Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 42051. |
Removal of anther from the floral bud is called |
|
Answer» Anthesis |
|
| 42052. |
Draw a graph showing the variation of reactance of (i) a capacitor and (ii) an inductor with the frequency of an a.c circuit. |
|
Answer» Solution :i. CAPACITIVE reactance `X_(c)=(1)/(2pigammac)` `X_(c)alpha(1)/(gamma)` The graph between `gammaandX_(C)andgammaandX_(L)`  II. Inductive reactance `XL=2pigammaL` `X_(L)alphagamma` |
|
| 42053. |
The red shift of radiation from a distant nebula consists of light known to have a wavelength of 434 nm. In the laboratory, this wavelength appears to be 6562 Å. What is the speed of the nebula in the line of sight relative to the earth ? Is it approaching or receding ? |
|
Answer» `lambda' = 6562 Å = 6562 xx 10^(-10)m`. As `v' = ((1 - v//c))/(sqrt(1 - v^(2)//c^(2))) = sqrt((1 - v//c)/(1 + v//c)) v` `:. (1 - v//c)/(1 + v//c) = ((v')/(v))^(2) = ((lambda)/(lambda'))^(2) = ((434 xx 10^(-9))/(6562 xx 10^(-10)))^(2)` `(1 - v//c)/(1 + v//c) = ((v')/(v))^(2) = 0.437`. On solving, we get `v = 1.2 xx 10^(8)ms^(-1)` As apparent wavelength increases, the NEBULA must be receding AWAY from earth. |
|
| 42054. |
In extrinsic p-type and n-type semiconductor materials, the ratio of the impurity atoms to the pure semiconductor atoms is about : |
|
Answer» 1 |
|
| 42055. |
Van der Waal's crystal are : |
|
Answer» very HARD |
|
| 42057. |
A large number of particles are placed around the origin, each at a distance R from the origin. The distance of the center of mass of the system from the origin is |
|
Answer» `=R` If are `ABto0` The position of CENTRE of mass will be at DISTANCE R from the origin. If are length AB increases, centre of mass of the system starts moving down ( < R). 
|
|
| 42058. |
Two small balls A and B, each of mass m, are joined rigidly at the ends of a light rof of length L. they are placed on a frictionless horizontal surface another ball of mass 2 m moving with speed u towards one of the ball and perpendicular to the length of the rod on the horizontal frictionless surface as shown int he figure. if the coefficient of restitution is 1/2 then the angular speed of the rod after the collision will be |
|
Answer» `(4)/(3)(u)/(L)` Velocity of ball 'B' just after the collision =0 `thereforeomega(u-0)/(L)=(u)/(L)` |
|
| 42059. |
A circular coil of radius 2R is carrying current 'i' . The ratio of magnetic fields at the centre of the coil and at a point at a distance 6R from the centre of the coil on the axis of the coil is |
|
Answer» 10 |
|
| 42060. |
Fora conducting wire V rarr I graph is as shown in figure given below, therefore its resistance will be ..... |
|
Answer» `SIN 50^(@)` Slope of graph = `(dy)/(dx) = tan THETA` Here, dy= DV, dx = dI Now R = `(V)/(I), R = (dV)/(dI)` `therefore R = (d V)/(d I) = (dy)/(dx) = tan theta = tan 50 ` 
|
|
| 42061. |
How electromagnetic waves are produced ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Stationary charges or charges moving with constant velocity (steady current) cannot be source of electromagnetic waves. This is due to reason that stationary charge produce electric field and moving charges produce electric field and magnetic field and these field do not change with time. According to Maxwell accelerated charges produces electromagnetic waves. Oscillating charge is example of accelerated motion. When charge is oscillating with some frequency, it produces electric and magnetic field oscillating in the space. When this phenomena is repeated electric and magnetic field propagates in the space which are called electromagnetic waves. It propagates in direction perpendicular to electric and magnetic field. Electric and magetic field oscillates perpendicular to each other. Frequency of electromagnetic waves is equal to frequency of charge oscillating. Energy of accelerated charge is imparted to electromagnetic waves propagating. It is easy to imagine that light is electromagnetic waves but difficult to test in laboratory because by using MODERN electronic CIRCUIT frequency on `10^(11)` Hz can be obtained by frequency of yellow light obtained in visible spectrum is about `6xx10^(14)Hz`. HENCE, to give experiment proof of electromagnetic waves Hertz experiment should be performed in lower range of radio waves. After success of Hertz experiment, Jagdish Chandra Bose working at KOLKATA succeeded in PRODUCING and observing electromagnetic wave of much shorter wavelength (25 mm to 5 mm). His experiment was confined to the laboratory. During this time Italian scientist Marconi want success in sending electromagnetic waves to serveral miles. |
|
| 42062. |
A charge q is placed at the centre of a hollow sphere of radius r, Total electric flux passing through the spherical surface is __________ |
|
Answer» |
|
| 42063. |
Point A on the rod AB has an acceleration of 5m//s^(2) and a velocity of 6m//s at an instant as shown in the figure. The acceleration of the end B at the same moment is: |
|
Answer» `-80/3hati m//s^(2)` `=-5j+4alphai+3alphaj-(12i-16j)` `a_(B)` along `y` axis should be ZERO `implies 11+3alpha=0` `impliesalpha=-4/3"RAD"//s^(2)` `a_(B)=(4alpha-12)i=-80/3im//s^(2)` |
|
| 42064. |
What is/are "tepui"? |
|
Answer» is a table-top mountain |
|
| 42065. |
We know that magnetic substances follow curie- weiss Law. In the given table, Column I shows the type of attraction with magnets of magnetic substances, Column II shows the example of magnetic substances and Column III shows the three figures- figure (I) shows direction of magnetic momentum of each electron when there is no magnetic field inside magnetic substance, figure (II) shows the direction of magnetic momentum of electron when there is magnetic field inside magnetic substance and figure (III) shows the curve between M and H inside magnetic substance. Which combination is characteristic of ferromagnetic materials ? |
|
Answer» (I)(III)(L) |
|
| 42066. |
The following table has 3 columns and 4 rows. Based on table, there are three questions. Each question has options (A), (B),(C ), and (D) ONLY ONE of these four options is correct. The AC generator shown in the figure supplies V volt at an angular frequency omega. The switch can be in two position 1 or 2 L, C, R have their usual meaning . then answer the following questions. The circuit is adjusted for resonance with the switch pushed to position 1. in witch case the sharpness of the resonance will be maximum ? |
|
Answer» <P>(IV) (iv) (P) |
|
| 42067. |
The logic gate circuit given below acts as |
|
Answer» an OR GATE |
|
| 42068. |
The following table has 3 columns and 4 rows. Based on table, there are three questions. Each question has options (A), (B),(C ), and (D) ONLY ONE of these four options is correct. The AC generator shown in the figure supplies V volt at an angular frequency omega. The switch can be in two position 1 or 2 L, C, R have their usual meaning . then answer the following questions. The circuit is adjusted for resonance as in the previous question and the frequency of the source is set to the appropriate value. The switch is now suddenly switched to position 1. For which case will the voltage drop across the capacitor be 50% of the that across the resistor ? |
| Answer» Answer :A | |
| 42069. |
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in figures above |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(i) `(16//3) OMEGA(II) 5 R` | |
| 42070. |
The following table has 3 columns and 4 rows. Based on table, there are three questions. Each question has options (A), (B),(C ), and (D) ONLY ONE of these four options is correct. The AC generator shown in the figure supplies V volt at an angular frequency omega. The switch can be in two position 1 or 2 L, C, R have their usual meaning . then answer the following questions. In which of the following cases the circruit will resonates at an angular frequency omega = 100 rad/sec with the switch in position 2? |
|
Answer» (II)(ii)(Q) |
|
| 42071. |
State the conditions under which power factor is (i) maximum, and (ii) minimum. |
|
Answer» Solution : (i) Power factor is maximum at 1 when EITHER the a.c. CIRCUIT is pure resistive circuitor is in resonance condition. (ii) Power factor is minimum at zero when a.c. circuit is either pure INDUCTIVE or pure capacitive or a combination of TWO. |
|
| 42072. |
A 1.00 xx 10^(-20)kg particvle is performing S.H.M. with a period of 1.00 xx 10^(-5) s andwith maximum velocity 1.00 xx 10^(3) m//s. The maximum displacement from the mean position is |
|
Answer» 10 mm |
|
| 42073. |
Lorentz force is given by |
|
Answer» Q `(E + V XX B)` |
|
| 42074. |
The dielectric strength of air is 3xx10^6Vm^(-1). At certain |
|
Answer» Solution :Dielectric strength of air `E_(0)=3xx10^6V m^-1` Electric field intensity between the PLATES , `E=(E_0)/(K)=3xx10^6Vm^(-1)[because "for air" K=1]` Distance between two plates , `d=1cm=10^-2m` Electric potential difference between plates ,`V=Ed =3xx10^6xx10^-2` `therefore V=3xx10^4` Volt. Hence we can't CHARGE the capacitor UPTO `3xx10^6` Volt. |
|
| 42075. |
In a photon-particle collision (sauch as photon-electron collision), which of the following may not be conserved ? |
|
Answer» Total ENERGY |
|
| 42076. |
A mobile phone lies along the principal axis of a concave mirror, as shown in Fig. 9.7. Show by suitable diagram, the formation of its image. Explain why the magnification is not uniform. Will the distortion of image depend on the location of the phone with respect to the mirror? |
|
Answer» Solution :`rArr`Mobile AB is placed such that is end B is at C and end A is between C and F. `rArr` IMAGE of B is obtained on the same PLANE but inverted at C is B. `rArr`Image of A is obtained on the same plane but inverted at C is B. `rArr` Image of A is obtained away from mirror beyond C and inverted and it is A. magnified than A. `rArr`Thus, magnification `m= -(v)/(u)` will not be same for all points as v and u are DIFFERENT. `rArr`YES, magnification of image changes withchange in distance of mobile from mirror. Hence, DISTORTED image is obtained. |
|
| 42077. |
What is potentiomter ? What is its principle ? How will you find the internal resistance of a cell by a potentiometer? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Potentiometer. It is an instrument used to compare to e.m.f. of two cells ND to find the internal resistance of a cell. Principle. It is based on the principle that when a constant currents is passed through a wire of uniform area of cross-section, the potential drop across any portion of the wire is directly proportional tot he length of that portion. 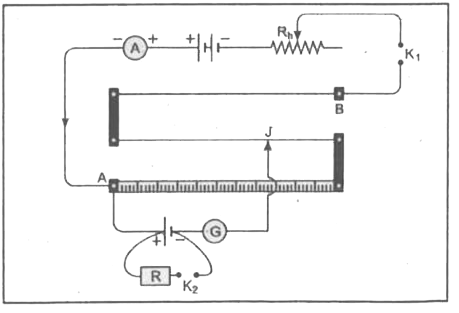 Internal resistance of a cell. The resistance offered by the electrolyte of the cell to the flow of the ions through the electrolyte is called internal resistance of the cell. To determine internal resistance of a cell by a potentiometer. The circuit used for FINDING the internal resistance of a cell is as shown in the figure. A constant CURRENT I is maintained through the potentiometer wire with the help of the rheostat. potentiometer wire with the help of the rheostat. Plug in the key `K_(2)` is kept out and the jockey is moved over the potentiometer wire so as to balance the e.m.f. E of the cell, whose intenral resistance is to befound. let `l_(1)` be the balancing length of the potentiometer wire between point A and jockey J. then `Epropl_(1)`. . (1) With the help of resistance box S, introduce resistance, say S and then put in key `K_(2)`. now find the balance point for the terminal potential difference V between the two poles of the cell. if `l_(2)` is the balancing length, then `Vpropl_(2)`. . (2) From equation (1) and (2), we have `(E)/(V)=(l_(1))/(l_(2))`. . (3) Since internal resistance (r) of cell is given by `r=[(E)/(V)-1]R` USING equation (3), we get `r=[(l_(1))/(l_(2))-1]R=[(l_(1)-l_(2))/(l_(2))]R`. |
|
| 42078. |
Four vessels A,B,C and D contain respectively 20g atom (T_(1//2) = 5h) 2g atom (T_(1//2)=1h) 5g atom (T_(1//2) = 2h)and 10g atom (T_(1//2) = 3h) of different radio nuclides in the 12 beginning, the maximum activity would be exhibited by the vessel is |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`R=lambdaN=0.693/T_(1//2)N` Hence, greater `(N/T_(1//2))` value , greater will be the RATE .So A has Maximum ACTIVITY. |
|
| 42079. |
What is the magnetic moment of a semi circular mag net of radius 'r' and pole strength 'm'? |
| Answer» Solution : A. Magnetic moment = distance between poles `XX` POLE STRENGTH = m `xx` 2R = 2mr | |
| 42080. |
The electric field in a region of space is given by E= 5i + 2j N//C. The electric flux due to this field through an area 2m^2 lying in the YZ plane, in S.I. units, is |
| Answer» ANSWER :A | |
| 42081. |
What is the focal length of a convex lens of focal length 30cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20cm? Is the system a converging or a diverging lens? Ignore thickness of the lenses. |
| Answer» SOLUTION :A diverging lens of focal LENGTH 60 cm | |
| 42082. |
Assertion : Magnetic field is useful in producing parallel beam of charged particle. Reason : Magnetic field inhibits the motion of charged particle moving across it. |
|
Answer» If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the CORRECT explanation of assertion. |
|
| 42083. |
In Melde's experiment, |
|
Answer» `TP^2=constant` |
|
| 42084. |
If the temperature of the hot body is increased by 50% the amount of radiation emitted is increased by nearly : |
|
Answer» `50%` `rArr""(E_(2))/(E_(1))-1=5*06-1` `(E_(2)-E_(1))/(E_(1))xx100=4*06xx100=400%` Thus correct choice is (d). |
|
| 42085. |
Two coherent point sources S_1 " and "S_2 vibrating in phase light of wavelength lambda. The separation between the sources is 2lambda. The smallest distance from S_(2) on a line passing through S_2 and perpendicular to s_(1)s_(2) where a minimum of intensity occurs is |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :Path difference at `s_(2)" is "2lambda`. Therefore for MINIMUM intensity at P let x be the minimum distance from `s_(2)`. Then`s_(1)P-s_(2)P= (3lambda)/(2) ne (lambda)/(2)"………"(1)` or `SQRT(4lambda^(2)+ x^(2))-x= (3lambda)/(2)` Solving this equation we get `x= (7lambda)/(12)`  . .
|
|
| 42086. |
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a compound microscope and give the expression for its overall magnification. |
Answer» Solution :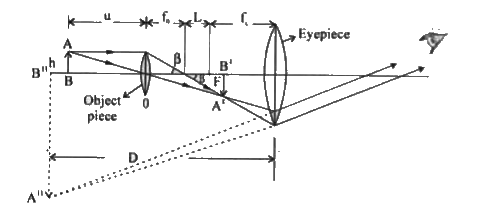 Here `m_(0)= (L+f_(e))/(-f_(0))` and `m_(1)=1+(D)/(f_(e))` so that overall magnification`m=m_(0)m_(e)=((L+f_(e))/(-f_(0))) (1+(D)/(f_(e)))` for image at near point and `m=((L)/(-f_(0)))((D)/(f_(e)))` for image at infinity. The image due to the object piece will be formed at or in FRONT of FOCUS of the EYE piece. The distance between the SECOND focal length of the objective and the first focal length of the eye piece is called the tube length (L) of the compoundmicroscope. |
|
| 42087. |
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV. If an electron makes a transition from an energy level -0.85 eV to -1.51 eV, Calculate the wavelength of the spectral line emitted. To which series of hydrogen spectrum does this wavelength belong? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :Here `Delta E = E_(2) - E_(1) = -0.85 - (-1.51)` ` = 0.66 eV` `Delta E = 0.66 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19)`J ` lambda = (he)/(Delta E) = (6.63 xx 10^(-34) xx 3 xx 10^(8))/(0.66 xx 1.6 xx 10^(-19))` ` = 18.84 xx 10^(-7)` `lambda = 18840 Å` This wavelength belongs to the Pachen series of the hydrogen spectrum. |
|
| 42088. |
The magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given by B. =(2 xx 10^(-7)T) sin[500x+1.5 xx 10^(11) t]What is the wavelength and frequency of the wave? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`1.26cm, 2.4 XX 10^(10)HZ` | |
| 42089. |
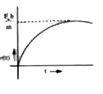
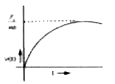
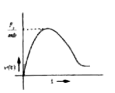
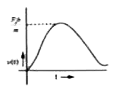
A particle of mass m is at rest at the origin at time t = 0. It is subjected to a force F(t) = F_0 e^(-bt) in the x direction. Its speed v(t) is depicted by which of the following curves? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 42090. |
A particle starts from origin af i = 0 with a velocity 5.0 hati m//s and moves in x-y plane under action of a force which produces a constant acceleration of (3.0i+2.0j) m//s^(2) ?. (a) What is the y-coordinate of the particle at the instant its x-coordinate is 84 mn? (b) what is the speed of the particle at this time? |
|
Answer» Solution :The position of the PARTICLE is given by `r(t)=v_(0)t+(1)/(2) "at"^(2)=5.0hati t+(1//2)(3.0 hati+2.0 hatj)t^(2)` `=(5.0t+1.5t^(2))hati+1.0 t^(2) hatj` THEREFORE `x(t)=5.0t+1.5t^(2), y(t)=+1.0 t^(2)` Given `x(t)=84 m , t= ` `5.0t+1.5t^(2)=84 rArr t=6s` At `t=s, y=1.0 (6)^(2)=36.0 m` Now the velocity `V=(dr)/(dt)=(5.0+3.0t)hati+2.0 t hatj` At `t=6 s, v=23. hatj+12.0 hatj` Speed `=|v|= sqrt(23^(2)+12^(2))=26 m s^(-1)` |
|
| 42091. |
Condition for n^(th) maximum in single slit diffraction is ..... where n = 1, 2, 3, |
|
Answer» `a sin theta_(n)=(n-(1)/(2))LAMBDA` |
|
| 42092. |
Show that the capacitance of an insulated spherical conductor is directly proportional to the radius of the conductor. |
|
Answer» Solution :Since the capacitance of a conductor C is given by `C=(Q)/(V)` . . (i) Potential of sphere of radius R is given by `V=(1)/(4piepsi_(0))(Q)/(r)` . . (ii) Putting eq. (ii) in eq. we GET `C=(Q)/((1)/(4piepsi_(0))(Q)/(r))=4piepsi_(0)r` or `Cpropr` i.e. capacitance of a spherical conductor is directly proportional to the radius of the conductor. |
|
| 42093. |
If one microgram of""_(92)^(235)Uis completely destroyed in an atom bomb, how much energy will be released ? |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 42094. |
वैद्युत द्विध्रुव से r दुरी पर विद्युत - क्षेत्र निम्न के अनुक्रमानुपाती होता है - |
|
Answer» `1/r` |
|
| 42095. |
The insulated plates of a charged parallel plate capacitor are approaching each other due to electrostatic attraction. Assuming no other force to be operative and no radiation taking place, which of the following graphs approximately shows the variation with time (t) of the potential difference (V) between the plates? |
|
Answer»
|
|
| 42096. |
Draw the ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a prism. |
Answer» SOLUTION :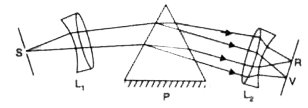
|
|
| 42097. |
A monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process as shown in the figure. The idealgas follows the equation T=bV^(2) for the process BtoC. During the cycle, the ratio of maximum to minimum pressure is 2and heat supplied to the gas BtoC is Q_(BtoC)=120J Assuming usual meanings for the symbols, pick correct option (s): |
|
Answer» `P_(A)=P_(C)` So, `Q_(BtoC)=nC(T_(C)-T_(B)=2NR(T_(C)-T_(B))` Also, `(T_(C))/(T_(B))=4, (T_(A))/(T_(B))=2` THUS, `Q_(BtoC)=6nRT_(B)`. `Q_("NET")=(-nRT_(B))/2impliesQ_(CtoAtoB)=-130J` |
|
| 42098. |
You testify as an expert witness in a case involving an accident in which car A slid into the rear of car B, which was stopped at a red light along a road headed down a hill (Fig. 6-40). You find that the slope of the hill is theta= 1.0^(@), that the cars were separated by distance d = 30.0 m when the driver of car A put the car into a slide (it lacked any automatic anti-brake-lock system), and that the speed of car A at the onset of braking was v=18.0 m/s. With what speed did car A hit car B if the coefficient of kinetic friction was (a) 0.60 (dry road surface) and (b) 0.10 (road surface covered with wet leaves)? mu Figure 6-20 Problem 16 |
| Answer» SOLUTION :`(a) 10.0 m//s(B) 19.7 m//s` | |
| 42099. |
An equil convex lens of focal length 10 cm (in air) and R.l.4//3 is put at a small opening on a tube of length 1 m fully filled with liquid of R.l.4//3.A concave mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm is cut into two halves m_(1) and m_(2) and placed at the end of the tube. m_(1) & m_(2) are placed such that thir principal axis AD, and CD respectively are separated by 1 mm each from the principal axis of the lens. A slit S placed in air illuminates the lens with light of frequency 7.5xx10^(14) Hz. The light reflected from m_(1) and m_(2) forms interference pattern on the left end EF of the tube. O is an opaque substance to cover the hole left by m_(1) & m_(2). Find : (a) the position of the iamge formed by lens water combination. (b) the distance between the images formed by m_(1) & m_(2). (c) width of the fringes on EF |
|
Answer» `(1)/(f)=(mu-1)((1)/(R)-(1)/(-R)) rArr (1)/(10)=((3)/(2)-1)((2)/(R)) rArr R=10 cm`. Now  for lins : `(1)/(V)-(1)/(-20)=(1)/(10) rArr (1)/(V)=(1)/(20)` `rArr` for surface of tube (of `R=10 cm`.) `(mu_(2))/(V)-(mu_(1))/(u)=(mu_(2)-mu_(1))/(R) rArr (4//3)/(V)-(1)/(+20)=(4//3-1)/(-10) rArr V=+80 cm`. (b) Now for mirrors. 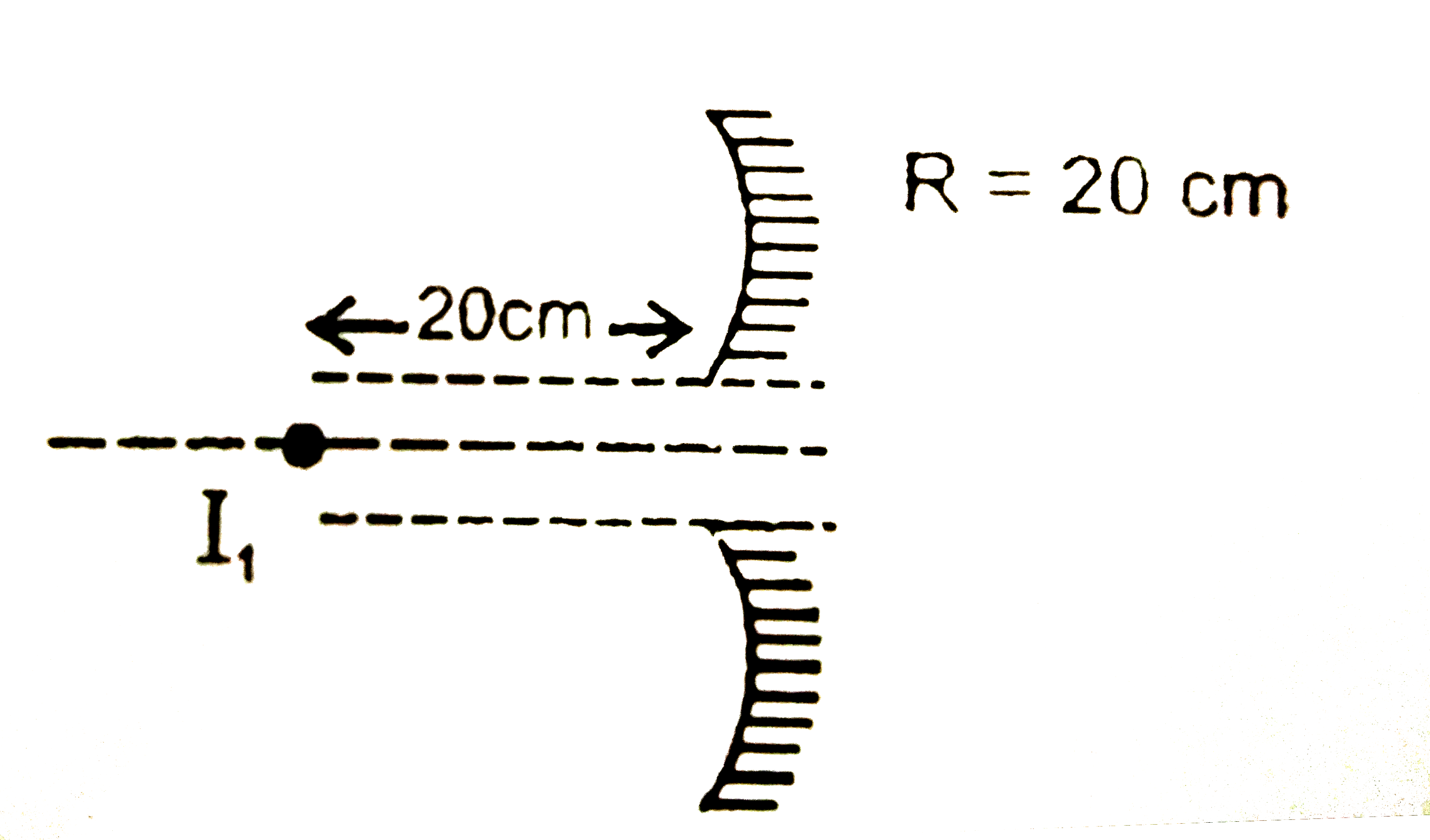 As the object for the mirrors is at `20 cm` so the image will be at `20 cm` only `therefore u=-2f` ALSO. `rArr` magnifiction `=m=(y_(1))/(y_(0))=(-v)/(u)` `rArr (y_(1))/(-(1mm))=^(-)((-20)/(-20)) rArr y_(1)=+(1 mm)` so the final images are like. 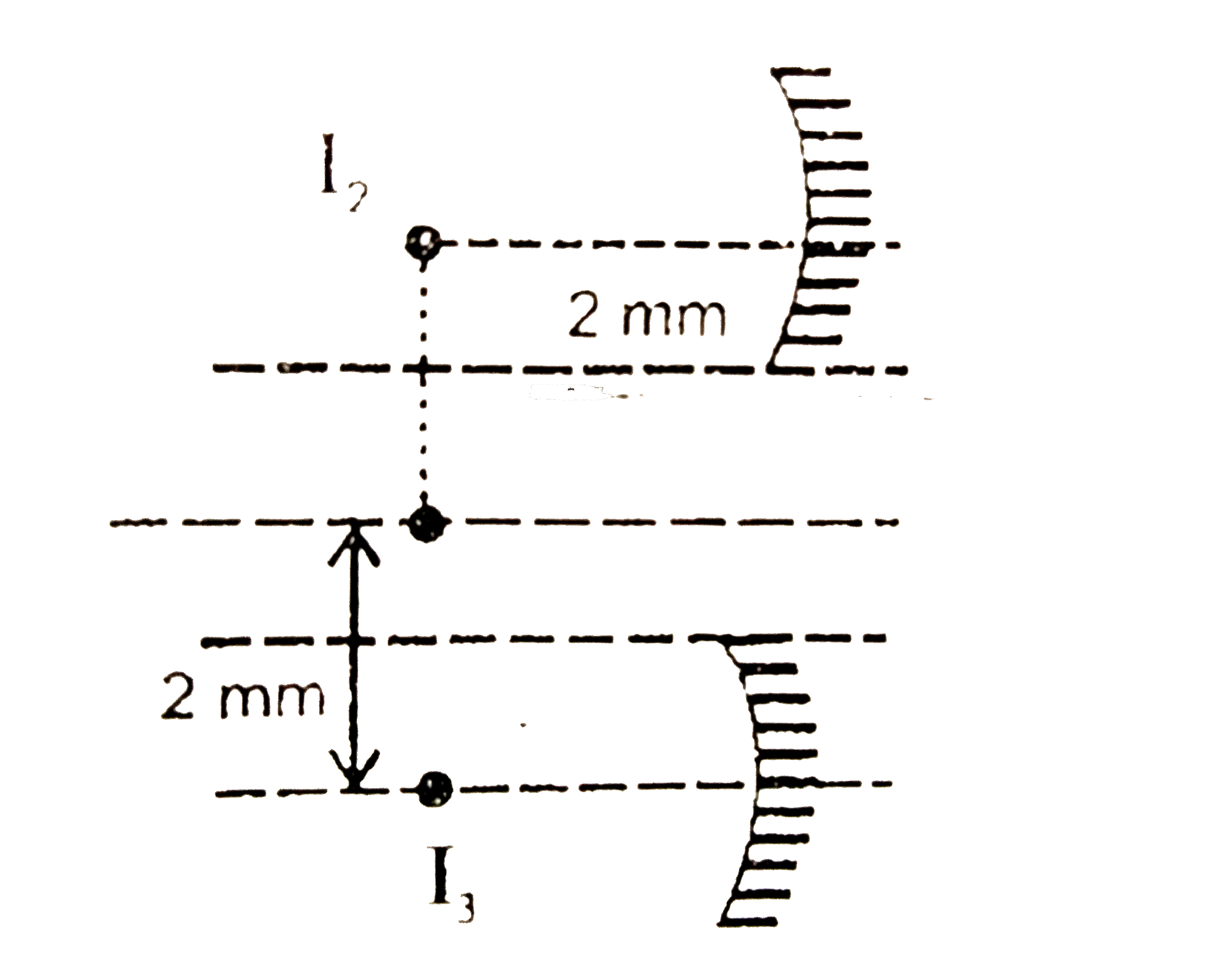 so the distance between the images is `4 mm`. (c) Now, these `I_(2) and I_(4)` BEHAVE as the `2` sources for fringe pattern. `rArr beta=(lambdaD)/(d)=(vD)/(fd) =((c//mu)D)/(fd)` `=((3xx10^(8))/((4)/(3)))xx(0.8)/((3)/(3)xx10^(15)xx(4xx10^(3))) =60 mum`. |
|
| 42100. |
A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved? |
|
Answer» Solution :Here, h=2.5 cm, `mu=-27 cm, R =-36 cm`. As per mirror formula `1/v + 1/u = 1/f = 2/R`, we have `1/v =1/f -1/u =2/R -1/u =2/(-36) -1/(-27) =-1/18 + 1/27 = -1/54 rArr v=-54 cm` Thus screen should be placed at a distance of 54 cm from the mirror in ORDER to obtain a sharp IMAGE of the candle. As `m=h./h =-v/u`, hence size of image `h. =-v/u. h =-(-54)/(-27) xx 2.5 = 5 cm` Thus, the image is real, MAGNIFIED and inverted image. If the candle is MOVED closer to the mirror, the screen has to be moved away from the mirror. In fact as `u lt f, v to infty`. However, if `u lt f` However, if `u lt f` then image formed is virtual and cannot be obtained on the screen. |
|