Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 2451. |
In the half-wave rectifier circuit shown, which one of the following waveform is true for V_(CD) the output across C and D? |
Answer» Solution :HALF WAVE rectifier, rectifies only the half cycle of input ac signal and it BLOCKS the other half. 
|
|
| 2452. |
A spherical surface of radius of curvature R separates air (refractive index 1.0) from glass (refractive index 1.5). The center of curvature is in the glass. A point object P placed in air is found to have a real image Q in the glass. The ling PQ cuts the surface at a point O, and PO=OQ. The distance PO is equal to |
|
Answer» 5R `(-mu_(1))/(mu)+(mu_(2))/(v)=(mu_(2)-mu_(1))/(R)` Here, `u=-x, v=+x, R=+R,mu_(1)=1, mu_(2)=1.5` `(-1)/(-x)+(1.5)/(x)=(1.5-1)/(R)` `rArrx=5R` 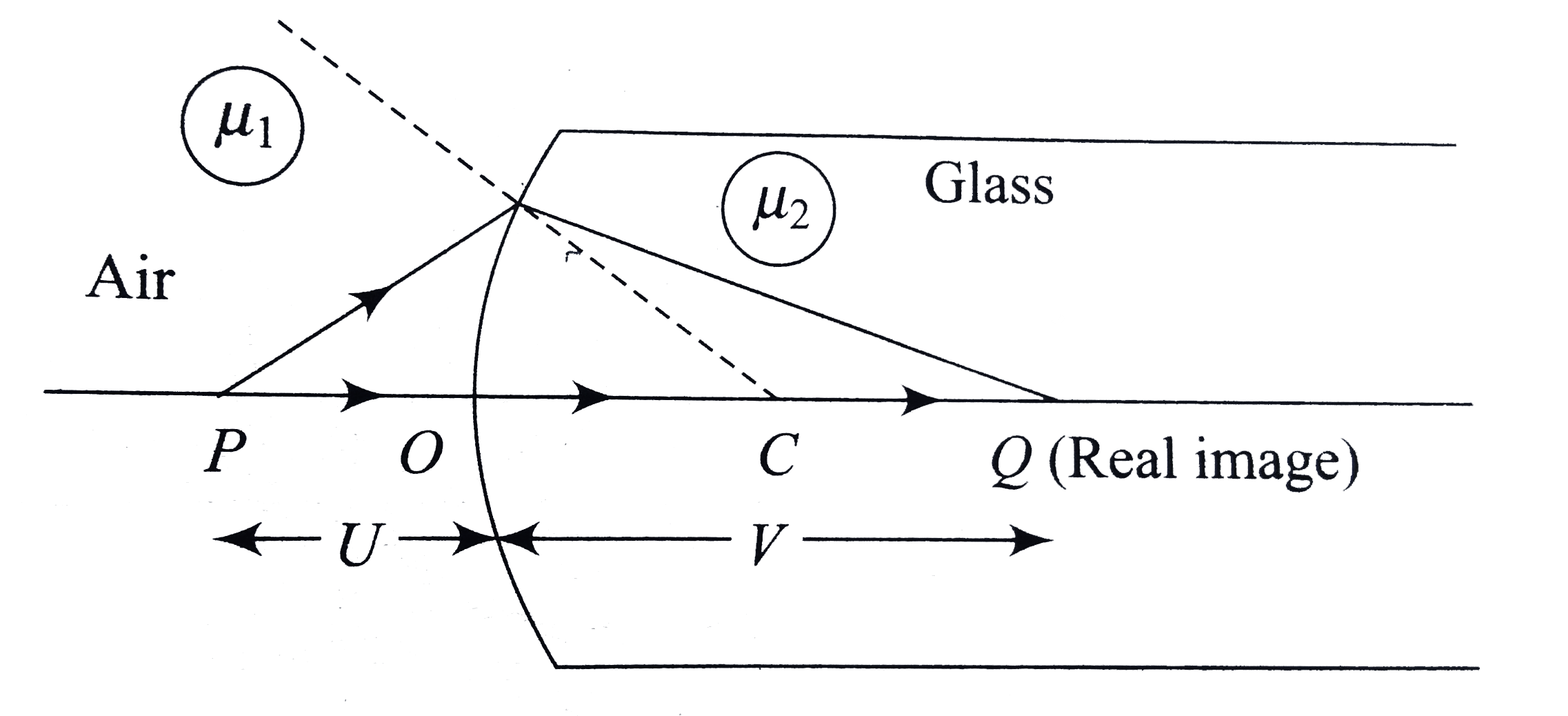
|
|
| 2453. |
A charged sphere of radius 0.02 m has charge density of 1 cm-2. The work done when a charge of 40 nano coulomb is moved from infinity to a point that is at a distance of 0.04 m from the centre of the sphere |
|
Answer» `1.44pi J` |
|
| 2454. |
A vertical pipe at both ends is partially submerged in water. A tuning fork of unknown frequency is placed near the top of the pipe and made to vibrate. The pipe can be moved up and down and thus length of air column in the pipe, standing waves will be setup as a result of directions. Smallest value of length of air column, for which sound intensity is maximum, is 10 cm. [take speed of sound, v = 344 m/s] The air column here is closed at one end because the surface of water acts as a wall. Which of the following is correct ? |
|
Answer» At the closed END of the AIR column, there is a DISPLACEMENT NODE and also a pressure node |
|
| 2455. |
A vertical pipe at both ends is partially submerged in water. A tuning fork of unknown frequency is placed near the top of the pipe and made to vibrate. The pipe can be moved up and down and thus length of air column in the pipe, standing waves will be setup as a result of directions. Smallest value of length of air column, for which sound intensity is maximum, is 10 cm. [take speed of sound, v = 344 m/s] Frequency of the tuning fork is |
|
Answer» 1072 HZ |
|
| 2456. |
A vertical pipe at both ends is partially submerged in water. A tuning fork of unknown frequency is placed near the top of the pipe and made to vibrate. The pipe can be moved up and down and thus length of air column in the pipe, standing waves will be setup as a result of directions. Smallest value of length of air column, for which sound intensity is maximum, is 10 cm. [take speed of sound, v = 344 m/s] Length of an column for second resonance will be: |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 2457. |
An achromatic combination of lenses is formed by joining |
|
Answer» 2 CONVEX lens |
|
| 2458. |
A vertical pipe at both ends is partially submerged in water. A tuning fork of unknown frequency is placed near the top of the pipe and made to vibrate. The pipe can be moved up and down and thus length of air column in the pipe, standing waves will be setup as a result of directions. Smallest value of length of air column, for which sound intensity is maximum, is 10 cm. [take speed of sound, v = 344 m/s] Length of air column for third resonance will be |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |
| 2459. |
A vertical pipe at both ends is partially submerged in water. A tuning fork of unknown frequency is placed near the top of the pipe and made to vibrate. The pipe can be moved up and down and thus length of air column in the pipe, standing waves will be setup as a result of directions. Smallest value of length of air column, for which sound intensity is maximum, is 10 cm. [take speed of sound, v = 344 m/s] Frequency of the second overtone is: |
|
Answer» 3400 HZ |
|
| 2460. |
What is the capacity having a plate area A of the figure given below? |
|
Answer» Solution :Capacity without dielectric `=C_(0)=(epsi_(0) A)/(2d)` Capacity with dielectric , `C=(epsi_(0) KA)/(2d)` Here capacity with dielectic constant `K_(1)=C_(1)=(epsi_(0) K_(1) (A/2))/(2d) =(epsi_(0)K_(1)A)/(4d)` Similarly with `K_(2), C_(2)=(epsi_(0) K_(2) (A/2))/(d)=(epsi_(0 K_(2)A))/(2d) and" with "K_(3), C_(3)=(epsi_(0)K_(3)A)/(2d)` `C_(2) and C_(3)" in SERIES "C.=(C_(2)C_(3))/(C_(2)+C_(3))=((epsi_(0)K_(2)A)/(2d).(epsi_(0)K_(3)A)/(2d))/((epsi_(0)K_(2)A)/(2d)+(epsi_(0)K_(3)A)/(2d))` `=(epsi_(0)K_(2)A epsi_(0)K_(3)A)/(4d^(2)) xx (2d)/(epsi_(0) A(K_(2)+K_(3))) =(epsi_(0) A.K_(2)K_(3))/(2d(K_(2)+K_(3))` `C. and C_(1)` are parallel `C=C. +C_(1)= (epsi_(0) AK_(2)K_(3))/(2d(K_(2)+K_(3))+(epsi_(0)K_(1)A)/(4d))=(epsi_(0)A)/(4d) [K_(1)+(2K_(2)K_(3))/((K_(2)+K_(3)))]` |
|
| 2461. |
If A=1, B=0, then in terms of Boolean algebra A+barB equals |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 2462. |
A stone is thrown with a velocity v at an angle 0 with the horizontal. Its speed when it makes an angle /3 with the horizontal is : |
|
Answer» `vcostheta` |
|
| 2463. |
What is the effect of temperature on the dielectric constant of a dielectrical medium ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :As the temperature is increased,the VALUE of DIELECTRIC CONSTANT decreases. | |
| 2464. |
When Bohr's theory is used to compute the energy levels in a hydrogen atom, only the Coulomb interaction between the electron and the proton is taken into account, the magnetic moments of these particles being ignored. Assess the resulting error. How will the energy level pattern change, if, in addition to the Coulomb interaction, the magnetic interaction between the electron and the proton is also taken into account? |
|
Answer» `epsi=epsi_("Coul")pmepsi_(mag)=-e^(2)/(4piepsi_(0)r)pm(2mu_(0)mu_(p)mu_(e))/(4pir^(3))` The relative error is `delta=|(delta-delta_("Coul"))/delta| ~~|(delta_(mag))/(delta_("Coul"))|=(2mu_(p)mu_(e))/(e^(2)c^(2)r^(2))le(2mu_(p)mu_(e))/(e^(2)c^(2)a_(0)^(2))` where `a_(0)` is the Bohr radius. Every energy level is seen to split into two sub-levels: the upper `epsi_(n).=epsi+|epsi_(mag)|`, and the lower `epsi_(n)..=epsi-|epsi_(mag)|`, where n is the number of the level and `|epsi_(mag)|` is the MAGNITUDE of the energy of magnetic interaction. Dashed LINES in Fig. show the first three energy levels stemming from Bohr.s theory, while the solid lines show the sub-levels due to magnetic interaction. The diagram is, of course, not to scale. 
|
|
| 2465. |
(a)Draw a ray diagram to show regraction of a ray of monochromatic light passing through a glass prism. Deduce the expression for the refractive index of glass in terms of angle of prism and angle of minimum deviation. (b)Explain briefly how teh pheomenon of total internal reflection is used in fibre optics. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a)Refraction in Prism : A ray PQ is incident on the face AB of prism at `anglei` and refracted ALONG QR at `ANGLER`.The angle of incidence (from glass to air) at the second face is r and the angle of regraction or emergence I'. The angle between the emergent ray RS and incident ray in the DIRECTION PQ is called the angle of deviation `delta`. In the quadraiateral AQNR, `angle Q and angle R` are RIGHT angles.  `:.angle A+angleQNR=180^@` `and "In" DeltaQNR,r+r'+angleQNR=180^@` Comparing these equations, we get `e+e'=A...(i)` Also`Delta=angleMQR+angleMRQ` `=e-r+i'-r'` `=i+i'-(r+r')` `Delta=i+i'-A...(ii)` In the minimum deviation position `i=i',r=r'and delta=delta_m` `:. r+r=ArArr r=A/2` `and delta_m=i+i-ArArri=((A+deltam)/2)` If `MU` is the refractive index of material of prism. Then by Snell's law `mu=sini/sinr=(sin(A+(deltam)/2))/(sin(A/2))` (b)Each optical fibre consists of a core and cladding. Refractive index of the material of the of light, is directed into the optical fibre, at an angle greater than the (relevant) critical angle, it undergoes repeated total internal reflections along the length of the fibre and comes out of it at the other end with almost negligible loss of intesity. 
|
|
| 2466. |
A 3.0 cm wire carrying a current of 10 A is placed inside a solenoid perpendicular to its axis. The magnetic field inside the solenoid is given to be 0.27 T.What is the magnetic force on the wire ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :I=3.0cm `= 3.0 xx 10^(2-) m, I=10A, B =0.27 T` `F=Bil = 0.27 xx 10xx 3 xx 10^(-2) = 8.1 xx 10^(-2) N` |
|
| 2467. |
n transparent slabs are arranged one on top of each other. The refractive indices of the material of the slabs are mu_(1),mu_(2),mu_(3) ***, mu_(n)and the thickness are t_(1),t_(2),t_(3), ***t_(n). An image is formed at a particular position when a point object is seen perpendicularly through this combination of slabs. If the image is formed at the same position when seen through a single glass slab instead of the combination of slabs, what is the equivalent refractive index of the new glass slab? |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2468. |
^amu_bxx^bmu_c is what ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`^amu_c` | |
| 2469. |
A diode having a potential difference of 0.5V across its junction is connected in series with a resistance of 20Omegaand a source. A current of 0.1 A passes through, the resistance. What is the voltage of the source ? |
|
Answer» `1.5V` |
|
| 2470. |
An ammeter gives full scale deflection when current of 1.0A is passed in it.To convert it into 10A range ammeter, the ratio of its resistance and thye shunt resistance will be- |
|
Answer» `1:9` |
|
| 2471. |
Mark the corrcet options. |
|
Answer» If the far point increases, the power of the divergent LENS should be REDUCED |
|
| 2472. |
An experiment is performed to obtain thevalue of acceleration due to gravity g by using a simple pendulum of length L. In this experiment time for 100 oscillations is measured by using a watch of 1 second least count and the value is 90.0 seconds. The length L is measured by using a meter scale of least count 1 mm and the value is 20.0 cm. The error in the determination of g would be: |
|
Answer» `1.7%` |
|
| 2473. |
A particle of mass m and charge (-q)enters the regions between the two chargedplatesinitially moving along x-axis with speed v_x(like particle 1 in.) The length of plate is Land an the particleat the far edge of the plateis qEL^(2)//(2mv_x^(2)) . |
|
Answer» Solution :Leta particle of mass m, charges -q andinitialspeed ` v_x` along x-axisenters a uniform electricfield region at O. The field `oversetto E ` is along y-axisas shown in and EXTENDS to a length L. As there is no field along x-axis , velocity `v_x`along x- axis remains uncharged and time taken by chargesparticle to cross the field t`= ( L)/( v_x) ` . Forceexperiencedby charged particle along y-axis. ` |oversetto F|=-qoversetto E `towards +ve charged plate. ` therefore ` Acceleration of charged particlealong y-axis `a_y =(F)/(m) = ( qE)/( m) ` (towards +ve chargedplate). ` therefore ` Deflection SUFFERED bycharged particle along y-axis,while crossing the ELECTRIC field, is GIVEN by ` y=(1)/(2)a_yt^(2)=(1)/(2)xx ( (qE)/(m )) xx ((L)/(v_x))^(2)=(qEL^(2))/( 2mv_x^(2)) ` (towards +ve charged plate) 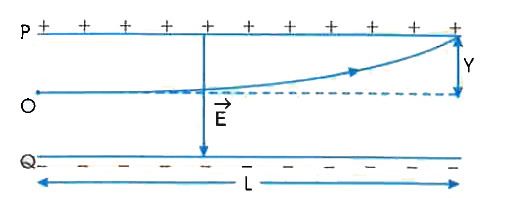
|
|
| 2474. |
Obtain the frequency of revolution of the electron in its circular orbit. Does the answer depend on the speed of the electron? Explain. |
|
Answer» Solution :When a particle of mass m and charge q performs uniform circular motion with CONSTANT speed v in a plane perpendicular to uniform magnetic field B, radius of its circular path is, `R=(mv)/(Bq)` `thereforer=(m(romega))/(Bq)""(becausev=romega)` `thereforeomega=(Bq)/m` (Where `OMEGA` = angular frequency) `therefore2pif=(Bq)/m` (Where f = frequency of revolution = no. of revolutions in unit time) `thereforef=(Bq)/(2pim)` `thereforef=((6.5xx10^(-4))(1.6xx10^(-19)))/((2)(3.14)(9.1xx10^(-31)))` `thereforef=18.2xx10^(6)Hz` (= 18.2 MHz) `thereforef=1.82xx10^(7)Hz` |
|
| 2475. |
The value of e.m.f. depends upon: |
|
Answer» The RATE of CHANGE of MAGNETIC flux |
|
| 2476. |
In the figure shown the wires AB and PQ carry constant currents I_(1) and I_(2) respectively. PQ is of uniformly distributed mass ‘m’ and length ‘l’ AB and PQ are both horizontal and kept in the same vertical plane. The PQ is in equilibrium at height ‘h’. Find ‘h’ is terms of I_(1) I_(2) , l, m, g and other standard constants. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :MAGNETIC repulsive force balnaces the WEIGHT. `(mu_(0)I_(1)I_(2))/(2pih)l=mgimpliesh=(mu_(0)I_(1)I_(2)l)/(2pimg)` |
|
| 2477. |
In the figure shown the wires AB and PQ carry constant currents I_(1) and I_(2) respectively. PQ is of uniformly distributed mass ‘m’ and length ‘l’ AB and PQ are both horizontal and kept in the same vertical plane. The PQ is in equilibrium at height ‘h’. Find If the wire PQ is displaced vertically by small distance prove that it performs SHM. Find its time period in terms of h and g. |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Let the wire be displaced downward by distance `x(ltlth)`. Magnetic force on it will increase, so it goes back towards its equilibrium position. Hence it PERFORMS oscillations. `F_(res)=(mu_(0)I_(1)I_(2))/(2pi(h-x))l-MG` `=(mgh)/(h-x)-mg=(mg(h-h+x))/(h-x)` `=(mg)/(h-x)x~=(mg)/(h)x" for "xltlth` `therefore T=2pisqrt((m)/(mg//h))=2pisqrt((h)/(g))` |
|
| 2478. |
The work function of carsium metal is 2.14eV. When light of frequency 6 xx10^14 Hz is incident on the metal surface, photoemission of electrons occurs. (h=6.6 xx 10 ^-34 js):-Define work function. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :WORK function is the amount of energy REQUIRED for a electron to just ESCAPE from a metal surface | |
| 2479. |
In a metre bridge, two unknown resistances R and S, when connected in the two gaps, give a null point at 40 cm from one end. What is the ratio of Rand S? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`R/S = (L)/((100 - l)) = 40/60 = 2/3` | |
| 2480. |
The photoelectric threshold wavelength for lithium is 8000 Å. Find the maximum kinetic energy in eV of the emitted electrons from the surface by light of wavelength 6000 Å. Take h=6.6 xx 10^(-34) Js. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 2481. |
An angular magnification (magnifying power ) of 30x is desired using on objective of focal length 1.25 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 5cm. How will you set up the compound microscope ? |
|
Answer» Solution :`m_(0) = (v_(0))/(-u_(0)) , m_(e) = 1 + (D)/(f_(e)) , m = m_(o) m_(e)` `m_(e) = 1 + (25)/(5) = 6 , m = 30"" m_(0) = (m)/(m_(e)) = (30)/(6) = 5 ` ` m_(0) = (v_(0))/(-u_(0)) "i.e," 5 = (v_(0))/(-u_(0)) , v_(0) = - 5u_(0), f_(0) = 1.25 cm "" therefore (1)/(v_(0)) - (1)/(u_(0)) = (1)/(f_(0))` `(1)/(-5u_(0)) - (1)/(u_(0)) = (1)/(1.25)` Sovling `rArr u_(0) = - 1.5 cm and v_(0) = + 7.5 cm` Then `(1)/(v_(e)) - (1)/(u_(e)) = (1)/(u_(e)) = (1)/(f_(e)) , (1)/(-25) - (1)/(u_(e)) = (1)/(5) ` `- (1)/(u_(e)) = (1)/(5) + (1)/(25) = (6)/(25) "" therefore u_(e)= (-25)/(6) = - 4.2 ` cm DISTANCE between objective and eyepiece = `v_(0) + |u_(e) |= 7.5 + 4.2 = 11.7 ` cm POSITION of the OBJECT from objective = `|u_(0)| = 1.5 ` cm |
|
| 2482. |
Read the following paragraph and answer the following questions. According to Kelvin Planck's statement of second law of thermodynamic no process is possible whose sole result is the adsorption of heat from a reservoir and the complete conversion of heat into work. A carnot heat engine works at temperatures 227^(@)C and 127^(@)C. It absorbs 6.0 xx 10^(4) calories of heat from the source at high temperature in each cycle. The amount of heat converted into work in above carnot engine is : |
|
Answer» `1.2xx10^(4)` cals `therefore eta =(W)/(theta_(1)) rArr W=(1)/(5) xx6xx10^(4)=1.2xx10^(4)` cal So, correct choice is (a). |
|
| 2483. |
Read the following paragraph and answer the following questions. According to Kelvin Planck's statement of second law of thermodynamic no process is possible whose sole result is the adsorption of heat from a reservoir and the complete conversion of heat into work. A carnot heat engine works at temperatures 227^(@)C and 127^(@)C. It absorbs 6.0 xx 10^(4) calories of heat from the source at high temperature in each cycle. The amount of heat rejected to sink at lower temperature is: |
|
Answer» `1.2xx10^(4)` cals `=6xx10^(4)-1.2xx10^(4)` `=4.8xx10^(4)` cal So, CORRECT CHOICE is (d). |
|
| 2484. |
Read the following paragraph and answer the following questions. According to Kelvin Planck's statement of second law of thermodynamic no process is possible whose sole result is the adsorption of heat from a reservoir and the complete conversion of heat into work. A carnot heat engine works at temperatures 227^(@)C and 127^(@)C. It absorbs 6.0 xx 10^(4) calories of heat from the source at high temperature in each cycle. The efficiency of engine is: |
|
Answer» 0.2 So, CORRECT CHOICE is (a). |
|
| 2485. |
Read the following paragraph and answer the following questions. According to Kelvin Planck's statement of second law of thermodynamic no process is possible whose sole result is the adsorption of heat from a reservoir and the complete conversion of heat into work. A carnot heat engine works at temperatures 227^(@)C and 127^(@)C. It absorbs 6.0 xx 10^(4) calories of heat from the source at high temperature in each cycle. By how much the temperature of the sink be decreased so as to make efficiency of engine 50% keeping temp. of source fixed. |
|
Answer» `25^(@)C` `(T_(2))/(T_(1))=(1)/(2) rArr T_(2)=(500)/(2)=250 K` `therefore T_(2)-T_(2)=400-250 =150 K` So, correct choice is (c ). |
|
| 2486. |
अंड - प्रजक निम्नांकित में कौन हैं ? |
|
Answer» सर्प |
|
| 2487. |
जब प्रकाश की एक किरण दो माध्यमों को अलग करनेवाली सतह पर लंबवत पड़ती है, तो वह |
|
Answer» अभिलंब से दूर मुड़ जाती है |
|
| 2489. |
In above case, if instantaneous value of electric field at a given point on the direction of propagation of wave is 24hat(i)(N)/(C ) then find magnetic field at the same point at the same instant. What would be its frequency of oscillations ? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`VEC(B)=8XX10^(-8)hat(j)T`and`v=10^(15)Hz` | |
| 2490. |
A person with a normal near point (25 cm) using a compound microscope with objective of focal length 8.0 mm and an eyepiece of focal length 2.5 cm can bring an object placed at 9.0 mm from the objective in sharp focus. What is the separation between the two lenses? Calculate the magnifying power of the microscope. |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, D = 25 CM, `f_(0) = 8.0 mm = 0.8 cm, f_(e) = 2.5 cm` and `u_(0) = -0.0 mm = -0.9 cm` using relation `1/v_(0) -1/u_(0) = 1/f_(0)` we have `1/v_(0) -1/(-0.9) rArr v_(0) = 7.2 cm` Again using the relation `1/v_(e) -1/u_(e) =1/f_(e)`, we have `1/(-25)-1/u_(e) =1/2.5` or `-1/u_(e) =1/2.5 + 1/26 = 11/25 rArr u_(e) =-25/11 cm = -2.27` cm `therefore` MAGNIFYING POWER of the microscope `=-v_(0)/u_(0) (1+D/f_(e)) =-7.2/(-0.9) xx (1 + 25/2.5) = 88` |
|
| 2491. |
The simplest form of 0.12bar3- |
|
Answer» `41/330` |
|
| 2492. |
The frequency of the first overtone of a closed-pipe of length l_(c) is equal to that of the second overtone of an open pipe of length l_(o). Then the ratio l_(c)//l_(o) is equal to |
|
Answer» `1/2` |
|
| 2493. |
(a) Write two properties by which electric potential is related to the electric field . (b) Twopoint chargesq_(1) and q_(2)separated by a distance of r_(12) are kept in an external electric field. Derive an expression for the potential energy of the system of two charges in the field. |
|
Answer» Solution :(a) From the relation `E =-(dv)/(dr)` (i)The magnitude of ELECTRIC field intensity is numerically equal to potential GRADIENT. (ii) Negative sign signifies the electric field intensity is in the direction of decreasing electric potential gradient. Consider a system of two point charge `q_(1) and q_(2) " such that " q_(2)` is intially far away from `q_(1)` in free space. Charge `q_(1)` PROVIDES necessary electric field all around it work is done to bring charge `q_(2)` from infinity to point B near A,` W= q_(2) V, ` V is potential at B due to `q_(1)` Also` V=1/(4pi in_(0))(q1)/(AB) rArr W=1/(4pi in _(0)) (q_(1)q_(2))/(AB),AB=|vec(r_(2))-vec(r_(1))|` `W_(1) = 1/(4pi in _(0)) (q_(1) q_(2))/(|vec(r_(2))-vec(r_(1))|)=1/(4piin_(0))(q_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12))` If `vec(E)_(r)` External electric field then the work -done to bring the CHARGES `q_(1) and q_(2)` to their position from the infinity are `W_(2)=q_(1)(r_(1)) E_(1) and W_(3)=q_(2)(r_(2))E_(2)` `:. " Total work done "W= w_(1) + w_(2) + w_(3)` `U=1/(4pi in_(0)) (q_(1)q_(2))/(|vec(r_(1)) -vec(r_(2))|)+q_(1)(r_(1))E + q_(2) (r_(2)) E` 
|
|
| 2494. |
The dimensional formula of angular momentum is equal to that of the |
|
Answer» FORCE X time |
|
| 2495. |
As shown in the figure, a particle is placed at O in front of a plane mirror M. A man at P can move along path PY and PY'. Then which of the following is true ? |
|
Answer» For all point on PY, the man can SEE the image of O |
|
| 2496. |
The plates of a parallel plate capacitor have an area of 90 cm^2? each and are separated by 2.5 mm. The capacitor is charged by connecting it to a 400 V supply. View this energy as stored in the electrostatic field between the plates and obtain the energy per unit volume u. Hence arrive at a relation between u and the magnitude of electric field E between the plates. |
|
Answer» Solution :Volume of the capacitor= A.d `= 90 xx 10^(-4) xx 2.5 xx 10^(-3) = 2.25 xx 10^(-3) = 2.25 xx 10^(-5) m^3` `:.` Energy per unit volume `u = (uu)/(Ad) = (2.55 xx 10^(-6))/(2.55 xx 10^(-5)) = 0.113 J m^(-3)` Relation between energy density u and electric FIELD E : We know that energy STORED in a capacitor is given by `uu = 1/2CV^2 = 1/2 (epsi_0AV^2)/d` and volume of the capacitor = Ad `:.` Energy density `u = u/(Ad)=((1/2epsi_0AV^2)/d)/(Ad) = 1/2epsi_0 V_2/d^2 = 1/2 epsi_0 E^2.` where `V/d = E` = electric field between the plates of capacitor. |
|
| 2497. |
In Young's double-slit experiment the distance between the slits is 1 mm and that between slit and screen is 1m. If 10th bright fringe is 5 mm away from the central bright fringe, then wavelength of light used will be |
|
Answer» 5000 Å here `d=1mm=10^(-3),D=1m,n=10,x=5mm=5xx10^(-3)m`, hence `LAMDA=(xd)/(nD)=(5xx10^(-3)xx10^(-3))/(10xx1)=5xx10^(-7)m=5000` Å |
|
| 2498. |
The plates of a parallel plate capacitor have an area of 90 cm^2? each and are separated by 2.5 mm. The capacitor is charged by connecting it to a 400 V supply. How much electrostatic energy is stored by the capacitor ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here `A = 90 cm^2 = 90 XX 10^(-4) m^2, d = 2.5 mm = 2.5 xx 10^(-3) m and V = 400 V` `:." Capacitance " C = (epsi_0A)/d = (8.85 xx 10^(-12) xx 90 xx 10^(-4))/(2.5 xx 10^(-3)) = 31.86 xx 10^(-12) F` `:. " Electrostatic energy " U = 1/2 CV^2= 1/2 xx 31.86 xx 10^(-12) xx (400)^2 = 2.55 xx 10^(-6)J` |
|
| 2499. |
(A) : Dimensionless quantities have no units. (R): Unitless quantities have no dimensions. |
|
Answer» Both (A) and (R) are TRUE and (R) is the correct EXPLANATION of (A) |
|
| 2500. |
A full wave rectifier uses two diodes, the internalresistance of each diode may be assumed constant at 25Omega. The transformer r.m.s. secondary voltage from centre tap to each end of the secondary is 50V and land resistance is 975Omega. Find the mean load current |
|
Answer» `45xx10^(-3)A` Max. load current, `I_(0)=(V_(0))/(r+R)` MEAN load current, `I_(m)=(2I_(0))/(pi)` `I_(r.m.s)=(I_(0))/(sqrt2)` |
|