Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 5401. |
What is the difference in the construction of an astronomical telescope and a compound microscope? The focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece of a compound microscope are 1.25cm and 5.0cm, respectively. Find the position of the object relative to the objective in order to obtain an angular magnification of 30 when the final image is formed at the near point. |
|
Answer» Solution :In an astronomical telescope we take a CONVEX lens of large focal LENGTH and large aperture as the objective lens and a convex lens of small focal length and SMALLER aperture as the eye PIECE. However, focal lengths as well as aperture of both objective and eye piece lenses is small in a compound microscope and focal length aperture of objective are even smaller than that of eyepiece. Since final image is formed at near point i.e., the least distance of distinct vision i.e., D = 25cm. In that case, angular magnification of eyepiece. `m_(e )=(1+(D)/(f_(e )))=1+(25)/(5)=6 "" [because f_(e )=+5cm]` As magnification of microscope m = 30 and `m=m_(0)xxm_(e )` `rArr m_(0)=(m)/(m_(e ))=(30)/(6)=5` `therefore m_(0)=(v_(0))/(u_(0))=5` `or v_(0)=5u_(0)` and as per sign convention`u_(0)` is -ve but `v_(0)` is +ve and `f_(0)=+1.25cm`. Hence, we have `(1)/(v_(0))-(1)/(u_(0))=(1)/(f_(0)) or (1)/(5u_(0)) -(1)/((-u_(0))) =(1)/(1.25) or (6)/(5u_(0))=(1)/(1.25)` `rArr u_(0)=1.5cm` |
|
| 5402. |
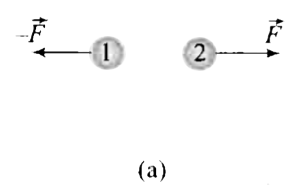
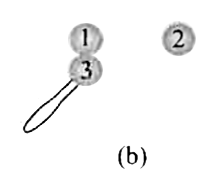
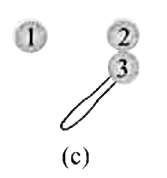
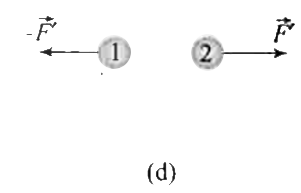
Indentical isolated conduction sphers 1 and 2 have equal charges and are separated by a distance that is large compared with their diameters (Fig.a). The electrostatic force acting on spkhere 2 due to sphere 1 is F. Suppose now that a third identical sphere 3, having an insulation handle and initially neutral, is touched first to sphere 1 (Fig. b), then to sphere 2 (Fig. c), and dinally removed (Fig. d). The electrostatic force that now acts on sphere 2 has magnitudeF'. What is the (F')/(F)? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 5403. |
A solenoid 1.0 m long and 4.0 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns/cm. A current of 5.0 A is flowing through it. Calculate the magnetic induction (a) inside and (b) at one end on the axis of solenoid. |
| Answer» Solution :`2 PI xx 10^(-3) T , pi xx 10^(-3) T` | |
| 5404. |
In a compound microscope, the nature of the intermediate image is ------------- |
| Answer» SOLUTION :REAL, INVERTED, MAGNIFIED | |
| 5405. |
When a light ray centers a refracing medium, it is found that the magnitude of the angle of refraction is equal to half the angle of reflection. If mu is the refractive index of the medium, then the angle of incidence is |
|
Answer» `2sin^(-1)((MU)/(2))` Angle of refraction = `(1)/(2)` (Angle of reflection) or `R.=(1)/(2)r` As `mu=(sini)/(sinr)` (where i is the angle of incidence) `mu=(sinr)/(sin((1)/(2)r))( :. "Angle of incidence", i= "Angle of refraction", r)` `mu=(sinr)/(sin((1)/(2)r))( :. "Angle of incidence", i= "Angle of refraction", r)` `cos^(-1)((mu)/(2))=(r)/(2)` or `r=2cos^(-1)((mu)/(2))` `:.i=r :.i=2cos^(-1)((mu)/(2))` |
|
| 5406. |
In Young.s double slit interferenceexperiment the wavelength of light used is 6000 A^(0). Ifthe path difference between waves reaching a point P on the screen is 1.5 microns, then at that point P |
|
Answer» SECOND BRIGHT BAND occurs |
|
| 5407. |
Four persons A, B, C and D initially at the corners of a square of side of length d. If every person starts moving with same speed v such that each one faces the other always, the person will meet after time |
|
Answer» `d/V` |
|
| 5408. |
A man who takes away another man's freedom is........ |
|
Answer» White |
|
| 5409. |
(a) An iron ring of relative permeability mu_(r)has windings of insulated copper wire of n turns per metre. When the current in the windings is I, find the expression for the magnetic field in the ring. (b) The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0.9853. Identify the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field. |
|
Answer» Solution :From Ampere.s circuital ,we have ` oint oversetto B d oversetto I =MU _ 0 mu , I_("enclosed")` For the field inside the ring , we can write `oint oversetto B d oversetto I =oint Bdl =B = 2pi r` ( r= radius of the ring )USING equation (i) ` therefore B = 2pi , = mu _0 mu_r .(2pin)l` ` therefore B= mu _ 0 mu_tnl ` [Award those `((1)/(2) + ( 1) /(2)) `makeeven file the RESULT is written without giving the derivation] 
|
|
| 5410. |
Which of the following does not support the wave nature of the light ? |
|
Answer» Interference |
|
| 5411. |
What is the difference between the structures of the light helium isotope nucleus and of the superheavy hydrogen (tritium) nucleus? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 5412. |
Assertion if wavelength is of the order of distance between the slits, then figure size is large. Reason Fringe width is given by beta=lambdaD//d |
|
Answer» |
|
| 5413. |
In the figure shown S_(1)O-S_(2)O=S_(3)O-S_(2)O=(lambda)/(4), Intensity at O due to any one of the slits is I_(0). What is the intensity due to all the three coherent sources S_(1), S_(2) and S_(3) ? |
|
Answer» `3I_(0)` |
|
| 5414. |
5 gm of water at 30^@ C is mixed with 5 gm of ice at -20^@C. What is the final temperature of the mixture? [Given that specific heat of ice is 0.5 cal/gm .^@C and latent heat of ice is 80 cal/gm] |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 5416. |
In a series LCR circuit, different physical quantities vary with frequency omega. Which of the following curves represent correct frequency variation of the corresponding quantity? |
|
Answer» Curve I for `R` (A) is true Current becomes maximum at RESONANCE (B) cannot be true `X_(L)=L=2pifL` (C) is true `Y=1/C=1/(2pifC)` (D) can not be true |
|
| 5417. |
An eye-piece is constructed by using two thin lenses of focal lengths 0.03 m and 0.04m respectively and are spaced so as to reduce spherical aberration to minimum. Find (a) separation between lenses required, (b) equivalent focal length and (c) magnifying power when the vision is distinct. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 5418. |
The bond angle between C-O and O-H bonds in alcohols is close to |
|
Answer» `109^@` 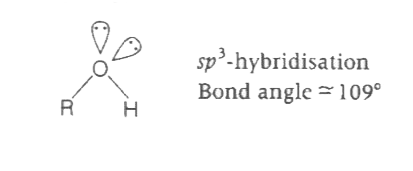
|
|
| 5419. |
What is the phase different between (i) the voltage across L and C in a LCR circuit connected to an a.c source (ii) applied a.c voltage and current in LCR circuit at resonance. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :i. `180^(@)(or)PI" radian "` ii. ZERO. |
|
| 5420. |
A magnetic field directed into the page changes with time according to the expression B = (0.03t^2+1.4)T , where t is in seconds. The field has a circular cross-section of radius R = 2.5cm. What is the magnitude and direction of electric field at P, when t=3.0s 1 and r = 0.02 m. |
|
Answer» Solution :`E =oint E.dl = (+dphi)/(dt)` `E(2pir) = A . (dB)/(dt) = PI r^2 xx (d)/(dt)(0.03 t^2 + 1.4)` ` E = (pi r^2)/(2pi r) xx (0.06t) = r/2 (0.06t)` `|E| = (0.02)/(2) xx 0.06 xx 3 = 18 xx 10^(-4) N//C` |
|
| 5421. |
In L-C-R circuit, the energy dissipated in ……. |
|
Answer» L only |
|
| 5422. |
A thin nonconducting ring of radius r has a linear charge density q=q_0costheta, where q_0 is a constant andtheta is the angle at the centre from the diameter of maximum charge density in the anticlockwise direction. Find the electric field at the centre of the ring. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 5423. |
A shell fired a cannon with speed v m/s at angle thetawith horizontal explodes into three pieces of equal masses at the highest point of trajectory. One piece falls down vertically while the other retraces its path. What is speed of the third piece? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :If .m. is mass of shell, at highest point, initial momentum =`m(vcostheta)`, along HORIZONTAL given, momentum of one fragment `=m/3 (-v cos theta)` momentum of SECOND along horizontal = 0 If `V_(1)` is speed of third fragment, from momentum CONSERVATION `=-m/3 v cos theta + m/3 v_(1) + 0 =m(v cos theta), v_(1) =4V cos theta` |
|
| 5424. |
All of the following statement are correct except |
|
Answer» The magnification produced by a convex mirror is always less than one |
|
| 5425. |
What Newton's corpuscular theory suggested ? |
| Answer» Solution :Light CONSISTS of TINY PARTICLES CALLED corpuscles which are sort out by LUMINOUS object | |
| 5426. |
Pure inductances of 3.0 H are connected as shown in figure. The equivalent inductance of the circuit is |
|
Answer» Solution :The three IDENTICAL inductances are in parallel. `THEREFORE L_(P)=(L)/(3)=(3)/(3)=1 H` |
|
| 5427. |
Figure shows a potentiometer circuit for comparison of two resistances. The balance point with a standard resistor R= 10.0 Omegais found to be 72.6 cm, while that with the unknown resistance X is 68.5 cm. Determine the value of X. What might you do if you failed to find a balance point with the given cell of emf epsi ? (Take internal resistance r=1Omega) |
| Answer» Solution :X=6.0`Omega`. If there is no balance POINT, it means potential drop across R or X is greater than the potential drop across the potentiometer WIRE AB. The obvious thing to do is to reduce CURRENT in the outside CIRCUIT and hence potential drops across R and X) suitably by putting a series resistor. | |
| 5428. |
Lens maker's formula is a formula corelating the power P (or focal length f) of a lens to radii of curvature of the two surfaces of the lens and the refractive index of lens material with respect to its surroundings. The formula is expressed as : P=(1)/(f)=(n-1)((1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2))) where n = refractive index of the material of lens with respect to its surroundings (ordinarily air) and R_(1) and R_(2) are the radii of curvature of two surfaces of the lens. The relation is true under all conditions but while applying it we should put values of P, f, R_(1) and R_(2) with their proper signs as per sign convention being followed by us. Let us have a bi- convex lens and let radii of curvature of both its curved surfaces is same i.e., |R_(1)|=|R_(2)|=R" (say)" How is your answer modified if the given biconvex lens is divided into two parts along a section XX' along its principal axis ? |
| Answer» Solution :If LENS is cut along the section XX., each PART is a complex biconvex lens and its power REMAINS as P. | |
| 5429. |
Calculate the amount of charge flowing in 2 minutes in a wire of resistance 10Omega when a potential difference of 20V is applied between its ends: |
|
Answer» 120C |
|
| 5430. |
Lens maker's formula is a formula corelating the power P (or focal length f) of a lens to radii of curvature of the two surfaces of the lens and the refractive index of lens material with respect to its surroundings. The formula is expressed as : P=(1)/(f)=(n-1)((1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2))) where n = refractive index of the material of lens with respect to its surroundings (ordinarily air) and R_(1) and R_(2) are the radii of curvature of two surfaces of the lens. The relation is true under all conditions but while applying it we should put values of P, f, R_(1) and R_(2) with their proper signs as per sign convention being followed by us. Let us have a bi- convex lens and let radii of curvature of both its curved surfaces is same i.e., |R_(1)|=|R_(2)|=R" (say)" If twoplanoconvex lenses fromed as a result of (a) are joined together as shown in Fig. (b), what is the net power of the combination ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :When two parts cut along section YY.. are joined TOGETHER as shown in FIG. (b), the net power `=P+P.=2P.=(2(n-1))/(R )=P="Power of original biconvex LENS"` |
|
| 5431. |
In the circuit shown in fig. R is a pure resistor, L is an inductor of ngligibe resistance (as compared to R), S is a 100 V , 50 Hz ac source of negligible resistnce. With either kiy (K-1) alone or (K_2) alone closed, the current is (I_0). If the source os changed to 100 V, 100 Hz the current with (K_1) alone closed and with (K_2) alone closed will be, respectively. |
|
Answer» `I_(0), (I_(0))/(2)` |
|
| 5432. |
Lens maker's formula is a formula corelating the power P (or focal length f) of a lens to radii of curvature of the two surfaces of the lens and the refractive index of lens material with respect to its surroundings. The formula is expressed as : P=(1)/(f)=(n-1)((1)/(R_(1))-(1)/(R_(2))) where n = refractive index of the material of lens with respect to its surroundings (ordinarily air) and R_(1) and R_(2) are the radii of curvature of two surfaces of the lens. The relation is true under all conditions but while applying it we should put values of P, f, R_(1) and R_(2) with their proper signs as per sign convention being followed by us. Let us have a bi- convex lens and let radii of curvature of both its curved surfaces is same i.e., |R_(1)|=|R_(2)|=R" (say)" Let the given biconvex lens be divided in two equal parts, as shown in Fig. (a), along a section YY' which is perpendicular to the principal axis of lens. What is the power of each part? |
|
Answer» Solution :For given biconvex lens `|R_(1)|=|R_(2)|=R` and as per sign CONVENTION `R_(1)` is positive but `R_(2)` is positive but `R_(2)` is NEGATIVE, hence power P of biconvex lens is `P=(n-1)[(1)/((+R))-(1)/((-R))]=(2(n-1))/(R )` When the lens is divided in TWO parts along the SECTION YY., each part behaves as PLANOCONVEX lens for which `R_(1)=R` and `R_(2)=oo`, Hence, power of each part is `P.=(n-1)((1)/(R )-(1)/(oo))=((n-1))/(R )=(P)/(2)` So power of each part is half of that of given biconvex lens. |
|
| 5433. |
Explain effect of potential on photoelectric current in experiment of photoelectric effect. |
|
Answer» Solution :In experiment of photoelectric effect collector A is kept at positive potential. When magnitude of positive potential is increased,photoelectric currentalso increases. For particular VOLTAGE on plate A,all emitted electrons will reach to collector (A) and current will become MAXIMUM. Now if collector voltage on collector is increased.Photoelectric current will not increase value of this collector current is called saturation current. For value of given collector potential photoelectric current become constant is called saturation current. Now collector voltage is sequentiallydecreased and made negative. There will be repulsion between electron and negative voltage on collector (A). When collector voltag is made more negative ,REPULSIVE force will increase and more energetic electrons only will reach to collector.Value of collector current will sequentially decrease rapidly. value of negative voltage on collector for which photoelectric current become zero is CUT off voltage or stopping potential .It is denoted by `V_(0)`. Energy of all electron emitted from metal surface are not equal.Stopping potential gives idea of maximum kinetic energy of photoelectron. When photoelectric current become zero maximum kinetic energy of photoelectron `(K_(max))`will be equal to energy of electron at `V_(0)` voltage. For photoelectric current to become zero maximum kinetic energy of phto electron=energy of electron at `V_(0)` voltage `K_(max)=eV_(0)` In this experiment when frequency of incident radiation is kept constant and intensity of radiation is kept costant and intensity of radiation is charge for three different value `I_(1)ltI_(2)ltI_(3)`, graph of photoelectric current versus stopping potential is shown in figure.  Graph shows that with increase in intensity saturation current increases.Thus no. of photo electrons emitted per second increases with increase in intensity of incident radiation. From graph,it can be said that for given frequency,stopping potential do not DEPEND on intensity. Thus,maximum kinetic energy of photoelectron depends on frequency of energy of photoelectron depends on frequency of incident radiation but it do not depend on intensity of incident radiation. |
|
| 5434. |
Monochromatic light of wavelength 3000 Å is incident normally on a surface of area 4cm^(2)If the intensity of light is 150(m W)/(m^(2)), the number of photon being incident on this surface in one second is …… |
|
Answer» Solution :`LAMBDA=3000Å =3xx10^(-7)m` `A=4cm^(2)=4xx10^(-4)m^(2)` `I=150(mW)/(m^(2))=150xx10^(-3)(W)/(m^(2))` `h=6.62xx10^(-34) Js` `"intensity" I=(E )/(Axxt)=(P)/(A)` `therefore P=IA=150xx10^(-3)xx4xx10^(-4)` If number of photon colliding on the surface are n,its energy =power `P=(NHC)/(lambda)` `therefore n=(plambda)/((hc))=(6xx10^(-5)xx3xx10^(-7))/(6.62xx10^(-34)xx3xx10^(8))` `therefore n=9xx10^(13)s^(-1)` |
|
| 5435. |
In a hydrogen atom, whenever there is transition of electron between different energy levels, energy is emitted or absorbed, and hydrogen spectrum is obtained. In the given table, Column I shows the names of the different series of hydrogen atom spectrum, Column II shows the energy levels from where electron transition takes place and Column III shows the EM wave region where these different series exists. Which series has the following wavelength v=RZ^(2)((1)/(1^(2))-(1)/(n_(2)^(2))),n_(2)=2,3,4,5,....? |
|
Answer» `(I)(IV)(M)` |
|
| 5436. |
In a hydrogen atom, whenever there is transition of electron between different energy levels, energy is emitted or absorbed, and hydrogen spectrum is obtained. In the given table, Column I shows the names of the different series of hydrogen atom spectrum, Column II shows the energy levels from where electron transition takes place and Column III shows the EM wave region where these different series exists. Which series does the diagram depict? |
| Answer» Answer :A::B | |
| 5437. |
A parallel beam of electrons travelling in X-direction falls on a slit of width d (see figure). If after passing the slit, an electron acquires momentum p_y in the Y-direction, then for a majority of electrons passing through the slit (h is Planck's constant): |
|
Answer» `|p_y|d = h` From de-Broglie `lambda = h/(|p_y|)` From the concept of DIFFRACTION, 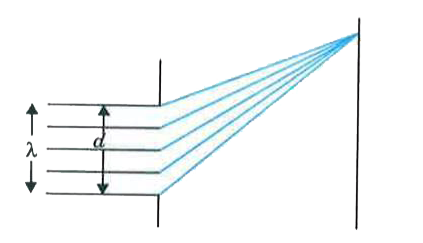 `Delta x = d sin theta` `lambda = d sin theta` `:. sin theta = lambda/d < 1` For diffraction , `lambda < d` `h/(|p_y|) < d` `:. |py| d > h` |
|
| 5438. |
Statement I :Electric current is distributed in differenent branches of a circuit in such a way , that the total heat evolved in the circuit is the lowest . Statement II : The transformation of electrical energy into heat energy in a circuit is less probable than its transformation into other forms of energy . |
|
Answer» STATEMENT I is true , Statement II is true , Statement II is a CORRECT explanation for Statement I |
|
| 5439. |
In a hydrogen atom, whenever there is transition of electron between different energy levels, energy is emitted or absorbed, and hydrogen spectrum is obtained. In the given table, Column I shows the names of the different series of hydrogen atom spectrum, Column II shows the energy levels from where electron transition takes place and Column III shows the EM wave region where these different series exists. Which series has the following wavelength v=RZ^(2)((1)/(4^(2))-(1)/(n_(2)^(2)))? |
|
Answer» `(II)(ii)(J)` |
|
| 5440. |
The decay constant , for a given radioactive sample, is 0.3465 "day"^(-1) .What percentage of this sample will get decayed in a period of 4 days ? |
|
Answer» `100%` `T_(1//2)=0.693/lambda=0.693/0.3465`=2 days `therefore n=1/T_(1//2)=4/2`=2 HENCE, sample LEFT decayed after a period of 4 days. `N/N_0=(1/2)^2 =(1/4)`=25% `therefore ` Sample decayed = 75% |
|
| 5441. |
A stone tied to the end of a string is whirled in a horizontal circle. The mass of the stone is 1.0 kg and the string is 0.50 m long. If the stone revolves at a constant speed for 10 times in 15.71 s, (a) what is the tension in the string ?(b) What would happen to the tension in the string if the mass was doubled and all the other quantities remained the same ?(c ) What would happen to the tension in the string if the period was doubled and all the other quantities remain the same ? |
|
Answer» Solution :The angular velocity, `omega = (2pi N)/(t)=(2pi xx 10)/(15.71)=(31.42xx2)/(15.71)=4.0 rad s^(-1)` (a)The tension on the string `= mr omega^(2)` `=1.0xx0.5xx(4.0)^(2)=8.0N`. (b)KEEPING r and `omega` constant if m was DOUBLED, the tension on the string would be doubled i.e., tension `= 16.0 N`, (c ) Keeping m and r constant if time period was doubled then the tension in the string is : `T=mr((2pi)/(2T))^(2)=(1)/(4)[mr((2pi)/(T))^(2)]=(8)/(4)=2N`. |
|
| 5442. |
A wire of mass 100 g is carrying a current of 2A towards increasing x in the form of y=x^2(-2mlexle+2m). This wire is plasced in a magnetic field B=-0.02hatk tesla. The ascceleration of the wire ("in"m/s^2) is |
|
Answer» `-1.6hatj`  MEGNETIC foerce on POQ=magnetic force on straight wire PQ having the CURRENT. Hence, `F=i(IxxB)i(PQxxB)` `=2[(4i)XX(-0.02hatk)]` `=(0.16hatj)` `:. A=F/m=((0.16hatj))/0.1=(1.6hatj)m/s^2` |
|
| 5443. |
In setallite launching, under what conditions is the path of the satellite (i) a parabola (ii) a hyperbola? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :The PATH of the SATELLITE is a parabola if its speed of projection `v=v_e` (escape speed). The path is a hyperbola if `vgtv_e`. | |
| 5444. |
Select incorrect order : |
|
Answer» `H_(2)OgtH_(2)SgtH_(2)SegtH_(2)Te` (Order of BOND angle ) `HFgtHIgtHBrgtHCl` |
|
| 5445. |
The anode voltage of a photo cell is kept fixed. The wavelength lamda of the light falling on the cathode is gradually changed. The plate current I of the photo cell varies as follows |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 5446. |
A: If objective and eye-piece of compoun microcscope are interchanged, then i becomes a telescope.R: Focal length of objective of telescope i small. |
|
Answer» Both ASSERTION and REASON are true and the reason is CORRECT explanation of the assertion. |
|
| 5447. |
Two capacitor of capacity 6 muF and 3muF are charged to 100 V and 50 V separately and connected as shown in figure. Now all the three switches S_1,S_2, and S_3 are closed. Let q_1, q_2, and q_3 be the magnitudes of charges flown from switches S_1, S_2, and S_3 after they are closed. Then |
|
Answer» `q_1 = q_3 and q_2=0`  Plates 2 and 3 are joined together and they are neither connected to any of the terminals of the battery nor to any other source of charge. So, they jointly form an isolated system. Before closing the switches, charge are SHOWN in Fig. After closing the switch let q charge goes from battery. Then charge on each will increase by q. Applying Kirchhoff's voltage LAW, we get `200-((600+q)/(6))-((150+q)/(3))=0` or `q=100muC` so charge on `6muF` capacitor will be `70muC` and `3muF` capacitor will be `250muC` from all the switches `100muC` of charge will flow. |
|
| 5448. |
Two capacitor of capacity 6 muF and 3muF are charged to 100 V and 50 V separately and connected as shown in figure. Now all the three switches S_1,S_2, and S_3 are closed. Charges on 6muF And 3muF capacitors in steady state will be |
|
Answer» `400muC,400muC`  Plates 2 and 3 are joined together and they are neither connected to any of the terminals of the BATTERY nor to any other source of charge. So, they jointly form an isolated system. Before closing the SWITCHES, charge are shown in Fig. After closing the switch let Q charge goes from battery. Then charge on each will increase by q. Applying Kirchhoff's voltage law, we GET `200-((600+q)/(6))-((150+q)/(3))=0` or `q=100muC` so charge on `6muF` capacitor will be `70muC` and `3muF` capacitor will be `250muC` from all the switches `100muC` of charge will flow. |
|
| 5449. |
(A): Two bulbs of same wattage, one having a carbon filament and the other having a metallic filament are connected in series. Metallic bulb will glow more brightly than carbon filament bulb. (R): Carbon is a semiconductor. |
|
Answer» Both 'A' and 'R' are TRUE and 'R' is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of 'A' |
|
| 5450. |
When a 6000Å light falls on the cathode of a photo cell and produced photoemission. If a stopping potential of 0.8 V is required to stop emission of electron, then determine the frequency of the light |
|
Answer» Solution :Wavelength, `lambda = 6000 Å = 6000 xx 10^(-10) m` stopping potential, `V_(0) = 0.8 V` (i) Frequency of the light, `upsilon = (c)/(lambda)` `= (3 xx 10^(8))/(6000 xx 10^(-10)) = 5 xx 10^(-4) xx 10^(18)` `upsilon = 5 xx 10^(14)` Hz (II) Energy of the INCIDENT photon, `E = h upsilon = 6.6 xx 10^(-34) xx 5 xx 10^(14)` `= 33 xx 10^(-20)J` `= (33 xx 10^(-20))/(1.6 xx 10^(-19)) = 20.625 xx 10^(-1)` E = 2.06 eV (iii) Work function of the cathode material, `W_(0) = h upsilon - e V_(0)` `= ((6.6 xx 10^(-34) xx 5 xx 1-^(14))/(1.6 xx 10^(-19))) - ((1.6 xx 10^(-19) xx 0.8)/(1.6 xx 10^(-19))) = 2.06 - 0.8` `W_(0) = 1.26 eV` (iv) Threshold frequency, `W_(0) = h upsilon_(0)` `upsilon_(0) = (W_(0))/(h) = (1.26 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19))/(6.6 xx 10^(-34)) = 0.3055 xx 10^(15)` `upsilon_(0) = 3.05 xx 10^(14)` Hz (v) Net energy of the electron after it leaves the surface `E = (upsilon - upsilon_(0))` `= 6.6 xx 10^(-34) (5 xx 10^(14) - 3.06 xx 10^(14))` `= 6.6 xx 10^(-34) xx 1.94 xx 10^(14)` `E = 12.804 xx 10^(-20) J` `= (1.2804 xx 10^(-19))/(1.6 xx 10^(-19))` E = 0.8 eV |
|