Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 39701. |
Satellite communication is generally carried out of frequencies above |
|
Answer» 1MHz |
|
| 39702. |
When a galss rod is rubbedwith a sild clothcharges appear on both a smilar phenomenon is observeed with many other pairsof bodies expalin howthis observation is consistent with thelaw of conservation of charge |
| Answer» Solution :CHARGEIS not created or destroyed it is merely transferred from ONE BODY to ANOTHER | |
| 39703. |
An obstacle such as a telephone pole can cast a clear shadow in the light from a distant source. No such effect is noticed for the sound from a distant car horn. Why? |
| Answer» Solution :Waves of SHORTER wavelength have LESS tendency to SPREAD out behind the barrier. Light waves have much shorter wavelength compared to that of sound waves. Light waves can not spread out behind the telephone pole hence cast a SHARP shadow. Here RECTILINEAR propagation of light is considered and diffraction effects are ignored. Sound waves have wavelength range (approximately `16.5m-16.5 xx 10^3`m) much greater than the wavelength range of light waves. Hence sound waves can spread behind the obstacle. So no shadow can be cast by sound waves, as their diffraction effect is more pronounced. | |
| 39704. |
A light of wavelength 500 nm is incident on a sensitive plate of photoelectric work function 1.235 eV. The kinetic energy of the photo electrons emitted is be (Take h = 6.6 xx 10^(-34) Js) |
|
Answer» 0.58 eV |
|
| 39705. |
In the figure shown co-efficient of friction between the block B and C is 0.4. There is no friction between the block C and hte surface on which it is placed. The system of blocks is released from rest in the shown situation. Find the distance moved by the block C when block A descends through a distance 2m. Given masses of the blocks are m_(A)=3 kg, m_(B)=5 kg and m_(C)=10 kg. |
Answer» Solution :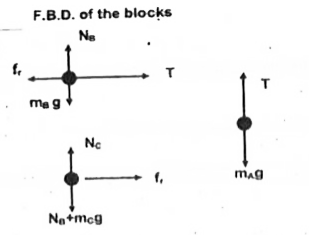 Let there is no relative motion between the blocks B and C Hence `T=(m_(B)+m_(C))a"" ...(1)` And`m_(A)g-T=m_(A)a ""...(2)` From (1) and (2), we get `a=(m_(A)g)/(m_(A)+m_(B)+m_(C))=(30)/(18)=(5)/(3)m//s^(2)` `rArr` Net force on the block C is, `F=m_(c)a=10xx(5//3)N=16.6N` If maximum value of FRICTIONAL force acting on block C is`f_("MAX")`, then `f_(("max"))=mu m_(B)g=0.4xx5xx10=20N "" because F le f_("max")` Hence there is no relative between the block B and C. Therefore distance moved by C is 2M only. |
|
| 39706. |
Examples of different means of communication used by man are mostly _____, _____ and _____. |
| Answer» Solution :TELEPHONES, TV, radio transmission and satellite COMMUNICATION | |
| 39707. |
Electric field intensity at a point on axis of a dipole at a distance of 20 cm from the centre of dipole is 0.015 N/C. When the distance of the point from the centre is made double to its initial value then electric field intensity is reduced to 0.001 N/C . Calculate the length of the electric dipole . |
|
Answer» <P> SOLUTION :Electric field at axial point of dipole of LENGTH 2l and dipole moment p, ata distance r from its centre is given by : `E=1/(4piepsilon_0).(2pr)/(r^2-l^2)^2`CASE I: `r_1`=20 CM =0.2 m , `E_1`=0.015 N/C `E_1=1/(4piepsilon_0)(2p(0.2))/((0.2)^2 -l^2)^2=0.015`...(i) Case II: `r_2=0.4`m ,`E_2`=0.001 N/C `therefore E_2=1/(4piepsilon_0)(2p(0.4))/((0.4)^2-l^2)^2` =0.001 ...(ii) Dividing (i) by (ii) , `0.015/0.001=((0.2)((0.4)^2-l^2)^2)/((0.4)((0.2)^2-l^2)^2)` `rArr 15/1=1/2 (0.16-l^2)^2/(0.04-l^2)^2` `rArr sqrt(30/1)=(0.16-l^2)/(0.04-l^2)` `rArr l^2`=0.013 m `rArr` l=0.114 m `therefore` Dipole length =2l = 0.228 m |
|
| 39708. |
A solid cylinder, a solid cube and a solid sphere are made of the same material and have the same mass. They are heated to the same temperature and kept in a room. The one that will cool at the minimum rate is |
|
Answer» cylinder |
|
| 39709. |
Two identical parallel plate capacitors are connected in parallel combination. Total chargeon capacitors is Q_(0). If one of the capacitorsis kept in a dielectric medium of constant K, then the total charge on both the capacitors will change to (P.D. across them is kept constant) |
|
Answer» `(KQ_(0))/(2)` |
|
| 39710. |
What is dimension of [M]? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`M^1L^2T^-2A^-2` | |
| 39711. |
A small fish is situated ft a depth of 6 ft in a tank and at a distance of 4.5 at from the bank. A boy of height 5 ft is standing at a distance of 8 ft from the bank. By what distance should the boy proceed towards the bank so that his movement will be visible to the fish? Refractive index of water = (4)/(3). |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39712. |
What is an LED? Give the principle of operation with a diagram. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) LED is a p-n junction diode which emits visible or invisible light when it is forward biased. (ii) Electric energy is converted into light energy , this process is also called ELECTROLUMINESCENCE. (iii) It consists of a p layer, and ba substrate. (iv) A transparent window is used to allow light to travel in the density direction. (v) An external resistance in series with the biasing source is required to limit the forward current through the LED.  (v) When the p-n junction is forward biased the construction band electrons on n-side and valence band holes on p - side DIFFUSE across the junction. (vi) When they cross the junction , they become excess minority CARRIERS (electrons in -side and holes in n - side). (vii) These excess minority carriers recombine with oppositely charged MAJORITY carriers in the respective regions , ie. the electrons in the conduction band recombine with holes in the valence band. (viii) During recombination process , energy is released in the form of light (radiative) or heat (non- radiative). |
|
| 39713. |
The special line of a given element in the light received froma distant star is shifted towards the longer wavelength by 0.032%. Duduce the velocity of star in the line of sight. |
|
Answer» `96 km"/"sec` |
|
| 39714. |
Distinguish between nuclear fission and fusion. Show how in both these processes energy is …… Calculate the energy release in MeV in the deuteriumtritium fusion reaction: ._(1)^(2)H+._(1)^(3)Hrarr._(1)^(3)He+nUsing the data.{:(m(._(1)^(2)H)=2.014102 u,m(._(1)^(3)H)=3.016049 u),(m(._(1)^(3)He)=4.002603 u,m_(n)=1.008665 u),(lu=931.5 Me V//c^(2),):} |
|
Answer» Solution :Elnstein’s photoelectric EQUATION: Where v = incident FREQUENCY,`v_(0 =`threshold frequency, `V_(0) =` stopping potential (i)Incident energy of PHOTON is used in to (a) to liberate electron from the metal surface (b) rest of the energy appears as maximum energy electron. (ii)Only one electron can absorb energy of one photon. Hence increasing intensity increases the numbers of electrons hence current. (iii)If incident energy is less than work function, no emission of electron will take PLACE. (iv)Increasing v (incident frequency) will increase maximum kinetic energy of electrons but number of electrons emitted will remain same. For wavelength `(hc)/(lambda_(1))=phi_(0)+K` `= phi_(0)+ ._(e )v_(0) ""` .... (i) where `K = ._(e )v_(0)` Form wavelength `lambda_(2)` `(hc)/(lambda_(1))=phi_(0)+2_(e )v_(0)` ....(ii)(because KE is doubled) Form equartion (i) and (ii), we get `(hc)/(lambda_(2))=f_(0)+2((hc)/(lambda_(1))-phi_(0))` `= phi_(0)+(2hc)/(lambda_(1))-2phi_(0)` `RARR "" lambda_(0)=(2hc)/(lambda_(1))-(hc)/(lambda_(2))` For thershold wavelength `lambda_(0)`, kinetic energy, K = 0 and work function`lambda_(0)=(hc)/(lambda_(0))` `therefore(hc)/(lambda_(0))=(2hc)/(lambda_(1))-(hc)/(lambda_(0))` `rArr "" (1)/(lambda_(0))=(2)/(lambda_(1))-(1)/(lambda_(2))` `rArr "" lambda_(0)=(lambda_(1)lambda_(2))/(2lambda_(2)-lambda_(1))` Work function, `lambda_(0)=(hc(2lambda_(2)-lambda_(1)))/(lambda_(1)lambda_(2))` |
|
| 39715. |
The current gain for a transistor working as common base amplifier is 0.96. If the emitter current is 7.2 mA, then the base current is |
|
Answer» 0.29 mA |
|
| 39716. |
When two resistance 10 Omegaand 20 Omegaare connected in series and 6 such sets are connected in parallel then the total resistance is |
|
Answer» `2.5Omega ` |
|
| 39717. |
Plot a graph showing variation of current versus voltage for the material GaAs |
Answer» Solution :There is more than one VALUE of V for the same current 1. A material EXHIBITING such BEHAVIOUR is GAAS. 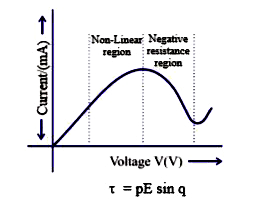
|
|
| 39718. |
A transmitting antenna at the top of the tower has a height 18 m and the height of the receiving antenna is 32m. The maximum distance between them for satisfactory communciation in line of sight mode is (Radius of earth= 6.4xx10^(6)m) |
|
Answer» 15.15km `R6.4xx10^(6)m=64xx10^(5) m` The maximum line or sight DISTANCE `d_(m)=SQRT(2Rh_(T))+sqrt(2Rh_(R))` `=sqrt(2xx64xx10^(5)xx18)+sqrt(2xx64xx10^(5)xx32)` `=112xx10^(2)xxsqrt(10) m=35417.5m=35.42km` |
|
| 39719. |
What is the Breswster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive indexof glass=1.5) |
|
Answer» <P> SOLUTION :`N=TAN i_(p)"" :. i_(p)=tan^(-1)n =tan^(-1)(1.5)=56.3^(@)` |
|
| 39720. |
The antenna current of an AM transmitter is 8A when only the carrier is sent but it increases to 8.93 A when the carrier is modulated .Find percentage modulatio . |
|
Answer» Solution :The modulated or total CARRIED by AM wave `P_(T)=P_(C)(2+(m^(3))/(2))` It R is load resistance, `I_(m)` is the current when carrier is modulated and `I_(C)` the current when unmodulated,then `(P_(T))/(P_(C))=(I_(m)^(2)R)/(I_(C)^(2)R)""therefore l+(m^(2))/(2)=(I_(m)^(2)R)/(I_(C)^(2)R)` Given `I_(m)`=8.93 A, `I_(C)`=8A `therefore m^(2)=2[((8.93)/(8.0))^(2)-1] therefore m=0.7` Therefore ,MODULATION index=70% |
|
| 39721. |
When a galvanometer having 20 divisions scale and 50Omega resistance is connected in series to a cell of emf 1.5V through a resistance of 100Omega, its shows full scale deflection. Find the figure of merit of the galvanometer. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 39722. |
The total flux linked with unit negative charge put in air is |
|
Answer» `(1)/(epsi_(0))` out wards |
|
| 39723. |
An air bubble in a glass slab with refractive index 1.5 (near normal incidence) is 5 cm deep when viewed from one surface and 3 cm deep when viewed from the opposite face. The thickness (in cm) of the slab is |
|
Answer» 12  THICKNESS of GLASS SLAB `t=n(h_i+h_i.)` `=1.5(5+3)` `=1.5xx8=12` CM |
|
| 39724. |
A body starting from rest moves along a straight line with a constant acceleration. The variation of speed (v) with distance (s) is represented by the graph |
|
Answer»
This is an equation of PARABOLA. It is symmetric about the axis of distance s. So, the correct graph is represented by the option (C ). |
|
| 39725. |
Obtain the formula for the electric field due to a along thin wire of uniform linear charge densitylambdawithout using Gauss's law. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider a long thin wire of length Land having uniform charge DENSITY `lambda.` Let P be a point situated at a normal distance r from the wire. Let there be asmall length elements situated at a distance y and having length DY as SHOWN in According to Coulomb.s law electric field due to this element at point P has a magnitude. `dE=( 1)/( 4pi in_0).(dq)/( (r^(2) +y^(2))) =(1)/( 4piin _0) .( lambda dy)/( (r^(2) +y^(2)) ` `oversetto (dE)` may be resolved into 2 components :(i)a COMPONENT`dE_x`in a DIRECTION normal to wire, and (ii)component `dE_y`in a direction parallwl to the wire. Obviously if we find electric field due to whole wire ,then `sum dE_y= 0 `because for every at +y there is corresponding element at -yand ` therefore ` Electric field due to whole conductor at point? ` E =int dE_x = int dE sin theta =(lambda )/( 4pi in _0) int (dy sin theta )/( (r^(2) +y^(2))` But` y= root theta , `hence dy ` =-r cosec ^(2)theta d theta` `therefore"" E= (lambda )/( 4pi in _0) underset( theta =pi ) oversetto ( theta =0 )int ((r-cosec ^(2) theta_x d theta ) sin theta)/( (r^(2) +r^(2)cot ^(2)theta) )=(lambda )/( 4pi in _0)underset ( pi ) overset (0) int-(1)/(r)sin theta d theta ` ` "" = (lambda )/( 4pi in _0)[cos theta ]underset pi overset 0=(lambda )/(4pi in _0)[cos 0^(@)-cos pi ] ` `=(lambda)/( 4 pi in _0)[1-(-1) ]= (lambda)/(2pi in _0r) ` ` (##U_LIK_SP_PHY_XII_C01_E02_006_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 39726. |
Current in a coil falls from 5 A to 0 A in 0.1 s, calculate the induced emf in a coil if its self inductance is 4H. |
|
Answer» Solution :When the current in the COIL falls from 5A to 0A in 0.15. The induced emf in a coil is , `E = L (DI)/(dt)` `E= 4xx (5)/(0.1) = 200V` |
|
| 39727. |
A particle of mass m = 5 units is moving with a uniform speed v = 3sqrt2 units in the XOY plane along the line Y = X + 4. The magnitude of the angular momentum of the particle about the origin is |
|
Answer» 60 units Y=X+ 4 line has been shown in the figure when x = 0,y = 4. So, OP = 4. The slope of the line can be obtained by comparing with the equation of line y=mx+c `rArrm=tantheta=1` `rArrtheta=45^(@)` `angleOQP=angleOPQ=45^(@)` If we draw a line perpendicular to this line. Length of the perpendicular= OR `rArrOR=OPsin45^(@)=4(1)/(SQRT2)=4/(sqrt2)=2SQRT2` Angular momentum of particle going ALONG this line `=rxxmv=2sqrt2xx5xx3sqrt2=60` units 
|
|
| 39728. |
The displacement of A particle at x = 0 of a stretched string carrying a wave in the positive X-direction is given by f(t)=Ae^(-t^2). The wave speed is V. Write equation of the wave. |
|
Answer» `f(X,t) = AE^(-(t + x)^2)` |
|
| 39729. |
Units of magnetic flux are |
|
Answer» Weber |
|
| 39730. |
The deflection in a moving coil galvanometer falls from 50 divisions to 10 divisions when a shunt of 12 ohm is applied. What is the resistance of the galvanometer? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :In case of a GALVANOMETER, `Iproptheta` So, `(I_(G))/I=10/50=1/5`, i.e., `I_(G)=1/5I` Now as in case of a SHUNTED galvanometer as SHOWN in fig. `(I-I_(G))S=I_(G)G`, i.e., `(I-1/5I)xx12=1/5IG` So, `G=4xx12=48Omega` 
|
|
| 39731. |
The corners A, B, C, and D of a square are occupied by charges q,-q,2Q, and Q, respectively. The side of square is 2b. The field at the midpoint of side CD is zero. What is the value of q//Q? |
|
Answer» `5sart5//2` `((q)/(4piepsilon_(0)(sqrt(5B))^(2))+(q)/(4piepsilon_(0)(sqrt(5b))^(2)))` or `costheta+(Q)/(4piepsilon_(0)b^(2))=(2Q)/(4piepsilon_(0)b^(2))` On SOLVING, we get `(2q)/(5)costheta=Q` or `(2q)/(5)((b)/(sqrt(5b)))=Q` or `(2q)/(5sqrt(5))=Q` or `(q)/(Q)=(5sqrt(5))/(2)` 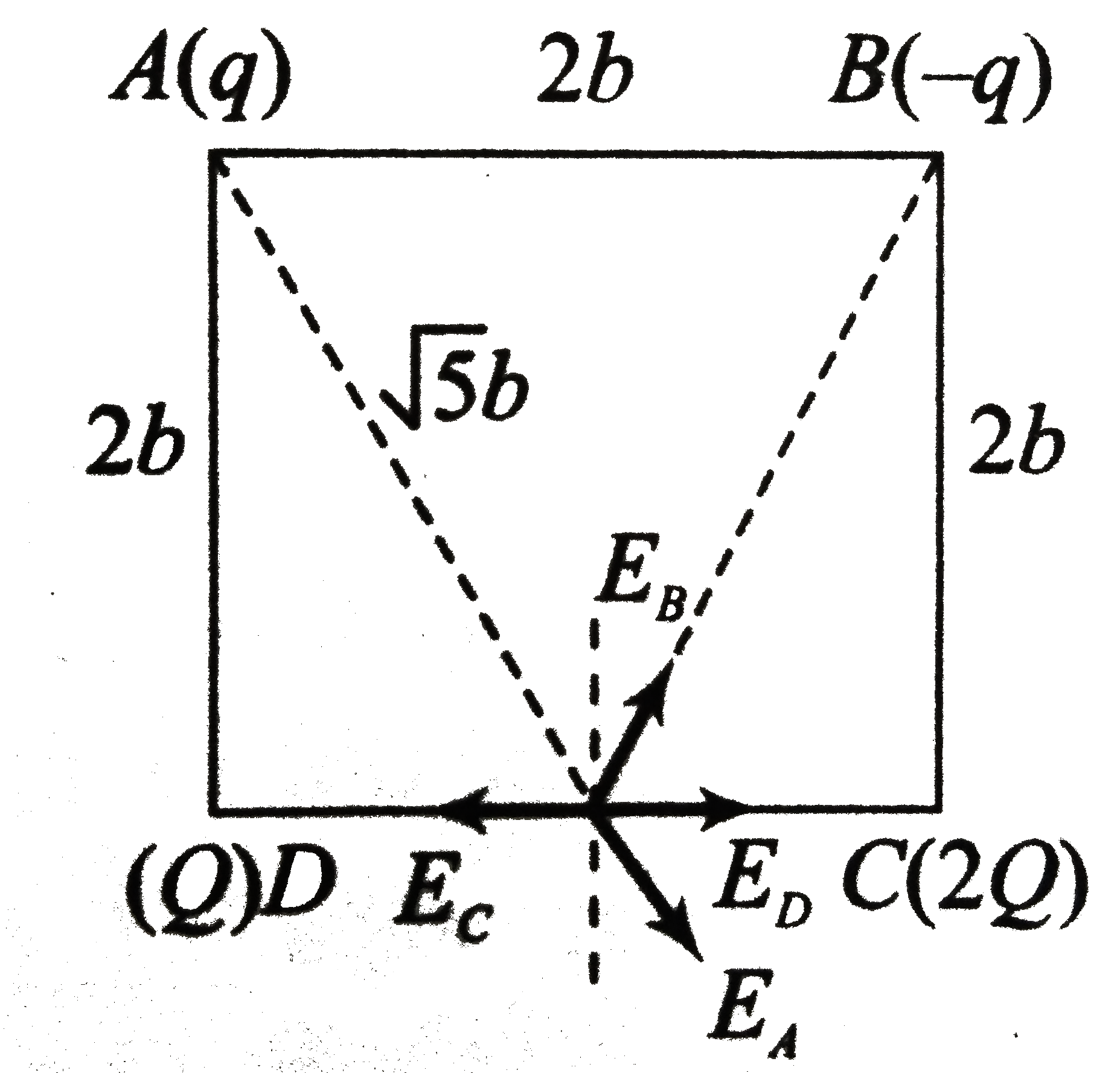
|
|
| 39732. |
A planet moves around the sun. At a given point P, it is closest from the sun at a distance d_(1) and has a speed v_(1). At another point Q, when it is farther from the sun at a distance d_(2), its speed will be |
|
Answer» `(d_(1)^(2))/(d_(2)^(2))v_(1)` `mv_(1)d_(1)=mv_(2)d_(2) rArr v_(2)=(v_(1)d_(1))/(d_(2))`. |
|
| 39733. |
Calculate the inductance of a closely wound solenoid of length l whose winding is made of copper wire of mass m. The winding has a total resistance equal to R. The solenoid diameter is considerably less than its length. Take density of copper = d and resistivity = phi. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`((mu_(0)MR)/(4pi//phi d))` | |
| 39734. |
In photoelectric effect stopping potential is the measured of the ____of the photoelectrons and it does not depends upon the _____ of incident radiation. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MAXIMUM ENERGY, INTENSITY. | |
| 39735. |
Best method to increase the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer is to increase : |
|
Answer» The suspension WIRE should be made stiff |
|
| 39736. |
What is magnitude and direction of above quan tity in the case of a point charge |
| Answer» Solution :Direction of electric field is OUTWARD for POSITIVE CHARGE and INWARD for negative charge. | |
| 39737. |
Give truth table for a circuit shown in figure. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :In figure combination of OR and AND gate is SHOWN. Hereinput A or OR gte and its OUTPUT y. is INPUT of AND gate, so its truth table is ACCORDING the follow. 
|
|
| 39738. |
Two charges are placed in vacuum at a distance d apart. The force between them is F. if a medium of dielectric constant 2 is introduced between them, the force will now be |
|
Answer» 4F |
|
| 39740. |
In a periodic table the average atomic mass of magnesium is given as 24.312 u. The average value is based on their relative natural abundance on earth. The three isotopes and their masses are ""_(12)^(24)Mg (23.98504u), ""_(12)^(25)Mg (24.98584u) and ""_(12)^(26)Mg (25.98259u). The natural abundance of ""_(12)^(24)Mg is 78.99% by mass. Calculate the abundances of other two isotopes. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`""_(12)^(25)Mg:9.3%, ""_(12)^(26)Mg:11.7%` | |
| 39741. |
In a transistor |
|
Answer» Emitter is HEAVILY doped |
|
| 39742. |
How can the neutral body be charged electrically ? |
|
Answer» Solution :When we TOUCH a pith ball with an electrified plastic rod, some of the negative charges on the rod are transferred to the pith ball and it ALSO GETS charged. Thus the pith ball is charged by contact. Two separated identical metal spheres, ONE with charge Q and ANOTHER uncharged, when brought in contact and then separated, both will have Q same charge `Q/2`. Hence, it is charging of second sphere. |
|
| 39743. |
Voltage obtained in one A.C. generator V=V_0 cos omegat . If V_0 = 10 volt and frequency v=50 Hz then voltage at time t=1/600s wiil be _____ |
|
Answer» 10 V `THEREFORE V=V_0 cos (2pivt) (because omega=2piv)` `=10 cos (2pixx50xx1/600)` `=10 cos (pi/6)` `=10xxsqrt3/2` `therefore V=5sqrt3` volt |
|
| 39744. |
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab? |
| Answer» Solution :The PIN appears raised by 5.0 cm. It can be seen with an explicit ray DIAGRAM that the answer is INDEPENDENT of the location of the slab (for small ANGLES of incidence). | |
| 39745. |
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on an opaque screen shaped as a long strip with a round hole in the middle. For the observation point P the hole corresponds to half the Fresnel zone, with the hole diameter being eta = 1.07 times less then the width of the strip. Using Fig. find the intensity of light at the point P provided that the intensity of the incident light is equal to I_(0). |
|
Answer» Solution :The radius of the first HALF Fresnel zone is `sqrt(b LAMBDA//2)` and the amplitude at `P` is obtained using problem `A = (a_(0))/(b) [[-etasqrt(b lambda//2) oo],[int + int],[-oo etasqrt(b lambda//2)]] E^(-ikb-(kx^(2))/(2b)) dx` `underset(-oo)overset(oo)int e^(-iky^(2)/(2b)) dy + (a_(0))/(b)e^(-ikb) underset(-oo)overset(sqrt(b lambda//2))int e^(-ikrho^(2)//2b) 2PI rho d rho` We use `underset(-oo)overset(-etasqrt(b lambda//2))int e^(-ikx^(2)//2b) dx` `= underset(eta sqrt(b lambda//2))overset(oo)int e^(-ikx^(2)//2b) dx =underset(eta sqrt(b lambda//2))overset(oo)int e^(-i(pix^(2))/(b lambda)) dx` `= underset(eta)overset(oo)int e^(-ik piu^(2)//2) sqrt((b lambda)/(2)) DU = sqrt((blambda)/(2))(underset(0)overset(oo)int -underset(0)overset(eta)int) e^(-i piu^(2)//2) du` `= sqrt((b lambda)/(2)) (((1)/(2)-C(eta)) -i(1)/(2)-S(eta)))` Thus `A = a_(0) (lambda)/(cancel(2)) xx cancel(2) xx (1 - i) e^(-ikb) [((1)/(2)-C(eta))` `-i((1)/(2)-S(eta))] + a_(0)lambda(1 - i)e^(-ikb)` where we have used `underset(0)overset(sqrt(b lambda//2))int e^(-ikrho^(2)/(2b)) 2pi rho d rho = (2pi ib)/(k) (-1-i) = (2pib)/(k)(1-i) = lambda b(1-i)` Thus the intensity is `I = |A|^(2) = a_(0)^(2)lambda^(2) xx 2[(3//2-C(eta))^(2) + ((1)/(2)-S(eta))^(2)]` From Cornu's Sprial, `C(eta) = C(1.07) = 0.76` `S(eta) = S(1.07) = 0.50` `I = a_(0)^(2)lambda^(2) xx 2 xx (0.74)^(2) = 1.09 a_(0)^(2) lambda^(2)` As before `i_(0) = a_(0)^(2)lambda^(2)` do `I ~~ I_(0)`. 
|
|
| 39746. |
Which of following can not be ferromagnetic ? |
|
Answer» Solid |
|
| 39747. |
A myopic adult has a far point at 0.1 m. His power of accomodation is 4 Diopters.(i) What power lenses are required to see distant objects ? (ii) What is his near point without glasses ? (iii) What is his near point with glasses ? (iii) What is his near point with glasses ? (Take the image distance from the lens of the eye to the retina to be 2 cm.) |
|
Answer» Solution :`rArr` (i) Required power for normal relaxed eye at far PIONT, `P_f = 1/f= 1/f_1 + 1/f_2` `thereforeP_f = (1)/(0.1) + (1)/(0.02) = (0.02 + 0.1)/(0.002) = (0.12)/(0.002)` `thereforeP_f = 60 D` `rArr` Now required power for shifting far point to INFINITY (using corrective lens) `P._(f) = (1)/(f.) = (1)/(oo) + (1)/(0.02) = 0 +(1)/(0.02)` `therefore P.f = 50 D` For the combined system of relaxed eye and spectacles, `P._(f) = P_(f) +P_(g)` `therefore 50 = 60 + P_g` `therefore P_g = -10 D` (ii) Power of normal eye P = 4D Now, if power eye P = 4D Now, if power of normal eye of given person for near vision is `P_n` then , `P = P_n - P_g` `therefore4 = P_n -60` `therefore P_n = 64 D` `rArr` SUPPOSE DISTANCE of near point without spectacles is `x_n` `therefore 1/(x_n) + (1)/(0.02) = 64` `therefore (1)/(x_n) + 50 = 64` `therefore 1/(x_n)= 14` `therefore x_n= (1)/(14)` `therefore x_n = 0.07 m ` (iii) With spectacles, `P._n = P._f +P` `54 = (1)/(x._n) +(1)/(0.02) = (1)/(x._n) + 50` `therefore (1)/(x._n) = 4` `therefore x._(n) = 1/4 = 0.25 m ` |
|
| 39748. |
A thin circular ring of mass M and radius r is rotating about its axis with a constant angular velocity omega. Two objects each of mass m are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring will now rotate with an angular velocity |
|
Answer» `(omega(M-2M))/M` `omega.=(Mr^(2)omega)/((M+2m)r^(2))=(omegaM)/(M+2m)` |
|
| 39749. |
If mole fraction of solute is 0.8 ,then mole fraction of solvent is...... |
|
Answer» 0.4 |
|
| 39750. |
A sample ofradioactive nuclide A^(150) is having half life 2 hours and produce B^(146) after emitting alpha particle. Initially in sample only A was present having mass 50 gm. After four hours difference in mass of sample (A + B) is x gm then value of X is. |
|
Answer» |
|



