^(2)_(max) = ho - phi_(0) ` is called Einstein,s photoelectric equation. (i) Threshold frequency : for a given photosensitive material, there is a certain minimum frequency of the incident radiations below which no emission of photoelectrons place. This frequency is called thsehold frequecy `(B_(0))` (ii) Stopping potential: The minimum negative potential given to ANODE in a photo-cell for which the photo-electric current befcomes is zero is called stopping potenial. It is denoted by `V_(0)` |
|
| 1068. |
Two plane mirrors are making an angle of 60^@ to each other. A light ray falls on one of the mirrors.The light ray is incident parallel to angular bisector of mirrors. How many reflection does the light ray undergo ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 1069. |
C, Si and Ge have same lattice structure . Why is C an insulator while Si and Ge are intrinsic semiconductors ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The 4 bondingelectrons of C , Si or Ge lie respectively , in the second , THIRD and fourth orbit . HENCE , ENERGY required to take out an electron from these atoms (i.e., ion ionisation energy `E_(g)`) will be least for Ge , followed by Si and highest for C . Hence number of free electrons for conduction in Ge and Si are significant but negligibly SMALL for C . | |
| 1070. |
A magician during a show makes a glass lens with n = 1.47 disappear in a trough of liquid. What is the refractive index of the liquid? Could the liquid be water? |
| Answer» Solution :The refractive index of the liquid must be equal to 1.47 in order to make the lens disappear. This MEANS` n_(1) = n_(2)` . This gives `1//f =0 or f RARR oo`. The lens in the liquid will act like a PLANE sheet of GLASS. No, the liquid is not water. It could be glycerine. | |
| 1071. |
A boy playing on the roof of a 10 m high building throws a ball with a speed of 10 m/s at an angle of 30° with the horizontal. How far from the throwing point will be ball be at the height of 10 m from the ground ?[g=10ms^(-2),sin30^@=1/2,cos30^@=sqrt(3)/2] |
|
Answer» 8.66 m `5sqrt(3)=8.66m` |
|
| 1072. |
An electron is moving with an initial velocity vecv=vecv_(0) hati and is in a uniform magnetic field vecB=B_(0) hatj. Then its de Broglie wavelength |
|
Answer» DECREASE with TIME `lamda =(H)/(p) =` constant |
|
| 1073. |
The diagram shows a semicircular ring carrying uniformly distributed charge +2muC on it. The radius of the ring is 4 cm A point charge +2muC is taken slowly from the point (0,0,8cm) to (0,8cm,0). The manitude of work done is equal to 4J After fixing the charge at its new position, the ring is rotated in anticlockwise sense about the x-axis as seen from (16cm,0,0)by an angle pi//2What is the magnitude of work done by electric field during the rotation of the ring? |
Answer»  `W=U_(B)-Q^(2)/((4piin_(0)sqrt(5))R)` …..(1) At new position `U'_(B)=Q^(2)/((4piin_(0)sqrt(5))R)` Work DONE `=U'_(B)=U_(B)=-W=-4J` |
|
| 1075. |
Ice starts forming in a lake with water at 0^@C when the atmospheric temperature is -10^@C. If the time taken for the first 1 cm of ice to be formed is 7 hour, then the time taken for the thickness of ice to change from 1 cm to 2 cm is |
|
Answer» 7 hour |
|
| 1076. |
As shown in figure. L is half part of an equiconvex lens (mu=1.5) whose surface have radius of curvature R=40cm and its right surface in silvered. Normal to principal axis, a plane mirror M is placed on the right of lens. A small object O is placed on left of the lens such that there is no parallax between final images formed by the lens and mirror. If transverse length of final image formed by the lens is twice that of image formed by the mirror. Calculate distance a between lens and object and distance b. |
Answer» SOLUTION :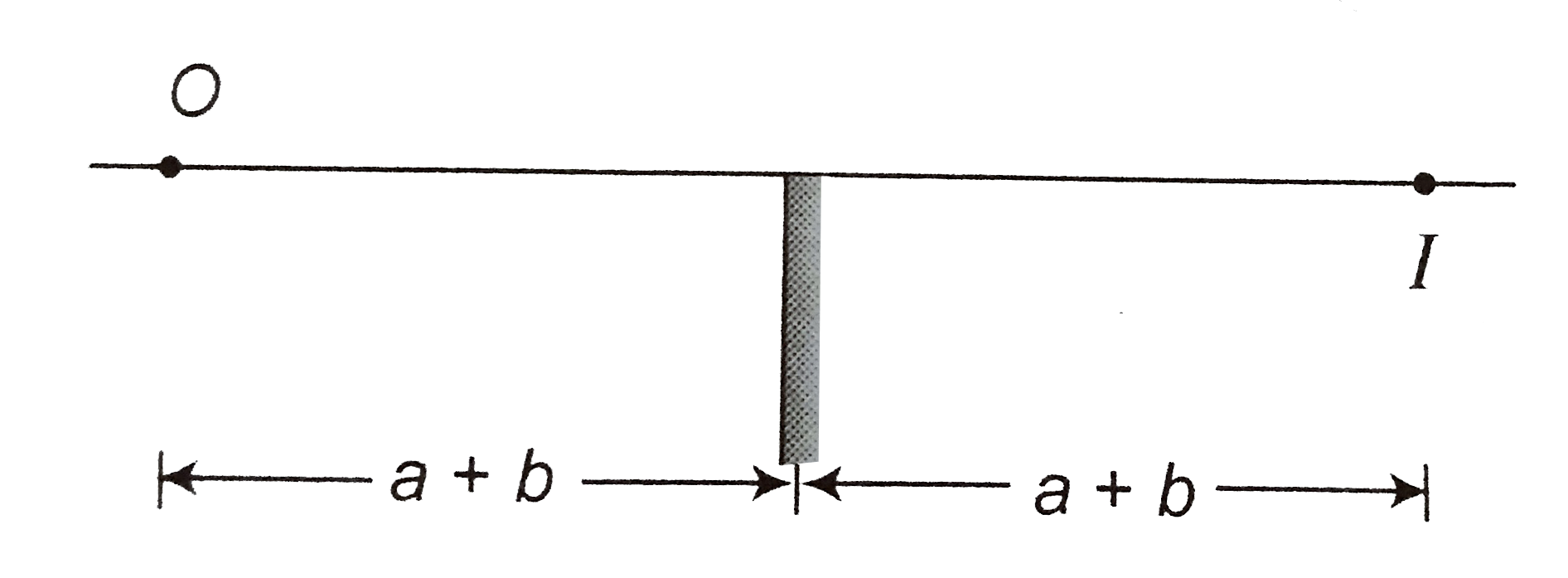  First CALCULATE focal LENGTH of silvered lens. `(1)/(F)=(1)/(f_l)+(1)/(f_m)+(1)/(f_l)=(2)/(f_l)+(1)/(f_m)` `=2((3)/(2)-1)((1)/(40)-(1)/(-40))+(1)/((40)/(2))` `=(1)/(20)+(1)/(20)=(1)/(10)impliesF=10cm` This silvered lens will behave as a CONCAVE mirror of focal length 10 cm. Image by plane mirror: Image by silvered lens/concave mirror: `(1)/(v)+(1)/(-a)=(1)/(-10)implies(1)/(v)=(1)/(a)-(1)/(10)=(10-a)/(10a)` `v=(10a)/(10-a)` `m=(I)/(O)=-(v)/(u)rArr2=-((10a)//(10-a))/(-a)` `10-a=5` `a=5cm` `v=(10a)/(10-a)=(10xx5)/(5)=10=a+2bimplies10=5+2b` `b=2.5cm` |
|
| 1077. |
A smooth pulley A of mass M_0 is lying on a smooth table. A light string passes round the pulley and has masses M_1 and M_2attached to its ends , the two portion of the string being perpendicular to the edge of the table so that the masses hang vertically . Calculate the acceleration of the pulley . |
|
Answer» Solution :Let the length of portions of string on the table be `l_0 , l_1 and l_2` as shown in figure . Let mass `M_0` MOVE to the right by x on the table , `M_1` goes down by `y_1 and M_2` goes up by `y_2` . Then `l_0` becomes `(l_0 -x),l_1` becomes ` (l_1 + y_1) and l_2` becomes ` (l_2 - y_2)`. As the length of string remains unchanged ` 2l_0 + l_1 + l_2 = 2(l_0-x) + l_1 + y_1 + l_2 - y_2` or ` 2 x = y_1 -y_2` Diff. twice w.r. to t, we get ` 2(d^(2)x)/(dt^(2)) = (d^(2) y_1)/(dt^(2)) - (d^(2)y_2)/(dt^(2))` If ` a_0 , a_1 and a_2` are acceleration of 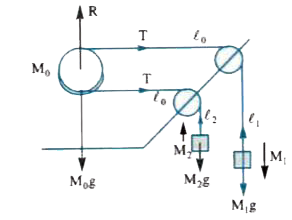 `M_0 , M_1 and M_2 ` respectively , then ` 2a_0 = a_1 - a_2` ......... (1) For motion of `M_0 , 2T= M_0a_0` ....... (2) `M_1g-T=M_1 a_1`....... (3) For motion of mass `M_2` , ` T-m_2g = M_2a_2` .......... (4) Substituting values of ` a_0 , a_1 and a_2` from (2) , (3) and (4) in equation (1) , we get ` 2((2T)/(M_0))=(g-(T)/(M_1)) -((T)/(M_2)-g)`, `(4T)/(M_0)= 2g-T((1)/(M_1) + (1)/(M_2)) i.e., ((4)/(M_0) + (1)/(M_1) + (1)/(M_2))T=2g ` This GIVES `T=(2M_0 M_1 M_2g)/(4M_1M_2+ M_0 (M_1 + M_2))`........ (5) `:.` Acceleration of puelly A from (2) `a_0 = (2T)/(M_0) = (4M_1M_2 g)/( 4M_1 M_2 + M_0(M_1 + M_2))` ............ (6) |
|
| 1078. |
A tuning fork is used to produce resonance in a glass tube. The length of the air column in this tube can be adjusted by a variable piston. At room temperature of 27^(@)C two successive resonances are produced at 20cm and 73cm of column length. If the frequency of the tuning fork is 320Hz, the velocity of sound in air at 27^(@)C is |
|
Answer» `330 m//s` |
|
| 1079. |
A bomb of mass 18 kg at rest explodes into two pieces of masses 6 kg and 12 kg. The velocity of 12 kg mass is 4 m/s. The kinetic energy of the other mass is : |
|
Answer» 288 J `:.6xxv_1+12xx4=0` `v_1=(-48)/(6)= -8 m//s` So K.E. of 6 KG MASS is `E_1=1/2xx6xx64` =192 J |
|
| 1080. |
Three condensers of capacities 3 mF, 6 mF, 12mF are connected in series with a battery. If the charge on 12 mF condenser is 24 mC, the P.D. across the battery is |
|
Answer» 2 V |
|
| 1081. |
The apparent dips in two mutually perpendicular planes are found to be delta_(1) and delta_(2) . Show that ture delta is related with delta_(1) and delta_(2) by cot^(2)delta=cot^(2)delta_(1)+cot^(2)delta_(2) [note, This is the principle of cot-method of finding true dip of a place. |
| Answer» | |
| 1082. |
A photodiode is made froma semiconductor In_(0.53) Gu_(0.47)A_(s), with E_(g)=0.73eV.What is the maximum wavelength which it can detect ?h=6.63xx10^(-34)J_(s) |
| Answer» Solution :The maximum wavelength`(LAMBDA)`, which a photodiode , which a photodiode can detect corresponds to the energy `E_(g).So h_(c)/lambda=E_(g)`,or`lambda=h_(c)/E_(g)=(6.63xx10^(-34)XX (3xx10^(8)))/(0.73xx1.6xx10^(-19))`=`1703xx 10^(-9)m=1703nm` | |
| 1083. |
What is threshold wave length ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The MAXIMUM ENERGY required for ejection of photoelectrons from METAL surfaces. | |
| 1084. |
A solenoid has a core of material of (relative) permeability 4000. the number of turn is 1000 turn per meter.A current of 2A flows through the solenoid find Magnetic intensity. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :H which depends upon the MATERIAL of the CORE is GIVEN by `H=ni=1000xx2=2xx10^3Am^(-1)` | |
| 1085. |
In the given circuit Ammeter reading is same when both switches S_1, S_2, are closed or opened. The value of resistance R is |
|
Answer» `200 OMEGA ` |
|
| 1086. |
Two similar balls of mass 'm' are hung by a silk thread of length L and carry similar charges as in figure Assuming the separation to be small, the separation between the balls (denoted by x) is equal to |
|
Answer» `[(Q^2 .2L )/( 4pi epsi_0 .mg)]^(1)/(3)` |
|
| 1087. |
A boy pulls a sled of mass 5.0 kg with a rope that makes a 60.0^(@) angle with respect to the horizontal surface of a frozen pond. The boy pulls on the rope with a force of 10.0 N, and the sled moves with constant velocity. What is the coefficient of friction between the sled and the ice? |
|
Answer» `0.09` |
|
| 1088. |
A point source of light S, placed at a distance L in front of the centre of a mirror of width d, hangs vertically on a wall. A man walks in front of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror at a distance 2L from it as shown in figure. Find the greatest distance over which he can see the image of the light source in the mirror. |
|
Answer» Solution :The ray diagram will be as shown in Figure. HI =AB=d, DS=CD=d/2 Since, AH=2AD, ` thereforeGH = 2CD= 2 (d)/(2) = d ` SIMILARLY IJ = d GJ = GH+HI+IJ = d+d+d=3d 
|
|
| 1089. |
There is a uniform magnetic field B normal to the xy plane. A conductor ABC has length AB=l_(1), parallel to the x axis, and lengthh BC=l_(2) parallel to the y-axis. ABC moved in the xy plane with velocity v_(x)hati+v_(y)hatj. The potential difference between A and C is proportional to |
|
Answer» `v_(X)l_(1)+v_(y)l_(2)` |
|
| 1090. |
How does the resistance of a conductor depend on its length? |
| Answer» Solution :DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL OR As length INCREASES, resistance increases | |
| 1091. |
A sonometer wire stretched by a load of densityrho has a fundamental frequency n_(1). When the load is completely immersed in water ( density rho_("w")), its fundametnal frequency is n_(2). Show thatn_(2)/n_(1) = sqrt((rho - rho_("w"))/rho). Two organ pipes , open at both ends, are sounded together and 5beats are heard per second. The length of the shorter pipe is0.25 m . Find the length of thelonger pipe. [Speed ofsound in air = 350 m/s, end correction at one end = 0.015 m for both pipes .] |
|
Answer» Solution :On immersing the load in water , theapparent weight of the load ( in water) and hence thetension in the WIRE decreases because of theforce due to buoyancy of water. Since the frequency of the vibrating wire is derectly proportional to thesquare root of thetension, thefrequency decreases. Let `W_(1)` = weight of the load in air , `W_(2)` = (apparent ) weight of the load in water If `T_(1) and T_(2)` are the respective tensions in thewire , `T_(1) = W_(1) and T_(2) = W_(2)`. By definition, relative density of a SOLID ` = ("density of the solid")/("density of water") ` ` = ("weight of the body in air")/"(apparent) loss in weight of the body in water )" ` ` :. ` Relative density , ` s = rho/rho_("w") = (W_(1))/(W_(1) - W_(2)) = T_(1)/(T_(1) -T_(2) )` ` :. T_(1)/T_(2) = rho/(rho -rho_("w"))` ` n _(1) = 1/(2L) sqrt(T_(1)/m) and n_(2) = 1/(2L) sqrt(T_(2)/m) ` ` :. n_(2)/n_(1) = sqrt(T_(2)/T_(1))"" :. n_(2)/n_(1) = sqrt((rho - rho_("w"))/rho)` which is the required expression. Data : ` l_(1) = 0.25` m beat frequency = 5 Hz, V = 350 m/s, e = 0.015 m Since `l_(1) LT l_(2) , n_(1) gt n_(2)`. ` :.n_(1) - n_(2) = 5` Hz Total end correction for each open pipe, 2e = 0.03 m. ` n_(1) = v/(2(l_(1) +2e)) = (350)/(2(0.25 + 0.03))` ` = 350/(2 xx 0.28)` ` = 350/(0.56) = 625 `Hz `{:(log 350,," "2.5441),(log 0.56,,UL(-bar(1).7482)),(,,ul(" "2.7959)):}` AL ` 2.7959 = 625.0` ` :. n_(2) = n_(1) - 5 = 625 - 5 = 620 - 5 = 620 ` Hz `n_(2) = (v/(2(l_(2)+2e)))` ` :. l_(2) + 2e = v/(2n_(2)) = 350/(2 xx 620 ) = 350/1240 ` ` = 0.2823` m `{:(log 350,," "2.5441),(log 1240,,ul(-3.0934)),(,,ul(" "bar(1).4507)):}` AL ` bar(1).4507 = 0.2823` ` :. ` The length of the longer pipe, ` l_(2) = 0.2823 - 0.03 = 0.2523` m |
|
| 1092. |
Which of the following does not represent unit of electric charge : |
|
Answer» Coulomb |
|
| 1093. |
The figure shows three infinite potential wells of widths L, 2L, and 3L, each contains an electron in the state for which n = 10. Rank the wells according to (a) the number of maxima for the probability density of the electron and (b) the energy of the electron, greatest first. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) all TIE, (B) a, b, C | |
| 1094. |
What is sensitivity of wheatstone's bridge ? |
| Answer» Solution :A wheatstone. s bridge is SAID to be sensitive if it a PRODUCES more defletion in the galvanometer for a small change of RSISTANCE in resistor ARM. | |
| 1095. |
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation in an astronomical telescope for normal adjustment position. Write down the expression for its magnifying power. |
|
Answer» Solution :A RAY DIAGRAM showing the image formation in an astronomical telescope for normal ADJUSTMENT is being shown in Fig. 9.50. Magnifying POWER of telescope in normal adjustment `m=-f_(0)/f_(e)` where `f_0` = focal length of objective and `f_e` = focal length of eyepiece. The length of the telescope tube L = distance between O and E lens = `f_(0) + f_(e)` 
|
|
| 1096. |
If the interatomic spacing in a steel wire is 2.8xx10^(-10)m. And Y_("steel")=2xx10^(11)N//m^(2),then force constant in N//m is |
|
Answer» 5.6 |
|
| 1097. |
There is formation of layer of snow x cm thick on water, when the temperature of air is -theta^(@)C (less than freezing point). The thickness of layer increased from x to in the time t, then the value of t is given by : |
|
Answer» `((X-y)(rhoLK))/(2theta)` `t(rhoL)/(2ktheta)(y^(2)-x^(2))=(rhoL(y-x)(y+x))/(2ktheta)` CORRECT CHOICE is (c). |
|
| 1098. |
Law of multiple proportion was given by ………. |
|
Answer» Lavoisier |
|
| 1099. |
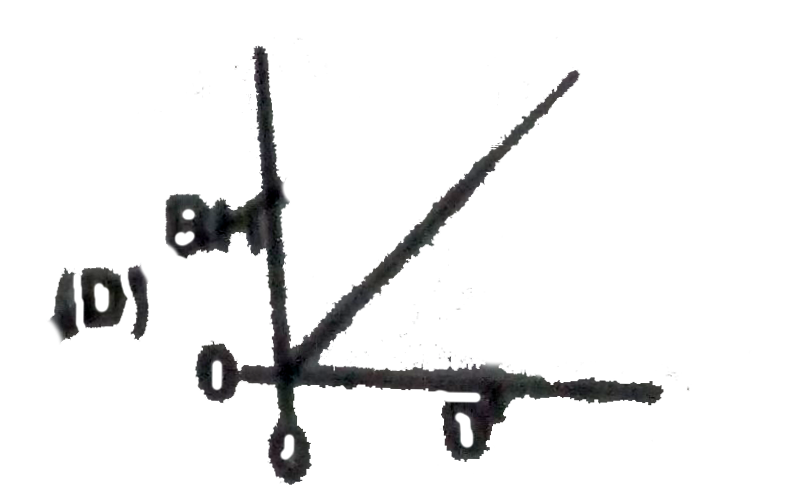
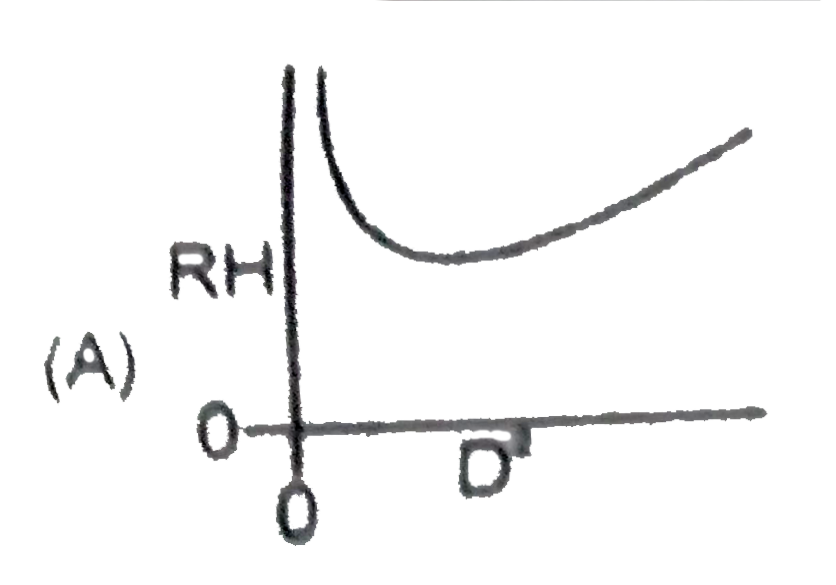
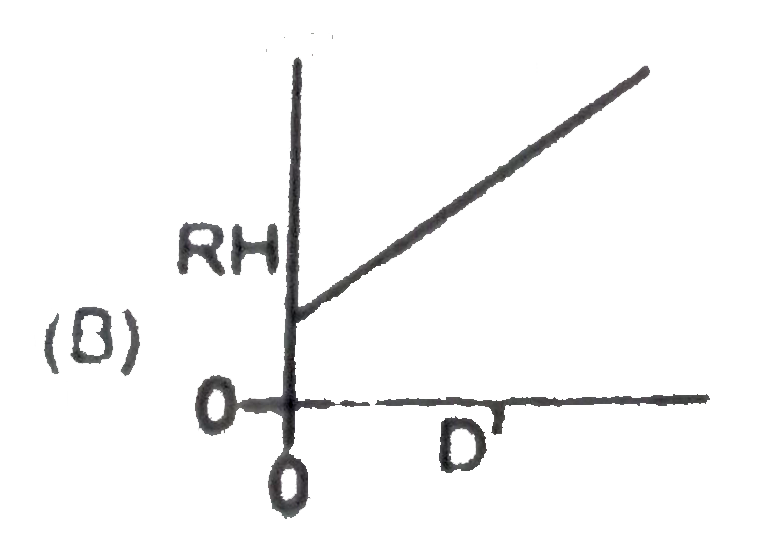
A semicircular wire of radius R is oriented vertically. A small bead is released from rest at the top of the wire, it slides without friction under the influence of gravity to the bottom, where is then leaves the wire horizontally and falls a distance H to the ground. The bead lands a horizontal distance D away from where it was launched. Which of the following is a correct graph of RH against D^(2) ? |
|
Answer»
`D=sqrt((2H)/(G))xxsqrt(4gR)=2sqrt(2RH)` `D^(2)=8RH` |
|
| 1100. |
Electric current is the flow of charges along a defi nite direction and take place through metals as well as semiconductors.Mention the charge carriers in the above cases. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :METALS - ELECTRONS ,SEMICONDUCTOR - Electrons and HOLES | |