Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 4051. |
Find magnetic induction at 4.5 cm from the centroid of region between the plates of capacitor in above case. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :B = 2.11 T | |
| 4052. |
The anode voltage of a photocell is kept fixed. The wavelength lambda of the light falling on the cathode is gradually changed. The plate current I of the photocell varies as follous : |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 4053. |
The maximum height that can be attained by a projection for a particular velocity v for an angle of projection of 45^@ is |
|
Answer» `(v^2)/(4G)` |
|
| 4054. |
A motor car of mass 200 kg is moving with a velocity of 72 km/hr. By the application of brakes it is brought to rest in a distance of 100m. What is the force applied ? |
|
Answer» 400 N |
|
| 4055. |
Two wires of same material and length have resistance 5 Omega and 10 Omega respectively. Find the ratio of radii of the two wires. |
|
Answer» Solution :`R = (rho l )/( A),` `therefore R _(1) = (rho l )/( PI r _(1) ^(2))` `and R _(2) = ( rho l )/( pi r _(2) ^(2))` `(R _(2))/( R _(1)) = (r _(1) ^(2))/( r _(2) ^(2))` `or (r_(1))/( r _(2)) = SQRT ((R _(2))/( R_(1)))= sqrt ((10)/( 5)) = (SQRT2 )/(1)` `r _(1) :r _(2) = sqrt2 :1` |
|
| 4056. |
In a p-n junction , |
|
Answer» NEW holes and conduction electorns are PRODUCED continuously THROUGHOUT the material |
|
| 4057. |
Arrange of following organic halides in correct order of reactivity towards S_N 2 displacement. |
|
Answer» `P GT Q gt R` 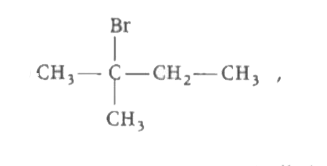 `3^@` alkyl HALIDE (highly sterically hindered) 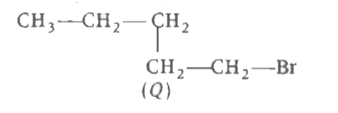 `1^@` alkyl halide (least sterically hindered) 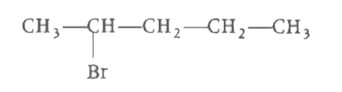 ( R) `2^@` alkyl halide RATE of `S_N 2` reaction `prop1/(sterically hi ndrance)` `therefore Rate is 1^@ gt 2^@ gt 3^@` alkyl halide. Hence, `Q gt R gt P` is CORRECT answer. |
|
| 4058. |
A 60 W load is connected to the secondary of a transformer whose primary draws line voltage. If a current of 0.54 A flows in the load, what is the current in the primary coil ? Comment on the type of transformer being used. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`P_S`=60 W, `I_S`=0.54 A `I_P`= ? , LINE voltage `V_P`= 220 V `P_S=V_S I_S` `therefore V_S=P_S/I_S=60/0.54` =111.1 V `therefore V_S APPROX` 110 V `therefore V_S lt V_P` hence , step-down transformer is used. The transformation ratio, `r=V_S/V_P=I_P/I_S` `therefore I_P=I_S xx V_S/V_P` `=0.54xx110/220` `therefore I_P`=0.27 A |
|
| 4059. |
The mass of the moon is 1//9 that of the earth. The value of the gravitational force of the earth on the moon is F newton. What is magnitude of the gravitational force of the moon on the earth. |
| Answer» Solution :g on the surface of the EARTH is given by `g'=(GM)//(R^2)`and for the planet `g'= (GM')/R^2=G. (5M)/(R^2) therefore g'/g=5therefore g'=5g therefore` WORK DONE in liffing the stone, through a distance of 1 m is `W= mg'h = 5xx 3xx10xx1 = 150 J` | |
| 4060. |
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in radar systems ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MICROWAVE REGION. | |
| 4061. |
A charge q_1 exerts some force on a second charge q_2 If third charge q_3, is brought near, the force of q_1 exerted on q_2 |
|
Answer» Decreases |
|
| 4062. |
The number of octahedral void per atom present in a face centred cubic lattice is............ |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 4063. |
In an experiment if the measured values of a physical quantity are highly concurrent, thesemeasurements are said to be |
|
Answer» ACCURATE |
|
| 4064. |
The spectral lines of hydrogen -like atom fall witin the wavelength range from 950A^(@) to 1350A^(@) Then, match the following . |
|
Answer» a-s b-p c-q d-r |
|
| 4065. |
The resistance of four arms P,Q.R and S in a Wheatstone's bridge are 10 ohm, 30 ohm, 30 ohm and 90 ohm respectively. If the galvanometer resistance is 50 Ohm, the current drawn from the cell will be: |
|
Answer» 1.0A |
|
| 4066. |
A motorboat with its engine ON, running along the river and blown over by a horizontal wind is observed to travel at 20 km/hr in a direction 53^(@) east of north The velocity of the boat with its engine in still water and blown over by the horizontal wind is 4 km/hr eastward and the velocity of the boat with its engine ON, over the running river in the absence of wind is 8 km/hr due south. Calculate (a) the velocity of the boat in magnitude and direction over still water in the absence of wind. (b) the velocity of the wind in magnitude and direction. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4067. |
A disc of mass 10 g is kept floating horizontal in the air by firing bullets, each of mass 5g, with the same velocity at the same rate of 10 bullets per second. The bullets rebound with the same speed in positive direction . The velocity of each bullet at the time of impact is (Take g = 9.8 ms^(-2)) |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 4068. |
Light with an energy flux of 25xx10^4 wm^(-2) falls on a perfectly reflecting surface at normal incidence of the surface area is 15cm^2, the average force exerted on the surface is: |
|
Answer» `1.25xx10^(-2)N` |
|
| 4069. |
The circuit shown below acts as |
|
Answer» high pass filter |
|
| 4070. |
Two conducting rails are connected to a source of e.m.f. and form an incline as shown in the figure. A bar of mass 50 g slides without friction down the incline through a vertical magnetic field B. If the length of the bar is 50 cm and a current of 2.5 A is provided by the battery, for what value of B will the bar slide at a constant velocity ? (g = 10 m//sec^(2)) |
Answer» Solution :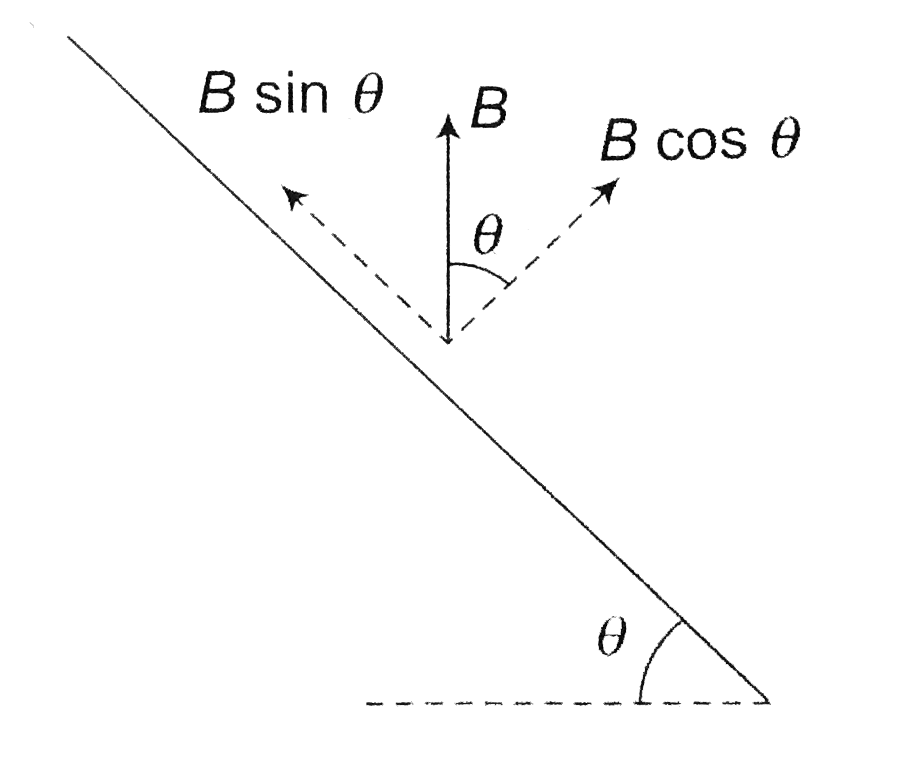 Magnetic force acting on rod (a) Due to `B cos theta, F_(1) = B cos theta iL` (b) Due to `B sin theta,F_(2) = B sin theta iL` 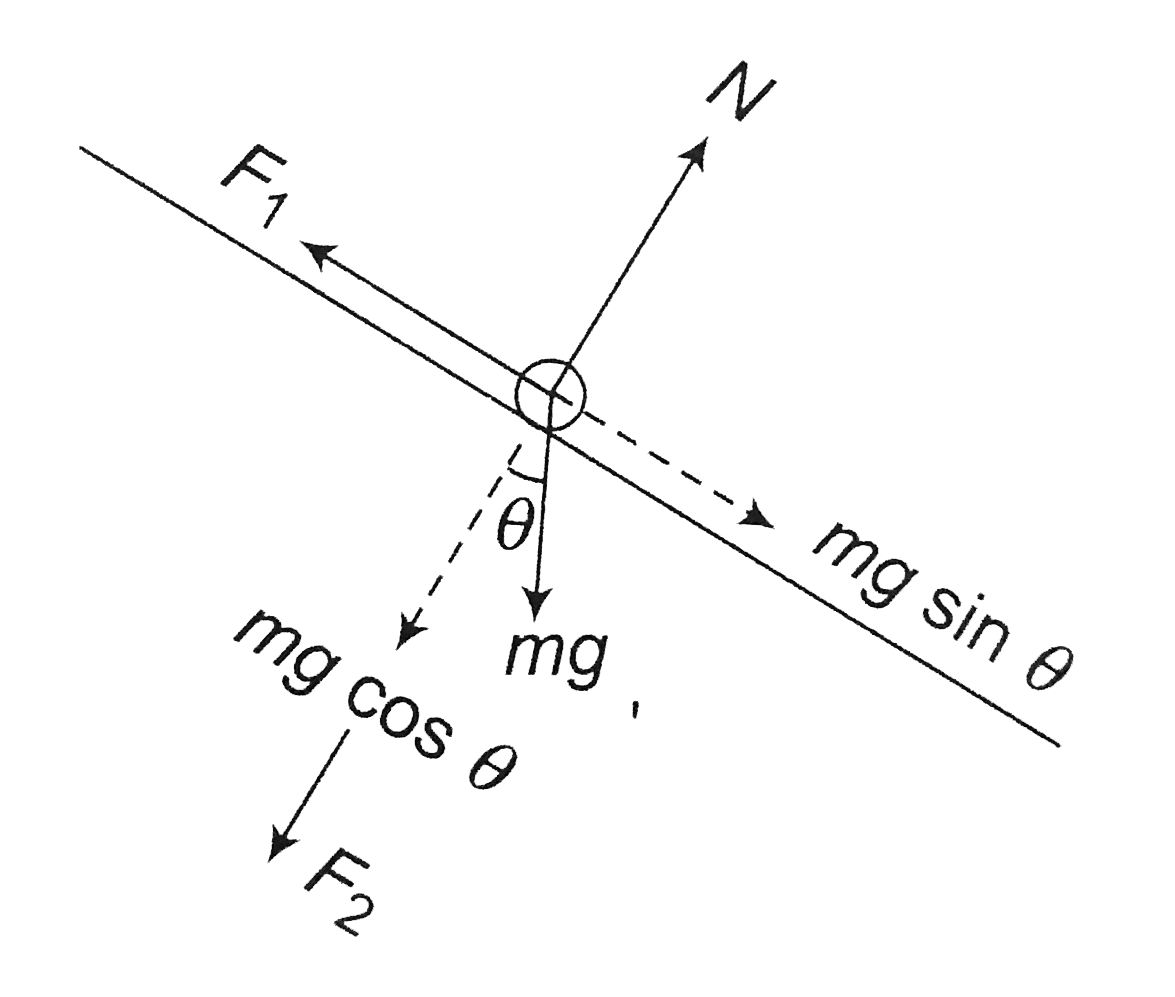 For equilibrium: `MG sin theta = F_(1) = B cos theta i L` `B = (mg TAN theta)/(i L)` `= (50 xx 10^(-3) xx tan 37^(@))/((2.5)(0.5))` |
|
| 4071. |
There is no change in the volume of a wire due to the change in its length on stretching. The Poisson's ratio of lhe material of the wire is : |
|
Answer» `+1/2` DIFFERENTIATING both sides, `(DV)/(dx)=pi/4[2xL+x^(2).(DL)/(dx)]`. Also volume remains CONSTANT `therefore (dV)/(dx)=0` `therefore2xL+x^(2)(dL)/(dx)=0rArr2xL=-x^(2)(dL)/(dx)` `rArr((dx)/x)/((dL)/L)=-1/2` `rArr` Poisson.s ratio `=-1/2` So the correct choice is (b). |
|
| 4072. |
Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circular orbit of radius R with a period of revolution T. If the gravitational force of attraction between the planet and the star is proportional to R^(-5//2), then T^2 is proportional to |
|
Answer» `R^3` CENTRIPETAL force = GRAVITATIONAL force or `mRomega^2 = (GmM)/R^(5//2)` or `R^(7//2)omega^2=GM` `R^(7//2)=(GM)/omega^2 =(GM)/(2pi//T)^2 =(T^2xxGM)/(4pi^2)` or `T^2 PROP R^(7//2)` |
|
| 4073. |
In a system of four unequal particles located in an arrangement of non - linear, coplanar system, the centre of mass |
|
Answer» must lie within or at the edge at LEAST ONE of the triangles formed by any THREE particles. |
|
| 4074. |
When was Saalumarada Thimmakka born: |
|
Answer» 1910 |
|
| 4075. |
In a transistor connected in a common emitter mode, R_o-4kOmega, R_i=1Omega,I_c=1mA and I_b =20mA. The voltaged gain is : |
|
Answer» 100 |
|
| 4076. |
A small block slides without friction down an inclined plane starting from rest. Lets s_n be the distance travelled from time t=n - 1 to t = n. Then (S_n)/(s_n+1) is: |
|
Answer» `(2N-1)/(2n)` As u=0 `:. S_(n)=a//2(2n-1)` ALSO `S_(n+1)=a//2 [2n(n+1)-1]=a//2[2n+1]` HENCE `(S_(n))/(S_(n+1))=(2n-1)/(2n+1)` |
|
| 4077. |
A ball is projected from a certain point on the surface of a planet at a certain angle with the horizontal surface. The horizontal and vertical displacements x and y vary with time t in second as x=10sqrt(3)t and y=10t-t^(2)The maximum height attained by the ball is: |
|
Answer» 100m At the highest POINT `v_(y)=0:.10-2t=0` or `t=5s` Putting above `h_(max)=10xx5-25=25m` |
|
| 4078. |
In CE transistor amplifier , if the base current is increased by 20 mu A , the collector current changes from 4 mA to 5 mA . The current amplification factor of the transistor is |
|
Answer» 200 |
|
| 4079. |
Express wavelength of light in terms of velocity and frequency. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :WAVELENGTH `LAMDA` = velocity/frequency = C/v | |
| 4080. |
A body takes ''n'' times as much time to slide down a rough inclined plane as it takes to slide down an identical but smooth inclined plane. If the angle of inclination of the inclined plane is ''theta''. What is the coefficient of friction between the body and the rough plane ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Let be the LENGTH of both the INCLINED planes and `THETA` be the inclination. Then the TIME taken by a body sliding the smooth and rough inclined planes are `t_("smooth")=sqrt((2l)/(g SIN theta))` and`t_("rough")=sqrt((2l)/(g(sin theta - mu_(k)cos theta)))` If `t_("rough")= nt_("smooth")` `sqrt((2l)/(g(sin theta - mu_(k)cos theta)))=n sqrt((2l)/(g sin theta))` On solving we get`mu_(k)=tan theta (1-(1)/(n^(2)))` |
|
| 4081. |
A lever PQ, hinged at P, of mass 'm' and length 'l' lies on the drum ( solid cylinder ) of mass 'm' and radius 'R'.The drum can rotate about the horizontal axis passing through O. The coefficient of friction between the lever and drum is 1//4. A block of mass 'm' is connected through the string with the drum as shown in the figure. The string does not slip on the drum. Then the acceleration of the block is |
|
Answer» `g//3` |
|
| 4082. |
Suppose that the lower half of the concave mirror.s reflecting surface as shown in figure is covered with an opaque (non-reflective) material. What effect will this have on the image of an object placed in front of the mirror ? |
| Answer» Solution :You may THINK that the IMAGE will now show only half of the object, but taking the laws of REFLECTION to be true for all points of the remaining part of the mirror, the image will be thatof the whole object. However, as the area of the REFLECTING surface has been REDUCED, the intensity of the image will be low (in this case, half). | |
| 4083. |
If for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the human reproductive system get blocked, the gametes will not transported from |
|
Answer» TESTES to epididymis |
|
| 4084. |
Three waves A,B and C of frequencies 1600 kHz, 5 MHz and 60 MHz, respectively are to be transmitted from one place to another.Which of the following is the appropriate mode of communication? |
|
Answer» A is TRANSMITTED VIA space WAVE while B and C are transmitted via sky wave |
|
| 4085. |
2 kcal of heat are supplied to a system. The internal energy of a system rises by 5030 J and external work done is 3350 J. Then mechanical equivalent of heat is |
|
Answer» 4190 J |
|
| 4086. |
Most of the solids are_____. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4087. |
The momentum of body decreases by 20% The percentage decrease in kinetic energy of the body is : |
|
Answer» 0.36 When MOMENTUM becomes N times then % change in `K.E=(n^(2)-1)xx100` =`[(4/3)^(2)-1]xx100=((16)/(25)-1)xx100=-36%` -ve SIGN show that ENERGY decreses by 36%. |
|
| 4088. |
Four monochronic and coherent sources of light , emitting waves in phase of wavelength lambda, are placed at the pointsx = 0 d,2d and 3d on the x - axis .Then |
|
Answer» points having `|x| GT gt d` appear dark if d= `LAMBDA//4` |
|
| 4089. |
In the fusion reaction ""_(1)H^(2)+ ""_(1)H^(2) tp ""_(2)He^(3) +""_(0)n^(1), douteron, helium and the neutron have masses 2.015 a.m.u., 3.017 a.mu, and 1-009 a.m.u. respectivoly. Find the total energy released if 1 kg of deuterium undergoes complete fusion : |
|
Answer» `3 xx 10^(12)` Energy released `=0.004 xx 931MeV` =3.724MeV Energy released PER deuteron `=1/2 xx 3.724 MeV` No. of deuterons in one KG `=(6.02 xx 10^(26))/(2)` Energy per kg `=9 xx 10^(13)J` |
|
| 4090. |
Internal forces acting within a system of particles can alter |
|
Answer» The LINEAR momentum as WELL as the KINETIC energy of the SYSTEM |
|
| 4091. |
Image of an object kept on the principal axis of transparent sphere with silvered rear surface A sphere of radius 1m and n=1.5 is silvered at its back. A point objet is kept at a distance of 1m from the front face (Fig. 34-30). Where will the final image be formed ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here , we can clearly see that there will be three events before the final IMAGE will be formed. Refraction, reflection , and refraction back into the air. Calculation : For the FIRST event O is the optical center, `n_(1)=1` , `n_(2)=1.5`, `u=-1m` , `R=+1m`. Therefore, we get `(1.5)/(v_(1))-(1)/(-1)=(1.5-1)/(1)` `v_(1)=3m` This image will act as an object for the rear silvered surface . However, for TAKING the object distance, we have to MEASURE it from the pole of the mirror. As we have discussed before, `u_(2)=v_(1)-x` `u_(2)=-3-2=-5m` Applying mirror formula, we get (radius of curvature is `-1m`, so final length of the mirror is `-1//2`m) `(1)/(v_(2))+(1)/(-5)=(1)/(-0.5)` `v_(2)=-(5)/(9)m`. These reflected rays will again be refracted from the spherical surface . Since now The direction of the light rays has reversed, therefore `u_(3)=-v_(2)-x` `u_(3)=-(-(5)/(9))-2=-(13)/(9)m`. This can be seen from Fig. 35-29 also. Now, `(1)/(v_(3))-(1.5)/((-13)/(9))=(1-1.5)/(-1)=0.5` Note here that the radius of this surface is negative becuase the direction of the incident rays has reversed. Solving we get `v_(3)=-13//7m`. Negative means that the image is virtual formed inside the spherical surface. This is distance from the left edge of the spherical surface. 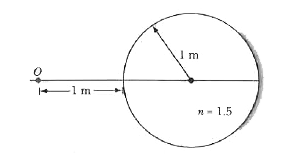
|
|
| 4092. |
Assertion : Magnetic field lines are continuous and closed. Reason : Magnetic monopole does not exist. |
|
Answer» If both assertion and reason are TRUE and reason is the CORRECT explanation of assertion. |
|
| 4093. |
A conducting rod AB of lemgth 2 l moves through a uniform magnetic field B. The rod makes an angle thetawith the vertical while it falls with a uniform linear velocity v. The potential difference between the two ends of the rod is Bv^(2)l . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4094. |
In the above question the average speed of the particle nearly is: |
|
Answer» 2 `ms^(-1)` |
|
| 4095. |
The work done in slowly moving an electron of charge e and mass m from A to B along semicircular path (as shown in the figure ) in vertical plane in the field of charge Q is . |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 4096. |
man wants to swim across a river of which 200 m along the shortest path . If the speed of river stream is 3 km h^(-1) and speed of swimmer in still water is 5 km h^(-1) , then the time of crossing the river is |
| Answer» Answer :C | |
| 4097. |
A square loop a, b, c, d of a conducting wire has been changed into a rectangular loop a′, b′, c′, d′ as shown in figure. What is the direction of induced current in the loop? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :CLOCKWISE. | |
| 4098. |
The following tables has 3 columns and 4 rows. Based on each table, there are THREE questions. Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C), and (D). ONLY ONE of these four options is correct Q |
|
Answer» (1) (i) (S) |
|
| 4099. |
An insulated wire is wound so that it forms a flat coil with N=100 turns. The radius of the innermost turns is R_(1)=4 cm . What magnetic moment will this coil have when a current of I=10 mA flows in it ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 4100. |
Figure shows a freeze-frame of a 0.500 kg particle moving along a straight line with a position vector given by vecr=(-2.00t^(2)-t)hati+5.00hatj, With vecr in meters and t in seconds, starting at t = 0. The position vector points from the origin to the particle. In unit-vector notation, find expressions for the angular momentum vecl of the particle and the torque vectau acting on the particle, both algebraic signs in terms of the particle's motion. |
|
Answer» Solution :(1) The point about which an ANGULAR momentum of a particle is to be calculated must always be specified. Here it is the origin. (2) The angular momentum `vecl` of a particle is given by Eq. `(vecl=vecrxxvecp=m(vecrxxvecv))`. (3) The sign associated with a particle.s angular momentum is set by the sense of ROTATION of the particle.s position vector as the particle moves: clock-wise is negative and counterclockwise is positive. (4) If the torque acting on a particle and the angular momentum of the particle are calculated around the smae point, then the torque is related to angular momentum by Eq. `(vectau=dvecl//dt)`. Calculations: In order to use Eq. to find the angular momentum about the origin, we first must find an expression for the particle.s velocity by taking a time derivative of its position vector. Following Eq. `(vecv=dvecr//dt)`, `vecv=d/dt((-2.00t^(2)-t)hati+5.00hatj)` = `(-4.00t-1.00)hati`, with `vecv` in METERS per second. Next, let.s take the cross product of `vecrandvecv` using the template for cross products displayed in Eq. `vecaxxvecb=(a_(y)b_(z)-b_(y)a_(z))hati+(a_(z)b_(x)-b_(z)a_(x))hatj+(a_(x)b_(y)-b_(x)a_(y))HATK` Here the generic `veca` is `vecr` and the generic `vecb` is `vecv`. However, because we really do not want to do more work than needed, let.s first just think about our substitutions into the generic cross product. Because `vecr` lacks any z component and because `vecv` lacks any y or z component, the only nonzero term in the generic cross product is the very last ONE `(-b_(x)a_(y))hatk`. So, let.s cut to the chase by writing `vecrxxvecv=-(-4.00t-1.00)(5.00)hatk=(20.0t+5.00)hatkm^(2)//s` Note that, as always, the cross product produces a vector that is perpendicular to the original vectors. To finish up Eq. we multiply by the mass, finding `vecl=(0.500kg)[(20.0t+5.00)hatkm^(2)//s]` = `(10.0t+2.50)hatk kg*m^(2)//s`. The torque about the origin then immediately follows from Eq. `vectau=d/dt(10.0t+2.50)hatkkg*m^(2)//s` = `10.0hatkkg*m^(2)//2^(2)=10.0hatkN*m` 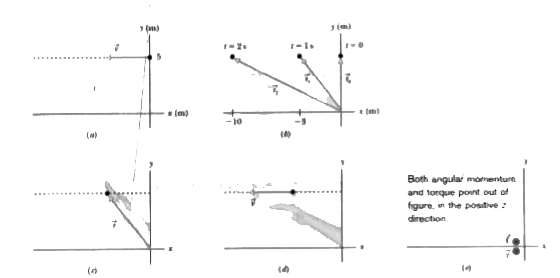
|
|



