Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39651. |
A dielectric slab of length 1, width b, thickness d and dielectric constant K fills the space inside a parallel plate capacitor. At t = 0, the slab begins to be pulled out slowly with speed v. At time t, the capacity of the capacitor is |
|
Answer» `(epsi_0 b) /( d )[ Kl - (K -1) v t]` |
|
| 39652. |
A lens whose focal length is 40 cm forms a Fraunhofer diffraction of 50 cm and the distance width 0.3 m m . The distance of the first dark band from the direct one is is 0.785 mm. calculate the wavelength of light. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :5889.5 Å | |
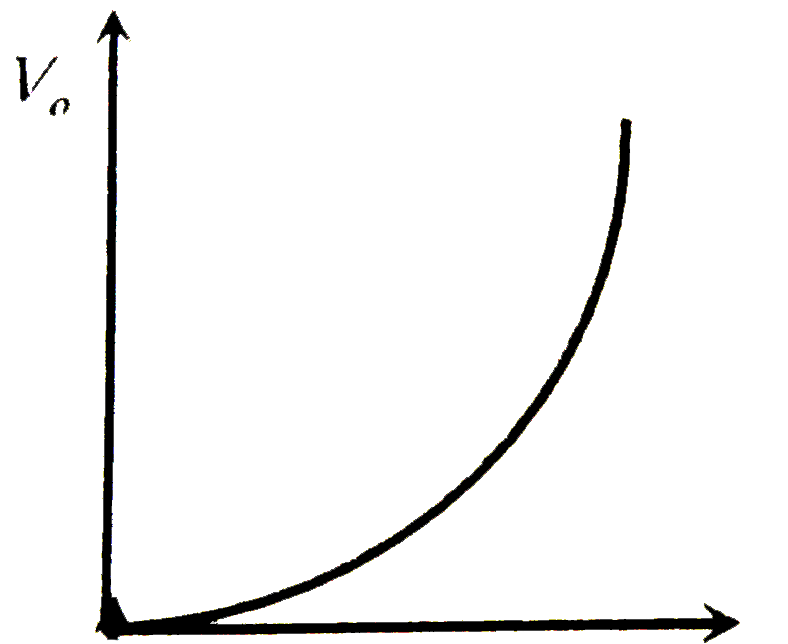
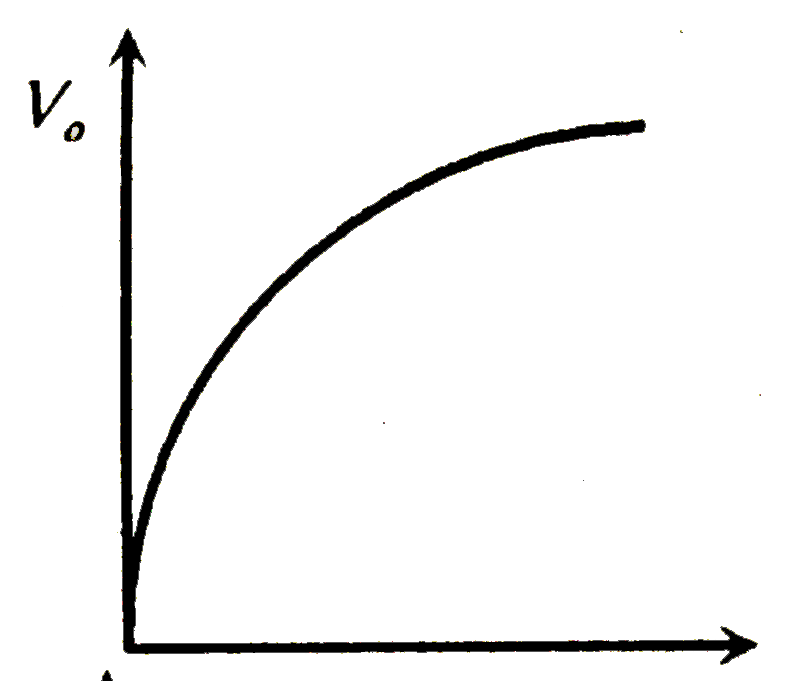
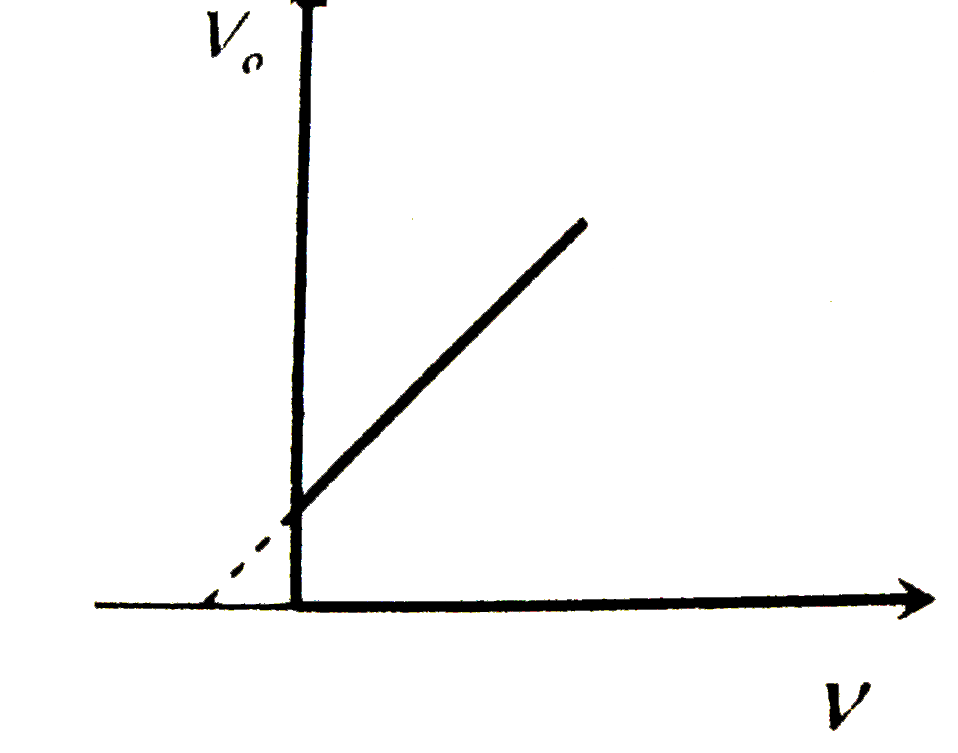
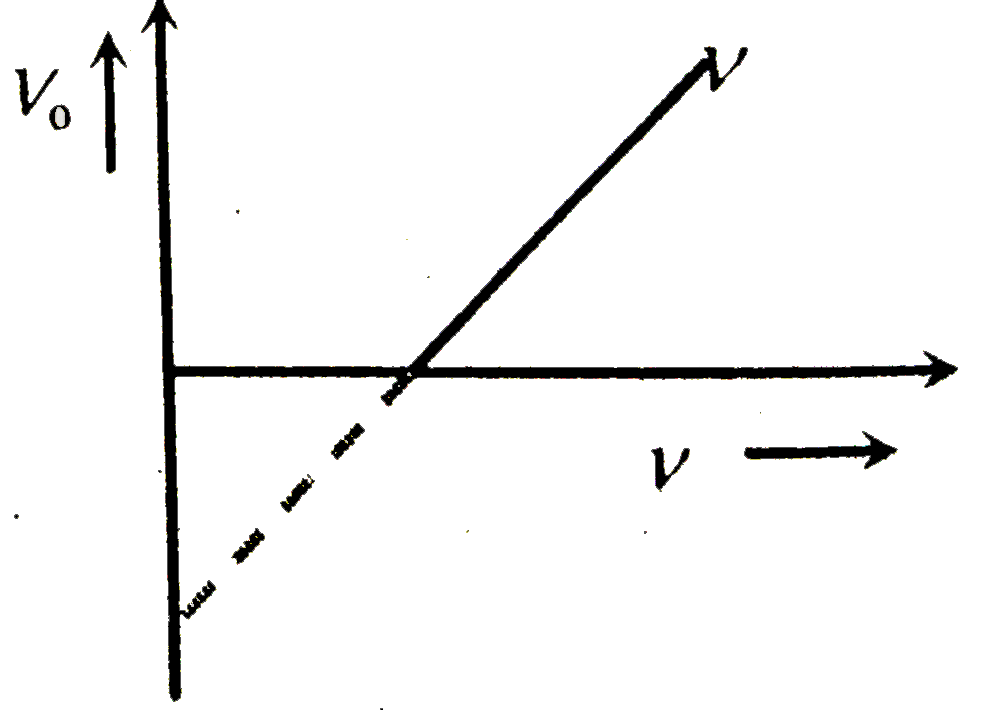
| 39653. |
For a photoelectric cell the graph showing the variation of cut of voltage (V) with frequency (v) of incident light is best represented by |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39654. |
A molecule with a dipole moment p is placed in electric field of strength E. Initially the dipole is aligned parallel to the field. If the dipole is to be rotated to be anti-parallel to the field, the work required to be done by an external agency is |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 39655. |
A layer of oil 3 cm thick is floating on a layer of coloured water 5 cm thick. The refractive index of the coloured water is 5/3 and the apparent depth of the two liquids is 36/7cm. Then the refractive index of the oil is, |
|
Answer» `7/4` |
|
| 39656. |
(A): A dynamo converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.(R): The dynamo is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. |
|
Answer» Both .A. and .R. are TRUE and .R. is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of .A. |
|
| 39657. |
A solid which is not transparent to visible light and whose conductivity increases with temp is formed by |
|
Answer» METALLIC BONDING |
|
| 39658. |
Why do helium atom and the hydrogen molecule have such different spectra? |
| Answer» Solution :The spectral lines of a helium ATOM are DUE exclusively to the electronic transitions from one energy level to ANOTHER. These transitions result in a line spectrum. In a HYDROGEN molecule there is a set of vibrational and rotational levels, in addition to the electronic levels. Because of this the spectrum of a hydrogen molecule consists not of isolated lines, but of bands. | |
| 39659. |
The attenuation of a signal is compensated by |
|
Answer» RECTIFIER |
|
| 39660. |
Why are control rods made cadmium an a nuclear reactor? |
| Answer» Solution :CADMIUM have high cross-section for neutron absorption. So they can EASILY absorb NEUTRONS and control ENERGY PRODUCTION. | |
| 39661. |
What happens during regulation action of zener diode? |
|
Answer» The CURRENT through the series RESISTANCE `(R_s)`changes |
|
| 39662. |
To transmit signals in the range 30-300 MHz space Sr wave propagation is used. Why It is called Line of Sight (Los)? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Because the receiving ANTENNA and TRANSMITTING antenna should be in LINE of SIGHT of wave. | |
| 39663. |
The self-inductance of two solenoids A and B having equal length are same. If the number of turns in two solenoids A and B are 100 and 200 respectively the ratio of the radii of their cross section will be ........ |
|
Answer» `2:1` `L=(mu_0N^2A)/l` `therefore N^2 PROP 1/r^2` `therefore N_2/N_1=r_1/r_2` `therefore (200/100)=r_1/r_2` `therefore r_1/r_2=2/1` |
|
| 39664. |
A coil carrying a heavy current and having large number of turns mounted in a N-S vertical plane and current flow in clockwise direction. A small magnetic needle at its centerwill have its north pole in |
|
Answer» EAST -NORTH direction |
|
| 39665. |
A moving charge produces |
|
Answer» an ELECTRIC FIELD only |
|
| 39666. |
Derive the equation for lateral magnification in spherical mirrors. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Consider an extended object OO' is kept perpendicular to the PRINCIPAL axis to theleft of the single spherical SURFACE. (II) The image formed on the other side of the surface is II'. Consider a ray from O' in the first medium towards C in the second medium. (iii) As this ray is incident normal to the spherical surface, it goes undeviated in the second medium. The position of image may be located using the Equation (2). (iv) The lateral or transverse magnification m is defined as the ratio of height of the image to the height of the object. ` m = (II')/(OO') ` (v) From the two similar triangles `DELTA`COO' and `Delta`CII', we can write, ` (II')/(OO') = (CI)/(CO)` From the geometry, ` (CI)/(CO) = (PI - PC)/(PC + PO)` Hence ` m = (II')/(OO') = (PI- PC)/( PC + PO)`.... (1) Applying sign conventions in the above equation (1), `II' = h_2 , OO' - h_1 , PI = +v, ` PC = +R, PO = u (vii) Where, h, is the height of the object and `h_2` is the height of the image. ` m = (-h_2)/(h_1) = (v - R)/(R +(-u)) , m= h_2/h_1= - ((v-R)/(R-u))` After rearranging, ` m = h_2/h_1= - (R - v)/(R-u) "" ....(2)` (viii) We can also arrive at an equation for lateral magnification involving the refractive indices of the two media.(ix) Let us consider the equation for single spherical surface as, ` (n_2)/(v)- (n_1)/(u) = ((n_2-n_1))/(R)` Further simplifying, ` (n_2u - n_1 v)/( vu) = ((n_2 - n_1))/(R)` Rewriting for R, ` R = ((n_2 - n_1)vu)/(n_2 u - n_1 v)`...(3 ) `R - v = (n_1v (v-u) )/(n_2 u - n_1 v) "" ....(4)` (x) Substituting equations (3) and (4) in equation (2) we get the equation for lateral magnification as, ` m= h_2/h_1 = (n_1 v)/(n_2 v)` |
|
| 39668. |
If earth decreases its rotational speed without changing other factors. Match the following. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39669. |
Two bar magnets of the same length and breadth but having magnetic moments M and 2M are joined together pole for pole and suspended by a string. The period of oscillation of this assembly in a uniform magnetic field B is 3sec, What will be the period of oscillation if the polarities of one of the magnets is changed and the combination is again made to oscillate in the same field? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`3 SQRT(3) SEC ` | |
| 39670. |
A machine gun has a mass 5 kg. It fires 50 gm bullets at the rate of 30 bullets per minute at a speed of 400 m/s. What force is required to keep the gun in position. |
|
Answer» 15N |
|
| 39671. |
Hydrogen atom is excited from ground state to another state with principle quantum number equal to 4. Then the number of spectral lines in the emission spectra will be ...... |
|
Answer» 2 `=(n(n-1))/(2)` `=(4(4-1))/(2)` `=(4xx3)/(2)=6` |
|
| 39672. |
IfvecA= 3 hati+ 4 hatjandvecB= 7hati+ 24hatj,findvector havingthe samemagnitudeasvecBandparalleltovecA |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`15 I + 20 J` | |
| 39673. |
In a ice rink, a skator moving with a velocity 3 m/s encounters a rough patch that reduces the speed by45%. Find the length of the rough patch if frictional force is 25 % of the weight |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 39674. |
Yellow light (lamda=6000Å) illuminates a single-slit of width 1xx10^(-4)m. calculate (i) the distance between two dark lines on either side of the central maximum when the diffraction pattern is viewed on a screen kept 1.5 m away from the slit, (ii) the angular spread of the first diffraction minima. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here `lamda=6000Å=6000xx10^(-10)m`, slit width `a=1xx10^(-4)`m, distance of screen from the slit D=1.5m (i) `THEREFORE` Distance between two dark lines on opposite sides of the CENTRAL MAXIMA in diffraction pattern. `x=(2lamda)/(a)D=(2xx6000xx10^(-10)xx1.5)/(1xx10^(-4))=1.8xx10^(-2)m=1.8m` (II) The angular spread of the first diffraction minima `theta_(1)=(lamda)/(a)=(6000xx10^(-10))/(1xx10^(-4))=6xx10^(-3)rad` |
|
| 39675. |
The wing span of an aeroplane is 40m. The plane is flying horizontally due north at 360 km/h. What is the potential difference developed between the wing-tips if the horizontla component of the Earth's magnetic field B_(h) = 3.2 xx 10^(-5)T and the angle of dip at the place is 60^(@) ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Data: l=40m, V=360 km/H `=360 xx 5/18= 100` m/s, `B_(h) = 3.2 xx 10^(-5) T, delta = 60^(@)` The area swept out by the wing per UNIT time= lv. The magnetic lines of induction perpendicular to this area are those of the vertical component `B_(v)` of the Earth's magnetic field. `B_(v) = B_(h) tan delta` where `delta` is the angle of DIP. `therefore` The magnetic FLUX cut by the wing per unit time `=(dPhi_(m))/(dt) = B_(v)(lv) = B_(h)tan delta(lv)` `=(3.2 xx 10^(-5))(tan 60^(@))(40)(100)` `=(12.8 xx 10^(-2))(1.732) = 0.2217 Wb//s` `therefore` The induced emf, `E=-(dPhi_(m))/(dt)` (nummerically) `=0.2217` V |
|
| 39676. |
In the following diagram, the arm PQ of the rectangular conductor is moved from x = 0 , outwards. The unfirom magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane and extends from x=0 to x=b and is zero for xgtb. Only the arm PQ possesses substantial resistance 'r'. Consider the situation when the arm PQ is pulled outwards from x = 0 to x = 2b, and then moved back to x = 0 with constant speed 'v'. Obtain expressions from the (i) magnetic flux, (ii) the induced emf, (iii) the force necessary to pull the arm and (iv) the power dissipated as joule heat. Sketch the variation of these quantities with distance. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :As per FIGURE given with the question let us first consider the forward motion from x= 0 to x = 2b.(i) Magnetic flux `phi_(B)` linked with the circuit SPQR will be `phi_(B)=Blx` for `0lexleb` and `phi_(B)=Blb" for "b le x le 2b`. (II) The induced emf `epsilon=(dphi_(B))/(dt)` is `epsilon=-Blv" for "0lexleb` `and epsilon=0" for "b le x le 2b`. (iii) When `epsilon` is non - zero induced current `I=(epsilon)/(r)`. `therefore` Force required to keep the arm PQ in constant NOTION will be `F=IlB` towards left. Thus, `F=(B^(2)l^(2)v)/(r) " for "0lexleb and F = 0 " for " b le x le 2b` (IV) Power dissipalated as Joule heat `P=I^(2)r` So, `P=(B^(2)l^(2)v^(2))/(r)" for "0lexleb` and `P=0" for "b le x le 2b.` For inward motion from x = 2b to x = 0, we get similar results. The variation of `phi_(B), E, F and P` with x si shown in the figure. 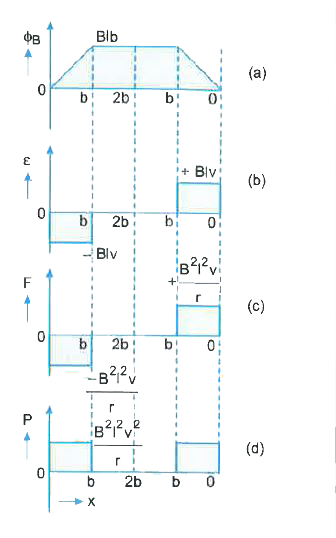
|
|
| 39677. |
As per Bohr atom model if the radius of the first orbit in an hydrogen atom is to, then the radius of the third orbit is. |
|
Answer» `(r_(0))/( 9)` |
|
| 39678. |
To obtain the current gain (beta) of a transistor, when it is in CE mode, we use |
|
Answer» its INPUT characteristics |
|
| 39679. |
Velocity of any fluid particle in a steadyincompressible, two dimehsional flow is given by vecv=3xhati-3yhatj Then resultant streamline (for xgt0) can be plotted as |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 39680. |
Refractive index of prism of prism angle 6^@ is 1.5, then minimum deviation is ...... . |
|
Answer» `3^@` For SMALL values of A and `delta_m` `sin((A+delta_m)/(2))` `=(A+delta_m)/(2)` and `sin(A/2)~~A/2` `n=((A+delta_m)/(2))/(A/2)` `THEREFORE n=(A+delta_m)/(A)impliesnA-A=delta_m` `therefore delta_m=(n-1)A therefore delta_m=(1.5-1)6^@therefore delta_m=3^@` |
|
| 39681. |
A source of sound with natural frequency v_(0) moves uniformly along a straight line separated from a stationary observer by a distance l . The velocity of the source is equal to eta fraction of velocityof sound. Find the frequency of sound received by the observer at the moment when the source gets closest to him and also find the distance between the source and the observer at the moment, when the observer receives a frequency v = v_(0) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39682. |
A sound wave of frequency f travels horizontally to the right. It is reflected from a large vertical plane surface moving to tin left with a speed v. The speed of sound in the medium is c, then |
|
Answer» The frequency of the reflected WAVE is `(f(C+v))/(c-v)` |
|
| 39683. |
Maximum height of a bullet when fired at 30° with the horizontal is 11m. Then height when it is fired with the horizontal at 60° is : |
|
Answer» 22m Also `u^(2)/gxxsin^(2)60^@=H` or `h=44xx3/4=33m` |
|
| 39684. |
Deduce coulomb's law in electrostatics from Gauss theorem. Or State and prove Gauss's law in electrostatics. |
|
Answer» Solution :Gauss.s Theorem. It states that the total electric flux through any closed surface is equal to `(1)/(epsi_(0))` TIMES the total electric CHARGE enclosed by the surface. Mathematically, `phi=ointvec(E).dvec(S)=(q)/(epsi_(0))` Proof. Consider a closed spherical surface S and a point charge +q be placed at its centre O as shown in the figure. consider a small element of area dS around point P through which the electric flux `dphi` is given by `dphi=vec(E),dvecS` 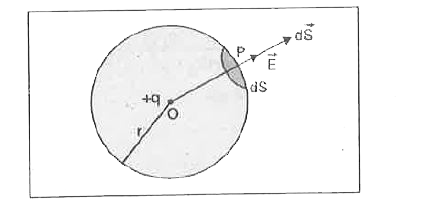 Total electric flux linked whole closed surface S will be `phi=ointdphi=ointvecE.dvecS` or `phi=ointEdScos0^(@)=ointEdS`. .(i) The electric FIELD intensity E at P due to charge q at O is given by `E=(1)/(4piepsi_(0))(q)/(r^(2))`. . (ii) Putting Eq. (ii) in Eq. (i), we GET `phi=oint(1)/(4piepsi_(0))(q)/(r^(2))dS` `=(1)/(4piepsi_(0)r^(2))ointdS` `=(1)/(4piepsi_(0)r^(2))4pir^(2)` or `phi=(q)/(epsi_(0))` This is Gauss theorem. Coulomb.s law from Gauss Theorem Consider an isolated positive charge +q at O. imagine a sphere of radius r and centre O. Electric field `vecE` at every point on the sphere is the same and is DIRECTED outwards. direction of small area element `vec(dS)` is also along `vecE` i.e., the angle between `vec(E)` and `vec(dS)` is `0^(@)`, According to Gauss theorem, `oint_(S)vecE.vec(dS)=(q)/(epsi_(0))` 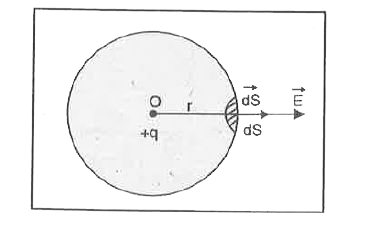 or `oint_(S)EdScos0^(@)=(q)/(epsi_(0))` or `Eoint_(S)dS=(q)/(epsi_(0))` or `Exx4pir^(2)=(q)/(epsi_(0))` or, `E=(q)/(4piepsi_(0)r^(2))` If another charge `q_(0)` is placed on the sphere then force F on it is `F=q_(0)E=(q_(0)q)/(4piepsi_(0)r^(2))` which is coulomb.s law. |
|
| 39685. |
A microscope is focussed on the scratch at the bottom of a beaker. Water is pured into it and the microscope is focussed again on the scratch at the bottom of the beaker. Some lycopodium power is sprinkled on the surface of water and microscope is focussed on to the powder. The corresponding readings are 1.17, 2.02 and 4.57 cm respectively, the refractive index of water is |
|
Answer» `(3)/(2)` |
|
| 39686. |
A concave mirror of radius of curvature two meter is placed at the bottom of the tank of water. The mirror forms an image of the sun when it is directly overhead. Calculate the images from the mirror for (i) 160 cm and (ii) 80 cm of water in the tank. (Take,µ=4/3 for water) |
Answer» Solution :(i)  Focal lengh of mirror, `f=R/2=200/2=100 cm` For PARALLEL rays, image is formed at focus of mirror, PI=100 cm (II) When DEPTH of water is 80 cm  `musini=1xxsinr` As angles i and r are small, sin i= tan i, SINR =tanr `4/3cdot(AB)/(OB)=(AB)/(BI)rArr4/3cdot1/20=1/(BI)` `BI=15cmrArrPI=80+BI=80+15=95 cm` Alternatively `MU(BI)=BOrArr4/3xxBI=20rArrBI=15cm` |
|
| 39687. |
The frequency of the second overtone in a pipe open at both ends is n_(1). The frequency of the second overtone in a pipe of the same dimensions but closed at one end is n_(2). Then, |
|
Answer» `n_(1)=(6)/(5)n^(2)` |
|
| 39688. |
The gravitational field strength at the surface of a certain planet is g. Which of the following is the gravitational field strength at the surface of a planet with twice the mass? |
|
Answer» `g//2` `(E.)/(E )=(g.)/(g)=(M^(1))/(M)xx(R^(2))/(R^(2,))=(2M)/(M)=(R^(2))/(4R^(2))=(1)/(2)` `therefore E.=(E )/(2)=(g)/(2)`. So CORRECT choice is (a). |
|
| 39689. |
A cylinderical glass rod of radius 0.1 m and refractive index sqrt3 lies on a horizontal plane mirror. A horizontal ray of light moving perpendicular to the axis of the rod is incident on it. At what height from the mirror should the ray be incident so that it leaves the rod at a height of 0.1 m above the plane mirror? At what centre to centre distance a second similar rod, parallel to the first, be placed on the mirror, such that the emergent ray from the second rod is in line with the incident ray on the first rod? |
|
Answer» `:. angleOPQ = angleOQP = r("say")` 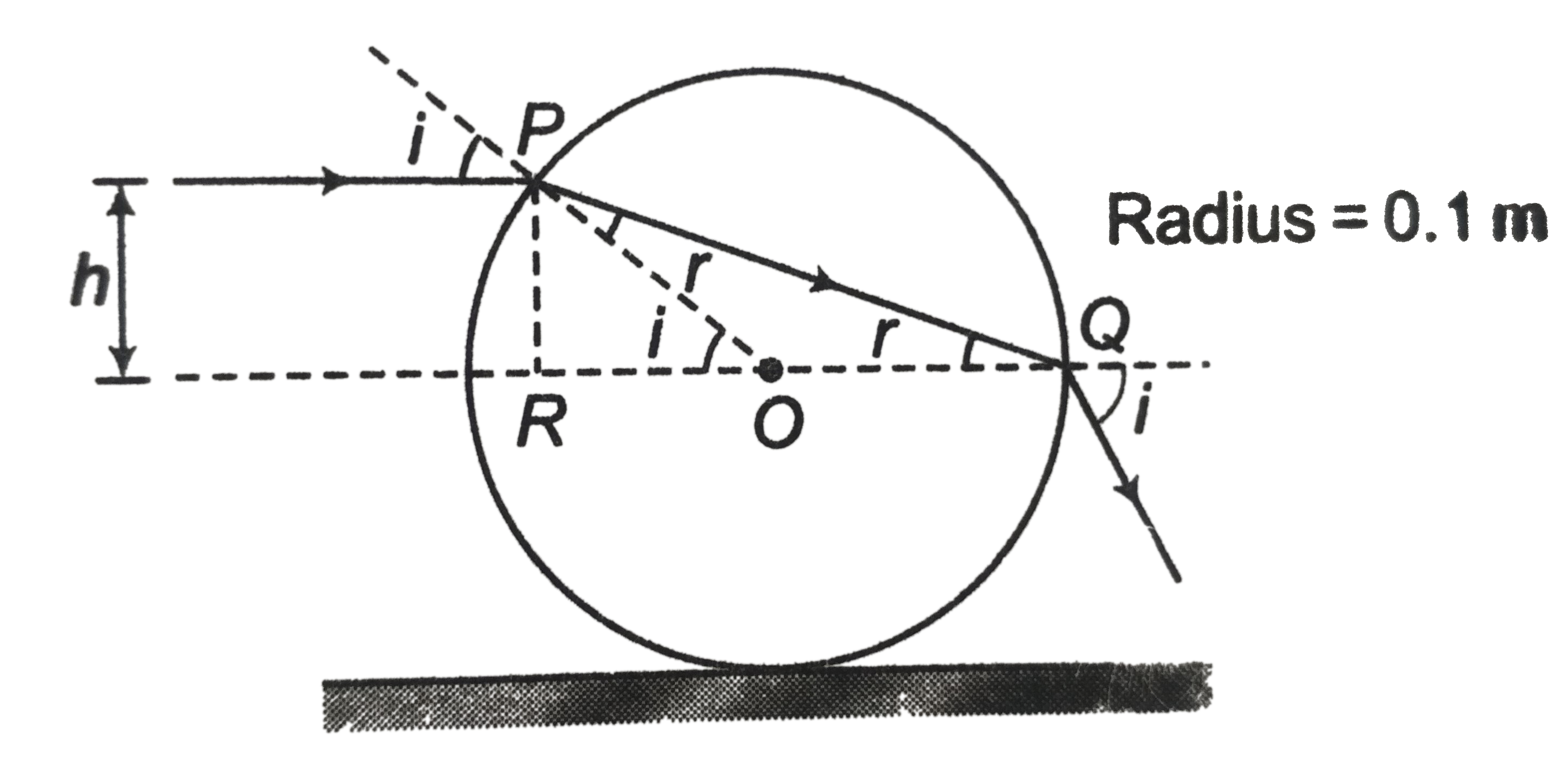 ALSO, `i = r + r = 2r` In `DeltaPQR, h = OP sin I = 0.1 sin t` `= 0.1 sin 2r` or `h = .0.2 sim r cosr`……(i) Also `sqrt(3) = (sin i)/(sin r) = (2 sin r cos r)/(sin r)` `= 2 cos r ` `:. r = 30^(@)` Substituting in Eq. `(i)`, we get ` h = 0.2 XX (1)/(2) xx (sqrt(3))/(2)` `= 0.086 m`. Hence, height from the MIRROR is `0.1 + 0.086 = 0.186 m` (ii) Use the principle of reversiblity 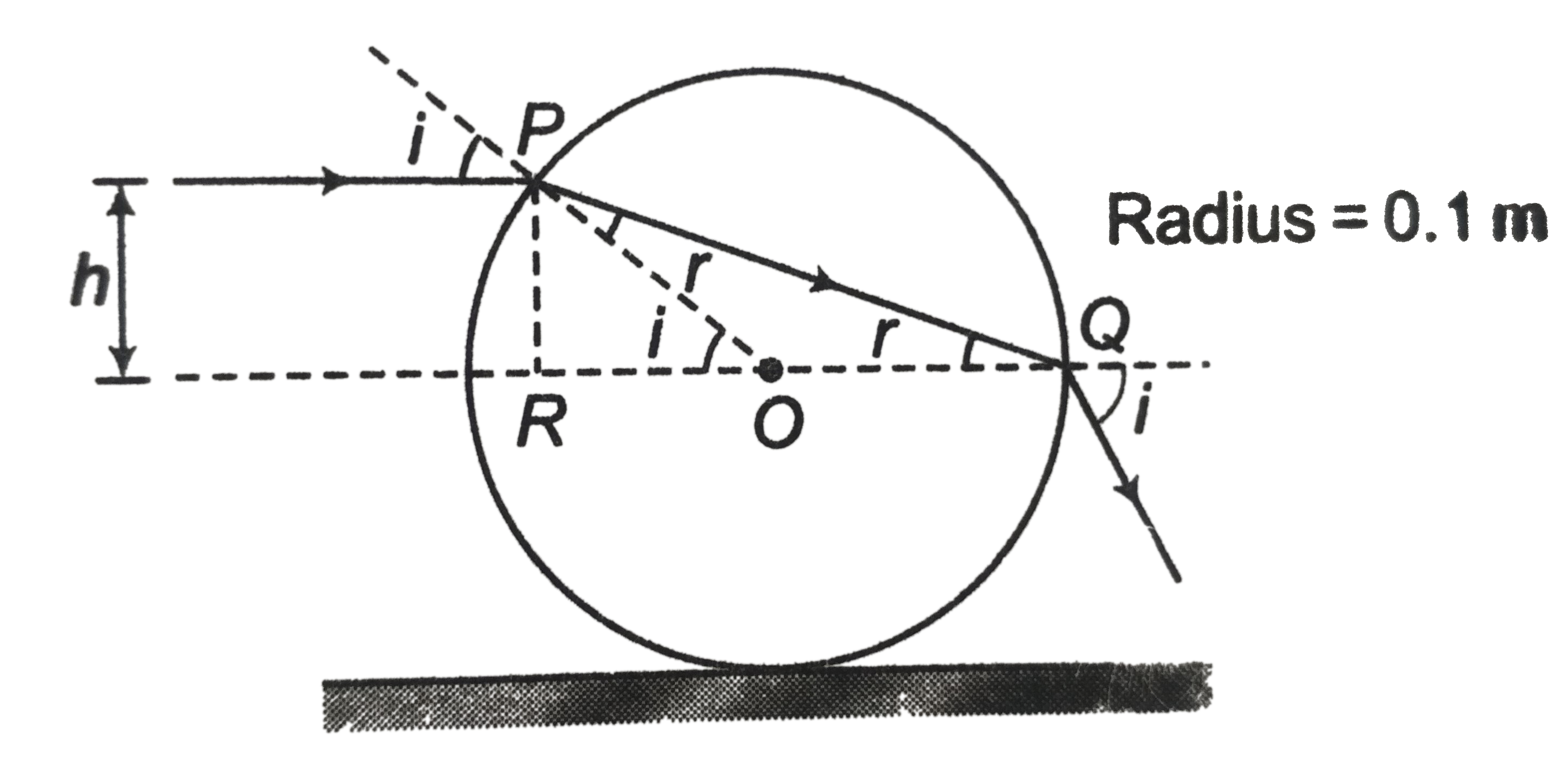 `i = 2r = 60^(@)` Now, `(QS)/(MS) = coti = cot 60^(@) = (1)/(sqrt(3))` `:. QS = (MS)/(sqrt(3)) = (0.1)/(sqrt(3))` `:.` The disered distance, `OC = 2 xx 0.1 + (2 xx 0.1)/(sqrt(3))` `0.315` |
|
| 39690. |
What is the relation between rms and average values of a sinusoidal A.C. voltage? |
|
Answer» Solution :`V_(rms)=(V_("PEAK"))/sqrt(2)andV_(ave)=(2V_("peak"))/(pi)` `V_(rms)=(pi)/(2sqrt(2))(V_(ave))` |
|
| 39691. |
Radius of curvature of a biconvex lens is 20 cm. An object of 2 cm height is placed at 30 cm from lens, then which option represents the image ? |
|
Answer» Virtual, erect, of HEIGHT 1 cm Now `1/f=(mu-1)((1)/(R_1)-(1)/(R_2))` `=(3/2-1)[(1)/(20)-(-(1)/(20))]` `1/f=(3/2-1)XX(2)/(20)` `THEREFORE f=20` cm Also,`1/f=1/v-1/u` `therefore(1)/(20)=1/v+(1)/(30)` `therefore 1/v=(1)/(20)-(1)/(30)` `=(10)/(600)` `therefore v=60` cm `m=(h_1)/(h_0)-v/u` `therefore h_i=v/uxxh_0` `=(60)/(30)xx2` `therefore h_i=-4` cm negative sign represents that the image is inverted |
|
| 39692. |
A baseball is thrown striaght upward. What is the ball's acceleration at its highest point ? |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 39693. |
What are two special characterstics of manganin for which it is used in making standard resistances. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :It.s temperature co.efficient is low It has high VALUE of RESISTIVITY. |
|
| 39694. |
If charge distribution within a Gaussian surface charges inside it, will electric field strength change inside and outside the Gaussian surface? |
| Answer» Solution :As the TOTAL charge inside the Gaussian SURFACE REMAINS unchanged, the same ELECTRIC flux will pass through the Gaussian surface. However, due to the change in charge distribution, the value of E will change inside as WELL as outside the Gaussian surface. | |
| 39695. |
The number density of electrons and holes in intrinsic silicon at a given temperature is 4.94xx10^(10)cm^(-3). Calculate the resistivity and conductivity of the silicon. Given electron mobility =100cm^(2)V^(-1)s^(-1) and hole mobility =1000cm^(2)V^(-1)s^(-1) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39696. |
If I_0 is the intensity of the principal maximum in the single slit diffraction pattern, the what will be its intensity when the slit width is doubled? |
|
Answer» `2I_(0)` |
|
| 39697. |
Standing waves can be produced |
|
Answer» on a STRING clamped at both ENDS |
|
| 39698. |
Two identical coils A and B are kept on a horizontal tube side by side without touching each other. If the current in the coil A increases with time, in response, the coil B |
|
Answer» is attracted by A The direction of INDUCED current in coil B is opposite to that of the direction of current in coil A as shown in FIGURE. 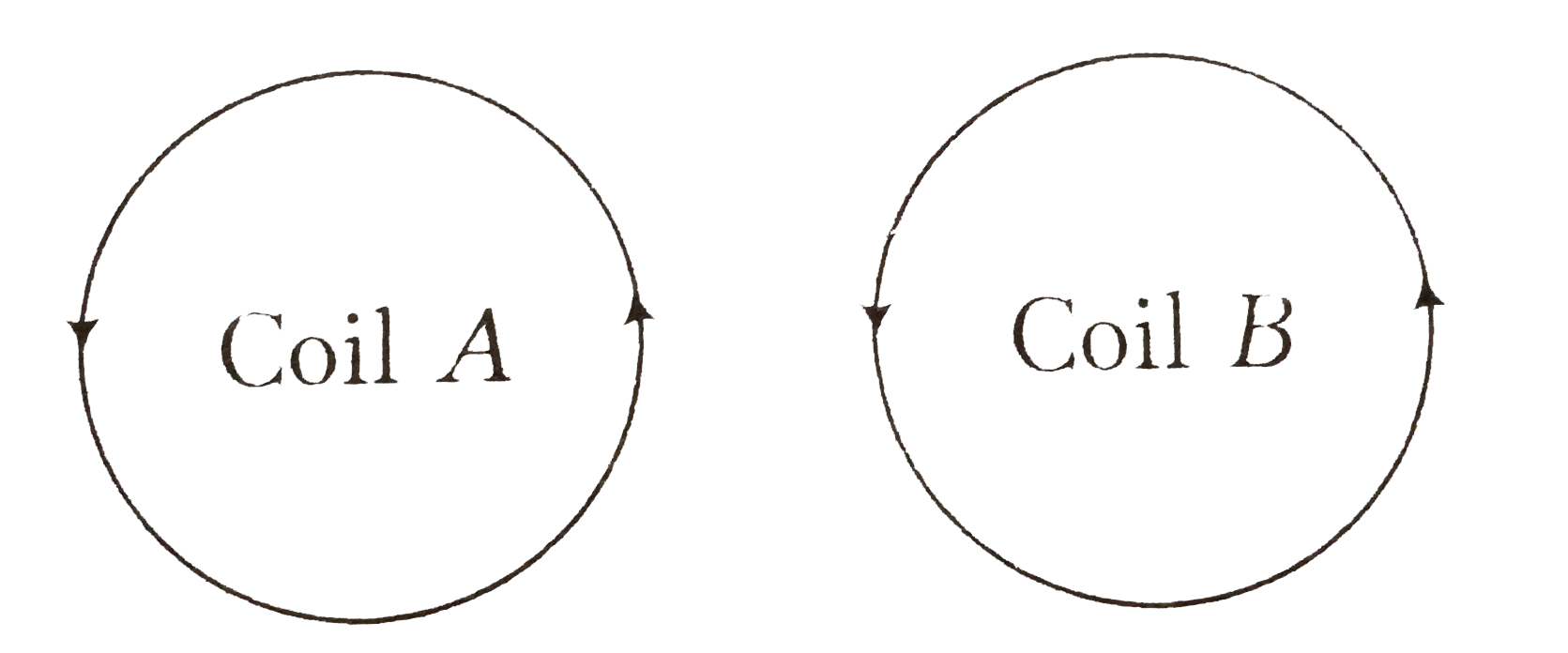 Due to currents in opposite directions in the near by SIDES of the COILS, the coil B is repelled. |
|
| 39699. |
Direction : Question number 89 contain Statement-1 and Statement-2. Of the four choices given after the statements, choose the one that best describes the two statements. Statement-1: When ultraviolet light is incident on a photocell, its stopping potential is V_(0) and the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is K_(max). When the ultraviolet light is replaced by X-rays. Both V_(0) and K_(max) increase. Statement-2: Photoelectrons are emitted with speeds ranging from zero to a maximum value because of the range of frequencies present in the incident light. |
|
Answer» STATEMENT-1 is TRUE, Statement-2 is FALSE. |
|
| 39700. |
A flat coil carrying a cuJTent has a magnetic moment μ . It is initially in equilibrium, with its plane perpendicular to a magnetic field of magnitude B. If it is now rotated through an angle theta, the work done is |
|
Answer» `muBtheta` |
|