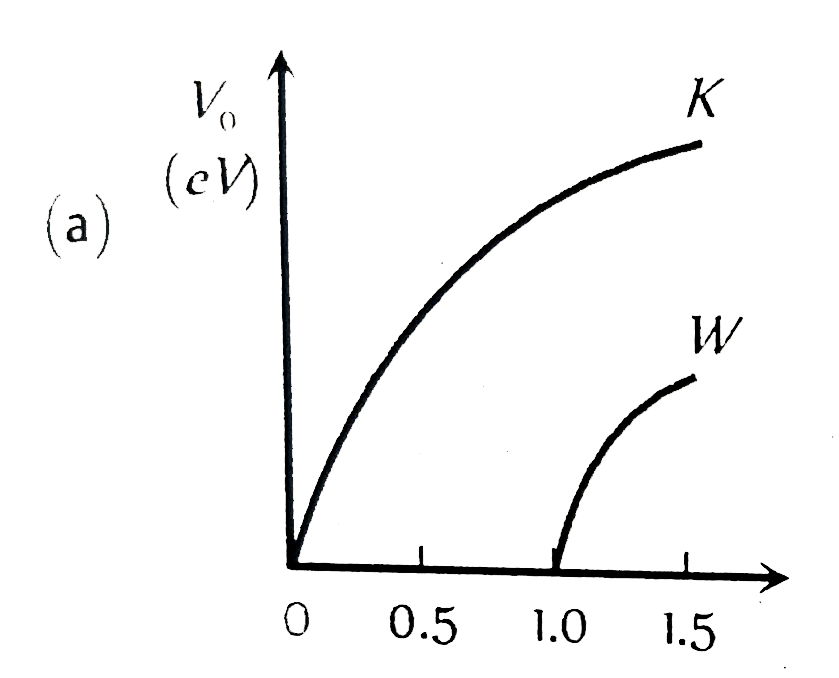Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 6501. |
Holes are charge carriers in a) Intrinsic semiconductors b) Ionic solids c) p - type semiconductors d) Metals |
|
Answer» Only a and B are CORRECT |
|
| 6502. |
In the previous problem what will be the frequency of electric field if the charge particle is alpha-particle? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`2.675 XX 10^(7) HZ` | |
| 6503. |
At a given instant of time the position vector a particle moving in a circle with a velocity 3 hati - 4 hatj +5k is hati + 9 hatj -3 hatk. Itsangular velocity at that time is |
|
Answer» `(( 13 hati+ 29 hatj -31 hatk))/sqrt146` `H=1/2g t^2=1/2g((t_1+t_2)/2)^2` (`:.` The TIME taken by the body to REACH maximum height,where time of ascending is equal to time of Decending ,`t=(t_1+t_2)/(2)` `:.H=2g(t_1+t_2)/(4^2)` |
|
| 6504. |
A thin circular ring of area A is held perpendicular to a uniform field of induction B. A small cut is made in the ring and a galvanometer is connected across the ends such that the total resistance of the circuit is R. When the ring is suddenly squeezed to zero area, the charge flowing through the galvanometer is _____ |
|
Answer» `(BR)/A` `therefore` The change in flux associated with ring is `Deltaphi=phi_2-phi_1=-AB` Now according to Faraday.s law `EPSILON=-(Deltaphi)/(Deltat)` `therefore IR=(AB)/(Deltat)"" [because epsilon=IR]` `therefore Q/(Deltat) .R = (AB)/(Deltat) "" [becauseI=Q/(Deltat)]` `therefore Q=(AB)/R` |
|
| 6505. |
A concave mirror and convex lens (both of refractive index 1.5) have focal length 3 cm in air. When they are placed in water ofrefractive index 4/3, then their new focal lengths will be ...... |
|
Answer» `f_("lens")`=12 cm ,`f_("MIRROR")`=3 cm |
|
| 6506. |
The waves used by artificial satellites for communication purposes are |
|
Answer» microwaves |
|
| 6507. |
Discuss contribution of different scientists in electromagnetic. Define electromagnetic induction. |
|
Answer» Solution :Electricity and magnetism were considered separate and unrelated phenomena for a long time. In the early decades of the nineteenth century, EXPERIMENTS on electric current by Oersted, AMPERE and a few others established the fact that electricity and magnetism are INTERRELATED. They found that moving electric CHARGES produce magnetic fields. For example, an electric current DEFLECTS a magnetic compass needle placed in its vicinity. The experiments of Michael Faraday in England and Joseph Henry in USA, conducted around 1830, demonstrated conclusively that electric currents were induced in closed coils when subjected to changing magnetic fields. "The phenomenon in which electric current is generated by varying magnetic fields is called electromagnetic induction." |
|
| 6508. |
A short light pulse of enegry E = 7.5J falls in the form of a narrow and almost parallel beam on a mirror plate whose reflection coefficient is rho = 0.60. The angle of incidence is 30^(@). In terms of the corpuscular theory find the momentum transfered to the plate. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :The momentum transferred to the plate is ` underset(("momentum transfered on ab sor ption")) underset(darr)(=(E)/(c )(1-rho){sin theta HTI - COS theta hatj})underset(("momentum transfered on reflection")) underset(darr) (+(E)/(c )rho{12cos theta hatj})` `=(E)/(c)(1-rho) sin theta hatj - (E)/(c)(1-P) cos theta hatj` Its MAGNITUDE is `(E)/(c)sqrt((1-rho)^(2)sin^(2)theta+(1+rho)^(2)cos^(2)theta) = (E)/(c)sqrt((1-rho)^(2)+2rho cos 2 theta)` SUBSTITUTION gives `35n` N.s as the answer. 
|
|
| 6509. |
Thereis a conductor with cavity of radius R as shown in figure. A point charge Q is placed at R//2 distance from centre of cavity. A point P is at r distance from centre of conductor. Then, |
|
Answer» <P>CHARGE density at iner SURFACE of cavity will be NON uniform |
|
| 6510. |
For two equal non parallel forces acting at a point the square of the resultant is 3 times the product of forces. The angle between the forces is |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 6511. |
To investigate the beta-decay of Mg^(23) radionuclide, a counter was activated at moment t=0. It registered N_(1) beta-particles by a moment t_(1)= 2.0s, and by a moment t_(2)=3t_(1) the number of registered beta-particles was 2.66 times greater. Find the mean lifetime of the given nuclei. |
|
Answer» Solution :If `N_(0)` is the number of radionuclei present initially,then `N_(1)=N_(0)(1-e^(-t_(1)//tau))` `etaN_(1)=N_(0)(1-e^(-t_(2)//tau))` where `eta=2.66` and `t_(2)= 3t_(1)`. Then `eta=(1-e^(-t_(2)//tau))/(1-e^(-t_(1)//tau))` or `eta-eta e^(-t_(1)//tau)= 1-e^(-t_(2)//tau)` Substituting the VALUES `1.66= 2.66e^(-2//tau)-e^(-6//tau)` PUT `e^(-2//tau)=x`. Then `x^(3)-2.66x+1.66=0` `(x^(2)-1)x-1.66(x-1)=0` or `(x-1)(x^(2)+x-1.66)=0` Now `x~~1 so x^(2)+x- 1.66=0` `x=(-1+-sqrt(1+4xx1.66))/(2)` NEGATIVE sign has to be rejected as `xgt0`. Thus `x= 0.882` This gives `tau=(-2)/(In 0.882)= 15.9 sec`. |
|
| 6512. |
The final product obtained in the reaction |
|
Answer»
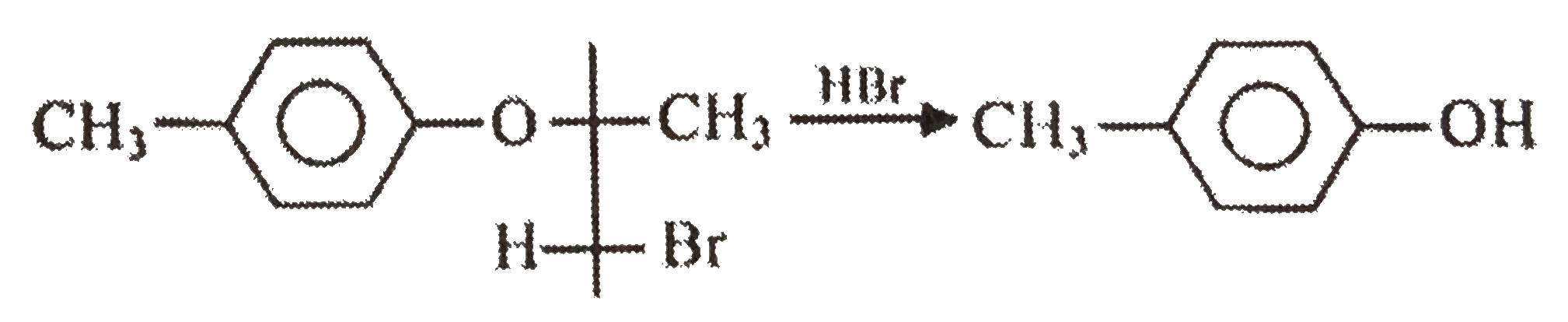
|
|
| 6513. |
A town, situated 20 km away from a power plant generating power at 440 V, requires600 kW of electric power at 220 V. The resistance of the two-wire line carrying power is 0.4 Omegaper km. The town gets power from the line through a 3000 - 220 V step down transformer at a substation in the town. (i) Find the line power losses in the form of heat. (ii) How much power must the plant supply, assuming there is negligible power loss due to leakage ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, total length of LINE wier `=20 xx 2 = 40 km` Total resistance of line wier `R = 40 xx 0.4 = 16 OMEGA` (i) As 600 kW power is received through a line at 3000 V, hence the current `I = P/V = (600 kW)/(3000 V) = (600 xx 1000 W)/(3000 V) = 200 A` `therefore` Line power loss in the form of heat `= I^(2)R =(200)^(2) xx 16 = 640,000 W = 640 kW` (ii) Total power to be supplied by the plant = Power NEED + Power loss = 600 kW + 640 kW = 1,240 kW |
|
| 6514. |
Arrange the intensities of the transmitted light in their increasing order of magnitudeswhen they are passed through a system of two polarisers (A) When incident light is unpolarisedand of intensity I and the angle between the polarisers is 30^(@) (B) When incident light is polarised of intensity 2I and the anglebetween the polarisers is 45^(@) (C ) When polarisedlight of intensity 4I is incidentandthe anglebetween the polarisers is 90^(@) (D) When incident light is unpolarised and of intensity 3I and the angle between the polarisers is 30^(@) |
|
Answer» C,D,A,B |
|
| 6515. |
Find out which of the following transitions are forbidden by the selection rules: .^(2)D_(3//2)rarr.^(2)P_(1//2),.^(3)P_(1)rarr.^(2)S_(1//2),.^(3)F_(3)rarr.^(3)P_(2), .^(4)F_(7//2)rarr.^(4)D_(5//2) |
|
Answer» <P> SOLUTION :Selection rules are `Delta=0``DeltaL=+-1` `DeltaJ=0, +-1(no 0rarr 0)` Thus `.^(2)D_(3//2) rarr .^(2)P_(1//2)` is ALLOWED `.^(3)P_(1)rarr .^(2)S_(1//2)` not allowed `.^(3)F_(3)rarr.^(3)P_(2)` is not allowed `(DeltaL=2)` `.^(F_(7//2)rarr .^(4)D_(5//2)` is allowed . |
|
| 6516. |
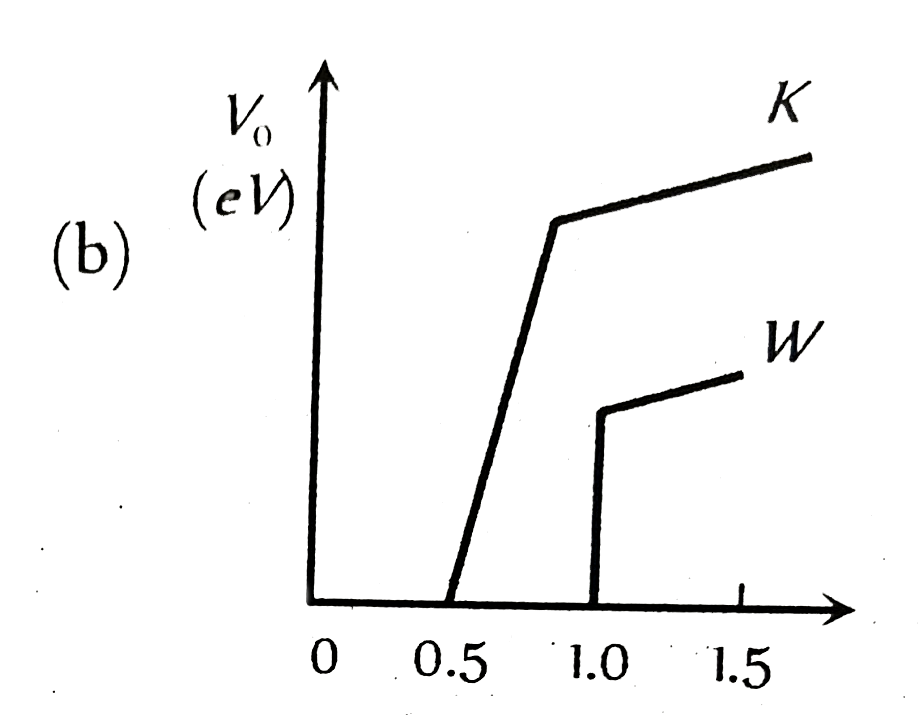
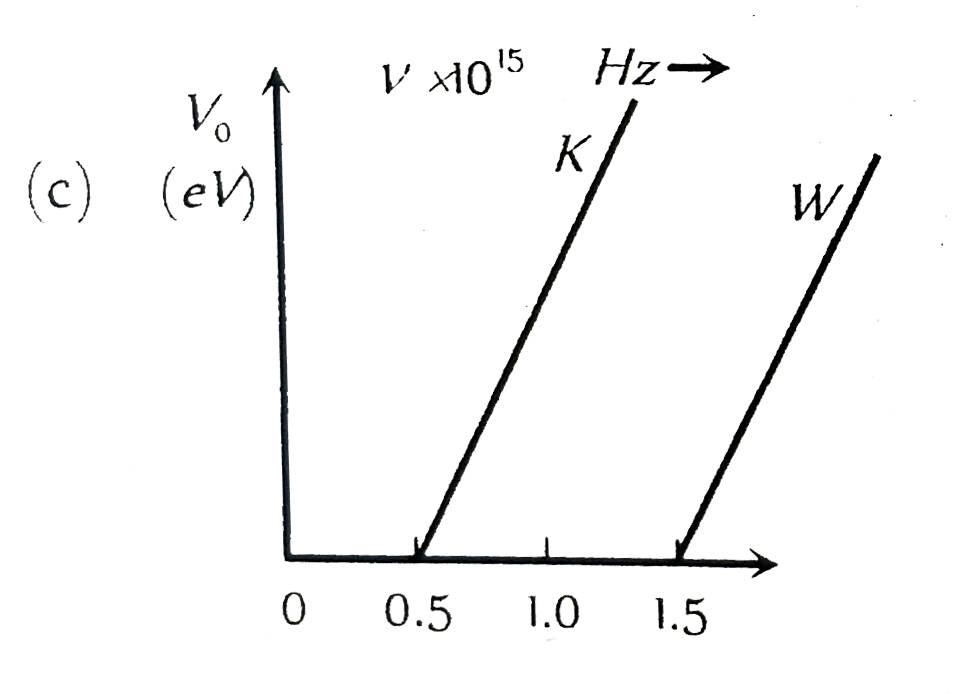
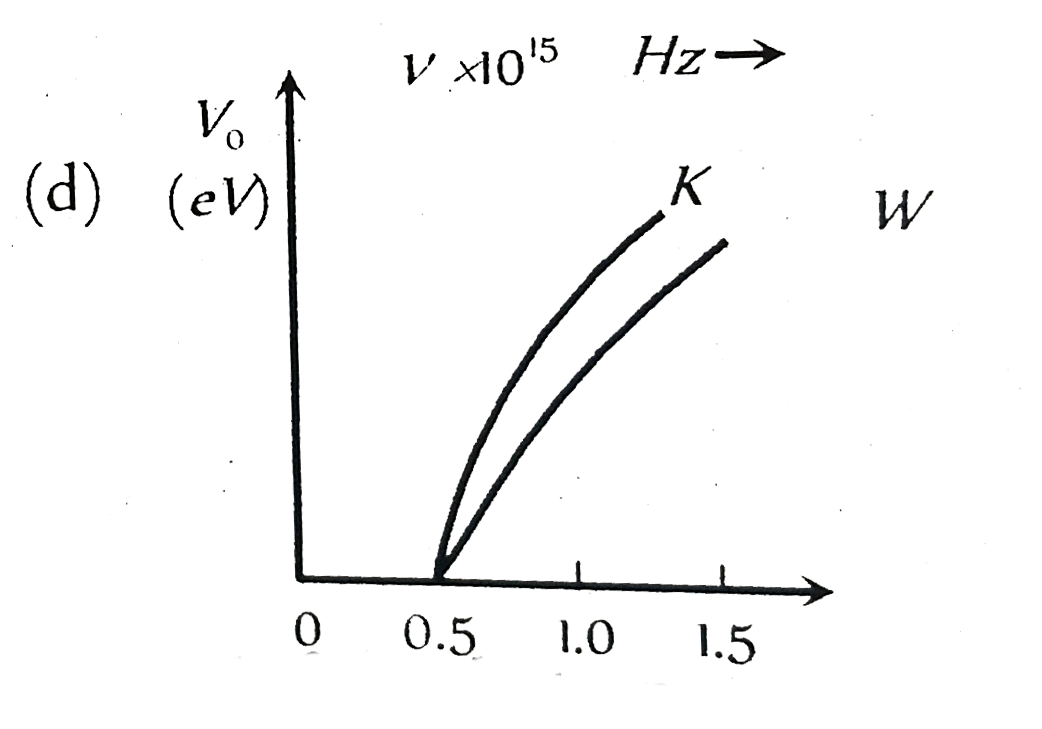
The figure showing the correct relationship between the stopping potential V and the frequency v of the light for potassium and tungsten is |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 6517. |
State Lenz's Law. A metallic rod held horizontally along east-west direction, is allowed to fall under gravity. Will there be an emf induced at its ends ? Justify your answer. |
|
Answer» Solution :Lenz.s law gives the direction of induced emf/current. According to it, the POLARITY of the induced emf is such that it tends to produce a current which OPPOSES the change in magnetic flux that produced it. If a metal rod of LENGTH l held horizontally in east-West direction is allowed to fall vertically DOWNWARD under gravity then an induced emf `varepsilon = B_(H) l v` is set up across its ends on account of HORIZONTAL component of earth.s magnetic field `.B_(H).` pointing in north-south direction and v is the instantaneous speed of rod. The emf is induced on account of motional emf. |
|
| 6518. |
Particles of mass 1.6xx10^(-27) kg and charge 1.6xx10^(-19)C are accelerated in a cyclotron of dee radius 40cm. It employs a magnetic field 0.4T. Find the kinetic energy (in MeV) of the particle beam imparted by the accelerator. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here mass of charged PARTICLE `m=1.6xx10^(-27)kg`, charge `q=1.6xx10^(-19)C`, RADIUS of dee `R=40cm=0.4m` and magnetic field B = 0.4T. `therefore` KINETIC energy of the particle beam imparted by the cyclotron accelerator `K_("max")=(B^(2)q^(2)R^(2))/(2m)=((0.4)^(2)xx(1.6xx10^(-19))^(2)xx(0.4)^(2))/(2xx(1.6xx10^(-27)))J` `=((0.4)^(2)xx(1.6xx10^(-19))^(2)xx(0.4)^(2))/(2xx(1.6xx10^(-27))xx(1.6xx10^(-13)))=128MeV` |
|
| 6519. |
S^(32) absorbs energy and decays into which element after two -emissions? |
|
Answer» CARBON |
|
| 6520. |
……NOT gateis required for NAND gate. |
|
Answer» 0 |
|
| 6521. |
A force is inclined at 60^@ to the horizontal. If it's rectangular component in the horizontal direction is 50 N, then magnitude of the force in the vertical direction is |
|
Answer» 25 N |
|
| 6522. |
A cell supplies a current i_(1) trhough a resistnace R_(1) and a current i_(2) through a resistance R_(2). The internal resistance of this cell is |
|
Answer» `R_(2)-R_(1)` |
|
| 6523. |
A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm, carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude field vecB at the centre of the coil? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `N = 100 , R = 8.0 cm = 8 xx 10^(-2) m, l = 0.40 A` `:.` Magnitude of the MAGNETIC FIELD at the centre of coil `B = (mu_0 NI)/(2R) = (4 pi xx 10^(-7) xx 100 xx 0.4)/(2 xx 8 xx 10^(-2)) = pi xx 10^(-4) T " or " 3.14 xx 10^(-4) T`. |
|
| 6524. |
Everyone told the narrator that the squirrel would not ……… after being attacked so badly by the crows. |
|
Answer» move |
|
| 6525. |
The resistance of a thermistor varies with temperature according to the relation |
|
Answer» `R = a E^(b//T)` |
|
| 6526. |
Figure shows an irregular shaped wire AB moving with velocity v, as shown. Find the emf induced in the wire |
Answer» Solution :The same emf will be induced in the STRAIGHT imaginary wire JOINING A and B, which is `Blv SIN THETA `
|
|
| 6527. |
3% of energy of 100 W bulb is converted into visible light. Find the average intensity on a spherical surface 1 m away from the bulb consider the bulb is point source and medium is isotropic. |
|
Answer» Solution :Energy used per second in bulb, U = 3 % of `P=100xx(3)/(100)` `therefore U=3J` Area of curcular SURFACE considering it bulb at CENTRE `A=4pi r^(2)` `A=4xx3.14xx(1)^(2)` `therefore A = 12.56 m^(2)` Average INTENSITY of light on CIRCULAR surface `t=(U)/(A)=(3)/(12.56)=0.23885` `therefore I ~~ 0.24 W//m^(2)` |
|
| 6528. |
When a sphere of moment of inertia I moves down an inclined plane, the percentage of energy which is rotational, is approximately : |
|
Answer» `100%` `=(1)/(2)mv^(2)+(1)/(2)Iomega^(2)` `=(1)/(2)mv^(2)+(1)/(2).(2)/(5)mr^(2)omega^(2)=(1)/(2)mv^(2)+(1)/(5)mv^(2)` `=(7)/(10)mv^(2)=(7)/(10)xx50xx25=875ergs` |
|
| 6529. |
The electric intensity, at points near a charged conducting surface is sigma//epsilon_0Using this equation derive an expression for the electric intensity due to a conducting sphere of radius rata point on it’s surface, if it gains a total charge q |
| Answer» SOLUTION :E NEAR the surface of the SPHERE =`sigma/epsilon_0`But `sigma="charge"/"AREA"=q/(4pir^2)E=q/(epsilon_0xx4pir^2)=1/(4piepsilon_0)xxq/r^2` | |
| 6530. |
A student finds the balancing length to be .l. with a cell of constant emf in the secondary circuit. Another student connects the same cell in the secondary circuit of potentio meterof double the length but with a cell of half the emf in the primary circuit. The balancing length will be [cell in primary is ideal and no series resistance is present in primary circuit] |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 6531. |
Twp pulses in a stretched string whose centers are initially 8 cm aprt moving towards each other as shown in fig. The speed of each pulse is 2 cm /s. After 2 seconds, the total energy of the pulses will be : |
|
Answer» zero Correct choice is (C). |
|
| 6532. |
An object is placed at a certain distance from a screen. A convex lens of focal length 20cm is placed between the screen and the object. A real image is formed on the screen for two positions of the lens, which differ by a distance of 10cm. What is the distance of the object from the screen ? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 6533. |
The waves associated with every moving particle what we call them ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MATTER WAVES. | |
| 6534. |
In the circuit shown as potential difference of 60 V is appliled across AB. The potential difference between the points M and N is |
Answer» SOLUTION :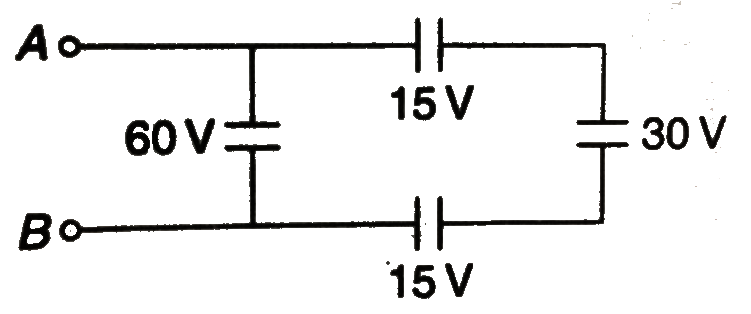
|
|
| 6535. |
(a) Deduce the expression for the torque acting on a dipole of dipole moment vecP in the presence of uniform electric field vecE. (b) Consider two hollow concentric spheres, S_(1) and S_(2), enclosing charges 2Q and 4Q respectively as shown in the figure. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) Dipole in a uniform external field : Consider an electric dipole consisting of charge`-q and +q` and of length 2A placed in a uniform electric field `vecE` making an angle * with electric field. Force on charge -q at `A=-q" " vecE("opposite to " vecE)` Electric dipole is under the action of two equal and unlike parallel forces, which give rise to a torque on the dipole. 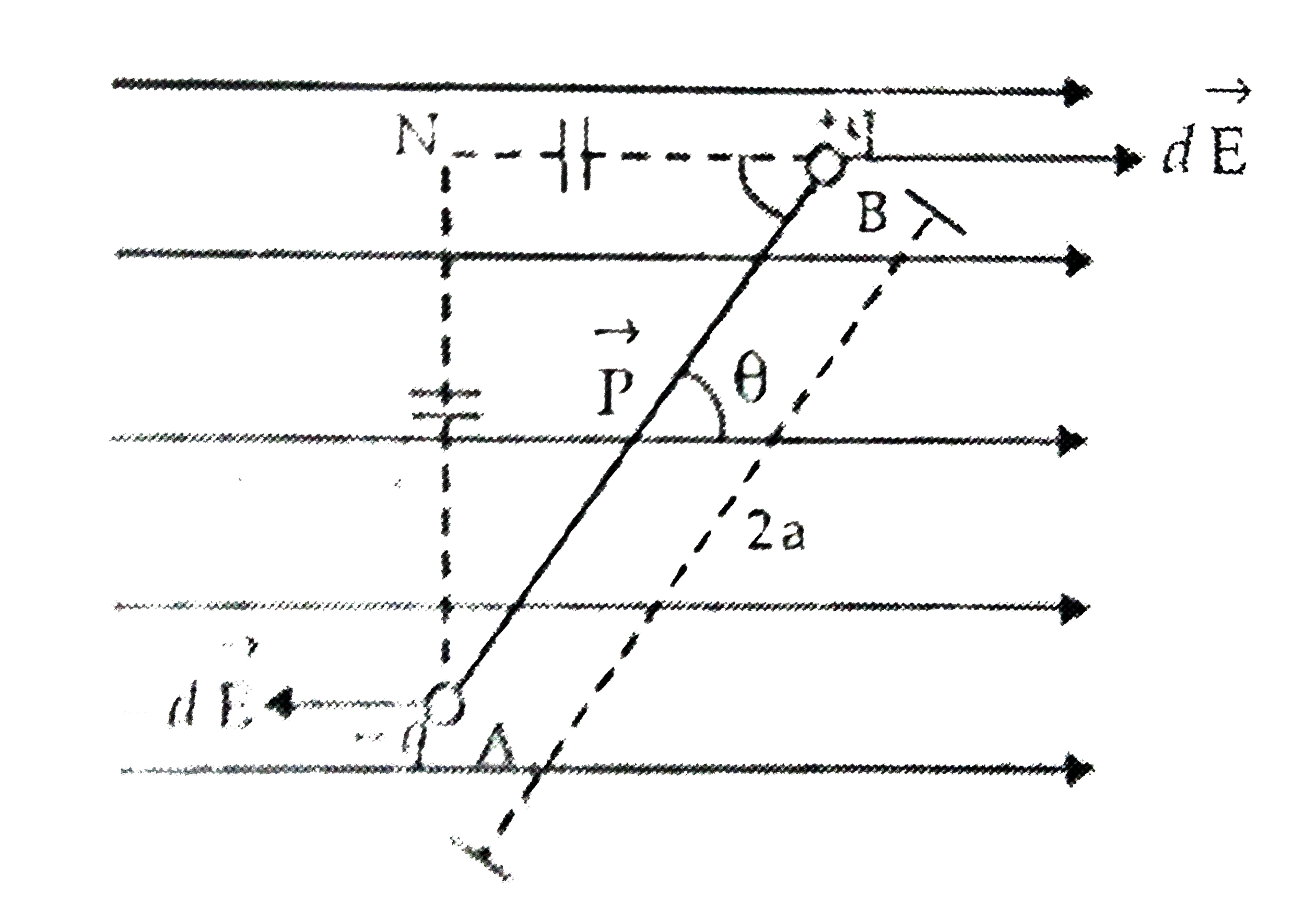 `tau="Force"xx"perpendicular idstance between the forces"` `tau=qE(AN)=qE(2a sintheta)` `tau=q(2a)E sintheta` `tau=pE sintheta` `therefore""tau=vecPxxvecE` (b)(i) Charge ENCLOSED by sphere `S_(1)=2Q`. by Gauses law, electric flux through sphere `S_(1)` is `phi=2thetaepsi_(0)` Charge enclosed by sphere, `S_(1)=2Q+4Q=6Q` `phi_(1)=6theta//epsi_(0)` The ratio of the electric flux is `phi_(1)//phi_(2)=2Qepsi_(0)//6Qepsi_(c)=(2)/(6)=(1)/(3)` (ii) For sphere `S_(1),` the electric flux is `phi'=2Q//epsi_(r)` `phi'//phi_(1)=(2theta)/(inr)divide (6theta)/(in_(0))=(in_(0))/(inr)*(1)/(3)` `therefore epsi_(r)gtepsi_(0),phi,ltphi_(1)` ltbr. Therefore, the electric flux through the sphere `S_(1)` decreases with the introduction of the dielectric INSIDE it. |
|
| 6536. |
The element curium ._96^248 Cm has a mean life of 10^13s. Its primary decay modes are spontaneous fission and alpha-decay, the former with a probability of 8% and the later with a probability of 92%, each fission releases 200 MeV of energy. The masses involved in decay are as follows ._96^248 Cm=248.072220 u, ._94^244 P_u=244.064100 u and ._2^4 He=4.002603u. Calculate the power output from a sample of 10^20 Cm atoms. (1u=931 MeV//c^2) |
|
Answer» `4.42xx10^(-3)` W (ii)`alpha`-decay(probability 92%) The nuclear reaction is GIVEN below : `._96Cm^(248) to ._94Pu^244 + ._2He^4` `therefore` Mass defect in the reaction =`Deltam` `therefore Deltam`=mass of Cm - mass of Pu - mass of He or `Deltam`=248.072220 - 244.064100-4.002603 or `Deltam`=0.005517 u `therefore ` Energy released = (0.00517 x 931 ) MeV `E_alpha` =5.136 MeV Given : `E_f`=Each fission releases 200 MeV of energy . MEAN life of Cm = `10^13` sec. `therefore lambda = 1/"mean life"=10^(-13) s^(-1)` Again `"dN"/"DT"=lambdaN` where N is given to be `10^20`. `therefore ` Rate of decay = `(10^(-13))(10^20)` or Rate of decay = `10^7` dps Of these `10^7` dps, 8% are in fission and 92% are in `alpha`-decay process. Energy released per second due to fission. `=8/100xx10^7 xx200=16xx10^7` MeV Energy released per sec due to `alpha`-decay `=92/100xx10^7xx5.136=4.725xx10^7` MeV Total energy released per second =`(16+4.725)10^7` MeV =`20.725xx10^7` MeV `therefore ` Power output= Energy per second `=(20.725xx10^7)xx(1.6xx10^(-13))` J/s `=3.316xx10^(-5) W = 3.32xx10^(-5)` W. |
|
| 6537. |
Draw a ray diagram to show image formation when the concave mirror produces a real inverted and magnified image of the object |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Ray DIAGRAM to SHOW the required image FORMATION ` (##DBT_SM_PHY_XII_DL_18_E03_010_S01.png" width="80%"> |
|
| 6538. |
An angular magnification of 30 X is desired using anobject lens of focal length 1.25 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 5 cm. How will you set up the compound microscope? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Angular magnification of the EYE piece `=1+(D)/(f_(e))` i.e.,`m_(e)=1+(25)/(5)=6` where D = 25 cm (least distance of vision) We know that`m=m_(0)m_(e)` i.e., `m_(0)=(m)/(m_(e))=(30)/(6)=5` HENCE, `because (V)/(u)=m, v=5u` using`(1)/(v)+(1)/(u)=(1)/(f_(0))` we GET `(1)/(5u)+(1)/(u)=(1)/(1.25)` `(+6)/(5u)=(4)/(5)` `because u=1.5cm`. For a real object at u = -1.5 m v = |5u| = 7.5 cm The object should be placed 1.5 cm from the object lens. |
|
| 6539. |
Calculate the time required for 60% of a sample of radon undergo decay. Given T_(1//2) of radon = 3.8 days. |
|
Answer» Solution :Hereconsider `R_(n) - 222` with a half life of 3.823 days. From decay equation, Current amount = `"Initial amount" XX (2)^(-n)` `N = N_(0) (2)^(-n)` `(N)/(N_(0)) = (2) ^(-t)/(T_(1/2))` `log((N)/(N_(0)) = log (2) xx (-(t)/(T_(1/2)))` `log((N)/(N_(0)))/(log(2)) = (-(t)/(T_(1/2)))` `t = (log(0.4))/(log(2)) xx (-3.823)` Time t = `5.05` days. |
|
| 6540. |
A glass lens is coated on one side with a thin film of magnesium fluoride (MgF_(2))to reduce reflection from the lens surface (Fig. 2.26). The Index of refraction of MgF_(2) is 1.38, that of the glass is 1.50. What is the least coating thickness that eliminates (via interference) the reflections at the middle of the visible specturm (lambda = 550nm)? Assume that the light is approxmately perpendicular to the lens surface. |
|
Answer» 112.4nm For destructive interference, `2n_(1)t_(MIN)=lambda/2` `:. t_(min)=550/(4xx1.38)=99.64nm.` |
|
| 6541. |
A : 3-D movies are produced by pojecting two images onto a screen, with polarizing dissections that are 90^(@) relative to one another. R : When your eyes view 3D wearing 3D glasses, your right eye sees one view and left eye sees the other view, these views combines in the brain and produce 3D effect. |
|
Answer» Both A and R are TRUE and R is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of A |
|
| 6542. |
Radio waves and visible light in vacuum have |
|
Answer» Same velocity but DIFFERENT wavelength |
|
| 6543. |
Range of an electronic communication system is the |
|
Answer» distance to the nearest TV station. |
|
| 6544. |
In tha above problem ,minimum value oft for which the intensity at point P on the screen exactly in fromt of the upper slit becomes maximum |
|
Answer» `0.167` s |
|
| 6545. |
For the same objective, find the ratio of the least separation between two points to be distinguished by a microscope for light of 5000Å and electrons accelerated through 100 V used as the illuminating substance. |
|
Answer» Solution :Formula of linear limit of resolution of compound MICROSCOPE having oil immersion objective is : `d_(m)=(1.22lamda)/(2nsinbeta)` Now resolution power, `P=(1)/(d_(m))=(2nsinbeta)/(1.22lamda)` `:.Pprop(1)/(lamda)` `:.(P_(1))/(p_(2))=(lamda_(2))/(lamda_(1))""......(1)` Here, in the second case `W=DeltaK` `:.Ve=(1)/(2)mv^(2)=(P^(2))/(2M)""(":.P=mv)` `:.Ve=(h^(2))/(2mlamda^(2))` ( `"":.P=(h)/(lamda)` h=Planck.s CONSTANT) `:.lamda^(2)=(h^(2))/(2Vem)` `:.lamda=(h)/(SQRT(2Vem))` `:.lamda_(2)=(h)/(sqrt(2Vem))""(":.` In the second case `lamda=lamda_(2)`) `:.lamda_(2)=(6.625xx10^(-34))/(sqrt(2xx100xx1.6xx10^(-19)xx9.1xx10^(-31)))` `:.lamda_(2)=(6.625xx10^(-9))/(sqrt(200xx1.6xx9.1))m` `:.lamda_(2)=(6.625xx10^(-9))/(sqrt(200xx1.6xx9.1))xx10^(10)Å` `=(66.25)/(sqrt(200xx1.6xx9.1))` `=(66.25)/(53.96)` `:.lamda_(2)=1.2278Å` Now from equation (1), `(P_(1))/(P_(2))=(1.2278)/(5000)` `:.(P_(1))/(P_(2))=2.456xx10^(-4)` |
|
| 6546. |
The critical angle for a medium is 60°. Then the refractive index of the medium will be |
|
Answer» `ROOT3/2` |
|
| 6547. |
In the Milikan oil drop experiment the drop carries 10 electronic charges charge and a mass of 4.4 xx 10^(-15)kg. It is held almost stationary between two horizontal plate separated by 2cm. What is the potential between the plates? |
|
Answer» Solution :Data supplied Let V be the potential the plates separated by a distance d. Thus, electric field intensity, `E=V/d, d=2 xx 10^(-2)m` Charge `q=ne= 10 xx 10^(-19)C, Mass m=4.4 xx 10^(-15)kg` Since the drop is held stationary, the electrostatic field is EQUAL to the WEIGHT of the drop. i.e.qE=mg `(q V)/(d)=mg` `V=(mgd)/(q)=(4.4 xx 10^(-15) xx 9.8 xx 2 xx 10^(-2))/(10 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19))=539"volts"` |
|
| 6548. |
The rms value of an alternating current, which when passed through a resistor produces heat three times of that produced by a direct current of 2A in the same resistor, is |
|
Answer» 6A |
|
| 6549. |
How is a potential barrier formed in p-n junction diode ? |
Answer» Solution :Formation of junction diode. When a p-type CRYSTAL is place in CONTACT with n-type crystal so as to form one piece, the assembly so obtained is called p-n junction or junction diode or crystal diode. The SURFACE of contact of p-type and n-type crystals is called junction. In the p-section, holes are the majority carriers while in n-section, the majority carriers are electrons. Due to high concentration of different types of charge carriers in the two sections, holes from p-region diffuse into n-region and electrons from n-region diffuse into p-region. In both cases, when an electron meets a hole they cancel the effect of each other and as a result, a thin layer at the junction becomes devoid of charge carriers. This is called depletion layer as shown in the FIGURE. The thickness of depletion layer is of the order of `10^(-6)m`.  Due to the migration of holes and electrons, the two sections of the junction diode no longer remain neutral. The p-section of the junction diode becomes SLIGHTLY negative, while the n-section is rendered positive. Due to this, there is a potential gradient in the depletion layer, negative on the p-side and positive and the n-side. In other words, it appears as if some fictitious battery is connceted across the junction with its negative pole connected to p-region and positive pole connected to n-region. The potential difference developed across the junction diode due to migration of majority carriers is called potential barrier. |
|
| 6550. |
A paramagneticsubstanceof susceptibility 3xx10^(-4)is placed in magnetization in the units of Am^(-1) is |
|
Answer» `1.33xx10^(8)` =susceptibility x x field B `rarrI=Bx=(4xx10^(-4))xx(3XX10^(-4))=12xx10^(-8) am^(-1)` |
|