Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 41001. |
Find out the opposite of 'construct'.... |
|
Answer» Convoy |
|
| 41002. |
A galvanmeter of resistance 100 ohm gives a full scale deflection with a current of 10 mA. The value of shunt to be used so that it can measure a currend upto 100 mA is : |
|
Answer» `10 OMEGA` |
|
| 41003. |
A non conducting ring of radius R has uniformly distributed positive chargeq. A small particle of mass m and charge -q is placed on the axis of the ring at point P and released If R gt gt x. The particle will undergo oscillations along the axis of symmerty with an angular frequency that is equal to |
|
Answer» `sqrt((qQ)/(4piepsilon_(0)MR^(3)))` |
|
| 41004. |
At a place horizontal component of earth's magnetic field is sqrt(3) times its vertical component. The magnetic dip angle at the place is ...... radian. |
|
Answer» `0` but `tan PHI = (B_v)/( B_h)` `therefore tanphi = (1)/(sqrt(3))` `therefore phi = tan^(-1) ((1)/(SQRT3)) ""therefore= (pi)/(6) "rad"` |
|
| 41005. |
Give the relation between electric field and electric potential . |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider a positive charge q kept FIXED at the origin. To move a unit positive charge by a SMALL distance dx in the electric FIELD E, the work done is GIVEN by dW = -E dx. The minus sign IMPLIES that work is done against the electric field. This work done is equal to electric potential difference. Therefore, dW=dV(or)dV=-Edx Hence E=`-(dV)/(dx)` The electric field is the negative gradient of the electric potential. |
|
| 41006. |
The reverse saturation of p-n junction |
|
Answer» depends on DOPING concentration |
|
| 41007. |
Limiting value of static frictional force on a block placed on the rough surface depends on |
|
Answer» Nature of surfaces in contact |
|
| 41008. |
(A) :Shortwave band are used for transmission of radiowaves to a large distance. (R) : Shortwaves are reflected from ionosphere. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the correct EXPLANATION of 'A'. |
|
| 41009. |
The manifestion of band structure in solids is due to ……. |
|
Answer» Heisenberg's UNCERTAINTY principle. |
|
| 41010. |
In a double-slit arrangement the slits are separated by a distance equal to 100 times the wavelength of the light passing through the slits. (a) What is the angular separation in radians between the central maximum and an adjacent maximum? (b) What is the distance between these maxima on a screen 90.0 cm from the slits? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) 0.010 RAD, (B) 9.0 MM | |
| 41011. |
Figure shows a pulley block system in which a block A is hanging one side of pulley and an other side a small bead B of mass m is welded on pe=ulley. The moment of intertia of pulley is I and the sytem is in equilibrium position when bead is at an angle alpha from the vertical. If the system is slightly disturbed from its equlibrium position, find the time period of its oscillations. |
|
Answer» Solution :In equilibrium the net torque on pulley must be ze4ro, thus we have `MgR = mgRsinalpha` or `M = msinalpha` [if mass of block A is assumed tc be M] Now if block is displace dow by DISTANCE A and released, it starts oscillating with amplitude A. Now consider Now if block at distance x below the equilibrium position when it is going down at speed V. Fifure shows the corresponding sitution at this instant and the total energy of oscillating SYSTEM can be written as `E_(T) = (1)/(2)Mv^(2) + (1)/(2)mv^(2) + 1/2l((v)/(R))^(2) - Mgx + mgR[cos alpha - cos(theta + alpha)]` _S01_026_S01.png) Differenting the abvoe equation w.r.t to time, we get, `(dE_(T))/(dt) = 1/2M(2v(dv)/(dt))+1/2m(2v(dv)/(dt))+1/2(1)/(R^(2))(2v(dv)/(dt)) - Mg"((dx)/(dt))+mgR[+sin(0+alpha)(d0)/(dt)]=0` `rArr Mva = mva + (1)/(R^(2))VA - Mgv + mgR sin(theta+alpha)((v)/(R)) =0 , ["as" (d theta)/(dt) = omega = (v)/(R)]` `rArr (M + m+(I)/(R^(2))) a - Mg - mg[cosalpha + sinalpha] = 0` [For small angle `theta , sintheta = theta, cos 1]` `rArr (M + m + 1/(R^(2))) a + mg cosalpha. x/R = 0 ["as" M = m sin alpha "and" theta = (x)/(R)] rArr a = -(mgcosalpha)/(R(M+m+(I)/(R^(2))))x` Comparing equation with BASIC differential equation of SHM, we get the angular frequency of SHM of system as `omega = sqrt((mgcosalpha)/(R(M+m+(I)/(R^(2)))))` |
|
| 41012. |
An arc of radius R and having a total charge Q has its charge uniformly distributed. The arc subtends an angle 2theta at the centre O of the corresponding circle. Find the electric field intensity at O. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41013. |
Which of the following statements concerning depletion region of an p-n junction diode are true A) The width of the depletion region is independent of densities of dopants B) The width of the depletion region is dependent on the density of dopants C) The electric field in the depletion region is provided by the electrons in conduction band and holes in valency fand D) The electric field in the depletion region is produced by the ionized dopent atoms |
|
Answer» A and B are TRUE |
|
| 41014. |
A stationary hydrogen atom emits photon corresponding to the first line of Lyman series. If Ris the Rydberg constant and M is the mass of the atom, then the velocityacquiredby the atom is |
|
Answer» `[SQRT((3E)/(2m)+C^2)]-c` |
|
| 41015. |
Assertion : An electric motor converts electical energy to mechanical energy. Reason : The working of the motor is based on mutualn induction. |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 41016. |
Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41017. |
The electricfield E due to a point charge at any point near it is defined as "" E= underset( q_0to 0) lim (F)/(q_0)Draw the electric field lines of a point chargeQ when (i)Q gt 0, and (ii)Q lt 0. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :In the definition of ELECTRIC field E we TAKE test CHARGE `q_0` as small as possible so that presence of test charge does not AFFECT the electric field at all. That.s why we consider ` undersetto (qto 0) lim ` Electric field lines of a point charge (i) ` Q gt 0, and (ii) Q lt 0 ` have been plotted in respectively. |
|
| 41019. |
An electric bulb and a capacitor are connected in series to a source of an alternating current. If the frequency of the current source is increased then the bulb gives more intense light. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41020. |
A steady current flows in a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross-section. Which of these quantities is constant along the conductor: current, current density, electric field, drift speed? |
|
Answer» Solution :Only current will remain constant (according to LAW of conservation of electric CHARGE). Here, current density, electric FIELD and drift SPEED will not remain constant as they depend on area of cross-section. |
|
| 41021. |
Satement -1: A beam of electron passes undeflected through region oversetrarr(E)& oversetrarr(B) In the region oversetrarr(E)& oversetrarr(B) are present and perpendicular to each other and the particle is moving perpendicular to both of them . Statement-2: In the region vecE & vecB, both are present and perpendicular to each other and the particle is moving perpendicular to both of them. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41022. |
What is the area of plates of 2F parallel capacitor, given that the separation between the plates is 0.5 cm? [You will realise from your answer why ordinary capacitors are in the range of muF or less. However, electrolytic capacitors do have a much larger capacitance (0.1F) because of very minute separation between the conductors. |
|
Answer» Solution :`A=?, C=2F, d=0.5 XX 10^(-2)m` `2=(8.85 xx A xx 10^(-12))/(0.5 xx 10^(-2))` `A=(2 xx 10^(10))/(17.7) =1.13 xx 10^(9) m^(2)=1.13 xx 10^(3) xx (10^(3))^(2) m^(2)=1130(km)^(2)` |
|
| 41023. |
Mention characteristics of electric field |
|
Answer» Solution :Characteristics of electric field is as following : (i) The charge Q, which is producing the electric field is called a source charge and the charge q, which tests the effect of a source charge is called a test charge. However, if a charge q is brought at any point around Q, Q itself is bound to experience an electrical force DUE to q and will tend to move. A way out of this difficulty is to make q negligibly small. The force `vecF` is then negligibly small but the ratio `F/q` is finite and defines the electric field: `vecE = "lim"_(q=0) vecF/q` (ii) Note that the electric field `vecE`due to Q though defined operationally in terms of some test charge q is independent of q. This is because `vecF` is proportional to q, so the ratio `F//q` does not depend on q. The field EXISTS at every point in three-dimensional space. (iii) For a positive charge, the electric field will be directed radially outwards from the charge as shown in figure (a). 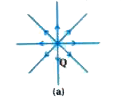 For a negative charge, electric field vector at each point, points radially inwards as shown in figure (b).  (IV) Since the magnitude of the force `vecF`on charge q due to charge Q depends only on the distance r of the charge q from charge Qthe magnitude of the electric field `vecE`will ALSO depend only on the distance r. `therefore E prop 1/r^(2)` Electric field produced by point charge has spherical acceptance. (v) The direction of electric force on unit charge at any point is considered as the direction of electric field. (vi) Faraday gave the first idea about electric field. |
|
| 41024. |
The value of current i_1 in the given circuit is |
|
Answer» `(i)/(5)` |
|
| 41025. |
The equation of a transverse wave travelling along a spring is y = 4.0 sin pi(2.0t -0.010x) , where y and x are in cm and t in second |
|
Answer» Amplitude , a=4 cm, wavelength `lambda = 200 cm` and frequency of the wire `v= 1s^(-1)` `y=a SIN[(2pi)/lambda(vt -x) + phi_(0)]`.......(i) where `phi_(0)` is the initial phase. Here, the given equation is, `y = 4.0 sin[(2pi)/200 (200t -x)]`............(ii) COMPARING equations (i) and (ii), we get Amplitude, a=4 cm Wavelength, `lambda = 200 cm//s` Wave velocity, `u =v/lambda = 200/200 = 1s^(-1)` Initial phase of the origin, i.e. at t=0 and x=0 `phi_(0)=0` Phase difference between a time interval `Deltat` is given by `Deltaphi = 2piv Deltat = 2pi xx 1 xx 0.5 = pi = 180^(@)` |
|
| 41026. |
In Young's double slit experiment S_(1) and S_(2) are two slits. Films of thickness t_(1) and t_(2) and refractive indices mu_(1) and mu_(2) are placed in front of S_(1) and S_(2) respectively. If mu_(1)t_(1) = mu_(2)t_(2), then the central maximum will : |
|
Answer» Not shift |
|
| 41027. |
Who is the story about? |
|
Answer» BURT Dubin |
|
| 41028. |
(a) Derie an expression for the force between two long parallel current carryng condcutors. (b) Use this expression to define SI unit of current. (c ) A long straight wire AB carries a current I. A proton P travels with a speed v, parallel to the wire, at a distance d from it in a direction oppositeto the current as shown in the fig. What is the force experienced by the proton and what is its direction? |
|
Answer» Solution :(c) The magnetic field produced due to long, straight current carrying wire AB at the position of proton is `B = (mu_0 I)/(2 pi d)` and it is directed perpendicular to the plane of paper pointing inward. The proton q = +E moving with a velocity v in a direction opposite to the current experience a force `F = qvB = EV CDOT (mu_0 I)/(2 pi d) = (mu_0 evI)/(2 pi d)` In accordance with Fleming.s left hand rule the force is repulsive in nature as shown in fig. Thus, the force is perpendicular to direciton of motion of proton directed AWAY from the current carrying conductor. 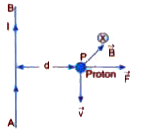
|
|
| 41029. |
In a CE transistor amplifier, the audio signal voltage across the collector resistance of 2kOmega is 2V. If the base resistance is 1kOmega and the current amplification of the transistor is 100, the input signal voltage is: |
|
Answer» 1 mV |
|
| 41030. |
Dalton's law is formulated as follows: the total pressure of a mixture of ideal gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of these gases. The partial pressure is the pressure of a given gas as if it alone occupied. |
|
Answer» Solution :In thermodynamical EQUILIBRIUM the temperature of all the components of a MIXTURE of gases is the same. The pressure of the individual component is `p_1 = n_1 kT = N_t kT//V, p_2 = n_2 kY = N_2kT//V`, ETC. The sum of partial PRESSURES is `p_1 + p_2 + p+= (N_1 + N_2 + N_3 + …) (kT)/V` Since the total number of molecules N is the sum of THO numbers of molecules of all the components making up the mixture, `N = N_1 + N_2 + N_3 + ….` the sum of the partial pressures is equal to the pressure of the gas. : `p_1 + p_2 + p_3 +. = NkT//V = p`. |
|
| 41031. |
A transmitting antenna at the top of a tower has a height 32 m and the height of the receiving antenna is 50 m . What is the maximum distance between them for satisfactory communication in LOS mode ? Given radius of earth 6.4 xx 10^(6) m . |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`d_(m)= sqrt(2 XX 64 xx 10^(5) xx 32)+ sqrt(2 xx 64 xx 10^(5)xx 50m)` `= 64xx 10^(2) xx sqrt(10) +8 xx 10^(3) xx sqrt(10)m = 144 xx 10^(2) xx sqrt(10)m= 45.5 km` |
|
| 41032. |
Let rho(r)=(Qr)/(piR^(4)) be the charge density distribution for a soild sphere of radius R and total charge Q. For a point P inside the sphere at a distance r_(1) from the centre of the sphere, the magnitude of electric field is |
|
Answer» `Q/(4piepsilon_(0)r_(1)^(2))` According to Gauss's theorem `ointvecE.d vecs=(q _("inside"))/(epsi_(0))` `ointE ds cos 0^(@)=(1)/(epsi_(0))ointrho(r)dV` `E(4pir_(1))^(2)=(Q)/(epsi_(0)piR^(4))underset(0)overset(r_(1))intr(4pir^(2))DR` `=(4Q)/(epsi_(0)R^(4))((r_(1)^(4))/(4))=(Q)/(epsi_(0))((r_(1))/(R))^(4)` `therefore E=(Q)/(4piepsi_(0))(r_(1)^(2))/(R^(4))`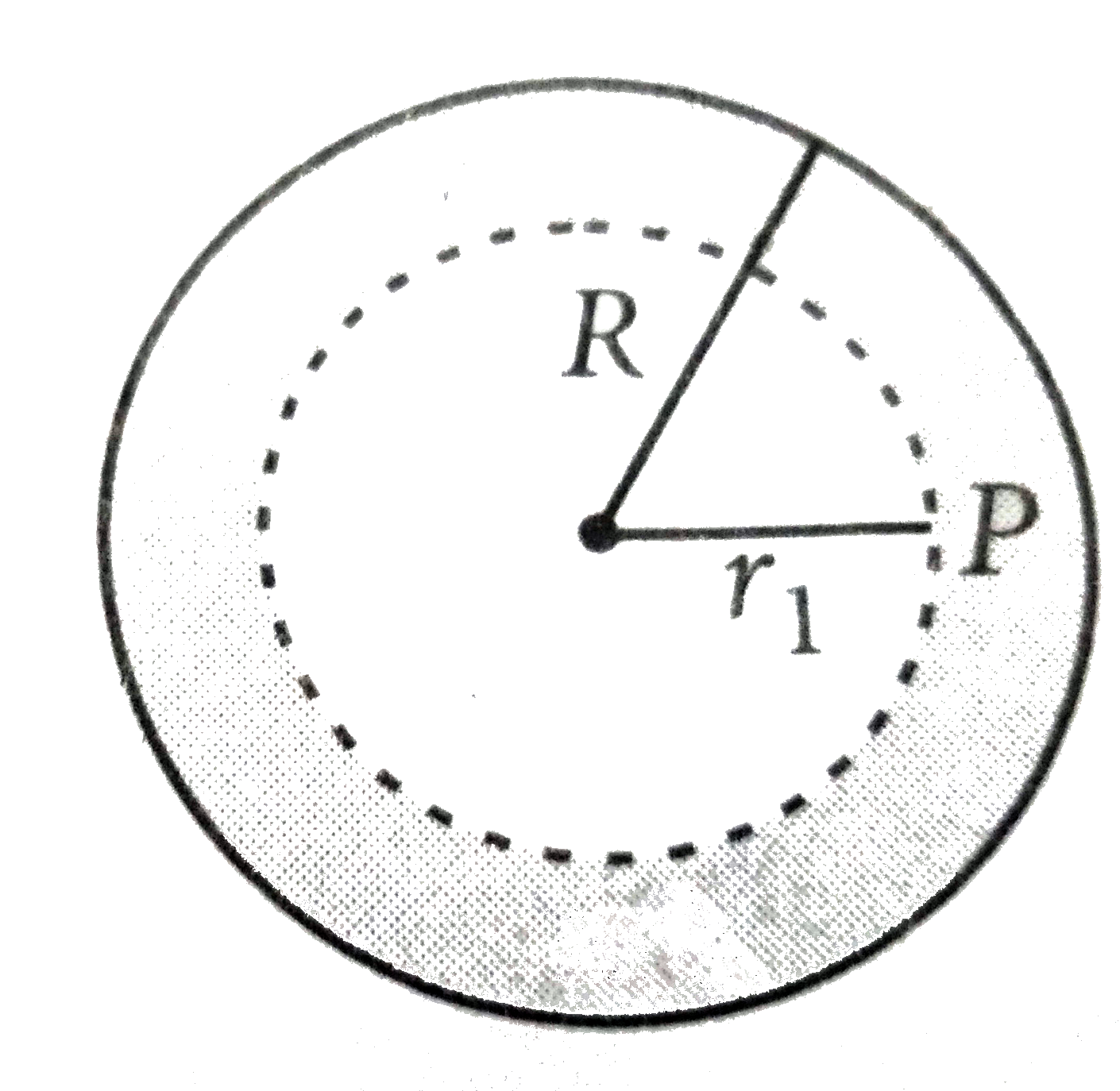 
|
|
| 41033. |
A playful astronaut raleases a bowling ball, of mass m= 7.20 kg, into circular orbit about Earth at an altitude h of 350 km. (a) What is the mechanical energy E of the ball in its orbit ? (b) What is the mechanical energy E_0 of the ball on the launchpad at the Kennedy Space Center (bofore launch) ? From there to the orbit, what is the change DeltaE in the ball's mechanical energy? |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) We can get E from the orbital energy, given by Eq. 13-42 `(E = -GMm//2r)`, if we first find the orbital radius r. (It is not simply the given altitude.) Calculations : The orbital radius must be `r = R + H= 6370 km + 350 km= 6.72 xx 10^6m`, in which R is the radius of Earth. Then,from Eq.13-42 with Earth MASS `M = 5.98 xx 10^24kg `, the mechanical energy is `E = -(GMm)/(2r)` `=-((6.67 xx 10^(-11) N.m^2 //Kg^2 )(5.98 xx 10^24kg)(7.20kg))/((2)(6.72 xx 10^6m))` `=-2.14 xx 10^8 J = -214 MJ`. (b) On the launchpad, the ball is not in orbit and thus Eq. 13-42 does not apply. INSTEAD, we must find `E_0 = K_0 + U_0`, where `K_0` is the ball.s kenetic energy and `U_0` is the gravitational potential energy of the ball-Earth system. Calculations :To find `U_0`, we use Eq. 13-23 to write `U_0 = -(GMm)/(R)` `=-((6.67 xx 10^(-11)N.m^2//kg^2)(5.98xx10^24 kg)(7.20kg))/(6.37 xx 10^6m)` `=-4.51 xx10^8 J = -451 MJ`. The kinetic energy `K_0` of the ball is due to the ball.s MOTION with Earth.s rotation. You can show that `K_0` is less than 1 MJ,which is negligible relative to `U_0`. Thus, the mechanical energy of the ball on the launchpad is `E_0 = K_0 + U_0~~ 0-451 MJ = -451 MJ`. The increase in hte mechanical energy of the ball from launchpad to orbit is `DELTAE = E-E_0 = (-214 MJ) -(-451 MJ)` `=237 MJ`. This is worth a few dollars at your utility company. Obviously the high cost of placing objects into orbit is not due to their required mechanical energy. |
|
| 41034. |
What is the change in radius of ring ? |
|
Answer» `(QQ)/(8pi^2epsilon_0RAY)` The AREA of cross section is A and so the longitudinal STRESS developed in the ring will be :`T/A =((qQ)/(8pi^2 epsilon_0R^2))/A=(qQ)/(8pi^2 epsilon_0 R^2 A)` Young.s modulus (Y)=`"Stress"/"Strain"=((qQ)/(8pi^2epsilon_0R^2A))/((DeltaR)/(R))=(qQ)/(8pi^2 epsilon_0 RADeltaR)` `rArr DeltaR=(qQ)/(8pi^2 epsilon_0 RAY)` |
|
| 41035. |
Two circular rings A and B each of radius 30 cm are placed coaxially with their axes horizontal in a uniform electric field E= 10^(5)NC^(-1) directed vertically up. Distance between the centres of these rings is h = 40 cm. Ring A has a positive charge q_(1) = 10mu C, while ring B has a negative charge of magnitude 20muC. A particle of mass m= 100 g and carrying a positive charge 104mu Cis released from rest at t=0 at the centre of the ring A. Find the velocity of the particle when it has moved through 40 cm? (g=10ms^(-2)) |
|
Answer» |
|
| 41036. |
A double slit experiment is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.33. Separation between the slits is 1.0 mm and the distance between slit and screen is 1.33 m. If slits are illumintated by a parallel beam of light whose wavelength is 6300 Å, then fringe width will be : |
|
Answer» `6.3 mm` `BETA = (lambda D)/(d)` In LIQUID, `beta = (lambda_(l)D)/(d) = (lambda_(air).D)/(mu_(l).d) = 0.63 mm` |
|
| 41037. |
If R is the radius of the earth and g the acceleration due to gravity on the earth's surface, the mean density of the earth is: |
|
Answer» `(4pi G)/(3gR)` `thereforerho=(3g)/(4pi RG)` So correct choice is (c ). |
|
| 41038. |
StateCoulomb's law . |
|
Answer» Solution :Statement : The electrostaticforce between two point charges is DIRECTLY proportional to the product of MAGNITUDE of charges and inversely proportional to the SQUARE of the distance between them . The direction of this forceis along the line joining the two charges. Explanation : Let `q_(1)andq_(2)` be the magnitudes of two charges separatedby a distance rLet F be the force between them . From COULOMB .s LAW, `Fprop(q_(1)q_(2))/(r^(2))rArrF=(1)/(4piepsilon_(0))(q_(1)q_(2))/(r^(2))` Where `epsilon_(0)` is the absolute permittivity of free space. |
|
| 41039. |
The system shown in the figure is initially in equilibrium. A is of mass 2 m and B,C D and E are of mass m Certain actions are performed on the system. Every action has been taken individually when the system is intact. Find the direction and magnitude of acceleration of the blocks after each action of the following actions has been taken {:((i)"Spting 1 is cut",(ii)"Spring 2 is cut"),((iii)"String between C and D is cut.",(iv)"String between B and C is cut."):} |
|
Answer» (ii) `a_(A)=0,a_(B)=g/3darr,a_(C)=g/3uarr,a_(D)=g/3uarr,a_(E=gdarr` (iii) `a_(A)=0,a_(B)=3gdarr,a_(C)=(3g)/(2)darra_(D)=2gdarr,a_(E)=0` (iv) `a_(A)=0,a_(B)=3gdarr,a_(C)=(3g)/(2)darr,a_(D)=(2g)/(2)darr,a_(E)=0` |
|
| 41040. |
Einstein got Nobel Prize in 1921 for his explanation of photoelectric effect. In order to start photoelectric emission, the mini mum energy acquired by free electron in the metal is called as………………….. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :WORK FUNCTION/ THRESHOLD ENERGY | |
| 41041. |
If foundamental frequency of closed pipe is 50 Hz, then frequency of second overtione is : |
|
Answer» Solution :Fundamental frequency `V_(1) = 50 ` Hz For closed organ , pipe, second overtone means FIFTH harmonic so its frequency is `V_(5)= 5 v_(1) = 5 xx 50 = 250 ` Hz correct choice is (b). |
|
| 41042. |
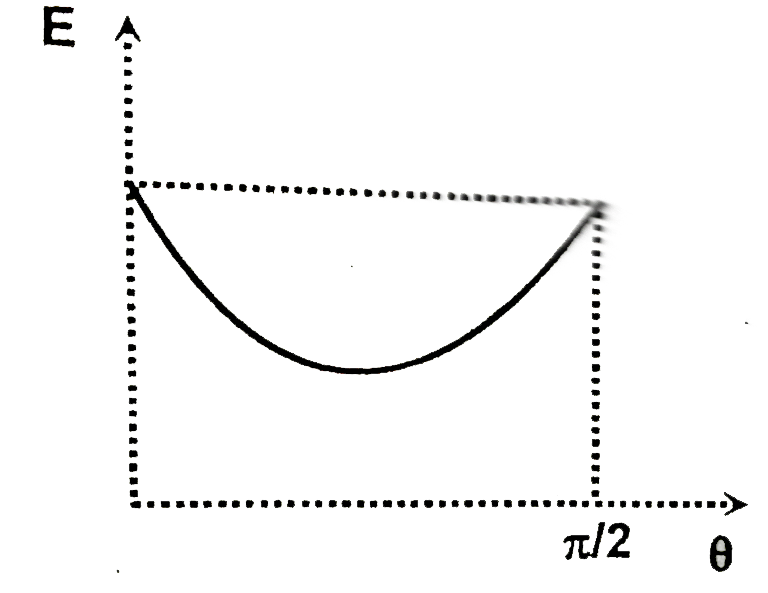
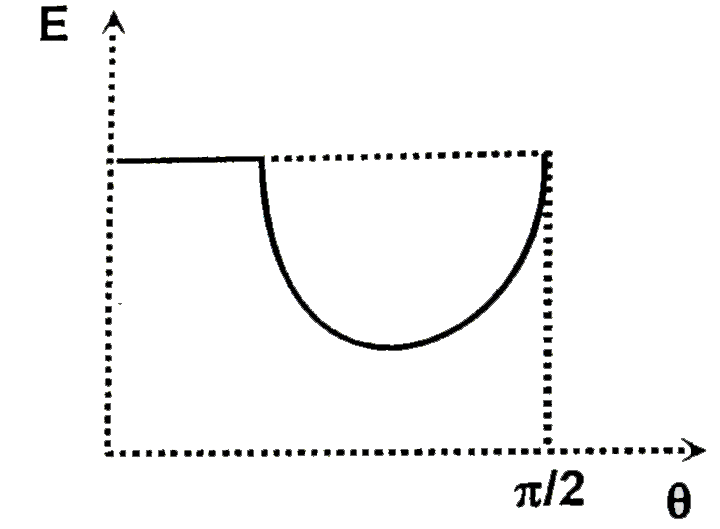
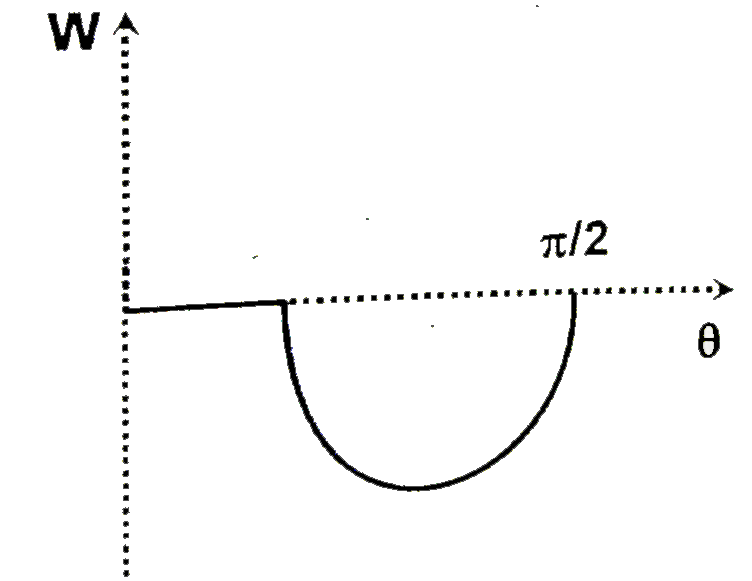
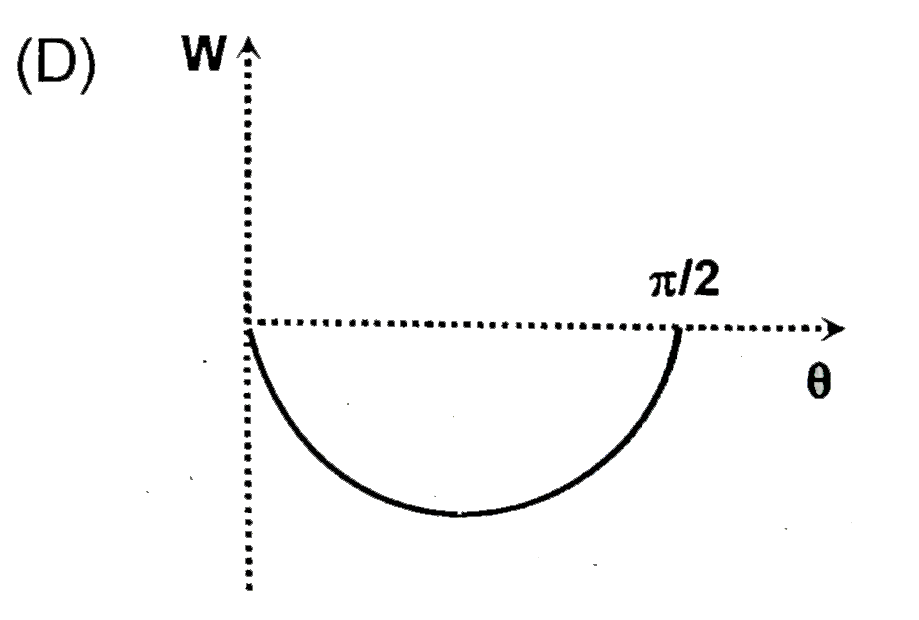
A solid spherical ball is released from rest on an incline of inclination angle theta (which can be varied ) but through a fixed vertical height h. The coefficient of static and kinetic friction are both equal to mu. If E represents the total kinetic energy of the ball at the bottom of the incline as a function of the angle of inclination theta. W represents the work done by friction for the whole time of motion as a function of the angle of inclination theta. Choose of correct graph (s) |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 41043. |
If 10^(9) electrons move out of a body to another body evergy second, how much time is required to get a total charge of 1 C on the other body? |
|
Answer» Solution :In one second `10^(9)` electrons move out of the body. The charge given out in one second is `1.6 xx 10^(-19) xx 10^(9)C = 1.6 xx 10^(-10)C`. The TIME required to accumulate a charge of 1C can then be ESTIMATED to be `t= 1C div (1.6 xx 10^(-10)C//s) = 6.25 xx 10^(9) s= 6.25 xx 10^(9) div (365 xx 24 xx 3600)` years = 198 years. One coulomb is a very large unit for many PRACTICAL purposes. |
|
| 41044. |
The frequency range of 3 MHz to 30 MHz is used for |
|
Answer» GROUND WAVE propagation |
|
| 41045. |
A body takes twice the time to slides down a rough inclined plane at 45° to an identical smooth inclined plane. What is the coefficient of friction of rough plane? |
|
Answer» 0.75 `a_(1)=gsin45^(@)=g/(sqrt2)` and `a_(2)=g(sin45^(@)-mu_(g)sin45^(@))` `=g/(sqrt2)(1-mu_(k))` where `mu_(k)` = COEFFICIENT of KINETIC FRICTION. Now as the square of the time of slide is inversely proportional to acceleration. Therefore, `(t_(2)^(2))/(t_(1)^(2))=(a_(1))/(a_(2))=1/(1-mu_(k))` Also, `t_(2)-2t_(1)` `therefore4=1/(1-mu_(k))rArrmu_(k).=0.75` |
|
| 41046. |
At a place of the Earth, horizontal component of magnetic field is equal to vertical component then dip angle (phi)= …........ . |
|
Answer» (A) `60^@` `THEREFORE tan phi = 1` `therefore phi= tan^(-1) (1)` `therefore = 45^@` |
|
| 41047. |
If x = a, y = b is the solution of the equations x + y = 5 and 2x - 3y = 4, then the values of a and b are - |
|
Answer» 6,-1 |
|
| 41048. |
Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer coil retraces backwards as shown in Fig. 9.33. A current in the coil produces a deflection of 3.5^(@) of the mirror. What is the displacement of the reflected spot of light on a screen placed 1.5 m away? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The reflected rays get deflected by TWICE the angle of ROTATION of the mirror. Therefore, `d//1.5 = TAN 7^(@)`. Hence `d = 18.4 cm.` | |
| 41049. |
Transconductance in CE amplifier circuit is defined as |
|
Answer» Ratio of CHANGE in COLLECTOR CURRENT to the change in emitter current |
|
| 41050. |
यदि X=sqrt5 -1 हो तो 1/x का मान होगा |
|
Answer» `sqrt5-1` |
|