Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 38352. |
There are different types of radioactive series that radioactivie decay follows. In the given table, Column I shows the end or stable nuclei which any one of theradioactive series produces, Column II shows the mass number ofdifferent tpes of ratioactive series and Column III shows different values of n different radioactive sereis. Determine the characteristics of neptunium. |
|
Answer» (I)(iii)(K) |
|
| 38353. |
Suppose, we think of fission of a ""(26)^(56)Fe nucleus into two equal fragments, ""_(13)^(28)Al . Is the fission energetically possible? Argue by working out Q of the process. Given m (""_(26)^(56)Fe ) = 55.93494 u and m (""_(13)^(28)Al ) = 27.98191 u. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`Q = m(""_(26)^(56) Fe) - 2m (""_(13)^(28)AL) = 26.90 MEV`, not possible. | |
| 38354. |
There are different types of radioactive series that radioactivie decay follows. In the given table, Column I shows the end or stable nuclei which any one of theradioactive series produces, Column II shows the mass number ofdifferent tpes of ratioactive series and Column III shows different values of n different radioactive sereis. Determine the characteristics of thorium. |
|
Answer» (III)(ii)(L) |
|
| 38355. |
Eight chraged water drops, each with a radius of 1 mm and a charge of 10^(10)C, coalesce to from a single drop. The potential of the big is |
|
Answer» ` Q =8q = 8 xx 10xx 10 ^(-10 ) C ` ` V = (1)/( 4pi EPSI _0) (Q)/(R ) ` `= (9 xx 10 ^(9)xx 8xx 10 ^(-9))/(2 xx 10 ^(-3) ) = 36000 `Volt |
|
| 38356. |
What we define the product of refractive index and distance travelled by light in a medium ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :OPTICAL PATH | |
| 38357. |
Two identical blocks of ice move in opposite directions with equal speed and collide with each other. What will be minimum speed required to make both the blocks melt completely, if the initial temperatures of the blocks were -8^@ C each? Specific heat of ice is 2100 J kg^(-1) K and latent heat of fusion of ice is 3.36 xx 10^5 J kg^(-1) |
|
Answer» `840 ms^(-1)`  whenthe identicalblockcollidewith eachotherthenthhelossin kineticenergywill beequalto thethermalenergygainedby them. ` therefore ` Lossin K.E =`1/2 muv^2 rel` `=1/2 [(m_1 m_2 )/( (m_1+m_2))] (v_1-v_2) ^2= 1/2 [(m XX m )/((m + m))] [u-(-u ) ]^2` ` (:.m_1= m_2 = m, v_1=u andv_2=- u)` `=1/2[(m^2 )/( 2m ) ](2u)^2=1/2 xx (m/2)xx 4 u^2 = mu^2` Lossin K.E `=(msDeltaTheta+ m L ) xx 2 ` `impliesmu ^2=- 2m ( sDelta+ m L) xx 2` `implies m u^2= 2m (sDelta theta+L) implies U^2= 2 ( s Deltatheta+L )` `impliesu= sqrt(2 (s Delta+L))` ` impliesu=sqrt(2 [(2100 xx 8) + 3.36 xx 10^5 ])impliesu= 840 m//s` |
|
| 38358. |
When the energy of the incident radiation is increased by 20%, the kinetic energy of photo electrons emitted from a matel surface increases from 0.5 e V to 0.8 eV. |
|
Answer» 0.65 E V |
|
| 38359. |
One bar magnet is suspended so as to rotate freely in horizontal magnetic field. Then ..... |
|
Answer» It would become steady along east-west direction. `tau= m(B_h) sin0^(@) = 0` Thus, bar magnet attains stable equilibrium when its axis is along north-south direction, with `overset(to)(m)` pointing towards north. |
|
| 38360. |
Find the equivalent capacitance between P and Q for the configuration shown below in the figure (a). |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The capacitors 1 `mu` F and `3muF` are connected in parallel and `6muF` and `2MUF` are ALSO separately connected in parallel . So these parallel COMBINATIONS reduced to equivalent single capacitances in their respective positions as shown in the figure (b) . `C_(eq)=1muF+3muF=4muF` `Ceq=6muF+2muF=8muF` From the figure (b) we infer that the tow `4muF` capacitors are connected in series and the TWO `8muF` capatiors are connected in series . By using formula for the series we can reduce to their equivalent capacitances as shown in figure (c) . `(1)/(C)=(1)/(4)+(1)/(4)=(1)/(2) implies C_(eq) =2muF "and " (1)/(C_(eq))=(1)/(8)+(1)/(8)=(1)/(4)implies C_(eq)=4muF` From the figure (c) we infer that `2muF` and `4muF` are connected in parallel . So the equivalent capacitance is given in the figure (d) . `(C_(eq)=2muF+4muF=6muF` Thus the combination of capacitances in figure (a) can be replaced by a single capacitance `6muF.` |
|
| 38361. |
Magnifying power of a simple microscope is (when final image is formed at D = 25 cm from eye) |
|
Answer» `(D)/(F)` |
|
| 38362. |
A galvanometer of resistance 20 Omega is shunted by a 2 Omega resistor. What part of the main current flows through the galvanometer ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`i_g/i = (S)/(G +S)`. Given `G = 20 Omega , S = 2 Omega` `therefore i_g/i = 2/22 = 1/11 , 1/11` th PART of CURRENT passes through galvanometer. |
|
| 38363. |
Two charges, Q each, are at a distance d apart. They are released. What is the velocity of each charged body of mass m when the distance between them is 2d. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38364. |
Two concentric circular coils A and B have radii 25cmand 15 cm and carry currents 10A and 15A respectively. A has 24 turns and B has 18 turns. The direction of currents are in opposite order. The magnetic induction at the common centre of the coils is |
|
Answer» `120mu_(0)T` |
|
| 38365. |
(a) State Ampère's circuital law expressing it in the integral form. (b) Two long coaxial insulated solenoids S_(1) " and " S_(2) of equal lengths are wound one over the other as shown in the figure. A steady current 'I'flows through the inner solenoid S_(1) , to the other end B which is connected to the outer solenoid S_(2) , through which the same current 'I'flows in the opposite direction so as to come out at end A. If n_(1)" , and " n_(2)are the number of turns per unit length, find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at a point (i) inside on the axis and (ii) outside the combined system. |
|
Answer» Solution :(b) (i) The magnetic FIELD DUE to solenoid `S_(1)` , is inupward direction and due to solenoid `S_(2)` , the magnetic field is in downward direction. `n_(1) =` NUMBER of turns in solenoid `S_(1)` `n_(2)` = number of turns in solenoid `S_(2)` `B_(1) = mu_(0) n_(1) I` `B_(2) = mu_(0)n_(2)I` Net magnetic field `B = B_(1)- B_(2)` ` = mu_(0) n_(1) I - mu_(0) n_(2)I` ` = mu_(0)I (n_(1) - n_(2))` in upward direction (ii) Magnetic field will be ZERO outside the system |
|
| 38366. |
Consider the two following statements A and B and identify the correct choice given in the answers. A) In photo voltaic cells photo electric current produced is not proportional to the intensity of incident light. B) In gas filled photoemissive cells, the velocity of photo electrons depends on the wave length of the incident radiation |
|
Answer» Both A & B are TRUE |
|
| 38367. |
A particle is projected at an angle of 45° from the foot of a wall, just touches the top of the wall and falls on the ground on the opposite sides at a distance 4 m from it. The height of wall is : |
|
Answer» `2/3m` `ucostheta,t=2,OR2/(ucostheta)` and y=height of wall, then `y=usintheta,t+1/2g t^(2)` `usinthetaxx2/(ucostheta)+1/2gxx4/(u^(2)cos^(2)theta)` or `y=8/3`m |
|
| 38368. |
A 5 kg stationary bomb is exploded in three parts having mass 1: 1: 3 respectively. Parts having same mass move in perpendicular direction with velocity 39 m/s, then the velocity of bigger part will be: |
|
Answer» `13sqrt(2)` m/s Applying conservation law of momentum `|p^2|=sqrt(p_1^2+p_2^2)` `(3xxV)^2=(1xx39)^2+(1xx39)^2` `V^2=1/9xx(39)^2(1+1)=((39)^2)/(9)xx2` `V=1/3xx39sqrt2=13sqrt2 MS^(-1)` |
|
| 38369. |
In given graph if V_(02)gtV_(01) then……. |
|
Answer» `lambda_(1)=sqrt(lambda_(2))` From GRAPH `(V_(0))_(2)gt(V_(0))_(1)` `therefore ((h)/(e ))V_(2)-(phi_(0))/(e )gt((h)/(e ))V_(1)-(phi_(0))/(e )` `therefore V_(2)gtV_(1)[V_(0)=(hv)/(e )-(phi_(0))/(e )]` `therefore lambda_(2)lt lambda_(1) [because LAMBDA prop(1)/(V)]` `therefore lambda_(1)gtlambda_(2)` |
|
| 38370. |
Calculate the binding Energy of an alpha (alpha) particle in Mev from the following data. Mass of Hlium Nucleus = 4.00260u Mass of neutron= 1.008662u Mass of proton = 1.007825u |
|
Answer» Solution :Alpha particle: `""_(2)^(4)He` Z=2 and A=4 Mass DEFECT: `Delta m= [Zm_(P) + (A -Z)m_(N)]-M` `Delta m= 2 XX 1.007825 + 2 xx 1.008662- 4.00260` `Delta m= 2.01565 + 2.017324-4.00260` `Delta m= 0.030374u` Binding energy : `E_(b)= Delta m xx 931 MeV= 0.030374 xx 931` MeV `E_(b)= 28.2782` MeV |
|
| 38371. |
A system comprises an atom in .^(2)P_(3//2) state and a d ekectron. Find the possible spectral terms of that system. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The atom has `s_(1)=1//2, l_(1)=1,j=(3)/(2)` The electron has `S_(2)=(1)/(2), l_(2)=2` so the total angular momentum quantum number must be `j_(2)=(3)/(2)` or `(5)/(2)` ltbtgt In `L-S` compling we get `S=0,1.L=1,2,3` and the terms that can be FORMED are the same as written in the problem above. The possible values of angular momentum are consistant with the addition `j_(1)=(3)/(2) to j_(2)=(3)/(2)` or `(5)/(2)`. The latter gives us `J=0,1,2,3, 1,2,3,4` All these values are reached above. |
|
| 38372. |
Calculate the binding energy of an alpha-particle. Given that mass of proton = 1.0073 u, mass of neutron = 1.0087 u, and mass of alpha- particle = 4.0015 u. |
|
Answer» 26.4 Mev |
|
| 38373. |
In given circuit, ratio of charge on 2 muF capacitor to the charge of 3 mu F capacitor will be |
|
Answer» `2 : 3 ` |
|
| 38374. |
A pipe of length 1.5m closed at one end is filled with gas and resonates inits fundamental mode with a tuning fork . Another pipe of same dimension filled with air resonates in its fundamental mode with same tuning fork. If experiment is performed at 30^@ C (speed of sound in air is 360 m/sec) the velocity of sound at 0^@C in gas is |
|
Answer» 580 m/sec |
|
| 38375. |
4^(7/5)⋅4^(5/7) निम्नलिखित में किसके बराबर है? |
|
Answer» `(16)^(24/35)` |
|
| 38376. |
An electron accelerated through a potential difference 'V' passes through a uniform transverse magnetic field and experiences a force F. If the accelerating potential is increased to 2V, the electron in the same magnetic field will experience a force |
| Answer» ANSWER :C | |
| 38377. |
What will be ratio of speed in first two seconds to the speed in next 4s |
|
Answer» `sqrt2:1` |
|
| 38378. |
Frequency of photon having 100 eV energy is ……Hz [h=6.62xx10^(-34)Js,1eV=1.6xx10^(-19)Js] |
|
Answer» `2.417xx10^(-16)` `THEREFORE f=(E )/(h)=(100xx1.6xx10^(-19))/(6.62xx10^(-34))` `=24169xx10^(17)` `~~2.417xx10^(16)`Hz |
|
| 38379. |
For examples 15, find the potential energy of the block at0.05 m from the mean position Hint : P.E. = (1)/(2) kx^(2) |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :P.E. of the block `= (1)/(2) kx^(2)` `= (1)/(2) XX 100 xx 0.05 ^(2)` `= 0.125 J` |
|
| 38380. |
Three equal charges q_1 ,q_2 ,q_3are placed at the three corners ABC of a square ABCD. If the force between the charges at A and B (on q_1and q_2) is F_(12)and that between A and C is F_(13)then the ratio of magnitudes F_(12) and F_(13) is |
|
Answer» `1//2` |
|
| 38381. |
मोटरगाड़ी के चालक के सामने लगा रहता है |
|
Answer» समतल दर्पण |
|
| 38382. |
An emf of 25.0 mV is induced in a 500-turn coil when the current is changing is at the rate of 10.0A/s. What is the magnetic flux through each turn of the coil at an instant when the current is 4.0A? |
|
Answer» `20muT.m^2` |
|
| 38383. |
A circular coil of radius 5 cm and has 50 turns carries a current of 3 ampere. The magnetic dipole moment of the coil is |
|
Answer» 1.0 AMP - `m^(2)` |
|
| 38384. |
In textilemills , the atmosphereis renderedhumid to |
|
Answer» PREVENT the CLOTH from GETTING heated |
|
| 38385. |
The north and south poles of two identical magnets approach a coil, containing a condenser, with equal speeds from opposite sides. Then |
|
Answer» PLATE 1 will be negative and plate 2 POSITIVE |
|
| 38386. |
(a) Determine the 'effective focal length' of the combination of the two lenses in Exercise 9.10, if they are placed 8.0cm apart with their principal axes coincident. Does the answer depend on which side of the combination a beam of parallel light is incident? Is the notion of effective focal length of this system useful at all? (b) An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement (a) above. The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40 cm. Determine the magnification produced by the two-lens system, and the size of the image. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) (i) Let a PARALLEL beam be the incident from the left on the convex lens first `f_(1)=30cm and u_(1) =-oo`. , give `v_(1) = + 30cm`. This image BECOMES a virtual OBJECT for the second lens. `f_(2) = -20 cm, u_(2) = + (30 - 8) cm = + 22 cm` which gives, `v_(2) = - 220 cm`. The parallel incident beam appears to diverge from a point 216 cm from the centre of the two-lens system. (ii) Let the parallel beam be incident from the left on the concave lens first:`f_(1)=-20cm, u_(1)=-oo, " give "v_(1)=-20cm`. This image becomes a real object for the second lens: `f_(2)=+30cm, u_(2)=-(20+8)cm=-28cm`which gives, `v_(2) = - 420cm`. The parallel incident beam appears to diverge from a point 416 cm on the left of the centre of the two-lens system. Clearly, the answer depends on which side of the lens system the parallel beam is incident. Further we do not have a simple lens equation true for all U (and v) in terms of a definite constant of the system (the constant being determined by f1 and f2 , and the separation between the lenses). The notion of effective focal length, THEREFORE, does not seem to be meaningful for this system. (b) `u_(1) = - 40 cm, f_(1) = 30 cm," gives "v_(1) = 120 cm`. Magnitude of magnification due to the first (convex) lens is 3. ` u_(2) = + (120 – 8) cm = +112 cm" (object virtual), "f_(2) = -20 cm` which gives `v_(2)=-(112xx20)/(92)cm` Magnitude of magnification due to the second (concave) lens `= 20//92`. Net magnitude of magnification `= 0.652` Size of the image = 0.98 cm |
|
| 38387. |
The diagram shows a circuit having a coil of resistance R = 2.5 (Omega) and inductance L connected to a conducting rod PQ which can slide on perfectly conducting circular ring of radius 10 cm with its centre at 'P'. Assume that friction and gravity are absent and a constant uniform magnetic field of 5 T exist as shown in Fig. At t = 0, the circuit is switched on and simultaneously a time varying external torque is applied on the rod so that it rotates about P with a constant angular velocity 40 rad//s. Find magnitude of this torque (in milli Nm) when current reaches half of its maximum value. Neglect the self-inductance of the loop formed by the circuit. |
|
Answer» Maximum current : `i_(0) =(Bomegal^(2))/(2R)` TORQUE about the hinge P is `tau=int_()^(1) i(dx)Bxd implies tau = 1/2 iBl^(2)` put `i=i_(0)//2`, we GET , `tau = (B^(2)omegal^(4))/(8R)=5 MMM`. |
|
| 38388. |
Define the term 'threshold frequency' in photoelectric emission. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :It is least FREQUENCY of incident radiation for which photoelectric emission may take place from the surface of GIVEN photosensitive MATERIAL. | |
| 38389. |
When a train is approaching the observer, the frequency of the whistle is 100 cps while when it has passed the observer, it is 50 cps. Calculate the frequency when the observer' moves with the trail. |
|
Answer» Solution :ACCORDING to Doppler EFFECT in case of approachign of source, `f. = f V/(v -v_s) , i.e., 100 = (fv)/(v -v_s)` `i.e., v -v_s = (fv)/(100)`, while in case of recession of source. `f.= f v/(v +v_s) i.e., 50 = (fv)/(v +v_s) , v +v_s =(fv)/50` So adding the TOW eqns., `2V =(3fv)/100` `i.e.,f =200/3 = 66.67 Hz` |
|
| 38390. |
If light of intensity lo is incident at an angle 45^(@) with optical axis of polaroid, so intensity of emerging light is...... |
|
Answer» `I_(0)` `I=I_(0)cos^(2) theta` `=I_(0) cos^(2)45^(@)` `=I_(0)xx(1)/(2)=0.5I_(0)` |
|
| 38391. |
Two coplanar and concentric coils 1 and 2 have respectively the number of turns N_(1) and N_(2) and radii r_(1) and r_(2) (r_(2) gtgt r_(1)). Deduce the expression for mutual inductance of this system. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Let us have two concentric coils of no. of turns `N_(1)` and `N_(2)` and radii `r_(1)` and `r_(2) (r_(2) gtgt r_(1))`. Let a CURRENT `I_(2)` flows through the OUTER coil no 2. Then magnetic field at the COMMON centre of coils. `B=(mu_(0)N_(2)I_(2))/(2r_(2))` Since `r_(1)ltltr_(2)` field may be considered to be uniform across entire coil no 1. Hence, total magnetic flux linked with inner coil is : `phi_(1)=N_(1)BA_(1)=N_(1)B(pi_(1)^(2))=N_(1)xx(mu_(0)N_(2)I_(2))/(2r_(2))xxpir_(1)^(2)=(mu_(0)piN_(1)N_(2)r_(1)^(2)l_(2))/(2r_(2))` 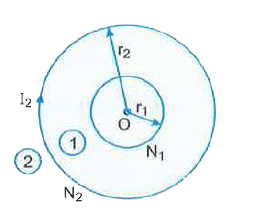 `therefore` Mutual inductance of the system M =`(phi)/(I_(2))=(mu_(0)piN_(1)N_(2)r_(1)^(2))/(2r_(2))` |
|
| 38392. |
The equation of state for 5 g , ofO_(2) at a pressure P and temperatureT , when occupying in avolume V, will be |
|
Answer» `PV = 5/32 RT` ACCORDINGTO an idealgas EQUATION. ` PV = nRTthereforePV = (5/32) RT` |
|
| 38393. |
Find the speed of a motor launch, if the water in the Pitot-Prandtl tube has risen to a height of 1.8 m. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 38394. |
A convex lens of focal length 40 cm is in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. The power of the combination is ________. |
|
Answer» Solution :HINT : Here `f_(1)=+40 CM = 0.4 m and f_(2)=-20cm =-0.2 m` `therefore""P_(1)=(1)/(f_(1))=+2.5 D and P_(2)=(1)/(f_(2))=-5.0D` `RARR""P=P_(1)+P_(2)=-2.5D` |
|
| 38395. |
The size of the bacteria can be magnified 60,0000 times using an electron microscope. The wave natureof electron is used in electron microscope. a. Name the type of waves used here c. Why is this wave character not observed in large bodies? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :a. de-Broglie waves c. `LAMBDA PROP (1)/(m)`. For LARGE bodies m is very large and HENCE `lambda` is very small. |
|
| 38396. |
In Young's experiment, the wavelength of monochromatic light is: |
|
Answer» `LAMBDA=(AD)/D` |
|
| 38397. |
In YDSEintensity at central maxima is I_0The ratio I/I_0, at path difference lamda/8 on the screen from central maxima , is closed to |
|
Answer» 0.74 |
|
| 38398. |
A magician during a show makes a glass lens with n=1.47 disappear in the trough of liquid. What is the refractive index of the liquid. |
|
Answer» Solution :The lens ofrefractive index same as of liquid will be INVISIBLE in that liquid As `n_1 = 1.47` , then refractive index of lens `n_2 = 1.47` From lens maker.sformula `1/f = ((n_1 - n_2)/(n_2))[1/R_1 - 1/R_2]` `1/f = ((n_2-n_2)/(n_2))[1/R_1 - 1/R_2]` `= (0) [ 1/R_1 - 1/R_2]` `thereforef = 1/0 = " infinity " (OO)` Hence, lens will behave as plane surface in liquid. `rArr` No, this liquid can.t be water because itsrefractive index is `(4)/(3)`, This liquid can be glycerine. |
|
| 38399. |
Consider a uniformly charged sheet ABCD, which is a part of an equilateral triangular sheet of a side a as shown in the figure. Choose the correct options regarding the electric field E at point O due to this sheet. |
|
Answer» Magnitude of `vecE`, increases with the increase in (Keeping CHARGE density same) `dE=(sigma)/(4piepsilon_(0)) (DX)/x` `E=(7sigma)/(44epsilon_(0) In sqrt(2)` 
|
|
| 38400. |
State main characteristics of an equipotential surface. |
|
Answer» Solution :The main characteristics of an EQUIPOTENTIAL surface are as given below : (i) An equipotential surface is a surface with a constant value of electric potential at all points. (ii) No work is REQUIRED to be done to move a charge on an equipotential surface. (iii) For any charge configuration, equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field at that point. (iv) No TWO equipotential surfaces can EVER intersect each other. (v) Relative CLOSENESS of equipotential surfaces having a given potential difference means a region of stronger electric field. |
|