Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 6401. |
A ship is moving due east with a velocity of 12 m/ sec, a truck is moving across on the ship with velocity 4 m/sec. A monkey is climbing the vertical pole mounted on the truck with a velocity of 3m/sec. Find the velocity of the monkey as observed by the man on the shore |
|
Answer» 10 m/sec |
|
| 6402. |
What is the mechanical equivalent of spring constant k in LC oscillating circuit? |
|
Answer» `(1)/(L)` |
|
| 6403. |
Kamla peddles a stationary bicycle the pedals of the bicycle are attached to a 100 turn coil of area 0.10m^(2). The coil rotates at half a revolution per second and it is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.01 T perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the coil. What is the maximum voltage generated in the coil? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here `f=0.5Hz,N=100,A=0.1m^(2)andB=0.01T`. `epsilon_(0)=NBA(2piupsilon)=100xx0.01xx0.1xx2xx3.14xx0.5=0.314V` |
|
| 6404. |
What do you mean by internal resistance, e.m.f. (electromotive force) and terminal potential difference of a cell? Derive a relation between the three. How will you determine it? |
|
Answer» Solution :Internal Resistance. The resistance offered by the electrolyte to the flow of etectric current through it is claled the internal resistance of the CELL. Electromotive force. The potential difference between the two poles of a cell in an open circuit (when no current is drawn from the cell), is called the e.m.f. of the cell. DUE to its e.m.f., a cell DRIVES the charge round the circuit. therefore, e.m.f. of a cell is also defined as the energy supplied by the cell to drive a unit charge round the complete circuit. it is denoted by E. In S.I., the unit of e.m.f. is volt (V) or joule per coulomb `(J" "C^(-1))`. The e.m.f. of a cell is called one volt, if 1 joule of work is performed by the cell to drive one coulomb of charge round the circuit. When the current flows through the cell, its electrolyte offers resistance to the flow of current. Terminal Potential Difference of a Cell The potential difference between the two poles of a cell in a closed circuit (when current is drawn from the cell) is called the terminal potential difference of the cell. It is denoted by V. ,br> When current flows through the circuit, there is fall of potential across the internal resistance of the cell. the potential difference between the two poles of the cell is less than the e.m.f. of the cell by an amount equal to potential drop across the internal resistance. therefore, the terminal potential difference ofacell is always less than its e.m.f. Relation between e.m.f., potential difference and internal resistance of a cell. (Expression for internal resistance of a cell) Consider the circuit as shown in the figure. 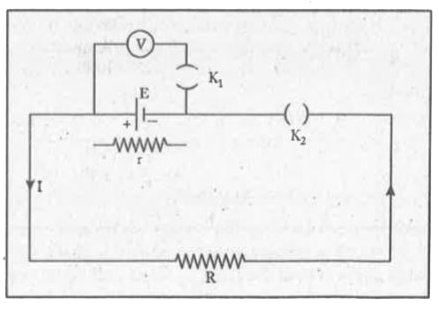 Insert the key `K_(1) and ` read the voltmeter. it GIVES the e.m.f. E of the cell. now insert some resistance in the circuit with the help of the resistance BOX and also close the key `K_(2)` so that the circuit becomes closed. again read the voltmeter. it gives the potential difference between the ends of the external resistance and let it be V. the value of V is smaller than E due to the fall of potential inside the cell. Let r be the internal resistance of the cell and I the current flowing through the circuit when `K_(2)` is closed. Now `I=(E)/(R+r)` or `E=(R+r)I`. . (1) Fall of potential in the external circuit is given by Dividing (1) and (2), `(E)/(V)=(R+r)/(R)=1+(r)/(R)` `(r)/(R)=(E)/(V)-1=(E-V)/(V)` or `r=R((E-V)/(V))=R((E)/(V)-1)` Thus knowing the values of E, V and R, the internal resistance r can be determined. |
|
| 6405. |
What are the different types of transformers. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :STEP up TRANSFORMER, stepdown transformer | |
| 6406. |
Out of the two magnetic materials. 'A' has relative permeability slightly greater than unity while 'B' has less than unity. Identify the nature of materials 'A' and 'B'. Will their susceptibilities be positive or negative? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`A to ` Paramagnetic (`because mu_r > 1` ) B `to` Diamagnetic (`because mu_r > 1` ) SUSCEPTIBILITY for A `to` POSITIVE Susceptibility for B `to` Negative |
|
| 6407. |
A particle of mass 5M at rest decays into two particle of masses 2 m and 3 m having non zero velocities. The ratio of de - broglie wavelengh of the particles is |
|
Answer» `3//2` |
|
| 6408. |
A steel wire is heated to 170^(@)C and held between two rigid supports which are 20cm apart. The wire is allowed to cool to a temperature of 29.6^(@)C. If the frequency of the note produced when the wire is plucked at the middle is 100 k, then find the value of k. (The density D of steel is 7.8xx10^(3)kg//m^(3) and for steel alpha=16xx10^(-6)K^(-1) and Y of steel =20xx10^(10)Pa.). |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :THERMAL STRESS in the wire `=alphaYDeltaT` Tension in the wire `=alphaYDeltaTpir^(2)` `N=(1)/(2L)sqrt((T)/(pir^(2)D))=(1)/(2L)sqrt((alphaYDeltaT.pir^(2))/(pir^(2)D))=(1)/(2L)sqrt((alphaYDeltaT)/(D))` Putting values `n=600Hz`. In the fundamental mode as the wire is plucked in the MIDDLE. |
|
| 6409. |
A sphere has a mass 10 kg and radius 1 m. What is the radius of gyration of a sphere about its tangent? |
|
Answer» 1.18 m |
|
| 6410. |
In a plane electomagnetic wave, the electric field oscillates sinusoidally at a frequency of 2.0xx106(10)Hz and amplitude 48Vm^(-1). (a) What is the wavelength of the wave? (b) What is the amplitude of the ocillating magnetic field ? (c ) Show that the average energy density of thevecE field equals the average energy density of the vecB field. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) `LAMBDA=(C )/(v)=(3xx10^(8))/(2.0xx10^(10))=1.5xx10^(-2)m` (b) `B_(0)=(E_(0))/(c )=(48Vm^(-1))/(3xx10^(8)ms^(-1))=1.6xx10^(-7)T` (c ) We KNOW that average energy density of `vecE` field, `u_(E)=(1)/(2)epsilon_(0)E_("rms")^(2)` and average energy density of `vecB` field, `u_(B)=(1)/(2mu_(0))B_("rms")^(2)`. Now `E_("rms")=cB_("rms") and c=(1)/(sqrt(mu_(0)E_(0)))` `therefore""u_(E)=(1)/(2)epsilon_(0)E_("rms")^(2)=(1)/(2)epsilon_(0)c^(2)B_("rms")^(2)=(1)/(2)epsilon_(0)((1)/(sqrt(mu_(0)epsilon_(0))))^(2)B_("rms")^(2)=(1)/(2mu_(0))B_("rms")^(2)=u_(B)` Thus, it is clear the average energy densities of `vecE` field and `vecB` field are equal. |
|
| 6411. |
A uniform magnetic field exists in the space vecB=B_1hati+B_2hatj-B_3hatk. Find the magnetic flux through an area vecS if the area vecS is in X-Y plane |
|
Answer» Solution :Since the FIELD is UNIFORM , we can USE frmula `phi_B= vecB.VECS` Now when area `vecS` is in X-Y plane , it means `vecS=Shatk` Hence `phi_B=(B_1hati+B_2hatj-B_3hatk)(Shatk) =-B_3S` |
|
| 6412. |
A convex and a concave mrror of radius 10 cm each are placed 15 cm apart, facing each other. An object is placed mid - way between them. Find the position of final image if the reflection first takes place in the concave and then in the convex mirror : |
|
Answer» Final IMAGE isformed on the pole of concave mirror  `OP_(1) = OP_(2) = 7.5 CM` for reflection from concave mirror u = - 7.5 cm, R = - 10 cm, f = - 5.0 cm `(1)/(u) + (1)/(v) = (1)/(f),` then v = 15 cm This image is formed on the pole of convex mirror, which will act as an OBJECT for convex mirror `therefore u = - 0, v = ?, f = + 5.0 cm, then (1)/(v) = oo,` so v = 0 Again final image is formed on pole of convex mirror. |
|
| 6413. |
If u is thedistance of the real point object from thte principal focus of a spherical mirror or a focal length f and v is the distance of the real point image from the principal focus, then uv is equal to : |
|
Answer» f and F = - f then `(1)/(u) + (1)/(v) = (1)/(f) rArr - (1)/(u+f)-(1)/(v+f) = - (1)/(f)` `(1)/(u+f) + (1)/(v+f) = (1)/(f)` `THEREFORE (u+v+2f)/((u+f)(v+f))=(1)/(f)` `therefore "" uf + VF + 2f = (u + f)(v + f)` or `"" uf + vf = 2f^(2) = uf + uf + vf + f^(2)` Then `f^(2) = uv` `therefore"" uv = f^(2)` |
|
| 6414. |
A) In Tangent galvanometer the circular frame is rotated until the plane of the coil is parallel to magnetic meridian B) In Tangent galvanometer current through it is related to deflection of needle as ialpha tan theta |
|
Answer» A is true, D is FALSE |
|
| 6415. |
n-P-n transistors are preferred to P-n-p transistors because |
|
Answer» Low cost |
|
| 6416. |
Neon -23 decays in the following way ""_(10)^(23)Nerarr""_(11)^(23)Ne+""_(-1)e^0+barv. Find the minimum and maximum kinetic energy that the beta particle (""_(-1)e^(0)) can have . The atomic masses of ""^(23)Ne and ""^(23)Naare 22.9945u and 22.9898 u, respectively. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here, atomic masses are given (not the NUCLEAR masses ), but still We can beuse them for Calculating the mass defect because mass of electrons get cancelled both sides. THUS, Mass defect `Deltam = (22.9945-22.9898) = 0.0047u` `:. Q = (0.0047u) (931.5 MeV//u) = 4.4 MeV` Hence, the energy of beta poetical can range from 0.to 4.4 Me V. |
|
| 6417. |
An electric dipole is at 30° with uniform electric field of 2 xx 10^(5) N/C. The torque acting on it is 4 Nm. If length of dipole is 2 cm, then what will be the charge at one end of dipole ? |
|
Answer» 5 MC `tau=q(2a)Esintheta` `THEREFORE q=tau/(2a xx Esintheta)` `=4/(2 xx 10^(-2) xx 2 xx 10^(5) xx sin 30^(@))` `=1/(10^(3) xx 1/2)` `=1/500 = 0.002 C = 2 xx 10^(-3) C = 2mC` |
|
| 6418. |
एक स्थिर विद्युत-आवेश उतपन्न करता है |
|
Answer» केवल चुंबकीय क्षेत्र |
|
| 6419. |
The axes of the polariser and analyser are inclined to each other at 45^(@) . If the amplitude of the unpolarised light incident on the polariser is A , the amplitude of the light transmited through theanalyser is |
|
Answer» `A/2` |
|
| 6420. |
In a Germanium diode, the forward current increases from 100mA to 200 mA, when forward voltage changes from 5V to 10V. The forward resistance of the diode is |
|
Answer» `20 OMEGA ` |
|
| 6421. |
Who is the author of Lost Spring? |
|
Answer» JAMES Bond |
|
| 6422. |
A clock fixed on a wall shows time 04:25:37. What time will its image in a plane mirror hanging on an opposite vertical wall show? |
|
Answer» `07:43:32` |
|
| 6423. |
Hydrogen (""_(1)H^(1)). Deuterium (""_(1)H^(2)) singly ionised Helium and doubly ionised lithium (""_(3)Li^(6))^(++) all have one electron around the nucleus. Consider an electron transition from n= 2 to n=1. If the wavelengths of emited radiation are lambda_(1),lambda_(2),lambda_(3) and lambda_(4) respectively then approximately which one of the following is correct? |
|
Answer» `lambda_(1)=2lambda_(2)=3lambda_(3)=4lambda_(4)` `1/lambda=R(1)^(2) (3//4) , 1/lambda =R(1)^(2) (3//4)` `1/lambda=R 2^(2) (3//4), 1/lambda_(4)=R 3^(2) (3//4)` `1/lambda_(1)=(1)/(4lambda_(3))=(1)/(9 lambda_(4))=(1)/(lambda_(2))` So, `lambda_(1)=lambda_(2)=4lambda_(3)=9lambda_(4)` |
|
| 6424. |
The radius of Earth is 6400 km. If the height of an antenna is 500 m , then its range is |
|
Answer» 800 km = `sqrt(10^(3)xx64xx10^(5))` = `8xx10^(4)=80KM` |
|
| 6425. |
Electromagnetic field has two invariant quatities. Usingthe transformation formulas (3.6 i)demonstrate that thesequantiesare (a) EB, (b) E^(2) - c^(2) B^(2). |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) We see that, `vec(E').vec(B') = vec(E')_(|\|).vec(B')_(|\|) + vec(E')_(_|_).vec(B')_(_|_)` `= vec(E)_(|\|).vec(B)_(|\|) + ((vec(B)_(_|_) + vec(v) xx vec(B)).(vec(B)_(_|_)- (vec(v) xx vec(E))/(C^(2))))/(1 - (v^(2))/(c^(2)))` `= vec(E)_(|\|).vec(B)_(|\|) + (vec(E)_(_|_).vec(B)_(_|_) - (vec(v) xx vec(B)).(vec(v) xx vec(E))//c^(2))/(1 - v^(2)//c^(2))` `= vec(E)_(|\|).vec(B)_(|\|) + (vec(E)_(_|_).vec(B)_(_|_) - (vec(v) xx vec(B)_(_|_)).(vec(v) xx vec(E_(_|_)))//c^(2))/(1 - (v^(2))/(C^(2)))` But, `vec(A) xx vec(B).vec(C) xx vec(D) = A. C B. D - A.D B. C`, so, `vec(E').vec(B') = vec(E)_(|\|).vec(B)_(|\|) + vec(E)_(_|_).vec(B)_(_|_) ((1 - (v^(2))/(c^(2))))/(1 - (v^(2))/(c^(2))) = vec(E).vec(B)` (b) `E^(2) - c^(2) B'^(2) = E'_(|\|)^(2) - c^(2) B'_(|\|)^(2) + E_(_|_)^(2) - c^(2) B'_(_|_)^(2)` `=E_(|\|)^(2)c^(2) B_(|\|)^(2) + (1)/(1 - (v^(2))/(c^(2))) [(vec(E)_(_|_) + vec(v) xx vec(B))^(2) - c^(2) (B_(_|_)^(2) - (vec(v) xx vec(E))/(c^(2)))^(2)]` `=E_(|\|)^(2)c^(2) B_(|\|)^(2) + (1)/(1 - (v^(2))/(c^(2))) [E_(_|_)^(2) -c^(2) B_(_|_)^(2) + (vec(v) xx B_(_|_)^(2) - 91)/(c^(2)) (vec(v) xx E_(_|_))^(2)]` `=E_(|\|)^(2)c^(2) B_(|\|)^(2) + (1)/(1 - (v^(2))/(c^(2))) [E_(_|_)^(2) - c^(2) B_(_|_)^(2)] (1 - (v^(2))/(c^(2))) = E^(2) - c^(2) B^(2)`. since, `(vec(v) xx vec(A)_(_|_))^(2) = v^(2) A_(_|_)^(2)` |
|
| 6426. |
The magnitude of induced emf developed in a coils is 2V when the rate of change of current is unity.The self inductance of the coil is |
|
Answer» 1H |
|
| 6427. |
Three different objects of masses m_1 m_2and m_3 are allowed to fall from rest from the same point along three different frictionless paths, the speeds of the three objects on reaching the ground, will be in the ratio |
|
Answer» `m_1 : m_2 :m_3` |
|
| 6428. |
A compass needle when placed at a magneticpolestays along |
|
Answer» south NORTH DIRECTION only |
|
| 6429. |
A 10 V cells of negligible internal resistance is connected in parallel across a battery of emf 200 V and internal resistance 38Q . As shown in the figures , Find the value of current in the circuit In a potentiometer arrangement for determining the emf . of a cell the balance point of the cell in open circuit is 350 cm. When a resistance of 9Q . is used in the external circuit of the cells the balance point shift to 300 cm. Determine the internal resistance of the cell. |
|
Answer» Solution :Writing the equation FINDING the current By Kirchoffs law , we have ,for the LOOP ABCD `+ 200 -38i -1 (0) =0 ` ` therefore I =( 190 )/( 38 ) A = 5A ` ` (##DBT_SM_PHY_XII_DL_18_E02_002_S01.png" width="80%"> Finding the Net emf Stating that `I= (V)/® ` Calculating The two cells being in opposition ` therefore ` net emf = ` ( 200 -10 ) V = 190 V ` Now `I= (V) /(R) ` [Note : some students may use the formule] ` ( in )/( r) =( in _ 1) /( r_1) +(in _2) /(r_2) ` and ` "" r=( r_1r_2)//( r_1+ r_2)` For two cells connected in parallel they may then say that ` r=0` ` in ` is indeterminate and hence I is also indeterminate Award full marks (2) to students giving This line of REASONING |
|
| 6430. |
Arrange the ascending order of polarising angles for air-glass, air-water, and water-glass interfaces? |
|
Answer» water-glass, air-water, air-glass |
|
| 6431. |
To get an output Y = 1 from circuit of figure, the inputs must be : |
|
Answer» `{:(A,B,C),(0,1,0):}` |
|
| 6432. |
A sphere of mass m moving with a velocity u hits another stationary sphere of same mass. If e is the coefficient of restitution, what is the ratio of the velocities of two spheres after the collision? |
|
Answer» 1 `therefore e=(v_2-v_1)/(u_2-u_1)=(v_2-v_1)/(u-0)` or `v_2-v_1=eu` ….(i) By the LAW of conservation of momentum , `m u+m X 0 = mv_1 + mv_2` or `v_1+v_2=u` ….(ii) Adding (i) and (ii), `2v_2=u+eu=u(1+e)` or `v_2=(u(1+e))/2` Again , from (ii), `v_1=u-v_2=u- (u(1+e))/2 = (u(1-e))/2` Hence , `v_2/v_1=(1+e)/(1-e)` |
|
| 6433. |
The two ends of a train moving with uniform acceleration pass a certain point with velocity u and v.Find the velocity with which the middle point of the train passes the same point. |
Answer» Solution : Between A,B,`(V^(1))^(2)-u^(2)`=2a s/2 Between B,C ,`v^(2)-(v^(1))^(2)`=2as/2 `IMPLIES(v^(1))^(2)-u^(2)=v^(2)-v^(12)` `2(v^(1))^(2)=v^(2)+v^(2)` Velcity at mid POINT is `v^(1)=sqrt(u^(2)+v^(2))/(2)` |
|
| 6434. |
The unit of Intensity of polarization is ........ |
|
Answer» `(C)/(m^(2))` |
|
| 6435. |
Calculate the net flux emerging from given enclosed surface - Nm^(2) C^(-1) |
|
Answer» `4.5 XX 10^(11)` |
|
| 6436. |
Plane microwaves are incident on a long slit having a width of 5.0 cm . The wavelengthof the microwaves if the first diffraction minimum is formed attheta = 30^(0) |
|
Answer» 2.5 CM |
|
| 6437. |
A point object located at a distance of 20 cm from the pole of a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm with height 2 cm is moving with a velocity ( bar(V_(OG)) =4 hati - 5 hatj) m/s and velocity of the mirror is (bar(V_(mg)) = -6 hati + 10 hatj) m I s as shown. Find the velocity of image w.r.t ground. |
|
Answer» Solution :From the velocity diagram of object w.r.t mirror is `(V_(om))_(II)= 10 m//s implies (V_(om)) = -15 m//s` `implies m= F/(f-u) =3 implies v=60cm` `(V_(IM))_(II) = - v^(2)/u^(2) (V_(om))_(II) implies (V_(IM))_(II)` = -`(60/-20)^(2) (10)= -90`m/s `(dm)/(dt) = [(u(V_(IM)_(II) - V(V_(om)_(II))))]/u^(2)` = `[( (-20)xx(-90)xx(-60)xx10^(2)xx(10))/(-20xx10^(-2))^(2)]` per SEC `(dm)/(dt) = 3XX10^(2)` per sec `(V_(IM)) = h_(0) (dm)/(dt) + m(V_(om))` `bar(V_(IM))=(V_(IM))_(II) hati + (V_(IM)) hatj implies bar(V_(IM)) = (-90 hati + -51 hatj)` `bar(V_(IG)) = (-90 hati + -51 hatj) + (-6 hati + 10 hatj) implies ` `:. bar(V_(IG)) = (-96 hati + -41 hatj)` m/s |
|
| 6438. |
Two identical coils, each with N turns and radius R are Placed coaxiallyat a distance R as shown in the figure. If I is the current passing through the loops in the same direction, then the magnetic field at a point P which is at exactly at (R )/(2) distance between two coils is ........... . |
|
Answer» `(8Nmu_(0)I)/(SQRT(5)R)` |
|
| 6439. |
Two long parallel wires are carrying currents as shown Find magnitude and direction of magnetic field at P,Q and R. (b) (i) (ii) At what distance from left wire, magnetic field is zero on the line joining the wires. Find magnitude of magnetic field at P. (d) Two straight infinitely long and thin parallel wires are spaced d distance apart and carry a current i each. find the magnetic field at a point distance d from both wires when the currents are in the (i) same and (ii) opposite directions. |
Answer» SOLUTION :(a)  At `P:` Due to wire `①`, `B_(1)=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)`, upward Due to wire `②`, `B_(2)=(mu_(0)i)/(2pi(3d))` downward `B_(P)=B_(1)-B_(2)=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)(1-1/3)=(mu_(0)i)/(3pid)`, upward At `Q:` Due to wire `①` ,`B_(1)=(mu_(0)i)/(2pi(3d))`, downward Due to wire `②`, `B_(2)=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)`, downward `B_(Q)=B_(1)+B_(2)=(mu_(0)i)/(pid)`, downward At `R:` Due to wire `①` , `B_(1)=((mu_(0)i)/(2pi(3d)))`, downward Due to wire `②` , `B_(2)=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)`, upward `B_(R) =B_(2)-B_(1)=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)(1-(1)/(3))=(mu_(0)i)/(3pid)`, upward (b) (i)  Let magnetic field is zero at distance `x`, left wire At `P:` `B_(1)=B_(2)` `(mu_(0)i)/(2pix)=(mu_(0)(i))/(2pi(d-x)) implies 4/x =1/(d-x) implies x=(4d)/5` (ii) 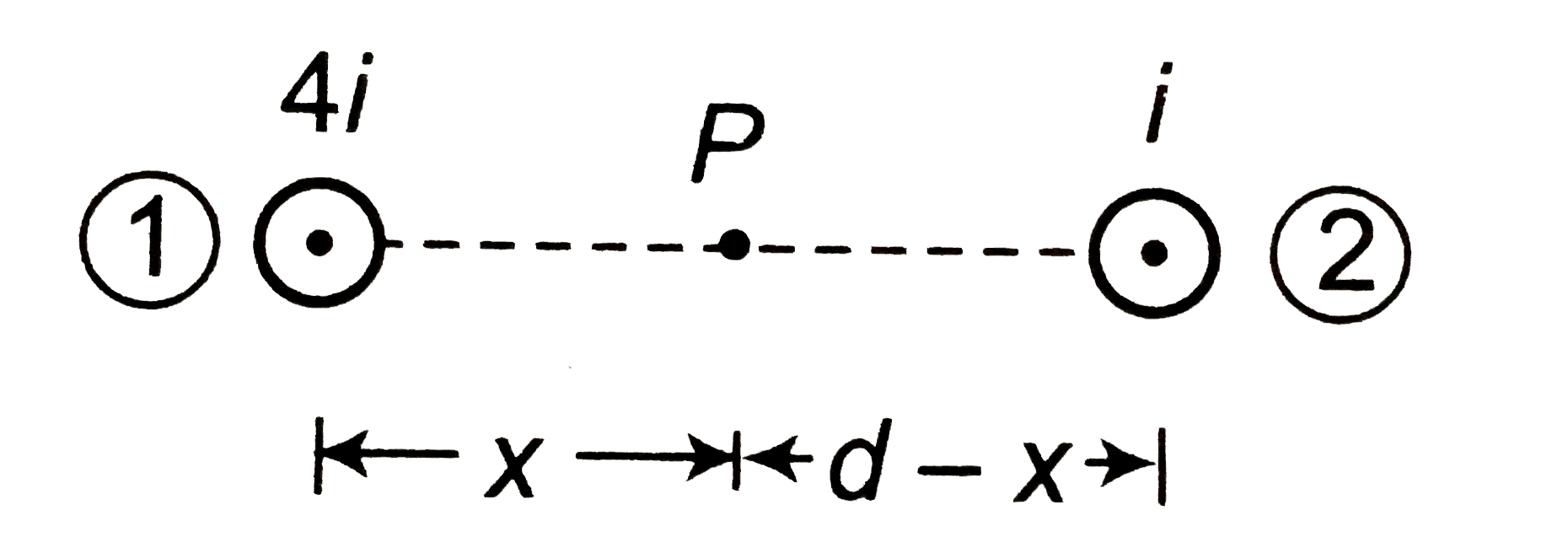 The magnetic field won't be zero between the wires because due to both wires magnetic field will be upward. The magnetic field will be zero nearer the smaller current outside `AB`. Let it be zero at distance `x` from wire `B` as shown. At `P:` Due to `①`, `B_(1)=(mu_(0)(4i))/(2pi(d+x))`, upward Due to `②` `B_(2)=(mu_(0)(i))/(2pix)`, downward `B_(P)=0 i.e., B_(1)=B_(2)` `=(mu_(0)(4i))/(2pi(d+x))=(mu_(0)(i))/(2pix) implies 4/(d+x)=1/x` `x=d/3` Magnetic field is zero at distance `d=d//3=4d//3` from left wire. (iii)  `angleAPB=90^(@)` At `P:` `B_(1)=(mu_(0)(3i))/(4pi(3d))=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)`, along `PB` `B_(2)=(mu_(0)(4i))/(4pi(4d))=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)`, along `PA` 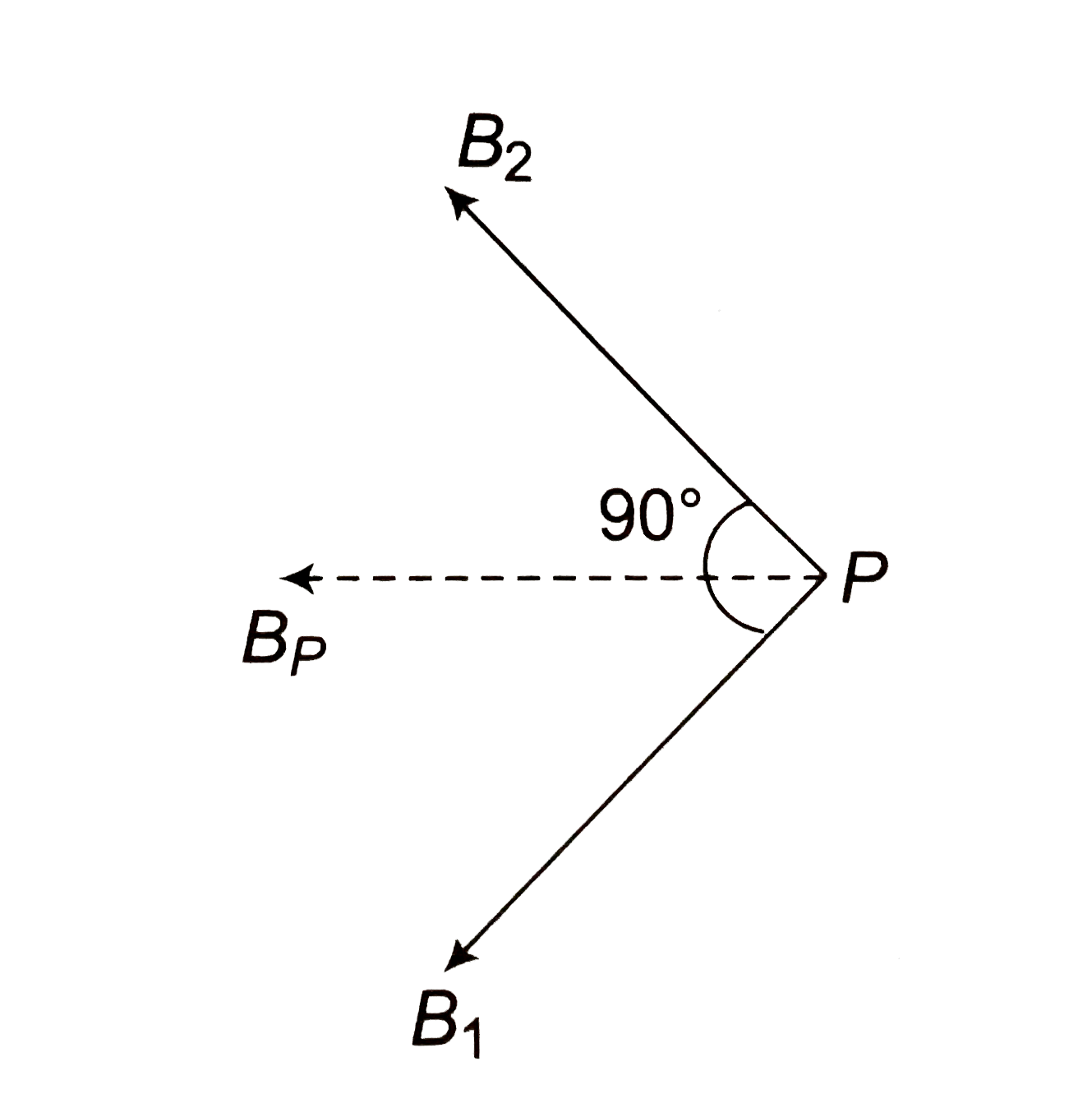 `B_(1)` and `B_(2)` are perpendicular `B_(P)=sqrt(B_(1)^(2)+B_(2)^(2))=(sqrt(2)mu_(0)i)/(2pid)=(mu_(0)i)/(sqrt(2)pid)` (d) (i)  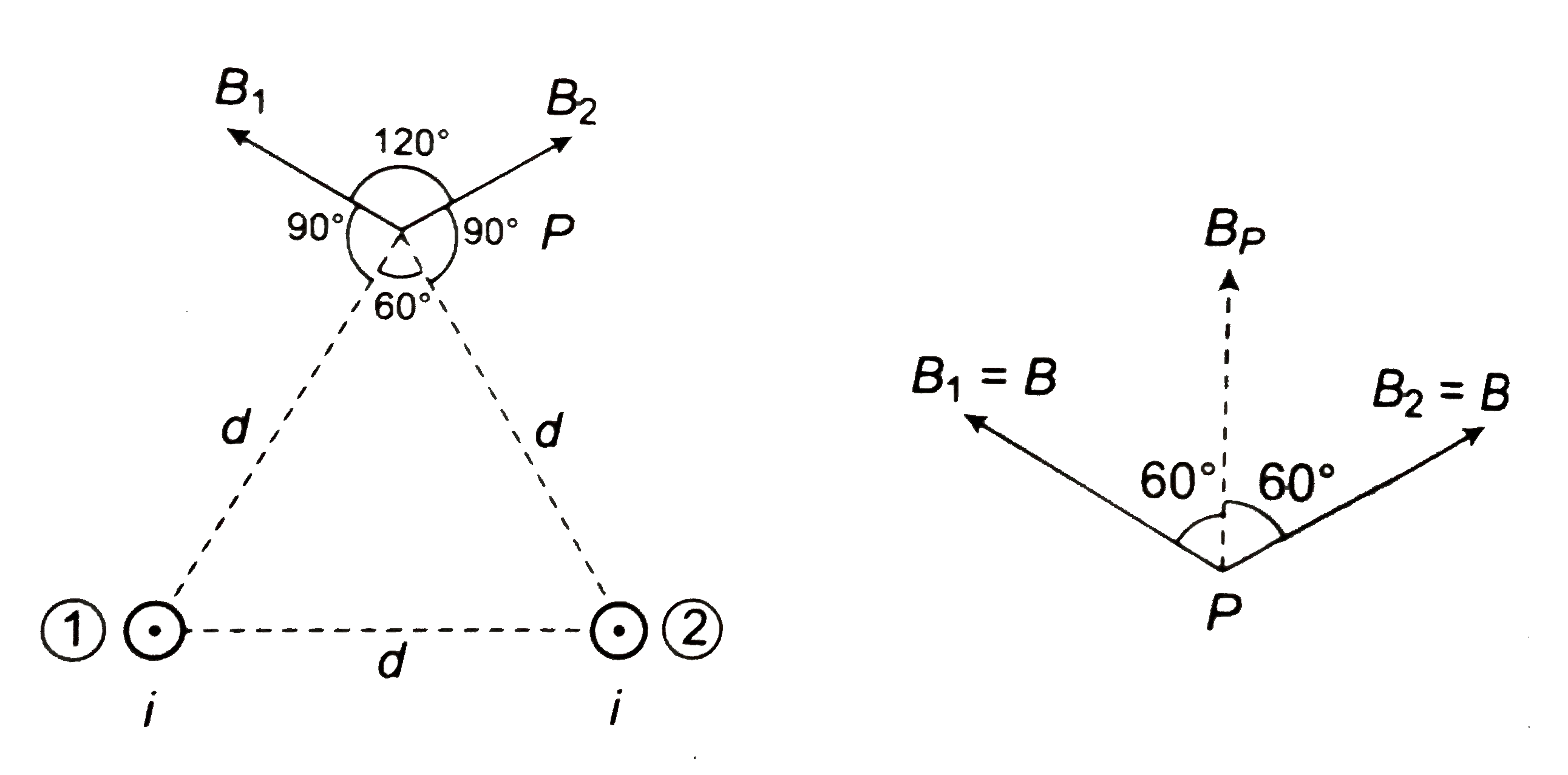 `B_(1)=B_(2)=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)=B` `B_(P)=2Bcos30^(@)=sqrt(3)B=(sqrt(3)mu_(0)i)/(2pid)` `B_(1)=B_(2)=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)=B` `B_(P)=2Bcos60^(@)=B=(mu_(0)i)/(2pid)` |
|
| 6440. |
The energy of a photon is equal to the kinetic energy of a proton. If lamda_(1) is the de Broglie wavelength of a proton, lamda_(2) the wavelength associated with the photon, and if the energy of the photon is E, then (lamda_(1)//lamda_(2)) is proportional to |
|
Answer» `E^(4)` |
|
| 6441. |
Can we neglect the quantization of charge ? If yes, then mention the situation ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Yes, the step size e is however very small because at the macroscopic level. We deal with charges of a few `muC` . At this scale the fact that charge of a body can increases or decrease in units of e is not visible. The grainy nature of the charge is lost and it APPEARS to be continuous. This situation can be compared with the geometrical concepts of points and lines. A dotted line viewed from a distance appears continuous to us but is not continuous in reality. As many points very close to each other normally give an impression of a continuous line, many small charges taken together appear as a continuous charge distribution. At the macroscopic level, one deals with charges that are enormous compared to the magnitude of charge e. A charge of magnitude 1 pC contains 1013 times the electronic charge. At this scale, the fact that charge can increase or decrease only in units of e is not very different from saying that charge can take continuous values. Thus, at the macroscopic level, the quantisation of charge has no practical consequence and can be ignored. At the microscopic level, where the charges involved are of the order of a few tens or HUNDREDS of e, i.e. they can be counted, they appear in DISCRETE lumps and quantisation of charge cannot be ignored. For more information : Characteristics of electric charge (1) Electric charge is of two types: i) Positive, (ii) Negative. (2) Like charges repel and unlike charges attract. (3) There is no existance of electric charge without mass. (4) Magnitude of charge doesn.t DEPEND on mass and speed. |
|
| 6442. |
A bullet moving with a velocity of 800 ms^(-1) strikes two wooden plates of width x_(1) and x_(2) and in pasing through each of them loses 200 ms^(-1) of its velocity. Assuming the resistance of the plates to be uniform the ratio n_(1)//n_(2) is : |
|
Answer» 15/13 `:. (1/2m(800^(2)-600^(2)))/(1/2m(600^(2)-400^(2)))=(Fx_(1))/(Fx_(2))` `:. (x_(1))/(x_(2))=(1400xx200)/(1000xx200)=7/5` |
|
| 6443. |
Dispersive power of prism is independent of |
|
Answer» REFRACTIVE index |
|
| 6444. |
You have 10^(23) carbon atoms imagine that all the nuclei are put at the north pole of the earth and the electron at the south pole of the earth (radius = 6400 km.) Then force between the charges is (Approx)- |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 6445. |
Find work done to bring a rest charge q_(0) from point A to point B, slowly. All parameters are in S.I. units. |
|
Answer» Solution :`W_(A rarr B) = U_(B) - U_(A) = q_(0) (V_(B) - V_(A))` `= [-(K(qa))/(125) - ((K(qa)(7))/(125))]` `rArr W_(A rarr B) = (Kq q_(0)a)/(125)(8)` |
|
| 6446. |
In the following question a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R ) A : Two large conducting spheres carrying charges Q_(1) and Q_(2) are brought close to each other. The magnitude of electrostatic force between themis exactly given by Q_(1) Q_(2)// 4 pi epsilon_(0) r^(2) , where r is the distance between their centres. R: Here charges Q_(1) and Q_(2) can be assumed to be concentrated at the centres of their respective spheres. |
|
Answer» If both Assertion & Reason are TRUE and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion , then mark (1). |
|
| 6447. |
What did you learn from the chapter, 'The Guitar Player and Svayamvara'? |
|
Answer» Men should accept the women with all their possessions |
|
| 6448. |
What we call if two unlike poles of equal strength separated by small distance ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MAGNETIC DIPOLE | |
| 6449. |
A polarizer - analyser set is adjusted such that the intensity of llight coming out of the analyser is just 36% of the original intensity. Assuming that the polarizer - analyser set does not absorb any light, the angle by which the analyser needs to be rotated further, to reduce the output intensity to zero, is (sin^(-1)((3)/(5))=37^(@)) |
|
Answer» `53^(@)` |
|
| 6450. |
Consider the circuit as shown in figure. The equivalent resistance between A and B is |
|
Answer» `(9)/(7)Omega` |
|