Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 6851. |
When is the series combination of cells advantageous and why? |
|
Answer» Solution :Series combination is advantageous when high e.m.f (terminal POTENTIAL difference at low current is required. In series combination of cells, `i= (n epsi)/(nr+R)` where `r LT lt R `, then `I = (n epsi)/(R)` `THEREFORE ir = n epsi` `therefore` Potential difference ACROSS the external resistance is n times e.m.f of each CELL. |
|
| 6852. |
Screen is placed at a distance 60 cm from an object. A convex lens of focal length f is placed between object and screen and it is attempted that real image of object is formed on the screen. But real image could not be formed for any position of lens between object and screen. |
|
Answer» f must be LESS than 15 CM. |
|
| 6853. |
The phenomenon of lagging of magnetic induction behind the magnetising field is called ............ . |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6854. |
A T.V. tower has a height of 100 m. How much population is covered by T.V. broadcast, if the average population density around the tower is 1000//km^(2)? |
|
Answer» `40 xx 10^(5)` |
|
| 6855. |
The equation of state of a real gas can be expressed as (P+(a)/(V^(2)))(v-b)=cT, where P is the pressure, V the volume, T the absolute temperature and a,b,c are constants. What are the dimensions of a'? |
|
Answer» <P>`M^(0)L^(3)T^(-2)` `(a)/((L^(3))^(2))=ML^(-1)T^(-2)impliesa=[ML^(5)T^(-2)]` So correct choice is `(c )`. |
|
| 6856. |
Which of the following statements is incorrect ? Standard Gibbs free energy change is always zero at equilibrium |
|
Answer» Addtion of solid does not affect equlibrium |
|
| 6857. |
The suspended body having weighs 75 N. Is T equal to, greater than, or less than 75 N when the body (a) at constant speed, (b) at increasing speed, and ( c ) at decreasing speed? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) INCREASE, (B) YES, ( C ) yes | |
| 6858. |
(a) Derive an expression for the force between two long parallel current carrying conductors . (b) Use this expression to define S.I. unit of current . (c) A long straight wire AB carries a current I.A proton P travels with a speed v , parallel to the wire , at a distance d from it in a direction opposite to the current as shown in the figure . What is the force experienced by the proton and what is its direction ? |
|
Answer» Solution :(c) Magnetic field induction at the POINT P is `B= (mu_(0))/(4 pi) . (2I)/(r)` The direction of `vecB` is perpendicular to the plane of paper directed inwards (ACCORDING to Right Hand Thumb rule ) The force on moving proton of charge q due to magnetic filed B is F = qvB sin `90^(@) = q V B ` Since charge of proton q = `1.6 XX 10^(-19) C` `therefore F = 1.6 xx 10^(-9) xx v B N.` The direction of force on proton , according to FLEMMING's left Hand Rule acts in the plane of paper towards right . |
|
| 6859. |
If the magnetic field B of a polarised electromagnetic wave oscillates parallel to y-axis and is given by : B_(y)=B_(m)sin(kz-omegat). What is the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave and parallel to which axis does the associated electric field oscillates ? |
|
Answer» `+ve" y - AXIS, X - axis"` |
|
| 6860. |
An illuminated object and a screen are placed 90 cm apart. Determine the focal length and nature of the lens required to produce a clear image on the screen, twice the size of the object. |
|
Answer» Solution :It is GIVEN that distance between an illuminated object and screen `|u+v| = 90 cm` and linear magnification of image m = 2 Since the image is being formed on the screen, it is a real image hence the lens used is a convex lens. `therefore |m| =|v/u| =2` or `|v|=2|u| rArr |u|=30 cm` and `|v| = 60 cm` As PER SIGN convention followed u is -ve and v is +ve. Hence, using lens formula `1/v - 1/u = 1/f`, we have `1/(+60) -1/(--30) = 1/f rArr 1/f = 1/60 + 1/30 = 1/20` or `f=+20` cm |
|
| 6861. |
In the Ohm'slaw experiment to find resistance of unknown resistor R following arrangements (a) and (b) are possible The resistance measured is given by R_(measured)=(V)/(i) V = voltage reading of voltmeter I = current Reading of ammeter But unfortunately the ammeters and voltmeter used are not ideal but having resistance R_(A) and R_(v) respect tively Yor are given two unknown resistors X and Y These resistances are to be determind using an ammeter of R_(A) = 0.5Omega and a voltmeter of R_(v) = 20kOmega It is known that X is in range of a few ohms and Y is in the range of several kilo ohm's Which circuit is perferable to measure X and Y {:("Resistor",Circuit),(x,(a)),(y,(b)):} . |
|
Answer» `xrarr(a),yrarr(b)` Then measured RESISTANCE from arrangment (a) will be `R_(measured) = R + R_(A) ~~R` So (a) will be perferred if `R` is very small (~few Ohm) then measured resistance from (b) will be `R_(measured) = (R)/(1+(R)/(R_(v)))` where `R//R_(v)` is NEGLIGIBLE `so R_(measured)RARR R` So (b) will be perferred . |
|
| 6862. |
A plane electromagnetic wave with frequency omega falls upon an elastically bonded electron whose natural frequency equals omega_(0). Neglecting the damping of oscillations, find the ratio of the mean enegry dissipated by the electron per unit time to the mean value of the enrgy flow density of the incident wave. |
|
Answer» Solution :For the elastically bound electron `mddotoversetrarr(R) =m omega_(0)^(2) overset(r ) = eoverset(E_(0)) cos OMEGAT` This equation has the particular intergal (i.e. neglecting the PART which does not have the frequency of the impressed force ) `oversetrarr(r) = (eoversetrarr(E_(0)))/(m) (cos omegat)/(omega_(0)^(2) - omega^(2))` so and `ddotoversetrarr(p) =- (e^(2)oversetrarr(E_(0))omega^(2))/((omega_(0)^(2)-omega^(2))m)cos omegat` HENCE `P =` mean radiated power `= (1)/(4piepsilon_(0)) (2)/(3c^(3)) ((e^(2)omega^(2))/(m(omega_(0)^(2)-omega2)))^(2)(1)/(2)E_(0)^(2)` The mean incident poynting flux is `lt S_("inx") gt = sqrt((epsilon_(0))/(mu_(0)) (1)/(2)E_(0)^(2)` Thus `(P)/( lt S_("inc") gt ) = (mu_(0)^(2))/(6PI) ((e^(2))/(m))^(2) (omega^(4))/((omega_(0)^(2) - omega^(2))^(2))`. |
|
| 6863. |
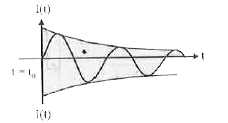
A seris LR circuit is connected to a voltage source with V(t) = V_(0)sin omegat. After very large time, current 1(t) behaves as (t_(0) gt gt (L)/(R)): |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 6864. |
STATEMENT-1: A charged particle is accelerated by a potential difference of V volts. It then enters perpendicularly to a uniform magnetic field. It rotates in a circle. Its angular momentum about centre is say L. Now if V is doubled, L also becomes two times because STATEMENT-2: If V is doubled, kinetic energy will become two times and therefore, L also becomes two times. |
|
Answer» Statement-1 is TRUE , Statement-2 is True , Statement-2 is a CORRECT EXPLANATION for Statement-1. |
|
| 6865. |
In Young's experiment, the upper slit is covered by a thin glass plate of refractive index 1.4 while the lower slit is covered another glass plate having the same thicknessas the first one but having refractive index Interference pattern is observed using light ofwavelength 5400A. It is observed that the point P on the screen where the central maximum (n=0) fell before the glass were inserted now has 3/4 th original intensity. It is further observed that what used to be the fifth maximum earlier, lies below the point P while the sixth minimum lies above P. Calculate the thickness of the glass plate. |
Answer» Solution : PATH DIFFERENCE `= (XD)/(D) + (n_2 - n_1) t` For P, x = 0 , Path difference ` = (n^2- n^1) t = 0.3t` ` I = I_0 cos^2 phi/2` `(I)/(I_0) = cos^2 phi/2, cos phi/2 = (sqrt3)/(2)` ` phi/2 = phi/6 , phi = pi/3` Path difference ` = (LAMDA)/(2 pi) phi = (lamda)/(2pi) pi/3 =pi/6` ` 0.3 t = 5 lamda + pi/6` |
|
| 6866. |
A insulating cylindrical rod of diameter d and length l(l gt gt d) has a uniform surface charge density such that the electric field just outside the curved surface of the cylinder at point M is E_(0). Find the electric field due to charge distribuition at point P (r gt gt l). |
|
Answer» <P>`E_(0)(ld)/(2R^(2))` `lambda=pi epsilon_(0)dE_(0)` So, `E_(p)=(E_(0)dl)/(4r^(2))` |
|
| 6867. |
An electron having a charge c moves with a velocity v in X - direction . An electric field acts on it in Y - direction ? The force on the electron acts in |
|
Answer» positive direction of Y - axis |
|
| 6868. |
The mass number of He is 4 and that for sulphur is 32. The radius of sulphur nucleus is large the helium by : |
|
Answer» `SQRT8` |
|
| 6869. |
Obtain an expression for the magnetic dipole moment of current loop. |
|
Answer» Solution :We know that magnetic induction on the axial line of a circular COIL is `B=(mu_(0) N I R^(2))/(2(R^(2)+X^(2)))^(3//2)` where N = Number of turns in the coil R= Radius of the coil X= Distance from centre of the coil i= Current in a coil If `X gt gt R," Then "B=(mu_(0) Ni R^(2))/(2X^(3))` Multiplying and dividing with `2pi` `B=(mu_(0) Ni R^(2))/(2X^(3))xx(2pi)/(2pi)` `B=(mu_(0))/(4PI). (2Ni A)/(x^(3))rarr(1)` We know that magnetic induction field on the axial line of a bar magnet `B=(mu_(0))/(4pi). (2M)/(x^(3))rarr(2)` Comparing the equations (1) and (2) Magnetic moment (M) = Ni A |
|
| 6870. |
A single strand of DNA, the building blocks of all living things, is about ____nanometers wide. |
|
Answer» Two |
|
| 6871. |
In the previous question the reading of ammeter A_(1) will be : |
|
Answer» 6.75 A |
|
| 6872. |
Prove that the current flowing through an ideal inductor connected across a.c. source lags behind the voltage in phase by pi/2. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :Show as in Short Answer Question Number 2 above that for V = V, sin ot, the current `I = I_(m) sin (omegat - pi/2)` This proves that the current flowing through an ideal INDUCTOR LAGS behind an a.c. VOLTAGE in phase by `pi/2`. | |
| 6873. |
Explain AC voltage applied to a resistor and explain it with necessary graph. |
Answer» Solution :Figure SHOWS a resistor connected to an ac voltage.  Here consider a source which produces sinusoidally varying potential difference across its terminals. Such type of potential difference is called ac voltage. `:.` ac voltage `V = V_(m) sin omega t `.....(1) where `V_(m)` is the amplitude of the oscillating potential difference. Means maximum voltage and `omega` is its angular frequency. From equation (1), V = IR where I can be found by applying Kirchhoff.s LOOP rule, `:.` IR = `V_(m) sin OMEGAT ` `:. I = ( V_(m))/( R ) sin omega t ` but `( V_(m))/( R ) = I_(m)` `:.` I `= I_(m) sin omega t `.....(2) where the current amplitude is, `I_(m) = ( V_(m))/( R ) ` is just a Ohm.s law. This relation works equally for both ac and dc voltage or current (signal ). The voltage across a pure resistor and current through it are plotted as a function of time is shown in below graph.  In a pure resistor, the voltage and current are in phase. The minima, zero and maxima occur at the same RESPECTIVE times. The voltage and current are in phase with each other in pure resistor. Both reach zero. minimum and maximum values at the same time. Here both V and I reach zero, minimum and maximum values at the same time, so the voltage and current are in phase with each other. |
|
| 6874. |
Photo-electric effect show …….nature of radiation. |
|
Answer» wave |
|
| 6875. |
Give the relation between half life and mean life |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6876. |
The focal length of objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope are icm and 5cm. An object is placed at a distance of 1.1 cm from the objective and if the final image is formed at infinity the magnifying power and distance between the lenses are respectively |
|
Answer» `60, 16 cm` |
|
| 6877. |
Maximum kinetic energy of positive ion in cyclotron is _____ (Where r_(0) = radius of cyclotron) |
|
Answer» `(Q^(2)Br_(0))/(2m)` `K=1/2mv^(2)` `thereforeK_(max)=1/2mv_(max)^(2)""...(1)` We have, `r=(mv)/(Bq)` `thereforev=(Bqr)/m` `thereforev^(2)=(B^(2)q^(2)r^(2))/m^(2)` `thereforev_(max)^(2)=(B^(2)q^(2))/m^(2)r_(max)^(2)""...(2)` `thereforev_(max)^(2)=(B^(2)q^(2))/m^(2)r_(0)^(2)""(becauser_(max)=r_(0))` From equation (1) and (2), `K_(max)=1/2mxx(B^(2)q^(2)r_(0)^(2))/m^(2)=(B^(2)q^(2)r_(0)^(2))/(2m)` |
|
| 6878. |
A convex lens and a concave lens, each havaing same focal length of 25 cm, are put in contact to from a combination of lenses. The power of the combination (in diopter) is |
|
Answer» zero |
|
| 6879. |
To easily obtain the zener effect …….. |
|
Answer» thicknessof depletion layer should be INCREASED by increasing the amount of IMPURITY. If the impurity is high and the width of depletionlayer is too low then the electric field in the reverse bias VOLTAGE becomes stronger in depletion layer. |
|
| 6880. |
In AM wave the amplitude of each side hand frequency is |
|
Answer» `E_(C)` |
|
| 6881. |
A positively charged particle moving along x - axis with a certain velocity enters a uniform electric field directed along positive y-axis. Its |
|
Answer» Vertical velocity changes but horizontal velocity remains CONSTANT |
|
| 6882. |
A spring is hanging from a rigid support. A force of 2000 dynes applied verticlly downwards at the lower end of the spring, extends it by 5 cm. The work done is given by: |
|
Answer» `5xx10^(3)` ERG =`1/2F.x.=1/2xx2000xx5=5000` ERGS` |
|
| 6883. |
What is the angle between the directions of electric field at any (i)axial point, (ii)equatorial point due to an electric dipole? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6884. |
A clsoed organ pipe and an open organ pipe of same length produce 2 beats /second while vibrating in their fundamental modes. The length of the open organ pipe is halved and that of closed pipe is doubled . Then the number of beats produced per second while vibrating in the fundamental mode is : |
|
Answer» 8 `(V)/(2l) - (v)/(4l) = 2 ` `(v)/(4l) = 2 rArr (v)/(l) = 8 ` . When length of open organ pipe is havlved and that of closed organ pipe is doubled then beat frequency will `be F._(0) - f._(c) = (v)/(2. (i)/(2))= (v)/(4.2) = (v)/(l) - (v)/(8l)` = `(7)/(8) (v)/(l)` = `(7)/(8) xx 8 = 7 ` HZ. so correct choice is b. |
|
| 6885. |
In a travelling plane electromagnetic wave, the maximum magnetic field is 1.26xx 10^(-4) T . The intensity of the wave is (Assume, mu_0 = 126 xx 10^(-6) H//m) |
|
Answer» `1.56 xx 10^6 (W)/(m^2)` `B_0 = 1.26 xx 10^(-4) t` ` mu_0 = 1.26 xx 10^(-6) H//m` ` therefore ` Intensity of EMW (Electromagnetic wave) is given by `I = 1/2 (B_0^2 C)/(mu_0) = 1/2 xx( (1.26 xx 10^(-4) )^2 xx 3 xx 10^8)/(1.26 xx 10^(-6) ) ` ` =1/2 xx (1.26 xx 1.26 xx 10^(-8) xx 3 xx 10^8)/(1.26 xx 10^(-6) )` `= 0.63 xx 3 xx 10^6 = 1.89 xx 10^6 W//m^2` |
|
| 6886. |
Paramagnetic or ferromagnetic substance The temperature at which a ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic is ______. |
|
Answer» TRANSITION TEMPERATURE |
|
| 6887. |
A concave lens has the same radii of curvature for both sides and has a refractive index 1.6 in air. In the second case, it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.4. Calculate the ratio of the focal lengths of the lens in two cases. |
|
Answer» Solution :When the LENS PREPARED from a material of REFRACTIVE index `n_L = 1.6` is placed in air, then its focal length `f_("air")` is GIVEN by: `1/(f_("air") =(n_(L)-1) (1/R_(1)-1/R_(2))) = (1.6-1) (1/R_(1)-1/R_(2))` When the lens is immersed in a medium of refractive index `n_m = 1.4`, then its new focal length `f_(m)`is given by: `1/f_(m) = (n_(L)/n_(m)-1)(1/R_(1) - 1/R_(2)) = (1.6/1.4-1)(1/R_(1)-1/R_(2))` `RARR f_(m)/f_("air") =((1.6-1) xx 1.4)/(1.6 - 1.4) = (0.6 xx 1.4)/2 = 4.2` or `f_(m)=4.2 f_("air")` |
|
| 6888. |
The rms value of ac is how many times the peak value of the current ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`1 SQRT 2` TIMES | |
| 6889. |
Construct a logic circuit using NAND gates only for Y = bar(A) + bar(BC). |
Answer» Solution :Each and every term in the given LOGIC expression is REPLACED by the CORRESPONDING basic gates using NAND gates. Hence the logic circuit for `Y = bar(A) + bar(BC)` using NAND gates is given below. 
|
|
| 6890. |
Do electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Yes, As Electromagnetic waves contain both electric and magnetic field, there is a non- zero energy DENSITY ASSOCIATED with it. E = `(hc)/(lambda)` Momentum p `= ("Total energy transferred to the surface ")/("Velocity of light in vacuum")` i.e.p `= (U)/(c )` = mc. U - total energy transfered to the surface . EM waves carries not only energy and momentum but also angular momentum. |
|
| 6891. |
Plane polarized light can be obtained by using |
|
Answer» A NICOLE prism |
|
| 6892. |
In the working of a transistor the emitter-base (EB) junction is forward biased while collector base (CB) junction is reverse biased. Why? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :In this ARRANGEMENT, the output resistance is larger than INPUT resistance. HENCE we get high output voltage | |
| 6893. |
Draw a plot showing the variation of potoelectric current with collector plate potential for two different frequencies, v_(1) gt v_(2), of incident radiation having the same intensity. In which case will the stopping potential be hgiher ? Justify your answer. |
Answer» SOLUTION :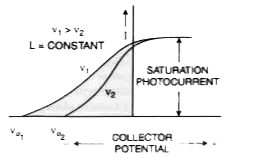 Stopping potential is more for the CORRESPONDING to FREQUENCY `v_(2)`. Stopping potential is directly proportional to the frequency of incident radiation. |
|
| 6894. |
The maximum intensity obtained due to the superposition of waves of 'n' coherent source having same intensity I_(0) is ...... |
|
Answer» NI `=I_(1)+I_(2)+2 sqrt(I_(1)I_(2)) "" [ :. cosphi=cos theta^(@)=1]` `=[ sqrt(I_(1))+sqrt(I_(2))]^(2)` `:.` Due to .n. waves of same intensity. `I_(max)=[ sqrt(I_(0))+sqrt(I_(0))+sqrt(I_(0)+....]^(2)` `I_(max)=[nsqrt(I_(0))]^(2)=n^(2)I_(0)` |
|
| 6895. |
यदि फलन fA से B में परिभाषित है तथा फलन g C से D में परिभाषित है तो fog परिभाषित होगा यदि- |
|
Answer» A=B |
|
| 6896. |
A prism of angle 80^@ has refractive index sqrt2. A light ray is incident at 45^@ on one face. The totaldeviation of the ray is |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 6897. |
Zener diodes are : |
|
Answer» SPECIALLY diped p-n JUNCTIONS |
|
| 6898. |
A chargo q is uniformly distributed on a ring-shaped conductor of radius a. Find the field potential in an arbitrary point on the conductor's axis a distance I away from the plane in which the conductor lies. Using the relation between the potential and the field intensity, find the field intensity at this point. |
|
Answer» Solution :To find the potential, DIVIDE the RING into small segments and add up the potentials of these segments. The field strength is `E=-(d varphi)/(dx)=-(Q)/(4pi epsi_(0))(d)/(dx) (x^(2)+a^(2))^(-1//2)` `=(1)/(2).(q)/(4pi epsi_(0))(z^(2)+a^(2))^(-1//2)*2x=(QZ)/(4pi epsi_(0) sqrt((x^(2)+a^(2))^(3)))` |
|
| 6899. |
In a transistor, the emitter circuit resistance is 100 kOmegaand the collector resistance is 100 Omega . The power gain, if the emitter and collector currents are assumed to be equal, will be |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :if ` I_C ~~ I_E impliesbeta ~~1` ` thereforeA_p =beta^2((R_L)/( R_i)) ~~ ((R_L)/(R_i)) = (100 XX 10^3 )/( 100 )= 1000` |
|
| 6900. |
Energy density of electric field E is |
|
Answer» `1//2epsi_(0)E^(2)` |
|