Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 40301. |
What are two important types of microscope ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :An objectiveof large APERTURE and EYE lens of small aperture. | |
| 40302. |
A block of mass mis placed on a surface with a vertical cross section given by y = (x^3)/(6).If the coefficient of friction is 0.5, the maximum height above the ground at which the block can be placed without slipping is: |
|
Answer» `1/2 m` |
|
| 40303. |
A plano-convex lens when silvered ono the plane side behaves like a concave mirror of focal length 60 cm. However, when silvered on the convex side, it behaves like a concave mirror of focal length 20cm. Then, the refractive index of the lens is |
|
Answer» `3.0` `(1)/(F)=(2)/(f_(1))+(2)/(f_(m))` or `(1)/(F)=2(mu-1)((1)/(R))+(1)/(oo)` or `F=(R)/(2mu(-1))` Now, `-60=(R)/(2(mu-1))` or `120(mu-1)=R`(i) Again, `(1)/(F)-(1)/(f_(1))+(1)/(f_(1))+(1)/(f_(m))` or `=(2)/(f_(1))+(1)/(R//2)` or `=2(mu-1)((1)/(R))+(2)/(R)` or `=(2)/(R)(mu-1+1)` or`F=(R)/(2mu)` Now, `-20=(-R)/(2mu)` or `40mu=R` (ii) Dividing (i) by (ii), we get `(120(mu-1))/(40mu)=(R)/(R)=1` or ` 120(mu-1)=40mu` or `120mu-40mu=120` or `80mu=120` or `mu=(120)/(80)=(3)/(2)=1.5`  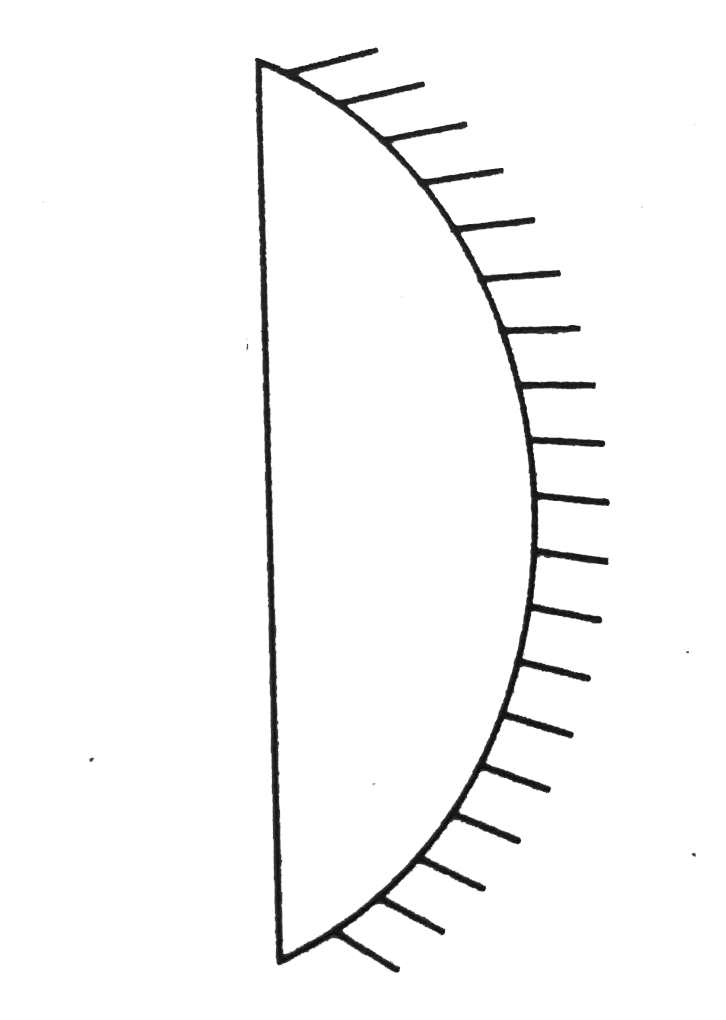
|
|
| 40304. |
The frequency of a stetched unifrom wire under tension is in resonance with the fundamental frequency of closed tube. If the tension in the wire is increased by 8 N, it is in resonance with the first overtone of the closed tube. The initial tension in the wire is |
|
Answer» 1N |
|
| 40305. |
A chunk of ice of mass m_1 = 100 g at a temperature t_1 = 100 g was at a temperature t_2. Assuming the heat capacity of the calorimeter to be negligible, find the entropy increment of the system by the moment the thermal equilibrium is reached. Consider two cases : (a) t_2 = 60 ^@C , (b) t_2 = 94 ^@C. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Here `t_2 = 60^@C`. Suppose the final temperature is `t^@C`. Then heat lost by water `= m_2 c (t_2 - t)` heat gained by ice `= m_1 q_m + m_1 c(t - t_1)`, if all ice melts In this case `m_1 q_m = m_2 xx 4.18(60 - t)`, for `m_1 = m_2` So the final temperature will be `0^@C` and only some ice will melt. Then `100 xx 4.18 (60) = m'_1 xx 333` `m'_1 = 75.3 gm` = amount of ice that will melt Finally `Delta S = 75.3 xx (333)/(273) + 100 xx 4.18 1n (273)/(333)` `Delta S = (m'_1 q_m)/(T_1) + m_2 c 1n (T_1)/(T_2)` =`m_2 c((T_2 - T_1))/(T_1) -m_2 1n (T_2)/(T_1)` =`m_2 C[(T_2)/(T_1) - 1- 1n(T_2)/(T_1)] = 8.8 J//K` (b) If `m_2 c t_2 gt m_1 q_m` then all ice will melt as one can CHECK and the final temperature can obtained like this `m_2 c(T_2 - T) = m_1 q_m + m_1 c(T - T_1)` `(m_2 T_2 + m_1 T_1) c - m_1 q_m = (m_1 + m_2) cT` or `T = (m_2 T_2 + m_1 T_1 - (m_1 q_m)/(c))/(m_1 +m_2) ~= 280 K` and `Delta S = (m_1 Q)/(T_1) + c(m_1 1n (T)/(T_1) -m_2 1n (T_2)/(T)) = 19 J//K`. |
|
| 40306. |
In an ammeter 0.2% of main current passes through the galvonometer. If resistance of galvonometer is G, the resistance of ammeter will be _____ |
|
Answer» `1/499G` `thereforeI_(G)R_(G)=I_(S)R_(S)` Now `I_(G)=0.2%I=0.002I` `thereforeI/I_(G)=1/0.002=500" "thereforen=500` Now SHUNT `S=G/(n-1)=G/(500-1)=G/499` Now resistance of AMMETER, `1/R_(A)=1/G+1/S` `therefore1/R_(A)=1/G+499/G` `therefore1/R_(A)=500/G` `thereforeR_(A)=G/500` |
|
| 40307. |
Magnification of a compound is 30. Focal length of eyepiece is 5 cm and the image is formed at a distance of distinct vision of 25 cm. The magnification of the objective lens is |
|
Answer» Solution :`m_(e)=(V)/(u)=(D)/(u_(c))=1+(D)/(f_e)=1+(25)/(5)=6` for the compound microscope , `m = m_(o) xx m_(e) rArr = 30= m_(a) xx 6 (or) m_(o) = 5` |
|
| 40308. |
Fig. shows a part of circuit. When a current I = 1.5 A passes through it in the direction shown, power delivered to it (section XY) is 75W. Potential difference between X and Y and also the emf E of the cell are respectively (assume that the cell has a negligible internal resistance) |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 40309. |
1 weber = _________ . |
|
Answer» `10^(6)` maxwell |
|
| 40310. |
A round dielectric disc of radius R and thicknessdis statically polarizedso thatit gainsthe uniform polarzationP. Withthe vector Plyingin theplaneof the disc. Findthe strength E ofthe electricfield at the centre of the disc if d lt lt R. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Because there is a discontinuity in polarization at the boundary of the dielectric disc, a bound surface charge appears, which is the SOURCE of the electric field inside and outside the disc.We have for the electric field at the origin. `vec(E) = -int (sigma dS)/(4pi epsilon_(0) r^(3)) vec(r)`, where `vec(r )` = radius vector to the origin form the element`dS`. `sigma' = P_(n) = P cos theta` on the CURVED surface `(P_(n) = 0` on the flat surface.) Here `theta` = angle between `vec(r )` and `vec(P)` By symmetry, `vec(E)` will be parallel to `vec(P)`. Thus `E = -int_(0)^(2x) (P cos theta R d theta cos theta)/(4pi epsilon_(0) R^(2)) .d` where, `r = R` it `d lt lt R`. So, `E = - (PD)/(4 epsilon_(0) R)` and `vec(E) = - (vecP d)/(4epsilon_(0) R)` 
|
|
| 40311. |
Calculate potential on the axis of a ring due to charge Q uniformly distributed along the ring of radius R. |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Suppose, + Q charge uniformly distributed on the ring of radius R = a Let us take point P to be at a distance x from the centre of the ring. The charge DQ is at a distance r from the point P then, `r = sqrt(x^(2)+a^(2))` and potential at P due to dq `V=(KDQ)/(r)` Potential at P due to charge on the whole ring, `V=kint(dq)/(r)=k int(dq)/(sqrt(x^(2)+a^(2)))` `V=(k)/(sqrt(x^(2)+a^(2)))int dq=(kQ)/(sqrt(s^(2)+a^(2)))[because int dq=Q]` `:.` The net electric potential `V = (Q)/(4piin_(0)sqrt(x^(2)+a^(2)))` |
|
| 40312. |
An electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z - direction : vec(E )=(E_(1)hat(i)+E_(2)hat(j))cos(kz-omega t). Choose the correct options from the following : |
|
Answer» The associated magnetic field is given as`vec(B)=(1)/(c )(E_(1)-E_(2)hat(j))cos (kz-omega t)` `vec(E )=(E_(1)hat(i)+E_(2)hat(j))cos (kz-omega t)` and Magnetic field vector, `vec(B)=(vec(E ))/(c )=((E_(1)hat(i)+E_(2)hat(j))cos (kz-omega t))/(c )` Thus,`vec(E )` and `vec(B)` propagate PERPENDICULAR to each other also perpendicular to DIRECTION of propagation. Hence electromagnetic WAVES is plane POLARIZED. |
|
| 40313. |
In a common emitter amplifier output resistance is 2000 ohm and input resistance is 5000 ohm. The input signal is of 10 mV and beta=50, Then power gain is |
|
Answer» 5000 V Then POWER gain, `A_p = beta xx A_v50 xx 125 = 6250` |
|
| 40314. |
In a common emitter amplifier output resistance is 2000 ohm and input resistance is 5000 ohm. The input signal is of 10 mV and beta=50, Then output voltage is |
|
Answer» 1.25 V `R_i=2000Omega` `Deltai_b=(Deltav_i)/(R_i)=15^2/2000=5xx10^(-6)A` `beta = (Deltai_c)/(Deltai_b)` Then `Delta_(IC)=beta Delta_(ib)= 2.5 xx10^(-4)A` Then OUTPUT voltage `DeltaV_0=DeltaI_c XX R_0 = 1.25 V` |
|
| 40315. |
The earth's magnetic field at the equator is approximately 0.4 G. Estimate the earth's dipole moment. |
|
Answer» Solution :The equatorial magnetic field is , `B_E=(mu_0m)/(4pir^3)` We are given that `B_B~0.4 G = 4 xx10^(-5)T.` For R, we take the earth `6.4xx10^6` m . Hence , `m=(4xx10^(-5)xx(6.4xx10^6)^3)/(mu_0//4pi)=4xx10^2xx(6.4xx10^6)^3""((mu_0)/(4pi)=10^(-7))` This is close to the value `8xx10^(22) Am^(-2)` as obtained in geomagnetic EXPERIMENTS . |
|
| 40316. |
Helium gas goes through a cycle ABCDA (consisting of two isochoric and two isobaric lines) as shown in figure. Eficiency of this cycle is nearly: (Assume the gas to be close to ideal gas) |
|
Answer» <P>`12.5%` `=(200)/(13) =15.4%` Correct CHOICE : (B). |
|
| 40317. |
Suppose that three points are set at equal (large) distances r from the center of the dipole in Fig. 24-33: Point a is on the dipole axis above the positive charge, point b is on the axis below the negative charge, and point c is on a perpendicular bisector through the line connecting the two charges. Rank the points according to the electric potential of the dipole there, greatest (most positive) first. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :a, C (ZERO), B | |
| 40318. |
Find equivalent capacitance between A & B |
|
Answer» `(C)/(4)` 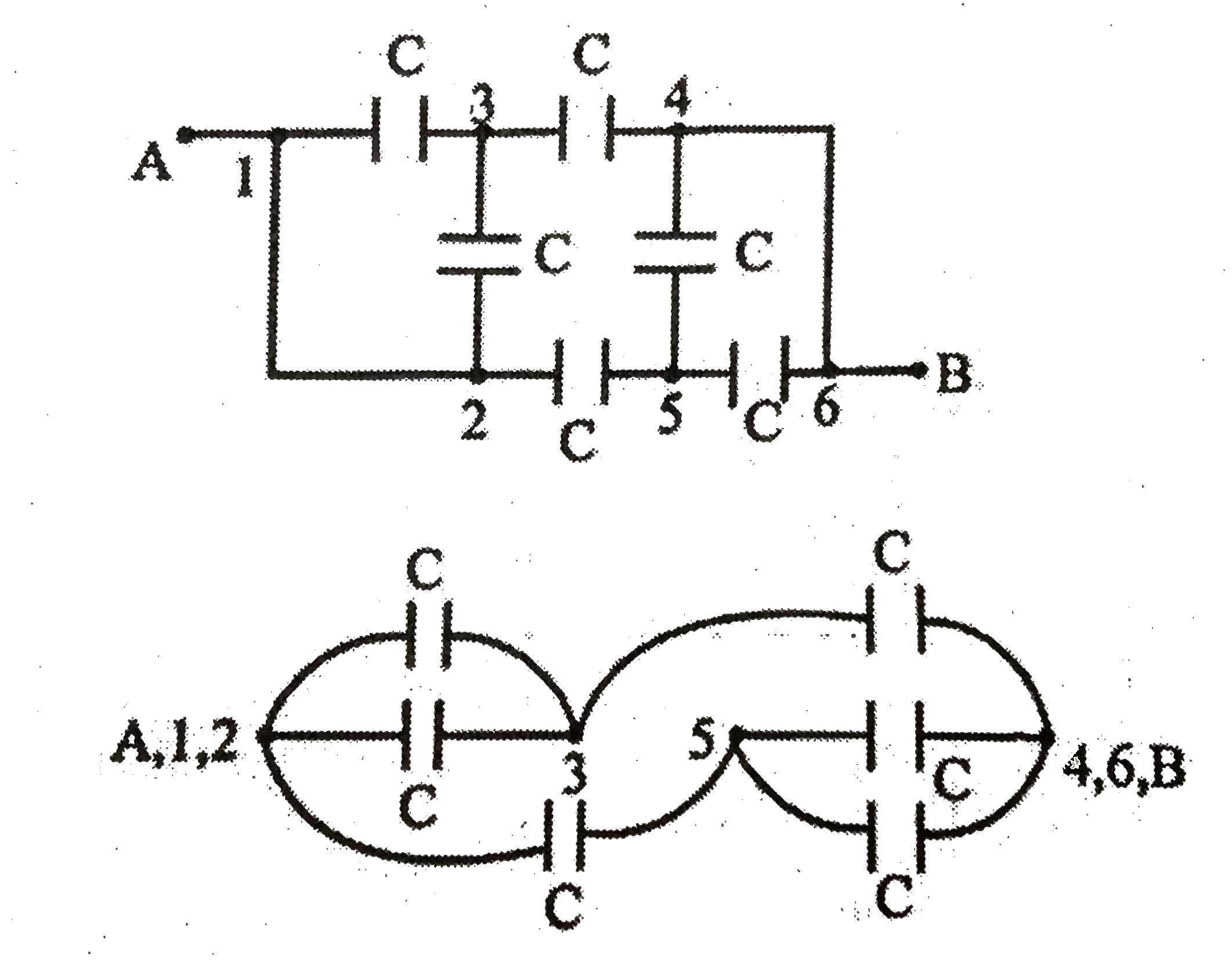 `C_(EQ)=(2C)/(3)+(2C)/(3)impliesC_(eq)=(4C)/(3)` |
|
| 40319. |
Three charged particles having charges q, -2q & q are placed in a line at points (-a, 0), (0,0) & (a , 0) respectively. The expression for electric potential at P(r, 0 ) for r gt gta is |
|
Answer» `(1)/(4 pi epsilon_(0))(qa^(2))/(r^(4))` |
|
| 40320. |
The half-life of ""_(92)^(238)U undergoing a-decay is 4.5 xx 10^9 years. What is the activity of 1g sample of ""_(92)^(238)U? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) The activity of a sample of radioactive NUCLEUS equals to its DECAY rate (or number of nuclei decaying per unit time). It.s SI unit is disintegration/s or BECQUEREL (b) `R = lambda N` `= (log_(e) 2xx 25.3 10^(20) xx 10)/( 4.5 xx 10^(9) )` `= ( 0.6931 xx 25.3 xx 10^(21) )/( 4.5 xx 109 xx 365 xx 24 xx 60 xx 60)` `=1.24 xx 10^(5)` dps |
|
| 40321. |
4किताबे मे कितने सार्थक अंक है - |
|
Answer» 1 |
|
| 40322. |
The electric flux through a cubical Gaussian surface enclosing net charge q is q/epsilon_0, While the electric flux through one face of a cube is |
|
Answer» `q/epsilon_0` |
|
| 40323. |
After a certain lapse of time, fraction of radioactive polonium undecayed is found to be 12.5% of the initial quantity. What is the duration of this time lapsed if the half life of polonium is 138 days? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 40324. |
Three rings, each having equal radius R, are placed mutually perpendicular to each other and each having its centre at the origin of co-ordinate system. If current Iis flowing through each ring then find the magnitude of the magnetic field at the common centre. |
|
Answer» Solution :B DUE to the ring LYING in XY - PLANE is : `(mu_0I)/(2R)` along Z-axis. B due to the ring lying in YZ - plane is `(mu_0I)/(2R)`along X - axis, and B due to the ring lying in XZ - plane is `(mu_0I)/(2R)` along Y - axis. `thereforeB_("net") = sqrt(3) (mu_0 I)/(2R)` |
|
| 40325. |
Which wave cannot be polarised and for what ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :SOUND, LONGITUDINAL. | |
| 40326. |
Quantity that remains unchanged in a transformer is |
|
Answer» voltage |
|
| 40327. |
What is meant by sensitivity of a potentiometer ? |
| Answer» Solution :A potentiometer is SAID to be sensitiive if (i) It can measure SMALL potential difference and (II) for a small change in pootential difference being measured, it show a large change in balancing length. | |
| 40328. |
The meaning of 'engulf'.. |
|
Answer» To be unconscious |
|
| 40329. |
Light waves appear to travel in straight lines since |
|
Answer» these are not ABSORBED by the atmosphere |
|
| 40330. |
Calculate the threshold kinetic energies of protons required to activate the reactions (p,n) and (p,d) with Li^(7) nuclei. |
|
Answer» Solution :The `Q` of the reaction `LI^(7)(p,N)Be^(7)` was calculated in problem 266(a). It is `-1.64MeV` Hence, the threshold `K.E`. Of proton for initiating this reaction is `T_(th)=(1+(m_(p))/(m_(Li)))|Q|=(8)/(7)xx1.64= 1.64= 1.87MeV` For the reaction `Li^(7)(p,d)Li^(6)` we find `Q=(Delta_(Li)^(7)+Delta_(M)-Delta_(d)-Delta_(Li)^(6))c^(2)` `=(0.01601+0.00783-0.01410-0.01513)am uxxc^(2)` `=-5.02MeV` The threshold proton ENERGY for initiating this reaction is `T_(th)=(1-(m_(p))/(m_(Li^(7))))xx|Q|=5.73MeV` |
|
| 40331. |
A convex lens is in contact with concave lens. If the ratio of their powers is 2/3 and focal length of the combination is 30 cm, then individual focal lengths are |
|
Answer» 75 cm and -50 cm `P_1=1//f_1``P_2=1//f_2` Let `f_1` and `P_1` are the focal length and power of concave lens. `f_2` and `P_2` are the focal length and power of convex lens. The focal length of combined lens f = 30 cm Now, `(P_1)/(P_2)=(-2)/(3)` `THEREFORE(f_2)/(f_1)=(-2)/(3)` `implies f_2=-f_1xx2/3` ............(1) Now `1/f=(-1)/(f_1)+(1)/(f_2)` `(1)/(30)=(-1)/(f_1)+(3)/(2f_1)` (From eqn.1) `=(-1)/(2f_1)`[2+3] `impliesf_1=(-30)/(2)(5)=-15` cm Now,`f_2=-f_1xx2/3=(+15(2))/(3)=10` cm Hence `f_1=-15` cm,`f_2=10` cm |
|
| 40332. |
In Young's double slit experiment, if th distance between two slits is double of the wavelength of light used. Prove that maximum 5 bright fringes will be obtained on the screen. |
|
Answer» Solution :CONDITION for bright fringe, `dsintheta=nlamda` where n=0,1 2, 3, …….. but `d=2lamda` is given. `:.2lamdasintheta=nlamda` `:.sintheta=(n)/(2)` but `sinthetale1` [RANGE of sine function] `:.(n)/(2)le1` `:.nle2` Thus, for `nle2` on SCREEN we have, (i) One central maximum for n = 0 (ii) Two first order maximum for n = 1. Two second order maximum for n = 2. `:.` We have TOTAL five bright FRINGES. |
|
| 40333. |
A sodium light source moves in a horizontal circle at a constant speed of 0.100c while emitting light at the proper wavelengthof lambda_(0)=589.00 nm. Wavelength lambda is measured for that light by a detector fixed at the center of the circle. What is the wavelength shift lambda-lambda_(0)? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 40334. |
An electromagnetic wave is traveling in the positive x direction with its electric filed along the z axis and its magnetic field along the y axis . The fields are related by |
|
Answer» `(DELE)/(delx)=(mu_(0)epsilon_(0)delB)/(delx)` |
|
| 40335. |
A 10.0 kg block falls 30.0 m onto a vertical spring whose lower end is fixed to a platform. When the spring reaches its maximum compression of 0.200 m, it is locked in place. The block is then removed and the spring apparatus is transported to the Moon, where the gravitational acceleration is g/6. A 50.0 kg astronaut then sits on top of the spring and the spring is unlocked so that it propels the astronaut upward. How high above that initial point does the astronaut rise ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 40336. |
If angular frequency of an A.C. source used in L-C-R circuit is decreased, then inductive reactance ....... and capacitive reactance...... |
|
Answer» Decrease, INCREASE |
|
| 40337. |
Obtain an expression for magnetic field in terms of magnetic dipole moment associated with circular current loop. ""(or) Show that circular current loop can be associated with a magnetic dipole. |
|
Answer» Solution :We KNOW that the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a circular loop. `""B=(mu_(0)/(4PI))(2piIR^(2))/(x^(2)+R^(2))^(3/2)` R - radius of the loop. For a distance `"x>>R", x^(2)+R^(2)=x^(2)` and `""(x^(2)+R^(2))^(3/2)=x^(3)` HENCE, `""B=(mu_(0)/(4pi))(2piIR^(2))/(x^(3))"where", piR^(2)=A` (area of circular loop) i.e., `""B=(mu_(0)/(4pi))(2IA)/(x^(3))"where", m=IA=` magnetic moment Hence,`""vec(B)=(mu_(0)/(4pi))(2vec(m))/(x^(3))"...(1)"` Hence circular loop acts as a magnetic dipole. Note : `*` As an analogous to the electric field intensity `""vec(E)=(1/(4piepsilon_(0)))(2vec(p)_(e))/(x^(3)) "...(2)"` `*` Comparing (1) and (2) we note that by substituting `mu_(0) " as " 1/epsilon_(0)` and `vec(B)` by `vec(E), vec(m) " by " vec(p)_(e)`, one can relate the magnetic and electric fields due to the corresponding dipoles. |
|
| 40338. |
Two small balls having equal positive charge QC on each are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length L metre, from a hook fixed to a stand. The whole setup is taken into space where there is no gravity (state of weightlessness). Then the tension in the string is |
|
Answer» `(1)/(4pi epsi_(0))(q^(2))/(4L^(2))` |
|
| 40339. |
Two convex lenses of focal lengths 30cm and 3cm are given. Which lens will you use as objective and eye piece to make an astronomical telescope? |
| Answer» Solution :The MAGNIFYING power of a telescope is given by M = `f_0/f_e` normal adjustment. In order to obtain higher magnification the focal length`(f_0)` of the OBJECTIVE should be large COMPARED to the focal length `(f_e)` of the eye PIECE. Therefore, objective should be of focal length 30cm and eye piece of focal length 3 cm | |
| 40340. |
The velocity of molecules of a gas at temperature 120 K is v. At what temperature will the velocity be 2v? |
|
Answer» 120 K `((v_(2))/(v_(1)))^(2)=(T_(2))/(T_(1))implies((2v)/(v))^(2)=(T_(2))/(120)` `therefore T_(2)=120xx4impliesT_(2)=480K` |
|
| 40341. |
Identify Z in the following sequence of reactions. |
|
Answer»
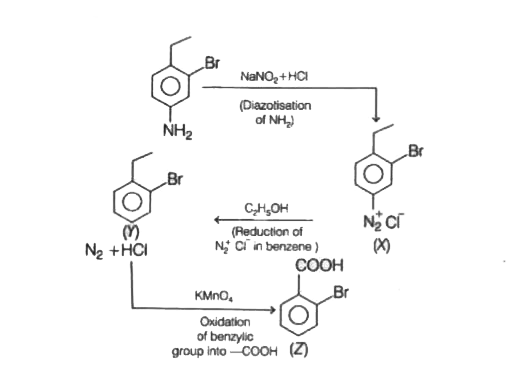 HENCE OPTION (d ) is CORRECT |
|
| 40342. |
Give three defferences between n-type and p-type semiconductors. |
Answer» SOLUTION :
|
|
| 40343. |
A storage battery of emf 8.0 V and internal resistance 0.5 Omegais being charged by a 120 Omegad.c.supply using a series resistor of 15.5 Omega . What is the terminal voltage of the battery duringcharging ? What is the purpose of having a series resistor in the charging circuit ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here` EPSI = 8.0V , r = 0.5 Omega , R = 15.5 Omega` and external supply voltage `epsi_0 = 120 V` If CHARGING current I, then during charging net effective emf `epsi_0 - epsi = I (R+ r)` ` RARR I = (epsi_0 - epsi)/(R + r) = (120 - 8.0)/( (15.5 + 0.5 ) ) = 7A` ` therefore ` Terminal voltage of the battery during charging ` V = epsi + RI = 8.0 + 0.5 xx 7 = 11.5 V` |
|
| 40344. |
A beam of X-rays with wavelength lambda = 174pm falls on the surface of a single crystal rotating about its axis which is parallel let to its surface and perpendicular to the direction of the incident beam. In this case the direction to the maxima of second and third order from the system of planes parallel to the surface of the single crystal from an angle alpha = 60^(@) between them. Find the corresponding interplanar disatnce. |
|
Answer» Solution :When the CRYSTAL is roated, the incident monochromatic beam is diffracted from a given crystal plane of interplanar spacing `d` whenever in the course of ROTATION the value of `theta` satisfies the Bragg equation. We have the EQUATIONS `2d sin theta_(1) = k_(1) lambda` and `2d sin theta_(2) = k_(2) lambda` But `pi-2theta_(1) = pi- 2 theta_(2) + alpha` or `2theta_(1) = 2 theta_(2) - alpha` so `theta_(2) = theta_(1) + (alpha)/(2)`. Thus `2d {sin .theta_(1) cos.(alpha)/(2) + cos theta_(1) sin.(alpha)/(2)} = k_(2) lambda` Hence `2d sin .(alpha)/(2)cos .theta_(1) = (k_(2) - k_(1)cos .(alpha)/(2))lambda` also `2d sin.(alpha)/(2)sin .theta_(1) = k_(1)lambda sin .(alpha)/(2)` SQUARING and adding `2dsin .(alpha)/(2) = (k_(1)^(2) + k_(2)^(2) - 2k_(1)k_(2)cos.(alpha)/(2))^(1//2)lambda` Hence `d = (lambda)/(2sin.(alpha)/(2)) [k_(1)^(2) + k_(2)^(2) - 2k_(1)k_(2)cos.(alpha)/(2)]^(1//2)` Substituting `alpha = 60^(@), k_(1) = 2, k_(2) = 3, lambda = 174pm` we get `d = 128pm = 2.81Å` (and not `0.281pm` as given in the BOOK) (Lattice parameters are typically in `Å's` and not in fractions of a pm.) 
|
|
| 40345. |
An electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of a current carrying long solenoid. Which of the following is true ? |
|
Answer» The electron will be ACCELERATED along the AXIS |
|
| 40346. |
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा फूल का भाग निषेचन के बाद फलभित्ति बनाता है ? |
|
Answer» बीजाण्डकाय |
|
| 40347. |
Long distance transmission is not possible using ground waves due to which characteristics of electromagnetic waves? |
|
Answer» SCATTERING |
|
| 40348. |
Sound waves in air are always longitudinal because, |
|
Answer» <P>of the inherent characteristics of sound waves in air |
|
| 40349. |
What is static electrical induction ? |
| Answer» Solution :When UNCHARGED conducting body is CHARGED by bringing any charged body near it this process is called charging through induction. This CHARGE STAYS at REST on the surface of the conductor. Hence, it is called electrostatic induction. | |
| 40350. |
A capacitor is formed by two square metal-plates of edge a, separated by a distance d. Dielectrics of dielectric constants K_(1) and K_(2)are filled in the gap as shown in fig. Find the capacitance. |
|
Answer» `(epsilon_0K_1K_2a^2"LN" (K_1/K_2))/((K_1-K_2)d)` |
|