Explore topic-wise InterviewSolutions in .
This section includes InterviewSolutions, each offering curated multiple-choice questions to sharpen your knowledge and support exam preparation. Choose a topic below to get started.
| 37001. |
In the carbon cycle of fusion, |
|
Answer» Four `""_(1)H^(1)`fuse to FORM `""_(2)He^(4)` and two POSITRONS `4_(1)H^(1) rarr _(2)H^(4) + 2_(H)e^(0) + 2V + Energy` Four `""_(1)H^(1)`fuse to form `""_(2)He^(4)` and two positrons |
|
| 37002. |
Suppose that barbara's velocity relative to alex is a constant v_(BA) = 52 km//h and car P is moving in the negative direction of the x axis (a) If alex measures a constant v_(PA) = -78 km//h for car P , what velocity v_(PB) will barbara measure ?(b) If car P brakes to a stop relative to alex (and thus relative to the ground ) in time t = 10 sat constant acceleration , what is its acceleration a_(PA) relative to alex?(c ) What is the acceleration a_(PB) of car P relative to barbara during the braking? |
|
Answer» <P> Solution :We can attach a frame of reference A RO alex and a frame of reference B to barbara. Because the frames move at constant velocity relative to each other ALONG one axis , we can use`((v_(PA) = v_(PB) + v_(BA))` to relate `v_(PB)` to `v_(PA)` and `v_(BA)`(a)We find ` - 78 km//h = v_(PB) + 52 km//h` `v_(PB) = -130 km//h` (b) The initial velocity of P relative to alex is `v_(PA) = -78 km//h` and the final velocity is 0 . thus , the acceleration relative to alex is `a_(PA) = (v - v_0)/(t ) = (0 - (-78 km //h))/(10 s)(1m//s)/(3.6 km//h)` ` = 2.2 m//s^2` `a_(PA) = (v - v_0)/(t ) = (-25 km//h) - (-130 km//h))/(10 s) (1m//s)/(3.6 km//h)` ` = 2.2 m//s^2` |
|
| 37003. |
Founder of binomial nomenclature was |
|
Answer» Linnaeus |
|
| 37004. |
Explain effect of frequency of incident radiation in th experiment of photoelectric effect. |
Answer» Solution :Figure shows graph of variation of frequency of incident radiation at constant intensity in the experiment of photoelectric effect.  For different frequency of incident radiation stopping potential value obtained is different but saturation current is same. For frequency `V_(3)gtV_(2)gtV_(1)`,then stopping potential obtained also will be `V_(03)gtV_(02)gtV_(01)`. From this it can be said that when frequency of incident radiation is more then its energy of phtoelectron emitted will depend on enrgy (frequency) of incident radiation. When energy of photoelectron is more then more disaccelerating voltage (stopping potential) is required to stop them. For different METALS if graph of frequency of incident radiation and CORRESPONDING stopping potential is drawn then it will be a straight line as shown in figure.  Graph shows that: (i)For given photosensitive surface ,stopping potential varies linearly with frequency . (ii)For given minimum cut-off frequency `V_(0)` stopping potential will be zero. The above observatio suggest that: (i)Maximum kinetic energy of photoelectron varies linearly with frequency.But it does not depend on intensity. (ii)When frequency of incident radiation is less than cut-off frequency `V_(0)` the photoelectric emission will not take PLACE for any large value of intensity. |
|
| 37005. |
A body of mass 1 Kg is moving with a velocity 1 m/s, a wave is associated with this body : Name the wave |
| Answer» SOLUTION :MATTER WAVE | |
| 37006. |
A 50V battery is connected across a 10 ohm resistor. The current is 4.5A is flowing through the resistor then the internal resistance of the battery is |
|
Answer» ZERO |
|
| 37007. |
Assertion : Vibrational degree of freedom of a di-atomic gas molecule appears at every high temperatureReason : Di-atomic gas has two vibrational degree of freedom in one direction. |
|
Answer» If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the CORRECT EXPLANATION of assertion. |
|
| 37008. |
A potentiometer wire of length 1 m is connected to a driver cellof emf 3 V as shown in the Fig. When a cell of 1.5 V emf is used in the secondary circuit, the balance point is found to be 60 cm. On replacing this cell and using a cell of unknown emf, the balance point shifts to 80 cm.(i)Calculate unknown emf of the cell.(ii) Explain with reason, whether the circuit works, if the driver cell is replaced with a cell of emf 1V.(iii) Does the high resistance R, used in the secondary circuit affect the balance point? Justify your answer. |
|
Answer» Solution :(i) Here EMF of first cell `epsi_1 = 1.5 V, l_1 = 60 cm " and " l_2 = 80 cm` ` therefore ` emf of 2nd cell `epsi_2 = epsi_1 l_2/l_1 = 1.5 xx 80/60 = 2.0 V` (ii) If the driver cell of 3 V emf is replaced with a cell of emf 1 V, the circuit will not work. It is because, in order to obtain a NULL point on the potentiometer wire the fall in potential due to driver cell must be greater than the emf of the cell, whose emf is to be determined. (iii) The high resistance R, used in the SECONDARY circuit does not affect the balance point because atthe TIME of null point no current flows in the secondary circuit. |
|
| 37009. |
Explain electrostatic potential energy difference and give the noteworthy comments on it |
Answer» SOLUTION :At every point in electric field a PARTICLE with charge q possesses a certain electrostatic potential energy this work done INCREASES its potentialenergyby an amount equal to the potential energy difference between points R and P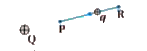 Thus potential energy difference , `U_(P)-U_(R)` `:. DeltaU=U_(p)-U_(R)` `:. DeltaU=W_(RP)` THEREFORE, we can define electric potential energy difference between two points as the work required to be done by an external force in moving (without accelerating) charge q from one point to another for electric field of any arbitrary charge configuration . Following comments may be made: (i) The right side of equation (1) depends only on the initial and final positions of the charge.It means that the work done by an electrostatic field in moving a charge from one point to another depends only on the initial and the final points and is independent of the path taken to go from one point to the other. This is the fundamental characteristic of a conservative force. (ii) The actual value of potential energy is not significant it is only the difference of potential energy that is significant. The potential energy difference, `(U_(P)-U_(R)=DeltaU_(RP)` f potential energy is zero at infinity an adding an arbitrary constant a to potentizenergy at every point then, `(U_(P)+alpha)-(U_(R)+alpha)=U_(P)-U_(R)` `:. (U_(P)+alpha-O-alpha)=U_(p)-U_(R)` `U_(P)=U_(P)-U_(R)` The work done for bringing a charge from point R to P at infinity distance, `W_(RP)=U_(P) or W_(propP) = U_(P)` SINCE above equation provides a definitior of potential energy of charge at any point F "Potential energy of charge q at a pointis the work done by the external force (equal and opposite to the electric field) in bringing the charge q from infinity to that point." |
|
| 37010. |
Find the angle of incident at face AB so that the emergent ray grazes along the face AC. |
|
Answer» Solution :CRITICAL angle, `theta_(c) = sin^(-1) ((1)/(mu)) = r_(2)` `therefore " " theta_(c) = sin^(-1) ((1)/(sqrt(2))) = 45^(@)` `A = r_(1) + r_(2)` `therefore " " r_(1) = A - r_(2) = 60^(@) - 45^(@) = 15^(@)` CONSIDERING refractionat face AB, `mu = (sini_(1))/(sinr_(1))` `therefore " " sini_(1) = musinr_(1) = sqrt(2)xx sin15^(@)` `therefore " " sini_(1) = musinr_(1) = sqrt(2)xx sin15^(@)` 
|
|
| 37012. |
In a compound microscope the objective and eyepiece have focal length of 0.95cm and 5cm and are kept at a distance of 20cm. If the final image is formed at least distance of distant vision, the position of object and the total magnification is |
|
Answer» `95/94 CM, 94` |
|
| 37013. |
When a resistance of 11 Omega is connected in series with an electric cell, 0.5A current flows thrugh it . If the 11 Omega resistor is replaced by 5 Omega resistor the current flowing through it is 0.9 A . Find the internal resistance of the cell. |
|
Answer» Solution :When the 11 `OMEGA` resistance is CONNECTED in series. i= 0.5 A, R = 11 Omega` `V=i(R+r)` = where is the INTERNAL in series. `=0.5 (11+r)""….(1)` When the `5Omega` resistance is connected in series i=0.9 A `V= 0.9 (5+r)"".....(2)` From (1)& (2) , `0.5(11 +r) = 0.9(5+r)` `0.5xx11+0.5 r = 0.9xx5+0.9r` `5.5 + 0.5r=4.5 + 0.9r ` `0.4r=1` `r=2.5 Omega` |
|
| 37014. |
Electric flux per unit area of surface of conductor is known as : |
|
Answer» ELECTRIC potential |
|
| 37015. |
Select and write the corrcet answer : When shunted , the current sensitivity of a galvanometer reduces by a factor of 100. Theresistance of the shunt is |
|
Answer» `22/33 OMEGA` ` :. 1/100 = S/(S+G) "" :. S/(S+G-S) = 1/(100 - 1) "" :. S = G/99 = 66/99 = 6/9 = 2/3 Omega` |
|
| 37016. |
An organ pipe closedat one end has a length 1m and an open organ pipe has a length 1.6 m . The speed of soundin air is 320 m/s . The two pipes can resonates for a sound of frequency |
|
Answer» 100 Hz |
|
| 37017. |
Two projectiles, one fired from earth with 5 ms -1 and other fired from a planet with 3 ms -1 at the same angle trace identical trajectories. Neglecting friction, what is the acceleration due to gravity on planet ? (g = 9.8 ms^(-1) ): |
|
Answer» 3.5 `MS^(-2)` since `R_(E)=R_(p):. 25/g_(e)=9/g_(p)` `:. G_(p)=9/25xx9.8=3.5ms^(-2)` |
|
| 37018. |
The momentum of photon of energy 1 MeV will approximately be |
| Answer» Answer :B | |
| 37019. |
The energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 10 ms^(-1) is W. the energy required to accelerate the car froms 10 ms^(-2) to 20 ms^(-1).is: |
|
Answer» 3 W |
|
| 37020. |
Two pointa white dots are 1 mm apart on a black paper.They are viewed by eye of pupil of diameter 3 mm. Nearly what is max. Distance at which these dots can be resolved by eye?(lambda of light is 500 mm) |
|
Answer» 3 m Then R = 4.92 m. |
|
| 37021. |
What amount of work is performed when 1 kg of water turns into steam at 100^(@)C ? How much energy is spent to break the bonds between the molecules? |
|
Answer» Solution :Since evaporation takes place at a constant pressure, `W= p(v_(0)^("vap")-v_(0)^("liq"))` where `v_(0)=1//rho` is the specific volume, i.e. the volume of 1 kg of the SUBSTANCE. Hence `W=p((1)/(rho_("vap"))(1)/(rho_(11Q)))` The density of steam at `100^(@)C` may be found from Table 35.1 (see35.3). Since the specific volume of VA pour is almost a thousand times gronter than the specifio volume of LIQUID, it follows with better than 1% accuracy that `W=p//rho_(vap)` The ENERGY spent on breaking the bonds between the molecules can be found from the first law of thermodynamics: `Delta = L - W` where L is the specific heat of evaporation. |
|
| 37022. |
In the Young's double slit experiment a point source of lambda=5000Å is placed slightly off the central axis as shown in the figure-6.127. (a) Find the nature and order of the interference at the point P. (b) Find the nature and other of the interference at O. (c ) Where should we place a film of refractive index mu = 1.5 and what should be its thickness so that maxima of zero order is obtained at O. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37023. |
A car drives along a straight level frictionless roaid by an engine delivering constant power. Then velocity is directly proportional to |
|
Answer» t |
|
| 37024. |
A point charge q is locatedin vacumm at a distancel fromthe planesurfaceof a unifrom isotropicdeilectric filling up all the half-space. The permittivity of the dielectricequals epsilon. Find : (a) the surfacedensityof the bound chagresas a function of distanc e r from the pointcharges q'. anayse the obtainedresultat l -. 0, (b) the total bound charge on the surfaceof the dielectric |
|
Answer» Solution :The charge is at `A` in the medium 1 and has an image point at `A'` in the medium 2. The electric FIELD in themedium 1 is due to the actual charge `q` at `A` and the image chagre `q'` at `A'`. The electric field in 2 is due to a connectedcharge `q'` at `A`. Thus on the boundary between 1 and 2. `E_(1n)= (q')/(4pi epsilon_(0) R^(2)) cos theta - (q)/(4pi epsilon_(0) r^(2)) cos theta` `E_(2n)= (-q'')/(4pi epsilon_(0) r^(2)) cos theta` `E_(1t)= (q')/(4pi epsilon_(0) r^(2)) sin theta + (q)/(4pi epsilon_(0) r^(2)) sin theta` `E_(2T)= (q'')/(4pi epsilon_(0) r^(2)) sin theta` The boundary conditions are `D_(1n) = D_(2n)` and `E_(1t) - E_(2t)` `eq" = q - q` `q" = q + q` So, `q" = (2q)/(epsilon + 1), q' = (epsilon - 1)/(epsilon + 1) q` (a) The surface DENSITYOF the round charge on the surface of the dielectric `sigma' = P_(2n) =D_(2n) - epsilon_(0) E_(2n) = (epsilon - 1) E_(0) E_(2n)` `=(epsilon -1)/(epsilon +1)(q)/(2pi r^(2)) cos theta = (epsilon - 1)/(epsilon +1) (ql)/(2pi r^(3))` (B) Total bound chargeis, `(epsilon - 1)/(epsilon +1) q int_(0)^(oo) (l)/(2pi (l^(2) + x^(2))^(3//2)) 2pi x dx = - (epsilon - 1)/(epsilon + 1) q` 
|
|
| 37025. |
The relation between time t and distance x is given by t=ax^(2)+ bx. Where a, b are constants. Then retardation is : |
|
Answer» `2alpha V^(3)` |
|
| 37026. |
The magnetic flux through a coil perpendicular to its plane is varying according to the relation phi_(B)= (5t^(3) + 4t^(2) + 2t -5) weber. Calculate the induced current through the coil at 1= 2 second. The resistance of the coil is 5 Omega |
|
Answer» Solution :`phi= 5t^(3) + 4t^(2) + 2t-5` `|e| = (d phi)/(DT) = 15T^(2) + 8t + 2` `iR = 15t^(2) + 8t + 2` `i xx 5 = 15 xx 4 + 8 xx 2 + 2 RARR i= 15.6A` |
|
| 37027. |
A solenoid of length 50cm with 20turns per centimetre and area of cross-section 40cm^(2) completely surrounds another co-axisal solenoid of the same length, area of cross-section 25cm^(2) with 25 turns per centimetre. Calculate the mutual inductance of the system. |
|
Answer» Solution :`l= 50cm = (1)/(2)m` `N_(1)= 20 xx 50 = 1000, A_(1)= 40 xx 10^(-4) m^(2)` `N_(2)= 25 xx 50 = 1250, A_(2)= 25 xx 10^(-4) m^(2)` `M= (mu_(0)N_(1)N_(2)A_(2))/(1)` `=(4pi xx 10^(-7) xx 1000 xx 1250 xx 25 xx 10^(-4))/(1//2)H` `=7.9 xx 10^(-3) H= 7.9mH` For CALCULATION of M, we have to consider the cross-sectional area of the inner solenoid. |
|
| 37028. |
A particle of mass m and charge (-q) enters the region between the two charged plates initially moving along x-axis with speed v_x (like particle 1 in figure. The length of plate is L and an uniform electric field E is maintained between the plates. Show that the vertical deflection of the particle at the far edge of the plate is qEL^(2)//(2m v_(x)^(2)). Compare this motion with motion of a projectile in gravitational field discussed in Section 4.10 of Class XI Textbook of Physics. |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider vertically upward electric field `vecE` between two horizontal plates as shown in the figure. A particle of mass m and charge - q, enters this electric field along X-axis with constant horizontal velocity vx at time t = 0. Because of negative charge, it gets deflected towards positive plate. Suppose it passes through points `P_(1)` and `P_2` at time `t_(1)`and `t_2` RESPECTIVELY. At time `t_2`, horizontal displacement of GIVEN charge is equal to L. Here, no force is exerted on this charge along horizontal DIRECTION and so its horizontal velocity `v_(x)`reminas constant. `therefore v_(x) = L/t_(2) rArr t_(2) = L/v_(x)`..........(1) Here electric force exerted on given charge is, `F_(e) = (-q)E = ma_(y)rArr a_(y) = (-qE)/(m)`.......(2) At time `t_2` if vertical displacement of given charge is, `y = v_(0y)t_(2) + 1/2a_(y)t_(2)^(2)` `therefore y =-1/2((qE)/(m))L^(2)/v_(x)^(2) rArr |y| = 1/2 ((qE)/(m))L^(2)/v_(x)^(2)`......(3) Above equation gives required result. Here, displacement of given charge is towads - Y-axis and so y is negative. Comparison with projectile motion : Here, at the end of time `t_(1)`horizontal displacement of given charge is `x_1` and so, `v_(x) = x_(1)/t_(1) rArr t_(1) = x_(1)/v_(1)`...........(4) At the end of time `t_(1)`vertical displacement of given charge is, `y_(1) = (v_(0))t_(1) + 1/2 a_(y)t_(1)^(2)` `therefore y_(1) = -(qE)/(2mv_(x)^(2))x_(1)^(2)y_(1) = x_(1)^(2)` ...............(5) Above equation is similar to equation of projectile motion. |
|
| 37029. |
Chaitanya pedals a stationary bicycle at one revolution per second. The pedals are attached to 100 turns coil of area 0.1m^(2) and placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.1 T. What is the maximum voltage generated in the coil ? |
|
Answer» SOLUTION :`EPSILON=NBA omega=NBA(2PI F)""( :. f=1)` `epsilon_(0)=100xx0.1xx0.1(2xx3.14xx1)V=6.28V` |
|
| 37030. |
A point charge q is placed at the centre of the edge of a cubical box. Find the total flux associated with that box. |
| Answer» Solution :If q is placed as shown, three more identical cubes are REQUIRED to enclose. That charge completely. Then the total flux through all faces of 4 cubes is`(q)/(in_0)`. Now CONTRIBUTION of this flux through each CUBE is `q/(4 in_0)` (given). Here it is interesting to note that the faces which have COMMON edge on which the given charge is kept have no flux and hence the flux `q/(4 in_0)` emerges through the REMAINING four faces of the cube. | |
| 37031. |
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror making an angle of 90° with the mirror surface. The angle of reflection for this ray of light will be- |
|
Answer» `45^(@)` |
|
| 37032. |
A rectangular loop consists of N closed wrapped turns and has dimensions a xx b. The loop is hinged along the y-axis. What is the magnitude of the torque exerted on the loop by a uniform magnetic field B = B_(0) directed along the x-axis when current i = i_(0) in the direction shown. What is the expected direction of rotation of the loop ? |
|
Answer» Solution :Area vector `vec(A) = vec(CO) xx vec(OA)` `= (-B cos 37^(@) hat(i) - b SIN 37^(@) hat(K)) xx (a hat(j))` `= -(ab)/(5)[4(hat(i) xx hat(j)) + 3(hat(k) xx hat(j))]` `= -(ab)/(5)[4hat(k) - 3hat(i)]` `= (ab)/(5) [3hat(i) - 4hat(k)]` MAGNETIC moment `vec(M) = N i_(0) vec(A)` `= (N i_(0) ab)/(5)(3hat(i) - 4hat(k))` `vec(B) = B_(0) hat(i)` `vec(tau) = vec(M) xx vec(B) = (N i_(0) ab B_(0))/(5)[3 (hat(i) xx hat(i)) - 4(hat(k) xx hat(i))]` `= -(4 N i_(0) ab B_(0))/(5) hat(j)` The loop will rotate in clockwise direction as seen from above. |
|
| 37033. |
What is the cause of refraction of light ? |
| Answer» Solution :LIGHT travels with different SPEEDS in different MEDIA. The bending or refraction of light OCCURS DUE to the change in speed of light as it passes from one medium to another . | |
| 37034. |
Motion of torsonal pendulum is |
|
Answer» periodic |
|
| 37035. |
To decrease the cut -off wavelength of continuousX-ray by 25% the potential difference across the X-ray tube. |
|
Answer» MUST be increased by `(100)/(3)%`, |
|
| 37036. |
A tangent gavanometer has 80 turns of wire. The internal and external diameters of the coil are 19 cm and 21 cm respectively. The reduction factor of the galvonometer at a place where H = 0.32 oersted will be (1 oersted =80 A//m) |
|
Answer» `0.0064` |
|
| 37037. |
In Fig. a cube of edge length L=0.500 m and mass 450 kg is suspended by a rope in an open tank of liquid of density 1030 kg/m^(3). Find (a) the magnitude of the total downward force on the top of the cube from the liquid and the atmosphere, assuming atmospheric pressure is 1.00 atm, (b) the magnitude of the total upward force on the bottom of the cube, and (c) the tension in the rope. (d) Calculate the magnitude of the buoyant force on the cube using Archimedes' principle. What relation exists among all these quantities? |
| Answer» SOLUTION :(a) `2.59 XX 10^(4) N , (b)2.71 xx 10^(4) N , (c) 3.15 xx 10^(3) N, (d) 1.26 xx 10^(3) N , T + F_(b) = MG ` | |
| 37038. |
Derive an expression for a one - dimensional simple harmonic progressive wave travelling in the direction of thepositive x - axis. Express it in terms ofA, lambda, v , t and x . |
|
Answer» Solution :Consider a simple harmonic progressive wave travelling with a speed valong the positive x-axis. Let y denote the displacement of a particle of themedium from its mean position. We assume that theinitial phase of the oscillatory motion is zero . At time t, the displacement of the particle of the medium situated at the origin is ` y = A sin omega t`...(1) where A is the amplitude of the wave and `omega` is related to thefrequency n of the wave motion by theequation `omega = 2 pi n`. 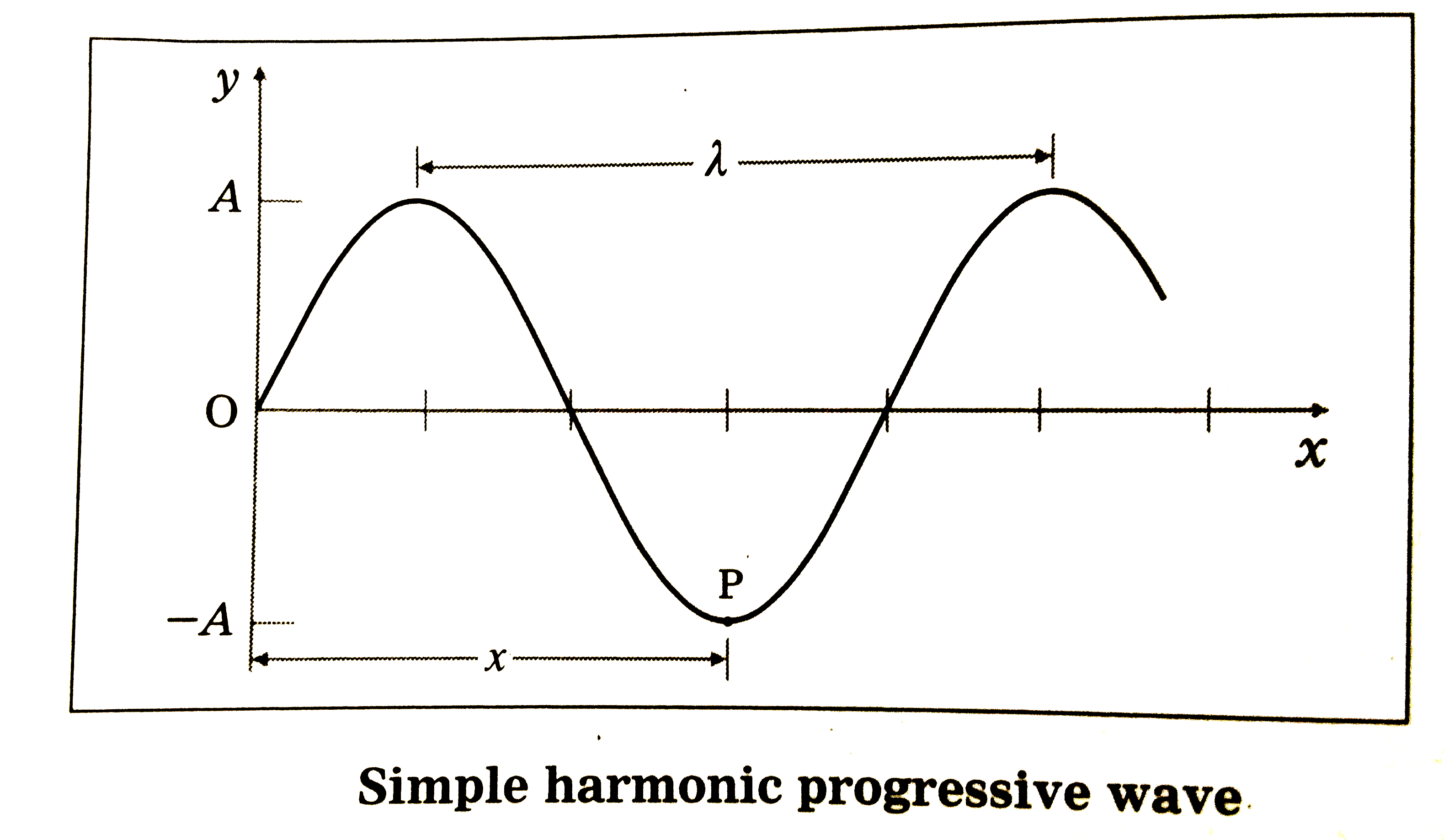 Simple harmonic progressive wave Consider a particle of the medium situated at point P at a distance x from the origin O as shown in thefigure. This particle also PERFORMS SHM with the same amplitude A and thefrequency n.However, thedisturbance at O reaches P only after some time , i.e., the particle at P displacement of the particle at P is ` y = A sin ( omega t - alpha)`...(2) Since a PATH difference of `lambda` (wavelength) corresponds to a phase defferenceof ` 2PI ` radians , a path difference of x corresponds to a phase difference of ` alpha` such that ` lambda/(2pi) = x/alpha . :.alpha = (2 pi)/lambda x`. `:. y = A sin (OMEGAT - (2pi)/lambda x)`....(3) If n is the frequency of vibration , `omega = 2 pi n = (2 pi v)/lambda`...(4) where v is the speed of the wave, ` :.y = A sin 2 pi (nt - x/lambda)` ...(5) Equation (5) is the equation of a simple harmonic progressive wave travelling in thepositive direction of the x - axis. Also from Eq. (4), `y = A sin 2 pi (v/lambda t - x/lambda)` ` :.y = A sin (2 pi)/lambda (vt - x)`....(6) in terms of v and `lambda` , as required. |
|
| 37039. |
The value of permittivity of vaccum is 8.85 xx 10^(-12) C^(2)N^(-1) m^(-2)and the dielectric constant of water is 81. So the permittivity of water will be………C^(2)N^(-1)m^(-2). |
|
Answer» `81 xx 8.86 xx 10^(-12)` `therefore epsilon = Kepsilon_(0) = 81 xx 8.86 xx 10^(-12) C^(2)N^(-1)m^(-2)` |
|
| 37040. |
Refer to above question , the potential difference between C and D is : |
| Answer» ANSWER :c | |
| 37041. |
The energyof a photonof sodiumlight ( lamda = 589nm)equalto thebandgapof asemiconducingmaterial . Find thevalueofE /kTat a temperatureof300 K. |
|
Answer» Solution :At T= 300 K, KT=(`8.62 xx 10^(-5) eV//K`) (300K) = 25.86 `xx 10^(-3) ` eV. Thus`(E )/(kT )= ( 2.1 eV )/( 25.86 xx 10^(-3)) = 81` The available thermal energy is nearly 81 times less than that of the required energy to CREATE electron hole pair. So it is difficult for the thermal energy to create the hole-electron pair but a PHOTON of light can do it easily. |
|
| 37042. |
The energyof a photonof sodiumlight ( lamda = 589nm)equalto thebandgapof asemiconducingmaterial . Findtheminimum energyE requiredto createahole-electronpair. |
|
Answer» Solution : The energy of the photon in eV =`( 12400 )/(lamda)` WAVELENGTH of photon = 589 NM `= 5890 A^0` `=(12400)/( 5890) = 2.1eV ` Thus the band gap is 2.1 eV. This is also the MINIMUM energy E required to push an ELECTRON from the valence band into the conduction band. Hence, the minimum energy required to create a hole-electron pair is 2.1eV. |
|
| 37043. |
The measurement of an unknown resistance R is to be carried out using Wheatstone bridge as given in the figure below. Twostudents perform an experiment in two ways. The first students takes R_(2) = 10 Omega and R_(1) = 5 Omega. The other student takes R_(2) = 1000 Omega and R_(1) = 500 Omega. In the standard arm, both take R_(3) = 5 Omega . bothfind R= (R_(2))/(R_(1)) , R_(3) = 10 Omega within errors. |
|
Answer» The errors of measurement of the two students are the same.  For balanced condition of Wheatstone bridge, `(R_(2))/(R) = (R_(1))/(R_(3)) ` `therefore R = R_(3) xx (R_(2))/(R_(1))` For first student :`R_(1)= 5 Omega , R_(2) = 10 Omega` and `R_(3) = 5 Omega` `therefore R = 5 xx (10)/(5)= 10 Omega` For SECOND student : `R_(1) = 500 Omega , R_(2) = 1000 Omega`, `"" R_(3) = 5 Omega` `therefore R = 5 xx (1000)/(500) = 10 Omega` If` R_(1) and R_(2)` are chosen in such a way that it is of very large then current flowing through galvanometer will be very small HENCE null point can be obtained accurately. |
|
| 37044. |
The horizontal component and vertical components of Earth's maganetic field at a plase are 0.15 G and 0.26 G respectively. Calculate the angle of dip and resultant magnetic field. |
|
Answer» Solution :`B_(H)` = 0.15 G and `B_(v)` = 0.26 G TAN 1 = `(0.26)/(0.15) RARR " I " = tan^(-1) (1.732) = 60^(@)` The resultant magnetic field of the earth is B = `sqrt(B_(H)^(2) + B_(H)^(2)) = 0.3G` |
|
| 37045. |
A point charge 2nC is located at origin. What is the potential at(1,0,0)? |
|
Answer» 12 |
|
| 37046. |
What are isotopes ? |
|
Answer» Isobars. The atoms which have the same mass number A, but different atomic number Z, are called isobars. |
|
| 37047. |
Protons and deuterons are accelerated through a same potential difference before they enter a region of uniform magnetic field applied perpendicular to their motion. If protons describe a circle of radius 10 cm then what will be the radius of circle of a deuteron? |
|
Answer» Solution :Let us ASSUME charge q is accelerated through a potential difference of V then we can write the following: `qV = 1//2 mv^(2)` `rArrmv = sqrt(2qmV)` Radius of circular path is given by ` r = (mv)/(qB) = sqrt(2qmV)/(qB) = sqrt((2mV)/(qB^(2)))` In this case potential difference VAND magnetic field intensity B are same.. Hence, the ratio of radii of deuteron to that of proton can be WRITTEN as follows: `r_(d)/r_(p) = sqrt((2m_(d)V)/(q_(d)B^(2)))/sqrt((2m_(p)V)/(q_(p)B^(2))) = sqrt(m_(d)/m_(p) xx q_(p)/q_(d)) = sqrt((2M)/m xx e/e) = sqrt2` We know that the radius of circle of proton is 10 cm. Hence, radius of the circular path followed by deuteron would be `10 root()()2 cm` . |
|
| 37048. |
A uniform conducting ring of mass pi kg and radius 1 m is kept on smooth horizontal table. A uniform but time varying magnetic field B = (hat (i) + t^(2) hat (j))T is present in the region, where t is time in seconds. Resistance of ring is 2 (Omega). Then Net magnetic field (in Newton) on conducting ring as function of time is |
| Answer» Answer :D | |
| 37049. |
A capacitor (C) and resistor (R) are connected in series with an a.c. source of voltage of frequency 50 Hz. The potential difference across C and R are respectively 120 V, 90 V, and the current in the circuit is 3 A. Calculate (i) the impedance of the circuit (ii) the value of the inductance, which when connected in series with C and R will make the power factor of the circuit unity. |
|
Answer» |
|
| 37050. |
A charge Q is placed at each of two opposite comers • of a square. A charge q is. placed at each of the other two comers. If the net electric force on Q is zero, then Q/q equals to: |
| Answer» ANSWER :D | |