Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 41501. |
What is myopia? What is its remedy? |
|
Answer» Solution :Myopia (or) short sightedness: It is a vision defect in which a preson can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see the DISTANT object elearly beyond a certain point. REMEDY (CORRECTION): A myopia eye is corrected by using a CONCAVE LENS of focal lenght equal to the distance of the far point F front the eye. |
|
| 41502. |
A particle of specific charge alpha starts moving from (0,0,0) under the action of electric field E = chati and magnetic field vecB = B_(0)hatk. Its velocity at (x, 0, 0) is 4hati + 3hatj. Find the value of x |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`1/2mv^(2)=vecF.vecS,1/2m(25)=Q(vecE.vecS)` `25/2=alpha(ehati.xhati),exalpha=25/2x=25/(2alphae)` |
|
| 41503. |
What is Rayleigh's scattering? |
| Answer» Solution :The SCATTERING of light by particles in a medium WITHOUT a change in WAVELENGHT is CALLED as Rayleigh.s scattering. | |
| 41504. |
In YDSE fringes are obtained using light of wavelength 4800 A^(@). One slit is covered with a thin glass film on refractive index 1.4 and another slit is covered by a film of same thickness but refractive index 1.7. By doing so the central fringe is shifted to fifth bright fringe in the original pattern. The thickness of glass film is x xx 10^(-3)mm, what is the value of x ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41505. |
Define the term .angle of dip.. Find the value of dip at a place if the vertical component of Earth.s magnetic field is sqrt3 times the horizontal component. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Angle of DIP : Dip at a place is the angle between the HORIZONTAL and the resultantmagnetic field (B). Given :`B_v = sqrt(3)B_H` We have` tan theta = (B_v)/(B_H)= ( sqrt(3) CANCEL(B)_H) /( cancel(B)_H)` `theta = tan^(-1)( sqrt(3))` ` theta = 60^@` |
|
| 41506. |
A wire connected to a power supply of 230V has power dissipation P_(1). Suppose the wire is cut into two equal pieces and connected parallel to the same power supply. In this case power dissipation is P_(2). The ration (P_(2))/(P_(1)) is. |
|
Answer» 1 |
|
| 41507. |
In going from one city to another a car travels-75 km north, 60 km north west and 20 km east. The appromoximate distance from between the two cities is |
|
Answer» 119 km |
|
| 41508. |
A packet of weight w is dropped with the help of a parachute and on striking the ground comes to rest with retardation equal to twice the acceleration due to gravity. The force exerted on the ground is |
|
Answer» w |
|
| 41509. |
The main source of sun.s energy is |
|
Answer» NUCLEAR FUSION |
|
| 41510. |
Draw ray diagram for an astronomical telescope. Define magnification and write its relation. |
|
Answer» Solution :Telescope. A telescope is an optical instrument used for observing distant OBJECTS very clearly. Astronomical telescope. It produces virtual and inverted image and is used to see heavenly bodies like SUN, stars, planets etc. so the inverted image does not affect the observation. Principle. It is based on the principle that when rays of light are made to incident on an objective from a distant object, the objective forms the real and inverted image at its focal plane. The eye lens is so adjusted that the final image is formed at least distance of DISTINCT vision. Construction. The refracting type astronomical telescope consists of two convex lenses one of which is called the objective and the other eye piece. The objective is a convex lens of large focal length and large aperture, It is generally a combination of two lenses in contact so as to reduce spherical and chromatic aberrations. The eye piece is also a convex lens but of short focal length and small aperture. The objective is mounted at one end of a brass tube and the eye piece at the other end in a smaller tube which can SLIDE inside the bigger tube carrying the objective. 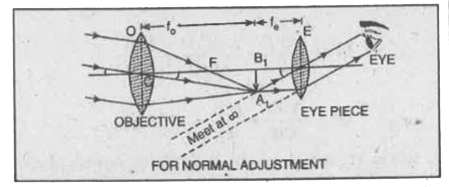 (i) When the final image is formed at infinity. The distance between the image `A_(1)B_(1)` and the eye piece is adjusted equal to the focal length of the eye piece so that the final image is formed at infinity. In this case telescope is said to be in normal adjustment or focussedto infinity. In normal adjustment, distance between two lenses = (`f_(0) + f_(e)`). The magnifying power of a telescope in normal adjustment is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended by the image at the eye as seen through the telescope to the angle subtended by the object at the unaided eye, the object and image both lying at infinity. Angle subtended by object at eye piece or at eye `/_A_(1)CB_(1) = alpha` The angle subtended by the image at the eye `/_B_(1)C_(1)A_(1)=beta` `:. "Magnifying power", M = (beta)/(alpha)` As the angles are small, therefore, they can be replaced by their tangents. Hence `M=(tan beta)/(tan alpha)=(A_(1)B_(1))/(B_(1)C_(1)) XX (B_(1)C)/(A_(1)B_(1))=(B_(1)C)/(B_(1)C_(1))` ...(i) When the rays emerging from the eye piece are parallel, the image `A_(2)B_(2)` lies at infinity and the distance `B_(1) C_(1)` is equal to `f_(e)` the focal length of the eye piece, as shown in Fig. Also the distance `B_(1)C=f_(0)` the focal length of the objective. `:. M=(B_(1)C)/(B_(1)C_(1))=(f_(0))/(f_(e))=("Focal length of the objective")/("Focal length of the eye piece")` (ii) When final image is formed at least distance of distinct vision. The objective O forms a real, inverted and diminished image `A_(1)B_(1)` of a far object at focal plane `B_(1)` of the objective in front of the eye piece E. The rays incident on the objective are taken in the form of a parallel beam as they are coming from a far off object. The distance between the eye lens and this image formed is adjusted so that it is less than the focal length of eye piece which, therefore, forms a magnified, virtual image `A_(2)B_(2)` at the least distance of distinct vision. 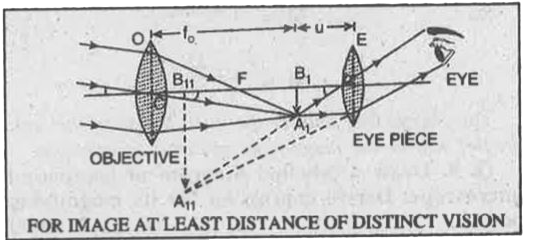 Magnifying power of a telescope is the ratio of angle subtended by the image at the eye formed at least distance of distinct vision to the angle subtended by ihe object (seen directly) at the eye lying at infinity. Angle subtended at the eye by the image formed at least distance of distinct vision `/_A_(11)C_(1)B_(11) = beta`. Angle subtended at the eye by the object seen directly lying at infinity `/_A_(1)CB_(1)=alpha` `:. "Magnifying power", M =(beta)/(alpha)` Since `alpha` and `beta` are small, so they can be replaced by their tangents. `:. M=(tan beta)/(tan alpha)=(A_(1)B_(1) // B_(1)C_(1))/(A_(1)B_(1) // B_(1)C)` `=(A_(1)B_(1))/(B_(1)C_(1)) xx (B_(1)C)/(A_(1)B_(1))` `=(B_(1)C)/(B_(1)C_(1))=(f_(0))/(u)` ...(1) For eye lens, `-(1)/(u)+(1)/(v)=(1)/(f_(e))` or `(1)/(u)=(1)/(v)-(1)/(f_(e))=(f_(e)-v)/(vf_(e))` or `u=(vf_(e))/(f_(e)-v)` Using sign conventions, we get `-u=((-D)(f_(e)))/(f_(e)-(-D))=(Df_(e))/(f_(e)+D)` or `u=(Df_(e))/(f_(e)+D)` ...(2) Putting eq. (2) in (1), we get `M=(f_(0)(D+f_(e)))/(Df_(e)=(f_(0))/(f_(e))((D+f_(e))/(D))` `M= (f_(0))/(f_(e))[1+(f_(e))/(D)]` ...(3) So, the magnification will be large, if focal length of objective (`f_(0)`) is very large as compared to focal length of eye piece (`f_(e)`). Since `1 + (f_(e))/(D) gt 1`, so we find that the amplification D produced is more when final image is formed at least distance of distinct vision than when final image is formed at infinity. In both cases, the final image is inverted hence it is not suitable for seeing terrestrial objects. |
|
| 41511. |
Consider an n-p-n transistor amplifier in common - emitter configuration. The current gain of the transistor is 100. If the collector current changes by 1 mA, what will be the change in emitter current? |
|
Answer» 1.1 mA |
|
| 41512. |
PotentialdifferenceacrossAB i.e.,V_(A) - V_(B) is(##AAK_P5_NEET_PHY_SP5_C18_E04_027_Q01.png" width="80%"> |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 41513. |
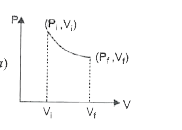
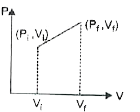
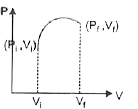
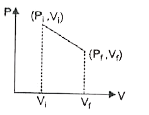
The initial state of certain gas is (P_(i)V_(i)T_(i)). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes V_(f) at constant temperture T, the corect plot of P-V diagram for it is : |
|
Answer»
At constant temperature `P_(i) V_(i) =nRT and P_(f) V_(f)=nRT` `rArr P_(i)V_(i)=P_(f)V_(f)` In the given P-V diagram (a) at every POINT on the plot P-V is constant which shows a process at constant temperature i.e. ISOTHERMAL process. CORRECT choice is (a). |
|
| 41514. |
A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. For what value of refractive index mu, the thin beam can be focussed at centre of sphere. |
|
Answer» 1.5 If BEAM is focussed at A, than ` y=2R` `rArr 2R=(muR)/(mu-1)=mu=2` The above is VALID for paraxial rays, hence beam should be THIN. If `mugt2` , then `ylt2R` , hence beam can be focussed before A. For thin beam to be focussed at A, `y=R`. `rArrR=(muR)/(mu-1)rArr mu=oo`(not possible) |
|
| 41515. |
A block of mass 0.50 kg is moving with speed of 2.00 ms^(-1) on a smooth surface. It strikes another mass of 1.00 kg and then they move together as a single body. The energy loss during the collisions is |
|
Answer» 0.16 J `KE_i=1/2"mu"^2+1/2M(0)^2=1/2xx0.5xx2xx2+0=1J` For collision applying CONSERVATION of linear momentum `mxxu=(m+M)xxv` `:. 0.5xx2=(0.5+1)xxvimplies v=2/3 m//s` FINAL kinetic energy of the system is `KE_f=1/2(m+M)v^2=1/2(0.5+1)xx2/3xx2/3=1/3J` `:.` Energy LOSS during collision=`(1-1/3)J=0.67J` |
|
| 41516. |
What is the net power absorbed by each circuit over a complete cycle. Explain your answer. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :ZERO in each CASE | |
| 41517. |
In the above problem . What is the least distance from the central maximum where the bright fringes due to blue - green light of wavelength 500 cm . The separation between the slits is 2.0xx10^(-3) m . |
|
Answer» `0.32` CM |
|
| 41518. |
Ultraviolet radiations of 6.2 eV falls on an aluminium surface. Kinetic energy of fastest electrons emitted is (work function = 4.2 eV) |
|
Answer» `3.2 xx 10^(-21)` J `= 2.0 eV = 2.0 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19) j = 3.2 xx 10^(-19) J` |
|
| 41519. |
High frequency waves are |
|
Answer» ABSORBED by F layer |
|
| 41520. |
The current that must flow through a galvanometer to have a deflection of l division on its scale is called |
|
Answer» METER sensitivily |
|
| 41521. |
A : When viewing through a compound microscope, our eyes should be positioned not on the eye piece but a short distance away from it for best viewing. R : The image of the objective in the eye-piece is known as 'eye-ring' and if we position our eyes on the 'eye-ring' and the area of the pupil of out eye is greater or equal to the area of the eye ring, our eyes will collect all the light refracted by the objective. |
|
Answer» If both Assertion & Reason are true and the reason is the correct EXPLANATION of the assertion, then mark (1). |
|
| 41522. |
Using Ampere's circuital law, obtaiin the expression for themagnetic field due to a long solneoid at a point inside the solenoid on its axis. (b) In what respect different from a solenoid? Draw and compare the pattern of the magnetic field lines in the two cases. (c )How is the magnetic field inside a given solenoid made strong? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) See, Q.14, 2008 O.D Set-I (b) Solenoid CONSISTS of a lonw wire wound in the form of a helix where the neighbouring TURNS are closely spaced, whereas, the toroid is a hollow circular ring on which a large number of turns of a wire is closely wound. (c )Increasing the CURRENT PASSING through the solenoid. |
|
| 41523. |
A charged particle is travelling in the figure. ( ## EXP_SPS_PHY_XII_C04_E04_027_Q01 .png" width="80%">: If the charge reaches the region III without any change in its initial direction of motion find the ve locity of the charged particle in terms of E and B. |
| Answer» Solution :`[F= Q(E + V*B)]` | |
| 41524. |
Natural system of classification depend on |
|
Answer» TAXONOMIC characters |
|
| 41525. |
A conducting rod of length I and velocity v moves in a magnetic field B. If rho is the resistivity of the material of rod, then the induced current produced in the rod is _____ |
|
Answer» `(BvA sin THETA)/RHO` `therefore` IR=Bvl `therefore I=(BvlxxA)/(rhol) [ because R=(rhol)/A]` `therefore I=(BvA)/rho` |
|
| 41526. |
A coil with resistance 8 Omegaand having 8 turns is connected with a galvanometer having resistance 8 times the resistance of coil. In 4 ms, if magnetic flux linked with this loop changes from 12xx10^(-5) Wb to 18xx10^(-5)Wb then current induced in the loop will be ...... |
|
Answer» 1.6 A `=6xx10^(-5)` Wb N=8 `R=8 Omega, G=8xx8=64 Omega` `t=4xx10^(-3)` s `THEREFORE` Induced current, `I=epsilon/R` , `=(N Delta PHI)/(Deltat)xx1/(R+G)` [Where R.=R+G] `=(8xx6xx10^(-5))/(4xx10^(-3)xx72)` `=0.166xx10^(-2)` `therefore I approx 1.6xx10^(-3)` A |
|
| 41527. |
Two bodies A and B have the same surface area and mass the bodies have absolute temperatures T_(A)" and" T_(B) emissivities e_(a) and e_(b) and specific heat capacities s_(A)and s_(B). The intensity, E , of radiation near a given wavelength is shown plotted against the wavelength lambda, ofradiation for both the bodies. Which of the following is possible? |
|
Answer» `T_(A)=T_(B),e_(A)=e_(B),s_(A)NE s_(B)` |
|
| 41528. |
A physical quantity x is calculate from x=(ab^(2))/(sqrt(c)). Calculate the percentage error in measuring x when the percentage errors in measuring a,b,c are 4,2 and 3 percent respectively : |
|
Answer» `7%` `=[4+2xx2+1//2xx3]%` `9.5%.` Hence correct choice is `(d).` |
|
| 41529. |
Law of Constant Composition was given by ………. |
|
Answer» Lavoisier |
|
| 41530. |
Consider thr network as shown in fig. Current is supplied to the network by two batteries as shown. Find the values of currents I_1 , I_2, I_3 . The direction of the currents are as indicated by the arrows. |
|
Answer» Solution :Applying Kirchhoff.s 1st LAW to junction C, we get `I_1 + I_2 + I_3 = 0` Applying Kirchhoff.s Iind law to the closed meshes ACDA and BCDB, we get `5 I_1 + 2I_3 = 12""…..(2)` `3I_2 + 2I_3 + 6 ""….(3)` SUBTRACTING eq (3) from eq (2) we get `5I_1 - 3I_2 = 6 "".....(4)` Multiplying eq.(1) by 2 adding with eq. (2) we get `7I_2 + 2I_2 = 12 ""......(5)` Multiplying eq (4) by 2 and eq. (5) by 3 and adding them we get `31I_1 = 48 impliesI_1 = 1.548 A.`  Putting value of `I_1 ` in eq. (5) we get `I_2 =0.58 A`and from eq. 1 we get `I_3 = I_1 + I_2 = 2.128 A` |
|
| 41531. |
In the previous question, |
|
Answer» velocity of B, OBSERVED by F (relative to itself), is equal to `4.25 ms^(-1)` we get `(dr_(1))/(dt)=(dx)/(dt)+(1)/(mu)(dy)/(dt)=4.50ms^(-1)` Hence, OPTION (d) is correct. Similarly, velocity of bird, as observed by the fish, will be equal to `(dr_(2))/(dt)` `(dr_(2))/(dt)=(1)/(mu^('))(dx)/(dt)+(dy)/(dt)=6.0ms^(-1)` Hence, option (b) is correct. . |
|
| 41532. |
A man of height 2.0 m is standing on a level road because of temprature variation the refractive index of air is varying as mu=sqrt(1+ay), where y is height from road. If a=2.0xx10^-6 m^-1. Then, find distant point that he can see on the road. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41533. |
The speed of a homogenous solid sphere after rolling down an inclined plane of vertical height h from rest without sliding is |
|
Answer» `SQRT(10/7gh)` `rArrv=sqrt((10gh)/7)` |
|
| 41534. |
The ratio of wave length of first line of Lyman series to the first line of Balmer series is |
| Answer» ANSWER :B | |
| 41536. |
If r and T are radius and surface tension of a spherical soap bubble respectively then find the charge needed to double the radius of bubble |
|
Answer» Solution :For smaller bubble `P_(1) = (P_(0) + (4T)/(R )) and V_(1) = (4)/(3) pi r^(3)` For larger bubble `P_(2) = P_(0) + (4T)/(R ) - (sigma^(2))/(2in_(0)) and V_(2) = (4)/(3) pi R^(3) " where " sigma= (q)/(4pi R^(2))` for air in the bubble, `P_(1) V_(1) = P_(2)V_(2)` `(P_(0) + (4T)/(r )) r^(3) = [(P_(0) + (4T)/(R ))- (q^(2))/(16pi^(2) R^(4) xx 2 in_(0))]R^(3)` `P_(0) [R^(3) -r^(3)] + 4T [R^(2) - r^(2)] - (q^(2))/(32pi^(2) in_(0)R)=0` But R= 2r `P_(0) [7r^(3)] + 4T [3r^(2)] - (q^(2))/(32pi^(2) in_(0)(2r))=0` `(q^(2))/(64PI^(2) in_(0)r) = 7P_(0)r^(3) + 12Tr^(2)` `q^(2)= 64pi^(2) in_(0)r^(3) [7P_(0)r + 12T]` `q= 8pi r [in_(0)r (7P_(0)r + 12T)]^(½)` |
|
| 41537. |
An electron microscope uses electrons accelerated by a voltage of 50 kV. Determine the de Broglie wavelength associated with the electrons. If other factors (such as numerical aperture, etc.) are taken to be roughly the same, how does the resolving power of an electron microscope compare with that of an optical microscope which uses yellow light? |
|
Answer» Solution :`lambda=5.5xx10^(-12)m` `lambda" (yellow light)"=5.9xx10^(-7)m` Resolving Power (RP) is inversely proportional to wavelength. Thus, RP of an electron microscope is about `10^(5)` times that of an optical microscope. In practice, differences in other (GEOMETRICAL) factors can change this comparison somewhat. |
|
| 41538. |
An applied voltage signal consists of a superposition of a dc voltage and an ac voltage of high frequency. The circuit consists of an inductor and a capacitor in series. Show that the dc signal will appear across C and the ac signal across L. |
|
Answer» Solution :Inductive reactance is `X_(L ) = 2pi f LrArr X_(L) PROP f ` CAPACITIVE reactance is `X_(C ) = ( 1)/( 2pi fC ) rArr C_(C ) prop (1)/(f)` For dc signal, `f=-0 rArr X_(C ) = oo rArr dc` can notpass through capacitor and so dc signal will appear across C. For AC signal of very high frequency , `f rarr oo rArr X_(L) rarr oo rArr` such ac can not pass through an inductor and so very highfrequency ac signal will appear across L. |
|
| 41539. |
A body having a mass of 100 gm falls freely under the action of gravity. What is the force that acts on it ? Calculate the momentum it possesses after 10 seconds. |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 41540. |
(i) Three resistors 2 Omega, 4 Omega " and " 5 Omega are comined in parallel. What is the total resistance of the combination ? (ii) If the comnbination is connected to a battery of 20 V and negligible internal resistance, determine the current through each resistor, and the total current drawn. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41541. |
A transformer is based on the principle of |
|
Answer» MUTUAL INDUCTANCE |
|
| 41542. |
The temperature coefficient of copper is 0.004^(@)C^(-1). Find the resistance of a 5 m long copper wire of diameter 0.2 mm at 100^(@)C, if the resistivity of copper at 0^(@)C is 1.7xx10^(-8) Omega m. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41543. |
a. Give the expression showing the relation between energyand momentum of a photon. b. "de-Broglie wavelength supports Bohr's model of stationary orbits." Comment on this statement. c. Is there any difference between the wavelength of the radiation and d-Broglie wavelength of a photon of that radiation? Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :a. Momentum of PHOTON `=(hupsilon)/(c )` B. Bohr orbit condition, `mvr=(nh)/(2pi)` i.e., `pr=(nh)/(2pi)` taking `(h)/(p)=(2pi r)/(N)=(L)/(n)`. This suggests that `lambda=(L)/(n)` or total length of the orbit is n times de Broglie.s wavelength. c. No. Wavelength of RADIATION `lambda=(c )/(upsilon)` de Broglie.s wavelength `lambda=(h)/(p)=(c )/(upsilon)` |
|
| 41544. |
A tube is inverted in a mercury vessel as.P is the pressureinsidethe tubeabovethe mercurylevel as shown.{:(,P,Q,R,S),((A),4,2,1,3),((B),2,3,3,2),((C ),1,2,3,4),((D),2,4,3,1):} |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41545. |
Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs and magnitude 17.0xx10^(-22)Cm^(-2). What is the electric field a. in the outer region of the first and the second plates? b. between the plates? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`10MU C//m` | |
| 41546. |
Explain two advantage of a reflecting telescope over a refracting telescoope. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Two advantage of a reflecting telescope over a REFRACTING telescope Advantage of reflecting telescope aver refracting telescope (ii) Mechanical support is easier (iii) Magnifying power is large (iii) Resolvingpower is large (iv) SPHERICAL abrration is reduced (v) FREE from chromatic aberration |
|
| 41547. |
In Young's double slit experiment, an interference pattern is obtained on a screen by a light of wavelength 6000 overset(circ)(A) coming from the coherent sources S_(1) and S_(2). At certain point P on the screen third dark fringe is formed. Then, the path difference S_(1) P – S_(2) P in micron is |
|
Answer» `0.75` |
|
| 41548. |
A 100 uF capacitor in series with a 40 Omegaresistance is connected to a 110 V, 60 Hz supply. (a) What is the maximum current in the circuit ? (b) What is the time lag between the current maximum and the voltage maximum ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here C = 100 `muF = 100 xx 10^(-6) F = 10^(-4) F, R = 40 Omega, V_(rms) = 110 V` and v= 60 Hz or `omega = 2pi v = 3.14 xx 60 xx 376.8 s^(-1)` `therefore` Impedance `Z = sqrt(R^(2) + X_(C)^(2)) = sqrt(R^(2) + (1/(Comega))^(2)) = sqrt((40)^(2) + (1/(10^(-4) xx 376.8))^(2)) = 48 Omega` `therefore` Maximum current `I_(m) = V_(m)/Z = (sqrt(2) V_(rms))/Z = (sqrt(2) xx 110)/48 = 3.24 `A (b) Phase difference between current and voltage. `PHI = tan^(-1)(X_(C))/R = tan^(-1) ((1//Comega)/R) = tan^(-1)(1/(10^(-4) xx 376.8 xx 40))` `=(33.6 xx pi)/180` rad `therefore` Time lag between current maximum and voltage maximum `t= phi/(2pi v) = (33.6 xx pi)/(180 xx 2pi xx 60) = 1.55 xx 10^(-3)`s. |
|
| 41549. |
A height of a tower formed by a objective lens of a telescope is 4.7 cm. What is the height of the final image of the tower if it is formed at 25 cm ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Angular magnification of eyepiece = `(1 + (D)/(f_(e)) ) = 1 + (25)/(5 ) = 6 ` `therefore` Height of the final IMAGE = 6H = ` 6 XX 4.7 = 28.2 ` CM |
|
| 41550. |
The dimensional formula of magnctic induction is |
|
Answer» `MT^(-1) A^(-1)` |
|